Kuntarti, SKp, M.Biomed
|
|
|
- Janel Fleming
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Kuntarti, SKp, M.Biomed
2 Introduction 4 Major Nutrient Types: 1. Macronutrients (Carbohydrate, protein, lipid) to supply energy for body 2. Vitamins help to use the macronutrients & maintain body s tissues 3. Minerals & Electrolytes to maintain the homeostasis 4. Water as a solvent in the body, media of body s chemical reaction, & distribute the nutrients to tissues
3 HEALTHY BALANCED DIET HEALTHY BALANCED DIET BALANCED VARIATION MODERATION
4 VITAMIN The organic chemical substances are essential for life. Work as a regulator or modulator to keep biological reactions in the body functioning normally Vitamins act as coenzymes for enzymes so that nutrients such as amino acids and glucose are enzymatically utilized for muscle growth or energy. Vital for growth, maintenance and reproduction
5 VITAMIN An exception vitamin D, our bodies cannot synthesize vitamins all vitamins must be consumed daily as a part of the diet. The body only need a small amount of vitamin daily, which can be easily obtained through one s diet. The intake of vitamins should be increased: - during periods of rapid body growth, - by who are pregnant or are breastfeeding, - by those with inadequate diet (ex: alcoholic, geriatrics) - by children who have poor nutrient or are malnourished
6 VITAMIN Vitamin deficiencies can cause cellular and organ dysfunction that may result in a slow recovery from illness When there is lack of these in diet replacement drug therapy For those who maintain a nutritionally balanced daily diet vitamin replacements are not necessary
7 Justification for Vitamin Categories Inadequate absorption Inability to utilize vitamins Increased vitamin losses Increased vitamin requirements Supplement Deficiencies Malabsorption, diarrhea, infectious & inflammatory diseases Liver disease, renal disease, certain hereditary deficiencies Fever from infection process, hyperthyroidism, hemodialysis, cancer, starvation, crash diet Early childhood, pregnancy, debiliting disease (cancer, alcoholism), gastrointestinal surgery, special diets
8 VITAMIN Two groups of Vitamins : fat-soluble and watersoluble. Fat-soluble vitamins are vitamins A, D, E and K. Water-soluble vitamins are vitamins B1, B2, B6, B12, C, niacin, pantothenic acid, folic acid and biotin Based on solubility, some vitamins are absorbed differently. Ex: fat is required for vitamins A, D, E and K and is an intrinsic factor for vitamin B12.
9 VITAMIN Some vitamins are labile during food processing and cooking, ways of consuming and timing must be considered for proper nutrition. Unlike proteins, carbohydrates or fats, vitamins are not metabolized to build tissues or organs.
10 Fat-soluble Vitamin Vitamin A, D, E, & K Pharmacokinetics 1) Are absorbed easily 2) Are metabolized slowly 3) Can be stored in fatty tissue, liver, & muscle in significant amounts 4) Are excreted in the urine at a slow rate Vitamin A & D are toxic if taken in excess amounts over time. Vitamin A can be store in the liver up to 2 years Vitamin E & K are less toxic than vitamin A & D
11 Vitamin A A family includes retinol, retinal or retinaldehyde, retinyl esters, retinoic acid, and provitamin carotenoids such as β-carotene. Vitamin A is essential for growth and life, taking part not only in vision but also in developmental processes that begin early in embryogenesis. Vitamin A continues to be necessary to maintain normal cellular differentiation throughout life. Preformed vitamin A comes from animal origin, such as liver and egg yolk, while the provitamin β - carotene is found only in foods of plant origin, particularly carrots and dark leafy vegetables.
12 Vitamin A The human body stores only limited amounts of vitamin A, mostly in the liver, making dietary intake essential. The liver stores 50 80% of body vitamin A. Small amounts are also found in lungs, body fat and kidneys. Carotenoids are deposited more widely throughout the body than retinoids and are found in adipose tissues, adrenals, and the liver. Excess and deficiency of vitamin A in the mother s diet during pregnancy has been shown to cause malformations of fetal brain and hydrocephalus.
13 Function of Vitamin A Night vision, due to its involvement in photochemical reactions in the retina. Growth and maintenance of epithelial tissue including the cornea, all mucous membranes of gastrointestinal tract, lungs, vagina, urinary tract, bladder and skin. Reproductive function in humans. Nerve formation and function.
14 Function of Vitamin A Epithelial cell proliferation and epidermal differentiation. Natural and synthetic retinoids have been used increasingly as systemic or topical agents in the treatment of hyperkeratotic disorders, acne, and certain skin cancers. Antioxidants may play a preventive role in heart disease and epithelial cancers. Both cell-mediated and antibody-mediated immune response. Signal transduction, via retinoic acid s hormonal action.
15 Deficiency Symptoms of Vitamin A The symptoms of vitamin A deficiency skin, bone, and dental health and immune function. The earliest symptom the inability to see in dim light, called night blindness or nyctalopia. Other symptoms rough, scaly skin (called follicular hyperkeratosis), sinus infection, chronic sore throat and abscesses in the mouth and ears.
16 Deficiency Symptoms of Vitamin A In children, deficiency growth retardation, impaired bone and tooth formation. Both a deficiency and an excess of vitamin A fetal malformations. Vitamin A deficiency the cessation of spermatogenesis and interrupts the estrus cycle.
17 Requirements and Recommendations of Vitamin A
18 Toxicity of Vitamin A Symptoms: loss of appetite, headache, blurred vision, irritability, hair loss, drying and flaking of the skin, swelling in the extremities, drowsiness, diarrhea, nausea, and enlargement of the spleen and liver. Since vitamin A stores increase with age, the elderly are at particular risk for toxicity.
19 Toxicity of Vitamin A Vitamin A excess during the first trimester of pregnancy can result in severe craniofacial and oral clefts and limb defects of the fetus. High doses of vitamin A (retinol and retinyl esters) during pregnancy have been associated with birth defects. It is recommended that women who are pregnant or may become pregnant consume no more than 2667 IU/day of vitamin A.
20 Dietary Sources of Vitamin A Rich sources of vitamin A are liver and cod liver oil. The major source of vitamin A in the diet is from carotene; provitamin A. They are yellow and green leafy vegetables such as carrots, spinach, sweet potatoes, squash, and yellow fruits.
21 Indication, Contraindication, Side effects & Adverse reactions Indication: deficiency of Vitamin A, prevent night blindness, skin disorders, promote bone development Contraindication: hypervitaminosis A, pregnancy (massive doses) Side effects: headache, fatigue, drowsiness, irritability, anorexia, vomiting, diarrhea, dry skin, visual changes Adverse reactions: evident only with toxicity: leucopenia, aplastic anemia, papiledema, increased intracranial pressure, hypervitaminosis A
22 Pharmacokinetic & Pharmacodynamic of Vitamin A Pharmacokinetics: A: per oral 1 h; is absorbed faster than if there is no deficiency or intestinal obstruction D: protein-binding M: half-life: weeks-months E: urine & feces Pharmacodynamics: Per oral : Onset: 1-2 h; Peak: 4-5 h; duration: unknown (is stored in the liver)
23 Drug-vitamin Interaction Warfarin, an anticoagulant, increases the risk of abnormal bleeding Cholestyramine are used to lower cholesterol concentrations by preventing reabsorption of bile acids from the digestive system and by preventing micelle formation in gastrointestinal (GI) lumen. Fat-soluble vitamin A requires the presence of bile for absorption, deficiency may occur if these drugs are used for a long period of time. Oral antibiotics such as neomycin decrease the absorption Orlistat, a weight loss GI agent, may decrease GI absorption of fat-soluble vitamins.
24 Vitamin D Vitamin D consists of a group of similar molecules that are involved in calcium absorption and metabolism and bone formation and that also act as a human hormone. the two are equally useful to humans: Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol) is produced by plants, while vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) is made by animals: Human skin can synthesize it when exposed to sunlight and is only essential in the diet if we do not have enough exposure to sunlight. Vitamin D is a hormone precursor that can be manufactured by the body, therefore it is not an essential nutrient.
25 Function of Vitamin D Maintenance of bone health. It is essential for calcium absorption and it regulates parathyroid hormone (PTH). Vitamin D deficiency Ca absorption & PTH concentrations bone resorption; bone resorption without sufficient vitamin D and calcium bone loss and osteoporosis. Helps regulate excretion of calcium from the kidney and maintains normal blood Ca concentrations Vitamin D receptors are found in variety of other tissues in the body the rate of cell growth and differentiation.
26 Deficiency of Vitamin D A vitamin D deficiency can result from: 1. Inadequate dietary intake, 2. Reduced endogenous production due to limited exposure to sunlight, 3. Kidney and/or liver dysfunctions, which inhibit conversion of vitamin D to its metabolically active forms, 4. Fat-malabsorption syndromes, such as cystic fibrosis and cholestatic liver diseases.
27 Deficiency Symptoms of Vitamin D Rickets in children: skeletal deformities and muscular weakness Osteomalacia in adults; develops in women with closely spaced, multiple pregnancies or in people confined indoors with no exposure to sunlight. Symptoms in adults: painful softening and bending of bones, low serum ca concentrations and tetany. Less severe vitamin D deficiency can result in hyperparathyroidism and bone turnover bone loss and osteoporosis. Osteoporosis: The disease results in fractures of the vertebra, hip and wrist that occur either spontaneously or with minimal daily activities such as opening a window.
28 Requirements and Recommendations of Vitamin D
29 Toxicity of Vitamin D Prolonged exposure to sunlight does not cause vitamin D toxicity. The NOAEL (the No Observed Adverse Effect Level) is 50 mcg (2000 IU). The majority of dietary supplements include 400 IU of vitamin D. There are no reports of adverse effects at this concentration of intake. There is no evidence of any benefit in taking more than 800 IU. The effects of excessive vitamin D intake include hypercalcemia and hypercalciuria deposition of calcium in soft tissue and irreversible renal and cardiovascular damage. Symptoms of toxicity: loss of appetite, excessive thirst, nausea, vomiting, irritability, weakness and weight loss.
30 Dietary Sources of Vitamin D The only frequently consumed dietary source of vitamin D is vitamin D-fortified milk. Muscle meat, milk (nonfortified), fruits and vegetables are negligible sources of vitamin D. Liver, butter, cream, mushrooms, fatty fish oil and egg yolk contains varying amounts of vitamin D, and some ready-to-eat cereals are fortified with the vitamin. Cod liver oil and fatty fish oils are excellent sources of vitamin D.
31 Indication of Vitamin D Deficiency of Vitamin D ricketsia & osteomalacia; Elderly (> 70 years old) capacity of skin to synthesize vitamin D3 in the elderly is approximately half that of younger people; in people with AIDS: vitamin D deficiency hypocalcemia; infants who are breastfed without supplemental vitamin D or exposure to sunlight are at an increased risk for deficiency; vegetarians; low fat,high fiber diets of vegetarians reduce the absorption of dietary vitamin D; alcoholsm; smoker the rate of bone turnover requirement of vitamin D.
32 Contraindication & Adverse reactions of Vitamin D Contraindication: hypervitaminosis D hipercalcemia nefrolitiasis Adverse reactions: evident only with toxicity: anorexia, nausea, vomiting (earl symptoms of vitamin D toxicity
33 Pharmacokinetic of Vitamin D Pharmacokinetics: A: in intestine need bile calcifediol in the liver calcitriol (active form) in kidneys D: protein-binding E: primarily in bile, only a small amounts in urine
34 Drug-vitamin Interaction Warfarin absorption of vitamin D osteoporosis (a loss of bone tissue) or osteopenia (a decrease of bone density). Laxatives that contain mineral oil the intestinal absorption 30 of many nutrients, including vitamin D. Cholestyramine, colestipol and mineral oil absorption of vitamin D. Thiazide diuretics hypercalcemia. Anticonvulsant drugs: phenobarbital and phenytoin plasma vitamin D concentrations by inhibiting enzyme activity in the liver and by preventing the conversion of the vitamin to its active form.
35 Drug-vitamin Interaction The concentrations of magnesium-containing antacids hypomagnesemia in patients on chronic renal dialysis. To minimize potential problems, take these antacids 2 to 3 hours apart from meals or mineral supplements. Vitamin D may hypocalcemia in patients on digitalis cardiac arrhythmias. Ketoconazole, an antifungal agent, may inhibit vitamin D synthetic and catabolic enzymes Long-term therapy (longer than 2 weeks) with corticosteroids, anti-inflammatory drugs, the body s ability to activate vitamin D the risk of bone loss.
36 Drug-vitamin Interaction Vitamin D may interfere with the effectiveness of verapamil, a calcium-channel blocker Orlistat, a weight loss agent, gastrointestinal absorption of fat-soluble vitamins such as vitamin D. An interval of at least two hours (before or after) between Orlistat and vitamin D analog administration is recommended. However, taking multivitamins including fat-soluble vitamins did not decrease drug concentrations in clinical studies.
37 Vitamin E Is a fat-soluble vitamin and a powerful antioxidant Divided into two major groups: tocopherol (have saturated side chains) and tocotrienols (have unsaturated chains); natural vitamin E (d-αtocopherol) is the most potent. Natural and synthetic forms of α-tocopherol: to be absorbed equally well both of them are as effective inhibiting the oxidation of LDL-C in humans
38 Function of Vitamin E Tocopherols act as antioxidants and prevent the peroxidation of phospholipids of the cellular membranes maintains membrane activity. To prevent membranes from destruction by oxidation maintenance of intracellular membrane integrity Vitamin E located in cell membranes break the chain of radical attack by reacting with the peroxide radical Vitamin E and selenoenzyme glutathione peroxidase protect against peroxidation of membrane lipids preventing cellular damage. To prevent LDL oxidation the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
39 Deficiency Symptoms of Vitamin E Red blood cell hemolysis, shorter red blood cell life Creatinuria, and deposits of ceroid in muscle; Neurologic changes of cerebellar ataxia, demyelination of the peripheral nerves posterior column dysfunction, and possibly peripheral, neuropathy; progressive loss of proprioceptive and vibratory sensation, areflexia and gaze paresis Retinopathy of prematurity in neonates Edema and flaky dermatitis risk of cardiovascular disease.
40 Requirements &Recommendations of Vitamin E
41 Toxicity of Vitamin E Relatively large doses of vitamin E (up to 3200 mg) have been taken for months to years with no significant side effects. At doses > 800 mg muscle weakness, nausea, fatigue, diarrhea and most commonly gastrointestinal disturbances. High doses of vitamin E in animals interfere with intestinal absorption of vitamins A and K. Doses > 1 g/d effect of anticoagulant medications. Vitamin E or its quinone may inhibit the function of vitamin K in the formation of prothrombin haemorrhage Large doses of vitamin E (100 mg/kg/day) in low-birthweight infants necrotizing enterocolitis and sepsis.
42 Dietary Sources of Vitamin E Spinach Bean sprouts Green peas; Blackeyed peas Sweet potatoes Almonds Cashews Peanuts Sunflower seeds Mayonnaise
43 Indication of Vitamin E Primary deficiency may occur in early infancy, particularly in formulas high in unsaturated oils. Protein-energy malnourished children may have low vitamin E concentrations. A secondary deficiency may be seen in malabsorption syndrome, steatorrhea (sprue, celiac disease, cystic fibrosis, or biliary atresia), cholestasis, and in abetalipoproteinemia.
44 Pharmacokinetics of Vitamin E Optimal vitamin E absorption requires presence of bile salts and pancreatic juice in the intestine. Absorbed tocopherol is incorporated into chylomicrons and transported through the lymph into circulation and blood where it is equilibrated with other plasma lipoproteins. Tocopherol is distributed to body tissues mainly by the low-density lipoproteins (LDL). The largest storage area for vitamin E is in adipose tissue. Tocopherol in the liver is depleted rapidly, whereas in deficiency loss of vitamin E in the fatty tissue is slow.
45 Drug-vitamin Interaction Vitamin E absorption, utilization and storage of vitamin A Intake of > 10 IU/kg daily delay the response to iron therapy in children with iron-deficiency anemia and lowbirth weight infants treated with iron supplements vitamin E- deficiency hemolytic anemia. Vitamin E + aspirin, an antiplatelet agent, and nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), risk of bleeding. A large dose of vitamin E (>4000 IU) anti-vitamin K effects; with oral anticoagulants, warfarin at risk of hemorrhage Cisplatin, a chemotherapeutic oral mucositis, an inflammation of the membranes lining the inside of the mouth. Vitamin E the duration of this condition
46 Vitamin K Vitamin K is known as the anti-hemorrhagic vitamin that is necessary for the synthesis of four of the 13 cofactors required for the normal coagulation of blood. Two naturally occurring forms of vitamin K exist: vitamin K1 (phylloquinone or phytylmenaquinone) and K2 (menaquinone or multiprenyl-metaquinone) are fat soluble and stable during cooking. Vitamin K1 is not stable under sunlight. Vitamin K1 and K2 are found in green plants and in microorganisms, respectively. Synthetic forms of vitamin K, one of which is menadione; watersoluble and destroyed to a great degree during cooking. Natural vitamin K (K1 and K2) requires bile and pancreatic juice for absorption in the small intestine. Vitamin K2 is synthesized by microflora in the small and large intestine. Menadione is converted to vitamin K2 in the body. Synthesis of osteocalcin that promotes mineral deposition in bone is dependent on vitamin K.
47 Function of Vitamin K For synthesis of blood clotting factors in the liver; factor II or prothrombin; factor VII or proconuertin; factor IX or Christmas factor and factor X or Stuart-Power. Vitamin K has hemostatic activity and is used to treat anticoagulant-induced prothrombin deficiency. Vitamin K may have anti-osteoporotic activity; vitamin K2 has been shown in vitro and in vivo to inhibit bone resorption substances such as prostaglandin E2 and interleukin-6 and enhance human osteoblast-induced mineralization. Vitamin K may have antioxidant activity. Vitamin K- hydroquinone is a potent reactive oxygen species scavenger and has been found to inhibit lipid peroxidation. Synthetic vitamin K menadione has shown to have anti-tumor activity in vitro and in vivo. Vitamin K2 was shown to induce in vitro differentiation of myeloid leukemic cell lines.
48 Deficiency Symptoms of Vitamin K Hypoprothombinemia manifested by defective coagulation of the blood and hemorrhage. Lack of intestinal bacterial flora might explain part of the hypoprothrombinemia observed during the first 3 to 5 days of life in neonates. Low concentrations for plasma clotting protein factors: II, VII, IX, and X may reflect hepatic immaturity. Malabsorption secondary deficiency of vitamin K Severe liver disease prothrombin synthesis and may be unresponsive to vitamin K therapy. In obstructive jaundice, hemorrhage usually begins after the 4th or 5th day. Hemorrhage may ooze slowly from wounds, gums, nose, GI mucosa or may be a massive bleed into the GI tract. Some infants may have intracranial hemorrhages at birth or within the first days of life. Breast-fed infants who have not received vitamin K at birth are susceptible to deficiency because human milk is a poor source of vitamin K.
49 Requirements & Recommendation of Vitamin K
50 Toxicity of Vitamin K Natural forms of vitamin K have caused no symptoms of toxicity, even when supplemented in large amounts. The synthetic product, menadione, has an unsubstituted carbon 3 that can combine with tissue sulfhydryl groups the oxidation of membrane phospholipids. Toxic effects such as hemolytic anemia, hyperbilirubinemia, and kernicterus, have been reported in infants supplemented with menadione.
51 Indication of Vitamin K Newborn infants Persons who have been injured, have renal insufficiency and/or are being treated chronically with antibiotics are at risk for vitamin K deficiency. Malabsorption: obstructive jaundice, Celiac sprue, Steatorrhea, Crohn s disease, Chronic diarrhea, Liver disease, Intestinal bypass, Chronic pancreatitis, prolonged sulfa and antibiotic drug therapy Haemorrhage
52 Drug-Vitamin Interaction With non-absorbable sulfonamides or oral antibiotics interfere vitamin K synthesis in the intestines. Warfarin for anticoagulant therapy should not consume large amounts of vitamin K supplements or vitamin Mineral oil the gastrointestinal absorption of vitamin K Anticonvulsant agents, phenytoin, the normal breakdown of vitamin K into its inactive byproduct osteoporosis, and vitamin K deficiency (resulting in bleeding disorders or facial bone abnormalities) in babies born to mothers taking the drugs. Mothers on these medications may need to take vitamin K supplementation during pregnancy to prevent these problems.
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri
![VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S ] Deeba S. Jairajpuri](/thumbs/88/115610056.jpg) VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
VITAMINS-FAT SOLUBLE [LIPPINCOTT S 381-394] Deeba S. Jairajpuri VITAMIN A othe term retinoids includes both natural and synthetic forms of vitamin A essential for vision, reproduction, growth and maintenance
Vitamins. Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD
 Vitamins Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Vitamins Organic compounds required by an organism in tiny amounts as a vital nutrient Cannot be synthesized
Vitamins Nafith Abu Tarboush, DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Vitamins Organic compounds required by an organism in tiny amounts as a vital nutrient Cannot be synthesized
VITAMIN BASICS VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES TOO LITTLE TOO MUCH SOURCES. Night blindness Total blindness Reduced resistance to infection Can lead to death
 VITAMIN BASICS VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES TOO LITTLE TOO MUCH SOURCES Fat-Soluble Vitamin A Maintains vision Maintains epithelial tissues (skin) Develops immune cells Bone growth Night blindness Total blindness
VITAMIN BASICS VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES TOO LITTLE TOO MUCH SOURCES Fat-Soluble Vitamin A Maintains vision Maintains epithelial tissues (skin) Develops immune cells Bone growth Night blindness Total blindness
- Spontaneous hemorrhaging increase
 MEDCHEM 562-2014 Fat Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 1. Fill out the blanks in the table below. Vitamin Physiological Function Deficiency symptoms Toxicity A -Vision -Cell Differentiation -Inhibition of Cell
MEDCHEM 562-2014 Fat Soluble Vitamins Problem Set 1. Fill out the blanks in the table below. Vitamin Physiological Function Deficiency symptoms Toxicity A -Vision -Cell Differentiation -Inhibition of Cell
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nafeth
 number 38 Done by Omar Odeh Corrected by Doctor Nafeth 1 Micronutrients: Vitamins Chapter 28 lipp. In the end of this course, we will talk about fat soluble vitamins. We took water soluble vitamins last
number 38 Done by Omar Odeh Corrected by Doctor Nafeth 1 Micronutrients: Vitamins Chapter 28 lipp. In the end of this course, we will talk about fat soluble vitamins. We took water soluble vitamins last
Objectives: by reading this topic; the student would be able to:
 Objectives: by reading this topic; the student would be able to: 1. Describe the structure, dietary sources, and metabolism of fat soluble vitamins. 2. Identify the biochemical role of fat soluble vitamins.
Objectives: by reading this topic; the student would be able to: 1. Describe the structure, dietary sources, and metabolism of fat soluble vitamins. 2. Identify the biochemical role of fat soluble vitamins.
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water
 Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
Deficiency. - Night blindness - Dry, rough skin - Decreased resistance to infection - Faulty tooth development - Slower bone growth
 MEDCHEM 562 Fall 2013 Vitamin Problem Set 1: 1) Complete the table: Vitamin A D Physiological Function / Therapeutic Uses - Vision - Promotion of cell differentiation - Inhibition of cell proliferation
MEDCHEM 562 Fall 2013 Vitamin Problem Set 1: 1) Complete the table: Vitamin A D Physiological Function / Therapeutic Uses - Vision - Promotion of cell differentiation - Inhibition of cell proliferation
Vitamins. Vitamins (continued) Lipid-Soluble Vitamins (A, D, E, K) Vitamins Serve Important Roles in Function of Body
 Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Vitamins Drugs for Nutritional Disorders Organic substances are needed in small amounts Promote growth Maintain health Vitamins Human cells cannot produce vitamins Exception: vitamin D Vitamins or provitamins
Leaving Certificate Notes
 Leaving Certificate Notes VITAMINS Sources of vitamins Functions of vitamins Effects of vitamin deficiencies Recommended dietary allowances (RDA s) Properties of all the FAT-SOLUBLE & WATER-SOLUBLE vitamins
Leaving Certificate Notes VITAMINS Sources of vitamins Functions of vitamins Effects of vitamin deficiencies Recommended dietary allowances (RDA s) Properties of all the FAT-SOLUBLE & WATER-SOLUBLE vitamins
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals
 Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Vitamin A. Vitamin D
 Vitamin A Fat Soluble Vitamin Maintains hair and skin cells. Helps prevent night blindness. Orange and dark green vegetables, dairy products, and fish oils Works with calcium to build and maintain healthy
Vitamin A Fat Soluble Vitamin Maintains hair and skin cells. Helps prevent night blindness. Orange and dark green vegetables, dairy products, and fish oils Works with calcium to build and maintain healthy
Regulation of Enzyme Activity
 Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
Regulation of Enzyme Activity Enzyme activity must be regulated so that the proper levels of products are produced at all times and places This control occurs in several ways: - biosynthesis at the genetic
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins
 Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
Chapter 1 & 2 All of the following are macronutrients except Carbohydrates Lipids Protein * Vitamins Gram per gram blank provides the most k calories Alcohol Carbohydrates * Lipids Proteins Which of the
Nutritional Pathology SCBM341: General Pathology
 Nutritional Pathology SCBM341: General Pathology Assistance Professor Amornrat N.Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Nutrients: Chemicals
Nutritional Pathology SCBM341: General Pathology Assistance Professor Amornrat N.Jensen, Ph.D. Department of Pathobiology School of Science, Mahidol University amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Nutrients: Chemicals
Vitamins. Sagda kamal eldein 30/1/
 Vitamins Sagda kamal eldein 30/1/2019 0919106108 The discovery of the first vitamin was published in 1911 by a Polish biochemist, Casimir Funk. The term vitamine is derived from the words vita (meaning
Vitamins Sagda kamal eldein 30/1/2019 0919106108 The discovery of the first vitamin was published in 1911 by a Polish biochemist, Casimir Funk. The term vitamine is derived from the words vita (meaning
Vitamins. Dr. Syed Ismail. Compiled and Edited by. Associate Professor, SSAC VN Marathwada Agricultural University, Parbhani, India
 Vitamins Compiled and Edited by Dr. Syed Ismail Associate Professor, SSAC VN Marathwada Agricultural University, Parbhani, India What are vitamins? Organic molecules with a wide variety of functions Cofactors
Vitamins Compiled and Edited by Dr. Syed Ismail Associate Professor, SSAC VN Marathwada Agricultural University, Parbhani, India What are vitamins? Organic molecules with a wide variety of functions Cofactors
VITAMINS. Equine Nutrition #9 Created for Canadian Pony Club Education by Lezah Williamson
 VITAMINS Equine Nutrition #9 Created for Canadian Pony Club Education by Lezah Williamson Vitamins Vitamins are organic compounds They are required as vital nutrient Needed in limited amounts Have diverse
VITAMINS Equine Nutrition #9 Created for Canadian Pony Club Education by Lezah Williamson Vitamins Vitamins are organic compounds They are required as vital nutrient Needed in limited amounts Have diverse
Nutrition for Health. Nutrients. Before You Read
 CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
Biochemistry of Vitamin K
 Lecture 4 Biochemistry of Vitamin K The Objectives Types and chemistry of vitamin K Sources and daily requirements Functions Synthesis of γ-carboxyglutamate in: Prothrombin and blood clotting factors Osteocalcin
Lecture 4 Biochemistry of Vitamin K The Objectives Types and chemistry of vitamin K Sources and daily requirements Functions Synthesis of γ-carboxyglutamate in: Prothrombin and blood clotting factors Osteocalcin
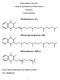
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity.
 D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
D. Vitamin K -- Group of naphthoquinones having antihemorrhagic activity. 1. Structures VITAMIN K1; Phytonadione; 2-Methyl-3-phytyl-1,4-naphthoquinone VITAMIN K2; Menaquinone-6 and 7; N=6,7 n 2. Function
Added Vitamins and Minerals
 Added Vitamins and Minerals What are Vitamins and Minerals? Vitamins and Minerals are essential micronutrients which are required in small quantities to perform all functions properly in the human body.
Added Vitamins and Minerals What are Vitamins and Minerals? Vitamins and Minerals are essential micronutrients which are required in small quantities to perform all functions properly in the human body.
Six Nutrients. Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy. Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water
 Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Micronutrients: Vitamin A Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo
 Micronutrients: Vitamin A Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship with a qualified health care professional and
Micronutrients: Vitamin A Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo Medical Disclaimer: The information in this presentation is not intended to replace a one-onone relationship with a qualified health care professional and
V i t a m i n s Vitamins Organic micronutrients required for reproduction, development, growth, & maintenance of body functions.
 V i t a m i n s MAIN QUESTIONS TO ANSWER: What is a vitamin? For each vitamin, what are the best food sources? what are the physiological functions? what are the results of deficiency? what are the results
V i t a m i n s MAIN QUESTIONS TO ANSWER: What is a vitamin? For each vitamin, what are the best food sources? what are the physiological functions? what are the results of deficiency? what are the results
Dietary Reference Intakes: Vitamins
 Biotin Coenzyme in synthesis of fat, glycogen, and amino acids Liver and smaller b amounts in fruits and 6* meats 8* 12* 20* 2 of biotin in humans or animals were found. This does not mean biotin are limited,
Biotin Coenzyme in synthesis of fat, glycogen, and amino acids Liver and smaller b amounts in fruits and 6* meats 8* 12* 20* 2 of biotin in humans or animals were found. This does not mean biotin are limited,
Josie Grace C. Castillo, M.D.
 Josie Grace C. Castillo, M.D. 2 types of nutrients Macronutrients Carbohydrate Fats Protein Micronutrients Vitamins Minerals 1 Occur when the quantity or quality of food is not sufficient to meet a persons
Josie Grace C. Castillo, M.D. 2 types of nutrients Macronutrients Carbohydrate Fats Protein Micronutrients Vitamins Minerals 1 Occur when the quantity or quality of food is not sufficient to meet a persons
FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS by Jerry Casados
 What are Fat-Soluble Vitamins? FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS by y Casados Fat soluble vitamins are essential to your health, and each one has its one very important function in the body. Vitamins A, D, E and K
What are Fat-Soluble Vitamins? FAT-SOLUBLE VITAMINS by y Casados Fat soluble vitamins are essential to your health, and each one has its one very important function in the body. Vitamins A, D, E and K
Vitamins and Minerals
 Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
Chapter Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients
 Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
Vitamins Minerals Chapter 12
 DH 250 Water soluble B1 Thiamin B2 Riboflavin B3 Niacin Vitamins Minerals Chapter 12 Role RDA Source Deficiency Toxicity Clinical Use intermediary coenzymes 1.2mg 1.1mg 1.2mg 1.1mg 16mg 14mg dairy B6 Pyridoxine
DH 250 Water soluble B1 Thiamin B2 Riboflavin B3 Niacin Vitamins Minerals Chapter 12 Role RDA Source Deficiency Toxicity Clinical Use intermediary coenzymes 1.2mg 1.1mg 1.2mg 1.1mg 16mg 14mg dairy B6 Pyridoxine
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
 NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
F. To provide energy, to spare body protein, to prevent ketosis. G. Food sources include breads, vegetables, fruit, and milk.
 Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station
 Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Multivitamins are a mixture of vitamins and minerals which are essential for the body to work and stay healthy.
 MULTIVITAMINS Multivitamins are a mixture of vitamins and minerals which are essential for the body to work and stay healthy. Vitamins are vital substances that are required for normal growth and functioning
MULTIVITAMINS Multivitamins are a mixture of vitamins and minerals which are essential for the body to work and stay healthy. Vitamins are vital substances that are required for normal growth and functioning
Nutrients. The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning.
 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
LABORATORY REPORT SAMPLE. Summary of Deficient Test Results. Vitamin B12 Pantothenate Biotin Spectrox Immunidex
 LABORATORY REPORT Account Number: Name: Jon Doe Gender: Male DOB: 12/28/1984 Requisition Number: Summary of Deficient Test Results Testing determined the following functional deficiencies: Oleic Acid Borderline
LABORATORY REPORT Account Number: Name: Jon Doe Gender: Male DOB: 12/28/1984 Requisition Number: Summary of Deficient Test Results Testing determined the following functional deficiencies: Oleic Acid Borderline
Vitamin K. Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib
 Vitamin K Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib What is Vitamin K? Fat soluble compound Necessary for the synthesis of several proteins required for blood clotting 1) Vit K 1 (Phylloquinone) - natural form - found in
Vitamin K Amina Ziyad Elaf Sohaib What is Vitamin K? Fat soluble compound Necessary for the synthesis of several proteins required for blood clotting 1) Vit K 1 (Phylloquinone) - natural form - found in
3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins
 3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins Overview of Vitamins essential for good health organic molecules individual units regulate body processes micronutrients solubility fat or water Water Soluble Vitamins B-complex;
3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins Overview of Vitamins essential for good health organic molecules individual units regulate body processes micronutrients solubility fat or water Water Soluble Vitamins B-complex;
Notes on Nutrition by Chamali Samarasekara. Notes on Nutrition
 Notes on Nutrition Patient groups particularly affected by their nutrition Pregnant and lactating women Babies (constipation) Children (malnutrition) The elderly (immobility/ visual impairment) Inpatients
Notes on Nutrition Patient groups particularly affected by their nutrition Pregnant and lactating women Babies (constipation) Children (malnutrition) The elderly (immobility/ visual impairment) Inpatients
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013
 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station
 Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Activity 3-F: Micronutrient Activity Station 1 Vitamin A deficiency 1 Instructions Please read through this Vitamin A information package and discuss amongst your group. You have 15 minutes to review this
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 8: Vitamins: Drivers of Cell Processes
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. antioxidant A substance
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. antioxidant A substance
Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Dietary Supplements: Calcium and Vitamin D
 1 Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Dietary Supplements: Calcium and Vitamin D Ashley Elliott, PharmD candidate Julie N. Bosler, PharmD McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham, AL Objectives:
1 Continuing Education for Pharmacy Technicians Dietary Supplements: Calcium and Vitamin D Ashley Elliott, PharmD candidate Julie N. Bosler, PharmD McWhorter School of Pharmacy Birmingham, AL Objectives:
Nutrition and Health. Micronutrients - Vitamins
 Nutrition and Health Micronutrients - Vitamins Topics Vitamins Water-soluble vitamins vitamin B vitamin C Fat-soluble vitamins vitamin A vitamin D vitamin E vitamin K 2 VITAMINS 3 Vitamins Vitamins are
Nutrition and Health Micronutrients - Vitamins Topics Vitamins Water-soluble vitamins vitamin B vitamin C Fat-soluble vitamins vitamin A vitamin D vitamin E vitamin K 2 VITAMINS 3 Vitamins Vitamins are
Vocabulary. 1. Deficiency: 2. Toxicity: 3. Water Soluble: 4. Fat Soluble: 5. Macro: 6. Micro or Trace: 7. Electrolyte:
 Vocabulary 1. Deficiency: Not enough of something (shortage) 2. Toxicity: 3. Water Soluble: Too much of something (can become toxic/poisonous) Dissolves in water 4. Fat Soluble: Dissolves in fat 5. Macro:
Vocabulary 1. Deficiency: Not enough of something (shortage) 2. Toxicity: 3. Water Soluble: Too much of something (can become toxic/poisonous) Dissolves in water 4. Fat Soluble: Dissolves in fat 5. Macro:
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 8 Vitamins: Drivers of Cell Processes
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 8 Vitamins: Drivers of Cell Processes Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 8 Vitamins: Drivers of Cell Processes Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrients. Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation
 Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Chapter 25 Nutrition, Metabolism, Temperature Regulation 25-1 Nutrients Chemicals used by body to produce energy, provide building blocks or function in other chemical reactions Classes Carbohydrates,
Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins. minerals vitamins fiber
 Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins minerals vitamins fiber WATER Essential nutrient 55-65% body weight Body loses water through evaporation, excretion, and respiration The only nutrient
Nutrients are: water carbohydrates lipids proteins minerals vitamins fiber WATER Essential nutrient 55-65% body weight Body loses water through evaporation, excretion, and respiration The only nutrient
Notes: A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or
 A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or strain a muscle Cooling down allows your heartbeat, breathing
A workout is an exercise program that focuses on high energy activity It s important to warm up before activity so that you do not tear or strain a muscle Cooling down allows your heartbeat, breathing
Classes of Nutrients A Diet
 Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Ch. 7 Notes Section 1: What is Nutrition? is the science or study of food and the ways the body uses food. are substances in food that provide energy or help form body tissues and are necessary for life
Chapter. The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals. Images shutterstock.com
 Chapter 13 The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Images shutterstock.com Objectives Differentiate between fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. List functions and sources of major minerals
Chapter 13 The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Images shutterstock.com Objectives Differentiate between fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. List functions and sources of major minerals
Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Special Topics Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals
 Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Special Topics Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Nutrients and diseases Introduction
Medicinal Chemistry/ CHEM 458/658 Special Topics Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Bela Torok Department of Chemistry University of Massachusetts Boston Boston, MA 1 Nutrients and diseases Introduction
VITAMINS BY William Cabot, M.D., FAAOS
 VITAMINS BY William Cabot, M.D., FAAOS THE VITAMIN PROTEIN CONNECTION At AMCO we deal with all types of protein products. Protein is composed of long or short chains of amino acids (1). The formation of
VITAMINS BY William Cabot, M.D., FAAOS THE VITAMIN PROTEIN CONNECTION At AMCO we deal with all types of protein products. Protein is composed of long or short chains of amino acids (1). The formation of
Macros and Micros. of a Healthy Diet. Macronutrients. Proteins
 Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Nutrients in foods replace those used by the body
 Fundamentals of Nutrition Nutrition: those processes that allow the body to use food for energy, maintenance of health, and growth. Nutritional status: the state of one s nutrition Wellness: state of good
Fundamentals of Nutrition Nutrition: those processes that allow the body to use food for energy, maintenance of health, and growth. Nutritional status: the state of one s nutrition Wellness: state of good
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion , version 1.1
 EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
EU RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN (EU RMP) Nutriflex Omega peri emulsion for infusion 13.7.2015, version 1.1 III.1. Elements for a Public Summary III.1.1. Overview of disease epidemiology Patients may need parenteral
LUXA-D PRESCRIBING INFORMATION. Cholecalciferol Capsules, Mfr. Std IU. Cholecalciferol Capsules, Mfr. Std IU
 Pr LUXA-D PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Pr Vitamin D 3 -softgel capsules 2000 IU 2 000 IU Pr Vitamin D 3 -softgel capsules 5000 IU 5 000 IU Pr Vitamin D 3 -softgel capsules 10 000 IU 10 000 IU Pr Vitamin D 3
Pr LUXA-D PRESCRIBING INFORMATION Pr Vitamin D 3 -softgel capsules 2000 IU 2 000 IU Pr Vitamin D 3 -softgel capsules 5000 IU 5 000 IU Pr Vitamin D 3 -softgel capsules 10 000 IU 10 000 IU Pr Vitamin D 3
VITAMINS OIL (FAT) SOLUBLE = A, D, E, F, K WATER SOLUBLE = B, C. VITAMIN A = RETINOL, derived in body from carotene (orange pigment in carrots)
 VITAMIS IL (FAT) SLUBLE = A, D, E, F, K WATER SLUBLE = B, C. VITAMI A = RETIL, derived in body from carotene (orange pigment in carrots) liver CH 2 H CH oxn 2 -carotene retinol (vitamin A alcohol) citral
VITAMIS IL (FAT) SLUBLE = A, D, E, F, K WATER SLUBLE = B, C. VITAMI A = RETIL, derived in body from carotene (orange pigment in carrots) liver CH 2 H CH oxn 2 -carotene retinol (vitamin A alcohol) citral
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions
 Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Lipids Types, Food Sources, Functions What Are Lipids? Lipids Diverse group of molecules that are insoluble in water Fats The lipid content of diets and foods 1 Lipids in Body Cells and Tissues Types of
Nutrition and Energy 1
 Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
THE ON VITAMINS VITAMIN B 1 VITAMIN A VITAMIN K VITAMIN B 2 VITAMIN B 12 VITAMIN B 3 VITAMIN B 6 VITAMIN C VITAMIN A VITAMIN E VITAMIN B 9
 THE EXTRASCOOP ON VITAMINS VITAMIN A (beta-carotenes) VITAMIN B 1 VITAMIN K (phytonadione) VITAMIN B 2 (riboflavin) VITAMIN B 3 (niacin) VITAMIN B 12 (cobalamin) VITAMIN B 6 (pyridoxine) PANTOTHENIC ACID
THE EXTRASCOOP ON VITAMINS VITAMIN A (beta-carotenes) VITAMIN B 1 VITAMIN K (phytonadione) VITAMIN B 2 (riboflavin) VITAMIN B 3 (niacin) VITAMIN B 12 (cobalamin) VITAMIN B 6 (pyridoxine) PANTOTHENIC ACID
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Colecalciferol Meda 800 IU tablet 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains colecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ) 800 IU
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Colecalciferol Meda 800 IU tablet 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each tablet contains colecalciferol (vitamin D 3 ) 800 IU
The human body contains approximately three grams of zinc, the highest concentrations of which are located in the prostate gland and the eye.
 Zinc AT A GLANCE Introduction Zinc (Zn) is found in nearly 100 different enzymes and as such is an essential building block for all life. Zinc is the second most common trace mineral in the body after
Zinc AT A GLANCE Introduction Zinc (Zn) is found in nearly 100 different enzymes and as such is an essential building block for all life. Zinc is the second most common trace mineral in the body after
Vitamin A Facts. for health workers. The USAID Micronutrient Program
 Vitamin A Facts for health workers The USAID Micronutrient Program What is vitamin A? Vitamin A Vitamin A is a nutrient required in small amounts for the body to function properly. It is called a micronutrient
Vitamin A Facts for health workers The USAID Micronutrient Program What is vitamin A? Vitamin A Vitamin A is a nutrient required in small amounts for the body to function properly. It is called a micronutrient
Sultan Qaboos University. College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences. Vitamin K. Lecture Summary
 Sultan Qaboos University College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences Vitamin K Lecture Summary Name: Mohsin Mohammed Taqi Mohsin Al-Saleh ID #: M020944-99 0 Introduction: Vitamin K is a group of structurally
Sultan Qaboos University College of Agricultural & Marine Sciences Vitamin K Lecture Summary Name: Mohsin Mohammed Taqi Mohsin Al-Saleh ID #: M020944-99 0 Introduction: Vitamin K is a group of structurally
The Basics of Human Nutrition
 The Basics of Human Nutrition Taken as a whole, all of the elements and materials that we eat or drink, and which our bodies require for good health, are referred to as our Nutritional Requirements. These
The Basics of Human Nutrition Taken as a whole, all of the elements and materials that we eat or drink, and which our bodies require for good health, are referred to as our Nutritional Requirements. These
When people don t eat enough complex carbohydrates they don t have enough energy and feel tired and less alert. They also may not get enough fiber.
 Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are compounds that come from plants and contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. These nutrients supply energy, which all living things need. Carbohydrates are the body s most
Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are compounds that come from plants and contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. These nutrients supply energy, which all living things need. Carbohydrates are the body s most
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS. A 2.5ml single-dose bottle containing IU Cholecalciferol (equivalent to 625 micrograms vitamin D 3 )
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Fultium 25 000 IU Oral Solution 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION A 2.5ml single-dose bottle containing 25 000 IU Cholecalciferol
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Fultium 25 000 IU Oral Solution 2 QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION A 2.5ml single-dose bottle containing 25 000 IU Cholecalciferol
Vitamins. Definition - Organic compound required in small amounts. A few words about each. Vitamin A. Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12
 Vitamins. Definition - Organic compound required in small amounts. A few words about each. Vitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Vitamin A - Retinol Retinol (vitamin
Vitamins. Definition - Organic compound required in small amounts. A few words about each. Vitamin A Vitamin B1, B2, B3, B5, B6, B7, B9, B12 Vitamin D Vitamin E Vitamin K Vitamin A - Retinol Retinol (vitamin
NUTRITION AND HEALTHY GUIDELINES
 NUTRITION AND HEALTHY GUIDELINES Tuna Stuffed Italian Mushrooms Zucchini Pasta The study of Nutrition may be described as the science of substances found in food that are essential to life. This area of
NUTRITION AND HEALTHY GUIDELINES Tuna Stuffed Italian Mushrooms Zucchini Pasta The study of Nutrition may be described as the science of substances found in food that are essential to life. This area of
what vitamins are what vitamins are for
 what vitamins are and what vitamins are for www.eurovit.eu page 1/23 Vitamins are essential for human body life. Vitamins are organic compounds that are needed in small quantities to sustain life. No vitamins
what vitamins are and what vitamins are for www.eurovit.eu page 1/23 Vitamins are essential for human body life. Vitamins are organic compounds that are needed in small quantities to sustain life. No vitamins
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS
 Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
Adams Memorial Hospital Decatur, Indiana EXPLANATION OF LABORATORY TESTS Your health is important to us! The test descriptions listed below are for educational purposes only. Laboratory test interpretation
TEST BANK FOR NUTRITIONAL FOUNDATIONS AND CLINICAL APPLICATIONS A NURSING APPROACH 6TH EDITION BY GRODNER
 Link download full:https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-nutritionalfoundations-and-clinical-applications-a-nursing-approach-6th-edition-by-grodner TEST BANK FOR NUTRITIONAL FOUNDATIONS AND
Link download full:https://testbankservice.com/download/test-bank-for-nutritionalfoundations-and-clinical-applications-a-nursing-approach-6th-edition-by-grodner TEST BANK FOR NUTRITIONAL FOUNDATIONS AND
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health. By Dr. Isaac Eliaz
 6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
Physiological Role: B-vitamins are coenzymes of many enzymes systems of body metabolism. Thiamine {B 1 }
 Food Constituents [continued] Micronutrients B-Vitamins The B group of vitamin {water soluble} includes: Thiamine: vitamin B 1, ant beriberi vitamin. Riboflavin: vitamin B 2. Niacin: nicotinic acid, PP
Food Constituents [continued] Micronutrients B-Vitamins The B group of vitamin {water soluble} includes: Thiamine: vitamin B 1, ant beriberi vitamin. Riboflavin: vitamin B 2. Niacin: nicotinic acid, PP
KEY INDICATORS OF NUTRITION RISK
 NUTRITION TOOLS KEY INDICATORS OF Consumes fewer than 2 servings of fruit or fruit juice per day. Consumes fewer than 3 servings of vegetables per day. Food Choices Fruits and vegetables provide dietary
NUTRITION TOOLS KEY INDICATORS OF Consumes fewer than 2 servings of fruit or fruit juice per day. Consumes fewer than 3 servings of vegetables per day. Food Choices Fruits and vegetables provide dietary
Infants. Lecture 21: Nutrition for Infants. Infants Metabolic Rate. Age 0-1 yrs. Massive weight gain. Calorie, vitamin and mineral needs are high
 Lecture 21: Nutrition for Infants Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Age 0-1 yrs Infants Massive weight gain Weight doubles by 5 months Weight triples by 12 months Calorie, vitamin and mineral needs are
Lecture 21: Nutrition for Infants Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Age 0-1 yrs Infants Massive weight gain Weight doubles by 5 months Weight triples by 12 months Calorie, vitamin and mineral needs are
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3
 Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
Nutrition and Deficiency Static GK Notes PDF 3 Let us talk about nutrition and deficiency. Science and Technology form an integral part of our society. But we often forget age-old wisdom passed to us from
JIGSAW READING CARBOHYDRATES
 Date: CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates provide an important source of energy for our bodies. There are two types of carbohydrates: Sugars are found in foods which taste sweet like candies, jams and desserts.
Date: CARBOHYDRATES Carbohydrates provide an important source of energy for our bodies. There are two types of carbohydrates: Sugars are found in foods which taste sweet like candies, jams and desserts.
Nutrition in Heterotrophs
 Nutrition in Heterotrophs Required Nutrients Water Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Makes up ~90% of some animals Makes up a major portion of many body parts Humans require at least
Nutrition in Heterotrophs Required Nutrients Water Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Makes up ~90% of some animals Makes up a major portion of many body parts Humans require at least
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis
 Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis Martin J. Shearer PhD, MRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist Honorary Senior Lecturer Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, Guy s and St. Thomas Foundation Trust London, UK
Vitamin K in Cystic Fibrosis Martin J. Shearer PhD, MRCPath Consultant Clinical Scientist Honorary Senior Lecturer Centre for Haemostasis and Thrombosis, Guy s and St. Thomas Foundation Trust London, UK
Vitamins. At the end of this unit you should be able to:- Understand why our bodies need certain vitamins.
 Vitamins At the end of this unit you should be able to:- Understand why our bodies need certain vitamins. Recognise the difference between fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Identify the sources and
Vitamins At the end of this unit you should be able to:- Understand why our bodies need certain vitamins. Recognise the difference between fat soluble and water soluble vitamins. Identify the sources and
BHARATH ACADEMY VITAMINS AND MINERALS CHART
 VITAMINS AND MINERALS CHART Different types of vitamins and minerals enable healthy body function, such as cell and tissue repair, production of cells, and healthy brain function. Your body doesn t produce
VITAMINS AND MINERALS CHART Different types of vitamins and minerals enable healthy body function, such as cell and tissue repair, production of cells, and healthy brain function. Your body doesn t produce
Importance of Nutrition
 The EAT WELL Plate Canada s food guide Food pyramid Importance of Nutrition Energy for body metabolism (nerve impulses, contraction of muscles, repair and replacement of cells Raw materials for building
The EAT WELL Plate Canada s food guide Food pyramid Importance of Nutrition Energy for body metabolism (nerve impulses, contraction of muscles, repair and replacement of cells Raw materials for building
Vitamin dan Mineral. Vitamin. General Concepts
 Vitamin dan Mineral Pengetahuan Bahan Agroindustri Vitamin Organic compound required in small amounts Divided into two major groups: fat soluble and water soluble fat soluble : Vitamin A, D, E, K water
Vitamin dan Mineral Pengetahuan Bahan Agroindustri Vitamin Organic compound required in small amounts Divided into two major groups: fat soluble and water soluble fat soluble : Vitamin A, D, E, K water
Vitamins. The word vitamins is derived from the word vita which means life, hence one can conclude
 Vitamins The word vitamins is derived from the word vita which means life, hence one can conclude that vitamins are essential for good health and growth. Although needed in small amounts, their intake
Vitamins The word vitamins is derived from the word vita which means life, hence one can conclude that vitamins are essential for good health and growth. Although needed in small amounts, their intake
WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET
 WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET Food gives us the energy required for chemical reaction to keep us alive Energy also required for many activities and to maintain body temperature Food also gives us
WHY DO WE NEED FOOD? FOOD AND DIET Food gives us the energy required for chemical reaction to keep us alive Energy also required for many activities and to maintain body temperature Food also gives us
In addition to bone health, emerging science reveals a non-skeletal benefit of vitamin D for several other health outcomes.
 Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Vitamin D AT A GLANCE Introduction Vitamin D comprises a group of fat-soluble compounds that are essential for maintaining the mineral balance in the body. The vitamin D form synthesized in humans is called
Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test
 Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test 1. List the ten dietary guidelines recommended for Americans. (10) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Multiple
Name Unit # Period Score 159 points possible Dietary Guidelines, Food Pyramid and Nutrients Test 1. List the ten dietary guidelines recommended for Americans. (10) a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Multiple
Nutrition and Allergy
 Nutrition and Allergy Who Cares? William Reisacher, MD FACS FAAOA Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College We should and why? Oxidant Load Chronic illnesses such as allergies have tremendous energy
Nutrition and Allergy Who Cares? William Reisacher, MD FACS FAAOA Assistant Professor Weill Cornell Medical College We should and why? Oxidant Load Chronic illnesses such as allergies have tremendous energy
This booklet is dedicated to : Done by :
 This booklet is dedicated to : Done by : Abdulaziz Y. Al-Turki Yasser N. Aseery We did our best to make this chapter easy and more clear ; we also explained some important points in the figures and we
This booklet is dedicated to : Done by : Abdulaziz Y. Al-Turki Yasser N. Aseery We did our best to make this chapter easy and more clear ; we also explained some important points in the figures and we
Nutritional Information
 Nutritional Information Fresh Green Chile Peppers The following information is for one serving of hot green chile peppers. That would be about one half cup of hot green chile peppers, or 75 grams. This
Nutritional Information Fresh Green Chile Peppers The following information is for one serving of hot green chile peppers. That would be about one half cup of hot green chile peppers, or 75 grams. This
Study of how your body takes in and uses food
 Chapter 10 Lesson 1 Study of how your body takes in and uses food Nutrients substances in food that your body needs to grow, repair, and supply energy Calorie unit of heat used to measure the energy your
Chapter 10 Lesson 1 Study of how your body takes in and uses food Nutrients substances in food that your body needs to grow, repair, and supply energy Calorie unit of heat used to measure the energy your
Vitamins are noncaloric essential nutrients necessary for many metabolic tasks and the prevention of associated deficiency diseases.
 Chapter 7 Vitamins Chapter 7 Lesson 7.1 Key Concept Vitamins are noncaloric essential nutrients necessary for many metabolic tasks and the prevention of associated deficiency diseases. Dietary Reference
Chapter 7 Vitamins Chapter 7 Lesson 7.1 Key Concept Vitamins are noncaloric essential nutrients necessary for many metabolic tasks and the prevention of associated deficiency diseases. Dietary Reference
Introduction to Nutrition
 Introduction to Nutrition What is meant by Nutrition Definition:- It means that food is taken in and uses for many purposes (maintenance and production). Introduction to Nutrition: what you will learn
Introduction to Nutrition What is meant by Nutrition Definition:- It means that food is taken in and uses for many purposes (maintenance and production). Introduction to Nutrition: what you will learn
Name Hour. Nutrition Notes
 Calorie: Measure of Name Hour Nutrition Notes = 9 calories per gram Carbohydrates and Protein = calories per gram. If you consume more calories than you use up, it will be stored as. Carbohydrates (CHO)
Calorie: Measure of Name Hour Nutrition Notes = 9 calories per gram Carbohydrates and Protein = calories per gram. If you consume more calories than you use up, it will be stored as. Carbohydrates (CHO)
Essential Standard. 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness.
 Warm Up What vitamins and minerals can you name? How do people get the vitamins and minerals they need? What are health benefits that you know about vitamins and minerals? Why do some people take supplements?
Warm Up What vitamins and minerals can you name? How do people get the vitamins and minerals they need? What are health benefits that you know about vitamins and minerals? Why do some people take supplements?
Fat Soluble Vitamins. Vitamin A
 Fat Soluble Vitamins Vitamin A The biochemical basis on which vitamin A requirements were established The EAR was set based on data pertaining to the assurance of adequate stores of vitamin A (Table 19).
Fat Soluble Vitamins Vitamin A The biochemical basis on which vitamin A requirements were established The EAR was set based on data pertaining to the assurance of adequate stores of vitamin A (Table 19).
