CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE
|
|
|
- Karin Alexander
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Kansas Association of Osteopathic Medicine April 13 th, 2018 Jami Jackson DO, FAAP, MPH Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor of Pediatrics
2 I have no disclosures.
3 Objectives To discuss history taking, work up, diagnosis and management of children with child physical abuse: - Bruises - Neurologic trauma - Abdominal trauma - Skeletal trauma - Burns
4 Legal Definition of Child Abuse The Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act (CAPTA) A recent act or failure that results in death, serious physical or emotional harm, sexual abuse or exploitation, or imminent risk of serious harm; involves a child; and is carried out by a parent or caregiver who is responsible for the child s welfare
5 Child Abuse Statistics Every 10 seconds, a report of child abuse is made More common than asthma Child abuse does not discriminate it occurs in every gender, age, race/ethnicity, religion, SES, and spans all education levels More then 4 children die every day Approximately 70% of children that die from child abuse are under the age of 4 Estimated annual cost = $124 billion
6 Children At Risk Family characteristics Low SES Unemployment Lack of education Single parent home Young maternal age Multiple children Families with drug/etoh abuse, domestic violence, or mental illness Homes where there are unrelated people living there Child characteristics Prematurity Physical or developmental disabilities Under the age of 4 years *Male and female children are abused at the same rate
7 Consequences of Child Abuse Risk for psychological disorders, substance abuse, suicide More likely to engage in sexual risk taking, putting them at increased risk for STIs 25% more likely to be a pregnant teen 30% will later abuse their own children 9 times more likely to be involved in criminal activity
8 Clues in the History Concerning for Abuse History does not match the physical exam i.e. a newborn cannot roll off the couch Requires that you know developmental milestones of children Delay in care seeking
9 Questions to Ask Event witnessed? Who are the caregivers when injury/event occurred? If unwitnessed, who are the caregivers for the child in general? Identify the last witness(es) to well/asymptomat behavior Last location/point in time where the child was well/asymptomatic? Specific location where injury occurred? Timing of injury/event Identify the position/location of child immediately prior to injurious event and what the child was doing
10 Questions to Ask Identify mechanics of injurious event (twisting/falling backwards, forward, etc.) Surfaces/objects potentially impacted during injurious event? Specific body part(s) impacted during injurious event? Child s physical position after the injurious event? Nature of the child s first symptoms/reaction to injurious event Determine the first person that identified the child s symptoms/reaction to injurious event Order of appearance of ill symptoms Duration of ill symptoms Clothing worn at time of injury
11 Physical Exam A thorough head to toe physical exam with the patient completely undressed to examine all of their skin/body Document all abnormalities in your exam and also in pictures if possible It s ok to ask the child, how did you get this ouchie? and this ouchie?
12 Case 1 2 month old term infant presents to the PCP s office for her WCC. Pt has been growing appropriately and developmentally normal. On your physical exam, there is bruising to the back without any other findings. Neuro exam is normal. What is your differential? What is work up needs to be done?
13 CHILD ABUSE PART 1: BRUISING
14 Bruising is the single most common presentation of child physical abuse
15 Young Infants and Bruises Bruises rare in children less than 6 months of age Increases as become more mobile and adventurous Relate to developmental stage No cruise, no bruise
16 Those who don t cruise rarely bruise Sugar NF, Taylor JA, Feldman KW. Bruises in infants and toddlers. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999:153: N=930 children Sugar, et al. "Bruises in infants and toddlers" Archives of Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. 1999; 153: 399-
17 Bruise Colors As blood cells and hemoglobin metabolized, bruise changes color Colors include red, purple, black, violet, blue, yellow, green and/or brown No predictable order or chronology Many factors affect rate of resolution
18 Factors Affecting Resolution Amount of blood Depth of leakage to surface Amount of force Amount of tissue damage Age of person Underlying skin color Vascularity of underlying tissue Location of the bruise Drugs Loosely attached skin (periorbital or genital) bruise easier than skin under tension Concurrent medical conditions
19 It is Not Possible to Date Bruises No predictable order or progression One study abused children? Literature review and synthesis. Pediatrics 1996;97: concluded that yellow = older than 18 hrs Schwartz AJ, Ricci LR. How accurately can bruises be aged in 2005 review of 167 articles Maguire S, Mann Mk, Sibert J, Kemp A. Can you age bruises accurately in children? A systematic review. Arch Diseases Child. 2005;90: found 3 fit for summarizing evidence: Timing of yellow unclear Physician accuracy of timing < 40% Inter-observer, intra-observer reliability poor Concluded use of color to date should be avoided
20 Patterns of Bruising in Childhood Suggestive of Abuse Maguire S, Mann MK, Sibert J and Kemp A. Arch Dis Child 2005;90: Systematic review investigate what patterns of bruising are diagnostic or suggestive of abuse , studies describing patterns of bruising in non-abused and abused children 23 studies: 7 non-abusive, 14 abusive, 2 both
21 Patterns of Bruising in Childhood Suggestive of Abuse Maguire S, Mann MK, Sibert J and Kemp A. Arch Dis Child 2005;90: Non Abusive Bruising: The prevalence, number, and location of bruising is related to increased motor development Non-mobile babies < 1%, crawling or cruising 17%, walking 53% Majority of school aged children have bruises Bruises are small, over bony prominences, and located in the front of body
22 Patterns of Bruising in Childhood Suggestive of Abuse Maguire S, Mann MK, Sibert J and Kemp A. Arch Dis Child 2005;90: Bruising common in abused children: Away from bony prominences Most common = head and neck, esp. face Second most common = buttocks, trunk, arms Bruises are large, multiple, clustered Patterned, imprint of object or uniform shape
23 Classification of Bruising (Jenny & Reece, 2009; Maguire, Mann, Sibert, & Kemp, 2005; Sugar, Taylor & Feldman, 1999) CONCERNING FOR ABUSE Face (not including forehead) Ears Neck Proximal arms (above the elbows) Wrist/hand Anterior or lateral chest Abdomen Back (excluding spinous/paraspinous) Buttock/genitalia Anterior/posterior thigh Foot Patterned/symmetric Any bruising in a child < 9 months of age NOT CONCERNING FOR ABUSE Head, not including face or ear Forehead Oral Distal arms (including elbow) Spinous/paraspinous Hips Anterior and posterior legs (shins, knees and calves) Ankle
24 Interpret Bruises in the Context of: Medical, social history Explanation given Clinical exam Developmental level of child Relevant work up
25 Other causes of unusual bruising Cultural practices Alternative medicine Illnesses associated with bruising Lab evaluation ITP, leukemia, Von Willebrand s
26 Challenges in the evaluation for possible abuse: Presentations of congenital bleeding disorders in childhood Jackson J, Carpenter S, Anderst J. Child Abuse Negl Feb;36(2): /189 (15.3%) children in the study that had bleeding disorder dx had an initial presentation of bruising that was concerning for child physical abuse 75.9 % of those 29 kids were <5 years of age 44.8% had von Willebrand disease (vwd) 51.8% had hemophilia 48.3% had a family history of a named bleeding disorder Children with bleeding disorders may present with bruising/bleeding that is clinically highly suggestive of child physical abuse
27 Bruising: Does the child need an evaluation for bleeding disorders? Situations in which a bleeding disorder evaluation may not be needed: clear disclosure of or independently witnessed abuse or nonabusive trauma other medical findings consistent with abuse or nonabusive trauma object- or hand-patterned bruising history clearly explains bruising Clues to presence of a bleeding disorder: petechiae at clothing line pressure sites bruising at sites of object pressure, such as in the pattern and location of infant seat fasteners severe bleeding disorders may also present with excessive diffuse bruising
28 Initial Testing Panel Prothrombin time Activated partial thromboplastin time VWF antigen VWF activity (Ristocetin cofactor) Factor VIII level Factor IX level Complete blood count with platelet count *Abnormal test results or further testing desired - consult a pediatric hematologist
29 Bruising in children: Practice patterns of pediatric hematologists and child abuse pediatricians (CAP) Jackson J, Miller M, Moffatt M, Sherman A, Anderst A. Clin Pediatr Jun; 54(6): total subjects, 275 CAP, 94 Pediatric Hematology with bruising concerning for abuse CAP saw 242 and 62 went to Heme % in CAP got head CTs, 0 in Heme - 31% in CAP got skeletal surveys, 0 in Heme seen by CAP dx with abuse, 0 in Heme dx with abuse - 61 with bruising not concerning for abuse Heme saw 28 and CAP saw 33-75% in Heme had testing for bleeding disorders, 0 in CAP - 11 in Heme dx with bleeding disorder, 0 in CAP In conclusion, Pediatric Hematologists and CAPs may perform different evaluations resulting in different diagnoses for similar clinical findings. Thus, where they are referred may play a big part in their final diagnosis
30 Case 1 Continued 2 month old term infant presents to the PCP s office for her WCC. You are discussing the bruises that you saw on your exam with the mom when the pt starts to have a generalized tonic clonic seizure x 5 minutes that self resolves. Afterwards, she is sleepy but arousable with normal vital signs. Head is atraumatic and normal in size/shape. Mom says that pt has been sleeping a little more since mom s boyfriend watched pt earlier this AM while mom went to work. Otherwise has been acting normal. Has not eaten since mom returned home about an hour ago. What is your differential? What is work up needs to be done?
31 CHILD ABUSE PART 2: NEUROLOGIC TRAUMA
32 Abusive Head Trauma Main cause of death from abuse Direct blow +/or shaking Subdural, subarachnoid, or intraparenchymal injury Evaluate for retinal hemorrhages
33 The most common trigger for abusive head injury but let s not call it the cause
34 Presentation of Inflicted Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) Spectrum of severity May be missed due to nonspecific symptoms: Vomiting Irritability Sleepiness Coma Seizure ALTE Apnea Cardiac Arrest
35 Who Needs A Head CT or MRI? Rubin, et al. Pediatrics. 2003;111: All patients with neurological symptoms and with concerns of child physical abuse If neurologically asymptomatic: Rib fractures Multiple fractures Facial injury All children < 6 months of age with suspicious injury * 30% of these children will have occult injury on imaging
36 Subdural Subarachnoid Intraparenchymal
37 Retinal Hemorrhage Caused from repetitive accelerationdeceleration forces due to shaking, causing shearing of the vessels in the eye
38 Sequelae of TBI Cognitive impairment Cerebral palsy loss/impairment of motor function Feeding problems Blindness Deafness
39 Case 1 Continued 2 month old term infant in your office for WCC. She had a bruising to the back and a seizure. Do you need to do any further work up?
40 CHILD ABUSE PART 3: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA
41 Abdominal Trauma 2 nd most common cause of death in abuse Usually blunt trauma May have delayed presentation
42
43 Who Needs Screening for Occult Abdominal Injury? Lindberg, et al. Pediatrics 2009; 124; <5 years old Suspected victim of physical abuse - Screening test AST and ALT - If AST or ALT >80 obtain abdominal CT * 3.2% of these children will have occult abdominal injuries
44 CHILD ABUSE PART 4: SKELETAL TRAUMA
45 Who Needs a Skeletal Survey? American Academy of Pediatrics, Section of Radiology. Pediatrics. 2000; 105 (6): All children <2 years of age with concerns of physical abuse Regardless of presentation (bruises, burns, TBI, or abdominal trauma) Patients 2-5 years of age should be handled on individual basis based on specific clinical indicators of abuse *Skeletal survey or bone scan has little value in children >5 years
46 Skeletal Survey Not a Babygram Skull frontal and lateral Spine- frontal and lateral Chest frontal Pelvis Extermities Upper frontal Lower frontal Hands Feet Wrists Knees Ankles
47 Spiral Fracture Spiral fractures are associated with twisting mechanism
48 Rib Fractures 90% of rib fractures in children <2 yo are due to abuse Often posterior, acutely hard to identify Usually unsuspected Rarely accidental due to compliance of thoracic rib cage
49 Rib Fractures
50 Skull Fracture
51 Skull Fracture Common fracture in abuse Can occur from accidental fall Complex fractures or neurologic findings are rarely compatible with a short fall
52 Classic Metaphyseal Lesion (CML) AKA corner fracture or bucket handle fracture Fracture through the zone of provisional calcification of the physis Highly specific for child abuse Usually from a hard pull or twist
53
54 Dating Fractures Most pertinent for rib and long bone fractures May see different stages of healing Callus development and calcification Not accurate for skull fractures Follow up skeletal survey may be useful
55 Skeletal Injury Differential Diagnosis Accidental injury toddler s fracture Rickets Osteogenesis imperfecta
56 Case 2 9 mo female presents to the PCP for bilat feet burns. Parents report that they were getting the bath ready and turned their back for a few seconds and then found pt had stepped into the bathtub and gotten burned. On exam, bilat feet with 2 nd burns to both feet but sparing the soles and there is a sharp demarcation where the burn starts at ankle level. Pt moves her feet and pulses are 2+ distally. What is your differential? What should you do?
57 CHILD ABUSE PART 5: ABUSIVE BURNS
58 Abusive Burns Scalding hot water immersion, most commonly reported mechanism Abusive burns more severe and complicated Typically < 6 yrs, on average 2 to 4 yrs Youngest child in sibship at greatest risk Abusive burn victims more likely to have signs abuse/neglect and/or CPS reports 14 19% children with suspicious burns have + skeletal survey
59 Clues to Abusive Burns Prior accidental burns History does not match burn pattern Burn history not consistent with child s development Delay in seeking care Certain patterns Burns localized to genitalia, perineum, buttocks, bilateral lower extremities, hands Presence of additional or older injuries
60 Examination of the Child with Burns Head to toe evaluation Photographs of the injury with multiple different views and positions Work up for other injuries skeletal survey for children < 2 yrs * Scene investigation from law enforcement and CPS
61 Patterns of Abusive Burns Scald Uniformity of burn depth restrained Bilateral symmetry without splash marks - immersion Dry contact Silhouette of object (ie iron) Cigarette or cigar Circular pattern
62 Abusive Immersion Burns Spare flexor creases restrained or withdraw reflex Spare soles of feet or point of contact with cooler surface Linear or clear demarcation between burned and unburned (glove and stocking) Uniformity of burn depth Absence of splash Hands, feet, genitalia, buttocks
63 Accidental Scald Burn Splash marks Hot water splash >140F results in burn Burn less intense as liquid runs down and dissipates heat Flexor creases spared due to withdraw reflex Distribution and margins are asymmetric Pattern influenced by clothing and type liquid
64 Duration of Exposure Required to Produce Full-thickness Burns Water temperature Duration of Exposure 120 o F 10 minutes 130 o F 10 seconds 140 o F 1 second 150 o F 0.5 seconds
65 Child versus Adult Skin Children's skin thinner (>5 yr approximate adult thickness) Inverse relationship thickness, temperature and time necessary to induce burning >130 F (54 C) children burn in a quarter of the time it takes adult skin to burn
66 Accidental Contact Burns Indistinct margins Do not occur in multiples Usually on parts of body not clothed (hands, feet, face)
67 Mimics Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Stevens Johnson Syndrome Staphylococcal Scalded Skin Syndrome Blistering distal dactylyitis Epidermolysis bullosa Bullous impetigo Focal pyoderma VZV scaring Ammoniacal diaper dermatitis Cultural practices Cupping, coining, etc.
68 Smoke alarms Burn Prevention Water heaters set to 120 degrees F Assistance with utility bills Prevents the dangerous use of using the stove or oven for heating water for bathing or laundry Proper use of space heaters Flame resistant sleepwear Proper handling, supervision of clothing and curling irons Appropriate supervision of children in the kitchen, bathroom
69 The child disclosed physical abuse/you found injuries consistent with child physical abuse, NOW WHAT?
70 Informing the Parents State only what you know for sure Delineate the injuries Explain the care and prognosis Stress mutual concern for the child This is not accidental or With injuries like these
71 Informing the Parents Explain social services involvement Coordinate explaining CPS/LE involvement With injuries like these/situations like this, we are required by law to inform the state child protection/law enforcement Explain community agency involvement
72 Documentation BE METICULOUS!!! Include conversations Include quotations in the history Diagram soft tissue injuries Photo documentation
73 Disposition Safety plan must be in place If you don t feel comfortable with the plan or there is not a safety plan (i.e. in Kansas on the weekend), you may have to take protective custody of the child or admit the child Maybe ok to dc home with parents vs. other family members vs. foster parents +/- Law enforcement involvement +/- Follow up in the SCAN Clinic +/- Forensic Interview
74 Disposition Decision to admit: Treat/monitor physical injuries Provide safe environment
75 Mandatory Reporters Mandatory reporters - those professionals who are responsible for the care and protection of children Doctors, nurses, PAs, police, teachers, counselors, social workers Overall, remember if you are concerned about any type of abuse or neglect of a child, you are a Mandatory Reporter
76
77 Investigative and Justice Systems Child Protective Services Law Enforcement Legal System Juvenile/Family Court Criminal Court
78 Role Definition Our role is addressing the child s health needs Perform and document the evaluation in a forensically sound fashion Medical Role is Not: Bad guy detection Child custody/placement decision Crime investigation Enforcement of criminal wrongdoing
79 Taking Care of Yourself Child abuse work can prompt intense emotional response Most children will return to their families of origin Vicarious trauma is a particular risk for health care workers in these cases Nurture your own and your coworkers resilience Be good to each other
80 Child Protector App Developed by the Child Abuse Pediatricians at Children s Mercy Hospital and Texas Health Science Center Free app to help with the diagnosis and work up of child abuse
81 QUESTIONS
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C)
 Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides
 The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May Leslie M. Quinn M.D.
 CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
Bilateral rib fractures 2 on right and 1 on left In different stages of healing, with left fracture older than right fractures
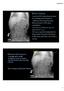 More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics
 Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse
 Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse Amy Baxter MD FAAP FACEP Associate Clinical Professor Medical College of Georgia 4 month old sleepy vomiting Mom works nights Wouldn t feed well Shivering
Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse Amy Baxter MD FAAP FACEP Associate Clinical Professor Medical College of Georgia 4 month old sleepy vomiting Mom works nights Wouldn t feed well Shivering
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines
 Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient
 September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma
 Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
10/8/17. I have no disclosures. What are they? Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma
 I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
Disclosure. Physical Abuse. Objectives. What is the Mechanism of the Injury?
 Disclosure Abuse or Not Abuse: What is the Answer? Natalie Kissoon, MD Assistant Professor Division of Child Abuse Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science Natalie Kissoon, MD has no relationships
Disclosure Abuse or Not Abuse: What is the Answer? Natalie Kissoon, MD Assistant Professor Division of Child Abuse Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science Natalie Kissoon, MD has no relationships
5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains
 5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains Kristen Reeder, MD Child Abuse Pediatrician, REACH Program Children s Health SM Children s Medical Center Dallas Assistant Professor
5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains Kristen Reeder, MD Child Abuse Pediatrician, REACH Program Children s Health SM Children s Medical Center Dallas Assistant Professor
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline
 Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
Recognising and Managing Child Abuse in General Practice. Dr Ceiridwen Davies Consultant Paediatrician Child Abuse Team Red Cross Children s Hospital
 Recognising and Managing Child Abuse in General Practice Dr Ceiridwen Davies Consultant Paediatrician Child Abuse Team Red Cross Children s Hospital Definition Outline Importance of Child Abuse Common
Recognising and Managing Child Abuse in General Practice Dr Ceiridwen Davies Consultant Paediatrician Child Abuse Team Red Cross Children s Hospital Definition Outline Importance of Child Abuse Common
ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS CHILD ABUSE. A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non-
 ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS OF CHILD ABUSE A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non- Accidental Injury with specific references to both the perpetrator and victim
ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS OF CHILD ABUSE A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non- Accidental Injury with specific references to both the perpetrator and victim
2/13/13. Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University
 Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
 3 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person. Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and
3 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person. Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and
They re not little adults, but they are little humans. Pearls for your next pediatric trauma patient. Children are little humans
 They re not little adults, but they are little humans Pearls for your next pediatric trauma patient Alisa McQueen MD, FAAP, FACEP Associate Professor of Pediatrics The University of Chicago Alisa McQueen
They re not little adults, but they are little humans Pearls for your next pediatric trauma patient Alisa McQueen MD, FAAP, FACEP Associate Professor of Pediatrics The University of Chicago Alisa McQueen
OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE
 2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect
 CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect I. IDENTIFY THE CHILD WHO MAY BE A VICTIM OF ABUSE OR NEGLECT. A. Injuries
CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect I. IDENTIFY THE CHILD WHO MAY BE A VICTIM OF ABUSE OR NEGLECT. A. Injuries
Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions
 Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions 1. Which question is important if your patient may be a candidate for surgery? p. 183 *A.) When did you last eat? B.) What is
Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions 1. Which question is important if your patient may be a candidate for surgery? p. 183 *A.) When did you last eat? B.) What is
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast
 The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
Radiological investigations
 Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Not All That Blisters Is a Burn! Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD CHAMP Webinar December 6, 2012
 Not All That Blisters Is a Burn! Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD CHAMP Webinar December 6, 2012 Objectives To review the epidemiology of burns in children including burns caused by abuse To review the steps
Not All That Blisters Is a Burn! Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD CHAMP Webinar December 6, 2012 Objectives To review the epidemiology of burns in children including burns caused by abuse To review the steps
PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation **
 PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation ** I. RECOGNITION A. History 1. Unexplained or un-witnessed injury 2.
PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation ** I. RECOGNITION A. History 1. Unexplained or un-witnessed injury 2.
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
 4 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and grabbing.
4 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and grabbing.
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS. December 19, 2012
 PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
6/23/2017. What do you see? skull fracture
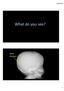 What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
CORE-INFO: fractures in children
 CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises. Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction Weight-bearing and resistance exercises have
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Patient Assessment. Chapter 8
 Patient Assessment Chapter 8 Patient Assessment Scene size-up Initial assessment Focused history and physical exam Vital signs History Detailed physical exam Ongoing assessment Patient Assessment Process
Patient Assessment Chapter 8 Patient Assessment Scene size-up Initial assessment Focused history and physical exam Vital signs History Detailed physical exam Ongoing assessment Patient Assessment Process
Core Stabilization for Low Back Pain Protocol
 Core Stabilization for Low Back Pain Protocol Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair General Information Low back pain is an extremely common condition that affects approximately 84% of adults at some
Core Stabilization for Low Back Pain Protocol Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair General Information Low back pain is an extremely common condition that affects approximately 84% of adults at some
Acute Lower Back Pain. Physiotherapy department
 Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Acute Lower Back Pain Physiotherapy department Back pain is a common condition and in the UK it affects 7 out of 10 people at some point in their lives. Back pain can be very uncomfortable but it is not
Information Guide. Your Health and Fitness. Chair-based mobility exercises
 Information Guide Your Health and Fitness Chair-based mobility exercises What this guide is about Mobility exercises involve taking joints through their range of motion. Their purpose is to lubricate the
Information Guide Your Health and Fitness Chair-based mobility exercises What this guide is about Mobility exercises involve taking joints through their range of motion. Their purpose is to lubricate the
LOW BACK PAIN. what you can do
 LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
LOW BACK PAIN what you can do Back pain Nearly 80 percent of adults will experience back pain at some point in their life. The good news is that back pain will normally go away within four to six weeks
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Pediatric Advanced Life Support
 Pediatric Advanced Life Support Pediatric Chain of Survival Berg M D et al. Circulation 2010;122:S862-S875 Prevention Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Prompt access to the emergency response system
Pediatric Advanced Life Support Pediatric Chain of Survival Berg M D et al. Circulation 2010;122:S862-S875 Prevention Early cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) Prompt access to the emergency response system
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
EXERCISES TO IMPROVE FUNCTIONAL STABILITY FOR PADDLERS
 EXERCISES TO IMPROVE FUNCTIONAL STABILITY FOR PADDLERS BCU in partnership with Joanne Elphinston Useful Tips for the Exercises Ensure you have the correct size of swiss ball inflated to the right pressure.
EXERCISES TO IMPROVE FUNCTIONAL STABILITY FOR PADDLERS BCU in partnership with Joanne Elphinston Useful Tips for the Exercises Ensure you have the correct size of swiss ball inflated to the right pressure.
Normal development & reflex
 Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
The Police Treatment Centres
 Ball Class Exercises The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you agree
Ball Class Exercises The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you agree
SIMPLE STRETCHES TO FREE 5YOUR BACK
 SIMPLE ES TO FREE 5YOUR BACK 1MOVE SLOWLY FOLLOW YOUR BREATH AND YOUR BODY - NOT THE CLOCK ING SHOULD NOT HURT. AT ANY POINT IN A YOU SHOULD FEEL ABLE TO BREATHE, AND TO TAKE 5-7 BREATHS. LESS THAN THAT,
SIMPLE ES TO FREE 5YOUR BACK 1MOVE SLOWLY FOLLOW YOUR BREATH AND YOUR BODY - NOT THE CLOCK ING SHOULD NOT HURT. AT ANY POINT IN A YOU SHOULD FEEL ABLE TO BREATHE, AND TO TAKE 5-7 BREATHS. LESS THAN THAT,
Full Body. Strengthening Routine
 Full Body Strengthening Routine Full Body Strengthening Routine Strengthening activities are recommended 2 to 4 days a week to help improve strength, reduce body fat, risk of osteoporosis, stress, and
Full Body Strengthening Routine Full Body Strengthening Routine Strengthening activities are recommended 2 to 4 days a week to help improve strength, reduce body fat, risk of osteoporosis, stress, and
Osteoporosis Exercise:
 Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Osteoporosis Exercise: Balance, Posture and Functional Exercises Osteoporosis Exercise: Weight-Bearing and Muscle Strengthening Exercises Introduction You can help improve and maintain your balance, posture
Identifying Suspicious Injuries: A Critical Step Toward Prevention
 Identifying Suspicious Injuries: A Critical Step Toward Prevention Melissa L. Currie, MD, FAAP Medical Director and Chief Kosair Charities Division of Pediatric Forensic Medicine Professor of Pediatrics
Identifying Suspicious Injuries: A Critical Step Toward Prevention Melissa L. Currie, MD, FAAP Medical Director and Chief Kosair Charities Division of Pediatric Forensic Medicine Professor of Pediatrics
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX
 EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX Finding Comfortable Positions Sex and Back Pain When your back hurts, simple actions such as getting undressed or giving a hug may cause pain. If just the thought of having
EASING BACK PAIN DURING SEX Finding Comfortable Positions Sex and Back Pain When your back hurts, simple actions such as getting undressed or giving a hug may cause pain. If just the thought of having
Copyright Cardiff University
 This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
This exercise programme has been developed by physiotherapists specifically for people with movement disorders. Exercise is not without its risks and this or any other exercise programme has potential
You Are the Emergency Medical Responder
 Lesson 32: Injuries to the Chest, Abdomen and Genitalia You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your police unit responds to a call in a part of town plagued by violence. When you arrive, you find the
Lesson 32: Injuries to the Chest, Abdomen and Genitalia You Are the Emergency Medical Responder Your police unit responds to a call in a part of town plagued by violence. When you arrive, you find the
Patient Details Hospital number NHS number. Surname First name DOB. Permanent address. Post code. Mobile No. Temporary. Mother DOB. Father.
 Burns Unit Page 12 Paediatric Burn Injuries - Assessment & Admission Burns Unit Page 1 Discharge Patient Details Hospital number NHS number Admission date Injury date Hospital Use time time Time: Discharge
Burns Unit Page 12 Paediatric Burn Injuries - Assessment & Admission Burns Unit Page 1 Discharge Patient Details Hospital number NHS number Admission date Injury date Hospital Use time time Time: Discharge
The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse
 CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse Cindy W. Christian, MD, FAAP, COMMITTEE ON CHILD ABUSE AND NEGLECT Child physical
CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse Cindy W. Christian, MD, FAAP, COMMITTEE ON CHILD ABUSE AND NEGLECT Child physical
Core Strengthening After Lower Limb Amputation
 After the loss of a leg, the muscles in the middle of your body will become very important to you. You can think of strength in the core or the middle of your body as a stable platform which makes it easier
After the loss of a leg, the muscles in the middle of your body will become very important to you. You can think of strength in the core or the middle of your body as a stable platform which makes it easier
International Childbirth Education Association. Postpartum Doula Program
 International Childbirth Education Association Postpartum Doula Program Part 5: Newborn Appearance Objectives: Describe general newborn appearance. Identify possible newborn skin conditions. Summarize
International Childbirth Education Association Postpartum Doula Program Part 5: Newborn Appearance Objectives: Describe general newborn appearance. Identify possible newborn skin conditions. Summarize
Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes. Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s
 Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s Very Little Research There has been very little research on the forces a crash
Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s Very Little Research There has been very little research on the forces a crash
Rehabilitation 2. The Exercises
 Rehabilitation 2 This is the next level from rehabilitation 1. You should have spent time mastering the previous exercises and be ready to move on. If you are unsure about any of the previous exercises
Rehabilitation 2 This is the next level from rehabilitation 1. You should have spent time mastering the previous exercises and be ready to move on. If you are unsure about any of the previous exercises
Bisan Salhi, M.D. 69 Jesse Hill Jr. Dr. Atlanta, GA Phone:
 Bisan Salhi, M.D. 69 Jesse Hill Jr. Dr. Atlanta, GA 30303 Phone: 734-657-4539 30 June 2006 Dear Sir or Madam: 1. Thank you for the opportunity to evaluate Mr. Liviu Negut. Enclosed is my preliminary medical
Bisan Salhi, M.D. 69 Jesse Hill Jr. Dr. Atlanta, GA 30303 Phone: 734-657-4539 30 June 2006 Dear Sir or Madam: 1. Thank you for the opportunity to evaluate Mr. Liviu Negut. Enclosed is my preliminary medical
The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children
 The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children Guided Notes for Online Learning Name: Date: 1 Table of Contents Section 1: The Opioid Crisis Page 3 Section 2: Addiction Page 4 Section 3: Trauma Informed Care
The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children Guided Notes for Online Learning Name: Date: 1 Table of Contents Section 1: The Opioid Crisis Page 3 Section 2: Addiction Page 4 Section 3: Trauma Informed Care
GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN. All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding
 GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN Reference: Bruising / Bleeding / NAI Version No: 1 Applicable to All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding Classification
GUIDELINE: ASSESSMENT OF BRUISING & BLEEDING IN CHILDREN Reference: Bruising / Bleeding / NAI Version No: 1 Applicable to All children in whom there is concern regarding bruising / bleeding Classification
Outreach and Working With Your PEDIATRICIAN
 Outreach and Working With Your PEDIATRICIAN Studies show you get only about 15 minutes of face time with your pediatrician during an average well visit Finding A Pediatrician When trying to find local
Outreach and Working With Your PEDIATRICIAN Studies show you get only about 15 minutes of face time with your pediatrician during an average well visit Finding A Pediatrician When trying to find local
Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol
 Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol Contents 1. Introduction 2. Definition 3. Recommended Action 4. Specific considerations for disabled children 5. Accidental / non-accidental / inconclusive categories
Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol Contents 1. Introduction 2. Definition 3. Recommended Action 4. Specific considerations for disabled children 5. Accidental / non-accidental / inconclusive categories
Safe, Healthy, Happy Children
 September 20, 2012 Safe, Healthy, Happy Children Parental Substance Abuse Negative Impact on Children Chaotic & Unpredictable Environments Drug Endangered Children Children are drug endangered when their
September 20, 2012 Safe, Healthy, Happy Children Parental Substance Abuse Negative Impact on Children Chaotic & Unpredictable Environments Drug Endangered Children Children are drug endangered when their
Pediatric Patient Overview
 Emergency Medical Services Seattle/King County Public Health 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 206.296.4863 Last Updated December 14, 2015 Pediatric Patient Overview Contents PEDIATRIC BASICS...
Emergency Medical Services Seattle/King County Public Health 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 206.296.4863 Last Updated December 14, 2015 Pediatric Patient Overview Contents PEDIATRIC BASICS...
34 Pictures That Show You Exactly What Muscles You re Stretching
 By DailyHealthPostJanuary 27, 2016 34 Pictures That Show You Exactly What Muscles You re Stretching Stretching before and after a workout is a great way to promote blood flow to the muscles and increase
By DailyHealthPostJanuary 27, 2016 34 Pictures That Show You Exactly What Muscles You re Stretching Stretching before and after a workout is a great way to promote blood flow to the muscles and increase
FLEXIBILITY PROGRAM UTE CONFERENCE
 FLEXIBILITY PROGRAM UTE CONFERENCE Flexibility is the range of motion possessed by an individual joint or combination of joints. Every athlete must strive for increased flexibility as this will improve
FLEXIBILITY PROGRAM UTE CONFERENCE Flexibility is the range of motion possessed by an individual joint or combination of joints. Every athlete must strive for increased flexibility as this will improve
PTA 210 PTA Techniques. Patient Positioning and Draping
 PTA 210 PTA Techniques Patient Positioning and Draping Review Last Lecture 5 vital signs you are responsible for? What is patency? How do you test it? Pressing too hard with HR can cause Contraindications
PTA 210 PTA Techniques Patient Positioning and Draping Review Last Lecture 5 vital signs you are responsible for? What is patency? How do you test it? Pressing too hard with HR can cause Contraindications
of Trauma Assembly 27 th Page 1
 Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Using Local Data to Drive Injury Prevention Strategies Disclosures Objectives
 Using Local Data to Drive Injury Prevention Strategies Lee Ann Wurster MS, RN, CPNP Trauma Coordinator Disclosures No financials interest or other relationships with commercial entities Objectives Analyze
Using Local Data to Drive Injury Prevention Strategies Lee Ann Wurster MS, RN, CPNP Trauma Coordinator Disclosures No financials interest or other relationships with commercial entities Objectives Analyze
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries. Chapter 28
 Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
Yoga to Aid Sound Sleep.
 Yoga to Aid Sound Sleep. Relaxation in itself is not enough to counteract the effects of the stress and tension, which can lead to disturbed sleep. In order to sleep well, we need to eliminate stress and
Yoga to Aid Sound Sleep. Relaxation in itself is not enough to counteract the effects of the stress and tension, which can lead to disturbed sleep. In order to sleep well, we need to eliminate stress and
FAB55 EXERCISES, 5 WEEKS, 5 MINUTES A DAY
 BANDED SIDE STEP Strengthening Hip Complex Starting Position: Start in a standing position with the strength mini-band placed around your ankles. Your knees, hips and toes should be in-line with each other.
BANDED SIDE STEP Strengthening Hip Complex Starting Position: Start in a standing position with the strength mini-band placed around your ankles. Your knees, hips and toes should be in-line with each other.
Kristin s Head Trauma Board Questions 11/07/14
 Kristin s Head Trauma Board Questions { 11/07/14 A healthy 15 y/o boy was playing football at a park near his home with a group of friends when he tripped over a friend s leg while trying to catch a pass.
Kristin s Head Trauma Board Questions { 11/07/14 A healthy 15 y/o boy was playing football at a park near his home with a group of friends when he tripped over a friend s leg while trying to catch a pass.
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures
 Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition
 Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
Restore adequate respiratory and circulatory conditions. Reduce pain
 Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
Pre-hospital management of the trauma patient is best performed by an integrated team focused on minimizing the time from injury to definitive care at an appropriate trauma center. Dispatchers, first responders,
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue. Injuries to. and Spine. December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief
 Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
7 Morning Stretches to Start Your Day
 7 Morning Stretches to Start Your Day Including some stretching in your daily morning routine can help energize you for the day. That could mean you can skip that coffee until midmorning, when you might
7 Morning Stretches to Start Your Day Including some stretching in your daily morning routine can help energize you for the day. That could mean you can skip that coffee until midmorning, when you might
Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect
 Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect Maria D. McColgan, MD Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine Director, Child Protection Program St. Christopher s Hospital for Children
Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect Maria D. McColgan, MD Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine Director, Child Protection Program St. Christopher s Hospital for Children
Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER
 Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER A foster child has been placed in your home. You are told that she has been prenatally exposed to alcohol and has a Fetal Alcohol
Homework #1: CARING FOR A CHILD IMPACTED BY FETAL ALCOHOL SPECTRUM DISORDER A foster child has been placed in your home. You are told that she has been prenatally exposed to alcohol and has a Fetal Alcohol
Exercises to Strengthen Your Back
 Exercises to Strengthen Your Back Your 15 Minute Workout By doing your 15 minute workout 3-5 times per week, you can condition the muscles and joints that support your back and keep it in healthy balance
Exercises to Strengthen Your Back Your 15 Minute Workout By doing your 15 minute workout 3-5 times per week, you can condition the muscles and joints that support your back and keep it in healthy balance
What are the causes of back pain? In the general population, there are several causes to back pain, below are two of the most common.
 How common is back pain? Back pain in adolescents (and adults) is very common. The most common reason for back pain is muscle strain. This can be caused by a single movement, a repetitive movement in a
How common is back pain? Back pain in adolescents (and adults) is very common. The most common reason for back pain is muscle strain. This can be caused by a single movement, a repetitive movement in a
THE GREAT EIGHT. Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13
 THE GREAT EIGHT Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13 ABOUT THE GREAT EIGHT Exercises that is! Eight GREAT exercises. By now you should have opened your Master Trainer elog Book (see Welcome section)
THE GREAT EIGHT Australian Institute of Fitness 1 / 13 ABOUT THE GREAT EIGHT Exercises that is! Eight GREAT exercises. By now you should have opened your Master Trainer elog Book (see Welcome section)
Spine Conditions and Treatments. Your Guide to Common
 Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Your Guide to Common Spine Conditions and Treatments The spine is made up of your neck and backbone. It allows your body to bend and move freely. As you get older, it is normal to have aches and pains.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
POSTNATAL EXERCISES. (Early In Patient Postnatal Days Until Six Weeks Post Delivery)
 POSTNATAL EXERCISES (Early In Patient Postnatal Days Until Six Weeks Post Delivery) Exercise Regularly This brochure is intended to educate women about mobility and exercises while as an In Patient and
POSTNATAL EXERCISES (Early In Patient Postnatal Days Until Six Weeks Post Delivery) Exercise Regularly This brochure is intended to educate women about mobility and exercises while as an In Patient and
Taking Care of Your Back
 Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
Taking Care of Your Back Most people will feel back pain at some point in their lives, but not all back pain is the same for everyone. The good news is, most low back pain improves without any treatment
Table of Contents. Summary of Tupler Technique Program How the Program Works Checking for Diastasis Splinting Tips...
 Tips Table of Contents Summary of Tupler Technique Program... 2 How the Program Works... 3 Checking for Diastasis... 4 Splinting Tips... 5-6 Exercise Tips... 7-8 Other Tips... 9 Ongoing Support with the
Tips Table of Contents Summary of Tupler Technique Program... 2 How the Program Works... 3 Checking for Diastasis... 4 Splinting Tips... 5-6 Exercise Tips... 7-8 Other Tips... 9 Ongoing Support with the
Back Protection. Training Guide
 Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
Back Protection Training Guide Use a Back Support Belt to Prevent Back Injuries Because of the incidious progression of back problems, it is always difficult to determine how a back problem began. If you
on Brain Development Infant brain development
 Effects of Child Abuse and Neglect on Brain Development Jodi Flick, LCSW, ACSW Family and Children s Resource Program Jordan Institute for Families UNC-Chapel Hill School of Social Work joflick@email.unc.edu
Effects of Child Abuse and Neglect on Brain Development Jodi Flick, LCSW, ACSW Family and Children s Resource Program Jordan Institute for Families UNC-Chapel Hill School of Social Work joflick@email.unc.edu
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR.
 Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
Exercise Program WARNING: DO NOT USE THIS OR ANY OTHER EXERCISE PROGRAM WITHOUT FIRST BEING CLEARED BY YOUR DOCTOR. Things you MUST know before you begin Posture It is absolutely critical to maintain proper
The Police Treatment Centres
 The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you agree to do at your own risk.
The exercises provided here are for general information only and should not be treated as a substitute for professional supervision or advice. By following these exercises you agree to do at your own risk.
GOLDEN PROTECTOR CLAIM DOCTOR S STATEMENT
 GOLDEN PROTECTOR CLAIM DOCTOR S STATEMENT * Please delete where appropriate For Official Use _ G E L S Name of Life Assured: NRIC/ Passport No.: of Birth (dd/mm/yyyy): Gender: M / F * 1. of Accident: of
GOLDEN PROTECTOR CLAIM DOCTOR S STATEMENT * Please delete where appropriate For Official Use _ G E L S Name of Life Assured: NRIC/ Passport No.: of Birth (dd/mm/yyyy): Gender: M / F * 1. of Accident: of
What Do You Think of My Posterior?
 What Do You Think of My Posterior? Posterior Stroke and Stroke Mimics Peter Panagos, MD, FACEP, FAHA Associate Professor Emergency Medicine and Neurology Washington University School of Medicine Disclosures
What Do You Think of My Posterior? Posterior Stroke and Stroke Mimics Peter Panagos, MD, FACEP, FAHA Associate Professor Emergency Medicine and Neurology Washington University School of Medicine Disclosures
LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS
 BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
BASICS LECTURE TOPIC ASSIGNMENTS LECTURE TOPIC: ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY Read the textbook: Ch. 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go To: Web Site > Folder: AnatTerm > A25terms09.pdf. Download the file &
Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair
 PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair a. Description Lumbar spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. The
PRODUCTS HELPING PEOPLE HELP THEMSELVES! Lumbar Stenosis Rehabilitation Using the Resistance Chair a. Description Lumbar spinal stenosis is a term used to describe a narrowing of the spinal canal. The
