Differential diagnosis of fetal hyperechogenic cystic kidneys unrelated to renal tract anomalies: a multicenter study
|
|
|
- Shauna Briggs
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 28: Published online 8 November 2006 in Wiley InterScience ( DOI: /uog.3856 Differential diagnosis of fetal hyperechogenic cystic kidneys unrelated to renal tract anomalies: a multicenter study K. CHAUMOITRE*, M. BRUN, M. CASSART, B. MAUGEY-LAULOM, D. EURIN, F. DIDIER and E. F. AVNI, for the Groupe Radiopédiatrique de Recherche en Imagerie Foetale (GRRIF) Departments of Medical Imaging, *Hôpital Nord, CHU Marseille and Regional Maternity, Nancy, Department of Medical Imaging A, Hôpital Pellegrin, CHU Bordeaux and Department of Pediatric Imaging, Charles Nicolle Hospital, Rouen, France and Department of Medical Imaging, Erasme University Hospital, Brussels, Belgium KEYWORDS: Bardet Biedl syndrome; cyst; fetus; kidney; Meckel Gruber syndrome; polycystic kidney diseases; prenatal diagnosis; ultrasonography ABSTRACT Objectives To identify important factors in the differential diagnosis of renal cysts associated with hyperechogenic kidneys. Methods This was a retrospective multicenter study. We identified 93 fetuses presenting between 1990 and 2002 with hyperechogenic kidneys and which had a diagnosis of nephropathy confirmed later. We analyzed retrospectively the prenatal ultrasound findings of those fetuses which were found sonographically to have renal cysts. Results Of the 93 fetuses presenting with hyperechogenic kidneys and with a later diagnosis of nephropathy, there were 28 with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), 31 with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), 11 with Bardet Biedl syndrome, nine with Meckel Gruber syndrome, six with Ivemark II syndrome, one with Jarcho Levin syndrome, one with Beemer syndrome and one with Meckellike syndrome. One third of the fetuses (30/93) had renal cysts. Cystic characteristics (size, location, number) were not very useful for diagnosis; more useful was diagnosis of an associated malformation. Three (11%) of the fetuses with ADPKD had cysts, as did nine (29%) of those with ARPKD, three (27%) of those with Bardet Biedl syndrome, all (100%) of those with Meckel Gruber syndrome, three (50%) of those with Ivemark II syndrome, and each of the three cases with other syndromes (Jarcho Levin, Beemer and Meckel-like syndromes). None of the cases with trisomy 13 had cysts. There were no associated malformations in the 12 cases with renal cysts and polycystic kidney disease; the other 18 cases with renal cysts were associated with malformations that were often specific, such as polydactyly in Bardet Biedl and Beemer syndromes, occipital defect and Dandy Walker malformation in Meckel Gruber or Meckel Gruber-like syndromes, and thoracic and/or vertebral abnormalities in Jarcho Levin and Beemer syndromes. Conclusion Renal cysts associated with hyperechogenic kidneys are not rare. The clue to diagnosis is the demonstration of an associated malformation. If no malformation is found, the main diagnosis remains polycystic kidney disease, i.e. ARPKD or ADPKD. Copyright 2006 ISUOG. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. INTRODUCTION The prenatal management of hyperechogenic kidneys is challenging. Kidney hyperechogenicity is diagnosed after 17 weeks gestation when the kidneys appear more echogenic than do the liver or spleen 1. Such abnormal echogenicity can result from the presence of multiple microscopic cysts, dysplasia or tubular dilatation. The differential diagnosis must take into account the family history and the presence of associated anomalies. Renal cystic diseases should be suspected in the case of macrocysts but also in the presence of hyperechogenic kidneys 1. In this retrospective study we analyzed renal sonographic data in 93 fetuses that presented with hyperechogenic kidneys and had a diagnosis of nephropathy confirmed later (renal tract anomalies, i.e. obstructive cystic dysplasia or multicystic dysplastic kidney (MKD), excluded) and we described the Correspondence to: Dr K. Chaumoitre, Service d Imagerie Médicale, Hôpital Nord, Chemin des Bourrellys, Cedex 20, Marseille, France ( kathia.chaumoitre@ap-hm.fr) Accepted: 18 May 2006 Copyright 2006 ISUOG. Published by John Wiley & Sons, Ltd. ORIGINAL PAPER
2 912 Chaumoitre et al. prenatal ultrasound patterns in the 30 that had associated cysts diagnosed by sonography. We have reported previously on the cases of ADPKD (Brun et al. 2 ) and Bardet Biedl syndrome (Cassart et al. 3 ) in our sample. METHODS This was a retrospective multicenter study, conducted in four prenatal centers (in Bordeaux, Nancy, Rouen and Brussels) for the Groupe Radiopédiatrique de Recherche en Imagerie Foetale (GRRIF). Ninety-three patients between 1990 and 2002 attending for routine ultrasound examination presented with fetal hyperechogenic kidneys. All these cases had the diagnosis confirmed subsequently (by clinical and biological follow-up, genetic testing, and fetopathological examination in cases of termination or perinatal death). We analyzed retrospectively prenatal clinical and sonographic data of those that had renal cysts at least 2 mm in diameter. All sonographic examinations were performed on an SSD-5500 (Aloka, Wallingford, CT, USA) or a Power Vision 8000 (Toshiba, Yashimoto, Japan) ultrasound machine by experienced radiologists using MHz probes. The following features were analyzed: renal size (according to the data of Cohen et al. 4 ), echogenic pattern, corticomedullary differentiation (CMD) (absent/present and, if present, normal/increased/reversed), presence of renal cysts (number, size and location), size of the collecting system and any other abnormal sonographic feature. Fetal gender, gestational age at diagnosis and amniotic fluid volume were assessed. All ultrasound images were reviewed by two observers. The whole procedure was in accordance with the recommendations of the institutional ethics board of each center. RESULTS The 93 fetuses with hyperechogenic kidneys included 28 cases of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), 31 cases of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD), 11 cases of Bardet Biedl syndrome, nine cases of Meckel Gruber syndrome, six cases of Ivemark II syndrome, five cases of trisomy 13, one case of Jarcho Levin syndrome, one case of Beemer syndrome and one case of Meckel-like syndrome. Approximately one third of these fetuses (30/93) had renal cysts diagnosed by prenatal ultrasound examination: cysts were presents in 11% (3/28) of those with ADPKD, 29% (9/31) of those with ARPKD, 27% (3/11) of those with Bardet Biedl syndrome, 100% (9/9) of whose with Meckel Gruber syndrome, 50% (3/6) of those with Ivemark II syndrome and in the three cases with other syndromes (Jarcho Levin, Beemer and Meckel-like syndromes). None of the five cases of trisomy 13 had renal cysts. There were no associated malformations in the 12 cases of polycystic kidney disease (PKD, i.e. ARPKD and ADPKD) with renal cysts. All the other cases with renal cysts were associated with malformations that were often specific, such as polydactyly in Bardet Biedl and Beemer syndrome, occipital defect and Dandy Walker malformation in Meckel Gruber or Meckel Gruber-like syndromes, and thoracic and/or vertebral abnormalities in Jarcho Levin and Beemer syndromes. Polycystic kidney disease (PKD): Table 1 Among the 28 cases of ADPKD, small bilateral cortical renal cysts were present in only three (11%) cases (Figure 1). There was a family history (maternal) in all Table 1 Characteristics of fetuses with hyperechogenic kidneys and cysts diagnosed with polycystic kidney disease (PKD) (n = 12) PKD Gender GA (weeks) Family history of PKD Kidney size* CMD AF Cyst size (mm) n Location Unilat/ Bilat Postnatal follow-up ADPKD M 22 Yes + 2 Dim Norm < 5 Few Cortex Bilat No CRF at 4 years (n = 3) M 22 Yes + 1 Dim Norm < 5 Few Cortex Bilat No CRF at 4 years F 30 Yes + 5 Abst Norm < 7 Few Cortex, paracalyceal Bilat CRF and hypertension at 3 years ARPKD M 22 No + 3 Rev Dim < 5 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 29 weeks (n = 9) M 19 Yes Inc Norm < 5 Num Cortex Bilat TOP 22 weeks F 13 Yes + 11 Rev Dim < 5 Num Cortex Unilat Death day 1 F 32 Yes Abst Norm > 5 Num Cortex Unilat CRF at 3 years, transplant M 22 Yes + 2 Rev Dim < 5 One Medulla Unilat TOP 24 weeks M 23 Yes + 15 Rev Dim > 5 One Medulla Unilat Death day 5 F 32 No + 4 Abst Dim < 5 Num Medulla Bilat TOP 33 weeks M 30 Yes + 4 Abst Dim > 5 One Medulla Unilat CRF at 7 years M 27 No + 3 Abst Abst < 5 Num Cortex Bilat CRF, death at 7 months None of these cases had associated malformations. *Renal length expressed as SD of the mean 4. Abst, absent; ADPKD, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; AF, amniotic fluid; ARPKD, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease; Bilat, bilateral; CMD, corticomedullary differentiation; CRF, chronic renal failure; Dim, diminished; F, female; GA, gestational age at diagnosis; Inc, increased; M, male; Norm, normal; Num, numerous; Rev, reversed; TOP, termination of pregnancy; Unilat, unilateral.
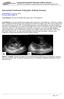
3 Hyperechogenic cystic kidneys 913 Figure 1 Ultrasound image of a 22-week fetus with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease showing hyperechogenic kidney with a rim of cortical cysts. The kidney is enlarged (+ 2 SD) and there is no corticomedullary differentiation. three.thekidneysizerangedfrom+ 1SDto+ 5 SD, the renal cortex was hyperechogenic, and the medulla was hyperechogenic and associated with diminished or absent CMD. Amniotic fluid volume was normal in all three cases. There were no associated malformations. After birth, follow-up revealed two to be normal at 4 years of age and one child had elevated blood pressure and moderate renal failure at 3 years of age. Among the 31 cases of ARPKD, prenatal renal cysts were present in nine (29%) cases (Figure 2). There was a family history (recurrence or consanguinity) in six (67%) cases. Size, number and location of the cysts were variable. Kidneys were markedly enlarged (mean + 5 SD) and amniotic fluid volume was diminished or absent in 78% of the cases. There were no associated malformations. Outcome was poor, with four terminations of pregnancy (TOP), two neonatal deaths, one death at 7 months and only two survivors (3 and 7 years of follow-up), both of which suffered severe renal failure. Syndromes: (Table 2) Among the 11 cases of Bardet Biedl syndrome, cystic lesions were present in three fetuses (27%). There was a solitary medullar lesion in one fetus, multiple medullar lesions in the second and a medullar cyst associated with multiple small cortical cystic lesions in the third. There was a family history in one case (brother). There were associated malformations in each of these cases, including polydactyly in all three. The kidney size ranged from + 1SDto+ 4 SD. There was an absence of CMD in all cases. The sonographic appearance of the kidneys changed over time; two of the three fetuses which presented with renal cystic lesions in utero showed complete regression of the cysts after birth; in the third, the cystic lesions increased in number and size for more than 2 years. Renal cystic lesions were present in all nine of our cases of Meckel Gruber syndrome. Cysts were tiny, their Figure 2 Ultrasound image of a 22-week fetus with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease showing hyperechogenic kidney with a medullar cyst (arrow). The kidney is moderately enlarged (+ 2 SD) and there is no corticomedullary differentiation. diffuse location involved the whole renal parenchyma, and there was no CMD (Figure 3). There were associated malformations in all cases, including occipital defect with or without encephalocele in seven cases and vermian agenesis or Dandy Walker malformation in five. There was a family history in one third of the cases. The kidney size was markedly enlarged (mean + 5 SD) and there was an absence of CMD in all cases. Amniotic fluid volume was decreased in 78% of the cases. All nine cases were terminated and the diagnosis was confirmed by fetopathological examination. One fetus in our series was diagnosed with Meckel Gruber-like syndrome, with hyperechogenic and cystic kidneys associated with vermian agenesis and femoral incurvation. A TOP was performed. Renal cystic lesions were present in three of our six cases of Ivemark II syndrome. In two of these cases, early diagnosis was easy because of a family history of Ivemark syndrome; no associated anomalies were diagnosed on sonography even though the fetopathological examinations showed liver and pancreatic dysplasia in both cases. In the third case, renal cysts were associated with severe oligohydramnios and a Potter sequence. In this case too, the final diagnosis of Ivemark II was made by fetopathological examination (pancreatic dysplasia). None of the three cases had splenic anomalies. Ultrasound examination of these three cases was difficult because of severe oligohydramnios.
4 914 Chaumoitre et al. Table 2 Characteristics of fetuses with hyperechogenic kidneys and cysts diagnosed with a syndrome (n = 18) Syndrome GA (weeks) Family history Kidney size* AF Malformation Cyst size (mm) n Location Unilat/Bilat Postnatal follow-up Bardet Biedl (n = 3) 25 No + 1 Norm Hexadactyly < 5 One Medulla Unilat Good outcome 36 No + 4 Dim Polydactyly, Hirschprung < 5 Few Medulla Bilat CRF at 1 year 24 Yes + 1 Inc Hexadactyly, minor ventriculomegaly, micropenis < 7 Few Cortex, Medulla Bilat Unilat Obesity and mental retardation at 4 years Meckel Gruber (n = 9) 25 No + 5 Dim Occ defect, vermian agenesis < 5 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 27 weeks 6 11 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 21 weeks 21 Yes + 5 Dim Occ defect, vermian agenesis, club feet 18 No + 5 Dim Occ encephalocele > 5 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 23 No + 5 Dim Ventriculomegaly, vermian agenesis 3 6 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 29 weeks 17 Yes + 3 Norm Occ encephalocele, microcephaly NA Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 22 No > 5 Dim Occ defect, DW, ventriculomegaly 2 10 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 22 weeks 24 No Dim Occ encephalocele, polydactyly NA Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 13 Yes + 3 Norm Occ encephalocele, polydactyly < 5 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 15 weeks 18 No + 3 Dim DW, ventriculomegaly < 5 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP 18 weeks Meckel Gruber like (n = 1) 22 Cons N Dim Vermian agenesis, femoral incurvation < 5 Few Cortex Bilat TOP Ivemark II (n = 3) 20 Yes Dim US: none < 5 Few Cortex Bilat TOP FP: liver and pancreatic dysplasia 26 No + 2 Dim US: Potter aspect < 5 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP FP: pancreatic dysplasia 21 Yes + 8 Dim US: none < 5 Num Diffuse Bilat TOP FP: liver and pancreatic dysplasia Jarcho Levin (n = 1) 22 No Dim Thoracic and vertebral 6 Num NA Bilat TOP Beemer (n = 1) 22 Cons 2 Dim Platyspondyly, narrow thorax, micromelia < 5 Num Cortex Bilat TOP In all of these cases, there was an absence of corticomedullary differentiation. *Renal length expressed as SD of the mean 4. Abst, absent; AF, amniotic fluid; Bilat, bilateral; Cons, consanguinity; CRF, chronic renal failure; Dim, diminished; DW, Dandy Walker malformation; FP, fetopathological examination; GA, gestational age at diagnosis; Inc, increased; NA, not available; Norm, normal; Num, numerous; Occ, occipital; TOP, termination of pregnancy; Unilat, unilateral; US, ultrasound.
5 Hyperechogenic cystic kidneys 915 Figure 3 Ultrasound examination of a 24-week fetus presenting with large cystic kidneys (a, calipers) associated with polydactyly (b, ellipse) and encephalocele (c, arrow) with ventriculomegaly (c, star). The kidney is markedly enlarged (+ 4.5 SD) and there is no corticomedullary differentiation. Sonographic diagnosis of Meckel Gruber syndrome was confirmed after termination of the pregnancy. Our only case of Jarcho Levin syndrome was diagnosed at 22 weeks and presented numerous renal cysts with an absence of CMD and severe oligohydramnios. The associated malformations (spondylocostal and costovertebral dysplasia) allowed sonographic diagnosis, and a TOP was performed. One case in our series was diagnosed with Beemer syndrome (short-rib polydactyly syndrome). Ultrasound examination performed at 22 weeks of gestation showed small hyperechogenic kidneys with numerous cortical cysts and oligohydramnios. The thorax was narrow and there was platyspondyly associated with micromelia and incurvated long bones. A TOP with fetopathological examination confirmed the diagnosis of Beemer syndrome and identified polydactyly of the feet that had not been noticed on ultrasound examination. The parents were first cousins. DISCUSSION Large hyperechogenic kidneys are seen occasionally at the time of a routine ultrasound examination. They represent a difficult diagnosis especially when the amniotic fluid volume is normal. The presence of renal cysts in association with hyperechogenic kidneys is not uncommon and management of these cases has not been described in the literature. Before searching for a nephropathy, diagnoses of renal tract anomalies (obstructive cystic dysplasia or MKD) must be excluded. MKD is usually unilateral, with a normal contralateral kidney, and the typical sonographic findings include a mass with multiple cysts of varying sizes without connections between them and without normal parenchyma. The main differential diagnosis is ureteropelvic junction (UPJ) obstruction 5. Obstructive cystic dysplasia can occur with UPJ obstruction or with other urinary tract obstructions, such as posterior urethral valves in male fetuses. Simple renal cyst can also be a differential diagnosis, especially in early pregnancy. Blazer et al. 6 described 28 fetuses with simple renal cyst (1/1100 pregnancies). In the absence of associated anatomical or chromosomal abnormalities, the majority of cysts will resolve during pregnancy without sequelae (89% in their series). They concluded that this transient evolution may represent a distinct entity within the spectrum of cystic kidney diseases 6. In the case of renal cysts associated with hyperechogenic kidneys, genetic survey and ultrasound examination of the parents and grandparents is useful. A detailed ultrasound examination is mandatory, with careful attention being paid to hands and feet, thorax and spine, and posterior fossa. Fetal kidneys must be measured and compared with reference tables 4, and CMD, renal echogenicity, cyst characteristics (size, location, number) and amniotic fluid volume must be analyzed. Karyotyping should be discussed, particularly if other malformations are detected 7. Our retrospective study was based on ultrasound examinations and none of the cases underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Over the last 10 years, fast single-shot MRI has become recognized as a powerful tool with which to explore fetal brain abnormalities. Its contribution to the analysis of urinary tract abnormalities is far less well-developed, although this method has been proved useful in small series 8 10.Withregardto nephropathy, the potential contribution of MRI is not currently well-defined and ultrasound examination is still the major imaging tool, despite its usefulness in cases with inconclusive sonographic findings (maternal obesity and/or oligohydramnios). T2-weighted images with high resolution have allowed visualization of cysts in cases of ARPKD 9,11. The fetal MRI appearance of ARPKD has been described with increased renal signal intensity on T2-weighted images 12 and low renal signal intensity on T1-weighted images 13 as a result of high water content in the renal parenchyma, consistent with tiny renal cysts. RARE-MR urography (thick-slab heavily T2-weighted sequence) can be used to show directly the microcystic dilatation of collecting ducts, as described by Kern et al. 14 in children. The use of this sequence in the fetus has been described recently 15,16. MRI is not hampered by a lack of amniotic fluid and, in addition to renal analysis, it can be used to look for pulmonary hypoplasia or associated brain malformations.
6 916 Chaumoitre et al. Table 3 Characteristics of hereditary cystic renal pathologies in our series Transmission Frequency Main findings Fetal renal cysts Autosomal dominant ADPKD 1/ Moderately enlarged hyperechogenic kidneys, increased CMD, normal amniotic fluid volume, uncommon associated malformations 2 Autosomal recessive ARPKD 1/ Enlarged hyperechogenic kidneys, absence of CMD, oligohydramnios 7, uncommon associated malformations Meckel Gruber Rare 22, 25% Medullary cystic dysplasia, severe oligohydramnios, CNS recurrence risk anomaly (occipital defect), polydactyly Bardet Biedl 1/ Enlarged hyperechogenic kidneys (30 100%), absence of CMD, digital anomalies (70%) 3,23,24,25, delayed onset of the classic symptoms 3 Ivemark II Rare 26,27 Asplenia-polysplenia, cystic liver, kidney and pancreas, often diagnosed only by FP examination, prognosis poor 28 Jarcho Levin Beemer Chromosomal aberration Trisomy 13 Rare, high prevalence in Puerto Rico Spondylothoracic dysplasia, generally lethal 29 Rare 2,18,19,20, 11% in our series 31% in our series 100% in our series 27% in our series 50% in our series Uncommon Narrow ribs, micromelia, multiple anomalies of major organs, Uncommon 30 with or without polydactyly 30,31,32 33% 1 (none in our five cases) ADPKD, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; ARPKD, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease; CMD, corticomedullary differentiation; CNS, central nervous system; FP, fetopathological. Hyperechogenic kidneys and renal cysts (32%) Exclusion of: simple renal cyst, multicystic dysplastic kidney, obstructive cystic dysplasia Family history, ultrasound examination of parents, genetic counseling, karyotyping PKD No Associated malformations Yes syndromes ARPKD polydactyly: (11% cortical cysts, Bardet Biedl AF normal, Beemer kidney size: +1 to +5 SD, family history +++) occipital defect, Dandy Walker malformation: MG or MG-like ADPKD (29% cysts (cortex or medulla), CMD variable, AF diminished in 78%, kidney size: +1.5 to +15 SD (mean +5 SD)) thoracic and/or spine malformation: Jarcho Levin Beemer Figure 4 Management flow chart based on our series, for cases of hyperechogenic kidney with renal cysts. ADPKD, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease; ARPKD, autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease; AF, amniotic fluid; CMD, corticomedullary differentiation; MG, Meckel Gruber syndrome. The most frequent genetically transmitted cystic renal diseases are ARPKD and ADPKD 1. Cystic kidneys are part of many hereditary diseases that may present many associated anomalies 1. The hereditary cystic renal pathologies in our series with their main findings are summarized in Table 3. Apart from the pathologies of our sample, renal cysts could be present in other autosomal dominant pathologies (tuberous sclerosis, Beckwith Wiedemann syndrome), autosomal recessive diseases (Jeune, Fryns and Zellwegger syndromes, glutaric aciduria II), chromosomal aberrations (T18, T21), orofacial X-linked syndrome and VACTERL syndrome 1. In our series, the characteristics of the cysts (size, location, number) were not very useful for diagnosis. In 56% of the cases, cysts were small (< 5 mm) and in the majority of the cases they were bilateral (73%), especially in cases of syndromes (89%). Cortical cysts were common in ADPKD (3/3) and occurred in four
7 Hyperechogenic cystic kidneys 917 of nine cases in ARPKD. The number of cysts varied according to the gestational age at diagnosis. It was the presence of an associated malformation that proved most useful in improving diagnostic accuracy. However, sonography is not 100% sensitive, especially in cases of severe oligohydramnios. In these cases amnioinfusion or fetal MRI could be used. In conclusion, renal cysts associated with hyperechogenic kidneys are not uncommon. In our series, location, size and number of cysts were not specific and ultrasound examination was particularly useful in looking for associated malformations (Figure 4). Familial history and genetic survey were also essential. Often, the clue to diagnosis will be the demonstration of an associated malformation. If no malformation is found, the main diagnosis remains PKD, i.e. ARPKD or ADPKD. REFERENCES 1. Avni FE, Garel L, Hall M, Rypens F. Perinatal approach to anomalies of the urinary tract, adrenal and genital system. In Perinatal Imaging from Ultrasound to MR Imaging, AvniFE (ed). Springer: Berlin, 2002; Brun M, Maugey-Laulom B, Eurin D, Didier F, Avni EF. Prenatal sonographic patterns in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: a multicenter study. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: Cassart M, Eurin D, Didier F, Guibaud L, Avni EF. Antenatal renal sonographic anomalies and postnatal follow-up of renal involvement in Bardet Biedl syndrome. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2004; 24: Cohen HL, Cooper J, Eisenberg P, Mandel FS, Gross BR, Goldman MA, Barzel E, Rawlinson KF. Normal length of fetal kidneys: sonographic study in 397 obstetric patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1991; 157: Eckoldt F, Woderich R, Smith RD, Heling KS. Antenatal diagnostic aspects of unilateral multicystic kidney dysplasia sensitivity, specificity, predictive values, differential diagnoses, associated malformations and consequences. Fetal Diagn Ther 2004; 19: Blazer S, Zimmer EZ, Blumenfeld Z, Zelikovic I, Bronshtein M. Natural history of fetal simple renal cysts detected in early pregnancy. JUrol1999; 162: Winyard P, Chitty L. Dysplastic and polycystic kidneys: diagnosis, associations and management. Prenat Diagn 2001; 21: Poutamo J, Vanninen R, Partanen K, Kirkinen P. Diagnosing fetal urinary tract abnormalities: benefits of MRI compared to ultrasonography. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 2000; 79: Cassart M, Massez A, Metens T, Rypens F, Lambot MA, Hall M, Avni FE. Complementary role of MRI after sonography in assessing bilateral urinary tract anomalies in the fetus. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2004; 182: Caire JT, Ramus RM, Magee KP, Fullington BK, Ewalt DH, Twickler DM. MRI of fetal genitourinary anomalies. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2003; 181: Liu YP, Cheng SJ, Shih SL, Huang JK. Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease: appearance on fetal MRI. Pediatr Radiol 2006; 36: Nishi T. Magnetic resonance imaging of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in utero. J Obstet Gynaecol 1995; 21: Nasu K, Yoshimatsu J, Anai T, Miyakawa I, Komatsu E, Maeda T. Magnetic resonance imaging of fetal autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 1998; 24: Kern S, Zimmerhackl LB, Hildebrandt F, Ermisch-Omran B, Uhl M. Appearance of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease in magnetic resonance imaging and RARE-MRurography. Pediatr Radiol 2000; 30: Chaumoitre K, Wikberg E, Shojai R, Merrot T, D Ercole C, Girard N, Panuel M. Fetal magnetic resonance hydrography: evaluation of a single-shot thick-slab RARE (rapid acquisition with relaxation enhancement) sequence in fetal thoracoabdominal pathology. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2006; 27: Brugger PC, Mittermayer C, Prayer D. A new look at the fetus: thick-slab T2-weighted sequences in fetal MRI. Eur J Radiol 2006; 57: Koptides M, Deltas CC. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: molecular genetics and molecular pathogenesis. Hum Genet 2000; 107: MacDermot KD, Saggar-Malik AK, Economides DL, Jeffery S. Prenatal diagnosis of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (PKD1) presenting in utero and prognosis for very early onset disease. JMedGenet1998; 35: Ceccherini I, Lituania M, Cordone MS, Prefumo F, Gusmano R, Callea F, Archidiacono N, Romeo G. Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease: prenatal diagnosis by DNA analysis and sonography at 14 weeks. Prenat Diagn 1989; 9: Edwards OP, Baldinger S. Prenatal onset of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. Urology 1989; 34: Zerres K, Mucher G, Becker J, Steinkamm C, Rudnik- Schoneborn S, Heikkila P, Rapola J, Salonen R, Germino GG, Onuchic L, Somlo S, Avner ED, Harman LA, Stockwin JM, Guay-Woodford LM. Prenatal diagnosis of autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD): molecular genetics, clinical experience, and fetal morphology. Am J Med Genet 1998; 76: Mittermayer C, Lee A, Brugger PC. Prenatal diagnosis of the Meckel-Gruber syndrome from 11th to 20th gestational week. Ultraschall Med 2004; 25: Gershoni-Baruch R, Nachlieli T, Leibo R, Degani S, Weissman I. Cystic kidney dysplasia and polydactyly in 3 sibs with Bardet-Biedl syndrome. Am J Med Genet 1992; 44: Ritchie G, Jequier S, Lussier-Lazaroff J. Prenatal renal ultrasound of Laurence-Moon-Biedl syndrome. Pediatr Radiol 1988; 19: Dar P, Sachs GS, Carter SM, Ferreira JC, Nitowsky HM, Gross SJ. Prenatal diagnosis of Bardet-Biedl syndrome by targeted second-trimester sonography. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2001; 17: Torra R, Alos L, Ramos J, Estivill X. Renal-hepatic-pancreatic dysplasia: an autosomal recessive malformation. JMedGenet 1996; 33: Abbi R, Daum F, Kahn E. Ontogeny of renal dysplasia in Ivemark syndrome: light and immunohistochemical characterization. Ann Clin Lab Sci 1999; 29: Neuhaus TJ, Sennhauser F, Briner J, Van Damme B, Leumann EP. Renal-hepatic-pancreatic dysplasia: an autosomal recessive disorder with renal and hepatic failure. Eur J Pediatr 1996; 155: Cornier AS, Ramirez N, Arroyo S, Acevedo J, Garcia L, Carlo S, Korf B. Phenotype characterization and natural history of spondylothoracic dysplasia syndrome: a series of 27 new cases. Am J Med Genet A 2004; 128: Myong NH, Park JW, Chi JG. Short-rib polydactyly syndrome, Beemer-Langer type, with bilateral huge polycystic renal dysplasia: an autopsy case. J Korean Med Sci 1998; 13: den Hollander NS, van der Harten HJ, Laudy JA, van de Weg P, Wladimiroff JW. Early transvaginal ultrasonographic diagnosis of Beemer-Langer dysplasia: a report of two cases. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 1998; 11: Vujanic GM, Hunt NC. New case of Beemer-Langer syndrome. Pediatr Dev Pathol 2000; 3:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review
 Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
Radiological and pathologic findings of fetal renal cystic diseases and associated fetal syndromes: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-2835 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors:
GU Ultrasound in First Trimester
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management Outline 1. Renal Anomalies Urinary Tract Dilation Aberrant Early Development Defects Terminal Maturation Alfred Abuhamad, M.D.
Urinary Tract Abnormalities
 Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Urinary Tract Abnormalities Dr Hennie Lombaard Senior Specialist Maternal and Fetal Medcine Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Level 7 Pretoria Academic Hospital Pictures from The 18 to 23 weeks scan
Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Congenital Renal Anomalies: A Pictorial Review
 J Radiol Sci 2014; 39: 77-84 Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Congenital Renal Anomalies: A Pictorial Review Yu-Peng Liu 1,3 Su-Chiu Chen 2,3 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial Hospital, Hsinchu,
J Radiol Sci 2014; 39: 77-84 Fetal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Congenital Renal Anomalies: A Pictorial Review Yu-Peng Liu 1,3 Su-Chiu Chen 2,3 Department of Radiology 1, Mackay Memorial Hospital, Hsinchu,
Hereditary polycystic kidney diseases in children: changing sonographic patterns through childhood
 Pediatr Radiol (2002) 32: 169 174 DOI 10.1007/s00247-001-0624-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fred E. Avni Gretel Guissard Michelle Hall Franc oise Janssen Viviane DeMaertelaer Franc oise Rypens Hereditary polycystic
Pediatr Radiol (2002) 32: 169 174 DOI 10.1007/s00247-001-0624-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Fred E. Avni Gretel Guissard Michelle Hall Franc oise Janssen Viviane DeMaertelaer Franc oise Rypens Hereditary polycystic
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management
 Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Fetal Renal Malformations: The Role of Ultrasound in Diagnosis & Management 12 weeks Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School 13 weeks 2nd trimester Medullary pyramids Renal Sinus Cortex 2nd
Renal Cystic Disease. Dr H Bierman
 Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Renal Cystic Disease Dr H Bierman Objectives Be able to diagnose renal cystic disease Genetic / non-genetic Be able to describe patterns of various renal cystic disease on routine imaging studies Be able
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Effective February 2007 10 16% renal agenesis complete absence of the kidneys occurs when ureteric buds fail to develop Or degenerate before
Fetal Urologic Anomalies
 Fetal Urologic Anomalies Kathryn Drennan, MD Elizabeth McKinney, MD MultiCare Regional Maternal-Fetal Medicine What you should know They are common Account for 15%-20% of all congenital anomalies Associated
Fetal Urologic Anomalies Kathryn Drennan, MD Elizabeth McKinney, MD MultiCare Regional Maternal-Fetal Medicine What you should know They are common Account for 15%-20% of all congenital anomalies Associated
Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System
 A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
A5 Developmental Abnormalities of the Kidneys and GU System Erin Parilla, MD Neonatologist Pediatrix Medical Group, Tampa, FL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated she has no significant
Ultrasound examination of fetuses with cystic renal changes or hyperechoic kidneys includes assessment of [1]:
![Ultrasound examination of fetuses with cystic renal changes or hyperechoic kidneys includes assessment of [1]: Ultrasound examination of fetuses with cystic renal changes or hyperechoic kidneys includes assessment of [1]:](/thumbs/84/90654767.jpg) Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of cystic renal disease Author: Tulin Ozcan, MD Section Editors: Louise Wilkins-Haug, MD, PhD, Deborah Levine,
Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2017 UpToDate Prenatal sonographic diagnosis of cystic renal disease Author: Tulin Ozcan, MD Section Editors: Louise Wilkins-Haug, MD, PhD, Deborah Levine,
Kidneycentric. Follow this and additional works at:
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker All Kidneycentric 2014 Renal Dysplasia Halana V. Whitehead Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis Follow this and additional
Renal Ultrasonography in Neonates. Abstract: Introduction:
 Renal Ultrasonography in Neonates. Mahmoud Adel Abdel-Moneim, Mahmoud Mohi-Eldin El-Kersh, Mohamed Alaa Thabet, Magdy Abdel-Fattah Ramadan and Hossam H. Zeid. From Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of
Renal Ultrasonography in Neonates. Mahmoud Adel Abdel-Moneim, Mahmoud Mohi-Eldin El-Kersh, Mohamed Alaa Thabet, Magdy Abdel-Fattah Ramadan and Hossam H. Zeid. From Department of Pediatrics, Faculty of
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One. Howard J. Sachs, MD
 Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
Cystic Renal Disease, for USMLE Step One Howard J. Sachs, MD www.12daysinmarch.com The Major Players Medullary Sponge Kidney (MSK) Polycystic Kidney Disease (PKD) Autosomal Recessive: Childhood Autosomal
CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View)
 Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
Imaging of the Fetal Brain; Normal & Abnormal Alfred Abuhamad, M.D. Eastern Virginia Medical School CNS Embryology 5th Menstrual Week (Dorsal View) Day 20 from fertilization Neural plate formed in ectoderm
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences. Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report
 International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences RESEARCH ARTICLE PATHOLOGY Meckel-Gruber Syndrome Associated with CNS Malformations A Case Report Corresponding Author DR. N. HIMA BINDU Assistant Professor,
Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XIX, nº 74, pág. 90-107, Abr.-Jun., 2007 Cystic Renal Disease of Childhood Ellen Chung Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Terminology Cyst Polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY
 RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
RENAL SCINTIGRAPHY IN THE 21 st CENTURY 99m Tc- MAG 3 with zero time injection of Furosemide (MAG 3 -F 0 ) : A Fast and Easy Protocol, One for All Indications Clinical Experience Congenital Disorders PROTOCOL
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management?
 Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Prenatal Diagnosis of Central Nervous System (CNS) Pathologies: does Fetal MRI help in their management? Daniela Prayer, Division of Neuroradiology and Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University Vienna/Austria
Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
 Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Impact of Prenatal Detection and Diagnosis Dr Merna Atiyah Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
Major Forms of Congenital Heart Disease: Impact of Prenatal Detection and Diagnosis Dr Merna Atiyah Consultant Pediatric and Fetal Cardiology King Abdulaziz Cardiac Center, National Guard Hospital Riyadh
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea
 Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Han-Sung Kwon M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Konkuk University School of Medicine Seoul, Korea Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain Embryologic features of the developing hindbrain
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound. trimester on
 Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
Spectrum of Cranio-facial anomalies during 2 Ultrasound nd trimester on Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Dave, S. Solanki; Ahmedabad/IN Keywords: Obstetrics (Pregnancy
ISUOG Basic Training. Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract. Seshadri Suresh, India
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Urinary Tract Seshadri Suresh, India Learning objectives 13 & 14 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: describe
Imaging and Classification of Congenital Cystic Renal Diseases
 Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective vni et al. Congenital Cystic Renal Disease Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective FOCUS ON: Fred E. vni 1 Catherine Garel 2 Marie Cassart 1 Nicky D Haene 3 Michele
Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective vni et al. Congenital Cystic Renal Disease Pediatric Imaging Clinical Perspective FOCUS ON: Fred E. vni 1 Catherine Garel 2 Marie Cassart 1 Nicky D Haene 3 Michele
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI
 Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Measurements of the Posterior Fossa in Normal Fetus MRI Ber Roee, 3 rd year medical student, Sackler School of Medicine, Tel Aviv University Supervised by: Dr. Katorza Eldad, Antenatal Diagnostic Unit,The
Association Of Single Umbilical Artery With Common And Rare Congenital Malformations
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 4 Number 1 Association Of Single Umbilical Artery With Common And Rare Congenital Malformations M Sur, S Nayler, R Muc Citation M Sur,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pediatrics and Neonatology Volume 4 Number 1 Association Of Single Umbilical Artery With Common And Rare Congenital Malformations M Sur, S Nayler, R Muc Citation M Sur,
Central nervous system. Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities
 Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Obstetrics Content Outline Obstetrics - Fetal Abnormalities Many congenital malformations of the CNS result from incomplete closure of the neural tube Effective February 2007 10 16% the most common neural
Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children
 Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of the M.Sc degree in Pediatrics Submitted by Ahmed Ibrahim Abulkhir Khayyal Under
Clinical characterization of polycystic kidney diseases in infants and children Thesis Submitted for partial fulfillment of the M.Sc degree in Pediatrics Submitted by Ahmed Ibrahim Abulkhir Khayyal Under
Renal ultrasonography not required in babies with isolated minor ear. anomalies
 ADC-FNN Online First, published on October 13, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2005.083329 Renal ultrasonography not required in babies with isolated minor ear Corresponding author: S A Deshpande Royal Shrewsbury
ADC-FNN Online First, published on October 13, 2005 as 10.1136/adc.2005.083329 Renal ultrasonography not required in babies with isolated minor ear Corresponding author: S A Deshpande Royal Shrewsbury
Hereditary polycystic kidney disease: genetic diagnosis and counseling
 GUIDELINES IN FOCUS Whittle M et al. Hereditary polycystic kidney disease: genetic diagnosis and counseling Doença policística renal hereditária: diagnóstico genético e aconselhamento Participants: Martin
GUIDELINES IN FOCUS Whittle M et al. Hereditary polycystic kidney disease: genetic diagnosis and counseling Doença policística renal hereditária: diagnóstico genético e aconselhamento Participants: Martin
DISCLOSURES THE FETAL GENITOURINARY TRACT LEARNING OBJECTIVES OUTLINE THE NORMAL URINARY TRACT THE NORMAL URINARY TRACT. Normal Fetal Kidneys
 THE FETAL GENITOURINARY TRACT Beverly G., MD Emeritus Professor of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Director of Fetal Imaging The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Philadelphia,
THE FETAL GENITOURINARY TRACT Beverly G., MD Emeritus Professor of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine University of Pennsylvania Director of Fetal Imaging The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia Philadelphia,
Genetics in Nephrology. Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory
 Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
Genetics in Nephrology Saeid Morovvati Associate Professor of BMSU Director of Biogene Laboratory Genetics in: A. Congenital Anomalies of the Kidney and Urinary Tract B. Cystic Diseases of the Kidney C.
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy. Basic Training
 ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
ISUOG Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the differences between the ultrasound appearances
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing Between Normal and Abnormal Appearances of the Fetal Anatomy Reem S. Abu-Rustum, Lebanon Learning Objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Compare the
Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients
 Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Article Diagnosis of Congenital Cardiac Defects Between 11 and 14 Weeks Gestation in High-Risk Patients Zeev Weiner, MD, Abraham Lorber, MD, Eliezer Shalev, MD Objective. To examine the feasibility of
Ultrasound Anomaly Details
 Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
Appendix 2. Association of Copy Number Variants With Specific Ultrasonographically Detected Fetal Anomalies Ultrasound Anomaly Details Abdominal wall Bladder exstrophy Body-stalk anomaly Cloacal exstrophy
28/04/2016. I have nothing to declare and no financial. interest or relationship to disclose
 I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Corporate Medical Policy Invasive Prenatal (Fetal) Diagnostic Testing File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: invasive_prenatal_(fetal)_diagnostic_testing 12/2014 3/2018
Summary and conclusions
 Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Summary and conclusions 7 Chapter 7 68 Summary and conclusions Chapter 1 provides a general introduction to this thesis focused on the use of ultrasound (US) in children with abdominal problems. The literature
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry
 ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
ADPedKD: detailed description of data which will be collected in this registry I. Basic data 1. Patient ID: will be given automatically 2. Personal information - Date of informed consent: DD/MM/YYYY -
Supplemental Information
 ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
ARTICLE Supplemental Information SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE 6 Mosaic and Partial Trisomies Thirty-eight VLBW infants were identified with T13, of whom 2 had mosaic T13. T18 was reported for 128 infants, of whom
Isolated Choroid Plexus Cyst
 Isolated Choroid Plexus Cyst This guideline was updated in April 2015 by Dr Joana De Sousa, with input from members of the New Zealand Maternal Fetal Medicine Network. Background Midtrimester soft markers
Isolated Choroid Plexus Cyst This guideline was updated in April 2015 by Dr Joana De Sousa, with input from members of the New Zealand Maternal Fetal Medicine Network. Background Midtrimester soft markers
Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter?
 Clinical Research Facility Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter? Nicholas J A Webb BMedSci DM FRCP FRCPCH Honorary Professor of Paediatric
Clinical Research Facility Central Manchester University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Unilateral renal agenesis does it matter? Nicholas J A Webb BMedSci DM FRCP FRCPCH Honorary Professor of Paediatric
Multicystic dysplastic kidney: a review of eleven years ( )
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advance Access publication 14 February 2012 Multicystic dysplastic kidney: a review of eleven years (2000 2010) Helena Rios, Raquel Santos, Clara Gomes, António Jorge Correia Paediatric
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Advance Access publication 14 February 2012 Multicystic dysplastic kidney: a review of eleven years (2000 2010) Helena Rios, Raquel Santos, Clara Gomes, António Jorge Correia Paediatric
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease. Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology
 Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Tubulointerstitial Renal Disease Anna Vinnikova, MD Division of Nephrology Part I: Cystic Renal Disease www.pathguy.com Simple cysts Simple cysts May be multiple Usually 1 5cm, may be bigger Translucent,
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal diagnosis of Bardet Biedl syndrome in a case of hyperechogenic kidneys: Clinical use of DNA sequencing
 CASE REPORT Prenatal diagnosis of Bardet Biedl syndrome in a case of hyperechogenic kidneys: Clinical use of DNA sequencing Santiago Garcia-Tizon Larroca, Vangeliya Blagoeva Atanasova, Maria Orera Clemente,
CASE REPORT Prenatal diagnosis of Bardet Biedl syndrome in a case of hyperechogenic kidneys: Clinical use of DNA sequencing Santiago Garcia-Tizon Larroca, Vangeliya Blagoeva Atanasova, Maria Orera Clemente,
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan
 ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
ISUOG The 20 Planes Approach to the Routine Mid Trimester Scan Learning objective At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Explain how to perform a structured routine examination, including measurements,
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Imaging in cystic renal disease
 Arch Dis Child 2000;83:401 407 401 CURRENT TOPIC Department of Radiology, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust, Great Ormond Street, London WC1N 3JH, UK RdeBruyn I Gordon Correspondence
Arch Dis Child 2000;83:401 407 401 CURRENT TOPIC Department of Radiology, Great Ormond Street Hospital for Children NHS Trust, Great Ormond Street, London WC1N 3JH, UK RdeBruyn I Gordon Correspondence
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound. Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa
 Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
UAB P30 CORE A: The Hepato-Renal Fibrocystic Diseases Translational Resource
 PKD Foundation UAB P30 CORE A: The Hepato-Renal Fibrocystic Diseases Translational Resource http://www.arpkdstudies.uab.edu/ Director: Co-Director: Lisa M. Guay-Woodford, MD William E. Grizzle, MD, PhD
PKD Foundation UAB P30 CORE A: The Hepato-Renal Fibrocystic Diseases Translational Resource http://www.arpkdstudies.uab.edu/ Director: Co-Director: Lisa M. Guay-Woodford, MD William E. Grizzle, MD, PhD
Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Nuclear Medicine Volume 5 Number 1 Congenital Pediatric Anomalies: A Collection of Abdominal Scintigraphy Findings: An Imaging Atlas V Vijayakumar, T Nishino Citation
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 587 591 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenoma(s), adrenal, gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging in, 533 534 hyperfunctioning versus
Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 12 (2004) 587 591 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adenoma(s), adrenal, gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging in, 533 534 hyperfunctioning versus
Original Article. Associated Anomalies and Clinical Outcomes in Infants with Omphalocele: A Single-centre 10-year Review
 HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:220-224 Original Article Associated Anomalies and Clinical Outcomes in Infants with Omphalocele: A Single-centre 10-year Review YY CHEE, MSC WONG, RMS WONG, KY WONG,
HK J Paediatr (new series) 2018;23:220-224 Original Article Associated Anomalies and Clinical Outcomes in Infants with Omphalocele: A Single-centre 10-year Review YY CHEE, MSC WONG, RMS WONG, KY WONG,
Basic Training. ISUOG Basic Training Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile
 ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
ISUOG Examining the Upper Lip, Face & Profile Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how to obtain the 3 planes required to assess the anatomy of the fetal face Recognise
Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease: Issues Regarding the Variability of Clinical Presentation1
 EDITORIAL COMMITTEE Tomas Berl. Editor William Heinrich Mark Paller Fred Silva Denver. CO Dallas. TX Minneapolis. MN Oklahoma City. OK DESCRIPTION OF THE NEPHROLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF
EDITORIAL COMMITTEE Tomas Berl. Editor William Heinrich Mark Paller Fred Silva Denver. CO Dallas. TX Minneapolis. MN Oklahoma City. OK DESCRIPTION OF THE NEPHROLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM AT THE UNIVERSITY OF
Gastrointestinal tract
 Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
Chapter 7 Gastrointestinal tract NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY Sonographically, the fetal stomach is visible from 9 weeks of gestation as a sonolucent cystic structure in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen.
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Foreword: Our Kidneys: A Lot Is Riding on Their Shoulders. Preface: Renal and Urologic Abnormalities in the Perinatal Period
 Renal and Urologic Issues Foreword: Our Kidneys: A Lot Is Riding on Their Shoulders Lucky Jain xv Preface: Renal and Urologic Abnormalities in the Perinatal Period Michelle N. Rheault and Larry A. Greenbaum
Renal and Urologic Issues Foreword: Our Kidneys: A Lot Is Riding on Their Shoulders Lucky Jain xv Preface: Renal and Urologic Abnormalities in the Perinatal Period Michelle N. Rheault and Larry A. Greenbaum
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Torch Infections and Prenatal Ultrasound Findings
 Tutorial [1] August 09, 2011 By Eran Casiff, MD [2] TORCH INFECTIONS AND PRENATAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Eran Casiff M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Kaplan Medical Center Rehovot 76100, Israel
Tutorial [1] August 09, 2011 By Eran Casiff, MD [2] TORCH INFECTIONS AND PRENATAL ULTRASOUND FINDINGS Eran Casiff M.D. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology Kaplan Medical Center Rehovot 76100, Israel
No conflict of interest to report
 Ultrasound Findings in Fetal Infection No conflict of interest to report Kim A. Boggess MD Ob Gyn UNC at Chapel Hill Learning Objectives At conclusion, participants will Identify maternal infections that
Ultrasound Findings in Fetal Infection No conflict of interest to report Kim A. Boggess MD Ob Gyn UNC at Chapel Hill Learning Objectives At conclusion, participants will Identify maternal infections that
Vesicoureteral Reflux in Neonates with Hydronephrosis; Role of Imaging Tools
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Dec 2009; Vol 19 (No 4), Pp:347-353 Vesicoureteral Reflux in Neonates with Hydronephrosis; Role of Imaging Tools Hamid Mohammadjafari 1, MD; Alireza Alam* 2,MD; Mehrnoosh
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Dec 2009; Vol 19 (No 4), Pp:347-353 Vesicoureteral Reflux in Neonates with Hydronephrosis; Role of Imaging Tools Hamid Mohammadjafari 1, MD; Alireza Alam* 2,MD; Mehrnoosh
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom. Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium
 Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
Controversies around antenatally detected PUJ syndrom Amy Piepsz, CHU St Pierre, Brussels, Belgium Editors : Anthony Caldamone, USA Pierre Mouriquand, France Newborn boy History of prenatally diagnosed
Congenital renal tract anomalies: outcome and follow-up of 402 cases detected antenatally between 1986 and 2001
 Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 134 143 Published online 19 January 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1788 Congenital renal tract anomalies: outcome and follow-up
Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 2005; 25: 134 143 Published online 19 January 2005 in Wiley InterScience (www.interscience.wiley.com). DOI: 10.1002/uog.1788 Congenital renal tract anomalies: outcome and follow-up
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except
 1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
1. Hypogonadism is usually encountered in the following conditions, except A. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia B. Noonan Syndrome C. Prader-Willi Syndrome D. Bardet-Biedl Syndrome 2. A 6 year old girl with
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2000) 15: 1373 1378 Original Article Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation Sonographic pattern of recessive polycystic kidney disease in young adults. Differences from the dominant
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal closure of the ductus arteriosus March 2007 Leone A, Fasnacht M, Beinder E, Arlettaz R, Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (LA, AR), University Hospital Zurich, Cardiology
Central nervous system
 Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Chapter 2 Central nervous system NORMAL SONOGRAPHIC ANATOMY The fetal brain undergoes major developmental changes throughout pregnancy. At 7 weeks of gestation, a sonolucent area is seen in the cephalic
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Coarctation of the aorta: difficulties in prenatal
 7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
7 Department of Fetal Cardiology, Guy's Hospital, London G K Sharland K-Y Chan L D Allan Correspondence to: Dr G Sharland, Department of Paediatric Cardiology, 1 lth Floor, Guy's Tower, Guy's Hospital,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Prenatal diagnosis and postnatal management of meconium pseudocysts September 2007 2 Burch E, Caduff JH, Hodel M, Berger TM, Neonatal and Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (BE,
Postnatal Imaging of Antenatal Hydronephrosis
 Review Special Issue: Pre- and Postnatal Management of Hydronephrosis TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 393 399 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.50 Postnatal Imaging of Antenatal Hydronephrosis
Review Special Issue: Pre- and Postnatal Management of Hydronephrosis TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2009) 9, 393 399 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2009.50 Postnatal Imaging of Antenatal Hydronephrosis
Case Based Fetal Lung Masses
 Case Based Fetal Lung Masses Advances in Fetal and Neonatal Imaging Course Orlando, Florida, January 28, 2017 Leann E. Linam, MD Associate Professor Radiology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences/
Case Based Fetal Lung Masses Advances in Fetal and Neonatal Imaging Course Orlando, Florida, January 28, 2017 Leann E. Linam, MD Associate Professor Radiology University of Arkansas for Medical Sciences/
Unilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney in children
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56: 75-79 Original Unilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney in children Çağla Serpil Doğan 1, Meral Torun-Bayram 1, Mustafa Devran Aybar 2 1 Division of Pediatric
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56: 75-79 Original Unilateral multicystic dysplastic kidney in children Çağla Serpil Doğan 1, Meral Torun-Bayram 1, Mustafa Devran Aybar 2 1 Division of Pediatric
Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot
 36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
36 Fetal Tetralogy of Fallot E.D. Bespalova, R.M. Gasanova, O.A.Pitirimova National Scientific and Practical Center of Cardiovascular Surgery, Moscow Elena D. Bespalova, MD Professor, Director Rena M,
Fetal MRI. Page 1 of 69
 Fetal MRI Poster No.: C-0878 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Kocaba# Köksel, M. A. Oztek, C. Y. Sanhal, S. Toru, #. Mendilcio#lu, M. #im#ek, K. Karaali; Antalya/TR Keywords: Obstetrics,
Fetal MRI Poster No.: C-0878 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: Y. Kocaba# Köksel, M. A. Oztek, C. Y. Sanhal, S. Toru, #. Mendilcio#lu, M. #im#ek, K. Karaali; Antalya/TR Keywords: Obstetrics,
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities. Basic Training
 ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Basic Training Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
ISUOG Basic Training Distinguishing between Normal & Abnormal Appearances of the Long Bones & Extremities Basic Training Learning objectives At the end of the lecture you will be able to: Describe how
Journal of Nephropathology
 www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.60 J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4):363-367 Journal of Nephropathology Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease
www.nephropathol.com DOI: 10.15171/jnp.2017.60 J Nephropathol. 2017;6(4):363-367 Journal of Nephropathology Rapidly progressive nephromegaly in a neonate with autosomal recessive poly cystic kidney disease
Fetal CNS MRI. Daniela Prayer. Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology. Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA
 Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART
 ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ULTRASOUND OF THE FETAL HEART Cameron A. Manbeian, MD Disclosure Statement Today s faculty: Cameron Manbeian, MD does not have any relevant financial relationships with commercial interests or affiliations
ISUOG Basic Training. Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon
 ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
ISUOG Basic Training Assessing the Neck & Chest Gihad Chalouhi, Lebanon Learning objectives 9 & 10 At the end of the lecture you will be able to: recognise the differences between the normal & most common
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain
 DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
DWI assessment of ischemic changes in the fetal brain Dafi Bergman, 4 th year Medical student in the 4-year program, Sackler school of medicine B.Sc Life and Medical Sciences, Tel Aviv University Supervised
G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve.
 G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. ANTENATAL HYRONEPHROSIS UROLOGICAL ASPECTS Dr Gianantonio Manzoni, FEAPU FRCS U.O.
G.Manzoni has documented that he has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. ANTENATAL HYRONEPHROSIS UROLOGICAL ASPECTS Dr Gianantonio Manzoni, FEAPU FRCS U.O.
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
 Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Case Studies [1] July 01, 2014 By Amar Udare, MBBS [2] Case History: 45-year-old female with vague pain in the abdomen. Case History: A 45-year-old female presented with vague pain in the abdomen. A USG
Summary. HVRA s Cardio Vascular Genetic Detailed L2 Obstetrical Ultrasound. CPT 76811, 76825, _ 90% CHD detection. _ 90% DS detection.
 What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
What is the role of fetal echocardiography (2D 76825, cardiovascular color flow mapping 93325) as performed in conjunction with detailed fetal anatomy scan (CPT 76811) now that AIUM requires limited outflow
Case Report Coexistent Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Extrapulmonary Sequestration
 Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 1460480, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1460480 Case Report Coexistent Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Extrapulmonary Sequestration Nao
Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 1460480, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/1460480 Case Report Coexistent Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia with Extrapulmonary Sequestration Nao
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma
 Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile ducts: a rare form of premalignant lesion of invasive cholangiocarcinoma Authors: R. Revert Espí, Y. Fernandez Nuñez, I. Carbonell, D. P. Gómez valencia,
A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES
 3 Original article A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES Dr. Urvish R. Parikh [1], Dr Sudhir B. Chandana [], Dr Vinay M. Rohra [3],, Dr Jay B. Pandya [5], Dr Ankit B. Kothari [4] Assistant
3 Original article A STUDY ON LONGTERM OUTCOMES OF POSTERIOR URETHRAL VALVES Dr. Urvish R. Parikh [1], Dr Sudhir B. Chandana [], Dr Vinay M. Rohra [3],, Dr Jay B. Pandya [5], Dr Ankit B. Kothari [4] Assistant
Comparative Effectiveness of a Pilot Patient-Centered Ultrasound Report for Hydronephrosis Management
 Comparative Effectiveness of a Pilot Patient-Centered Ultrasound Report for Hydronephrosis Management Geolani W. Dy, MD Society of Women in Urology 6 th Annual Winter Meeting January 21, 2017 Cultural
Comparative Effectiveness of a Pilot Patient-Centered Ultrasound Report for Hydronephrosis Management Geolani W. Dy, MD Society of Women in Urology 6 th Annual Winter Meeting January 21, 2017 Cultural

