o Nutrition in human beings 33
|
|
|
- Alban Reeves
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 KEY CONCEPTS & GIST OF THE LESSON Life processes The processes that are necessary for an organism to stay alive. Eg. Nutrition, respiration, etc. Criteria of life- (i) Growth (ii) Movement Nutrition- The process in which an organism takes in food, utilizes it to get energy, for growth, repair and maintenance, etc. and excretes the waste materials from the body. Types of nutrition 1. Autotrophic nutrition (Auto =self: trophos = nourishment) E.g. Plants, Algae, blue green bacteria. o Process Photosynthesis(Photo=light; Synthesis= to combine) o Raw materials- (i) Carbon dioxide (ii)water o Equation- sunlight o 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O C 6 H 12 O 6 + 6O 2 Chlorophyll o Energy conversion- Light/Solar energy to Chemical energy o Role off Chlorophyll- To trap the sun s energy for photosynthesis o Factors- (i) Carbon dioxide (ii) Water(iii) Light (iv) Temperature o Events/ Steps of photosynthesis- (i) Absorption of light energy by chlorophyll (ii) Conversion of light energy to chemical energy & Splitting of water molecule into Hydrogen & oxygen (iii) Reduction of Carbon dioxide to Carbohydrate o Gaseous exchange- (i) Gas used- Carbon dioxide (ii) By product - Oxygen o Source of raw materials- (i) Carbon dioxide Land plants- Air, Aquatic plants- Water (ii) Water & Minerals - Soil 2. Heterotrophic nutrition (Hetero =others: trophos = nourishment) Eg. Animals, plants lacking chlorophyll like fungi. (a) Saprophytic nutrition: Organisms feeds on dead decaying plants or animals material. E.g. Fungi, Bacteria (b) Parasitic nutrition: Organisms obtain food from the body of another living (host) o Endoparasite : Parasite lives inside the body of the host e.g. tapeworm, roundworm. o Exoparasite : Parasite lives on the body of the host. E.g. lice, leech. Note- The parasite benefits while the host is usually harmed e.g. Cuscutta-plant parasite (amar bel), plasmodium (malarial parasite). (c) Holozoic nutrition: Organism (mostly animals) take in whole food and then digest it into smaller particles with enzyme. Eg. Amoeba, Paramoecium. Animals, human beings. o Steps in Holozoic nutrition (i) Ingestion: taking in of food. (ii) Digestion: breaking down of complex food into simpler, absorbable form. (iii) Assimilation: Utilization of digested food from the body. (iv) Egestion: Removing undigested food from the body o Nutrition in human beings 33
2 Alimentary canal- Mouth Oesophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Important gland/juices (Refer to figure 6.6 page no.97 of N.C.E.R.T Text book) Organ Gland Enzyme/Juice Function Mouth Stomach Small intestine Salivary Salivary Amylase glands Gastric glands Gastric juice- (i) Hydrochloric acid 1) Liver 2) Pancreas (ii) Pepsin (iii) Mucus (i) Bile juice (ii) Pancreatic Juice Amylase Trypsin Lipase Converts starch into sugar (a) Kills harmful bacteria that enters with the food. (b) Makes the medium alkaline for the action of Pepsin Digests proteins Protects the inner lining of the stomach from the corrosive action of Hydrochloric acid. (a) Makes the medium acidic for the action of Pancreatic enzymes. (b) Breaks down large fat molecules into smaller globules so that enzymes can act upon them. Converts Carbohydrates to glucose Converts Proteins to Amino acids Converts Fats into Fatty acids & Glycerol Peristaltic movements- Rhythmic contraction of muscles of the lining of Alimentary canal to push the food forward. Sphincter muscle- Helps in the exit of food from the stomach. Villi- Small finger like projections on the walls of- (v) Small intestine- To increase the surface area for the absorption of food. (vi) Large intestine- For absorption of water. Respiration- The process by which digested food is broken down with the help of Oxygen to release energy. o Types of respiration- (i) Aerobic respiration (ii) Anaerobic respiration Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration 34
3 1. Takes place in presence of Oxygen. 2. End products- Carbon dioxide & Water 3. More energy is released. 4. Takes place in Cytoplasm & Mitochondria 5. Complete oxidation of glucose takes place. 6. It occurs in most organisms. 7. Equation- Glucose Pyruvate CO 2 + H 2 O + Energy 1. Takes place in absence of Oxygen. 2. End products- Ethanol & Carbon dioxide 3. Less energy is released. 4. Takes place in only in Cytoplasm. 5. Incomplete oxidation of glucose takes place. 6. It occurs in certain bacteria, yeast & certain tissues of higher organisms. E.g. In humans during vigorous exercise, when the demand for Oxygen is more than the supply, muscle cells respire anaerobically for some time. 7. Equation- In Yeast- Glucose Pyruvate Ethanol + H 2 O + Energy In muscle cells - Glucose Pyruvate Lactic acid + Energy o Some common features of Respiratory organs- (i) Large surface area- for greater rate of diffusion of respiratory gases. (ii) Thin permeable walls to ensure easy diffusion & exchange of gases. (iii) Extensive blood supply- Respiratory organs are richly supplied with blood vessels for quick transport of gases. o Gaseous exchange in plants- Process Diffusion Direction of diffusion depends on- (i) Environmental conditions (ii) Requirement of the plant. Day time- Carbon dioxide given out during respiration is used for photosynthesis. Therefore only Oxygen is released, which is a major activity during the day. Night time Only respiration takes place. Therefore only Carbon dioxide is released, which is a major activity during the night. o Gaseous exchange in animals- Terrestrial animals- take Oxygen from the atmosphere. Aquatic animals- take Oxygen dissolved in water. (Oxygen content is low in water, therefore they breathe faster. o Human Respiratory system- External nostrils Nasal cavity Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Alveoli Rings of cartilage present in the throat ensure that the trachea (air passage) does not collapse when there is less air in it. Lungs (i) Present in the thoracic cavity. (ii) They are spongy, elastic bags consisting of Bronchi, Bronchioles and Alveoli Refer to figure 6.9 page no. 104 of N.C.E.R.T Text book) 35
4 o Respiration occurs in two phaseso (i) External-Breathing, which is a mechanical process. (ii) Internal - Cellular respiration o Mechanism of breathing It includes : (i)inhalation (ii) Exhalation o Exchange of gases- Unicellular organisms- By Diffusion Animals- (i) As the body size is large, diffusion alone is not enough. (ii) Respiratory pigments also required. (iii) Respiratory pigment in human beings is Haemoglobin, which is present in red blood corpuscles. (iv) It has very high affinity for Oxygen. (iv) Carbon dioxide is more soluble in water than Oxygen, so it Gets dissolves in blood and is thus transported. Transportation o Transportation in human beings- Blood- (i) It is a fluid connective tissue. (ii) Components- (1) Fluid medium- Plasma (2) Red blood corpuscles (3) White blood corpuscles (4) Platelets suspended in plasma (iii) Plasma transports food, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nitrogenous wastes, etc. Functions of blood- (i) Transport of respiratory gases. (ii) Transport of nutrients. (iii) Transport of waste products. (iv) Defence against infection Blood vessels- (i) Arteries (ii) Veins (iii) Capillaries Arteries 1. Thick walled. 2. Deep seated. 3. Carry blood away from the heart. 4. Carry Oxygenated blood. 5. Valves absent. Veins 1. Thin walled. 2. Superficial. 3. Carry blood to the heart. 4. Carry Deoxygenated blood. 5. Valves present Heart- (Refer to figure 6.10 page no. 106 of N.C.E.R.T Text book) (i) It is a muscular organ, which works as a pump in the circulatory system. (ii) It is the size of our fist. (iii) It has two sides, which are separated by a partition so that the oxygenated and deoxygenated blood do not get mixed up. (iv) It has four chambers- Two upper chambers called Atria. Two lower chambers called Ventricles. Working of heart- Left side- (i) Left atrium relaxes & the Oxygenated blood enters it from the lungs through the pulmonary vein. (ii) Left atrium contracts & the blood enters the left ventricle through the valve. (iii) Left Ventricle contracts and the blood is pumped into the largest artery Aorta and is carried to all parts of the body. 36
5 Right side- (i) Right atrium relaxes & the deoxygenated blood from the body enters it through superior and inferior Vena cava. (ii) Right atrium contracts & the blood enters the right Ventricle through the valve. (iii) Right Ventricle contracts and the blood is pumped into the Pulmonary artery and is carried to lungs. Valves- Unidirectional to prevent the backward flow of blood. Pulmonary vein is the only vein that carries Oxygenated blood. Aorta is the only artery that carries Deoxygenated blood. Double circulation in man- because the blood passes through the heart twice in one complete cycle of the circulation. Capillaries- (i) Form the connection between arteries & veins. (ii) Walls are one cell thick only for easy exchange of blood. Platelets- Plug the leaks of arteries and veins by clotting the blood. Lymph- Extracellular fluid similar to plasma but colourless with lesser protein. Function of lymph- (i) Transportation of digested & absorbed fats from the small intestine. (ii) Drains excess fluid from the intercellular spaces back in the blood. Higher animals- E.g., birds, mammals. (i) Oxygenated blood & Deoxygenated blood are completely separate for (ii) efficient Oxygen supply. This is to fulfil higher energy needs and to maintain body temperature (warm blooded animals). Amphibians & reptiles- have 3 chambered heat where little mixing of Oxygenated blood & Deoxygenated blood takes place. Therefore their body temperature varies with the temperature of the environment. (cold blooded animals) o Transportation in plants- Plants need less energy needs- because they do not move and therefore have a slow transport system Transport of water- (i) (ii) Takes place by xylem tissue present in roots, stem, leaves and is therefore interconnected. Root cells take up ions from the soil, which creates a concentration difference between root and soil. Column of water therefore rises upwards. In very tall plants- transpiration creates a suction pressure, which pulls the water upwards. Importance of transpiration- (i) (ii) Helps in upward movement of water in plants. It regulates the temperature in plants. Transport of food- (i) Takes place by phloem tissue. (ii) Movement of prepared food in plants is called translocation. Excretion- The biological process of removal of harmful metabolic wastes in living organisms. 37
6 Excretion in human beings- (Refer to figure 6.13 page no. 110 of N.C.E.R.T Text book) Organs of excretory system- (i) Kidneys (iii) Urinary bladder (ii) Ureters (iv) Urethra Kidneys- (i) Two in number (ii) Bean shaped (iii) (iv) Present in abdomen on either side of the backbone Basic unit is nephron. a. Glomerulus- Group of capillaries (cluster) present in Bowman s capsule to receive blood from renal artery and filters it. b. Bowman s capsule- Cup shaped structure, which contains glomerulus. c. Convoluted tubule- is long and reabsorbs vital nutrients like glucose, amino acids, salts, urea and water. Note-Vital functions of kidneys- (a) Filtration & removal of Nitrogenous wastes (b) Reabsorption of vital nutrients Ureters- Transport the urine formed in the kidneys to the urinary bladder. Urinary bladder- Muscular bag like structure to store urine. Urethra- Helps in removal of urine when the Urinary bladder is full. Artificial kidney- Principle: Dialysis Excretion in plants- Gaseous wastes- CO 2 in respiration & O 2 in photosynthesis are removed by the process of diffusion. Excess water- is removed by transpiration. Other wastes- (i) Stored in cellular vacuoles or in leaves, which fall off or as gums, resins, etc. in old xylem. (ii) Excreted in soil. Important diagrams- 1. Open & close stomata 2. Steps of nutrition in Amoeba 3. Alimentary canal of human beings/ Digestive system of human beings 4. Respiratory system of human beings 5. Structure of heart. 6. Excretory system of human beings 7. Structure of nephron Important activities- 1. To prove that chlorophyll is necessary for photosynthesis. 2. To prove that Carbon dioxide is necessary for photosynthesis. 3. To prove that light is necessary for photosynthesis. 4. To prove that product of fermentation is Carbon dioxide. 5. To prove that leaves lose water by transpiration. 6. To study the action of salivary amylase on starch. 7. To demonstrate that Carbon dioxide is present in exhaled air. 8. To demonstrate the process of transpiration in plants. 38
7 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks 1. Name the site of photosynthesis. 2. What is osmoregulation? 3. Name the excretory unit of kidney. 4. What is neuron? 5. Name the term for transport of food from leave to other parts of the plant. 6. Draw the diagram of cross section of a lead and label the following in it: a. Chloroplast b. Guard cell c. Lower epidermis d. Upper epidermis 7. What do you mean by double circulation of blood? 8. Explain why Bile juice does not contain any digestive enzymes, yet it is essential for digestion. 9. How would non secretion of hydrochloric acid in our stomach affect food digestion? Explain. 10. How does nutrition takes place in Amoeba? 11. Draw a diagram of cross section of human heart. Show the path of flow of blood with the help of arrows. 12. How water is transported upwards in plants? 13. Descried the functioning of nephrons. 14. a. Draw a diagram of human alimentary canal. b. Label the following oesophagus, liver, gall bladder, and duodenum. c. What is the function of liver in human body? HOTS QUESTIONS (SOLVED / UNSOLVED) 39
8 Q1. Why is it necessary to separate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds? Ans. The mammals and birds are warm-blooded animals which have high energy needs because they constantly require energy to maintain their body temperature. It is necessary to separate oxygenated blood and deoxygenated blood in mammals and birds because such a separation allows a highly efficient supply of oxygen to the body cells which is required for producing a lot of energy needed by them. Q2. How is small intestine designed to absorb digested food? Ans. The inner surface of small intestine has millions of tiny, finger like projections called Villi. The presence of villi gives the inner walls of the small intestine a very large surface area. The large inner surface area of small intestine helps in the rapid absorption of the digested food. 1. Do plants also need oxygen? LIFE PROCESSES ORAL QUESTIONS 2. How does food passes through alimentary canal? 3. What regulate the exit of food from the stomach into small intestine? 4. In which part of the alimentary canal food is completely digested absorbed? 5. In which cell organelle breakdown of pyruvate takes place using oxygen? 6. Which structures stop backward flow of blood in atria and ventricles? 7. The filtered urine is collected in which part of nephron? 8. Which part of the plant excretes some waste substances into the soil? 9. Name the process used to remove urea from the blood. 10. The process by which evaporation of water from the plants mainly through the stomata. QUIZ 1. Digestion of starch in humans takes from which organ? 2. Absorption of energy takes place in sunlight by the pigment. 3. Is chloroplast is non lining structure? 4. What is the function of amylase? 40
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER
 MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
MARKS-30 LIFE PROCESS FORMATIVE ASSESSMENT I Q.PAPER TIME- 70 MINUTES Instructions: Questions : 1 to 5 1 Mark each Questions : 6 to 9 2 Marks each Questions : 10 to 13 3 Marks each Question 14 5 Marks
 CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
CHAPTER 6 LIFE PROCESSES All living things perform certain life processes like growth, excretion, respiration, circulation etc. All the processes like respiration, digestion, which together keep the living
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
CHAPTER6. Multiple Choice Questions NCERT
 CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
CHAPTER6 Life Processes Multiple Choice Questions 1. Which of the following statements about the autotrophs is incorrect? (a) They synthesise carbohydrates from carbon dioxide and water in the presence
Downloaded from
 BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
BAL BHARATI PUBLIC SCHOOL, PITAMPURA, DELHI-110034 CLASS 10 NOTES TERM 1 Topic: Life processes Q1. Define the following terms: 1) nutrition 2) photosynthesis 3) peristalsis 4) excretion 5) osmoregulation
Revision Question Bank
 Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
LIFE PROCESSES
 LIFE PROCESSES Usually we differentiate living organisms from non-living by observing the movements in them. These movements can be: Locomotion movements In animals, e.g. running, chewing cud, etc. Growth
LIFE PROCESSES Usually we differentiate living organisms from non-living by observing the movements in them. These movements can be: Locomotion movements In animals, e.g. running, chewing cud, etc. Growth
 CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
CHAPTER-6 LIFE PROCESSES SOLVED QUESTIONS (1) Due to availability of less water, how does the plant cope up with lack of water in desert conditions? (2) After a vigorous exercise, you may experience cramps
1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2) Nutrition in Human Beings. 3) transportation in human being 4) Excretion in human being
 1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
1 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA VSN NAGPUR HOLIDAY HOMEWORK Class X A and X B (SCIENCE) Learn Chapter 1, 6 And 10 Worksheet on Chapter 1 and Chapter 6 Prepare presentation on 1) Autotrophic nutrition in plants 2)
You downloaded from page [1]
![You downloaded from page [1] You downloaded from page [1]](/thumbs/76/73943662.jpg) 10th Biology: Life LIFE processes PROCESSES solved Questions 1. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms need more oxygen
10th Biology: Life LIFE processes PROCESSES solved Questions 1. Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms need more oxygen
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII BIOLOGY
 HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
HOLIDAY HOMEWORK - CLASS VII Respiratory System Vocabulary BIOLOGY Instructions: Use the word bank to complete each statement about the respiratory system. Word Bank: alveoli; bronchiole; carbon dioxide;
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
Chapter 24. Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill.
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 14. Mention two structural features of small intestine which add to the absorptive capacity.
![LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 14. Mention two structural features of small intestine which add to the absorptive capacity. LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 14. Mention two structural features of small intestine which add to the absorptive capacity.](/thumbs/76/73956409.jpg) LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 1. What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed? Xylem in plant transports water and dissolved mineral nutrients from the roots to all parts
LIFE PROCESSES VERY SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTION [1 MARK] 1. What will happen to a plant if its xylem is removed? Xylem in plant transports water and dissolved mineral nutrients from the roots to all parts
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
The Digestive System Key words Pharynx oesophagus stomach intestine epiglottis gall bladder Pancreas peristalsis liver enzyme rectum sphincter Pyloric duodenum jejunum ileum bile lipase Amylase trypsin
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
Biology Notes. Homeostasis
 Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Life Processes CHAPTER WHAT ARE LIFE PROCESSES?
 CHAPTER 6 Life Processes How do we tell the difference between what is alive and what is not alive? If we see a dog running, or a cow chewing cud, or a man shouting loudly on the street, we know that these
CHAPTER 6 Life Processes How do we tell the difference between what is alive and what is not alive? If we see a dog running, or a cow chewing cud, or a man shouting loudly on the street, we know that these
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
MT - SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - II (72) - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 6. Time : 2 Hours Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 40
 MT 07 00 MT - SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - II (7) - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 6 Time : Hours Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 40 A.. (A) Fill in the blanks: () In some plants, waste is in the form of calcium
MT 07 00 MT - SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY - II (7) - SEMI PRELIM - II : PAPER - 6 Time : Hours Model Answer Paper Max. Marks : 40 A.. (A) Fill in the blanks: () In some plants, waste is in the form of calcium
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Mouth. Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion. breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces.
 Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Digestive System Mouth Digestion begins in the Mouth. Chewing begins the process of digestion - Mechanical digestion is the physical breakdown of large pieces of food into smaller pieces. - Chemical digestion
Plants and animals are examples of multicellular organisms. They contain millions of cells in their body.
 Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
Revision 1 Q1. Which of the following statements is true? A. A cell is the basic unit for animals only. B. A multicellular organism has more than one cell in its body. C. Plant cells and animal cells only
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
Pharynx. crop. intestine
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system provides nutrients to the body (hearts) Pharynx esophagus gizzard crop intestine stages of digestion: Ingestion: taking in of nutrients Digestion: the breaking
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Life Processes. Properties of Living Beings Compared to Non - living -
 Life Processes All the plants and animals are alive or living things. Properties of Living Beings Compared to Non - living - a. Movement b. Grow c. Need Food d. Excrete e. Respiration f. Reproduce The
Life Processes All the plants and animals are alive or living things. Properties of Living Beings Compared to Non - living - a. Movement b. Grow c. Need Food d. Excrete e. Respiration f. Reproduce The
Intermediate 2. Biology. Learning Outcomes
 Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
Intermediate 2 Biology Learning Outcomes Intermediate 2 Biology Unit 2 Cell structure and function State the similarities and differences between animal, plant and microbial cells. (cheek epithelial cell,
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS AND THEIR ANSWERS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3.
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Excretion and Water Balance
 Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Excretion and Water Balance In the body, water is found in three areas, or compartments: Plasma, the liquid portion of the blood without the blood cells, makes up about 7 percent of body fluid. The intercellular
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages )
 Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Chapter 38 Digestive and Excretory Systems Section 38 1 Food and Nutrition (pages 971 977) Key Concepts What are the nutrients your body needs? Why is water such an important nutrient? Food and Energy
Fifth Year Biology. Excretion. Miss Rochford
 Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
Fifth Year Biology Excretion Miss Rochford In this Topic Excretion in plants Excretion and homeostasis Skin Organs of excretion Urinary system Kidneys Nephron Control of urine volume Characteristics of
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by. broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion ***ANSWERS**** Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets
 The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a
The Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive, and Excretory Systems Worksheets Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. (DWilkin) Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Post- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate prompt for each student
 Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Post- Assessment Concepts Assessed Time Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Chapter 10 EXCRETION
 Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition
 B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
B4 NUTRITION 4.3 Animal Nutrition 1. State the term balanced diet & describe how balanced diet is related to age, sex & activity of an individual. Balanced diet: A diet that contains all the main nutrients
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology
 A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
A summary of topics for 3 rd Year igcse Biology Practical work shown in bold is included in the specification Teachers can also include other practical work to support their teaching Third Year Topics
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Digestion. I. What is digestion? II. Enzymes involved in digestion
 Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
Digestion I. What is digestion? Digestion is the breakdown of large, insoluble food molecules into small, soluble food molecules so that they can be absorbed into the bloodstream. Large food molecules
12/7/10. Excretory System. The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by:
 Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Excretory System The basic function of the excretory system is to regulate the volume and composition of body fluids by: o o removing wastes returning needed substances to the body for reuse Body systems
Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest.
 1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
1 The human body is organised to carry out many different functions. (a) Use words from the box to complete Figure 1 by putting the parts of the body in order of size from smallest to largest. The smallest
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed.
 They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
They need to transport all these to various parts of their body. Further, animal need to transport wastes to parts from where they can be removed. PLASMA Carry various substances. Blood is a liquid, which
AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down. the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!!
 Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
Chemical Digestion Name Period Date AFTER mechanical digestion, the pieces of food are still to be used by broken down the cells. They MUST be EVEN MORE!!!!!! Special
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
>>> FOCUS. Context. Digestion. The human digestive system
 Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Context All living organisms need nutrients, which provide materials and energy for survival. These nutrients need to be broken down before they can be used by cells. Plants make their own food using energy
Digestion & The Alimentary Canal
 For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
For more awesome GSE and level resources, visit us at www.savemyexams.co.uk/ igestion & The limentary anal Question Paper Level Subject Exam oard Topic Sub Topic ooklet O Level iology ambridge International
Chapter 32 Excretion
 Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
Chapter 32 Excretion 3.4 Learning Objectives 3.4.6 The Excretory System in Humans 1. Role of the excretory system in homeostasis. 2. Importance of temperature regulation within the body. 3. Outline the
B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport. B2.2 Tissues, organs and organ systems
 B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
B2.1.1 Cells and simple cell transport B2.1 Cells and simple cell transport Know that most human and animal cells have the following parts: a nucleus, which controls the activities of the cell; cytoplasm,
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems
 Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology
 Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Grade 07 Angel International School - Manipay 3r d Term Examination July, 2015 Biology Duration: 2 Hours Part I Choose the correct answer and underline it. 1. Which of the following does not manufacture
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
You start digesting your food the moment you start chewing. This process involves several body structures along the digestive tube.
 The Digestive System This may sound strange, but your digestive system is basically one big tube that starts at your mouth and ends at your anus. The shape of the tube changes along its length, getting
The Digestive System This may sound strange, but your digestive system is basically one big tube that starts at your mouth and ends at your anus. The shape of the tube changes along its length, getting
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS
 2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
2 NUTRITION IN ANIMALS Q.1. You have studied in class VI that food consists of many components. Try to recall and list them below : Ans. 1. Carbohydrates 2. Fats 3. Proteins 4. Minerals 5. Vitamins 6.
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body.
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Directions: Review the digestive system lesson. Then, answer the questions. 1. List, in order, the seven major organs that move food through your body. 2. What is the job of the epiglottis?
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion
 Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Cell Organization, Nutrition, Digestion, and Excretion Cell Organization: 1. Put these terms in order from least complex to most complex: Tissue, cell, organ, organelle, organism, organ system 1. Organelle
Question 1: Solution 1: Question 2: Question 3: Question 4: Class X The Excretory System Biology
 A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
A. MULTIPLE CHOICE TYPE: (select the most appropriate option in each case) Book Name: Selina Concise Question 1: Excretion primarily involves (a) removal of all byproducts during catabolism (b) removal
1b. Credit: State the chemical elements present in carbohydrates, proteins and fats. See table below
 1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
1a. General: Explain in simple terms why food is required by animals. The main types of food are carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Carbohydrates and fats are required as sources of energy. Proteins are
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL BIOLOGY DEPARTMENT. 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys.
 Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Name Q1. Name the following: S.N.KANSAGRA SCHOOL Date 1. Fibrous connective tissue covering the kidneys. 2. The deep notch present on the inner surface of the kidney. 3. The peripheral dark reddish brown
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
Characteristics of living organism
 At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
At a glance : Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Living organisms are bundles of cells that carry out specialized functions. 1. Life is uncertain because Organic Matter is born, it Organic / Biotic Matter
Human Digestion. Junior Science
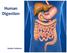 Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Human Digestion Junior Science True or False The word stomach comes from the Greek meaning Throat. Butterflies in the stomach have nothing to do with the stomach. It is possible to live without your stomach.
Unit 4: The circulatory and excretory systems
 Unit 4: The circulatory and excretory systems 1. The internal medium 2. The circulatory system 2.1. The blood 2.2. The heart 2.3. The blood vessels 3. The lymphatic system 4. The excretory system 4.1.
Unit 4: The circulatory and excretory systems 1. The internal medium 2. The circulatory system 2.1. The blood 2.2. The heart 2.3. The blood vessels 3. The lymphatic system 4. The excretory system 4.1.
