Isolation of DOM by adsorption onto hydrophobic resins
|
|
|
- Beryl Richard
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Isolation of DOM by adsorption onto hydrophobic resins Seawater (filtered; ph = 2) 0.1N NaOH or 1N NH 4 OH/MeOH (XAD = polystyrene) 5 10% of DOC sample Isola3on is chemically selec3ve based on affinity for resin. XAD selects for hydrophobic organic ma@er with an old radiocarbon age. Slide 5.1
2 Cross or tangential flow filtration, Ultra- or nanofiltration Separation based on size 1 nm 1 kd Selects for HMW fraction about 30-35% TOC (now up to 80% using electrically assisted UF) C/N = C/P = 150 to > 500 (f(z)) Membrane effects what is collected Slide 5.2
3 DOC sampling filter (1 nm) sample concentrate (> 1000 MW) pump filtrate (< 1000 MW) Slide 5.3
4 Slide 5.4 Final product 30% of total DOC C/N = 15 +/ 2 C/P =
5 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy (NMR) Can be tuned to different Nuclei of interest (C,N,P ). Gives information on functional groups which, combined with a knowledge of biochemicals can be used to deduce composition and origin. Internally quantitative. Slide 5.5
6 Slide 5.6
7 13 C Nuclear Magne3c Resonance Spectrum of high molecular weight dissolved organic ma@er (C/N = 15) Frequency Abundance Slide 5.7
8 13 C Nuclear Magne3c Resonance Spectrum of high molecular weight dissolved organic ma@er (C/N = 15) COOH CONH (10%) Slide 5.8
9 13 C Nuclear Magne3c Resonance Spectrum of high molecular weight dissolved organic ma@er (C/N = 15) OCO (12%) COOH CONH (10%) Slide 5.9
10 13 C Nuclear Magne3c Resonance Spectrum of high molecular weight dissolved organic ma@er (C/N = 15) OCO (12%) HCOH (55%) COOH CONH (10%) Slide 5.10
11 13 C Nuclear Magne3c Resonance Spectrum of high molecular weight dissolved organic ma@er (C/N = 15) OCO (12%) HCOH HCNH (55%) COOH CONH (10%) CH x (10%) Slide 5.11
12 Proximate analysis of algal cells Chlorophyceae Protein Carbohydrate Lipid Ash (green algae) Tetraselmis maculata (24) Dunaliela salina ( 8) Chrysophyceae (golden brown algae) Monochrysis lutheri (6) Syracosphaera carterae (37) Bacillariophyceae (brown algae, diatoms) Chaetoceros sp (28) Skeletonema costatum (39) Coscinodiscus sp (57) Phaeodactylum tricornutum ( 8) Dynophyceae (dinoflagellates) Amphidinium carteri (14) Exuriella sp (8) Average Most POM is protein, and this is probably a large fraction of reactive DOM Dissolved free amino acids have been measured in seawater at 10 s nm Slide 5.12
13 What are the biochemical ingredients of HMWDOM? From our knowledge of cell biochemicals C/N.COOH:OCO:HCOH:CH x HMWDOM C/N = 15 CHx:HCOH:OCO:COOH =1:5.5:1.2:1 Proteins C/N = 4, CH x (O):CON = 3:1 Carbohydrates C maybe N OCO:HCOH = 1:5 Lipids C only CH x :COOH = 2 18 CH x :COH = 2 30 unsolved mysteries #1 Carbohydrates are thought to be easily degraded by microbes, so why is the ocean filled with carbohydrate? Slide 5.13
14 13 CNMR of plankton tows 13 CNMR of HMWDOM Sargasso Sea (surface) Hedges et al GCA 2001 Chemical shid (ppm) Slide 5.14
15 13 CNMR spectra of HMWDOM Sargasso Sea 3 m 3 m North Pacific Subtropical Gyre unsolved mysteries #2 if the source of DOC is microorganisms and the dominant microbes change with location, why is the ocean filled with the same type of carbohydrate everywhere? Slide 5.15
16 HMWDOM in different aqua3c environments NPSG Andrews Creek m in Rocky Mountains Na3onal Park Great Salt Lake Diane McKnight et al, BGC 1997; Jim Leenher, BGC 2004 Slide 5.16
17 HMWDOM in the deep sea Sargasso Sea NPSG 3 m 3 m 2500 m 1800 m Slide 5.17
18 Spectral and chemical analyses of HMWDOC Carbohydrate 70-90% of surface water HMWDOC 13 CNMR Acid hydrolysis followed by Monosaccharide analyses yields 7 major neutral sugars that represent 10-20% of HMWDOC in surface water Acid hydrolysis Slide 5.18
19 Relative abundance of sugars in HMWDOC A good number of HMWDOM samples have been analyzed after hydrolysis for simple sugars or monosaccharides. In every case, hydrolysis yields seven major neutral sugars. Samples include HMWDOM from the North Pacific, North and South Atlantic, near shore, estuary, and open ocean water; surface and deep. The mixture of neutral sugars found in HMW- DOM is not typical of polysaccharides, which tend to have a narrower range of sugars, and a few dominant sugars. HMWDOM has a large number of sugars in about equal amounts. The small range in relative % composition suggests that these sugars are linked into a common macromolecular structure, and is not a mixture that can vary spatially and temporally. Slide 5.19
20 Sequestration of DOC in the deep sea New DOC Δ 14 C=DIC POC Modern 14 C Old DOC Δ 14 C = DOC (deep) Deep water forma3on Older 14 C Slide 5.20
21 Radiocarbon (Δ14C)analyses of HMWDOC carbohydrates in surface water Sample Hawaii NPSG DIC 72+7 (n=4) 89+7 * Glucose 47, Galactose Mannose Xylose 52, Arabinose 63 ND Fucose 49, Rhamnose 40, Average sugar *data from Ellen Druffel Slide 5.21
22 Enrichment of Δ 14 C in deep sea HMWDOM carbohydrate DICΔ 14 C( ) HMWDOCΔ 14 C sugars Δ 14 C Surface m m Slide 5.22
23 Hydrophobic (XAD collected) DOM in North Pacific Ocean water (ph = 2) 0.1N NaOH or 1N NH 4 OH/MeOH COOH HCOH CH x sample Slide 5.23
24 A comparison of 13 CNMR spectra of XAD and ultrafiltra3on collected DOM in surface (top) and 4200 m (bo@om) Pacific seawater XAD DOM HMWDOM Slide 5.24
25 The composition of humic substances in the Amazon River and North Pacific Ocean Slide 5.25
26 Dissolved Organic Nitrogen Total Dissolved N (TDN) = DON+DIN (where DIN = ammonia + nitrate + nitrite) Marine Inventories of N Slide 5.26
27 Soluble reac3ve phosphorus (SRP), dissolved organic phosphorus (DOP) and DOP as % total dissolved phosphorus (DOP/DOP+SRP) at Sta3on ALOHA Slide 5.27
28 Temporal varia3on in DON and DOP at sta3on ALOHA Slide 5.28
29 DIN vs DIP, and TDN vs TDP at sta3on ALOHA Slide 5.29
30 Slide 5.30
31 Torre-Valdes et al. GBC 2009 Slide 5.31
32 What else is in HMWDOM? 15 N NMR Amide N proteins C N O C N O Amino N amino sugars CH 3 C N H = O CH 3 C N H = O McCarthy et al, 1997; Aluwihare et al Slide 5.32
33 C/N = 15, if all N is amide, then CON should be about 7% of the total C, which it is. proteins C N C N CONH or COOH N = 1 O O amino sugars CH 3 C N H = O CH 3 C N H = O Slide 5.33
34 15 N NMR Amide N What else is in HMWDOM? 1 H NMR HCOH NR O=CCH 3 or OR O=CCH 3 CH 3 Amino N ppm McCarthy et al, 1997; Aluwihare et al Slide 5.34
35 Is a large frac3on of HMWDOC and HMWDON from amino sugars? 15 N NMR 1 H NMR (amide N) CH 3 CONH CH 3 CONH acid (amine N) (amide N) HNH + HNH CH 3 COOH Slide 5.35
36 Composition of HMWDOP Organic phosphorus nomenclature phosphonate (ortho) phosphate phosphate monoester polyphosphate phosphate mono- & di-esters phosphonate Kolowith et al., L&O 2001 Slide 5.36
37 What is the degradation stoichiometry of recalcitrant DOC? DOC (µm) C/N = DON (µm) Hopkinson and Vallino 2005 (Nature) Slide 5.37
38 Composi3on, reac3vity, flux and distribu3on of DOM Non reac3ve DOM Semi reac3ve DOM Very reac3ve DOM HO O CH 3 CH 2 CH 2 Aliphatic or Humic substances Concentration 40 µm Inventory = 640 GT C Δ 14 C= -400 to -600 Annual flux = 0.1 GTC Biopolymers (polysaccharides, proteins)* Concentration 0-40 µm Inventory = GT C Δ 14 C= modern (DIC) Annual flux = 10 s GT C? * = 80% of cell C, N C N O C N O C N O Simple biomolecules (amino acids, sugars)* Concentration 1-2 µm Inventory = GT C Δ 14 C= modern (DIC) Annual flux = 10 s GT C? * = 10-20% of cell C, N Slide 5.38
39 Summary DOM is isolated from seawater using either adsorption onto hydrophophic resin or ultrafiltration (molecular filtration). Adsorptive techniques selects DOM that has a high affinity for the adsorption media, while ultrafiltration relies on the hydrodynamic diameter of the organic matter. Adsorptive techniques select for DOM that is depleted in radiocarbon, while ultrafiltration selects for HMWDOM that is enriched in radiocarbon. NMR analysis of HMWDOM shows it to have a remarkably uniform distribution of functional groups that is conserved across ocean basins. Carbohydrates are the dominant biochemical class present in HMWDOM. Chemical hydrolysis Only recovers 10-20% of carbohydrate as neutral sugars, characterized by seven major neutral sugars (rhamnose, fucose, arabinose, mannose, glucose, xylose, galactose). These data suggest that the HMWDOM is a biopolymer with a specific composition. The old, hydrophobic fraction of DOM is relatively more enriched in aliphatic carbon and highly oxidized, with a high COOH/CHx ratio. Dissolved organic nitrogen (DON) and phosphorus (DOP) have high concentrations in surface water, and lower concentrations at depth. HMWDON occurs primarily as amide-n, linked through N-acyl amino sugars, while HMWDOP occurs primarily phosphate esters and some phosphonate. Slide 5.39
Biogeochemical cycling of dissolved organic C and nutrients. Figure by MIT OCW.
 Biogeochemical cycling of dissolved organic C and nutrients Figure by MIT OCW. The profile of [DOC] With depth in the ocean 1. Measured by HTCO or wet chemical oxidation 2. Surface values are 60-80µM C
Biogeochemical cycling of dissolved organic C and nutrients Figure by MIT OCW. The profile of [DOC] With depth in the ocean 1. Measured by HTCO or wet chemical oxidation 2. Surface values are 60-80µM C
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea
 Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Dissolved organic matter dynamics in the sea DOC distributions in the Atlantic Marine Microplankton Ecology OCN 626 Matthew Church Figures from Dennis Hansell DOC distributions in the Pacific Basin scale
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
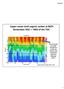 Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Upper ocean total organic carbon at BATS Remember DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
In steady state, new production = carbon export
 In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
In steady state, new production = carbon export Where does primary production go? Export Bacteria Dissolved organic matter Grazing What other components of the biological pump are important? The majority
Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC.
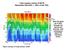 Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Total organic carbon at BATS Remember that DOC = ~98% of the TOC. Note the build up in DOC through the spring and summer, with subsequent export the following winter. Figure courtesy of Craig Carlson,
Guixue.Song 1, Julieta.Ferreira 1, Corinna.Byrne 1, Deirdre.Fay 2, Michael.H.B.Hayes 1
 Guixue.Song 1, Julieta.Ferreira 1, Corinna.Byrne 1, Deirdre.Fay 2, Michael.H.B.Hayes 1 1 Chemical & Environmental Sciences Department, University of Limerick 2 Johnstown Castle Research Centre, Teagasc
Guixue.Song 1, Julieta.Ferreira 1, Corinna.Byrne 1, Deirdre.Fay 2, Michael.H.B.Hayes 1 1 Chemical & Environmental Sciences Department, University of Limerick 2 Johnstown Castle Research Centre, Teagasc
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Isolation of NOM Lecture #3 A USGS Preparative-based method Leenheer, J.A. and Noyes, T.I. (1984) A Filtration and Column- Adsorption System
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Isolation of NOM Lecture #3 A USGS Preparative-based method Leenheer, J.A. and Noyes, T.I. (1984) A Filtration and Column- Adsorption System
Nature and dynamics of phosphorus-containing components of marine dissolved and particulate organic matter
 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70 (2006) 5868 5882 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca Nature and dynamics of phosphorus-containing components of marine dissolved and particulate organic matter Poulomi Sannigrahi
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 70 (2006) 5868 5882 www.elsevier.com/locate/gca Nature and dynamics of phosphorus-containing components of marine dissolved and particulate organic matter Poulomi Sannigrahi
Supplementary Figure 1: UV-Vis absorption (a) and excitation emission matrix (EEM) (b) spectra of the SN medium (Cyanosite ) used to grow
 Supplementary Figure 1: UV-Vis absorption (a) and excitation emission matrix (EEM) (b) spectra of the SN medium (Cyanosite ) used to grow Synechococcus cultures. Note: The same scale used in Figure 1 was
Supplementary Figure 1: UV-Vis absorption (a) and excitation emission matrix (EEM) (b) spectra of the SN medium (Cyanosite ) used to grow Synechococcus cultures. Note: The same scale used in Figure 1 was
Solid-phase extraction of dissolved organic matter (SPE-DOM) from river, estuarine and open ocean waters
 Solid-phase extraction of dissolved organic matter (SPE-DOM) from river, estuarine and open ocean waters Gerhard Kattner 1, Thorsten Dittmar 2, Boris Koch 1, and Norbert Hertkorn 3 1 Alfred Wegener Institute
Solid-phase extraction of dissolved organic matter (SPE-DOM) from river, estuarine and open ocean waters Gerhard Kattner 1, Thorsten Dittmar 2, Boris Koch 1, and Norbert Hertkorn 3 1 Alfred Wegener Institute
General Chemistry. Ch. 10
 General Chemistry Ch. 10 Essentials of Organic Chemistry Most biological important molecules are composed of organic compounds. These are mostly produced by biological systems. Organic molecules contain
General Chemistry Ch. 10 Essentials of Organic Chemistry Most biological important molecules are composed of organic compounds. These are mostly produced by biological systems. Organic molecules contain
 anna.ida3@gmail.com/2013 Have you ever heard HUMUS?? A brown to black complex variable of carbon containing compounds as possessing cellular organization in the form of plant and animal bodies Derived
anna.ida3@gmail.com/2013 Have you ever heard HUMUS?? A brown to black complex variable of carbon containing compounds as possessing cellular organization in the form of plant and animal bodies Derived
Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea
 The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
The following supplement accompanies the article Seasonal dynamics of dissolved organic matter and microbial activity in the coastal North Sea Eva Sintes 1, 2, *, Karen Stoderegger 1, Veronica Parada 1,
Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization
 Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Substances containing carbon are organic matter. Soil organic matter consists of decomposing plant
Soil organic matter composition, decomposition, mineralization and immobilization SOIL ORGANIC MATTER Substances containing carbon are organic matter. Soil organic matter consists of decomposing plant
What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials.
 What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials. It is composed of protons (+), neutrons (0), and electrons (-). The Periodic Table Elements are composed of all
What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials. It is composed of protons (+), neutrons (0), and electrons (-). The Periodic Table Elements are composed of all
Macronutrients in the ocean
 Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
Macronutrients in the ocean Philip Boyd NIWA/OTAGO, New Zealand September 2011 OUTLINE What is a macronutrient? Trends in nutrients & limitation The N cycle sources, sinks and recycling Silicate the body
Sources and Composition of Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter in the Delaware Estuary
 Sources and Composition of Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter in the Delaware Estuary Hadley McIntosh, Bauer, J.E., and E.A. Canuel Delaware Estuary Science & Environmental Summit 2013: January 30,
Sources and Composition of Dissolved and Particulate Organic Matter in the Delaware Estuary Hadley McIntosh, Bauer, J.E., and E.A. Canuel Delaware Estuary Science & Environmental Summit 2013: January 30,
Chem 60 Takehome Test 2 Student Section
 Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Sources of nutrients to the surface mixed layer of the ocean
 Sources of nutrients to the surface mixed layer of the ocean What are nutrients anyway? (to a chemist that is.) Where do they come from? Preformed (recycled, delivered from elsewhere) Biosynthesized Nutrient
Sources of nutrients to the surface mixed layer of the ocean What are nutrients anyway? (to a chemist that is.) Where do they come from? Preformed (recycled, delivered from elsewhere) Biosynthesized Nutrient
What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials.
 What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials. It is composed of protons (+), neutrons (0), and electrons (-). The Periodic Table Elements are composed of all
What is an atom? An atom is the smallest component of all living and nonliving materials. It is composed of protons (+), neutrons (0), and electrons (-). The Periodic Table Elements are composed of all
Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics. Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL
 Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL patricia.k.quinn@noaa.gov Marine Biota Climate Feedback Loop Charlson et al., Nature, 1987. Aerosol
Southern Ocean MBL CCN Budget: Contribution from Primary Sea Spray Aerosol Organics Trish Quinn NOAA PMEL patricia.k.quinn@noaa.gov Marine Biota Climate Feedback Loop Charlson et al., Nature, 1987. Aerosol
Loose Ends. Reactions. Polymers
 Today Loose Ends Reactions Polymers Names for isolated groups -OH Hydroxyl -NH2 Amino O -C- Carbonyl O -C-O Carboxyl Vitamin D4 Our friend the benzene ring Another important Functional Group Phenol Nomenclature
Today Loose Ends Reactions Polymers Names for isolated groups -OH Hydroxyl -NH2 Amino O -C- Carbonyl O -C-O Carboxyl Vitamin D4 Our friend the benzene ring Another important Functional Group Phenol Nomenclature
Kinetic model of the biomass hydrolysis by polysulfone. membrane with chemically linked acidic ionic liquids via.
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Kinetic model of the biomass hydrolysis by polysulfone membrane with chemically linked acidic
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for RSC Advances. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2018 Kinetic model of the biomass hydrolysis by polysulfone membrane with chemically linked acidic
Organic Chemistry Diversity of Carbon Compounds
 Organic Chemistry Diversity of Carbon Compounds Hydrocarbons The Alkanes The Alkenes The Alkynes Naming Hydrocarbons Cyclic Hydrocarbons Alkyl Groups Aromatic Hydrocarbons Naming Complex Hydrocarbons Chemical
Organic Chemistry Diversity of Carbon Compounds Hydrocarbons The Alkanes The Alkenes The Alkynes Naming Hydrocarbons Cyclic Hydrocarbons Alkyl Groups Aromatic Hydrocarbons Naming Complex Hydrocarbons Chemical
2 3 Carbon Compounds Slide 1 of 37
 1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
1 of 37 The Chemistry of Carbon The Chemistry of Carbon Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Carbon atoms have four valence electrons that can join with
Supplementary data. Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth
 Polar Biology Supplementary data Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth during sea ice formation in an ice tank study Shazia N Aslam 1*, Graham J.C. Underwood
Polar Biology Supplementary data Dissolved extracellular polymeric substance (deps) dynamics and bacterial growth during sea ice formation in an ice tank study Shazia N Aslam 1*, Graham J.C. Underwood
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*)
 NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
Ch 2 Molecules of life
 Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Ch 2 Molecules of life Think about (Ch 2, p.2) 1. Water is essential to life. If there is water on a planet, it is possible that life may exist on the planet. 2. Water makes up the largest percentage by
Geol Supplementary Notes 463-RWR-6,7 GEOL RWR-6 ORGANIC COMPOSITION OF PETROLEUM COMPOSITION OF LIVING ORGANISMS
 GEOL 463.3 RWR-6 ORGANIC COMPOSITION OF PETROLEUM Recommended sections to read in the textbook: Chapter 4 COMPOSITION OF LIVING ORGANISMS The main components of living organisms: Carbohydrates Sugar chains
GEOL 463.3 RWR-6 ORGANIC COMPOSITION OF PETROLEUM Recommended sections to read in the textbook: Chapter 4 COMPOSITION OF LIVING ORGANISMS The main components of living organisms: Carbohydrates Sugar chains
Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM?
 Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM? T. Nagata 1, D. L. Kirchman 2 1 Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Minami-dai, Nakano, Tokyo 164-8639 Japan 2 College of
Bacterial Mortality: A Pathway for the Formation of Refractory DOM? T. Nagata 1, D. L. Kirchman 2 1 Ocean Research Institute, University of Tokyo, Minami-dai, Nakano, Tokyo 164-8639 Japan 2 College of
BIOMOLECULES. (AKA MACROMOLECULES) Name: Block:
 BIOMOLECULES (AKA MACROMOLECULES) Name: Block: BIOMOLECULES POGIL All living things share the same chemical building blocks and depend on chemical processes for survival. Life without carbon (C) would
BIOMOLECULES (AKA MACROMOLECULES) Name: Block: BIOMOLECULES POGIL All living things share the same chemical building blocks and depend on chemical processes for survival. Life without carbon (C) would
Organic matter transformations in the upper mesopelagic zone of the North Pacific: Chemical composition and linkages to microbial community structure
 JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jc007141, 2012 Organic matter transformations in the upper mesopelagic zone of the North Pacific: Chemical composition and linkages to microbial
JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 117,, doi:10.1029/2011jc007141, 2012 Organic matter transformations in the upper mesopelagic zone of the North Pacific: Chemical composition and linkages to microbial
recovery of humic substances from ion exchange brine
 recovery of humic substances from ion exchange brine Elisabeth Vaudevire recovery of humic substances from ion exchange brine overview origin of the brine specific adsorption of humic substances by IEX
recovery of humic substances from ion exchange brine Elisabeth Vaudevire recovery of humic substances from ion exchange brine overview origin of the brine specific adsorption of humic substances by IEX
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater NOM and MS Methods Lecture #10 NOM Characterization Analytical Tests elemental analysis spectral properties functional group chemistry Separation/Fractionation
1 Preparation and Characterization of Lignin-Carbohydrate Complexes
 1 Preparation and Characterization of Lignin-Carbohydrate Complexes To explain the difficulty in separating lignin from carbohydrates in wood, Erdman (1866) hypothesized that the two combined chemically
1 Preparation and Characterization of Lignin-Carbohydrate Complexes To explain the difficulty in separating lignin from carbohydrates in wood, Erdman (1866) hypothesized that the two combined chemically
Synthesis of Macromolecules
 A child s building blocks are relatively simple structures. When they come together, however, they can form magnificent structures. The elaborate city scene on the right is made of small, simple building
A child s building blocks are relatively simple structures. When they come together, however, they can form magnificent structures. The elaborate city scene on the right is made of small, simple building
Organic Molecules. 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1
 Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
Organic Molecules 8/27/2004 Mr. Davenport 1 Carbohydrates Commonly called sugars and starches Consist of C, H, O with H:O ration 2:1 Usually classified as to sugar units Monosaccharide are single sugar
1/3/2011. Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
Organic Compounds: Carbohydrates
 Organic Compounds: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates include sugars and starches Contain the elements C,H,O (H & O ratio like water, 2 H s to 1O), ex. glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Word means hydrated carbon Classified
Organic Compounds: Carbohydrates Carbohydrates include sugars and starches Contain the elements C,H,O (H & O ratio like water, 2 H s to 1O), ex. glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 Word means hydrated carbon Classified
This place covers: Reducing the size of material from which sugars are to be extracted; Presses and knives therefor,
 CPC - C13B - 2017.08 C13B PRODUCTION OF SUCROSE; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR (chemically synthesised sugars or sugar derivatives C07H; fermentation or enzyme-using processes for preparing compounds
CPC - C13B - 2017.08 C13B PRODUCTION OF SUCROSE; APPARATUS SPECIALLY ADAPTED THEREFOR (chemically synthesised sugars or sugar derivatives C07H; fermentation or enzyme-using processes for preparing compounds
Marine Dissolved Organic Phosphorus Composition: Insights from Samples Recovered Using Combined Electrodialysis/Reverse Osmosis
 Marine Dissolved Organic Phosphorus Composition: Insights from Samples Recovered Using Combined Electrodialysis/Reverse Osmosis A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Cindy Jackson In Partial Fulfillment
Marine Dissolved Organic Phosphorus Composition: Insights from Samples Recovered Using Combined Electrodialysis/Reverse Osmosis A Thesis Presented to The Academic Faculty by Cindy Jackson In Partial Fulfillment
Metabolite: substance produced or used during metabolism such as lipids, sugars and amino acids
 Metabolomica Analisi di biofluidi mediante spettroscopia NMR Michael Assfalg Università di Verona Terminology Metabolite: substance produced or used during metabolism such as lipids, sugars and amino acids
Metabolomica Analisi di biofluidi mediante spettroscopia NMR Michael Assfalg Università di Verona Terminology Metabolite: substance produced or used during metabolism such as lipids, sugars and amino acids
Biological Chemistry. Is biochemistry fun? - Find it out!
 Biological Chemistry Is biochemistry fun? - Find it out! 1. Key concepts Outline 2. Condensation and Hydrolysis Reactions 3. Carbohydrates 4. Lipids 5. Proteins 6. Nucleic Acids Key Concepts: 1. Organic
Biological Chemistry Is biochemistry fun? - Find it out! 1. Key concepts Outline 2. Condensation and Hydrolysis Reactions 3. Carbohydrates 4. Lipids 5. Proteins 6. Nucleic Acids Key Concepts: 1. Organic
Recovery of nutrients from biomass for nutrient recycling
 Recovery of nutrients from biomass for nutrient recycling John Hewson, Ryan Davis, Todd Lane, Nicholas Wyatt Sandia National Laboratories Anthony Siccardi, Zachary Fuqua Texas A&M University 2013 Algae
Recovery of nutrients from biomass for nutrient recycling John Hewson, Ryan Davis, Todd Lane, Nicholas Wyatt Sandia National Laboratories Anthony Siccardi, Zachary Fuqua Texas A&M University 2013 Algae
Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms
 Name: Period: Date: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
Name: Period: Date: Elements & Macromolecules in Organisms Most common elements in living things are carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, and oxygen. These four elements constitute about 95% of your body weight.
IB Biology BIOCHEMISTRY. Biological Macromolecules SBI3U7. Topic 3. Thursday, October 4, 2012
 + IB Biology SBI3U7 BIOCHEMISTRY Topic 3 Biological Macromolecules Essential Questions: 1.What are the 4 main types of biological macromolecules and what is their function within cells? 2.How does the
+ IB Biology SBI3U7 BIOCHEMISTRY Topic 3 Biological Macromolecules Essential Questions: 1.What are the 4 main types of biological macromolecules and what is their function within cells? 2.How does the
Name: Per. HONORS: Molecules of Life
 Name: Per. HONORS: Molecules of Life Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are classes of organic molecules that are essential to the life processes of all living things. All three classes of molecules are
Name: Per. HONORS: Molecules of Life Carbohydrates, proteins, and fats are classes of organic molecules that are essential to the life processes of all living things. All three classes of molecules are
Two examples of biomarker lipid applica3ons to studies of carbon cycling in marine systems:
 Two examples of biomarker lipid applica3ons to studies of carbon cycling in marine systems: Part A: The determina/on of terrestrial organic ma6er in sediments via lignin oxida/on products by John I. Hedges
Two examples of biomarker lipid applica3ons to studies of carbon cycling in marine systems: Part A: The determina/on of terrestrial organic ma6er in sediments via lignin oxida/on products by John I. Hedges
Chapter 2 pt 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Life. Gregory Ahearn. John Crocker. Including the lecture Materials of
 Chapter 2 pt 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Life Including the lecture Materials of Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida with amendments and additions by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
Chapter 2 pt 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Life Including the lecture Materials of Gregory Ahearn University of North Florida with amendments and additions by John Crocker Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc..
BIOMOLECULES. Ms. Bosse Fall 2015
 BIOMOLECULES Ms. Bosse Fall 2015 Biology Biology is the study of the living world. Bio = life Major Molecules of Life Macromolecules giant molecules found in living cells; made from thousands of smaller
BIOMOLECULES Ms. Bosse Fall 2015 Biology Biology is the study of the living world. Bio = life Major Molecules of Life Macromolecules giant molecules found in living cells; made from thousands of smaller
Question #2 Fructose, galactose, and glucose are monosaccharides (simple sugars). The open chain form of glucose is drawn below:
 II. Carbohydrates Question #1: List two functions of carbohydrates 1. Energy source 2. Energy storage 3. Components of cell walls and other protective structures 4. Recognition and signaling 5. Components
II. Carbohydrates Question #1: List two functions of carbohydrates 1. Energy source 2. Energy storage 3. Components of cell walls and other protective structures 4. Recognition and signaling 5. Components
Biochemistry. Chapter 6
 Biochemistry Chapter 6 Game Plan for Today. - Collect your papers - Hand back quests - Go over Amoeba Sister Chart - Biochem Notes - Video Carbohydrate Lab Food Label Lab! Testing For Carbohydrates Benedict's
Biochemistry Chapter 6 Game Plan for Today. - Collect your papers - Hand back quests - Go over Amoeba Sister Chart - Biochem Notes - Video Carbohydrate Lab Food Label Lab! Testing For Carbohydrates Benedict's
Silicon Forms in Soluble Pectin Substances Extracted by Hot Water from Plant Cell Wall
 Received for Publication, October, Silicon Forms in Soluble Pectin Substances Extracted by Hot Water from Plant Cell Wall Shunji INANAGA, Naoya CHISHAKI and Neng Chang CHEN Laboratory of Plant Nutrition
Received for Publication, October, Silicon Forms in Soluble Pectin Substances Extracted by Hot Water from Plant Cell Wall Shunji INANAGA, Naoya CHISHAKI and Neng Chang CHEN Laboratory of Plant Nutrition
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids
 Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Is it made of carbohydrates? Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. A carbohydrate with 6 carbon atoms would have
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins, and Nucleic Acids Is it made of carbohydrates? Organic compounds composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen in a 1:2:1 ratio. A carbohydrate with 6 carbon atoms would have
Chemical Formulas. Chemical Formula CH 3 COCHCHOCHClCHNH Lewis Dot Structure
 Biochemistry . Chemical Formulas A chemical formula represents the chemical makeup of a compound. It shows the numbers and kinds of atoms present in a compound. It is a kind of shorthand that scientists
Biochemistry . Chemical Formulas A chemical formula represents the chemical makeup of a compound. It shows the numbers and kinds of atoms present in a compound. It is a kind of shorthand that scientists
Mir M. Seyedbagheri, Ph.D. Professor/Soil Agronomist 1
 The Following presentation was created by Dr. Mir Seyedbagheri. Dr. Seyedbagheri, is in no way endorsing Humic Growth Solutions or any of its products. This presentation is intended for educational purposes
The Following presentation was created by Dr. Mir Seyedbagheri. Dr. Seyedbagheri, is in no way endorsing Humic Growth Solutions or any of its products. This presentation is intended for educational purposes
The. Crash Course. Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O)
 The Biochemistry Crash Course Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O) This exercise is designed to familiarize you with
The Biochemistry Crash Course Basically, almost all living things are made up of these 4 Elements: - Carbon (C) - Nitrogen (N) - Hydrogen (H) - Oxygen (O) This exercise is designed to familiarize you with
APPLICATIONS OF FTIR SPECTROSCOPY IN ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES SUPPORTED BY TWO DIMENSIONAL CORRELATION ANALYSIS
 Global NEST Journal, Vol 11, No 4, pp 593-6, 29 Copyright 29 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved APPLICATIONS OF FTIR SPECTROSCOPY IN ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES SUPPORTED BY TWO DIMENSIONAL CORRELATION
Global NEST Journal, Vol 11, No 4, pp 593-6, 29 Copyright 29 Global NEST Printed in Greece. All rights reserved APPLICATIONS OF FTIR SPECTROSCOPY IN ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES SUPPORTED BY TWO DIMENSIONAL CORRELATION
I. Polymers & Macromolecules Figure 1: Polymers. Polymer: Macromolecule: Figure 2: Polymerization via Dehydration Synthesis
 I. Polymers & Macromolecules Figure 1: Polymers Polymer: Macromolecule: Figure 2: Polymerization via Dehydration Synthesis 1 Dehydration Synthesis: Figure 3: Depolymerization via Hydrolysis Hydrolysis:
I. Polymers & Macromolecules Figure 1: Polymers Polymer: Macromolecule: Figure 2: Polymerization via Dehydration Synthesis 1 Dehydration Synthesis: Figure 3: Depolymerization via Hydrolysis Hydrolysis:
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D
 LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
LC/MS Analysis of Various Hydrophilic Compounds Using a Polymer-Based Amino Column - Shodex TM HILICpak TM VG-50 2D Introduction Components of pharmaceutical products and food products often include high
Practice Questions for Biochemistry Test A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4
 Practice Questions for Biochemistry Test 1. The quaternary structure of a protein is determined by: A. interactions between distant amino acids of the same polypeptide. B.interactions between close amino
Practice Questions for Biochemistry Test 1. The quaternary structure of a protein is determined by: A. interactions between distant amino acids of the same polypeptide. B.interactions between close amino
Effects of increasing nutrient loads on the competition and succession between two predominant red tide algae of East China Sea
 Effects of increasing nutrient loads on the competition and succession between two predominant red tide algae of East China Sea Reporter:Yuping Zhou The Tutor:Jiangtao Wang Contents Background Experiments
Effects of increasing nutrient loads on the competition and succession between two predominant red tide algae of East China Sea Reporter:Yuping Zhou The Tutor:Jiangtao Wang Contents Background Experiments
Nutrients & iclicker Question Which is not a major ion? A) Sodium (Na + ) B) Potassium (K + ) C) Chloride (Cl - ) D) Silicon (Si) E) Sulfate (SO 4
 Nutrients & Tracers Non-conservative element: short residence time removed efficiently by biological or chemical processes Nutrients: used by living organisms Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Iron, silicate,
Nutrients & Tracers Non-conservative element: short residence time removed efficiently by biological or chemical processes Nutrients: used by living organisms Carbon, Nitrogen, Phosphorous, Iron, silicate,
Oxoacids of Phosphorus *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m35001 1 Oxoacids of Phosphorus * Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Phosphorous pentoxide (P 2
OpenStax-CNX module: m35001 1 Oxoacids of Phosphorus * Andrew R. Barron This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 Phosphorous pentoxide (P 2
2 3 Carbon Compounds (Macromolecules)
 2 3 Carbon Compounds (Macromolecules) Slide 1 of 37 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Slide 2 of 37 Carbon Living organisms are
2 3 Carbon Compounds (Macromolecules) Slide 1 of 37 Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of all compounds that contain bonds between carbon atoms. Slide 2 of 37 Carbon Living organisms are
TISSUES, CELLS AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 Inorganic Compounds: Water (2H: 1O) Minerals (Na, P, I, Ca, Fe, K, nitrates, phosphates) functions and deficiencies Fertilizers Organic molecules are made up of C, H, O and some contain other elements
Inorganic Compounds: Water (2H: 1O) Minerals (Na, P, I, Ca, Fe, K, nitrates, phosphates) functions and deficiencies Fertilizers Organic molecules are made up of C, H, O and some contain other elements
Why Carbon? What does a carbon atom look like?
 Biomolecules Organic Chemistry In the 1800 s it was believed to be impossible to recreate molecules in a lab Thus, the study of organic chemistry was originally the study of molecules in living organisms
Biomolecules Organic Chemistry In the 1800 s it was believed to be impossible to recreate molecules in a lab Thus, the study of organic chemistry was originally the study of molecules in living organisms
Chapter 1. Chemistry of Life - Advanced TABLE 1.2: title
 Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
Condensation and Hydrolysis Condensation reactions are the chemical processes by which large organic compounds are synthesized from their monomeric units. Hydrolysis reactions are the reverse process.
A. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule. B. Incorrect! No, this is not the description of this type of molecule.
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 08: Carbohydrates No. 1 of 10 1. have one aldehyde (-CHO) or one keto (-C=O) group and many hydroxyl (-OH) groups. (A) Amino acids (B) Proteins (C) Nucleic Acids (D) Carbohydrates
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 3 Chemistry of Cells
 Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 3 Chemistry of Cells Objectives Summarize the characteristics of organic compounds. Compare the structures and function of different types of biomolecules.
Copy into Note Packet and Return to Teacher Section 3 Chemistry of Cells Objectives Summarize the characteristics of organic compounds. Compare the structures and function of different types of biomolecules.
Chemistry of Carbon. All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon
 Ach Chemistry of Carbon All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon Carbon atom with an outer shell of four electrons can form covalent bonds with four atoms. In organic molecules,
Ach Chemistry of Carbon All living things rely on one particular type of molecule: carbon Carbon atom with an outer shell of four electrons can form covalent bonds with four atoms. In organic molecules,
2.1.1 Biological Molecules
 2.1.1 Biological Molecules Relevant Past Paper Questions Paper Question Specification point(s) tested 2013 January 4 parts c and d p r 2013 January 6 except part c j k m n o 2012 June 1 part ci d e f g
2.1.1 Biological Molecules Relevant Past Paper Questions Paper Question Specification point(s) tested 2013 January 4 parts c and d p r 2013 January 6 except part c j k m n o 2012 June 1 part ci d e f g
Chemical Tests For Biologically Important Molecules Do not write on this document
 Chemical Tests For Biologically Important Molecules Do not write on this document Introduction The most common and important organic molecules found in living things fall into four classes: carbohydrates,
Chemical Tests For Biologically Important Molecules Do not write on this document Introduction The most common and important organic molecules found in living things fall into four classes: carbohydrates,
Lecture 14. More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils
 Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
Lecture 14 More Soil chemistry and nutrients in soils SOIL INORGANIC SOLIDS saprolite development elemental changes that occur during weathering The gain or loss of chemical constituents in saprolite records
Biological Molecules
 Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
Photosynthesis Digestion Respiration. ., proteins. ... Glucose,.., fatty acids and glycerol, respectively.
 BIOMOLECULES Dear Reader In the previous chapter you have read about DNA present in the chromosomes. It is one of the many organic chemical compounds present in all living organisms. The organic compounds
BIOMOLECULES Dear Reader In the previous chapter you have read about DNA present in the chromosomes. It is one of the many organic chemical compounds present in all living organisms. The organic compounds
Effect of B-vitamins (B 1, B 12 ) and inorganic nutrients on algal bloom dynamics in a coastal ecosystem
 Vol. 49: 181 194, 27 doi: 1.3354/ame1132 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol Published November 15 Effect of B-vitamins (B 1, B 12 ) and inorganic nutrients on algal bloom dynamics in a coastal
Vol. 49: 181 194, 27 doi: 1.3354/ame1132 AQUATIC MICROBIAL ECOLOGY Aquat Microb Ecol Published November 15 Effect of B-vitamins (B 1, B 12 ) and inorganic nutrients on algal bloom dynamics in a coastal
For example, monosaccharides such as glucose are polar and soluble in water, whereas lipids are nonpolar and insoluble in water.
 Biology 4A Laboratory Biologically Important Molecules Objectives Perform tests to detect the presence of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Recognize the importance of a control in a biochemical
Biology 4A Laboratory Biologically Important Molecules Objectives Perform tests to detect the presence of carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids Recognize the importance of a control in a biochemical
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES PT. 3 FOUR MAIN TYPES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES THAT MAKE UP LIVING THINGS
 BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES PT. 3 FOUR MAIN TYPES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES THAT MAKE UP LIVING THINGS 1. 2. 3. 4. CARBOHYDRATES LIPIDS (fats) PROTEINS NUCLEIC ACIDS We call these four main types of carbon- based molecules
BIOCHEMISTRY NOTES PT. 3 FOUR MAIN TYPES OF ORGANIC MOLECULES THAT MAKE UP LIVING THINGS 1. 2. 3. 4. CARBOHYDRATES LIPIDS (fats) PROTEINS NUCLEIC ACIDS We call these four main types of carbon- based molecules
-are poly-hydroxylated aldehydes and ketones -can cyclise -can form polymeric chains
 CARBOHYDRATES -compounds of C, H and O -originally thought of as hydrates of carbon e.g. glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 thought to be C(H 2 O) carbohydrates: -are poly-hydroxylated aldehydes and ketones -can cyclise
CARBOHYDRATES -compounds of C, H and O -originally thought of as hydrates of carbon e.g. glucose C 6 H 12 O 6 thought to be C(H 2 O) carbohydrates: -are poly-hydroxylated aldehydes and ketones -can cyclise
Pathways to Biomolecules
 Week 12 Pathways to Biomolecules Are molecules such as fats and oils, carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids that are found in all living things. Have an essential role in the supply of energy to the
Week 12 Pathways to Biomolecules Are molecules such as fats and oils, carbohydrates, proteins and nucleic acids that are found in all living things. Have an essential role in the supply of energy to the
Chapter 18. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Monosaccharide composition of four humus fractions in an Andosol and a Cambisol
 Soil Science and Plant Nutrition (2007) 53, 7 11 doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00111.x Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. SHORT PAPER Monosaccharide ORIGINAL ARTICLE composition of humus fractions Monosaccharide
Soil Science and Plant Nutrition (2007) 53, 7 11 doi: 10.1111/j.1747-0765.2007.00111.x Blackwell Publishing, Ltd. SHORT PAPER Monosaccharide ORIGINAL ARTICLE composition of humus fractions Monosaccharide
Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate
 Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Introduction Lab 3: Inorganic Plant Nutrients: Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Silicate Compounds of nitrogen and phosphorus are major cellular components of organisms. Since the availability of these elements may
Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
Chemical Composition of the Cell. B. Balen
 Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
Microbial Metabolism & Growth
 Microbial Metabolism & Growth Basic Organic Chem Review Four Basic Types of Macromolecules A) Proteins (Made up of Amino Acids) B) Nucleic Acids (Made up of NucleoEdes) C) Carbohydrates (Mainly Carbon,
Microbial Metabolism & Growth Basic Organic Chem Review Four Basic Types of Macromolecules A) Proteins (Made up of Amino Acids) B) Nucleic Acids (Made up of NucleoEdes) C) Carbohydrates (Mainly Carbon,
Molecule - two or more atoms held together by covalent bonds. Ex. = water, H O
 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY NOTES Why study carbon? ORGANIC CHEMISTRY NOTES Why study carbon? * All of life is built on carbon * Cells are made up of about 72% water 3% salts (NaCl, and K) 25% carbon compounds which
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY NOTES Why study carbon? ORGANIC CHEMISTRY NOTES Why study carbon? * All of life is built on carbon * Cells are made up of about 72% water 3% salts (NaCl, and K) 25% carbon compounds which
Established Facts. Impact of Post Harvest Forage on the Rumen Function. Known Facts. Known Facts
 Impact of Post Harvest Forage on the Rumen Function Gbenga Ayangbile, Ph.D. Established Facts Most nutrients in fresh forages before harvesting are more available and efficiently utilized for productive
Impact of Post Harvest Forage on the Rumen Function Gbenga Ayangbile, Ph.D. Established Facts Most nutrients in fresh forages before harvesting are more available and efficiently utilized for productive
Most life processes are a series of chemical reactions influenced by environmental and genetic factors.
 Biochemistry II Most life processes are a series of chemical reactions influenced by environmental and genetic factors. Metabolism the sum of all biochemical processes 2 Metabolic Processes Anabolism-
Biochemistry II Most life processes are a series of chemical reactions influenced by environmental and genetic factors. Metabolism the sum of all biochemical processes 2 Metabolic Processes Anabolism-
CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater
 Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Origins of NOM II Lecture #5 Dave Reckhow - Organics In W & WW Carbohydrates empirical formula: C x (H 2 O) y CH 2 OH H H O H OH H OH OH
Print version CEE 697z Organic Compounds in Water and Wastewater Origins of NOM II Lecture #5 Dave Reckhow - Organics In W & WW Carbohydrates empirical formula: C x (H 2 O) y CH 2 OH H H O H OH H OH OH
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2.
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
Large Biological Molecules Multiple Choice Review
 New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 43 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
New Jersey enter for Teaching and Learning Slide 1 / 43 Progressive Science Initiative This material is made freely available at www.njctl.org and is intended for the non-commercial use of students and
Catalogue. Resins and Columns For High Performance Liquid Chromatography
 Catalogue Resins and Columns For High Performance Liquid Chromatography Updated August 11, 2008 Contents Benson Polymeric provides premium polymeric column packing materials and prepacked columns for use
Catalogue Resins and Columns For High Performance Liquid Chromatography Updated August 11, 2008 Contents Benson Polymeric provides premium polymeric column packing materials and prepacked columns for use
Macromolecules. 3. There are several levels of protein structure, the most complex of which is A) primary B) secondary C) tertiary D) quaternary
 Macromolecules 1. If you remove all of the functional groups from an organic molecule so that it has only carbon and hydrogen atoms, the molecule become a molecule. A) carbohydrate B) carbonyl C) carboxyl
Macromolecules 1. If you remove all of the functional groups from an organic molecule so that it has only carbon and hydrogen atoms, the molecule become a molecule. A) carbohydrate B) carbonyl C) carboxyl
Comparison of seasonal changes in fluorescent dissolved organic matter among aquatic lake and stream sites in the Green Lakes Valley
 Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jg000985, 2010 Comparison of seasonal changes in fluorescent dissolved organic matter among aquatic lake and stream
Click Here for Full Article JOURNAL OF GEOPHYSICAL RESEARCH, VOL. 115,, doi:10.1029/2009jg000985, 2010 Comparison of seasonal changes in fluorescent dissolved organic matter among aquatic lake and stream
Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical basis
 European Journal of Phycology ISSN: 0967-0262 (Print) 1469-4433 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp20 Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical
European Journal of Phycology ISSN: 0967-0262 (Print) 1469-4433 (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/tejp20 Redfield revisited: variability of C:N:P in marine microalgae and its biochemical
2 3 Carbon Compounds. Proteins. Proteins
 2 3 Carbon Compounds Proteins Proteins Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. There are 20 amino acids,
2 3 Carbon Compounds Proteins Proteins Proteins are macromolecules that contain nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. Proteins are polymers of molecules called amino acids. There are 20 amino acids,
