BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
|
|
|
- Bruno George
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 14 Digestive System 2 Pancreas, Liver, Small Intestine Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au
2 Session Plan o Pancreas Anatomy & Histology Pancreatic juice Functions o Liver and gall bladder Anatomy & Histology Bile Functions o Small intestine Anatomy and Histology Intestinal Juice and Brush Border Enzymes Chemical and Mechanical digestion Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 2
3 Pancreas Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 3
4 Anatomy of the Pancreas The pancreas: retroperitoneal gland o Size:12 15 cm long and 2.5 cm thick, o Location: Posterior to the greater curvature of the stomach. o Three parts: a head, body, and tail o Head close to curve in C-shaped duodenum Two major ducts: Convey the secretions into the small intestine Pancreatic duct (duct of Wirsung) Accessory duct (duct of Santorini) Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 4
5 Anatomy of the Pancreas Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 5
6 Histology of the Pancreas o Acini - dark clusters 99% of gland Exocrine portion Secrete pancreatic juice o Islets of Langerhans- pale staining cells 1% of gland Endocrine portion Secrete hormones glucagon, insulin, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 6
7 Histology of the Pancreas Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 7
8 Composition and Functions of Pancreatic Juice o a clear, colourless liquid o Produced liters/day o ph of 7.1 to 8.2 o Contains water, some salts, sodium bicarbonate, and several enzymes o Sodium bicarbonate: converts the acid stomach contents to a slightly alkaline ph ( ), halting stomach pepsin activity and promoting activity of pancreatic enzymes Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 8
9 Composition and Functions of o Digestive enzymes: Pancreatic Juice Pancreatic amylase: digest Starch Pancreatic lipase: digest triglycerides Proteases: digest proteins Trypsinogen - activated by enterokinase (a brush border enzyme) Chymotrypsinogen - activated by trypsin Procarboxypeptidase - activated by trypsin Proelastase - activated by trypsin Trypsin inhibitor - combines with any trypsin produced inside pancreas Ribonuclease and deoxyribonuclease: digest RNA and DNA Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 9
10 Regulation of Pancreatic Secretions Hormones secreted by Small intestine: o Secretin Stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice that are rich in bicarbonate ions, promotes normal growth and maintenance of pancreas, enhances effects of CCK. o Glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide (GIP) Stimulates pancreatic beta cells to release insulin. o Cholecystokinin (CCK) Stimulates secretion of pancreatic juice rich in digestive enzymes, promotes normal growth and maintenance of pancreas, enhances effects of secretin. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 10
11 Regulation of Pancreatic Secretions Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 11
12 Liver and Gallbladder Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 12
13 Liver and Gallbladder o The liver: Weight: the heaviest gland in the body about 1.4 kg in an average adult Size: the second largest organ in the body after the skin. Location: inferior to the diaphragm and occupies most of the right hypochondriac and part of the epigastric regions of the abdominopelvic cavity o The gallbladder: Size: Pear-shaped sac 7 10 cm long Location: in a depression of the posterior surface of the liver Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 13
14 o Liver: Anatomy of the Liver and Right and Left lobes Falciform ligament Quadrate lobe Caudate lobe Ligamentum teres (round ligament) Right and left coronary ligaments Gallbladder Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 14
15 Anatomy of the Gallbladder o Gallbladder: Fundus Body Neck Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 15
16 Histology of the Liver Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 16
17 Histology of the Liver o Hepatocytes: Major functional cells of the liver Metabolic, secretory, and endocrine functions Secrete bile: a yellow, brownish, or olive-green liquid serves as both an excretory product and a digestive secretion. o Bile canaliculi: Small ducts between hepatocytes that collect bile produced by the hepatocytes. Bile flow: Bile canaliculi Bile ductules Bile ducts Right and left hepatic ducts Common hepatic duct joins the Cystic duct Common bile duct Small intestine o Hepatic sinusoids o Central Vein o Stellate reticuloendothelial (Kupffer) cells Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 17
18 Bile flow Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 18
19 Histology of the Gallbladder Histology: o Mucosa: Simple columnar epithelium arranged in rugae o Submucosa: not present o Muscular coat: smooth muscle fibers Contraction of the smooth muscle fibers ejects the contents of the gallbladder into the cystic duct. o Serosa or visceral peritoneum Functions of the gallbladder: To concentrate the bile produced by the liver (up to tenfold) by absorbing water and ions. To store bile until it is needed in the small intestine. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 19
20 Blood Supply to the Liver o Double blood supply: from Hepatic artery: oxygenated blood from branch of the aorta Hepatic portal vein: Nutrient rich blood from stomach, spleen and intestines o Hepatic vein: All blood eventually leave the liver via hepatic vein Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 20
21 Composition and Function of Bile o Secreted by hepatocytes ml of bile/day a yellow, brownish, or olive-green liquid ph 7.6 to 8.6 o Transported by a duct system to the gallbladder for concentration and temporary storage. o Excretory product: containing components of worn-out red blood cells o Digestive secretion Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 21
22 Composition and Function of Bile o Components: Water, cholesterol and several ions A phospholipid called lecithin Bile salts = Na and K salts of bile acids: digestive product Play a role in emulsification, the breakdown of large lipid globules into a suspension of small lipid globules. Aid in the absorption of lipids following their digestion. Bile pigments = bilirubin from haemoglobin: excretory product Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 22
23 Regulation of Bile Secretion o Parasympathetic impulses and vagus nerves o Cholecystokinin(CCK) o Secretin Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 23
24 Functions of Liver o Carbohydrate metabolism: maintains normal blood glucose level by Glycogenolysis: Break down glycogen to glucose and release the glucose into the bloodstream Gluconeogenesis: Convert certain amino acids, triglycerides and lactic acid to glucose. Glycogenesis: Converts glucose to glycogen and triglycerides for storage. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 24
25 Functions of Liver o Lipid metabolism: Storage: Hepatocytes store some triglycerides; Lipolysis: Break down fatty acids to generate ATP; Lipogenesis: Synthesize lipoproteins, which transport fatty acids, triglycerides, and cholesterol to and from body cells; Cholesterol synthesize Synthesize bile salts from cholesterol Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 25
26 Functions of Liver o Protein Metabolism: Deamination: Removes NH2 (amine group) from amino acids so can use what is left as energy source Urea cycle: Converts resulting toxic ammonia (NH3) into urea for excretion by the kidney Protein synthesis: Synthesizes plasma proteins alpha and beta globulins, albumin, prothrombin, and fibrinogen. Converts one amino acid into another amino acids Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 26
27 Functions of Liver o Processing of drugs and hormones: Detoxify substances such as alcohol and excrete drugs such as penicillin, erythromycin, and sulfonamides into bile. Chemically alter or excrete thyroid hormones and steroid hormones such as estrogens and aldosterone. o Synthesis of bile and bile salts o Excretion of waste products: Bilirubin from RBC recycling Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 27
28 Functions of Liver o Storage: Fat soluble vitamins - A, B12, D, E, K and minerals iron and copper o Phagocytosis: aged RBCs, WBCS and some bacteria o Activation of vitamin D Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 28
29 Small intestine Anatomy and Histology Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 29
30 Small Intestine o The small intestine: Long tubular structure (2.5 cm in diameter and about 3 m in length), extends from the pyloric sphincter to the ileocecal sphincter. o Functions: Mix chyme with digestive juices and bring food into contact with mucosa for absorption Completes digestion of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids; begins and completes digestion of nucleic acids. Absorbs about 90% of nutrients and water that pass through digestive system. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 30
31 Anatomy of the Small Intestine o Gross anatomical subdivisions: Duodenum Jejunum Ileum o Ileocecal sphincter Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 31
32 Histology of the Small Intestine o Layers of small intestinal wall: Mucosa Submucosa Muscularis Serosa Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 32
33 Histology of the Small Intestine o Mucosa: Composed of o The epithelial layer: Simple columnar epithelium contains Absorptive cells and Goblet cells o Intestinal glands: formed by glandular epithelial cells. Deep crevices o Lamina propria: areolar connective tissue with mucosaassociated lymphoid tissue (MALT) Solitary lymphatic nodules: most numerous in the distal part of the ileum Peyer s patches: in the ileum o Muscularis mucosae: smooth muscle Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 33
34 Histology of the Small Intestine Cells of Intestinal glands: Absorptive cell Goblet cell Paneth cells Enteroendocrine cells: S cells CCK cells K cells o Intestinal Juice: The secretion of absorptive, goblet and paneth cells Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 34
35 Histology of the Small Intestine o Submucosa: Duodenal (Brunner s) glands: In duodenum, secrete an alkaline mucus that helps neutralize gastric acid in the chyme. Lymphatic tissue of the lamina propria: may extends through the muscularis mucosae into the submucosa. o Muscularis: consists of 2 layers of smooth muscles. outer, thinner longitudinal and the inner, thicker circular fibers layer. o Serosa: Visceral peritoneum completely surrounds the small intestine except for a major portion of the duodenum. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 35
36 Special structural features o Special structural features of the small intestine: Circular folds (Plicae circularis) Villi Microvilli o Function: Massive increase in surface area of the small intestine to facilitate the process of digestion and absorption. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 36
37 Special structural features Circular folds (Plicae circularis) Villi Microvilli Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 37
38 Special structural features o Circular folds/plicae circularis: Folds of the mucosa and submucosa Permanent ridges, about 10 mm long Begin near the proximal portion of the duodenum and end at about the midportion of the ileum. o Function: Enhance absorption by increasing surface area and causing the chyme to spiral, rather than move in a straight line, as it passes through the small intestine. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 38
39 Special structural features o Villi: Finger-like projections of the mucosa mm tall villi per square millimetre of small intestine Outer cover: Epithelial cells; Core: Lamina propria An arteriole, a venule, a blood capillary network, and a lacteal o Functions: Increase the surface area of the epithelium available for absorption and digestion Gives the intestinal mucosa a velvety appearance Nutrients absorbed by the epithelial cells covering the villus pass through the wall of a capillary or a lacteal to enter blood or lymph, respectively Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 39
40 Special structural features o Microvilli: Projections of the apical (free) membrane of the absorptive cells. 1 µm-long cylindrical, membrane-covered projection contains a bundle of actin filaments (allow movement) 200 million microvilli per square millimetre of small intestine. o Functions: Form brush border, extending into the lumen of the small intestine Increase the surface area of the plasma membrane and allows larger amounts of digested nutrients can diffuse into absorptive cells in a given period. Contains several brush-border enzymes that have digestive functions Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 40
41 Intestinal Juice and Brush Border Enzymes o Intestinal juice: a clear yellow fluid, secreted by intestinal glands About 1 2 litres/day. ph: 7.6 slightly alkaline Contains water and mucus, brush-border enzymes and lysozyme o Brush-border enzymes: Carbohydrate digesting enzymes: ɑ-dextrinase, maltase, sucrase, and lactase Protein-digesting enzymes: peptidases (aminopeptidase and dipeptidase) Nucleotide-digesting enzymes: nucleosidases and phosphatases Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 41
42 Intestinal Juice and Brush Border o Functions: Enzymes o Intestinal juice: Absorption of substances from the chyme as they come in contact with the villi. o Brush border enzymes: Digestion at brush border Digestion in the lumen of the small intestine. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 42
43 Small intestine chemical and mechanical digestion Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 43
44 Mechanical Digestion in the Small o Segmentation: Localized, mixing contractions that occur in portions of intestine distended by a large volume of chyme. o Migrating motility complex (MMC): The type of peristalsis that occurs in the small intestine when distension of the small intestinal wall lessens. Intestine Marieb, and Hoehn, 2011 Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 44
45 Regulation of Secretion and Motility o Enteric reflexes that respond to the presence of chyme increase intestinal motility VIP (vasoactive intestinal polypeptide) stimulates the production of intestinal juice segmentation depends on distention which sends impulses to the enteric plexus and CNS distention produces more vigorous peristalsis 10 cm per second o Sympathetic impulses decrease motility Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 45
46 Chemical Digestion in the Small Intestine o Digestion by pancreatic juice, bile, and intestinal juice. o Breakdown of nutrients into absorbable forms carbohydrates proteins lipids Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 46
47 Readings and Resources o Tortora, GJ & Derrickson, B Principles of Anatomy and Physiology, 14th edn, Wiley. o Harris, P, Nagy, S & Vardaxis, N 2010, Mosby s Dictionary of Medicine, Nursing and Health Professions, 2nd edn, Mosby Elsevier. o Guyton, AC & Hall, JE 2011, Textbook of Medical Physiology, 12th edn, Saunders Elsevier. o Marieb, EN & Hoehn, K 2011, Human Anatomy and Physiology, 9th edn, Benjamin Cummings Pearson. o Moore, KL, Dalley, AF & Agur, AMR 2010, Clinically Orientated Anatomy, 6th edn, Lippincott, Williams & Wilkins. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 47
48 Copyright COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of the Endeavour College of Natural Health pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968 (the Act). The material in this communication may be subject to copyright under the Act. Any further reproduction or communication of this material by you may be the subject of copyright protection under the Act. Do not remove this notice. Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 48
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 15 Digestive System 2 Stomach and Accessory Structures Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Stomach anatomy
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 15 Digestive System 2 Stomach and Accessory Structures Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Stomach anatomy
DIGESTIVE. CHAPTER 17 Lecture: Part 1 Part 2 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II CHAPTER 17 Lecture: DIGESTIVE Part 1 Part 2 Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. SMALL INTESTINE DUODENUM > JEJUNUM
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Physiology Unit 4 DIGESTIVE PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Functions Motility Ingestion Mastication Deglutition Peristalsis Secretion 7 liters/day! Exocrine/endocrine Digestion Absorption Digestion of
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4
 Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Bio& 242 Unit 1 / Lecture 4 system: Gastric hormones GASTRIN: Secretion: By enteroendocrine (G) in gastric pits of the mucosa. Stimulus: Stomach distention and acid ph of chyme causes Gastrin. Action:
Gastric Contrac,le Ac,vity. Regula,on of Gastric Emptying
 Gastric Contrac,le Ac,vity Figure 23.18 Regula,on of Gastric Emptying Gastric emptying is regulated by: Neural enterogastric reflex Hormonal (enterogastrone) mechanisms In the presence of gastric gastrin
Gastric Contrac,le Ac,vity Figure 23.18 Regula,on of Gastric Emptying Gastric emptying is regulated by: Neural enterogastric reflex Hormonal (enterogastrone) mechanisms In the presence of gastric gastrin
Chapter 14: The Digestive System
 Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of Muscular tube (digestive tract) alimentary canal Accessory organs teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6.
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
The Digestive System. Chapter 25
 The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 25 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
The Digestive System. What is the advantage of a one-way gut? If you swallow something, is it really inside you?
 The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
The Digestive System What is the advantage of a one-way gut?! If you swallow something, is it really inside you? Functions and Processes of the Digestive System: Move nutrients, water, electrolytes from
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4
 Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Digestive Lecture Test Questions Set 4 1. Which of the following is not associated directly with the small intestine: a. villi b. circular folds c. microvilli d. haustrae e. secretin 2. The largest (longest)
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology. Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross
 Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Gastrointestinal Anatomy and Physiology Bio 219 Napa Valley College Dr. Adam Ross Functions of digestive system Digestion Breakdown of food (chemically) using enzymes, acid, and water Absorption Nutrients,
Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder
 Connexions module: m49293 1 Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Donna Browne Based on Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and
Connexions module: m49293 1 Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Donna Browne Based on Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine
 Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Anatomy & Histology of The Small intestine Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Jejunum Ileum Histology: Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System
 Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
Chapter 15 Gastrointestinal System Dr. LL Wang E-mail: wanglinlin@zju.edu.cn Rm 608, Block B, Research Building, School of Medicine, Zijingang Campus Pancreatic Secretion The exocrine cells in the pancreas
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas
 Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
Anatomy of the liver and pancreas Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk abdulameerh@yahoo.com Liver Aorta Pulm. Trunk Rt. At, Duct. Art. Lt. Ven. Rt. Ven. Internal Posterior
An overview of the digestive system. mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus
 An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
An overview of the digestive system mouth pharynx esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine rectum anus Why GIT? What are the main steps in the digestive process? Ingestion intake of food via the
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
General Structure of Digestive Tract
 Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Dr. Nabil Khouri General Structure of Digestive Tract Common Characteristics: Hollow tube composed of a lumen whose diameter varies. Surrounded by a wall made up of 4 principal layers: Mucosa Epithelial
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Small intestine. Small intestine
 General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
General features Tubular organ longest part; 5-6 m most of chemical digestion absorption of nutrients reabsorption of H2O occurs. Two structural features; maximize the lumenal surface area villi microvilli
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 16 Urinary System 1 The Kidneys Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Functions of Urinary system o The Kidneys:
Lecture Overview. ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages
 ** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
** Digestive System ** (cont d) A&P II Lecture Notes Pages 103-111 Lecture Overview Gall Bladder/Ducts Pancreas GI Tract Movements Chemistry of Digestion Secretion and Absorption Metabolism 2 Liver, Bile
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 18 Urinary System 3 Tubular Reabsorption and Secretion Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Principles of
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM TYPES OF DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS Ingested food may be stored or first subjected to physical fragmentation Chemical digestion occurs next Hydrolysis reactions liberate the subunit molecules
Chapter 24, Part 2! Chapter 24 Digestion PART 2! The Digestive System!
 Chapter 24, Part 2! The Digestive System! SECTION 24-6! The small intestine digests and absorbs nutrients, and associated glandular organs assist with the digestive process 2 Small Intestine Regions! 21
Chapter 24, Part 2! The Digestive System! SECTION 24-6! The small intestine digests and absorbs nutrients, and associated glandular organs assist with the digestive process 2 Small Intestine Regions! 21
Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46496 1 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
OpenStax-CNX module: m46496 1 Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number. Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet.
 BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
BIO 132 Anatomy and Physiology II Spring, 2016 Exam 1 Name: BIO 132 ID Number Section 1 Answer questions 1 40 on the scan sheet. 1. The homeostatic value of a particular controlled variable in the body
Chapter 24, Part 2! The Digestive System!
 Chapter 24, Part 2! The Digestive System! SECTION 24-6! The small intestine digests and absorbs nutrients, and associated glandular organs assist with the digestive process 2 1! Small Intestine Regions!
Chapter 24, Part 2! The Digestive System! SECTION 24-6! The small intestine digests and absorbs nutrients, and associated glandular organs assist with the digestive process 2 1! Small Intestine Regions!
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014
 HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
HUMAN NUTRITION: ABSORPTION & ASSIMILATION 14 MAY 2014 In this lesson, we: Absorption Lesson Description Examine and understand absorption Define absorption and describe where it occurs Study the structure
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II. THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D.
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM LAB ANALOGY PAGES 248-265 MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE ORGANS ALIMENTARY CANAL MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE
Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
 Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
Phosphorylation Hydrolysis Energy, Chemical Reactions and Enzymes Chapter 2 (selections) What is Energy? Energy is the capacity to do work Potential Energy Kinetic Energy Chemical Bond Energy Like a rechargeable
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4)
 Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Vert Phys PCB3743 Pancreas Fox Chapter 18 part 2 (also Chapter 19.3 & 19.4) T. Houpt, Ph.D. Anatomy of Digestive System Peristalsis Stomach and Acid Secretion Liver and Bile Secretion Pancreas and pancreatic
Paneth Cells. Road Map to the Finish. No Review this Friday. Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs. Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I
 Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
Road Map to the Finish No Review this Friday Today 11/29 Finish digestion/accessory organs Wednesday 12/1 Immune System I Paneth Cells - base of intestinal glands -! large -! intense acidophilic granules
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13
 Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
Business Reminder: No class Monday (Memorial Day) Midterm 2 is Tuesday 5/28/13 Optional review session tomorrow @ 5pm Homework due in Lab 1. PreLab 8 (1pt) 2. Replace a Missing Assignment (4 pts) Homework
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B
 Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
Dr Nadine Gravett School of Anatomical Sciences Room 2B10B Nadine.Gravett@wits.ac.za Oral cavity Mechanical breakdown Formation of bolus Oesophagus Conduit from mouth to stomach Stomach Digestion Temporary
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 13 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The digestive system also known as the alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract consists of a series of hollow organs joined in a
Chapter 9. The digestive system. Glossary. Louise McErlean
 Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 9 The digestive system Louise McErlean Glossary Absorption Process whereby the products of digestion move into the blood or lymph fluid. Acini glands Produce pancreatic juice. Amylase Carbohydrate
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
BIO 139 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM MARY CATHERINE FLATH, Ph.D. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ORGANS MOUTH PHARYNX ESOPHAGUS STOMACH SMALL INTESTINE LARGE INTESTINE SALIVARY GLANDS PANCREAS LIVER
Digestive System. Digestive System. Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body.
 Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
Digestive System Digestion is the process of reducing food to small molecules that can be absorbed into the body. 2 Types of Digestion Mechanical digestion physical breakdown of food into small particles
The Digestive System. Chapter 16. Introduction. Overview of Digestive System. Histological Organization. Movement and Mixing of Digestive Materials
 The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System Chapter 16 Introduction Structure of the digestive system A tube that extends from mouth to anus Accessory organs are attached Functions include Ingestion Movement Digestion Absorption
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 24 The Digestive System Introduction The purpose of this chapter is to Identify the anatomical components of the digestive system as well as their
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism
 14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
14 PART B The Digestive System and Body Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment
 _ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
_ Date: Mark: /45 Chapter 9: Digestion Review Assignment 45 Multiple Choice = 45 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following roles do
The gallbladder. Bile secretion:
 The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
The gallbladder is a thin walled green muscular sac on the inferior surface of the liver. The gallbladder stores bile that is not immediately needed for digestion and concentrates it. When the muscular
Class XI Chapter 16 Digestion and Absorption Biology
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Unit 2 : The Digestive System
 Unit 2 : The Digestive System Mind Map Components and Histology Digestion Oral Cavity Small Intestine Digestive System Digestion Stomach Large intestine Absorption Digestion Absorption Digestion Absorption
Unit 2 : The Digestive System Mind Map Components and Histology Digestion Oral Cavity Small Intestine Digestive System Digestion Stomach Large intestine Absorption Digestion Absorption Digestion Absorption
The Small Intestine. The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine.
 The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
The Small Intestine The pyloric sphincter at the bottom of the stomach opens, squirting small amounts of food into your small intestine. approximately six metres (the longest section of your digestive
 Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Question 1: Choose the correct answer among the following: (a) Gastric juice contains (i) pepsin, lipase and rennin (ii) trypsin lipase and rennin (iii) trypsin, pepsin and lipase (iv) trypsin, pepsin
Tissues and organs PART 1
 Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Tissues and organs PART 1 Animals and plants are multicellular (made of many cells). Cells become specialised according to their function Tissues: Many cells that perform one or several functions; they
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture:
 السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
السالم عليكم [HISOLOGY 2] April 27, 2014 The doctor mentioned a few things about the esophagus from the previous lecture: Esophagus - It is about 25 cm in length (from the incisor it is 45 cm) Histological
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
1. Approximately 21 ft. long: duodenum (one ft.), jejunum (eight ft.), and ileum (twelve ft.)
 IV. Small Intestines A. General features and functions 1. Approximately 21 ft. long: duodenum (one ft.), jejunum (eight ft.), and ileum (twelve ft.) 2. Functions: move forward chyme, continue digestion,
IV. Small Intestines A. General features and functions 1. Approximately 21 ft. long: duodenum (one ft.), jejunum (eight ft.), and ileum (twelve ft.) 2. Functions: move forward chyme, continue digestion,
Ali Yaghi. Yaseen Fatayer. M.Khatatbeh
 6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
6 Ali Yaghi Yaseen Fatayer M.Khatatbeh P a g e 1 pancreatic secretions note: The pancreas has endocrine (secretions are released toward the blood) and exocrine(secretions are released through the canalicular
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 20 The Digestive System Exam Study Questions 20.1 Overview of GI Processes 1. Describe the functions of digestive system. 2. List and define the four GI Processes: 20.2 Functional Anatomy of the
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder
 Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
Chapter 18 Liver and Gallbladder 解剖學科徐淑媛 本堂重點 1. Liver : functions & histology 2. Gallbladder Physiology Liver Produce circulating plasma proteins Vitamin Iron Degradation Metabolism Bile manufacture (exocrine)
The stomach is formed of three parts: -
 The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
The stomach is formed of three parts: - (a) CARDIAC STOMACH: - It receives the oesophagus through Cardiac aperture guarded by a cardiac sphincter which prevents regurgitation of food. (b) FUNDIC PART:
Digestive Anatomy Lab
 Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive Anatomy Lab In-Lab Exercises I have included the word list in this document. Any descrepencies between this document and the wordlist, you should default to this document. There is a lot of repetition
Digestive System. Part 3
 Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
Digestive System Part 3 Digestion Ingested materials must be broken down for absorption Majority of absorption in small intestine Water and alcohol in stomach mucosa Some salts and vitamins in large intestine
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2)
 NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
NOTES: The Digestive System (Ch 14, part 2) PANCREAS Structure of the pancreas: The pancreas produces PANCREATIC JUICE that is then secreted into a pancreatic duct. The PANCREATIC DUCT leads to the The
Summary of chemical breakdown of food by hydrolytic enzymes (Protein enzymes).
 Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Biology 12 Digestive System Digestion Overview: The digestive process can be divided into 4 phases: 1. ingestion - includes swallowing and peristalsis 2. digestion - the physical (by teeth) and chemical
Nutrition. Autotrophs. plants, some protists & bacteria producers
 Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
Nutrition Autotrophs plants, some protists & bacteria producers Nutrition Heterotrophs animals, fungi, some protists & bacteria consumers Animal Nutrition Most obtain food by ingestion take in their food
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2
 BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
BIOH122 Human Biological Science 2 Session 17 Urinary System 2 Glomerular Filtration Bioscience Department Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au Session Plan o Overview of Renal Physiology
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology
 The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
The Digestive System and Body Metabolism Premedical Biology Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings The Digestive System and Body Digestion Metabolism Breakdown of ingested
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Human Nutrition (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) o Balanced diet: getting all the right nutrients in correct proportions o Diet related to: - Age - Gender - Activity - Pregnant women o Malnutrition:
Two main groups Alimentary canal continuous coiled hollow tube Accessory digestive organs
 Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Digestion Breakdown of ingested food Absorption of nutrients into the blood Metabolism Production of cellular energy (ATP) Constructive and degradative cellular activities Two main groups Alimentary canal
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans
 Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Ch 7 Nutrition in humans Think about (Ch 7, p.2) 1. The stomach churns food into smaller pieces physically. The stomach wall secretes proteases to chemically digest proteins. It also releases hydrochloric
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers
 Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Biology 20: Digestive System Did you get it? Questions and Answers Mouth 1. What is the purpose of chewing? a. break food into smaller pieces so there is a greater SA for chemicals to work on. 2. Salivary
Overview of Gastroenterology
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.121: Gastroenterology, Fall 2005 Instructors: Dr. Jonathan Glickman Overview of Gastroenterology Gastroenterology Made Really Simple! Food Waste
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM (PART II)
 THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM (PART II) 1 FUNCTIONS OF THE DS Ingestion Secretion Mixing and propulsion Digestion Absorption Defecation Ingestion This process involves taking foods and liquids into the mouth (eating).
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM (PART II) 1 FUNCTIONS OF THE DS Ingestion Secretion Mixing and propulsion Digestion Absorption Defecation Ingestion This process involves taking foods and liquids into the mouth (eating).
The Digestive System Laboratory
 The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
The Digestive System Laboratory 1 The Digestive Tract The alimentary canal is a continuous tube stretching from the mouth to the anus. Liver Gallbladder Small intestine Anus Parotid, sublingual, and submaxillary
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption. Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs
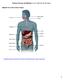 Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Nutrients, Enzymes and Digestion Lesson 4: Digestion and Absorption Digestive Tract and Accessory Organs http://highered.mheducation.com/sites/0072495855/student_view0/chapter26/animation organs_of_digestion.html
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look
 Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
Chemical Digestion and Absorption: A Closer Look Bởi: OpenStaxCollege As you have learned, the process of mechanical digestion is relatively simple. It involves the physical breakdown of food but does
Digestive Tract. Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract. stomach small intestine large intestine - anus
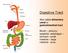 Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Digestive Tract Also called alimentary canal or gastrointestinal tract Mouth pharynxepiglottis- esophagus stomach small intestine large intestine - anus Digestive Tract Digestion: The mechanical and chemical
Chapter 16. Lecture and Animation Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
Chapter 16 Lecture and Animation Outline To run the animations you must be in Slideshow View. Use the buttons on the animation to play, pause, and turn audio/text on or off. Please Note: Once you have
e. Undigested material is compacted and stored until the colon is full. When the colon is full, a signal to empty it is sent by sensors in the walls
 Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Digestive System 1. General a. Animals obtain energy by breaking food molecules into smaller pieces. b. The basic fuel molecules are amino acids, lipids and sugars c. Digestion is the chemical breakdown
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes
 Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
Biology 12 - Digestion Notes Anatomy Physiology Functions of the Digestive System -------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- food (enzymes, bile, HCl) to assist
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food &
 The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
The process of digestion is accomplished by mechanical & chemical processes:- The buccal cavity performs two major functions, mastication of food & facilitation of swallowing. The teeth & the tongue with
Digestive System. In one end and out the other.
 Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Digestive System In one end and out the other. Overview Every cell in the body needs nourishment, yet most cells cannot leave their position in the body and travel to a food source, so the food must be
Nutrition and Digestion
 Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Nutrition and Digestion Classes of Nutrients Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Minerals Vitamins Water Macronutrients Carbon-containing compounds Energy and raw material Includes carbohydrates, lipids, & proteins
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.1 Digestion and Absorption D.1 Human Nutrition D.2 Digestion Essential Understandings: The structure of the digestive system allows it to move, digest, and absorb food. A balanced
General functions of digestive system. Ch. 15 The Digestive System. General histology of the wall of the digestive tract. Overview of digestive organs
 Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
Overall idea: obtain nutrients from food (for energy and raw materials for synthesis), and defecate the leftover waste 2 types of organs involved: 1. Parts of the digestive tract (= a long muscular tube
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM II ACCESSORY DIGESTIVE ORGANS Dr. Larry Johnson Texas A& M University Objectives Distinguish between the parotid and submandibular salivary glands. Understand and identify the structural
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy
 The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
The Wiltshire School of Beauty and Holistic Therapy Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology W: www.wsbht.co.uk E: holistics@wsbht.co.uk T: 07824 337333 Certificate of Merit in Anatomy and Physiology
