Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Review Article
|
|
|
- Paul Ellis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Pharmaceutical and Scientific Innovation Review Article FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A NOVEL APPROACH Mahale G. S.* and Derle Nikita D. Department of Pharmaceutics, M.V.P.s College of Pharmacy, Gangapur Road, Nashik , Maharashtra, India * dvderle@yahoo.com Received on: 05/04/12 Revised on: 08/05/12 Accepted on: 15/05/12 ABSTRACT Floating Drug Delivery System is a Novel drug delivery system used to achieve the gastric retention of dosage form which will leads to prolonged release and action of drugs. This delivery system retained in the stomach for a longer period of time and thereby improves the bioavailability of drugs. Several approaches are currently used in the prolongation of gastric residence time (GRT) including floating drug delivery system also called as hydrodynamically balanced system, swelling and expanding system, polymeric bioadhesive systems, high density systems etc. This review also contains current and recent advances in floating drug delivery systems. Key words: Floating Drug Delivery System, Floating Systems, Effervescent Systems, Non-Effervescent Systems. INTRODUCTION A tablet is a pharmaceutical dosage form. It consist a mixture of active substances and excipients, usually in a powder form, and then pressed into a tablet. The excipients include diluents, binders, granulating agents, glidants (flow aids) and lubricants to ensure efficient tablet; disintegrants are used to promote tablet break-up in the digestive tract; sweeteners or flavors to enhance taste; and pigments to make the tablets visually attractive. A polymer coating is also applied to make the tablet smoother and easier to swallow. Oral drug delivery is the most useful form of drug delivery, having the highest degree of patient compliance, and still the preferred route of drug administration. Drugs that are easily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and having short biological half-life are eliminated quickly from the blood circulation. An incomplete release of the drug and shorter residence time of the dosage form in the upper gastro intestinal tract, will lead to lower bioavailability. Therefore, prolonged gastric retention is important in achieving control over the gastro retention time because this helps to retain the controlled release system in the stomach for a longer and predicted time. Drugs that require to be designed as gastro retentive systems are those, 1) Acting locally in stomach. 2) Primarily absorbed from the stomach. 3) Poorly soluble in alkaline ph. 4) Absorbed rapidly from the gastrointestinal tract, and that degrades in the colon. 1 To formulate a successful gastro-retentive drug delivery system, several techniques are currently used such as hydrodynamically balanced systems (HBS)/ floating drug delivery system, low-density systems, raft systems incorporating alginate gels, bioadhesive or mucoadhesive systems, high density systems, superporous hydrogels, single and multiple unit gas generating systems, hollow microsphere, and magnetic systems. There are three possible techniques to rendered drug floating, Gas contains floating systems:- Generation of co2 gas via chemical reaction between sodium bicarbonate and hydrochloric acid of gastric juice. The gas kept in the stomach ensures its floating Systems with low density core not subject to rapid chemical and physical changes, providing for the drug floatation. The core is coated with a gel or other polymeric shells from which drug are gradually released. 2 Requirements for Gastric Retention:- To achieve gastric retention, the dosage form must satisfy the following requirements, a) The dosage form must be able to withstand the forces caused by peristaltic waves in the stomach and the constant contractions and grinding and churning mechanisms. b) It must resist the premature gastric emptying. c) Once its purpose has been served, the device should be removed from the stomach with ease. 1 FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS) Floating systems, first described by Davis in 1968, FDDS have bulk density lower than that of the gastric fluid, and thus remain float in stomach for a prolong period. Sustainedrelease dosage forms gives prolonged action of a drug in the body. A floating drug-delivery system floats in the gastric juice without affecting the gastric emptying rate. It forms a cohesive gel barrier that serves as a reservoir and releases the drug over the desired period of time. This technique helps to increase the drug's gastric residence time and reduces the variability in bioavailability. 1 while the system is floating on the gastric contents the drug is released slowly at the desired rate. After release of drug, the system is eliminated from the stomach. This results in an increased GRT and a better control on fluctuations in plasma drug concentrations. The floating sustained release dosage forms exhibit most of the characteristics of hydrophilic matrices and are known as hydrodynamically balanced systems (HBS) since they are able to maintain their low apparent density, while the polymer hydrates and builds a gel like barrier at the outer surface. The drug is released progressively from the swollen matrix, as in the case of conventional hydrophilic matrices. These forms are expected to remain buoyant (3 4 h) in the gastric contents without affecting the intrinsic rate of emptying because their bulk density is lower than that of the gastric fluid. Among the different hydrocolloids recommended for floating form formulations, cellulose ether polymers are the most popular, especially hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC). Fatty material with a bulk density lower than one may be added to the formulation to decrease the water intake rate and increase buoyancy. In parallel with formulation studies, investigations have been undertaken in animals and humans to evaluate the intragastric retention performance of floating. These assessments were carried out either indirectly through
2 pharmacokinetic studies with a drug tracer, or directly by means of X-ray and gamma scintigraphic monitoring of the transit through the GI tract. When a floating capsule is administered to subjects who have consumed a fat and protein meal, it remains buoyant at the surface of the gastric contents in the upper part of the stomach and moves to the lower region progressively as the meal empties from the stomach. The reported gastric retention times range from 4 to 10 h. Pharmacokinetic and bioavailability evaluation studies confirm the favorable effect of this prolonged gastric residence time. 2 MECHANISM OF FLOATING SYSTEMS Various attempts have been made to retain the dosage form in the stomach as a way of increasing the retention time. These attempts include introducing floating dosage forms (gasgenerating systems and swelling or expanding systems), Floating drug delivery systems (FDDS) have a bulk density less than gastric fluids and so remain buoyant in the stomach without affecting the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period of time. While the system is floating on the gastric contents (given in the Figure 1 (a)), the drug is released slowly at the desired rate from the system. After release of drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach. This results in an increased GRT and a better control on the fluctuations in plasma drug concentration. However, besides a minimal gastric content needed to allow the proper achievement of the buoyancy retention principle, a minimal level of floating force (F) is also required to keep the dosage form reliably buoyant on the surface of the meal. To measure the floating force kinetics, a novel apparatus for determination of resultant weight has been reported in the literature. The apparatus operates by measuring continuously the force equivalent to F (as a function of time) that is required to maintain the submerged object. The object floats better if F is on the higher positive side (Figure 1(b)). This apparatus helps in optimizing FDDS with respect to stability and durability of floating forces produced in order to prevent the drawbacks of unforeseeable intragastric buoyancy capability variations. 3 F = F buoyancy - F gravity = (Df - Ds) gv Where, F= total vertical force, Df = fluid density, Ds = object density, v = volume and g = acceleration due to gravity 3, 4 FIG. 1 MECHANISM OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM 4 CLASSIFICATION OF FDDS BASED ON MECHANISM OF BUOYANCY A. Single Unit Floating Dosage Systems a) Effervescent Systems ( Gas generating system) b) Non-effervescent Systems B. Multiple Unit Floating Dosage Systems a) Non-effervescent Systems b)effervescent Systems c) Hollow Microspheres C. Raft Forming Systems D. Expandable, Unfoldable, and Swellable systems. E. Mucoadhesive or Bioadhesive systems. Effervescent Systems/ Gas-generating Systems:- These buoyant systems use matrices prepared with swellable polymers like HPMC, polysaccharides like chitosan, effervescent components like sodium bicarbonate, citric acid and tartaric acid or chambers containing a liquid that becomes a gas at body temperature. The optimal stoichiometric ratio of citric acid and sodium bicarbonate for gas generation is reported to be 0.76: 1. The common approach for preparing these systems involves resin beads loaded with bicarbonate and coated with ethyl cellulose. The coating, which is insoluble but permeable, allows permeation of water. Thus, carbon dioxide is released, causing the beads to float in the stomach. Other approaches and materials that have been reported are highly swellable hydrocolloids and light mineral oils, a mixture of sodium alginate and sodium bicarbonate, multiple unit floating pills that generate carbon dioxide (co2) when ingested. 1, 2 FIG.2 Mechanism of floatation via CO2 generation. 4 Non-effervescent systems :- Colloidal gel barrier system Such systems contains drug with gel forming hydrocolloids meant to remain buoyant on stomach contents. This system incorporates a high level of one or more gel forming highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids. e.g. HEC, HPMC, NaCMC, Polysacchacarides and matrix forming polymer such as polycarbophil, polyacrylates and polystyrene etc. when coming in contact with gastric fluid, the hydrocolloid in the system hydrates and forms a colloidal gel barrier around the gel surface. The air trapped by the swollen polymer maintains a density less than unity and confers buoyancy to these dosage forms. Microporous Compartment System: This technology is based on the encapsulation of drug reservoir inside a Microporous compartment with aperture along its top and bottom wall. The peripheral walls of the drug reservoir compartment are completely sealed to prevent any direct contact of the gastric mucosal surface with the undissolved drug. In stomach the floatation chamber containing entrapped air causes the delivery system to float over the gastric contents. Gastric fluid enters through the apertures, dissolves the drug, and carries the dissolve drug for continuous transport across the intestine for absorption.
3 Alginate beads Multiple unit floating dosage forms have been developed from freeze-dried calcium alginate. Spherical beads of approximately 2.5 mm in diameter can be prepared by dropping a sodium alginate solution in to aqueous solutions of calcium chloride, causing precipitation of calcium alginate. The beads are then separated snap and frozen in liquid nitrogen, and freeze dried at -40 C for 24 hours, leading to the formation of porous system, which can maintain a floating over a 12 hours. 1,4,5 Hollow microspheres Hollow microspheres (microballons), loaded with drug in their outer polymer shells were prepared by a novel emulsion-solvent diffusion method. The ethanol : dichloromethane solution of the drug and an enteric acrylic polymer was poured in to an agitated aqueous solution of PVA that was thermally controlled at 40 C.The gas phase generated in dispersed polymer droplet by evaporation of dichloromethane formed in internal cavity in microspheres of the polymer with drug. The microballons floated continuously over the surface of acidic dissolution media containing surfactant for greater than 12 hours in vitro. 5 Raft Forming system Raft forming systems have received much attention for the delivery of antacids and drug delivery for gastrointestinal infections and other disorders. The mechanism involved in the raft formation includes the formation of a viscous cohesive gel in contact with gastric fluids, wherein each portion of the liquid swells forming a continuous layer called a raft. This raft floats on gastric fluid because of the low bulk density created by the formation of CO2. Usually, the system contains a gel forming agent and alkaline bicarbonates or carbonates responsible for the formation of CO2 to make the system less dense and able to float on the gastric fluids. It is used for the treatment of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections in the GIT. 2 Expandable, Unfoldable, and Swellable Systems The dosage form must be small enough to be swallowed and must not cause gastric obstruction either singly or by accumulation. Thus, their configurations are required to develop expandable system to prolong gastric retention time (GRT). Thus, gastroretentivity is improved by the combination of substantial dimension with high rigidity of dosage form to withstand peristalsis and mechanical contractility of the stomach. Unfoldable and swellable systems are used to develop an effective gastro retentive drug delivery. Unfoldable systems are made of biodegradable polymers. They are available in different geometric forms like tetrahedron, ring or planner membrane of biodegradable polymer compressed within a capsule which extends in the stomach. Swellable systems are also retaining in the gastro intestinal tract (GIT) due to their mechanical properties. The swelling is usually results from osmotic absorption of water. Expandable systems have some drawbacks like problematic storage of much easily hydrolysable, biodegradable polymers. 3 FIG 3. DRUG RELEASE FROM SWELLABLE SYSTEMS. 3 Mucoadhesive or Bioadhesive Systems The basis of mucoadhesion is that a dosage form can stick to mucosal\ surface by different mechanisms. Different theories to explain these mechanisms are, 1. Mucoadhesion take place by attractive electrostatic forces between the glycoprotein mucin network and the bioadhesive material. 2. Adsorption theory- Bioadhesion is due to secondary forces as Vander Waals forces and hydrogen bonding. 3. Wetting theory- Based on the ability of bioadhesive polymers to spread and develop intimate contact with mucus layers. 4. Diffusion theory- Physical entanglement of mucin strands and the flexible polymer chains, or an interpenetration of mucin strands into the porous structure of polymer substrate. 3 FACTORS AFFECTING GASTRIC RETENTION: Density Density of the dosage form is inversely proportional to the gastric retention. Density of the dosage form should be less than the gastric content density. (1.004 gm/ml) Size and Shape Dosage form unit with a diameter of more than 7.5 mm are reported to have an increased GRT competed to with those with a diameter of 9.9 mm. The dosage form with a shape tetrahedron and ring shape devises with a flexural modulus of 48 and 22.5 kilopond per square inch (KSI) are reported to have better 90 to 100 % retention at 24 hours compared with other shapes. 6 Fed or Unfed State Under fasting conditions, the GI motility is characterized by periods of strong motor activity or the migrating myoelectric complexes (MMC) that occurs every 1.5 to 2 hours. The MMC sweeps undigested material from the stomach and if the timing of administration of the formulation coincides with that of the MMC, the GRT of the unit can be expected to be very short. However, in the fed state, MMC is delayed and GRT is considerably longer. Nature of the meal Feeding of indigestible polymers of fatty acid salts can change the motility pattern of the stomach to a fed state, thus decreasing the gastric emptying rate and prolonging the drug release. 6 Caloric Content GRT can be increased between 4 to 10 hours with a meal that is high in proteins and fats. Frequency of feed The GRT can increase by over 400 minutes when successive meals are given compared with a single meal due to the low frequency of MMC.
4 Age Elderly people, especially those over 70 years have a significantly longer GRT. Posture GRT can vary between supine and upright ambulatory states of patient. 8 Concomitant drug administration Anticholinergic like atropine and propentheline Opiates like codeine and prokinetic agents like metoclopramide and cisapride. ADVANTAGES OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEAM: Floating drug delivery systems have numerous advantages listed below: Acidic substances like aspirin cause irritation on the stomach wall when come in contact with it. Hence, HBS formulation may be useful for the administration of aspirin and other similar drugs. The FDDS are useful for drugs which are absorbed through the stomach. E.g. Ferrous salts and for drugs meant for local action in the stomach and treatment of peptic ulcer disease e.g. Antacids. When there is vigorous intestinal movement and short transit time as might occur in certain type of diarrhea, poor absorption is expected. Under such circumstances it may be advantageous to keep the drug floating condition in stomach to get a relatively better response. This method is also effective with medicaments which are absorbed from the intestine. E.g. Clorpheniramine maleate Drugs which has narrow absorption window in the small intestinal region, that are formulated as Floating drug delivery system (FDDS). Certain types of drugs can benefit from using FDDS, these includes, a) Drugs acting locally in the stomach. b) Drugs those are primarily absorbed in stomach. c) Drugs those are poorly soluble in alkaline ph. d) Drugs with narrow absorption window. e) Drugs those are degrade in the colon. FDD minimizes the counter activity of the body leading to higher drug efficiency. FDDS minimizes the fluctuations of drug concentration and effects. Therefore, the concentration dependant adverse effects that are associated with peak concentration can be presented. This feature is of special importance for drugs with narrow therapeutic index. DISADVANTAGES OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS There are certain situations where gastric retention is not desirable. Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are known to cause gastric lesions, and slow release of such drugs in the stomach is unwanted. Thus, drugs that may irritate the stomach lining or are unstable in its acidic environment should not be formulated in gastroretentive system. Other drugs, such as isosorbide dinitrate, that are absorbed equally well throughout the GI tract will not benefit from incorporation into a gastric retention system. Not suitable for drugs that have solubility or stability problem in GIT. Drugs such as nifedipine which is well absorbed along the entire GIT and which undergoes first pass metabolism, may not be desirable. Not suitable for drugs that have solubility or stability 1, 3, 10, 11 problem in GIT. EVALUATION PARAMETERS OF FDDS Weight variation: Uniformity of Weight according to Indian pharmacopoeia, 20 tablets were selected at random, weight together and individually for the determination of weight of tablets. The mean and standard deviations were calculated. Hardness : Hardness or tablet crushing strength (fc ), the force required to break a tablet in a diametric Compression was measured using Monsanto tablet hardness tester. It is expressed in kg/cm2. Friability: Friability The friability test was carried out in Roche Friabilator. Ten tablets were weighted (Wo) initially and put in a rotating drum. Then the tablets were subjected to 100 falls of 6 in. height. After completion of rotation, the tablets were again weighted (W). % Weight loss or friability (f) = (1 - w/ w0) 100 Disintegration time: In vitro disintegration time was determined using disintegration test apparatus. For this, a tablet was placed in each of the six tubes of the apparatus and one disc was added to each tube. The time taken for complete disintegration of the tablet with no palpable mass remaining in the apparatus was measured. Buoyancy time (Floating time) : A tablet was introduces in to beaker containing 100ml of 0.1N HCL. The time taken by the tablet to come up to the surface and floated was taken as the buoyancy time. An average of three determinations was taken for the floating forms. Drug release: Dissolution tests are performed using the dissolution apparatus. Samples are withdrawn periodically from the dissolution medium with replacement and then analyzed for their drug content after an appropriate dilution. Content uniformity: The drug content in each formulation was determined by triturating 20 tablets and powder equivalent to average weight was added in 100ml of solvent, followed by stirring for 30 minutes. The solution was filtered through a 0.45μ membrane filter, diluted suitably and the absorbance of resultant solution was measured spectrophotometrically in UV. X-ray/gamma scintigraphy X-ray/gamma scintigraphy is currently a very popular method for evaluating parameters for floating dosage forms. It helps to locate the dosage form in the GIT and it can be used to predict and correlate the gastric emptying time and the passage of the dosage form in the GIT. Here, the inclusion of a radio-opaque material into a solid dosage form enables it to be visualized by X- rays. Similarly, the inclusion of a γ- emitting radio-nuclide in a formulation allows indirect external observation using a γ-camera or scintiscanner. In case of γ-scintigraphy, the γ-rays emitted by the radio-nuclide are focused on a camera, which helps to monitor the location of the dosage form in the GI tract. RECENT ADVANCES IN FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Ninan Ma et al developed a type of multi-unit floating alginate (Alg) microspheres by the ionotropic gelation method with calcium carbonate (CaCO3) being used as gasforming agent. Attempts were made to enhance the drug encapsulation efficiency and delay the drug release by adding
5 chitosan (Cs) into the gelation medium and by coating with Eudragit, respectively. The gastrointestinal transit of optimized floating sustainedrelease microspheres was compared with that of the nonfloating system manufactured from identical material using the technique of gammascintigraphy in healthy human volunteers. It was found that the drug encapsulation efficiency of Cs Alg microspheres was much higher than that of the Ca Alg microspheres, and coating the microspheres with Eudragit RS could extend the drug release significantly. Both uncoating and coating microspheres were able to continuously float over the simulated gastric fluid (SGF) for 24 h in vitro. Prolonged gastricretention time (GRT) of over 5 h was achieved in the volunteer for the optimized coating floating microspheres (FM). In contrast, non-floating system (NFM) could be emptied within 2.5 h. Sungthongjeen et al have prepared a floating multilayer coated tablets based on gas formation. The system consists of a drug-containing core tablet coated with a protective layer (hydroxypropyl methylcellulose), a gas forming layer (sodium bicarbonate) and a gas-entrapped membrane, respectively. Eudragit RL 30D was chosen as a gasentrapped membrane due to its high flexibility and high water permeability. The obtained tablets enabled to float due to the CO2-gas formation and the gas entrapment by polymeric membrane. The effect of formulation variables on floating properties and drug release was investigated. The floating tablets using direct-compressed cores had shorter time to float and faster drug release than those using wet-granulated cores. The increased amount of a gas forming agent did not affect time to float but increased the drug release from the floating tablets while increasing coating level of gasentrappe membrane increased time to float (more then 8 hours) and slightly retarded but sustained drug release. Rajnikanth and Mishra have developed a floating in situ gelling system of clarithromycin (FIGC) using gellan as gelling polymer and calcium carbonate as floating agent for potentially treating gastric ulcers, associated with Helicobacter pylori. Gellan based FIGC was prepared by dissolving varying concentrations of gellan in deionized water to which varying concentrations of drug and sucralfate were dispersed well. The addition of sucralfate to the formulation significantly suppressed the degradation of clarithromycin at low ph. FIGC showed a significant anti-h. pylori effect than that of clarithromycin suspension. The in situ gel formulation with sucralfate cleared H.pylori more effectively than that of formulation without sucralfate. In addition, the required amount of clarithromycin for eradication of H. pylori was found to be less from FIGC than from the corresponding clarithromycin suspension. It was concluded that prolonged gastrointestinal residence time and enhanced clarithromycin stability resulting from the floating in situ gel of clarithromycin might contribute better for complete clearance of H. pylori. 2, 4 DRUGS USED IN THE FORMULATIONS OF FLOATING DOSAGE FORMS Floating microspheres Aspirin, Griseofulvin, p- nitroaniline, Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, Piroxicam, Verapamil, Cholestyramine, Theophylline, Nifedipine, Nicardipine, Dipyridamol, Tranilast and Terfinadine Floating granules - Diclofenac sodium, Indomethacin and Prednisolone Films Cinnarizine, Albendazole Floating tablets and Pills Acetaminophen Acetylsalicylic acid, Ampicillin, Amoxycillin trihydrate, Atenolol, Fluorouracil, Isosorbide mononitrate, Para- aminobenzoic acid, Piretanide, Theophylline, Verapamil hydrochloride, Chlorpheniramine maleate, Aspirin, Calcium Carbonate, Fluorouracil, Prednisolone, Sotalol, pentoxyfilline and Diltiazem HCl. Floating Capsules - Chlordiazepoxide hydrogen chloride, Diazepam, Furosemide, Misoprostol, L-Dopa, Benserazide, Ursodeoxycholic acid and Pepstatin, and Propranolol. 2, 4 MARKETED PRODUCTS OF FDDS Some of the marketed formulations are listed as follows:- Table. 1. GASTRORETENTIVE PRODUCTS AVAILABLE IN THE MARKET. 3, 5 BRAND NAME DELIVERY SYSTEAM DRUG (DOSE) COMPANY NAME Val Floating Capsule Diazepam (15mg) Hoffmann-LaRoche Topalkan@ Floating liquid alginate preparation Al Mg Antacid Pierre Fabre Drug, France Conviron Cytotech Cifran OD Liquid Gaviscon Madopar HBS Colloidal gel forming FDDS Bilayer floating capsule Gas-generating floating form Effervescent Floating liquid alginate preparations Floating CR capsule Ferrous sulphate Misoprostol (100μg/200μg Ciprofloxacin (1gm) Al hydroxide (95 mg), Mg Carbonate (358 mg) Levodopa & benserazide Ranbaxy, India Pharmacia, USA Ranbaxy, India GlaxoSmithKline, India Roche product, USA. APPLICATIONS OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Floating drug delivery offers several applications for drugs having poor bioavailability because of the narrow absorption window in the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract. It retains the dosage form at the site of absorption and thus enhances the bioavailability. Sustained Drug Delivery :- HBS systems can remain in the stomach for long periods and hence can release the drug over a prolonged period of time. The problem of short gastric residence time encountered with an oral CR formulation hence can be overcome with these systems. These systems have a bulk density of <1 as a result of which they can float on the gastric contents. These systems are relatively large in size and passing from the pyloric opening is prohibited
6 E.g. Sustained release floating capsules of nicardipine hydrochloride were developed and were evaluated in vivo. The formulation compared with commercially available MICARD capsules using rabbits. Plasma concentration time curves showed a longer duration for administration (16 hours) in the sustained release floating capsules as compared with conventional MICARD capsules (8 hours). Site-Specific Drug Delivery :- These systems are particularly advantageous for drugs that are specifically absorbed from stomach or the proximal part of the small intestine, e.g., riboflavin and furosemide. E.g. Furosemide is primarily absorbed from the stomach followed by the duodenum. It has been reported that a monolithic floating dosage form with prolonged gastric residence time was developed and the bioavailability was increased. AUC obtained with the floating tablets was approximately 1.8 times those of conventional furosemide tablets. Absorption Enhancement Drugs that have poor bioavailability because of site-specific absorption from the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract are potential candidates to be formulated as floating drug delivery systems, thereby maximizing their absorption. E.g. A significantly increase in the bioavailability of floating dosage forms(42.9%) could be achieved as compared with commercially available LASIX tablets (33.4%) and enteric 10, 12 coated LASIX-long product (29.5%). CONCLUSION Gastroretentive floating drug delivery systems have emerged as an efficient means of enhancing the bioavailability and controlled delivery of many drugs. The increasing sophistication of delivery technology will ensure the development of increase number of gastroretentive drug delivery system which has the high absorption window and therapeutic index. The FDDS become an additional advantage for drugs that are absorbed primarily in the upper part of GI tract, i.e., the stomach, duodenum, and jejunum. ACKNOWLEDGMENT We are thankful to College of pharmacy, Nasik for providing me knowledge about work. We are also thankful to Dr. D. V. Derle who generously shared his wisdom and expertise with me & has provided me an excellent guidance and general interest. REFERENCES: 1. Shukla S, Patidar A, Agrawal S, Chouske R. Recent Advancement of Stomach Specific Floating Drug Delivery System: International Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Archives 2011; Shah SH, Patel JK, Patel NV. An Overview of a Gastroretentive Floating Drug Delivery Systems: A better approach. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2009; Zaware SR, Gaikwad PD, Bankar VH, Pawar SP. A Review on Floating Drug Delivery System: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2010; Shah SH, Patel JK, Patel NV. Stomach specific Floating drug delivery system: International journal of PharmTech Research 2009; Hetangi R, Vishnu P, Moin M. Floating Drug Delivery System: Innovative Approach of Gastroretention: International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences Review and Research 2010; Lachman L, Liberman HA, and Kanig JL. The Theory and Practice of Industrial Pharmacy (3rd Edn.), Varghese publishing House Bombay; Sangekar S, Vadino WA, Chaudhary I, Parr A, Beihn, R, and Digenis G. Evaluation of the effect of food and specific gravity of tablets on gastric retention time: International Journal Pharmaceutics 1987; 35: Tripathi KD. Essentials of medical pharmacology 2008; 6 th edition, JAYPEE Brothers Medical Publishers Ltd. New Delhi Fukuda M, Nicholas AP, James WM. Floating hot-melt extruded tablets for gastroretentive controlled drug release system: European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2003; 18: Mayavanshi AV, Gajjar SS. Floating Drug Delivery System to increase gastric retention of drugs: A Review: Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 2008; Vinod KR., Vasa S, David B, Padmashri A, Sandhya S. Approaches for Gastrotentive Drug Delivery Systems: International Journal of Applied Biology and Pharmaceutical Technoology 2010; Chandel A, Chauhan K, Bharat P, Arora S. Floating Drug Delivery Systems A Better Approach: International Current Pharmaceutical Journal 2012; Sauzet C, Brunob MC, Nicolasc M, Kister J, Piccerelle P, Prinderrea P. An innovative floating gastro retentive dosage system: Formulation and in vitro evaluation: International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2009; 378: Rouge N, Cole ET, Doelker E, Buri P. Buoyancy and drug release patterns of floating mini tablets containing piretanide and atenolol as model drugs. Pharm. Dev. Technol 1998; 3: Singh BN, Kim HK. Floating drug delivery systems: an approach to oral controlled drug delivery via gastric retention: Journal of Controlled Release 2000; 63: Rosa M, Jimenez C, Zia H, Rhodes TC. Design and testing in vitro of a bioadhesive and floating drug delivery system for oral application: International Journal of Pharmaceutics 1994; 105: Sungthongjeen S, Paeratakul O, Limmatvapirat S, Puttipipatkhachorn S. Preparation and in vitro evaluation of a multiple-unit floating drug delivery system based on gas formation technique: International Journal of Pharmaceutics 2006; 324: Sokar AH, Algamal MS, Naggar SS. Preparation and evaluation of ketoprofen floating oral drug delivery system: International Journal of Pharm. 2001;220: Klausner EA, Lavy E, Michael F, Hoffman A. Expandable gastroretentive dosage forms: Journal of Controlled Release 2003; 90:
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN PHARMACY, BIOLOGY AND CHEMISTRY Research Article Formulation and Development of Sustained Release Tablets of Valsartan Sodium G. Sandeep * and A. Navya Department of
A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac
 Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Asian Journal of Chemistry Vol. 22, No. 6 (2010), 4239-4244 A Comparative Evaluation of Cross Linked Starch Urea-A New Polymer and Other Known Polymers for Controlled Release of Diclofenac K.P.R. CHOWDARY*
Formulation and Evaluation
 Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Chapter-5 Formulation and Evaluation 5.1 OBJECTIVE After successful taste masking and solubility enhancement of drugs in preliminary studies, by using Mannitol Solid Dispersion, next step includes the
Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery System
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 4(1), 1-26 Research Article ISSN: 976-822X Design and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Drug Delivery
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Scholars Research Library
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(1): 121-137 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
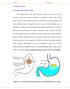 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Global College of Pharmacy, Kahnpur Khui, Tehsil Anandpur Sahib, Distt.- Ropar, Punjab, India
 IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 09 (Research Article) Received on 19 May, 2012; received in revised form 25 June, 2012; accepted 27 August, 2012 IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TWO MARKETED BRANDS OF PARACETAMOL TABLETS
IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 09 (Research Article) Received on 19 May, 2012; received in revised form 25 June, 2012; accepted 27 August, 2012 IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TWO MARKETED BRANDS OF PARACETAMOL TABLETS
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin Bilayer Tablets
 CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-6465 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article Design and In-vitro Evaluation of Silymarin
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use
 Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
DEVELOPMENT OF NON SODIUM EFFERVESCENT TABLET OF PARACETAMOL USING ARGININE CARBONATE
 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 5 (Research Article) Received on 17 July, 2012; received in revised form, 23 February, 2013; accepted, 14 April, 2013 DEVELOPMENT OF NON SODIUM EFFERVESCENT TABLET OF PARACETAMOL
IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 5 (Research Article) Received on 17 July, 2012; received in revised form, 23 February, 2013; accepted, 14 April, 2013 DEVELOPMENT OF NON SODIUM EFFERVESCENT TABLET OF PARACETAMOL
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
FORMULATION AND EVALUATIONOF AMOXYCILLIN: THREE-LAYER GUAR GUM MATRIX TABLET
 Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Gupta and Singh, IJPSR, 2013; Vol. 4(7): 2683-2690. ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 7 (Research Article) Received on 05 March, 2013; received in revised form, 29 April, 2013; accepted, 29 June,
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 8(1), 2010, 405-414 STABILITY STUDIES OF FORMULATED CONTROLLED RELEASE ACECLOFENAC TABLETS V. L. NARASAIAH, T. KARTHIK KUMAR, D. SRINIVAS, K. SOWMYA, P. L. PRAVALLIKA and Sk. Md. MOBEEN
Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H.
 Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Pharmaceutical Research Design and Characterization of Gastroretentive Bilayer Tablet of Amoxicillin Trihydrate and Ranitidine Hydrochloride for H. pylori Infection Shikha Jain, Vikas Jain, S.C. Mahajan
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation
 Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
Development of Metclopramide Floating Tablets Based on HPMC Matrices: A Comparison Study with Marketed Formulation Shammy Jindal*, Amit Sharma & Kamya Jindal Laureate Institute of Pharmacy, Kathog - Himachal
The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation
 METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
METHOCEL Premium Cellulose Ethers Application Data The Relevance of USP Methodology in the Development of a Verapamil Hydrochloride (240 mg) Extended Release Formulation INTRODUCTION Hydrophilic matrices
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride
 Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
Development and evaluation of controlled release mucoadhesive tablets of Tramadol Hydrochloride R. Margret Chandira*, C.M. Sahu and B. Jayakar Department of Pharmaceutics Vinayaka Mission s College of
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol.4 (2), April-June, 2014 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
REVIEW ON- GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM PRAFULL GHORPADE* 1, SHRENIK KAMBLE 2 1 Marathwada Mitra Mandal s College of Pharmacy, Kalewadi (Thergaon), Pune, Maharashtra, India *Corresponding author
Asian Journal of Pharmacy and Life Science ISSN Vol. 2 (2), July-Sept,2012
 STUDIES ON EFFECT OF SUPERDISINTEGRANTS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS Chowdary K. P. R 1, Venugopal. K *2 1 College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Andhra University, Vishakapattanam. 2 * Nirmala college
STUDIES ON EFFECT OF SUPERDISINTEGRANTS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS Chowdary K. P. R 1, Venugopal. K *2 1 College of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Andhra University, Vishakapattanam. 2 * Nirmala college
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept ISSN FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL
 Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Volume: 2: Issue-3: July-Sept -2011 ISSN 0976-4550 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF NICORANDIL Ajaykumar Patil*, Ashish Pohane, Ramya Darbar, Sharanya Koutika, Alekhya
Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets of lisinopril
 Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
Journal of GROVER Scientific & Industrial AGARWAL: Research FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF SUBLINGUAL TABLETS OF LISINOPRIL Vol. 71, June 2012, pp. 413-417 413 Formulation and evaluation of sublingual tablets
STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 1934-1942 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com STUDIES ON EFFECT OF BINDERS ON ETORICOXIB TABLET FORMULATIONS K. VENUGOPAL * and K. P. R. CHOWDARY a Nirmala College
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Venkateswara Rao et.al Indian Journal of Research in Pharmacy and Biotechnology ISSN: (Print) ISSN: (Online)
 Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
Design and development of Metformin hydrochloride Tried sustained release tablets Venkateswara Rao T 1 *, Bhadramma N 1, Raghukiran CVS 2 and Madubabu K 3 Bapatla College of Pharmacy, Bapatla, Guntur-522101
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Research Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF CLARITHROMYCIN ORAL DOSAGE FORM AGAINST HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Research Article FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF CLARITHROMYCIN ORAL DOSAGE FORM AGAINST HELICOBACTER PYLORI INFECTION
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche
 Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: Journal homepage:
 Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Indian J.Pharm.Biol.Res. 2018; 6(1):22-29 CODEN (USA): IJPB07 ISSN: 2320-9267 Indian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biological Research (IJPBR) Journal homepage: www.ijpbr.in Review Article A REVIEW ON
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS
 Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct ISSN APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS. Nalanda College of Pharmacy, Nalgonda, A.P.
 Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
Int J Pharm Bio Sci. Harshal P. Gahiwade *et al Available Online through IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH
 Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
Page166 IJPBS Volume 2 Issue 1 JAN-MARCH 2012 166-172 FORMULATION AND IN-VITRO EVALUATION OF TRIFLUOPERAZINE HYDROCHLORIDE BILAYER FLOATING TABLET Harshal P. Gahiwade *, Manohar V. Patil, Bharat W. Tekade,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate
 Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Formulation and evaluation of gastro retentive floating tablets of Terbutaline sulphate Lokesh Kumar*, Virendra Singh, Rakesh Kumar Meel Department of Pharmaceutics, Goenka College of Pharmacy, NH-11,
Research Article. Chemical equivalence three brands of Aspirin sold in Sokoto State
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(2):47-51 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chemical equivalence three brands of Aspirin sold
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(2):47-51 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Chemical equivalence three brands of Aspirin sold
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 0975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 2011, 3(3):159-164 Studies on formulation and in vitro evaluation
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES
 Research Article [Dhakar et al., 3(2): Feb., 12] ISSN: 9767126 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and evaluation of floating tablet of rosiglitazone malate Koushlendra Singh,
Research Article [Dhakar et al., 3(2): Feb., 12] ISSN: 9767126 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACY & LIFE SCIENCES Formulation and evaluation of floating tablet of rosiglitazone malate Koushlendra Singh,
Patel B et al. IRJP 1 (1)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article IMPROVEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF CINNARIZINE BY USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Patel Bipin*, Patel Jayvadan,
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article IMPROVEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF CINNARIZINE BY USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Patel Bipin*, Patel Jayvadan,
Innovations in Design: NIA-West. Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017
 Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
 Human Journals Research Article May 2015 Vol.:3, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Tanvi P Gunjal et al. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
Human Journals Research Article May 2015 Vol.:3, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Tanvi P Gunjal et al. Formulation Development and Evaluation of Sitagliptin Floating Tablets Containing Natural Polymer
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Easy, fast and reliable!
 Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review
 Volume 1, issue1 (2011), 01-13 Review Article International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review Shivram Shinde*, Imran Tadwee, Sadhana Shahi
Volume 1, issue1 (2011), 01-13 Review Article International Journal of Pharmaceutical Research & Allied Sciences Gastro retentive Drug Delivery System: A Review Shivram Shinde*, Imran Tadwee, Sadhana Shahi
Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug
 Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
Formulation and evaluation of immediate release salbutamol sulphate
 5 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of immediate release layer of salbutamol sulphate Salbutamol is moderately selective beta (2)-receptor agonist similar in structure to terbutaline and widely
5 Formulation, optimization and evaluation of immediate release layer of salbutamol sulphate Salbutamol is moderately selective beta (2)-receptor agonist similar in structure to terbutaline and widely
Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs
 Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
Mansoura University Faculty of Pharmacy Department of Pharmaceutics Pharmaceutical Studies on Formulation and Evaluation of Sustained Release Tablets Containing Certain Drugs Thesis presented by Ali Saeed
