Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect
|
|
|
- Raymond Hensley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Recognizing and Responding to Child Abuse & Neglect Maria D. McColgan, MD Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine Director, Child Protection Program St. Christopher s Hospital for Children
2 Disclosures I provide expert opinion in cases of child abuse and neglect.
3 Goals Describe your role as a mandated reporter of Child Abuse and Neglect Identify risk factors and indicators of suspected child abuse and neglect Know how to: Report a case of suspected child abuse Communicate your concerns with caregivers/others involved in the investigation Provide appropriate medical treatment to the child
4 Agenda Definitions Epidemiology Etiology Evaluation Reporting Prevention Resources
5 One day last November, we had four battered children in our pediatrics ward. Two died in the hospital and one died at home four weeks later. For every child who enters the hospital this badly beaten, there must be hundreds treated by unsuspecting doctors. The battered child syndrome isn't a reportable disease, but it damn well ought to be. Dr. Henry Kempe, Newsweek, April 1962
6 How far have we come? 1874 Rescue of Mary Ellen Wilson 1875 New York Society for Prevention of Cruelty to Children 1935 Social Security Act with obscure provision for protection and care of homeless, dependent and neglected children 1946 Article by pediatric radiologist John Caffey 1962 The Battered Child Syndrome Henry Kempe 1967 All states have reporting laws 1974 Child Abuse Prevention and Treatment Act (CAPTA) 2009 First Child Abuse Pediatrics Board Examination
7 Facts at a Glance 4 million abuse & neglect referrals on 7.2 million children 683,000 child victims 77% - neglect (includes medical neglect) 1,670 deaths average of 5 per day 75% of fatalities under age 3 National Center for Injury Prevention and Control, 2015 Child Maltreatment Report
8 NJ State Law Definition Of Child Abuse "Abused child" means a child under the age of 18 years whose parent, guardian, or other person having his custody and control: Inflicts or allows to be inflicted upon such child physical injury by other than accidental means which causes or creates a substantial risk of death, or serious or protracted disfigurement, or protracted impairment of physical or emotional health or protracted loss or impairment of the function of any bodily organ; Creates or allows to be created a substantial or ongoing risk of physical injury to such child by other than accidental means which would be likely to cause death or serious or protracted disfigurement, or protracted loss or impairment of the function of any bodily organ; or Commits or allows to be committed an act of sexual abuse against the child; Or a child who has been willfully abandoned by his parent or guardian, or such other person having his custody and control.
9 Mandated Reporters of Abuse New Jersey Any person having reasonable cause to believe that a child has been subjected to child abuse or acts of child abuse shall report the same immediately to the Division of Youth and Family Services by telephone or otherwise. Granted legal immunity Penalties Disorderly person
10
11 If maltreatment is suspected Referral to Department of Children and Families Call NJ ABUSE ( ) Call 911 if child in immediate danger Referral Appropriate mental health therapy for age/abilities Counseling for the family
12 Why doctors do not report Physician recognition of child abuse Lack of knowledge Psychological barrier to recognition Family, racial, economic factors Flaherty, Sege 2005 Barriers to reporting Do not report all cases Lack of training on how to report Report will harm child Poor experience with Child Protective Services Poor experience with legal system Misunderstanding of MD role
13
14 Categories of Adverse Childhood Experiences Abuse Psychological 11% Physical (parent) 11% Sexual (anyone) 22% Household Dysfunction Substance abuse 26% Mental Illness 19% Domestic Violence 13% Imprisoned household member 3%
15
16 Etiology Multi-factorial Child Characteristics Parental Characteristics Family/Environmental Factors Triggering Situations
17
18
19
20
21
22 Medical Evaluation Performing the H&P
23 Chief Complaint Diagnosis Differential Goal: Correct diagnosis Prevent misdiagnosis of abuse
24 Medical Evaluation of Victim of Suspected Abuse History Physical Examination Collect Forensic Evidence; photographs Laboratory Evaluation? Radiologic Studies? Subspecialist Consults/Child Abuse Pediatrician/SW? Refine Differential Diagnosis & Plan Documentation
25
26 Thorough Medical History HPI, PMH Birth history, previous trauma Developmental Milestones Family History Bleeding disorders, easy bruising, collagen vascular disease, easy fractures, bone disease, dental or hearing abnormalities Small children, early death Thorough Review of Systems
27 Sentinel injuries Previous injury reported in the medical history that was suspicious for abuse because the infant could not cruise, or the explanation was implausible.
28 Sentinel injuries missed opportunities OBJECTIVES: primary objective of this study was to determine how frequently abusive fractures were missed by physicians during previous examinations. A secondary objective was to determine clinical predictors that are associated with unrecognized abuse. METHODS: Children who were younger than 3 years and presented to a large academic children's hospital from January 1993 to December 2007 and received a diagnosis of abusive fractures by a multidisciplinary child protective team RESULTS: Of 258 patients with abusive fractures, 54 (20.9%) had at least 1 previous physician visit at which abuse was missed. ~ 17% of missed abuse cases, children sustained repeat injuries. CONCLUSION: 20.9% of cases missed; 17% of missed cases sustained repeat injuries Ravichandiran, Schuh, Beiuk, Al-Harthy, Shouldice, Au, Boutis.Delayed identification of pediatric abuse-related fractures.pediatrics Jan;125(1):60-6. Epub 2009 Nov 30
29 Thorough Physical Exam Emergent care first Complete head to toe evaluation Must look at all skin surfaces Remove ALL clothing Ears, Neck, Mouth, Genitalia Description of all skin findings
30 What are we looking for? Physical Exam Red Flags Bruises most common indication of physical abuse Occurs in >50% of abused children Bruises are uncommon in infants < 6 months. Those who don t cruise rarely bruise. Two characteristics separate abusive from accidental bruises: LOCATION & PATTERN
31 Location ACCIDENTAL ABUSIVE Shins Anterior thigh Lower arms Upper arms Under chin Neck Forehead Face Hips Buttocks Elbows Trunk Ankles Ears Bony prominences Genitalia
32 TEN-4 Bruising Rule Be aware of any bruising to the: Torso Ears Neck or bruising anywhere on a child 4 months old or younger. This is significant for abuse. Bruising on babies is not normal! Pierce MC, Kaczor K, Aldridge S, O Flynn J, Lorenz DJ. Bruising characteristics discriminating physical child abuse from accidental trauma. Pediatrics. 2010;125(1): Epub Dec. 7, Erratum in Pediatrics. 2010;125(4):861.
33
34 Aging of Bruises Swelling resolves over the first 2-3 days Color changes occur as bruises age Colors vary widely with age of bruises Dependent upon Depth of bruise Location Vascularity of underlying tissue Age and complexion of child
35 Aging of Bruises Visual aging of bruises inexact Bruise with yellow is > 18 hours Red color can be present anytime Blue, purple present 1 hour to resolution Bruises of same age on same person can vary in color Document findings; Photographs Langlois, NEI, Gresham GA. The aging of bruises: a review and study of the color changes with time. Forensic Sci Int 1999;50:
36
37 Bruises and Other Skin Findings If you don t cruise, you don t bruise. Those Who Don t Cruise Rarely Bruise. Sugar NF, Taylor JA, Feldman KW. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 1999;153: Used by permission from AAP
38
39 Protective Custody Any physician, director of a hospital or his designee involved in the examination or treatment of a child may take the child into protective custody for a period not to exceed three (3) court days when the child has suffered serious injury, the probable inference from the available information is that the injury was caused by other than accidental means, and the child would normally be returned to the custody of the person suspected of inflicting or allowing the infliction of the injury N.J.S.A. 9: See CP&P-II-B for a description of CP&P role in protective custody (hospital hold) situations
40
41 Discipline or abuse? Used by permission from AAP
42
43
44
45 Differential Diagnosis of Bruises Must consider Bleeding disorders, ITP or other coagulopathies Erythema multiforme Henoch-Schönlein purpura Secondary syphilis Allergic shiners Phytophotodermatitis Cultural practices
46
47
48
49
50 Evaluation for Bleeding Disorders in Suspected Child Abuse Prevent misdiagnosis of abuse Bruises CBC, PT/PTT VWP Factor 8 & Factor 9 American Academy of Pediatrics Clinical Report Evaluation for Bleeding Disorders in Suspected Child Abuse, Pediatrics Subdural Hemorrhage/ICH CBC, PT/PTT DIC panel (d-dimer and fibrinogen) Factor 8 &9 Hematology Consult?
51 What else should we look for? Occult Trauma Skeletal findings/fractures 2nd most common manifestation of abuse 80% cases in children < 18 months of age 43% unsuspected at time of evaluation Rib Fractures/Classic Metaphyseal Lesions (CML s) Imaging Skeletal survey and repeat skeletal survey All children < 2 years of age 2-5 years: selective survey Bone scan Labs Ca, Phos, Alk Phos, Vitamin D 25 OH, Vitamin D 1,25 OH, PTH and Copper
52 The Skeletal Survey Skull: frontal and lateral views Spine: frontal, lateral thoracolumbar spine (including sternum) Chest: frontal, obliques Extremities: Upper - frontal to include shoulders and hands Lower - frontal to include lower lumbar spine, pelvis, feet
53 Repeat skeletal survey Stage Time Characteristics Induction 3-7 days Inflammation, pain, swelling Soft callus Infants 7-10 days Children Periosteal new bone formation Hard callus days Union at fx site Remodelling 3 months-1 year Woven to lamellar bone
54
55
56 Femur fracture Used by permission from AAP
57 Case study Used by permission from AAP
58 Rib Fractures Nearly 25% of all abusive fractures 90% of abusive rib fractures seen < 2 yrs of age
59 Differential Diagnosis Must consider/rule out medical diagnosis other than abuse Accidental Trauma Studies show very low incidence of fractures from short falls Obstetrical/birth trauma Usually only humeral and clavicular fractures, no rib fractures
60 DDX: Skeletal Fractures Congenital Osteogenesis imperfecta Menke s syndrome Nutritional / Metabolic Copper deficiency Rickets Scurvy Renal osteodystrophy Osteopenia Thompson 2005 Infectious Congenital syphilis Osteomyelitis Neoplasm Leukemia Langerhans cell histiocytosis Bony metastases Normal variant Physiologic periosteal new bone Neuromuscular disease Cerebral palsy Congenital insensitivity to pain
61 What else should we look for? Head Trauma
62 Inflicted Traumatic Brain Injury Shaken Baby Syndrome Leading cause of death from child abuse The cause of up to 95% of severe TBI in children <1yr Leading cause of death from brain injury in children less than 4 yrs of age At least 1,500 cases/year in the United States For children < 1 year of age: incidence of severe or fatal itbi is about 1 in 3,300 Incidence of less severe itbi may be 150 times greater
63 Abusive Head trauma misdiagnosed as Accidental trauma Viral gastroenteritis Reflux Apnea, ALTE, SIDS Seizure disorder Sepsis Otitis media Analysis of missed cases of abusive head trauma. Jenny, Hymel, Titzen, Reinert, Hay. JAMA 1999;281:
64 itbi work-up Ct Head with 3-D reconstruction Ophthalmology consult MRI Head and Neck Labs
65 Eye Exam Subconjunctival Hemorrhages Retinal Hemorrhages
66 Retinal Hemorrhages Few Hemorrhages Multiple Multilayer Hemorrhages
67 2 year old present to ED at 6:30 AM Fell from bottom bunk bed about 5 AM Multiple episodes of vomiting
68 2 year old present to ED at 6;30 AM Fell from bottom bunk bed about 5 AM Multiple episodes of vomiting PE: Ill Appearing, Bruises on Abdomen
69 Abdominal Trauma 2 nd Leading Cause Of Abuse Fatalities Average age is months More common as children become more mobile Shift from fatal site of injury from brain to the abdomen May Have Delayed Presentation Injury May Mimic Common Surgical Illnesses Liver & Spleen & Duodenum Most Commonly Injured
70 Monteleone, ed. Child Maltreatment 1994
71 Differential Diagnosis Labs Trauma labs Include LFT and Amylase Lipase Radiology Studies Skeletal survey All children < 2 years of age 2-5 years: selective survey CT / MRI Ophthalmology Medical photography
72
73 Evidence collection Photographs DO NOT need consent for forensic photographs Photographs DO NOT take the place of documentation, they support visual cues to the documented description Used to appropriately visualize described lesions/marks Have a marker, (ruler or coin) within the photograph that can assist with determining size of lesion Put the child s name, date of birth, medical record number, and date of ED visit on the photograph/ diskette
74 Bites ADULT BITE CHILD BITE Canine to canine To second molar Involves 1 arch Both arches cm. between canines < 2.5 cm.
75 Bite Mark Evaluation Photography of bite marks Ruler and patient ID in photograph Multiple views Swabs for forensic evaluation Forensic Dentistry/Wax impressions for matching
76 Burns What s wrong with this picture?
77
78 Burns in children
79 Arrow down
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87 Documentation Carefully Documented In A Stepwise Approach History Verbatim Documentation/Quotes Physical Exam Pictures Are Helpful Lab & Radiographic Studies Impression Instructions for follow up
88
89 Communicate Effectively Communicate empathetically with families Be available to help law enforcement or CPS understand the child/adolescent s special needs (health care, meds, communication, developmental processes, abilities) Be available for follow up and/ or testimony Suny Upstate Medical University. Children and Adolescents with Disabilities. ChildAbuseMD.com. 17 Feb <
90 Statement of Concern be specific Name, age, sex of child; date seen, reason for presentation. Then, These injuries are (circle one): Concerning for physical abuse Highly concerning for physical abuse Diagnostic of physical abuse The injuries caused (circle if applicable): Substantial pain Impairment of function Current Status (discharged/admitted; siblings to be evaluated) Injury consistent with history provided by caretaker? Yes/No/Possibly/Unknown
91 An ounce of Prevention
92 Pediatrician s Role in Prevention Maintain a high index of suspicion for child maltreatment Discuss child abuse prevention, anticipatory guidance of developmental milestones, and indicators of abuse, with parents and caregivers Advocate for policy reform American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Child Abuse and Neglect & Committee on Children with Disabilities. Assessment of Maltreatment of Children with Disabilities. Pediatrics, Vol. 108, No. 2. Aug. 2001
93 Resources Department of Children & Families Child Welfare Information Gateway disabilities.cfm
94 Conclusions Child abuse is very common Often missed by clinicians Must have high index of suspicion, yet avoid the misdiagnosis of abuse Mandated reporters must report suspicion of abuse Complete careful histories and examinations Document, document, document! Communicate effectively and empathetically with parents and investigators
95 Maria McColgan, MD, MSEd, FAAP Phone: Thank you!
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline
 Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May Leslie M. Quinn M.D.
 CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
Bilateral rib fractures 2 on right and 1 on left In different stages of healing, with left fracture older than right fractures
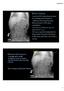 More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient
 September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
2/13/13. Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University
 Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE
 2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
2011 MFMER slide-1 OVERVIEW OF CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Mark S. Mannenbach, MD Mayo Medical Center Rochester, MN 2011 MFMER slide-2 Objectives At the conclusion of this session, the participant will be able
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast
 The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
The Medical Assessment of Fractures in Suspected Child Maltreatment: Infants and Young Children with Skeletal Injury CPS Podcast September 27, 2018 Introduction: Hello everyone, my name is Dominique Piché
Disclosure. Physical Abuse. Objectives. What is the Mechanism of the Injury?
 Disclosure Abuse or Not Abuse: What is the Answer? Natalie Kissoon, MD Assistant Professor Division of Child Abuse Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science Natalie Kissoon, MD has no relationships
Disclosure Abuse or Not Abuse: What is the Answer? Natalie Kissoon, MD Assistant Professor Division of Child Abuse Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science Natalie Kissoon, MD has no relationships
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines
 Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides
 The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation **
 PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation ** I. RECOGNITION A. History 1. Unexplained or un-witnessed injury 2.
PHYSICAL ABUSE: INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT **Child Protection MD is available by pager for questions or formal consultation ** I. RECOGNITION A. History 1. Unexplained or un-witnessed injury 2.
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics
 Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
Abuse or Accident? Suzanne B. Haney, MD, FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Disclosure I have nothing to disclose Objectives Describe common accidental injuries which can be confused with child abuse Describe
5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains
 5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains Kristen Reeder, MD Child Abuse Pediatrician, REACH Program Children s Health SM Children s Medical Center Dallas Assistant Professor
5 B s of Child Physical Abuse: Bruises, Burns, Bones, Bellies, and Brains Kristen Reeder, MD Child Abuse Pediatrician, REACH Program Children s Health SM Children s Medical Center Dallas Assistant Professor
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C)
 Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
Subtle Signs of Child Abuse Child s Protection Office MOH Presented by Dr.Fatoumah Alabdulrazzaq M.D,FRCPC,FAAP,PEM(C) Cutaneous Injuries Bruise : injury to soft tissues in which skin is not broken, characterized
ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS CHILD ABUSE. A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non-
 ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS OF CHILD ABUSE A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non- Accidental Injury with specific references to both the perpetrator and victim
ORTHOPEDIC ASPECTS OF CHILD ABUSE A summary of the physical, metaphysical, psychological, and sociological aspects of Non- Accidental Injury with specific references to both the perpetrator and victim
The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse
 CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse Cindy W. Christian, MD, FAAP, COMMITTEE ON CHILD ABUSE AND NEGLECT Child physical
CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care The Evaluation of Suspected Child Physical Abuse Cindy W. Christian, MD, FAAP, COMMITTEE ON CHILD ABUSE AND NEGLECT Child physical
 3 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person. Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and
3 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person. Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma
 Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
Pediatric Abusive Head Trauma Rebecca Girardet Associate Professor of Pediatrics Director, Division of Child Protection Pediatrics McGovern Medical School at The University of Texas Health Science Center
Paediatric Assessments
 Paediatric Assessments When a Paediatric Assessment is Necessary Where the child appears in urgent need of medical attention, e.g. suspected fracture, bleeding, loss of consciousness, s/he should be taken
Paediatric Assessments When a Paediatric Assessment is Necessary Where the child appears in urgent need of medical attention, e.g. suspected fracture, bleeding, loss of consciousness, s/he should be taken
Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse
 Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse Amy Baxter MD FAAP FACEP Associate Clinical Professor Medical College of Georgia 4 month old sleepy vomiting Mom works nights Wouldn t feed well Shivering
Abuse Or Not? Interactive Visual Clues in Child Abuse Amy Baxter MD FAAP FACEP Associate Clinical Professor Medical College of Georgia 4 month old sleepy vomiting Mom works nights Wouldn t feed well Shivering
10/8/17. I have no disclosures. What are they? Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma
 I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
I have no disclosures Upper extremity fractures Lower extremity fractures Non accidental trauma What are they? Fractures of the radius, ulna and/or humerus Who gets them? Active children usually after
They re not little adults, but they are little humans. Pearls for your next pediatric trauma patient. Children are little humans
 They re not little adults, but they are little humans Pearls for your next pediatric trauma patient Alisa McQueen MD, FAAP, FACEP Associate Professor of Pediatrics The University of Chicago Alisa McQueen
They re not little adults, but they are little humans Pearls for your next pediatric trauma patient Alisa McQueen MD, FAAP, FACEP Associate Professor of Pediatrics The University of Chicago Alisa McQueen
CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect
 CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect I. IDENTIFY THE CHILD WHO MAY BE A VICTIM OF ABUSE OR NEGLECT. A. Injuries
CLINICAL PRACTICE RESOURCE FOR HOSPITALS AND EMERGENCY DEPARTMENTS: Evaluation and Management of Suspected Child Abuse or Neglect I. IDENTIFY THE CHILD WHO MAY BE A VICTIM OF ABUSE OR NEGLECT. A. Injuries
Radiological investigations
 Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions
 Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions 1. Which question is important if your patient may be a candidate for surgery? p. 183 *A.) When did you last eat? B.) What is
Patient Assessment From Brady s First Responder (8th Edition) 83 Questions 1. Which question is important if your patient may be a candidate for surgery? p. 183 *A.) When did you last eat? B.) What is
Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures
 July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
6/23/2017. What do you see? skull fracture
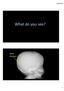 What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
What do you see? skull fracture 1 Head CT On soft tissue windows, posterior soft tissues swelling and hemorrhage, no definite evidence of fracture Head CT On bone windows, fracture now seen subjacent to
CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE
 CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Kansas Association of Osteopathic Medicine April 13 th, 2018 Jami Jackson DO, FAAP, MPH Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor
CHILD PHYSICAL ABUSE Kansas Association of Osteopathic Medicine April 13 th, 2018 Jami Jackson DO, FAAP, MPH Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Department of Emergency Medicine Assistant Professor
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries
 Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Child Protection Guidelines in Suspected Non-Accidental Head Injury (NAHI) in Children Under 2 years of age. DRAFT REVIEW May 2008
 Child Protection Guidelines in Suspected Non-Accidental Head Injury (NAHI) in Children Under 2 years of age DRAFT REVIEW May 2008 Responsibility for monitoring Review and update CPU Dr. Jean Herbison Current
Child Protection Guidelines in Suspected Non-Accidental Head Injury (NAHI) in Children Under 2 years of age DRAFT REVIEW May 2008 Responsibility for monitoring Review and update CPU Dr. Jean Herbison Current
Safe, Healthy, Happy Children
 September 20, 2012 Safe, Healthy, Happy Children Parental Substance Abuse Negative Impact on Children Chaotic & Unpredictable Environments Drug Endangered Children Children are drug endangered when their
September 20, 2012 Safe, Healthy, Happy Children Parental Substance Abuse Negative Impact on Children Chaotic & Unpredictable Environments Drug Endangered Children Children are drug endangered when their
Battered-child syndrome - What the radiologist needs to know
 Battered-child syndrome - What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-1487 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. B. S. Santos, C. A. P. Braga, U. D. C. Haddad, R. S. 1 1 2 1 1 3
Battered-child syndrome - What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-1487 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. B. S. Santos, C. A. P. Braga, U. D. C. Haddad, R. S. 1 1 2 1 1 3
CHILD PROTECTIVE SERVICES M A N D A T E D R E P O R T I N G A N D B E Y O N D
 CHILD PROTECTIVE SERVICES M A N D A T E D R E P O R T I N G A N D B E Y O N D CPS TOPICS OVERVIEW What happens when a report is made? Makeup of Jefferson County CPS Unit CPS Statistics When do we decide
CHILD PROTECTIVE SERVICES M A N D A T E D R E P O R T I N G A N D B E Y O N D CPS TOPICS OVERVIEW What happens when a report is made? Makeup of Jefferson County CPS Unit CPS Statistics When do we decide
Non-accidental Trauma: An unresponsive infant with bilateral retinal hemorrhages.
 Non-accidental Trauma: An unresponsive infant with bilateral retinal hemorrhages. Lucas J. A. Wendel, MD, Susannah Q. Longmuir, MD, and Nasreen A. Syed, MD February 12, 2009 Chief Complaint: 7 month old
Non-accidental Trauma: An unresponsive infant with bilateral retinal hemorrhages. Lucas J. A. Wendel, MD, Susannah Q. Longmuir, MD, and Nasreen A. Syed, MD February 12, 2009 Chief Complaint: 7 month old
 4 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and grabbing.
4 The definition of elder physical abuse is any action by a caregiver that is meant to cause harm or fear in another person Physical abuse includes pain or injury, hitting, pushing, pinching, and grabbing.
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Medical Aspects of Child Physical Abuse the approach to physically abused kids. Objectives
 Center for Safe & Healthy Children Medical Aspects of Child Physical Abuse the approach to physically abused kids Nancy S. Harper, MD FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Associate Professor of Pediatrics, University
Center for Safe & Healthy Children Medical Aspects of Child Physical Abuse the approach to physically abused kids Nancy S. Harper, MD FAAP Child Abuse Pediatrics Associate Professor of Pediatrics, University
Recognising and Managing Child Abuse in General Practice. Dr Ceiridwen Davies Consultant Paediatrician Child Abuse Team Red Cross Children s Hospital
 Recognising and Managing Child Abuse in General Practice Dr Ceiridwen Davies Consultant Paediatrician Child Abuse Team Red Cross Children s Hospital Definition Outline Importance of Child Abuse Common
Recognising and Managing Child Abuse in General Practice Dr Ceiridwen Davies Consultant Paediatrician Child Abuse Team Red Cross Children s Hospital Definition Outline Importance of Child Abuse Common
Guide to the Medical Evaluation in Suspected Physical Abuse
 Guide to the Medical Evaluation in Suspected Physical Abuse Introduction Every year more than 3 million referrals are made to child protective services for concerns of child abuse and neglect with almost
Guide to the Medical Evaluation in Suspected Physical Abuse Introduction Every year more than 3 million referrals are made to child protective services for concerns of child abuse and neglect with almost
HEALTH. Doctors. Level: Materials Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None. Technology Needed:
 HEALTH Doctors Level: Materials Needed: Technology Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None Santa Ana College, School of Continuing Education Parts of the Body Directions: Write
HEALTH Doctors Level: Materials Needed: Technology Needed: High Beginning ESL Telephone Directory (yellow pages) None Santa Ana College, School of Continuing Education Parts of the Body Directions: Write
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
12/13/16. Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016
 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD Medical Director, Queens CAC December 14, 2016 Jamie Hoffman-Rosenfeld, MD, has no financial relationships with any commercial interests. The learner will be able to:! Articulate
X-ray (Radiography) - Bone
 Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Scan for mobile link. X-ray (Radiography) - Bone Bone x-ray uses a very small dose of ionizing radiation to produce pictures of any bone in the body. It is commonly used to diagnose fractured bones or
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease.
 Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Learn the steps to identify pediatric muscle weakness and signs of neuromuscular disease. Listen Observe Evaluate Test Refer Guide for primary care providers includes: Surveillance Aid: Assessing Weakness
Evaluation of Children with Blunt Abdominal Trauma. James F. Holmes, MD, MPH UC Davis School of Medicine
 Evaluation of Children with Blunt Abdominal Trauma James F. Holmes, MD, MPH UC Davis School of Medicine Objectives Epidemiology of intra-abdominal injury (IAI) Physical examination findings with IAI Laboratory
Evaluation of Children with Blunt Abdominal Trauma James F. Holmes, MD, MPH UC Davis School of Medicine Objectives Epidemiology of intra-abdominal injury (IAI) Physical examination findings with IAI Laboratory
Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol
 Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol Contents 1. Introduction 2. Definition 3. Recommended Action 4. Specific considerations for disabled children 5. Accidental / non-accidental / inconclusive categories
Injuries in Non Mobile Infants Protocol Contents 1. Introduction 2. Definition 3. Recommended Action 4. Specific considerations for disabled children 5. Accidental / non-accidental / inconclusive categories
The medical assessment of bruising in suspected child maltreatment cases: A clinical perspective
 The medical assessment of bruising in suspected child maltreatment cases: A clinical perspective Michelle GK Ward, Amy Ornstein, Anne Niec, C Louise Murray; Canadian Paediatric Society Child and Youth
The medical assessment of bruising in suspected child maltreatment cases: A clinical perspective Michelle GK Ward, Amy Ornstein, Anne Niec, C Louise Murray; Canadian Paediatric Society Child and Youth
CORE-INFO: fractures in children
 CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
CORE-INFO: fractures in children This leaflet summarises what is currently known about the relationship between fractures and physical abuse and will be of particular interest to paediatricians, general
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist Certification Exam. Detailed Content Outline
 Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist Certification Exam Detailed Content Outline Description of the Specialty The Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist (PMHS) builds upon the Advanced
Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist Certification Exam Detailed Content Outline Description of the Specialty The Pediatric Primary Care Mental Health Specialist (PMHS) builds upon the Advanced
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma
 Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
Routine Guide EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION. 14x17 CW* 14x17LW 14x17LW. 14x17LW 14x17LW 14x17LW
 EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
EXAMINATION PROJECTION CASSETTE SIZE NOTES PRINT ORIENTATION A-C Joints without weights with weights 14x17 CW* One 14x17 divided; both shoulders on one exposure. *If part does not fit, do 10x12s CW. Both
Vulnerable Elder Protection Team: A Collaborative Intervention
 Vulnerable Elder Protection Team: A Collaborative Intervention Tony Rosen, MD MPH Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Emergency Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Deborah Holt-Knight, MSG Deputy
Vulnerable Elder Protection Team: A Collaborative Intervention Tony Rosen, MD MPH Assistant Professor of Medicine Division of Emergency Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Deborah Holt-Knight, MSG Deputy
A N.S. Technologists Experiences
 A N.S. Technologists Experiences I have nothing to disclose What does appropriate imaging mean For radiologists? For technologists? How does this affect patients and technologists? Discuss ordering trends
A N.S. Technologists Experiences I have nothing to disclose What does appropriate imaging mean For radiologists? For technologists? How does this affect patients and technologists? Discuss ordering trends
Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) Protocol
 Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) Protocol All children suspected of non-accidental trauma will have a complete work-up including a complete history and physical exam with a focus on injuries and explanation
Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) Protocol All children suspected of non-accidental trauma will have a complete work-up including a complete history and physical exam with a focus on injuries and explanation
Appendix H. Child and Adolescent Health Assessment and Intervention Guide
 Appendix H Child and Adolescent Health Assessment and Intervention Guide Description: This assessment guide is intended to assist the community health nurse to assess the health status of children. The
Appendix H Child and Adolescent Health Assessment and Intervention Guide Description: This assessment guide is intended to assist the community health nurse to assess the health status of children. The
Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident
 Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL3 level Prerequisites: Successful completion or waiver
Subspecialty Inpatient Rotation: Pediatric Oncology at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center Senior Resident Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL3 level Prerequisites: Successful completion or waiver
Stair falls: caregiver s missed step as a source of childhood fractures
 J Child Orthop (2014) 8:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0551-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Stair falls: caregiver s missed step as a source of childhood fractures Andrew T. Pennock George D. Gantsoudes Jennifer
J Child Orthop (2014) 8:77 81 DOI 10.1007/s11832-014-0551-x ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Stair falls: caregiver s missed step as a source of childhood fractures Andrew T. Pennock George D. Gantsoudes Jennifer
Outreach and Working With Your PEDIATRICIAN
 Outreach and Working With Your PEDIATRICIAN Studies show you get only about 15 minutes of face time with your pediatrician during an average well visit Finding A Pediatrician When trying to find local
Outreach and Working With Your PEDIATRICIAN Studies show you get only about 15 minutes of face time with your pediatrician during an average well visit Finding A Pediatrician When trying to find local
Orthopedics. 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Orthopedics 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for orthopedic injury, disease and dysfunction.
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Orthopedics 1. GOAL: Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing and screening for orthopedic injury, disease and dysfunction.
Forty-Eighth Annual Teaching Conference Pediatrics for the Practitioner -UT Health Science Center San Antonio School of Medicine June 10-12, 2011
 James L. Lukefahr, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Division of Child Abuse, UTHSCSA Medical Director CHRISTUS Santa Rosa Children s Hospital Center for Miracles James L. Lukefahr, M.D. has no relevant financial
James L. Lukefahr, M.D. Professor of Pediatrics Division of Child Abuse, UTHSCSA Medical Director CHRISTUS Santa Rosa Children s Hospital Center for Miracles James L. Lukefahr, M.D. has no relevant financial
Introduction to WVU Radiology
 Introduction to WVU Radiology Lana Winkler, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Section of Cardiothoracic Imaging Special thanks to Jeffery P. Hogg, MD Radiology Orientation Objectives Why is
Introduction to WVU Radiology Lana Winkler, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology Section of Cardiothoracic Imaging Special thanks to Jeffery P. Hogg, MD Radiology Orientation Objectives Why is
Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms
 Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms P. Ellen Grant MD Associate Professor of Radiology, HMS Director, Center for Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging & Developmental Science Children s
Brain and Cervico-Medullary Injury : Patterns and Mechanisms P. Ellen Grant MD Associate Professor of Radiology, HMS Director, Center for Fetal-Neonatal Neuroimaging & Developmental Science Children s
TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS. Interpretation by Marge Hanna
 TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS Interpretation by Marge Hanna 1. Nose: The area, with its underlying cartilage, from the top edge of the nose leather up to the bottom of the bridge of
TERMINOLOGY AS IT APPLIES TO TICA BREED STANDARDS Interpretation by Marge Hanna 1. Nose: The area, with its underlying cartilage, from the top edge of the nose leather up to the bottom of the bridge of
A Probable Case of Child Abuse from Historic Gloucester
 A Probable Case of Child Abuse from Historic Gloucester Bernadette M Manifold Department of Archaeology, School of Human and Environmental Sciences, University of Reading, Whiteknights, Reading Address
A Probable Case of Child Abuse from Historic Gloucester Bernadette M Manifold Department of Archaeology, School of Human and Environmental Sciences, University of Reading, Whiteknights, Reading Address
Validity of Caregivers Reports on Head Trauma Due to Falls in Young Children Aged Less than 2 Years
 Clinical Medicine Insights: Pediatrics Original Research Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Validity of Caregivers Reports on Head Trauma Due
Clinical Medicine Insights: Pediatrics Original Research Open Access Full open access to this and thousands of other papers at http://www.la-press.com. Validity of Caregivers Reports on Head Trauma Due
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
4. Counsel patients and families regarding athletic participation, including:
 Sports Medicine Primary Goals for this Rotation GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening. Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing sports-related injuries, disorders and dysfunction in children
Sports Medicine Primary Goals for this Rotation GOAL: Prevention, Counseling and Screening. Understand the pediatrician's role in preventing sports-related injuries, disorders and dysfunction in children
Health Care Information for Families of Children with Down Syndrome
 American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome. Those extra genes change development during pregnancy, and
American Academy of Pediatrics Introduction Down syndrome is a common condition caused by having extra copies of genes on the 21st chromosome. Those extra genes change development during pregnancy, and
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures
 Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
Evidence Base for Child Abuse Fractures SPR Sunrise Session May 17, 2018 Megan B. Marine, MD, FAAP Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology, Pediatric Division Co-Director, Pediatric Radiology Fellowship
Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes. Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s
 Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s Very Little Research There has been very little research on the forces a crash
Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s Very Little Research There has been very little research on the forces a crash
PEDIATRIC PREVENTIVE HEALTH GUIDELINES
 PEDIATRIC PREVENTIVE HEALTH GUIDELINES Each child and family is unique; therefore, these Guidelines for Preventive Pediatric Health Care are designed for the care of children who are receiving competent
PEDIATRIC PREVENTIVE HEALTH GUIDELINES Each child and family is unique; therefore, these Guidelines for Preventive Pediatric Health Care are designed for the care of children who are receiving competent
AYSA Concussion/Serious Injury Policy 2013
 AYSA Concussion/Serious Injury Policy 2013 Although it is the beautiful game, soccer is one of the leading sports when it comes to its players sustaining concussions. In conjunction with the 2011 Pennsylvania
AYSA Concussion/Serious Injury Policy 2013 Although it is the beautiful game, soccer is one of the leading sports when it comes to its players sustaining concussions. In conjunction with the 2011 Pennsylvania
CONTENT OUTLINE. Child Abuse Pediatrics
 THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PEDIATRICS CONTENT OUTLINE Child Abuse Pediatrics Subspecialty In-Training, Certification, and Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examinations INTRODUCTION This document was prepared
THE AMERICAN BOARD OF PEDIATRICS CONTENT OUTLINE Child Abuse Pediatrics Subspecialty In-Training, Certification, and Maintenance of Certification (MOC) Examinations INTRODUCTION This document was prepared
Pediatric Emergencies. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012
 Pediatric Emergencies Lesson Goal Explain special characteristics of infants and children to become both comfortable & efficient in treating pediatric emergencies Lesson Objectives Identify physical &
Pediatric Emergencies Lesson Goal Explain special characteristics of infants and children to become both comfortable & efficient in treating pediatric emergencies Lesson Objectives Identify physical &
Child Victims of Violence: Forging Multidisciplinary Approaches
 Child Victims of Violence: Forging Multidisciplinary Approaches Identifying and Caring for Child Victims of Violence, Part II Genevieve Preer, MD Department of Pediatrics Boston Medical Center/ Boston
Child Victims of Violence: Forging Multidisciplinary Approaches Identifying and Caring for Child Victims of Violence, Part II Genevieve Preer, MD Department of Pediatrics Boston Medical Center/ Boston
The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children
 The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children Guided Notes for Online Learning Name: Date: 1 Table of Contents Section 1: The Opioid Crisis Page 3 Section 2: Addiction Page 4 Section 3: Trauma Informed Care
The Impact of the Opioid Crisis on Children Guided Notes for Online Learning Name: Date: 1 Table of Contents Section 1: The Opioid Crisis Page 3 Section 2: Addiction Page 4 Section 3: Trauma Informed Care
I have no financial disclosures.
 In the Belly of the Whale: Surviving Thoracoabdominal Trauma Debra Esernio Jenssen, MD, FAAP I have no financial disclosures. Objectives Review epidemiology of abusive chest and abdominal trauma. Identify
In the Belly of the Whale: Surviving Thoracoabdominal Trauma Debra Esernio Jenssen, MD, FAAP I have no financial disclosures. Objectives Review epidemiology of abusive chest and abdominal trauma. Identify
Disclaimer. This is a broad survey and cannot cover all differential diagnoses or each condition in thorough detail
 Objectives Pediatric Infections: Differentiating Benign from Serious Eileen Klein, MD, MPH Rashes Infectious vs non-infectious Viral vs bacterial Respiratory and GI illnesses When do you treat When do
Objectives Pediatric Infections: Differentiating Benign from Serious Eileen Klein, MD, MPH Rashes Infectious vs non-infectious Viral vs bacterial Respiratory and GI illnesses When do you treat When do
Contributors. Thanks to Peter Miller, MD; LCDR Kevin Preston, MD; and Keith Newbrough, MD for their generous contribution of images:
 Contributors Thanks to Peter Miller, MD; LCDR Kevin Preston, MD; and Keith Newbrough, MD for their generous contribution of images: Peter Miller, MD, Indiana University School of Medicine Chapter 1: Figure
Contributors Thanks to Peter Miller, MD; LCDR Kevin Preston, MD; and Keith Newbrough, MD for their generous contribution of images: Peter Miller, MD, Indiana University School of Medicine Chapter 1: Figure
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level
 Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Subspecialty Rotation: Child Neurology at SUNY (KCHC and UHB) Residents: Pediatric residents at the PL1, PL2, PL3 level Prerequisites: Any prior pediatric rotations and experience Primary Goals for this
Efficacy Of A Novel Vision Screening Tool For Detection Of Vision Disorders: Birth To Three Study
 Efficacy Of A Novel Vision Screening Tool For Detection Of Vision Disorders: Birth To Three Study Gayathri Srinivasan OD, MS, FAAO Assistant Professor of Optometry New England College of Optometry, Boston,
Efficacy Of A Novel Vision Screening Tool For Detection Of Vision Disorders: Birth To Three Study Gayathri Srinivasan OD, MS, FAAO Assistant Professor of Optometry New England College of Optometry, Boston,
Talking About The Facts: Stroke In Children
 Talking About The Facts: Stroke In Children AWARENESS LEADS TO A QUICKER RESPONSE AND LIFESAVING OUTCOMES FOR CHILDREN. Pediatric Stroke Warriors continues to strengthen communities by providing support
Talking About The Facts: Stroke In Children AWARENESS LEADS TO A QUICKER RESPONSE AND LIFESAVING OUTCOMES FOR CHILDREN. Pediatric Stroke Warriors continues to strengthen communities by providing support
Pediatric head trauma: the evidence regarding indications for emergent neuroimaging
 DOI 10.1007/s00247-008-0996-5 ALARA: BUILDING BRIDGES BETWEEN RADIOLOGY AND EMERGENCY MEDICINE Pediatric head trauma: the evidence regarding indications for emergent neuroimaging Nathan Kuppermann Received:
DOI 10.1007/s00247-008-0996-5 ALARA: BUILDING BRIDGES BETWEEN RADIOLOGY AND EMERGENCY MEDICINE Pediatric head trauma: the evidence regarding indications for emergent neuroimaging Nathan Kuppermann Received:
Aleutians & Pribilofs
 Aleutians & Pribilofs DV/SV Resource Guide Promoting WellNess Changing Harmful Behaviors If you or someone else needs help with safety: Photo Credit: Brendan Smith Emergency Contacts: Unalaskans Against
Aleutians & Pribilofs DV/SV Resource Guide Promoting WellNess Changing Harmful Behaviors If you or someone else needs help with safety: Photo Credit: Brendan Smith Emergency Contacts: Unalaskans Against
Scoliosis. About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment. Patient and Family Education. What types of scoliosis are there?
 Patient and Family Education Scoliosis About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment This handout covers the most common type of scoliosis, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Other types of scoliosis may
Patient and Family Education Scoliosis About idiopathic scoliosis and its treatment This handout covers the most common type of scoliosis, adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Other types of scoliosis may
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS
 JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
Who is responsible for this account Relationship to patient. How did you hear about us (referral, facebook, etc.)?
 EMERGENCY CONTACT INSURANCE PATIENT INFORMATION Name of Minor/Child SSN Sex: M F Age Birthdate Nickname Mailing Address City, State, Zip Physical Address City, State, Zip Home Phone Work Cell Email Address
EMERGENCY CONTACT INSURANCE PATIENT INFORMATION Name of Minor/Child SSN Sex: M F Age Birthdate Nickname Mailing Address City, State, Zip Physical Address City, State, Zip Home Phone Work Cell Email Address
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Skin Susceptible to injury; longer time Senses of the senses Respiratory system Decreased ability to exchange
 1 Geriatric Review 2 Geriatrics Geriatric patients are individuals older than years of age. In 2000, the geriatric population was almost 35 million. By 2020, the geriatric population is projected to be
1 Geriatric Review 2 Geriatrics Geriatric patients are individuals older than years of age. In 2000, the geriatric population was almost 35 million. By 2020, the geriatric population is projected to be
NEW PATIENT FORM. Please print in ink and fill in all blanks Please fill out front and back. Patient s Full Name
 NEW PATIENT FORM Please print in ink and fill in all blanks Please fill out front and back Patient s Full Name Date of Birth Age Sex Social Security Number Referring Doctor or Family Physician Phone #
NEW PATIENT FORM Please print in ink and fill in all blanks Please fill out front and back Patient s Full Name Date of Birth Age Sex Social Security Number Referring Doctor or Family Physician Phone #
OTTO BREMER TRUST CENTER FOR SAFE AND HEALTHLY CHILDREN NEWSLETTER Issue 2 BECAUSE WE TRANSFORM THE LIVES OF CHILDREN AND FAMILIES
 OTTO BREMER TRUST CENTER FOR SAFE AND HEALTHLY CHILDREN NEWSLETTER Issue 2 Quarterly Newsletter Feb 2018 BECAUSE WE TRANSFORM THE LIVES OF CHILDREN AND FAMILIES Z.UMN.EDU/OBTCSHC Program Update The Otto
OTTO BREMER TRUST CENTER FOR SAFE AND HEALTHLY CHILDREN NEWSLETTER Issue 2 Quarterly Newsletter Feb 2018 BECAUSE WE TRANSFORM THE LIVES OF CHILDREN AND FAMILIES Z.UMN.EDU/OBTCSHC Program Update The Otto
Subdural haematoma and effusion in children aged < 2 years
 Subdural haematoma and effusion in children aged < 2 years Zurynski YA 1,2, Marks S 3, Chaseling R 3 on behalf of the Subdural Haematoma study group 1. Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit 2. The University
Subdural haematoma and effusion in children aged < 2 years Zurynski YA 1,2, Marks S 3, Chaseling R 3 on behalf of the Subdural Haematoma study group 1. Australian Paediatric Surveillance Unit 2. The University
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program. Primary Goals for Rotation. Neurology
 The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
The University of Arizona Pediatric Residency Program Primary Goals for Rotation Neurology 1. GOAL: Understand the role of the pediatrician in preventing neurological diseases, and in counseling and screening
Name Age Date. Please list All your current health complaints, including the reason that brought you to our office:
 Name Age Date Please list All your current health complaints, including the reason that brought you to our office: List any other doctors see for current problems and list treatment received and results:
Name Age Date Please list All your current health complaints, including the reason that brought you to our office: List any other doctors see for current problems and list treatment received and results:
Use of CT in minor traumatic brain injury. Lisa Ayoub-Rodriguez, MD Bert Johansson, MD Michael Lee, MD
 Use of CT in minor traumatic brain injury Lisa Ayoub-Rodriguez, MD Bert Johansson, MD Michael Lee, MD No financial or other conflicts of interest Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury (TBI) Risks associated
Use of CT in minor traumatic brain injury Lisa Ayoub-Rodriguez, MD Bert Johansson, MD Michael Lee, MD No financial or other conflicts of interest Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury (TBI) Risks associated
S.U.M.Ph. "Nicolae Testemitanu" Department of Forensic Medicine 2013/2014. Prelection by Vasile Șarpe MD, MS, PhD, Assoc.
 S.U.M.Ph. "Nicolae Testemitanu" Department of Forensic Medicine 2013/2014 Prelection by Vasile Șarpe MD, MS, PhD, Assoc. Professor Lecture items General concepts, classification Trauma due to fall down
S.U.M.Ph. "Nicolae Testemitanu" Department of Forensic Medicine 2013/2014 Prelection by Vasile Șarpe MD, MS, PhD, Assoc. Professor Lecture items General concepts, classification Trauma due to fall down
Emergency Medicine Scope of Practice
 Emergency Medicine Scope of Practice All Physician Assistants working in Emergency Medicine will encounter a wide variety of non acute, urgent and emergent patient complaints and conditions. Given the
Emergency Medicine Scope of Practice All Physician Assistants working in Emergency Medicine will encounter a wide variety of non acute, urgent and emergent patient complaints and conditions. Given the
