A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development
|
|
|
- Ezra Chandler
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Okajimas Fol. anat. jap., 47: , 1971 A Study on the Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, with Special Reference to the Development By Hsi-Kuei Tsai Department of Anatomy, College of Medicine, National Taiwan University (Taipei, Taiwan) Introduction By reviewing the literatures so far published on this subject, Krause (1922) stated that occasionally lymphfollicles had been discovered in the interstitial connective tissue of the pancreas of doves. Hellman (1927), in addition, reported the existence of lymphatic apparatus in human pancreas. Furthermore, Ma t s u o k a (1944) confirmed these discoveries by the above authors, and at the same time, carefully extended the scope of study on the distribution of lymphatic tissue on mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibia and other various vertebrates. The results revealed that lymphatic apparatus would not appear in the pancreas of primates. Even among mammals, only in rabbits was there a few lymphatic infiltrations which were distributed in the interstitial connective tissue of the pancreas. In contrary to these findings, lymphatic infiltrations and solitary nodules usually showed better development in the pancreas of birds and those vertebrates which were lower in class. According to 0 g a- m i (1955), in the pancreas of human fetus the lymphatic apparatus mostly appeared as lymphatic infiltration and solitary nodules. The author has definitely detected the existence of lymphatic apparatus in the pancreas of adult monkeys in this study, and has further followed the progress during its development. Those interesting findings are therefore presented in this paper. Materials and Method Ten Macaca cyclopis were used as the study subjects. They were 24 and 48 hours after birth, and also at the approximate ages of 6, * The present work is supported by the grant of the National Science Coun cil, Republic of China,
2 434 lisi-kuei Tsai 11, 16, 20, 28, 36, 48 and 60 months. Somatometry for the sitting height, height, length of tails, body weight, breadth of shoulders, trunk length, length of limbs, etc. were performed. The results obtamed were compared with that by Schultz on the Rhesus monkeys and the age of these monkeys were thus estimated. 10% formalin was sufficiently injected through the abdominal aorta under Ravonal narcosis on all subjects. Then the subjects were immersed and preserved in the same solution. After fixation, the whole pancreas were removed and embedded in celloidin. Serial sections along the long axis were made for the microscopical examination. For the convenience of recording, the age distribution of the Macaca cyclopis was classified according to Harm 's report (1956) ; i. e. for those within two weeks after birth were designated as in the lactation period ; for those within 6 months, infantile period ; and for those within 3-4 years, juvenile period. Results Case 1. Macaca cyclopis (0.35 kg), female. 24 hours after birth. Pancreas (0.41 g). The outer margin of the pancreas was wrapped with capsule of thick fibrous connective tissue. From the capsule, the septa of connective tissue of uncertain sizes enter to and for towards the inner parts of the organ to divide the parenchyma into a number of lobules of various sizes. Inside the lobules, here was thickly observed distribution of terminal portion, in which cell was pyramidal in shape, containing a light round nucleus. Intercalated duct was composed of lightly stained simple cuboidal epithelium, and generally was short. 'Various sizes of branch of ducts ran everywhere of the interlobular connective tissue. These ducts were composed of simple cuboidal epithelium or simple columnar epithelium, in the wall associated with membrane of muscle fiber. Pancreatic duct of this case was relatively thick and composed of simple columnar epithelium and well developed lamina propria with few muscle fibers. No lymphatic apparatus could be observed in this case. Case 2. Macaca cyclopis (0.45 kg), male. 48 hours after birth. Pancreas (0.46 g). In this case, the microscopical finding was not significantly different in comparision with the previous one. No lymphatic apparatus could be found in pancreas in this case. Case 3. Macaca cyclopis (1.0 kg), male. 6 months old. Pancreas (2.0 g). In this case, generally the lobules were large in size with rich interlobular connective tissue. A few oval cells were found in the lumen of terminal portion. Long intercalated portion, which was formed by the simple squamous epithelium, is
3 Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis 435 predominant in the lobules. Branch of the ducts in interlobular connective tissue was formed by simple columnar epithelium surrounded by connective tissue with small amount of muscle fiber and this in turn formed a thicker lamina propria. Pancreatic duct consists of high columnar epithelium, well developed lamina propria and thin layer of circular muscle fibers in the adjacent area. No lymphatic apparatus was found in this case. Case 4. Macaca cyclopis (1.5 kg), male. 11 months old. Pancreas (3.0 g). The histological structure was not significantly different from case 3. No lymphatic apparatus could be found in this case. Case 5. Macaca cyclopis (1.9 kg), male. 16 months old. Pancreas (3.9 g). In this case, four lymphatic apparatus were found. A) Head of pancreas Four lymphatic infiltrations about 180 X 120 x x 80 x 60u in size were found. They were all developed in the interlobular connective tissue, especially in the tunica adventitia of the medium or small bifurcated duct (Fig. 1). B) Body of pancreas No lymphatic apparatus was found. C) Tail of pancreas No lymphatic apparatus was found. Case 6. Macaca cyclopis (2.0 kg), male. 20 months old. Pancreas (4.5 g). Eighteen lymphatic infiltrations were found. A) Head of pancreas Eighteen lymphatic infiltrations about 550 x 200 x x 50 x 90p in size were found. These infiltrations were all located along extralobular bifurcated duct or pancreatic duct. Most of them were found in the tunica adventitia, occasionally seen at the connective tissue of lamina propria. Those lymphatic infiltrations showed some relationship with small veins and lymphatic vessels (Figs. 2-4): B) Body and tail of pancreas No lymphatic apparatus could be detected in this region. Case 7. Macaca cyclopis (2.6 kg), female. 28 month old. Pancreas (5.5 g). Eight lymphatic infiltrations and one solitary nodule were found in the whole area of the pancreas. A) Head of pancreas Five lymphatic infiltrations about 370 X 220 x x 100 x 120p in size were found. One of them was found in the intralobular connective tissue, connected with intercalated portion and small veins. The others were mainly located in the tunica adventitia of the diverging part of the interlobular duct or in pancreatic ducts. The majority of them showed some relationship with lymphatic vessels and small blood vessels (Fig. 5). One solitary nodule, about 400 x 220 x 300p in size was found and it was located at the border zone between the inter- and intralobular
4 436 Hsi-Kuei Tsai parts surrounding the diverging part of the small duct, and was developed in the connective tissue along the lymphatic vessels and small veins. Neither formation of secondary nodule nor differentiation of germinal center could be detected from the solitary nodules (Fig. 6). B) Body of pancreas One lymphatic infiltration about 230 x 150 x 120p in size was found. This apparatus developed in the connective tissue of the border zone between the inter- and intralobular parts and closely contacted with the diverging parts of small ducts and small veins. C) Tail of pancreas Two lymphatic infiltrations about 300 X 150 x x 150 x 120p in size were found. One of them appeared in the small bifurcated duct in the border zone between the interand intralobular portions. The other one appeared in the tunica adventitia of the medium sized bifurcated duct in the connective tissue and it was associated with small veins. Case 8. Macaca cyclopis (3.2 kg), male. 36 months old. Pancreas (7.0 g). Eight lymphatic apparatus were found and all of them were lymphatic infiltrations. A) Head of pancreas Five lymphatic infiltrations about 420 x 120 x x 80 x 270p in size were found. All of these apparatus distributed in extralobular part, mostly appeared in the tunica adventitia of the medium sized bifurcated ducts and pancreatic ducts, only occasionally seen in lamina propria. In general, the lymphatic infiltrations showed some relationship with the lymphatic vessels and small veins (Fig. 7). B) Body of pancreas Two lymphatic infiltrations about 200 x 150 x x 80 x 150p in size were found. All of them were distributed in interlobular connective tissue and most of them could be found in the tunica adventitia of the diverging part of the small or medium sized ducts. These infiltrations were invariably in close contact with small vessels and lymphatic vessels (Fig. 8). C) Tail of pancreas One lymphatic infiltration about 190 x 100 x 150p in size was found. It ran along the extralobular part and it was developed from the tunica adventitia of the diverging part of the small duct. It was also connected with small veins. Case 9. Macaca cyclopis (4.4 kg), female. 48 months old. Pancreas (7.0 g). Eleven lymphatic infiltrations were found. A) Head of pancreas Three lymphatic infiltrations about 220 x 70 x x 70 x 120p in size were found in the tunica adventitia of the medium or small sized bifurcated duct in the interlobular connective tissue. Rarely they could be found in lamina propria. All were in close contact with lymphatic vessels or small veins (Fig. 9).
5 Lymphatic Apparatus in the Pancreas of Macaca cyclopis 437 B) Body of pancreas Two lymphatic infiltrations about 370 X 90 x X 80 x 150p in size were found. These lymphatic apparatus usually appeared in the connective tissue of the tunica adventitia of interlobular bifurcated duct. Both were related with lymphatic vessels. C) Tail of pancreas Six lymphatic infiltrations about 300 x 190 X x 90 x 150p in size were found. All of the lymphatic infiltrations were found in the tunica adventitia of the medium sized bifurcated duct within extralobular connective tissue. They were associated with lymphatic vessels (Fig. 10). Case 10. Macaca cyclopis (5.3 kg), female. 60 month old. Pancreas (7.5 g). Fifteen lymphatic infiltrations were found. A) Head of pancreas Two lymphatic infiltrations about 1400 x 100 x x 70 x 120p in size were found. All were developed in the interlobular connective tissue. They were found in tunica adventitia of pancreatic ducts and in the lamina propria of small ducts in connection with small veins (Fig. 11). B) Body of pancreas Nine lymphatic infiltrations about 210 x 140 x x 60 x 90p in size were found. Most of the lymphatic apparatus were developed in the tunica adventitia or lamina propria of the medium or small sized interlobular bifurcated ducts. These lymphatic infiltrations were mainly developed along the lymphatic vessels or small veins. One lymphatic infiltration appeared in the border zone between the inter- and intralobular portions, and was seen at the tunica adventitia of medium sized ducts. C) Tail of pancreas Four lymphatic infiltrations about 370 x 220 x x 60 x 90p in size were found. Two of them spread along the intercalated ducts in the intralobular connective tissue. The other two accompanied with small ducts and small veins were found in the connective tissue of the border zone between the inter- and intralobular portions (Fig. 12). Discussion and Conclusion In the present study, the author has used Macaca cyclopis in different age groups as the subjects to examine in detail the formation and distribution of the lymphatic apparatus in their pancreas. In brief, the following results were obtained : 1. In the pancreas of mature Macaca cyclopis, the existence and distribution of lymphatic apparatus were definitely recognized and its developmental basis was clarified. 2. In the lactation and infantile periods, however, the lymphatic apparatus could not be found. Lymphatic infiltrations were first
6 438 Hsi-Kuei Tsai found after 16 months, the juvenile period. According to previous literature, similar findings were found in the large oral glands of Macaca cyclopis, but in the human pancreas lymphatic apparatus were developed in earlier period, i. e. in 6th month fetus. 3. In the pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, the lymphatic apparatus which first appeared in the head portion, are gradually increased and extend to the whole area of pancreas with the increasing age. 4. The lymphatic apparatus of the pancreas of Macaca cyclopis, generally accompanied with the differentiation of solitary nodules, showed the increasing tendency through the whole juvenile period and until reaching the adulthood. The development of such lymphatic apparatus was essentially consistent with the findings in human pancreas during the fetal stage of development. 5. Through the cases, it has been found that in the interlobular connective tissue of the pancreas of Macaca cyclopis there were the concentrated and prominent distribution of the lymphatic apparatus, rapidly decreasing in number from here toward the inner part of the lobules. Very similar findings were also found in the pancreas of human fetus. In contrary to this, lymphatic apparatus showed remarkable development within the lobules in the large oral glands of monkeys. 6. Among all the cases of Macaca cyclopis, their lymphatic apparatus and the glandular ducts were, with no exception, interrelated and most of the lymphatic apparatus were developed in the diverging part of excretory ducts. In addition to this, most of the apparatus were also in close contact with veins and lymphatic vessels. 7. In the lymphatic apparatus of the pacreas in Macaca cyclopis, just like those in the case of human fetus, the formation and differentiation of the secondary nodules or germinal center could not be found. References 1) Kraus e, R.: Mikroskopische Anatomie der Wirbeltiere II. Vogel und Reptilien. Berlin und Leipzig ) H e 11 m a n, T.: LymphgefaBe, LymphknOtchen und Lymphknoten in v. M011endorffs Handbuch d. mikr. Anatomie d. Menschen. Bd. VI, Teil I, Berlin ) Mat u o k a, M. : Kyoto Igaku Zassi. Bd. 41; Nr. 1, ) Ogam i, T.: Arbeiten a. Anat. Inst. d. Univ. Tottori. Hf. II, ) H a r t ma n, C. G. etc. : Anatomy of the rhesus monkey. Now York ) Harm s, J. W.: Fortpflanzungsbiologie in Primatologia. Vol. I, ) K i h a r a, T.:,Berichte d. harnat. Symp. Nr. 6, ) T s a i, H-K. : Arbeiten a. Anat. Inst. d. Univ. Tottori Hf. XIV, ) K e n g, T-T. : Ebenda. Hf. XV, 1969.
7 Plate
8 440 Hsi-Kuei Tsai Explanation of figures (Plate I, II) Fig. 1. Lymphatic infiltration, which develops in the tunica adventitia of small excretory duct in the extralobular connective tissue, in close contact with lymphatic vessel. Head of pancreas, case 5. x 280. Fig. 2. Lymphatic infiltration, which spreads in the tunica adventitia of bifurcated duct in interlobular connective tissue. Head of pancreas, case 6. x 100. Fig. 3. Lymphatic infiltration, which surrounds the small bifurcated duct in the interlobular connective tissue. Head of pancreas, case 6. x 100. Fig. 4. Lymphatic infiltration, which develops in the lamina propria of pancreatic duct. Head of pancreas, case 6. x 100. Fig. 5. Lymphatic infiltration, which surrounds a lymphatic vessel in the tunica adventitia of pancreatic duct. Head of pancreas, case 7. x 100. Fig. 6. A solitary nodule, which surrounds a small bifurcated duct in the border zone between the inter- and intralobular parts. Head of pancreas, case 7. x 100. Fig. 7. Lymphatic infiltration, which develops in the lamina propria of pancreatic duct. Head of pancreas, case 8. x 100. Fig. 8. Lymphatic infiltration coming in contact with the small bifurcated duct in interlobular part. Body of pancreas, case 8. x 100. Fig. 9. Lymphatic infiltration, which is seen near a small bifurcated duct in the interlobular connective tissue. Head of pancreas, case 9. x 100. Fig. 10. Lymphatic infiltration, which appears in the tunica adventitia of interlobular duct. Tail of pancreas, case 9. x 100. Fig. 11. Subepithelial lymphatic infiltration, which appears in the lamina propria of pancreatic duct. Head of pancreas, case 10. x 100. Fig. 12. Lymphatic infiltration, which spreads along the intercalated duct in the border zone between the inter- and intralobular parts. Tail of pancreas, case 10. x100.
9 441 Plate I Fig. I. Fig. 2 Fig. 3. Fig. 4. Fig. 5. Fig. 6. H.K.Tsai
10 443 Plate II Fig. 7. Fig. 8. Fig. 9. Fig. 10. Fig. II. Fig. 12.
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY GASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM LIP (Slides GI 1, 2) Identify the outer portion lined by stratified squamous (keratinized) epithelium. Note the hair follicles and sebaceous glands
Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs
 Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs Slide #77 (C007- H- 107A). Pancreas, dog. pancreatic islets CENTROACINAR CELLS ARE THE BEGINNING CELLS OF THE INTERCALATED DUCTS THAT DRAIN THE SECRETORY ACINI
Laboratory exercises for abdominal organs Slide #77 (C007- H- 107A). Pancreas, dog. pancreatic islets CENTROACINAR CELLS ARE THE BEGINNING CELLS OF THE INTERCALATED DUCTS THAT DRAIN THE SECRETORY ACINI
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Urinary system. Urinary system
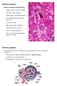 Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT) Highly coiled, ~ 5 mm in length Last part of the nephron. Wall; simple cuboidal epithelium Less metabolically active than the PCT no brush border light eosinophilic cytoplasm
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL
 Lecture 2 ESS_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER - is the largest gland of
Lecture 2 ESS_3rd semester MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER, GALLBLADDER, GALL DUCTS, AND PANCREAS OVERVIEW OF DEVELOPMENT OF THE ALIMENTARY CANAL MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE OF LIVER - is the largest gland of
Urinary system. Urinary system
 INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
INTRODUCTION. Several organs system Produce urine and excrete it from the body Maintenance of homeostasis. Components. two kidneys, produce urine; two ureters, carry urine to single urinary bladder for
Behzad Mobini* Islamic Azad University, Shahrekord Branch, Shahrekord, Iran. Received: 25 October 2010, Accepted: 4 January 2011
 Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
Original Article Veterinary Research Forum Vol: 2, No: 1, March, 2011, 25-29 Histological Studies on Pancreas of Goose (Anser Albifrons) Behzad Mobini* * Department of Anatomical Sciences, Faculty of Veterinary
Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing. Squamous Cuboidal Columnar
 Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Epithelia Epithelia will be discussed according to the following scheme: Type Number of layers Shape Line drawing Simple Squamous Cuboidal Columnar Covering and Lining epithelium Pseudostratified Stratified
Histology Lab. looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira book and you can use BlueHistolgy website
 Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Done By: Aseel Twaijer & Laith Sorour Histology Lab *These notes help in differentiating tissues and you must read them while looking at microscopic pictures of tissues, for more information use Junqueira
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system. Lab activity 1: esophagus stomach - small intestines
 Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
Lab activity manual - Histology of the digestive system Jeanne Adiwinata Pawitan Prerequisite: Histology of the 4 basic tissues In this module we learn about the histology of the digestive system, from
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Histology Urinary system
 Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
Histology Urinary system Urinary system Composed of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder, and the urethra, the urinary system plays a critical role in: 1- Blood filtration,(filtration of cellular
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas
 Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Digestive system L 4. Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section
 Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Digestive system L 4 Lecturer Dr. Firdous M. Jaafar Department of Anatomy/Histology section objectives 1-Describe the structure of liver. 2-Define liver lobule, and identify its zones. 3-Define portal
Anatomy & Physiology Revealed Instructions. 1. From the Module dropdown menu, chose the 12. Digestive system.
 #10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
#10 - Objectives: Examine the histology of selected body organs using Anatomy & Physiology Revealed software and microscope slides. Be able to identify each organ and the specific structures indicated
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system
 Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
Tongue In the buccal cavity of the digestive system same layers as those of tubular organs Mucosa, submucosa, and muscularis muscularis = the muscularis externa no muscularis mucosa 1 Tongue ling = tongue
川北医学院讲稿. Under low power note the testis is enclosed by a strong fibrous. layer of serous epithelium. These fibrous tissue
 川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
川北医学院讲稿 Experiment 5: Male and Female Reproductive System Hello, everybody, class is begin,keep quiet, please. And this is the last experimental class. Today we will learn 5 slices and review all structures
Urinary System Laboratory
 Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Urinary System Laboratory 1 Adrenal gland Organs of The Urinary System Renal artery and vein Kidney Ureter Urinary bladder Figure 26.1 2 Urethra Functions of the urinary system organs: Urethra expels urine
Organs Histology D. Sahar AL-Sharqi. Respiratory system
 Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Respiratory system The respiratory system provides for exchange of O2 and CO2 to and from the blood. Respiratory organs include the lungs and a branching system of bronchial tubes that link the sites of
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Urinary System. Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal
 Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
Urinary System Dr. Ahmed Maher Dr. Ahmed Manhal Presentation Map Kidney (cortex & medulla). Nephron. Duct system. Juxtaglomerular apparatus. Ureter, bladder & urethra. Definition & General Structure The
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Chapter 12 The Digestive Glands
 Chapter 12 The Digestive Glands Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Components of digestive glands large salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder. These organs
Chapter 12 The Digestive Glands Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Components of digestive glands large salivary glands, pancreas, liver, gallbladder. These organs
21 Endocrine organs and cells
 21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
21 Endocrine organs and cells The endocrine system consists of discrete organs, portions of organs and distributed cells that secrete hormones into surrounding tissues or structures. Objectives You should
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel
 Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel Now we will take about A granulocytes : Lymphocyte Monocytes 1- Lymphocyte - The second major type of presence
Lecture name: blood 2 & The Circulatory System Edited by: Buthainah Al masaeed & Yousef Qandeel Now we will take about A granulocytes : Lymphocyte Monocytes 1- Lymphocyte - The second major type of presence
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 20: Immunity and the Lymphatic System Question No. 1 of 10 The lymphatic system is formed early during human development. Which of the following statements
HISTOLOGY. GIT Block 432 Histology Team. Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih
 HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
HISTOLOGY Lecture 1: Alimentary Canal (1) (Esophagus & Stomach) Done by: Ethar Alqarni Reviewed by: Ibrahim Alfuraih Color Guide: Black: Slides. Red: Important. Green: Doctor s notes. Blue: Explanation.
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
DIGESTIVE TRACT ESOPHAGUS
 DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
DIGESTIVE TRACT From the lower esophagus to the lower rectum four fundamental layers comprise the wall of the digestive tube: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis propria (externa), and adventitia or serosa (see
Alimentary Canal (I)
 Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
Alimentary Canal (I) Esophagus and Stomach (Objectives) By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to discuss the microscopic structure in correlation with the function of the following organs:
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
A adipose cells. B capillary. C epithelium
 EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
EPITHELIA Objective The objective of this class is to observe how different epithelia vary in terms of cell shape, size and number of cell layers enabling them to be well adapted for functions in different
GI Histology Lab 1. Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji
 GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
GI Histology Lab 1 Prepared by: Zeina Kalaji Lip ORAL MUCOSA -Arrow shows labial salivary glands in the submucosa. VERMILLION transitional zone. SKIN Stratified Squamous epithelium, keratinized -Arrow
H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
SCPA 602- Anatomical Basis For Pathological Study H I S T O L O G Y O F T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M S O M P H O N G N A R K P I N I T, M. D. D E P A R T M E N T O F P A T H O B I O L O G Y F A C U
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung
 Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Lower Respiratory Tract (Trachea, Bronchi, Bronchioles) & the Lung Color code: Important Extra & Doctor notes Editing file Objectives: By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe:
Organs Associated with the Digestive Tract. Dr. Emad I H Shaqoura M.D, M.Sc. Anatomy Faculty of Medicine, IUG March, 2016
 Organs Associated with the Digestive Tract Dr. Emad I H Shaqoura M.D, M.Sc. Anatomy Faculty of Medicine, IUG March, 2016 2 Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major 90% of saliva Minor 10% of saliva Parotid
Organs Associated with the Digestive Tract Dr. Emad I H Shaqoura M.D, M.Sc. Anatomy Faculty of Medicine, IUG March, 2016 2 Salivary Glands Salivary Glands Major 90% of saliva Minor 10% of saliva Parotid
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Gla dular epithelia are tissues for ed y ells spe ialized to produ e se retio. Secretion: if substances produced
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Histology. There are four basic tissue types in the body are :-
 Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Histology Lab.I There are four basic tissue types in the body are :- 1- Epithelial tissues (Epithelium) 2- Connective tissues 3- Muscular tissues 4- Nervous tissues 1-Epithelial tissues epithelial tissues
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine. Breast. Dr. Ahmed Salman. Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology
 Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
Jordan University Faculty Of Medicine Breast Dr. Ahmed Salman Assistant professor of anatomy & embryology The breasts are specialized accessory glands of the skin that secretes milk. They are situated
Lab Activity 25. Blood Vessels & Circulation. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
Lab Activity 25 Blood Vessels & Circulation Portland Community College BI 232 Artery and Vein Histology Walls have 3 layers: Tunica intima Tunica media Tunica externa 2 Tunica Intima Is the innermost layer
THE ORAL CAVITY
 THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
URINARY SYSTEM. Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3
 URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Glandular epithelium Gland: Is a collection of epithelial cells the secrets a certain product, like: proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. Secretion : A certain material that is produced
5 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Glandular epithelium Gland: Is a collection of epithelial cells the secrets a certain product, like: proteins, lipids and carbohydrates. Secretion : A certain material that is produced
Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System
 Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
Chapter 26 Figure 26.1 An Introduction to the Urinary System Components of the Urinary System Kidney Produces urine Ureter Transports urine toward the urinary bladder Urinary Bladder Temporarily stores
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART
 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY PART 1 DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Urinary System Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra Eliminates nitrogenous wastes from the body Regulates water, electrolyte, and ph
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology
 Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
Basic Urinary Tract Anatomy and Histology The two kidneys are located in the retroperitoneum on either side of the vertebral bladder and the contraction of the detrusor muscle. Any mechanical barrier,
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 7, No 5, 2018, 1608 1614 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) COMPARATIVE HISTOLOGICAL STUDIES OF DUEODENUM IN CATTLE SHEEP AND GOATS Thete
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
General Human Histology. The Urinary System
 General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
General Human Histology Lecture 8 Assist. Prof. Ahmed Anwar Albir The Urinary System Collecting Tubules & Ducts Urine passes from the distal convoluted tubules to collecting tubules that join each other
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas in mature pigeon (Columba Livia)
 Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2013, 3(2):148-152 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas
Available online at www.pelagiaresearchlibrary.com European Journal of Experimental Biology, 2013, 3(2):148-152 ISSN: 2248 9215 CODEN (USA): EJEBAU Histochemical and histological studies on the pancreas
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE
 ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
ALL PHOTOS ARE IDENTIFIED IN THE LOWER RIGHT CORNER WITH THE MAGNIFICATION POWER THAT THE PHOTO WAS TAKEN WITH. SCAN - THIS IS A VERY LOW POWER IMAGE THAT WE USE WHEN A SAMPLE IS SO BIG THAT YOU CAN T
Urinary Anatomy. Lab 40. Kidneys. Nephrons. Renal Corpuscle
 Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
Urinary Anatomy Lab 40. Urinary Anatomy and Kidney Dissection Kidneys: filters blood, produces urine Ureters: convey urine to bladder Bladder: holding tank Urethra: carries urine to the outside for elimination
SCPA602 Respiratory System
 SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
SCPA602 Respiratory System Associate Professor Dr. Wannee Jiraungkoorskul Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Tel: 02-201-5563, E-mail: wannee.jir@mahidol.ac.th 1 Objectives
Histology and development of the respiratory system
 Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Histology and development of the respiratory system Árpád Dobolyi Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology Outline of the lecture 1. Structure of the trachea 2. Histology
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
The Repr duct ve System. Function: producing offspring
 The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal
 Dept. of Anat., Tokyo Med. and Dent. Univ. (Chief: Prof. T. KIRINO). On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal Bodies in Man. In the course of studies on the ZUCKERKANDL's paraganglia, by careful
Dept. of Anat., Tokyo Med. and Dent. Univ. (Chief: Prof. T. KIRINO). On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal Bodies in Man. In the course of studies on the ZUCKERKANDL's paraganglia, by careful
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Oral cavity Lab exercises
 Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
Oral cavity Lab exercises Slide #190 (GT-1-32). Oral cavity, goat. large conical buccal papillae stratified squamous epithelium keratinized or non-keratinized no muscularis mucosae connective tissue represents
Lymphoid Organs. Dr. Sami Zaqout. Dr. Sami Zaqout IUG Faculty of Medicine
 Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Lymphoid Organs Dr. Sami Zaqout Cells of the Immune System Lymphocytes Plasma cells Mast cells Neutrophils Eosinophils Cells of the mononuclear phagocyte system Distribution of cells of the immune system
Objectives. Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract
 GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
GI Histology 1 Objectives Describe the cells of the GI tract and their function Describe the histological features of each part of the GI tract. Differentiate between different parts of the GI tract Appreciate
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
PRACTICAL ROADMAP GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE WJ van der Spuy & T Tshabalala GLANDS AFFECTING LIFESTYLE Submandibular gland (salivary gland) Liver Pancreas Hypophysis (pituitary gland) Thyroid Suprarenal
Sinusoids and venous sinuses
 LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
LYMPHOID SYSTEM General aspects Consists of organs that are made of lymphoid tissue; Immune defense Breakdown of red blood cells. 1 Sinusoids In place of capillaries Endothelium; often fenestrated More
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Gastrointestinal Tract
 CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
CTO Lab #5 GI TRACT & GLANDS; ENDOCRINE SYSTEM Page 1 Gastrointestinal Tract Slide 126 This section through the esophagus shows the characteristic layers of the gastrointestinal tract. Examine the non-keratinized
Epithelium. Four primary tissue types:
 Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
Epithelium Four primary tissue types: Epithelial (covering) Connective (support) Nervous (control) Muscular (movement) Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal muscle 1 Epithelial Tissue Features Epithelial
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi
 Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Histology of the myocardium and blood vessels Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E-mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Histology of blood vessels The walls of arteries and veins are
Lec #2 histology. Bronchioles:
 Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
Lec #2 histology. Last lecture we talked about the upper respiratory tract histology, this one is about the lower part histology. We will discuss the histology of: -bronchioles -respiratory bronchioles
CVS HISTOLOGY. Dr. Nabil Khouri.
 CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY
 Original Research Article PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY A.R. Sreeranjini * 1, N. Ashok 2. ABSTRACT Back ground: Studies about the normal development
Original Research Article PRENATAL DEVELOPMENT OF EXOCRINE PANCREAS IN CROSSBRED GOATS: A HISTOLOGICAL STUDY A.R. Sreeranjini * 1, N. Ashok 2. ABSTRACT Back ground: Studies about the normal development
Flow Cytometry. Hanan Jafar (2017)
 1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
1 Flow Cytometry Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence intensity produced by fluorescent-labeled
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Basic histology 5/4/2015
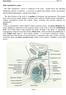 Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic System
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
Lymphatic System and Immunity Lymphatic System Lymphatic System High hydrostatic pressure in the arterioles and capillaries at the arterial part of the circulation leads to move plasma fluid from the capillaries
CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
Biology 325 Fall 2003
 Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
Name: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following is not one of the primary tissue types? A) germinative tissue B) muscle
HISTOLOGY. Simple squamal lungs
 HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
HISTOLOGY Lab Objectives: Students should be able to... 1. Visually identify each class of tissue and examples within each class 2. Indicate the location (in the human body and/or organ) and function of
TISSUES TYPES. CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I. HISTOLOGY = the study of tissues
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 CHAPTER 05 Histology: EPITHELIUM Part 01: Brief Introduction Part 02: Survey of Types Dr. Lawrence G. G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy
LYMPH GLAND. By : Group 1
 LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
LYMPH GLAND By : Group 1 ANATOMY LYMPH NODE Lymphatic Organs Red bone marrow Thymus gland Lymph nodes Lymph nodules Spleen Primary organs Secondary organs Lymph Nodes Firm, smooth-surfaced, bean-shaped
Tissues. Tissues - Overview. Bio 101 Laboratory 3. Epithelial Tissues and Integument
 Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Bio 101 Laboratory 3 Epithelial Tissues and Integument 1 Tissues Tissues to be examined under the microscope Epithelial Tissue Integument Connective Tissue **We will be doing muscle and nervous tissues
Chapter10 Immune system
 Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
Chapter10 Immune system Lyu Zhengmei Department of Histology and Embryology, Anhui Medical University Ⅰ.General Introduction Function ------ Defense The human body immune system has the ability to distinguish
