Blood and Blood Spatter Chapter 11
|
|
|
- Austin Griffith
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Blood and Blood Spatter Chapter 11 1
2 BLOOD OBJECTIVES You will understand: That an antibody and an antigen of different types will agglutinate, or clump, when mixed together. That the significance of the evidence depends on a characteristic s relative occurrence in the population. You will be able to: Determine whether a stain is blood. Determine whether a bloodstain is human or animal blood. Determine the blood type of a simulated bloodstain using the ABO/Rh system. Explore bloodstain patterns as a function of velocity, direction, and height of fall. Use technology and mathematics to improve investigations and communications Forensic Science Today 2
3 Introduction What does blood typing provides to an investigation? Blood typing provides class evidence DNA profiling provides individual evidence The truthfulness of an account by a witness or a suspect. The origin of the blood The angle and velocity of impact The type of weapon used 3
4 Opening Questions: Blood 1. What do you think is the role of blood in the human body? 2. What makes up blood? 3. Do you think all human blood is the same? Explain 4. Do you think you could determine where the blood originated based upon the blood spatter stain? 4
5 Composition of Blood Plasma - a liquid suspending other blood components Red blood cells - (erythrocytes) carries oxygen to the body s cells and carbon dioxide away. White blood cells - (leukocytes) fights disease and foreign invaders and, alone, contain cell nuclei. Platelets (thrombocytes) aids in blood clotting and the repair of damaged blood vessels. 5
6 Composition of Blood 6
7 Composition of Blood A bag containing one unit of fresh frozen plasma
8
9 Forensic Serology Serology involves the study of body fluids and stains at a crime scene, particularly blood. If blood contains DNA matching: It could link a suspect to a scene It can prove a link between suspect, victim and crime 2009 Forensic Science Today 9
10 Cellular Components of Blood 2009 Forensic Science Today 10
11 2009 Forensic Science Today 11
12 2009 Forensic Science Today 12
13 2009 Forensic Science Today 13
14 2009 Forensic Science Today 14
15 2009 Forensic Science Today 15
16 2009 Forensic Science Today 16
17 History of DNA Profiling In 1982 white blood cells were used as a source of DNA by Dr. Alec Jeffreys to produce the first DNA profile. 17
18 The first method for creating a DNA profile was RFLP, or restriction fragment length polymorphism. RFLP is not used as often today because it requires a large sample of DNA -- as much as 25 hairs or a nickel-sized spot of bodily fluid -- and can take as long as a month to complete. It also requires examining multiple sections of the DNA strand to find variations, which is time-consuming and leaves more room for human error Forensic Science Today 18
19 Questions Copy and answer these questions: 1. What part of blood can be used for DNA analysis? 2. How long has DNA analysis been possible? 3. Why is DNA an important tool for forensic scientists? Answers: 1. White blood cells 2. Since 1982 (29 years) STOP 3. Because it determines with a high degree of certainty the identity of an individual. 19
20 Discovery of Blood Types Discovered in 1900 by Karl Landsteiner. Identifies the presence or absence of particular proteins embedded in the cell. In 1901, Landsteiner described the A and B proteins found on red blood cells. The Rh factor (protein) were also identified. An antibody reaction test is used to identify each blood type. 20
21 A and B Proteins 42% 12% 3% 43% of the population in the United States 21
22 Rh Factor 85% of the human population has a protein called RH factor on their red blood cells. 22
23 Rhesus monkeys have an important history with humans and have aided a great deal of medical and scientific research. Rhesus antigens found in their blood enabled doctors to identify the different human blood groups. These primates also preceded humans into space. 23
24 Cayo Santiago is a small island (38 acres) just off the southeastern coast of Puerto Rico. Cayo Santiago is a research field station which is home to approximately 800 free-ranging rhesus macaques. The colony is run and maintained by the Caribbean Primate Research Center (CPRC) and the University of Puerto Rico, Medical Sciences Campus. The monkeys currently living on Cayo are divided into a few natural social groups. The individuals in the current colony are the direct descendants of 409 monkeys who were brought to the island in Monkeys are fed a diet of Purina monkey chow from three feeding locations on the island. The population also eats a variety of other indigenous foods, including leaves, fruits, flowers, and soil. Monkeys have access to water at a number of locations. Because of almost 70 years of research at this field site, subjects are well habituated to human experimenters. We have tested subjects from the Cayo Santiago population for the past nine years. At no point can you step onto the island. These are wild animals with Herpes B and they may attack. 24
25 Naming of Blood Types A person s blood type is based on the presence or absence of the AB and Rh proteins. The presence of different blood types was not discovered until Wrong blood = cause clumping = death 2009 Forensic Science Today 25
26
27 Blood Groups Type Antigen Antibody Can Give Blood To Can Get Blood From A A B A, AB O, A B B A B, AB O, B AB A and B Neither A nor B AB A, B, O, AB O Neither A nor B A and B A, B, O, AB O 27
28 Blood Donation 28
29 29
30 Blood Spatter A grouping of bloodstains composes a blood-spatter pattern. It helps to reconstruct the series of events surrounding a shooting, stabbing, or beating. Blood Spatter video clip 30
31 Blood Spatter Analysis Given BSP, it is possible to determine: 1. direction blood was traveling 2. angle of impact 3. point of origin of the blood 4. manner of death 2009 Forensic Science Today 31
32 How does forces of gravity, air resistance (friction), cohesion, adhesion, and surface tension act on blood? Gravity Falling Blood Drop Air Resistance Surface Tension, in the case of any fluid containing a high % of H 2 O Air drag drag pulling down Gravity pulling down Molecules attracted to one another causing spherical shape Molecules attracted to one another causing spherical shape 32
33 Cohesion Blood is cohesive. Blood is attracted to similar blood mixtures and tends to stick together as it falls. Cohesive forces in a blood droplet resist droplet flattening. 33
34 Dripping Blood Blood trickles downwards Blood drop grows until Wt (G) > S.T. Single drop breaks free (teardrop shape) Surface tension pulls in vertically And horizontally Shape settles into sphere (0.05 ml) Does not break up until impact 2009 Forensic Science Today 34
35 Blood Spatter Analysis Satellite droplets When blood falls from a height, or at a high velocity, it overcomes its natural cohesiveness, and separates from the main droplet. Spiking patterns Form around the droplet edges when blood falls onto a less-than-smooth surface. Notice that spikes are still connected to the main droplet whereas 35 satellites are totally separated.
36 2009 Forensic Science Today 36
37 2009 Forensic Science Today 37
38 Effect of Target Surface Blood Spatter animations..... Spreads out smoothly ST of spreading edge is broken by irregular surface 2009 Forensic Science Today 38
39 Blood Spatter Analysis In 1902, Dr. John Glaister describe the six patterns into which blood spatters could be classified. They include: 1. Passive fall 39
40 2. Arterial spurts or gushes Bloodstain pattern(s) resulting from blood exiting the body under pressure from a breached artery Forensic Science Today 40
41 3. Splashes 4. Smears 2009 Forensic Science Today 41
42 5. Trails of 6. Pools of Blood Blood 2009 Forensic Science Today 42
43 Effect of Angle of Impact The size and shape of blood droplets help identify the direction from which the blood originated. 43
44 No change in diameter beyond 7 ft Forensic Science Today 44
45 2009 Forensic Science Today 45
46 2009 Forensic Science Today 46
47 Direction of Movement Tail shows direction 47
48 Spatter Patterns Spatter patterns can help the investigator determine the type of wound. A fine mist spatter is produced by a high velocity impact, such as a gunshot wound. A beating with a pipe will produce blood cast off with a lower-velocity pattern Forensic Science Today 48
49 Blood Spatter Categories Categories are based on how fast the blood drops were traveling when they hit the target surface. Low-velocity Impact Spatter Medium-velocity Impact Spatter High-velocity Impact Spatter 2009 Forensic Science Today 49
50 High-velocity Impact Spatter Blood droplets have been highly spattered. Measure less than 2 mm. Associated with high speed collisions and gunshot wounds. 50
51 High-velocity Impact Spatter 2009 Forensic Science Today 51
52 Medium-velocity Impact Spatter Most drops are broken into smaller droplets of 2 to 4 mm resulting from a force of greater than 25 feet/sec (terminal velocity) Most common types are: Projected blood blood will gush onto surface. Sharp edges and be on the direction on the surface in which blood has projected. Repetitive dripping pattern - blood dripping down into a pool of blood. Cast-off bloodstain pattern an already bloody object is swung through the air, casting off droplets of blood as it arcs through the air. Linear pattern 2009 Forensic Science Today 52
53 Medium-velocity Impact Spatter Projected Blood 53
54 24 Cast-off from Weapon Cast-off bloodstain pattern 2009 Forensic Science Today 54
55 25 Cast-off from Weapon ceiling 2009 Forensic Science Today 55
56 32 Cast-off & medium velocity spatter 2009 Forensic Science Today 56
57 2009 Forensic Science Today 57
58 Low-velocity Impact Spatter Most blood drops remain full-sized. Original drops are not broken into small drops. Drop diameter is 4mm or more Forensic Science Today 58
59 Point of Origin Point of origin can be determined by the mathematical relationship between the width and length of blood droplets. Calculate with two measurements Length and width of stain Impact Angle θ = sin -1 (length/width) Width Length 59
60 Shapes of Blood Drops How will the point of impact compare with the rest of a blood pattern? 60 Darker and wider than the rest of the drop.
61 Questions: What four properties of a crime scene can be identified from blood spatter? 1. Direction blood was traveling 2. Angle of impact 3. Point of origin 4. Manner of death Can blood spatter be used to identify a victim or suspect? Explain your answer. Yes. By using blood spatter patterns investigators can reconstruct the events of a crime and link victims/suspects to crime scenes Forensic Science Today 61
62 Presumptive Chemical Color Tests Phenolphthalein or Kastle-Meyer A cotton swab is moistened with saline solution and rubbed against the suspected bloodstain, and then a drop of (ph) plus a drop of hydrogen peroxide is added to the swab. If the stain contains blood, the swab will turn pink-to-red within 15 sec Forensic Science Today 62
63 What do bloodstain patterns tell us about the crime? Distance Speed Direction Position of victim Position of perpetrator Direction in which weapon may have been swinging Direction in which blood may have trailed after impact. Whether blood was wiped or smeared Time elapsed Movement of blood between focal points Sequence of events 63
64 Blood Stains on Victim s Jeans Sections removed & initialed for testing 2009 Forensic Science Today 64
65 Other Blood Patterns Not all bloodstains will fit neatly into either a dropped or impacted blood category. Some of the variations are: Blood Pools Contact-transfer bloodstain patterns Wipe/swipe patterns Blood imprint patterns 2009 Forensic Science Today 65
66 Pool of blood Splash Forensic Science Today 66
67 Contact-transfer bloodstain pattern 2009 Forensic Science Today 67
68 Wipe/swipe patterns Transfer from hair (hair-swipe) Forensic Science Today 68 70
69 Blood imprint patterns 2009 Forensic Science Today 69
70 52 Neck incisions (scene) Forensic Science Today 70
CHAPTER 8 PHYSICAL EVIDENCE: BLOOD
 CHAPTER 8 PHYSICAL EVIDENCE: BLOOD Is blood class evidence or individual evidence? What is the function of blood? What information can be determined from a sample of blood? Plasma Mainly water, also proteins,
CHAPTER 8 PHYSICAL EVIDENCE: BLOOD Is blood class evidence or individual evidence? What is the function of blood? What information can be determined from a sample of blood? Plasma Mainly water, also proteins,
Unit 5: Blood and Blood Stain Analysis
 Name Period Blood Composition and Function By the end of this chapter you will be able to: Explain the composition of blood Describe the function of blood cells Determine the blood type of a blood sample
Name Period Blood Composition and Function By the end of this chapter you will be able to: Explain the composition of blood Describe the function of blood cells Determine the blood type of a blood sample
Blood. Chapter 10. Kendall/Hunt Publishing Company 1
 Blood Students will learn: That an antibody and an antigen of different types will agglutinate, or clump, when mixed together. That the significance of the evidence depends on a characteristic s relative
Blood Students will learn: That an antibody and an antigen of different types will agglutinate, or clump, when mixed together. That the significance of the evidence depends on a characteristic s relative
Objectives. You will understand: Blood
 Objectives You will understand: That an antibody and an antigen of different types will agglutinate, or clump, when mixed together. That the significance of the evidence depends on a characteristic s relative
Objectives You will understand: That an antibody and an antigen of different types will agglutinate, or clump, when mixed together. That the significance of the evidence depends on a characteristic s relative
Chapter 10 Blood. William Shakespeare s Lady Macbeth, in Macbeth
 Blood Out damned spot! Out, I say Here s the smell of the blood still, All the perfumes of Arabia will not Sweeten this little hand. Oh, Oh, Oh! William Shakespeare s Lady Macbeth, in Macbeth Blood Students
Blood Out damned spot! Out, I say Here s the smell of the blood still, All the perfumes of Arabia will not Sweeten this little hand. Oh, Oh, Oh! William Shakespeare s Lady Macbeth, in Macbeth Blood Students
Unit 7: Blood/ Serology
 Unit 7: Blood/ Serology Forensic Serology the examination and analysis of body fluids including: saliva semen urine Blood 1950-1980 s, forensic serology = most important part of lab procedures (until DNA).
Unit 7: Blood/ Serology Forensic Serology the examination and analysis of body fluids including: saliva semen urine Blood 1950-1980 s, forensic serology = most important part of lab procedures (until DNA).
Unit 9b: Blood: (Spatter Analysis)
 Name: Per: Date: Unit 9b: Blood: (Spatter Analysis) By the end of the unit, you will be able to: Describe how blood flows through the body Conduct a blood spatter analysis Discuss the science behind various
Name: Per: Date: Unit 9b: Blood: (Spatter Analysis) By the end of the unit, you will be able to: Describe how blood flows through the body Conduct a blood spatter analysis Discuss the science behind various
FORENSIC SCIENCE" Serology!
 FORENSIC SCIENCE" Serology! 1! Serology!The study of body fluids including blood, semen, and saliva 2 I. What is Blood? A.!slightly basic solution made of Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, Platelets
FORENSIC SCIENCE" Serology! 1! Serology!The study of body fluids including blood, semen, and saliva 2 I. What is Blood? A.!slightly basic solution made of Red Blood Cells, White Blood Cells, Platelets
JEOPARDY. CCNA1 v3 Module 1. K. Martin
 v3 JEOPARDY K. Martin All About Router Blood Modes Vocabula WAN Blood WAN ry Encapsulation Stains Services Blood Spatter Router Types Router Random Basics of Tests Commands F i n a l J e o p a r d y 100
v3 JEOPARDY K. Martin All About Router Blood Modes Vocabula WAN Blood WAN ry Encapsulation Stains Services Blood Spatter Router Types Router Random Basics of Tests Commands F i n a l J e o p a r d y 100
What makes up our blood?
 Serology Ch. 12 What makes up our blood? RED BLOOD CELLS (Erythrocytes) The most abundant cells in our blood; they are produced in the bone marrow and contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen
Serology Ch. 12 What makes up our blood? RED BLOOD CELLS (Erythrocytes) The most abundant cells in our blood; they are produced in the bone marrow and contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen
Forensic Science. Forensic Serology
 Forensic Science Forensic Serology Composition of Blood Blood is a complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances Main Components: Erythrocytes = red blood cells (RBCs) Leukocytes
Forensic Science Forensic Serology Composition of Blood Blood is a complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances Main Components: Erythrocytes = red blood cells (RBCs) Leukocytes
Warning: Some material in this presentation and related videos may be considered graphic.
 Warning: Some material in this presentation and related videos may be considered graphic. This is How Hollywood Does Blood Spatter Analysis: The first step in analyzing blood: Making sure a substance
Warning: Some material in this presentation and related videos may be considered graphic. This is How Hollywood Does Blood Spatter Analysis: The first step in analyzing blood: Making sure a substance
FORENSIC SCIENCE Serology
 FORENSIC SCIENCE------ Serology Serology is: I. What is Blood? A. slightly basic solution made of 1. (55% of blood) fluid portion of the blood which contains: 2. Cells ( ) a. (Thrombocytes) -responsible
FORENSIC SCIENCE------ Serology Serology is: I. What is Blood? A. slightly basic solution made of 1. (55% of blood) fluid portion of the blood which contains: 2. Cells ( ) a. (Thrombocytes) -responsible
Blood Basics What makes up our blood? tissue infection wounds Karl Landsteiner
 Blood Basics What makes up our blood? The most abundant cells in our blood; they are produced in the bone marrow and contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen to our cells. They are part
Blood Basics What makes up our blood? The most abundant cells in our blood; they are produced in the bone marrow and contain a protein called hemoglobin that carries oxygen to our cells. They are part
Serology Unit Review. Match the following words on the left to their definitions on the right.
 Name: Serology Unit Review Match the following words on the left to their definitions on the right. 1. Erythrocytes 2. Leukocytes 3. Thrombocytes 4. Plasma 5. Antigen 6. Rh Factor 7. Antibody 8. Coagulate
Name: Serology Unit Review Match the following words on the left to their definitions on the right. 1. Erythrocytes 2. Leukocytes 3. Thrombocytes 4. Plasma 5. Antigen 6. Rh Factor 7. Antibody 8. Coagulate
Forensic Serology. Chapter 8
 Forensic Serology Chapter 8 Chronological History of Blood 2500 B.C. Egyptians bloodletting Cure disease 500 B.C. Greeks Vein v. Artery 175 A.D. Galen Circulatory paths 1628 Sir William Harvey Continuous
Forensic Serology Chapter 8 Chronological History of Blood 2500 B.C. Egyptians bloodletting Cure disease 500 B.C. Greeks Vein v. Artery 175 A.D. Galen Circulatory paths 1628 Sir William Harvey Continuous
Blood Characteristics
 Blood Characteristics Plasma is the fluid portion of the blood (55 percent). Cells (45 percent) Erythrocytes are red blood cells. They are responsible for oxygen distribution. Leukocytes are the white
Blood Characteristics Plasma is the fluid portion of the blood (55 percent). Cells (45 percent) Erythrocytes are red blood cells. They are responsible for oxygen distribution. Leukocytes are the white
The Composition of Blood
 Forensic Serology 1 The Composition of Blood A complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances. It mainly consists of Erythrocytes = red blood cells (rbc) Leukocytes = white blood
Forensic Serology 1 The Composition of Blood A complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances. It mainly consists of Erythrocytes = red blood cells (rbc) Leukocytes = white blood
 http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/units/basics/blood/types.cfm BLOOD FACTS blood - living tissue that carries oxygen & nutrients to all parts of the body carries carbon dioxide & other waste products back
http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/units/basics/blood/types.cfm BLOOD FACTS blood - living tissue that carries oxygen & nutrients to all parts of the body carries carbon dioxide & other waste products back
Name: Unit 5: Serology
 Name: Unit 5: Serology Objective 1: Identify the components and chemical properties of blood. List the components of blood. Identify the antigens and antibodies that determine the ABO blood types and the
Name: Unit 5: Serology Objective 1: Identify the components and chemical properties of blood. List the components of blood. Identify the antigens and antibodies that determine the ABO blood types and the
Blood History Karl Landsteiner first typed blood into A, B, AB, O Rh factor was discovered (positive or negative i.e.
 Blood Blood History 1901 Karl Landsteiner first typed blood into A, B, AB, O He was awarded the Nobel Prize for this 1937 Rh factor was discovered (positive or negative i.e. AB+, O- Blood Information At
Blood Blood History 1901 Karl Landsteiner first typed blood into A, B, AB, O He was awarded the Nobel Prize for this 1937 Rh factor was discovered (positive or negative i.e. AB+, O- Blood Information At
Forensic Serology. Forensic Science
 Forensic Serology Forensic Science The Composition of Blood A complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances It mainly consists of Erythrocytes = red blood cells (rbc) Leukocytes
Forensic Serology Forensic Science The Composition of Blood A complex mixture of cells, enzymes, proteins, and inorganic substances It mainly consists of Erythrocytes = red blood cells (rbc) Leukocytes
Blood History Karl Landsteiner first typed blood into A, B, AB, O Rh factor was discovered (positive or negative i.e.
 Blood Blood History 1901 Karl Landsteiner first typed blood into A, B, AB, O He was awarded the Nobel Prize for this 1937 Rh factor was discovered (positive or negative i.e. AB+, O- Blood Information At
Blood Blood History 1901 Karl Landsteiner first typed blood into A, B, AB, O He was awarded the Nobel Prize for this 1937 Rh factor was discovered (positive or negative i.e. AB+, O- Blood Information At
Lecture 1: Characteristics & Testing Of Blood
 Lecture 1: Characteristics & Testing Of Blood Blood Physiology: Composition of Blood Plasma (55% of the mix) is the fluid portion of the blood. Cells (45% of the mix ) Red Blood Cells are responsible for
Lecture 1: Characteristics & Testing Of Blood Blood Physiology: Composition of Blood Plasma (55% of the mix) is the fluid portion of the blood. Cells (45% of the mix ) Red Blood Cells are responsible for
Blood evidence. The examination of blood is divided into two parts. biological (serology) physical (spatter)
 Blood evidence Blood evidence The examination of blood is divided into two parts biological (serology) physical (spatter) What can blood evidence tell you? manner of blood loss position of victim and suspect
Blood evidence Blood evidence The examination of blood is divided into two parts biological (serology) physical (spatter) What can blood evidence tell you? manner of blood loss position of victim and suspect
T. Trimpe Forensic Science
 T. Trimpe 2006 http://sciencespot.net/ Forensic Science What makes up our blood? RED BLOOD CELLS (Erythrocytes) The most abundant cells in our blood; they are produced in the bone marrow and contain a
T. Trimpe 2006 http://sciencespot.net/ Forensic Science What makes up our blood? RED BLOOD CELLS (Erythrocytes) The most abundant cells in our blood; they are produced in the bone marrow and contain a
How much blood is in the human. About 5 liters. body?
 How much blood is in the human About 5 liters body? Why is blood red? Blood is red because it contains hemoglobin, an iron rich pigment. What makes up our blood? 7-8% of human body weight is from blood.
How much blood is in the human About 5 liters body? Why is blood red? Blood is red because it contains hemoglobin, an iron rich pigment. What makes up our blood? 7-8% of human body weight is from blood.
What makes up our blood?
 Forensic Science What do you know? Take out a sheet of paper. Label each line with a letter A to Z. Write a word or phrase that relates to blood that begins with that letter. What makes up our blood? RED
Forensic Science What do you know? Take out a sheet of paper. Label each line with a letter A to Z. Write a word or phrase that relates to blood that begins with that letter. What makes up our blood? RED
12. Describe the Luminol Test for the presence of blood:.? Instead a color reaction: it is a reaction to create LIGHT called Luminescence.
 Name Date Points Forensic Science Midterm Review 1.What is Forensic Science? A. Forensics- is the direct application of scientific knowledge and techniques to matters of law. 2.What is Locard Exchange
Name Date Points Forensic Science Midterm Review 1.What is Forensic Science? A. Forensics- is the direct application of scientific knowledge and techniques to matters of law. 2.What is Locard Exchange
Go to slide 11
 11-29-17 Go to slide 11 Blood Typing & Spatter Come in and get your notebooks out. We have notes today! Forensic serology is the detection, classification and study of various bodily fluids such as blood,
11-29-17 Go to slide 11 Blood Typing & Spatter Come in and get your notebooks out. We have notes today! Forensic serology is the detection, classification and study of various bodily fluids such as blood,
Mr. & Mrs. Smith s Blood Tests
 Mr. & Mrs. Smith s Tests Mr. Smith Mrs. Smith Type A Test Type B Test Mr. & Mrs. Jones Tests Mr. Jones Mrs. Jones Type A Test Type B Test Child 1 & 2 s Tests Child 1 Child 2 Type A Test Type B Test Samples
Mr. & Mrs. Smith s Tests Mr. Smith Mrs. Smith Type A Test Type B Test Mr. & Mrs. Jones Tests Mr. Jones Mrs. Jones Type A Test Type B Test Child 1 & 2 s Tests Child 1 Child 2 Type A Test Type B Test Samples
Serology: ABO and Rh (D) blood group system
 Serology: ABO and Rh (D) blood group system Introduction Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic
Serology: ABO and Rh (D) blood group system Introduction Blood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic
DUE 2/13/17. HOMEWORK: Student Weekly Grade Tracking #24. What is Inheritance? Video Clip. What is Mutation? Video Clip. Admit Ticket.
 Admit Ticket What is Inheritance? Exit Ticket What is Mutation? DUE 2/13/17 HOMEWORK: Student Weekly Grade Tracking #24 http://www.powerpointhintergrund.com/uploads/newyearpptbackground8.jpg DUE 2/13/17
Admit Ticket What is Inheritance? Exit Ticket What is Mutation? DUE 2/13/17 HOMEWORK: Student Weekly Grade Tracking #24 http://www.powerpointhintergrund.com/uploads/newyearpptbackground8.jpg DUE 2/13/17
The fluid medium (blood) is a highly specialized connective tissue that consists of various blood cells (formed elements) suspended in a fluid matrix
 Blood In Detail The fluid medium (blood) is a highly specialized connective tissue that consists of various blood cells (formed elements) suspended in a fluid matrix (blood plasma). The formed elements
Blood In Detail The fluid medium (blood) is a highly specialized connective tissue that consists of various blood cells (formed elements) suspended in a fluid matrix (blood plasma). The formed elements
Blood CHAPTER. Lesson Objectives. Lesson Vocabulary. Introduction. Structure and Functions of Blood. Chapter 1. Blood
 www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Blood CHAPTER 1 Blood Lesson Objectives Describe blood components, and list functions of the blood. Define blood type, and explain its medical significance. Identify some diseases
www.ck12.org Chapter 1. Blood CHAPTER 1 Blood Lesson Objectives Describe blood components, and list functions of the blood. Define blood type, and explain its medical significance. Identify some diseases
Forensics Final Review. 1. Fill in the following table about search methods. Search Method Picture When it is Used Strip or Line Search
 Name: Forensics Final Review Unit 1-Scientific Method, Observation, and Eyewitness Reporting 1. Fill in the following table about search methods. Search Method Picture When it is Used Strip or Line Search
Name: Forensics Final Review Unit 1-Scientific Method, Observation, and Eyewitness Reporting 1. Fill in the following table about search methods. Search Method Picture When it is Used Strip or Line Search
FORENSIC SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW
 Introduction to Forensic Science 1) The Crime Scene Investigative team can be divided into a. first responders and field investigative. b. crime lab team and law enforcement. c. first responders and crime
Introduction to Forensic Science 1) The Crime Scene Investigative team can be divided into a. first responders and field investigative. b. crime lab team and law enforcement. c. first responders and crime
Forensic Science Final Exam Review
 Forensic Science Final Exam Review Human Identity (Fingerprints, Forensic Anthropology, DNA) 1.Who developed the system known as anthropometry? 2.Who postulated the exchange of evidence principle? 3.In
Forensic Science Final Exam Review Human Identity (Fingerprints, Forensic Anthropology, DNA) 1.Who developed the system known as anthropometry? 2.Who postulated the exchange of evidence principle? 3.In
Blood and Blood Spatter
 CHAPTER 1 2 3 4 CHAPTER Blood and Blood Spatter 8 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 BLOOD PAINTS A PICTURE Concerned neighbors called the police after hearing a woman screaming in the upstairs apartment.
CHAPTER 1 2 3 4 CHAPTER Blood and Blood Spatter 8 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 BLOOD PAINTS A PICTURE Concerned neighbors called the police after hearing a woman screaming in the upstairs apartment.
DAY ONE BLOOD. What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made?
 BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
BLOOD AND THE HEART DAY ONE BLOOD What do you know about blood? What does it do? What is it made of? Where is it made? BLOOD Transports gases Brings in oxygen Removes carbon dioxide MAIN FUNCTIONS OF
!!!!!Blood ---Ch 14. Whole blood consists of a plasma and cellular component.
 !!!!!Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various
!!!!!Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
Biological Evidence: Goals
 Biological Evidence: Goals 1. Identify a stain/tissue 2. Identify species of origin - is it human? 3. Individualize it i.e. get a DNA profile? 4. Compare it to a known sample Serology and DNA Profiling
Biological Evidence: Goals 1. Identify a stain/tissue 2. Identify species of origin - is it human? 3. Individualize it i.e. get a DNA profile? 4. Compare it to a known sample Serology and DNA Profiling
Name: Per: Date: Unit 9a: Blood (Composition/Types/Inheritance)
 Unit 9a: Blood: (Composition/Types/Inheritance) By the end of the unit, you will be able to: Explain the components of blood Describe the function of blood cells Describe how to determine the blood type
Unit 9a: Blood: (Composition/Types/Inheritance) By the end of the unit, you will be able to: Explain the components of blood Describe the function of blood cells Describe how to determine the blood type
Chapter 12. Blood Spatter. Broughton High School. Forensic Science Edition I Master Work Book 2017 Sherlock Holmes Style Edwin P. Davis, M.Ed.
 Page 1 of 44 Chapter 12 Blood Spatter The study of Blood and Blood Spatter Broughton High School Objectives By the end of this chapter you will be able to Explain the composition of blood. Describe the
Page 1 of 44 Chapter 12 Blood Spatter The study of Blood and Blood Spatter Broughton High School Objectives By the end of this chapter you will be able to Explain the composition of blood. Describe the
HS FORENSICS CURRICULUM
 HS FORENSICS CURRICULUM Born On Date: August 2018 216 S. Main Street Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 1 Page Content Area: Forensics Grade(s) 10-12 Unit Plan Title: Observations Lab Safety, Witnesses, Innocence
HS FORENSICS CURRICULUM Born On Date: August 2018 216 S. Main Street Cape May Court House, NJ 08210 1 Page Content Area: Forensics Grade(s) 10-12 Unit Plan Title: Observations Lab Safety, Witnesses, Innocence
Co-dominance. Dr.Shivani Gupta, Department of Zoology, PGGCG-11, Chandigarh
 Co-dominance Dr.Shivani Gupta, Department of Zoology, PGGCG-11, Chandigarh Blood groups and Rhesus factor History of Blood Groups and Blood Transfusions Experiments with blood transfusions have been carried
Co-dominance Dr.Shivani Gupta, Department of Zoology, PGGCG-11, Chandigarh Blood groups and Rhesus factor History of Blood Groups and Blood Transfusions Experiments with blood transfusions have been carried
Forensic Science Final Review
 Forensic Science Final Review Name: Instructions: Answer the following questions on YOUR OWN PAPER! Remember that it is important to do your best job on this Study Guide because your Final Exam is worth
Forensic Science Final Review Name: Instructions: Answer the following questions on YOUR OWN PAPER! Remember that it is important to do your best job on this Study Guide because your Final Exam is worth
Blood ---Ch 14. Whole blood consists of a plasma and cellular component.
 Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various parts
Blood ---Ch 14 Circulating blood provides a vital function for survival: transports hormones to their destination, waste products to the kidneys for removal and transports ions / chemicals to various parts
Forensics Blood Typing
 The Biotechnology Education Company Forensics Blood Typing EDVO-Kit 191 See Page 3 for storage instructions. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to some of the
The Biotechnology Education Company Forensics Blood Typing EDVO-Kit 191 See Page 3 for storage instructions. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE: The objective of this experiment is to introduce students to some of the
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes).
 Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
Bellwork Define: hemostasis anticoagulation hemophilia (Then write the underline portion of the two state standards in your notes). A&P Standards 31) Identify the liquid and cellular components of blood
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Blood: A Fluid Tissue
 11.2 Blood: A Fluid Tissue Humans have long recognized the importance of blood, even without understanding the true nature of its role in the body. Modern science has shown that blood is fundamental to
11.2 Blood: A Fluid Tissue Humans have long recognized the importance of blood, even without understanding the true nature of its role in the body. Modern science has shown that blood is fundamental to
14-2: Blood and Lymph. 7 th Grade Life Science
 7 th Grade Life Science Blood Blood has four components: 1. Plasma 2. Red blood cells 3. White blood cells 4. Platelets Plasma Plasma is the liquid part of blood 90% of which is water. The other 10% is
7 th Grade Life Science Blood Blood has four components: 1. Plasma 2. Red blood cells 3. White blood cells 4. Platelets Plasma Plasma is the liquid part of blood 90% of which is water. The other 10% is
The Reliability of Current Methods of Sequencing
 Terry L Laber, et al. The Reliability of Current Methods of Sequencing Bloodstain., 214, 4(1): 35-39 Received 3 June 214 Received in revised form 3 August 214 Accepted 11 October 214 Available online 28
Terry L Laber, et al. The Reliability of Current Methods of Sequencing Bloodstain., 214, 4(1): 35-39 Received 3 June 214 Received in revised form 3 August 214 Accepted 11 October 214 Available online 28
BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM. Chapter 11
 BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 11 BLOOD 5 L of blood 55% fluid 45% blood cells Blood cells produced in bone marrow Hematocrit-percentage of red blood cells PLASMA Plasma-fluid portion of blood(90%
BLOOD AND THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 11 BLOOD 5 L of blood 55% fluid 45% blood cells Blood cells produced in bone marrow Hematocrit-percentage of red blood cells PLASMA Plasma-fluid portion of blood(90%
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
#2 - Hematology I Blood Typing
 #2 - Blood Typing Objectives: Learn the theory behind blood typing Be able to perform simulated blood typing and analysis Understand the theory behind blood transfusions (donors and recipients) Observe
#2 - Blood Typing Objectives: Learn the theory behind blood typing Be able to perform simulated blood typing and analysis Understand the theory behind blood transfusions (donors and recipients) Observe
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
What is Locard s Exchange Principle and how is this principle important to forensic science?
 What is the definition of forensic science? The application of science and technology to those criminal and civil laws that are enforced by police agencies in a criminal justice system. What are the major
What is the definition of forensic science? The application of science and technology to those criminal and civil laws that are enforced by police agencies in a criminal justice system. What are the major
Section 12.1 Your Cardiovascular System
 Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
Objectives Describe the main functions of the cardiovascular system. Trace the pathway of blood through the heart. Identify three types of blood vessels and the four components of blood. Slide 1 of 31
DNA Fingerprinting & Forensic Analysis
 DNA Fingerprinting & Forensic Analysis DNA Fingerprint & Genetic Profiling DNA fragments show unique patterns from one person to the next. A technique used by scientists to distinguish between individuals
DNA Fingerprinting & Forensic Analysis DNA Fingerprint & Genetic Profiling DNA fragments show unique patterns from one person to the next. A technique used by scientists to distinguish between individuals
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Introduction The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, is an organ system that allows blood to flow to all the cells in
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration Introduction The circulatory system, also called the cardiovascular system, is an organ system that allows blood to flow to all the cells in
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies
 Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting Administrative and Clinical Competencies THIRD EDITION CHAPTER 27 The Cardiovascular System Lesson 2: Composition and Function of Lesson Objectives Upon completion
TRAVELING FORENSIC EDUCATION PROGRAM
 TRAVELING FORENSIC EDUCATION PROGRAM INDEX -Program Overview Page 3 -Forensics Lab Total Experience Page 4 -Crime to Courtroom Workshop Page 4 -Impressions Workshop Page 5 -Blood & DNA Workshop Page 5
TRAVELING FORENSIC EDUCATION PROGRAM INDEX -Program Overview Page 3 -Forensics Lab Total Experience Page 4 -Crime to Courtroom Workshop Page 4 -Impressions Workshop Page 5 -Blood & DNA Workshop Page 5
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Plasma Red blood cells White blood cells. Leucocytes KEYWORDS Phagocytes
 Blood Plasma Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets Lymphocytes Leucocytes KEYWORDS Phagocytes Monocytes Erythocytes ABO groups Haemoglobin Blood components: Components of blood: Plasma Red blood
Blood Plasma Red blood cells White blood cells Platelets Lymphocytes Leucocytes KEYWORDS Phagocytes Monocytes Erythocytes ABO groups Haemoglobin Blood components: Components of blood: Plasma Red blood
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
STATION 1 - Types of Blood Vessels
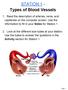 STATION 1 - Types of Blood Vessels 1. Read the description of arteries, veins, and capillaries on the computer screen. Use the information to fill in your Notes for Station 1 2. Look at the different size
STATION 1 - Types of Blood Vessels 1. Read the description of arteries, veins, and capillaries on the computer screen. Use the information to fill in your Notes for Station 1 2. Look at the different size
Chapter 21 Outline. General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements
 Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
Chapter 21 Outline General Composition and Functions of Blood Blood Plasma Formed Elements in the Blood Hemopoiesis: Production of Formed Elements Introduction Blood serves many functions. Some examples
Principles of Biomedical Sciences Semester 1 Review
 Unit 1 The Mystery Lesson 1.1: Investigating the Scene 1. Why is it important to be careful and methodical when investigating a crime scene? 2. What are the main parts in the experimental design process?
Unit 1 The Mystery Lesson 1.1: Investigating the Scene 1. Why is it important to be careful and methodical when investigating a crime scene? 2. What are the main parts in the experimental design process?
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY
 BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
BLOOD RUNS THROUGH YOUR BODY WORKSHEET A Your heart and blood vessels make up your blood system. At the centre of your blood system is your heart. Its job is to pump the blood around your body. The rest
A closer look at BLOOD Lab
 A closer look at BLOOD Lab Name Synthetic by Part 1 a drop of blood White Cell Plasma Platelet White Cell Background: All blood will contain Red Cells (RBC), White Cells (WBC), and Platelets. The number
A closer look at BLOOD Lab Name Synthetic by Part 1 a drop of blood White Cell Plasma Platelet White Cell Background: All blood will contain Red Cells (RBC), White Cells (WBC), and Platelets. The number
4/5/17. Blood. Blood. Outline. Blood: An Overview. Functions of Blood
 Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Outline Blood Biol 105 Chapter 11 I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood cells
Procedure for Blood Analysis. 1.0 Purpose - This procedure specifies the methods for performing blood analysis in forensic casework.
 Procedure for Blood Analysis 1.0 Purpose - This procedure specifies the methods for performing blood analysis in forensic casework. 2.0 Scope - This procedure applies to those Forensic Scientists who have
Procedure for Blood Analysis 1.0 Purpose - This procedure specifies the methods for performing blood analysis in forensic casework. 2.0 Scope - This procedure applies to those Forensic Scientists who have
Blood ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
10 Blood PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Blood The only fluid tissue in the human
Blood. Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11
 Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
Blood Biol 105 Lecture 14 Chapter 11 Outline I. Overview of blood II. Functions of blood III. Composition of blood IV. Composition of plasma V. Composition of formed elements VI. Platelets VII. White blood
LEANN FLETCHER Michael Fletcher was in the bathroom when he heard the gunshot. Fletcher ran out of the bathroom and found his wife, Leann, face down
 Body Systems LEANN FLETCHER Michael Fletcher was in the bathroom when he heard the gunshot. Fletcher ran out of the bathroom and found his wife, Leann, face down in a pool of blood on their bedroom floor.
Body Systems LEANN FLETCHER Michael Fletcher was in the bathroom when he heard the gunshot. Fletcher ran out of the bathroom and found his wife, Leann, face down in a pool of blood on their bedroom floor.
Components of the Blood
 Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Hemoglobin is responsible for distributing oxygen, and to a lesser extent, carbon dioxide, throughout the circulatory systems of humans, vertebrates, and many invertebrates. The blood
Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Hemoglobin is responsible for distributing oxygen, and to a lesser extent, carbon dioxide, throughout the circulatory systems of humans, vertebrates, and many invertebrates. The blood
I B I B or I B i. Rule: Match the antigen of the donor with the antibodies of the recipient. Blood Type Can Donate To Can Receive From A A, AB A, O
 Blood Typing Lab Key: I A = type A antigen I B = type B Antigen i = no antigen ABO BLOOD GROUPS Blood Type A B AB O Genotype I A I A or I A i I B I B or I B i I A I B ii Type A Type B Types A & B none
Blood Typing Lab Key: I A = type A antigen I B = type B Antigen i = no antigen ABO BLOOD GROUPS Blood Type A B AB O Genotype I A I A or I A i I B I B or I B i I A I B ii Type A Type B Types A & B none
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS. 1. The microscope can be used as a tool for investigation.
 Disease Fighters 46 40- to 2 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW I N V E S T I O N I G AT SUMMARY Students investigate how the human immune system helps fight invading organisms. Students view microscope
Disease Fighters 46 40- to 2 50-minute session ACTIVITY OVERVIEW I N V E S T I O N I G AT SUMMARY Students investigate how the human immune system helps fight invading organisms. Students view microscope
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity
 Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Unit Seven Blood and Immunity I. Introduction A. Definition Blood is a sticky fluid that is heavier and thicker than water. Blood is a type of, whose cells and suspended in a liquid intercellular material.
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 19 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Functions and Properties of Blood Blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells surrounded by
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 19 The Cardiovascular System: The Blood Functions and Properties of Blood Blood is a liquid connective tissue consisting of cells surrounded by
Simulated ABO & Rh Bood Typing Lab Activity Student Study Guide
 TM Simulated ABO & Rh Bood Typing Lab Activity Student Study Guide BACKGROUND Agglutinogens (Antigens): Agglutinogens are substances found on the surface of erythrocytes. Agglutinins (Antibodies): Agglutinins
TM Simulated ABO & Rh Bood Typing Lab Activity Student Study Guide BACKGROUND Agglutinogens (Antigens): Agglutinogens are substances found on the surface of erythrocytes. Agglutinins (Antibodies): Agglutinins
Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum
 Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum Course Title: Science Length of Course: 36 weeks Week Number Week 1 Chapter/ Topic Introduction/ Syllabus Lab Safety procedures, review and test COS Biology COS 1. Select
Pacing Guide for 7-12 Curriculum Course Title: Science Length of Course: 36 weeks Week Number Week 1 Chapter/ Topic Introduction/ Syllabus Lab Safety procedures, review and test COS Biology COS 1. Select
It s Totally Tubular, Dude!
 It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
It s Totally Tubular, Dude! Objective: To learn the structure and function of the Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Bell Work: For the following, place the items in order from most simple to most complex:
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
temperature 38 o C (100.4 o F) The temperature of blood is slightly higher than the normal body temperature of 37 o C (98.6 o F).
 1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
1 Chapter 1 Blood Definition -Blood is a type of connective tissue that consists of cells surrounded by a fluid extracellular matrix. -Blood, blood vessels, and the heart collectively form the cardiovascular
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood
 Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
Adapted form Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 20 The Cardiovascular System: Blood Introduction The cardiovascular system functions as a system to transport numerous substances throughout the body
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Worksheet NAME Section A: Blood Basics http://www.psbc.org/hematology/01_index.htm Although blood appears to be red liquid it is actually composed of yellowish liquid called plasma
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Forensic Science Final Exam Study Guide. 2. What is an infraction? What would some examples of an infraction be?
 Name: Chapter 1 History of Forensics 1. What is the definition of forensic science? Forensic Science Final Exam Study Guide 2. What is an infraction? What would some examples of an infraction be? 3. What
Name: Chapter 1 History of Forensics 1. What is the definition of forensic science? Forensic Science Final Exam Study Guide 2. What is an infraction? What would some examples of an infraction be? 3. What
Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions. Plasma
 Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions 19-1 Plasma Liquid part of blood. Colloid: liquid containing suspended substances that don t settle out of solution 91% water. Remainder proteins, ions,
Chapter 19 Cardiovascular System Blood: Functions 19-1 Plasma Liquid part of blood. Colloid: liquid containing suspended substances that don t settle out of solution 91% water. Remainder proteins, ions,
It is essential to have the victim(s) examined by a medical
 Sexual Offenses Chapter 7 It is essential to have the victim(s) examined by a medical professional as soon as possible after the assault and before the affected areas (pubic area, vagina, rectum, etc.)
Sexual Offenses Chapter 7 It is essential to have the victim(s) examined by a medical professional as soon as possible after the assault and before the affected areas (pubic area, vagina, rectum, etc.)
Traits of Simple Inheritance. Polymorphisms in Human Blood
 1 Traits of Simple Inheritance 2 Traits of Simple Inheritance Traits of monogenic control (as opposed to polygenic control) 3 Polymorphisms Discrete genetic traits in which there are at least two alleles
1 Traits of Simple Inheritance 2 Traits of Simple Inheritance Traits of monogenic control (as opposed to polygenic control) 3 Polymorphisms Discrete genetic traits in which there are at least two alleles
Name Class Date. Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank.
 Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
Skills Worksheet Chapter Review USING KEY TERMS Complete each of the following sentences by choosing the correct term from the word bank. red blood cells veins white blood cells arteries lymphatic system
