Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes. Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s
|
|
|
- Holly Thornton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Little Kids in Big Crashes The Bio-mechanics of Kids in Car Crashes Lisa Schwing, RN Trauma Program Manager Dayton Children s
2 Very Little Research There has been very little research on the forces a crash has on a child s body. Most research has occurred on scaled down models of the adult body.
3 Kids are not little adults Because children are smaller than adults, traumatic forces in children usually affect a larger region of the body. Multisystem injuries are more common among pediatric patients. High incidence of pulmonary contusion, liver and spleen injuries. Compact - organs are more tightly packaged. Most often, less fat, less muscular, therefore less protection.
4 Speed vs Velocity Kenetic Energy = ½ mass X velocity E=½ MV 2 When mass is doubled, so is the energy. When velocity is doubled, energy is quadrupled. 2 Bottom line speed kills!
5 Children have big bobble heads In comparison to body size, the child s head is larger in size and weight. A child s neck ligaments are weaker.
6 Child Thrown from a Vehicle During a Crash Any child that goes airborne up to the age of 10 will land on their head.
7 The Child s Skull is Thinner Predisposing the skull to fractures that are often accompanied by epidural or subdural bleeding. Head injury is the number one cause of death in children involved in car crashes.
8 Epidural or subdural bleeding on the Brain Can be fatal An epidural bleed is usually the result of a torn artery (the middle meningeal artery) in the brain that bleeds under pressure.
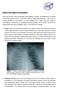
9 A Child s Ribs are Made of Cartilage. Ribs of a child are horizontal and have little calcium. Fractures are difficult to identify, but underlying organs are easily injured. Chest radiograph taken 6 days after injury reveals multiple healing fractures at costovertebral junction and lateral ribs bilaterally. Adult ribs are at an angle, are calcified and hard and provide better protection in a crash.
10 Lungs are Smaller and Respiratory Rates Higher The lungs have disproportionately smaller inside surfaces for oxygen exchange compared to an adult. Depleted oxygen and fatal chemical changes in the blood occur very quickly in children without adequate oxygen.
11 What we do know Abdominal Muscles are less developed. Baby Buda belly Think potential for multisystem injuries.
12 Motor Vehicle Crashes Put Children at Risk for Abdominal Injuries High velocity crashes cause extreme energy transfer to the body. The combination of tightly packaged abdominal organs and in some cases ill fitting safety restraints put a child at increased risk for abdominal injuries.
13 Excessive Energy Transfers to a Small Area Chance fracture Flexion injury around the lap belt.
14 Airbag injuries to children
15 Back to the math E=½ MV 2 5 kg baby 50 mph 921 pound force/foot Zero chance you will hold this child in a 50 mph crash.
16 Chest and Abdominal injuries Chest and Abdominal Injuries are the second leading cause of death in pediatric trauma associated with car crashes. Because the physical exam is often not reliable and the history may be incomplete, missed injuries can lead to increased morbidity and mortality.
17 FAST Exam in Children Negative predictability fairly reliable Positive predictability about 56% and uncertain due to modest sensitivity. Varying study results
18 Ruptured Spleen Goal Children keep their spleens. The 2 children requiring splenectomies due to trauma done at DC in the last 12 years were both in MVC s and both inappropriately restrained. (3yo in booster and 6 yo in seatbelt ) Both had ruptures with massive bleeding. Both had multisystem injuries with ISS >40. Both recovered completely.
19 Blunt Abdominal Injuries Hollow Organs Hollow organ injuries usually require urgent surgical intervention. Esophageal and stomach Bowel Bladder
20 Skeletal Differences Children have incomplete bone calcification. Children s bones are still growing. Injuries to growth plates can arrest bone growth.
21 Penetrating vs. Blunt Abdominal Trauma Penetrating trauma accounts for < 4% of all injuries seen at Dayton Children s. Blunt trauma is common. While falls are the most common cause of injury, severe injuries related to blunt force trauma are usually associated with motor vehicle crashes (not accidents) or children hit by a car while riding a bike or walking Percent of Injury Types at Dayton Children's 1 Burns Penetrating Injuries Blunt Injuries
22 How bad was the crash? Delta v Consider the crashworthiness of the vehicle, the passenger characteristics, and restraint usage. Factor in the speed change of the vehicle as a result of the crash known as the Delta v. This is the measure of the severity of the impact. However, mechanism is not always a factor in the severity of the injury and at Dayton Children s was found to be a poor indicator for predicting injuries.
23 Disbursing the energy in a crash When the energy transfer is isolated to one line or one spot, the impact to that line or spot is greater. Take the energy and spread it out across a larger surface and the energy transfer to any one spot is. A helmet absorbs the energy, spreads it out and protects the head much like seatbelts protect the body.
24 Seatbelt stats Children 4-8 years old restrained in seatbelts are 3 times more likely to be admitted for injuries from a motor vehicle crash than children from birth-4 years. They are too big for car seats and too little for seatbelts. Ohio legislators passed a law October 7, 2009 requiring booster seats for all children 4 to <8 years-of-age and shorter than 4 9. No Perfect
25 What is wrong here? The neck The lap belt / buckle The position of the legs
26 What s wrong here The lap belt The shoulder harness The 5 point restraint buckle Transfer of crash energy to a single area
27 What s wrong here? Too small/young for seatbelts. Shoulder strap across abdomen. No neck protection.
28 What s wrong here? Nothing
29 Seat Belt Injury = Tier II Trauma Activation Though seat belts contribute to a number of predictable injury patterns, proper use of seat belts is statistically the single best prevention for motor vehicle crash fatalities. Note the lack of shoulder strap markings.
30 What s wrong here? Lucky baby involved in a roll over crash.
31 5-Point Restraints Spread the Crash Impact
32 Seatbelt Sign Dayton Children s admitted 65 children with positive seatbelt signs in the last 2 years. The most common injuries associated with seat belt sign: deaths 0 spleen lacerations 11 liver laceration 1 renal lacerations 4 perforated bowel 1 intracranial bleeds 3 concussion 8 skull fracture 2 lumbar fracture 1 femur fracture 5 humerus fracture 3 pelvis fractures 4 pulmonary contusions 4 rib fractures 3 clavicular fracture 3 facial injuries 3 Seat Belt sign with associated lumbar compression fracture
33 There is No Substitute for Good Judgment
34 Kids can Survive Most Car Crashes if Properly Restrained
35 Summary Researchers are striving to develop accurate ways to predict a child s injuries in a motor vehicle crash. Kids are not little adults. Prevention is key. Thank you for all you do!
Kinetic Energy Energy in Motion KE = Mass (weight) X Velocity (speed)² 2 Double Weight = Energy Double Speed = Energy IS THE GREATEST DETERMINANT
 1 Chapter 17 Blunt Trauma 2 Introduction to Blunt Trauma Most common cause of trauma death and disability exchange between an object and the human body, without intrusion through the skin 3 Blunt trauma
1 Chapter 17 Blunt Trauma 2 Introduction to Blunt Trauma Most common cause of trauma death and disability exchange between an object and the human body, without intrusion through the skin 3 Blunt trauma
Trauma Overview. Chapter 22
 Trauma Overview Chapter 22 Kinematics of Trauma Injuries are the leading cause of death among children and young adults. Kinematics introduces the basic physical concepts that dictate how injuries occur
Trauma Overview Chapter 22 Kinematics of Trauma Injuries are the leading cause of death among children and young adults. Kinematics introduces the basic physical concepts that dictate how injuries occur
Pediatric Trauma Karim Rafaat, MD
 Pediatric Trauma Karim Rafaat, MD Goals Time is short I m going to presume you know your basic ATLS (that s that whole ABCD thing, by the way) Discuss each general trauma susceptible region Focus on: Epidemiology
Pediatric Trauma Karim Rafaat, MD Goals Time is short I m going to presume you know your basic ATLS (that s that whole ABCD thing, by the way) Discuss each general trauma susceptible region Focus on: Epidemiology
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #2 Blunt Trauma
 McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #2 Blunt Trauma Blunt trauma is the most common cause of traumatic death and disability. The definition
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT-B and PHRN Optional Continuing Education 2019 #2 Blunt Trauma Blunt trauma is the most common cause of traumatic death and disability. The definition
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma
 Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
Pediatric Abdomen Trauma Susan D. John, MD, FACR Pediatric Trauma Trauma is leading cause of death and disability in children and adolescents Causes and effects vary between age groups Blunt trauma predominates
Review. 1. Kinetic energy is a calculation of:
 Chapter 22 Review Review 1. Kinetic energy is a calculation of: A. weight and size. B. weight and speed. Caring for victims of traumatic injuries requires the EMT to have a solid understanding of the trauma
Chapter 22 Review Review 1. Kinetic energy is a calculation of: A. weight and size. B. weight and speed. Caring for victims of traumatic injuries requires the EMT to have a solid understanding of the trauma
CASPER CASPER. COVER Workshop - 13th March 2012 Berlin, Germany CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS. Abdominal injuries
 CASPER CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS COVER Workshop - 13th March 2012 Berlin, Germany Content Agenda Context Biomechanical aspects Analysis - per type of CRS - per impact type Influence
CASPER CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS COVER Workshop - 13th March 2012 Berlin, Germany Content Agenda Context Biomechanical aspects Analysis - per type of CRS - per impact type Influence
Pediatric Trauma. Sept 2nd, Patrick Murphy Neil Merritt
 Pediatric Trauma Sept 2nd, 2015 Patrick Murphy Neil Merritt Objectives Objectives Medical Expert 1. Describe the types of pediatric injuries sustained with a given mode of trauma, and identify the most
Pediatric Trauma Sept 2nd, 2015 Patrick Murphy Neil Merritt Objectives Objectives Medical Expert 1. Describe the types of pediatric injuries sustained with a given mode of trauma, and identify the most
Activity Three: Where s the Bleeding?
 Activity Three: Where s the Bleeding? There are five main sites of potentially fatal bleeding in trauma, remembered by the phrase on the floor and four more. On the floor refers to losing blood externally
Activity Three: Where s the Bleeding? There are five main sites of potentially fatal bleeding in trauma, remembered by the phrase on the floor and four more. On the floor refers to losing blood externally
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue. Injuries to. and Spine. December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief
 Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
Shenandoah Co. Fire & Rescue Injuries to the Head and Spine December EMS Training Bill Streett Training Section Chief C.E. Card Information BLS Providers 2 Cards / Provider Category 1 Course # Blank Topic#
Body Changes With Aging
 Body Changes With Aging University of Michigan Program for Injury Research and Education Automotive Safety Vehicles are safer than they have ever been. Laboratory testing using idealized occupants and
Body Changes With Aging University of Michigan Program for Injury Research and Education Automotive Safety Vehicles are safer than they have ever been. Laboratory testing using idealized occupants and
Paediatric Trauma. A/Prof Drew Richardson. The Canberra Hospital May MB BS (Hons) FACEM Grad CertHE MD
 Paediatric Trauma A/Prof Drew Richardson MB BS (Hons) FACEM Grad CertHE MD The Canberra Hospital May 2013 Objectives Identify unique anatomic and physiologic characteristics of injured children Describe
Paediatric Trauma A/Prof Drew Richardson MB BS (Hons) FACEM Grad CertHE MD The Canberra Hospital May 2013 Objectives Identify unique anatomic and physiologic characteristics of injured children Describe
Cases from the Streets. Kelly Buchanan MD, ATC/L EMS Fellow December, 2011
 Cases from the Streets Kelly Buchanan MD, ATC/L EMS Fellow December, 2011 The Scene Car vs Light Pole, 35 mph, front right side damage 10 with no PCI + airbag deployment, starring on windshield Given the
Cases from the Streets Kelly Buchanan MD, ATC/L EMS Fellow December, 2011 The Scene Car vs Light Pole, 35 mph, front right side damage 10 with no PCI + airbag deployment, starring on windshield Given the
Professional Development & Training MM3. Firefighter Prehospital Care Program. Maintenance Module 3 Course Mill Version
 Professional Development & Training MM3 Firefighter Prehospital Care Program F T Maintenance Module 3 Course Mill Version S Objectives Upon successful completion of the Firefighter Prehospital Care Maintenance
Professional Development & Training MM3 Firefighter Prehospital Care Program F T Maintenance Module 3 Course Mill Version S Objectives Upon successful completion of the Firefighter Prehospital Care Maintenance
Focused History and Physical Examination of the
 Henry: EMT Prehospital Care, Revised 3 rd Edition Lecture Notes Chapter 10: Focused History and Physical Examination of Trauma Patients Chapter 10 Focused History and Physical Examination of the Trauma
Henry: EMT Prehospital Care, Revised 3 rd Edition Lecture Notes Chapter 10: Focused History and Physical Examination of Trauma Patients Chapter 10 Focused History and Physical Examination of the Trauma
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Advanced Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle crash and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
PROTOCOLS. Lap-belt syndrome. Principal investigator. Background
 Lap-belt syndrome Principal investigator Claude Cyr, MD, Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke, 3001 12 e Avenue Nord, Sherbrooke QC J1H 5N4; tel.: (819) 346-1110, ext. 14634; fax: (819) 564-5398;
Lap-belt syndrome Principal investigator Claude Cyr, MD, Centre hospitalier universitaire de Sherbrooke, 3001 12 e Avenue Nord, Sherbrooke QC J1H 5N4; tel.: (819) 346-1110, ext. 14634; fax: (819) 564-5398;
Mechanism of injury Assessment of the trauma patient. Humaryanto
 Mechanism of injury Assessment of the trauma patient Humaryanto Categories of trauma Kinetics Injury severity score Common mechanism of injury How not to miss an injury Why is it necessary to determine
Mechanism of injury Assessment of the trauma patient Humaryanto Categories of trauma Kinetics Injury severity score Common mechanism of injury How not to miss an injury Why is it necessary to determine
Side Impact Simulations using THUMS and WorldSID
 Side Impact Simulations using THUMS and WorldSID 25 th September, 213 Tsuyoshi Yasuki, Yuichi Kitagawa, Shinobu Tanaka, Satoshi Fukushima TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION CONTENTS 1. Background 2. Objective 3.
Side Impact Simulations using THUMS and WorldSID 25 th September, 213 Tsuyoshi Yasuki, Yuichi Kitagawa, Shinobu Tanaka, Satoshi Fukushima TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION CONTENTS 1. Background 2. Objective 3.
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition
 Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
Injuries to the Head and Spine From Bradys Emergency Care 10 th Edition 1. When performing the four-rescuer log roll, which responder pulls the board into position? A.) Head B.) Waist C.) Knee D.) Shoulder
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials
 Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Trauma Life Support Pre-Hospital (TLS-P) Preparatory Materials 1 1. A high-risk bodily fluid for spreading infection is blood. 2. Items that can reduce the spread of infection include masks, gloves, and
Summary of Pediatric Trauma Patients
 Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Trauma Services Summary of Pediatric Trauma Patients Reporting Dates Jan 1, 2004 May 31, 2006 The mission of the Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Trauma Services is to provide
Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Trauma Services Summary of Pediatric Trauma Patients Reporting Dates Jan 1, 2004 May 31, 2006 The mission of the Santa Rosa Memorial Hospital Trauma Services is to provide
Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting
 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 Chapter 8: Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Abdominal Injuries Abdomen is major body cavity extending from to pelvis. Contains organs that make up digestive, urinary, and genitourinary systems.
Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? David A. Spain, MD
 Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? David A. Spain, MD Granted, some patients don t t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special CT Scan Head Neck Chest Abdomen Pelvis Takes about 20 minutes to do
Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? David A. Spain, MD Granted, some patients don t t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special CT Scan Head Neck Chest Abdomen Pelvis Takes about 20 minutes to do
Imaging in the Trauma Patient
 Imaging in the Trauma Patient David A. Spain, MD Department of Surgery Stanford University Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? 1 Granted, some patients don t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special
Imaging in the Trauma Patient David A. Spain, MD Department of Surgery Stanford University Pan Scan Instead of Clinical Exam? 1 Granted, some patients don t need CT scan Platinum Package Stanford Special
Using Local Data to Drive Injury Prevention Strategies Disclosures Objectives
 Using Local Data to Drive Injury Prevention Strategies Lee Ann Wurster MS, RN, CPNP Trauma Coordinator Disclosures No financials interest or other relationships with commercial entities Objectives Analyze
Using Local Data to Drive Injury Prevention Strategies Lee Ann Wurster MS, RN, CPNP Trauma Coordinator Disclosures No financials interest or other relationships with commercial entities Objectives Analyze
PARA107 Summary. Page 1-3: Page 4-6: Page 7-10: Page 11-13: Page 14-17: Page 18-21: Page 22-25: Page 26-28: Page 29-33: Page 34-36: Page 37-38:
 PARA107 Summary Page 1-3: Page 4-6: Page 7-10: Page 11-13: Page 14-17: Page 18-21: Page 22-25: Page 26-28: Page 29-33: Page 34-36: Page 37-38: Injury, Mechanisms of Injury, Time Critical Guidelines Musculoskeletal
PARA107 Summary Page 1-3: Page 4-6: Page 7-10: Page 11-13: Page 14-17: Page 18-21: Page 22-25: Page 26-28: Page 29-33: Page 34-36: Page 37-38: Injury, Mechanisms of Injury, Time Critical Guidelines Musculoskeletal
Overview. Overview. Chapter 30. Injuries to the Head and Spine 9/11/2012. Review of the Nervous and Skeletal Systems. Devices for Immobilization
 Chapter 30 Injuries to the Head and Spine Slide 1 Overview Review of the Nervous and Skeletal Systems The Nervous System The Skeletal System Devices for Immobilization Cervical Spine Short Backboards Long
Chapter 30 Injuries to the Head and Spine Slide 1 Overview Review of the Nervous and Skeletal Systems The Nervous System The Skeletal System Devices for Immobilization Cervical Spine Short Backboards Long
CLINICAL MANUAL. Trauma System Activation Trauma Code Criteria
 CLINICAL MANUAL Policy Number: CM T-28 Approved by: Nursing Congress, Management Forum Issue Date: 09/1999 Applies to: Downtown Value(s): Respect, Integrity, Innovation Page(s): 1 of 4 Trauma System Activation
CLINICAL MANUAL Policy Number: CM T-28 Approved by: Nursing Congress, Management Forum Issue Date: 09/1999 Applies to: Downtown Value(s): Respect, Integrity, Innovation Page(s): 1 of 4 Trauma System Activation
STREETS AND PUBLIC SAFETY
 STREETS AND PUBLIC SAFETY Peter Swift, PE SwiftLLC.com Fire vs. Vehicle Injuries and Fatalities 3,500,000.00 3,000,000.00 3,032,672.00 2,500,000.00 Incidents per Year 2,000,000.00 1,500,000.00 Fire Vehicle
STREETS AND PUBLIC SAFETY Peter Swift, PE SwiftLLC.com Fire vs. Vehicle Injuries and Fatalities 3,500,000.00 3,000,000.00 3,032,672.00 2,500,000.00 Incidents per Year 2,000,000.00 1,500,000.00 Fire Vehicle
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries. Chapter 28
 Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
Abdomen and Genitalia Injuries Chapter 28 Hollow Organs in the Abdominal Cavity Signs of Peritonitis Abdominal pain Tenderness Muscle spasm Diminished bowel sounds Nausea/vomiting Distention Solid Organs
DATA COLLECTION AND MANAGEMENT
 DATA COLLECTION AND MANAGEMENT PURPOSE To specify the components of the data collection and management processes. RELATED POLICIES Patient Care Record, # 8115; Quality Improvement and System Evaluation,
DATA COLLECTION AND MANAGEMENT PURPOSE To specify the components of the data collection and management processes. RELATED POLICIES Patient Care Record, # 8115; Quality Improvement and System Evaluation,
Child Passenger Safety: An Evidence-Based Review. Robert D. Barraco MD, MPH, Chair 1. Julius D. Cheng, MD, MPH, Vice Chair 2
 Child Passenger Safety: An Evidence-Based Review Robert D. Barraco MD, MPH, Chair 1 Julius D. Cheng, MD, MPH, Vice Chair 2 William J. Bromberg, MD 3 Richard A. Falcone, MD 4 Jeffrey S. Hammond, MD, MPH
Child Passenger Safety: An Evidence-Based Review Robert D. Barraco MD, MPH, Chair 1 Julius D. Cheng, MD, MPH, Vice Chair 2 William J. Bromberg, MD 3 Richard A. Falcone, MD 4 Jeffrey S. Hammond, MD, MPH
The Dynamics of Trauma. Jamie Syrett, MD Director of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System
 The Dynamics of Trauma Jamie Syrett, MD Director of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System Me Boarded EM physician Fellowship trained in EMS Volunteer EMT-B,D,P,L5...etc etc etc Today - Commitment
The Dynamics of Trauma Jamie Syrett, MD Director of Prehospital Care Rochester General Health System Me Boarded EM physician Fellowship trained in EMS Volunteer EMT-B,D,P,L5...etc etc etc Today - Commitment
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
Review. 1. Peritonitis would MOST likely result following injury to the: A. liver. B. spleen. C. kidney. D. stomach.
 Chapter 28 Review Review 1. Peritonitis would MOST likely result following injury to the: A. liver. B. spleen. C. kidney. D. stomach. Review Answer: D Rationale: In general, solid organs bleed when injured
Chapter 28 Review Review 1. Peritonitis would MOST likely result following injury to the: A. liver. B. spleen. C. kidney. D. stomach. Review Answer: D Rationale: In general, solid organs bleed when injured
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 31.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 13 15, 17, 19, 28 31.2 Describe the components and function of the nervous system and the anatomy
Pediatric Patient Overview
 Emergency Medical Services Seattle/King County Public Health 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 206.296.4863 Last Updated December 14, 2015 Pediatric Patient Overview Contents PEDIATRIC BASICS...
Emergency Medical Services Seattle/King County Public Health 401 5th Avenue, Suite 1200 Seattle, WA 98104 206.296.4863 Last Updated December 14, 2015 Pediatric Patient Overview Contents PEDIATRIC BASICS...
SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services OBJECTIVES DEFINITION 11/8/2017. Identify SCIWORA.
 SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services Identify SCIWORA. OBJECTIVES Identify the population at risk. To identify anatomic and physiologic reasons for SCIWORA. To
SCIWORA Rozlyn McTeer BSN, RN, CEN Pediatric Trauma Coordinator Trauma Services Identify SCIWORA. OBJECTIVES Identify the population at risk. To identify anatomic and physiologic reasons for SCIWORA. To
Pediatric Trauma. July 27 th, Suzana Buac, PGY4. Dr. Neil Merritt
 Pediatric Trauma July 27 th, 2016. Suzana Buac, PGY4 Dr. Neil Merritt Case 5yoM fall from roof Fall from roof of home while father was shingling 5yoM fall from roof Fall from roof of home while father
Pediatric Trauma July 27 th, 2016. Suzana Buac, PGY4 Dr. Neil Merritt Case 5yoM fall from roof Fall from roof of home while father was shingling 5yoM fall from roof Fall from roof of home while father
Stephen A. Ridella, Amanda Beyersmith National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Kristin Poland, PhD National Transportation Safety Board
 Stephen A. Ridella, Amanda Beyersmith National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Kristin Poland, PhD National Transportation Safety Board 1 Studies conducted on injury incidence by age Hanna and Hershman
Stephen A. Ridella, Amanda Beyersmith National Highway Traffic Safety Administration Kristin Poland, PhD National Transportation Safety Board 1 Studies conducted on injury incidence by age Hanna and Hershman
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 17 Orthopedic Techniques Key Points 2 17.1 Traction Use an appropriate method of traction to treat fractures of the extremities and cervical spine Apply extremity
Pediatric Aspects of Advanced Trauma Life Support: Transition from EMS to the Trauma Room PEDIATRIC TRAUMA DIRECTOR, HASBRO CHILDREN S HOSPITAL
 Pediatric Aspects of Advanced Trauma Life Support: Transition from EMS to the Trauma Room HALE WILLS, MD PEDIATRIC TRAUMA DIRECTOR, HASBRO CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Objectives 1. Identify the critical components
Pediatric Aspects of Advanced Trauma Life Support: Transition from EMS to the Trauma Room HALE WILLS, MD PEDIATRIC TRAUMA DIRECTOR, HASBRO CHILDREN S HOSPITAL Objectives 1. Identify the critical components
Child as a victim of injury. Maciej Dudkiewicz M.D. Ph.D. Dpt of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medical University of Lodz
 Child as a victim of injury Maciej Dudkiewicz M.D. Ph.D. Dpt of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medical University of Lodz Epidemiology Trauma is most common cause of mortality and morbidity in the US pediatric
Child as a victim of injury Maciej Dudkiewicz M.D. Ph.D. Dpt of Anaesthesia and Intensive Care Medical University of Lodz Epidemiology Trauma is most common cause of mortality and morbidity in the US pediatric
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test
 ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
ITLS Pediatric Provider Course Basic Pre-Test 1. You arrive at the scene of a motor vehicle collision and are directed to evaluate a child who was in one of the vehicles. The patient appears to be a child
SPECIAL DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES IN BLUNT TRAUMA OLEH : Prof.DR.Dr Abdul Rasyid SpRad (K),Ph.D Dr.Evo Elidar Sp.Rad
 SPECIAL DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES IN BLUNT TRAUMA OLEH : Prof.DR.Dr Abdul Rasyid SpRad (K),Ph.D Dr.Evo Elidar Sp.Rad Trauma Emergency Room layout Ideally the trauma emergency room is centrally located to provide
SPECIAL DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES IN BLUNT TRAUMA OLEH : Prof.DR.Dr Abdul Rasyid SpRad (K),Ph.D Dr.Evo Elidar Sp.Rad Trauma Emergency Room layout Ideally the trauma emergency room is centrally located to provide
1. Which of the following organs is contained in the retroperitoneal region of the abdomen? A. Stomach B. Liver C. Kidney D.
 1. Which of the following organs is contained in the retroperitoneal region of the abdomen? A. Stomach B. Liver C. Kidney D. Uterus 2. What is Sellick's maneuver? A. A method allowing the rescuer to hold
1. Which of the following organs is contained in the retroperitoneal region of the abdomen? A. Stomach B. Liver C. Kidney D. Uterus 2. What is Sellick's maneuver? A. A method allowing the rescuer to hold
Disclosure. Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies. I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program or presentation.
 Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS. December 19, 2012
 PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA I: ABDOMINAL TRAUMA BURNS Niel F. Miele,, M.D. December 19, 2012 EPIDEMIOLOGY Major Trauma responsible for
George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon
 George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon Health and Sciences University. Portland, OR Outline
George M Wadie, MD Director Division of Pediatric Surgery Sacred Heart Medical Center. Springfield, OR Adjunct Assistant Professor of Surgery Oregon Health and Sciences University. Portland, OR Outline
Bilateral rib fractures 2 on right and 1 on left In different stages of healing, with left fracture older than right fractures
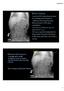 More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of
 Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
Daniel A. Beals MD, FACS, FAAP Pediatric Surgery and Urology Community Medical Center Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatrics University of Washington Seattle Children s Hospital Objectives Define
Selective Spine Assessment & Spinal Motion Restriction
 Selective Spine Assessment & Spinal Motion Restriction Supersedes: 02-09-15 Effective: 10-20-15 Spinal cord injury may be the result of direct blunt and/or penetrating trauma, compression forces (axial
Selective Spine Assessment & Spinal Motion Restriction Supersedes: 02-09-15 Effective: 10-20-15 Spinal cord injury may be the result of direct blunt and/or penetrating trauma, compression forces (axial
Chapter 32. Objectives. Objectives 01/09/2013. Spinal Column and Spinal Cord Trauma
 Chapter 32 Spinal Column and Spinal Cord Trauma Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1.
Chapter 32 Spinal Column and Spinal Cord Trauma Prehospital Emergency Care, Ninth Edition Joseph J. Mistovich Keith J. Karren Copyright 2010 by Pearson Education, Inc. All rights reserved. Objectives 1.
NHTSA s Ease of Use Rating System for Child Restraint Systems
 Transmitted by the expert from the United States of America NHTSA s Ease of Use Rating System for Child Restraint Systems Informal document No. GRSP-43-14 (43rd GRSP, 19-23 May 2008 agenda items 12(a))
Transmitted by the expert from the United States of America NHTSA s Ease of Use Rating System for Child Restraint Systems Informal document No. GRSP-43-14 (43rd GRSP, 19-23 May 2008 agenda items 12(a))
The etiology of the trauma was defined as the mechanism by which the traumatic event occurred and
 APPENDIX 2: Additional Methodological Details The etiology of the trauma was defined as the mechanism by which the traumatic event occurred and consisted of the following fifteen categories: motor vehicle
APPENDIX 2: Additional Methodological Details The etiology of the trauma was defined as the mechanism by which the traumatic event occurred and consisted of the following fifteen categories: motor vehicle
Trauma Patients What do we really know?
 Patients What do we really know? Dan Talbert MHS, EMT-P, FP-C TraumaOne / UF Health Jacksonville Objectives Introduction to trauma Overview of the trauma system Overview of the traumatic injury Case review
Patients What do we really know? Dan Talbert MHS, EMT-P, FP-C TraumaOne / UF Health Jacksonville Objectives Introduction to trauma Overview of the trauma system Overview of the traumatic injury Case review
Injuries to the Head and Spine
 Injuries to the Head and Spine Anatomy Review Skull Protects the brain Made up of several bones with seam like sutures Regions of the scalp-frontal, occipital, parietal, temporal Bones of face Orbits Mandible
Injuries to the Head and Spine Anatomy Review Skull Protects the brain Made up of several bones with seam like sutures Regions of the scalp-frontal, occipital, parietal, temporal Bones of face Orbits Mandible
A Severely Injured Pediatric Trauma Patient: Case Presentation and Discussion
 A Severely Injured Pediatric Trauma Patient: Case Presentation and Discussion Christopher Butts PhD, DO Surgical Critical Care Fellow Cooper University Hospital H&P 10 year old female presents as a trauma
A Severely Injured Pediatric Trauma Patient: Case Presentation and Discussion Christopher Butts PhD, DO Surgical Critical Care Fellow Cooper University Hospital H&P 10 year old female presents as a trauma
Sasha Dubrovsky, MSc MD FRCPC Pediatric Emergency Medicine Montreal Children s Hospital - MUHC October 2010
 Sasha Dubrovsky, MSc MD FRCPC Pediatric Emergency Medicine Montreal Children s Hospital - MUHC October 2010 Learning objectives 1. Discuss diagnostic goals in pediatric trauma Diagnose All vs. Severe Injuries
Sasha Dubrovsky, MSc MD FRCPC Pediatric Emergency Medicine Montreal Children s Hospital - MUHC October 2010 Learning objectives 1. Discuss diagnostic goals in pediatric trauma Diagnose All vs. Severe Injuries
SAN LUIS OBISPO COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY PREHOSPITAL POLICY
 SAN LUIS OBISPO COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY PREHOSPITAL POLICY Policy Reference No: 153 [01/08/2013] Formerly Policy No: 201.3 Effective Date: 11/01/2012 Review Date: 03/01/2014 TRAUMA PATIENT
SAN LUIS OBISPO COUNTY EMERGENCY MEDICAL SERVICES AGENCY PREHOSPITAL POLICY Policy Reference No: 153 [01/08/2013] Formerly Policy No: 201.3 Effective Date: 11/01/2012 Review Date: 03/01/2014 TRAUMA PATIENT
Every day thousands of people become the accidental victims of trauma.
 Aurora Health Care South Region EMS 2010 2 nd Quarter CE Packet Spinal Cord Trauma Every day thousands of people become the accidental victims of trauma. Approximately 43,000 people die in motor vehicle
Aurora Health Care South Region EMS 2010 2 nd Quarter CE Packet Spinal Cord Trauma Every day thousands of people become the accidental victims of trauma. Approximately 43,000 people die in motor vehicle
The ABC s of Chest Trauma
 The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
The ABC s of Chest Trauma J Bradley Pickhardt MD, FACS Providence St Patrick Hospital What s the Problem? 2/3 of trauma patients have chest trauma Responsible for 25% of all trauma deaths Most injuries
Chapter 29 - Chest_and_Abdominal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 29.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 18, 27 29.2 Describe mechanisms of injury commonly associated with chest injuries. Slides
Overview. Worsening situation Top 10 leading causes of death /7/2017. Seat belt sign
 Timothy Woods, M.D., FACS Trauma Medical Director CoxHealth Overview Seat belts save lives Seat belt injury patterns Seat belt sign Vertebral injuries Blunt hollow viscus injury Blunt abdominal wall hernia
Timothy Woods, M.D., FACS Trauma Medical Director CoxHealth Overview Seat belts save lives Seat belt injury patterns Seat belt sign Vertebral injuries Blunt hollow viscus injury Blunt abdominal wall hernia
of Trauma Assembly 27 th Page 1
 Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Eastern Association for the Surgery of Trauma 27 th Annual Scientific Assembly Sunrise Session 08 To Scan or Not To Scan Thatt is the Question January 16, 2014 Waldorf Astoria Naples Naples, Floridaa Page
Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and
 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and involuntary activities Voluntary activities
1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 26 Head and Spine Trauma The Nervous System The nervous system controls virtually all of our body activities including reflex, voluntary and involuntary activities Voluntary activities
Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: April 2015
![Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: April 2015 Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # [] Date accepted: April 2015](/thumbs/83/87309292.jpg) Radiological Category: Enter category here Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none Case Report # [] Submitted by: Varun Rachakonda, M.D.
Radiological Category: Enter category here Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): Enter modality here Enter modality here, enter none if none Case Report # [] Submitted by: Varun Rachakonda, M.D.
Road Traffic Accidents and Brain Injury.
 Road Traffic Accidents and Brain Injury www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Aims RTA Figures Mechanics of RTA Brain injuries Types Assessment Treatment Development Mood disorders / Secondary complications Whiplash
Road Traffic Accidents and Brain Injury www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Aims RTA Figures Mechanics of RTA Brain injuries Types Assessment Treatment Development Mood disorders / Secondary complications Whiplash
Abdominal V.A.C. Therapy in Trauma
 Abdominal V.A.C. Therapy in Trauma Stefaan Nijs, M.D., Ph.D. Mathieu D Hondt, M.D. Dept Abdominal Surgery UZ Leuven 1 2 Damage control = naval technique Damage Control in Trauma 3 USS Nevada 4 In extremis
Abdominal V.A.C. Therapy in Trauma Stefaan Nijs, M.D., Ph.D. Mathieu D Hondt, M.D. Dept Abdominal Surgery UZ Leuven 1 2 Damage control = naval technique Damage Control in Trauma 3 USS Nevada 4 In extremis
BODY SYSTEMS BODY CAVITIES THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Movements BODY CAVITIES. Pediatric Considerations In Respiratory System
 BODY SYSTEMS A body system is a group of organs and other structures work together to carry out specific functions. The following systems work together to carry out a function needed for life: Respiratory
BODY SYSTEMS A body system is a group of organs and other structures work together to carry out specific functions. The following systems work together to carry out a function needed for life: Respiratory
Selective Spinal Immobilization
 Selective Spinal Immobilization Objectives Understand the background of spinal immobilization. Understand the rationale for developing a current selective spinal immobilization protocol. Review the data
Selective Spinal Immobilization Objectives Understand the background of spinal immobilization. Understand the rationale for developing a current selective spinal immobilization protocol. Review the data
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides
 The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
The Viewing Study Guide for Physical Abuse Slides Adapted From The Visual Diagnosis of Non-Accidental Trauma and Failure to Thrive A Study Guide By Barton D. Schmitt, M.D. in Cooperation with The American
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHILDHOOD MOTOCROSS TRUNCAL INJURIES: HIGH VELOCITY, FOCAL FORCE TO THE CHEST AND ABDOMEN: A Cohort Study For peer review only
 CHILDHOOD MOTOCROSS TRUNCAL INJURIES: HIGH VELOCITY, FOCAL FORCE TO THE CHEST AND ABDOMEN: A Cohort Study Journal: Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-00 Article Type: Research Date Submitted by the Author: -Jul-0
CHILDHOOD MOTOCROSS TRUNCAL INJURIES: HIGH VELOCITY, FOCAL FORCE TO THE CHEST AND ABDOMEN: A Cohort Study Journal: Manuscript ID: bmjopen-0-00 Article Type: Research Date Submitted by the Author: -Jul-0
Looking Toward State Health Assessment.
 CONNECTICUT DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH Policy, Planning and Analysis. Looking Toward 2000 - State Health Assessment. Table of Contents Glossary Maps Appendices Publications Public Health Code PP&A Main
CONNECTICUT DEPARTMENT OF PUBLIC HEALTH Policy, Planning and Analysis. Looking Toward 2000 - State Health Assessment. Table of Contents Glossary Maps Appendices Publications Public Health Code PP&A Main
Supplementary Table 1. ICD-9/-10 codes used to identify cycling injury hospitalizations. Railway accidents injured pedal cyclist
 Supplementary Table 1. ICD-9/-10 codes used to identify cycling injury hospitalizations. ICD Code ICD-9 E800-E807(.3) E810-E816, E818-E819(.6) E820-E825(.6) E826-E829(.1) ICD-10-CA V10-V19 (including all
Supplementary Table 1. ICD-9/-10 codes used to identify cycling injury hospitalizations. ICD Code ICD-9 E800-E807(.3) E810-E816, E818-E819(.6) E820-E825(.6) E826-E829(.1) ICD-10-CA V10-V19 (including all
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION
 COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
COURSE OUTLINE-IB 128: SPORTS MEDICINE INTRODUCTION Definition of sports medicine Pre-participation physical exam Epidemiology of sports injuries injury rates for various sports sports risks relative to
Purely Ligamentous Flexion-Distraction Injury in a Five-Year-Old Child Treated with Surgical Management
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1130 Purely Ligamentous Flexion-Distraction Injury in a Five-Year-Old Child Treated with Surgical Management Ryan M. Schiedo 1, William Lavelle 2, Nathaniel
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.1130 Purely Ligamentous Flexion-Distraction Injury in a Five-Year-Old Child Treated with Surgical Management Ryan M. Schiedo 1, William Lavelle 2, Nathaniel
UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT
 UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT PremierOrtho.com UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT Table of Contents Introduction...3 Causes...4 Who s at Risk?...5
UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT PremierOrtho.com UNDERSTANDING FRACTURE CARE CAUSES, DIAGNOSIS, AND TREATMENT Table of Contents Introduction...3 Causes...4 Who s at Risk?...5
17. Imaging and interventional radiology
 17. Imaging and interventional radiology These guidelines have been adapted from the Leeds Major Trauma Centre Imaging in Paediatric Major Trauma guidelines Written by Dr Annmarie Jeanes (Consultant Paediatric
17. Imaging and interventional radiology These guidelines have been adapted from the Leeds Major Trauma Centre Imaging in Paediatric Major Trauma guidelines Written by Dr Annmarie Jeanes (Consultant Paediatric
Hospital-Based Injury & Violence Prevention Intervention
 Hospital-Based Injury & Violence Prevention Intervention Presented by: Nichole Kent Spivey, MBA Injury Prevention Coordinator Palmetto Health Richland Level I Trauma Center # 1 Killer for Ages 1-44 Source:
Hospital-Based Injury & Violence Prevention Intervention Presented by: Nichole Kent Spivey, MBA Injury Prevention Coordinator Palmetto Health Richland Level I Trauma Center # 1 Killer for Ages 1-44 Source:
Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/02/2010 History Restrained teenager involved in motor vehicle accident. Diagnosis Chance Fracture (Hyperflexion-Distraction Injury) Discussion Chance-type spinal
Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/02/2010 History Restrained teenager involved in motor vehicle accident. Diagnosis Chance Fracture (Hyperflexion-Distraction Injury) Discussion Chance-type spinal
Brain Injuries. Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama
 Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Brain Injuries Presented By Dr. Said Said Elshama Types of head injuries 1- Scalp injuries 2- Skull injuries 3- Intra Cranial injuries ( Brain ) Anatomical structure of meninges Intra- Cranial Injuries
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
CASPER. March 2012 CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS
 CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS Study on the influence of the child dummy stature reproducing real life situations on the dummy readings March 2012 AGENDA Context Setup Dummy Use and Misuse
CHILD ADVANCED SAFETY PROJECT FOR EUROPEAN ROADS Study on the influence of the child dummy stature reproducing real life situations on the dummy readings March 2012 AGENDA Context Setup Dummy Use and Misuse
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY
 PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
PEDIATRIC MILD TRAUMATIC HEAD INJURY October 2011 Quality Improvement Resources Illinois Emergency Medical Services for Children is a collaborative program between the Illinois Department of Public Health
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
 Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries Mark L. Wood, MD The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the most commonly injured ligaments of the knee. The incidence of ACL injuries is currently estimated
Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing
 1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing D-Disability Chief complaint and/or Mechanism
1 2 3 4 5 6 Chapter 8 Trauma Patient Assessment The Patient Assessment Process The Primary Assessment ABCDE s Airway, Breathing, Circulation while securing D-Disability Chief complaint and/or Mechanism
COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes. Chapter 7
 COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes Chapter 7 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD 4 th leading cause of death in the U.S. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Any chronic conditions
COPD, Pneumonia & Influenza, Accidents, Diabetes Chapter 7 Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease COPD 4 th leading cause of death in the U.S. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Any chronic conditions
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury. Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center
 Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Pre-hospital Response to Trauma and Brain Injury Hans Notenboom, M.D. Asst. Medical Director Sacred Heart Medical Center Traumatic Brain Injury is Common 235,000 Americans hospitalized for non-fatal TBI
Spinal fractures associated with ejection from jet aircraft: two case reports and a review
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 240-244 Spinal fractures associated with ejection from jet aircraft: two case reports and a review M. R. JAMES Department of Accident and Emergency, Lincoln County
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 240-244 Spinal fractures associated with ejection from jet aircraft: two case reports and a review M. R. JAMES Department of Accident and Emergency, Lincoln County
Paramedic Trauma
 Western Technical College 10531920 Paramedic Trauma Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 Total Hours 72.00 This course teaches the
Western Technical College 10531920 Paramedic Trauma Course Outcome Summary Course Information Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 3.00 Total Hours 72.00 This course teaches the
Radiographic Procedures 1
 Western Technical College 10526149 Radiographic Procedures 1 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Textbooks Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 5 Prepares radiography students
Western Technical College 10526149 Radiographic Procedures 1 Course Outcome Summary Course Information Textbooks Description Career Cluster Instructional Level Total Credits 5 Prepares radiography students
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series. Urological Trauma
 UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
UBC Department of Urologic Sciences Lecture Series Urological Trauma Disclaimer: This is a lot of information to cover and we are unlikely to cover it all today These slides are to be utilized for your
Keeping Children Safe: Child Passenger Safety Programs in the DFW Metro Area
 Keeping Children Safe: Child Passenger Safety Programs in the DFW Metro Area Sharon Evans RN, BSN, CPN, CPSTI Injury Prevention Coordinator Cook Children s Medical Center The Facts Motor vehicle crashes
Keeping Children Safe: Child Passenger Safety Programs in the DFW Metro Area Sharon Evans RN, BSN, CPN, CPSTI Injury Prevention Coordinator Cook Children s Medical Center The Facts Motor vehicle crashes
Chapter 13. Injuries to the Thorax and Abdomen
 Chapter 13 Injuries to the Thorax and Abdomen Anatomy Review Thoracic cage has 12 pairs of ribs. The first 7 pairs connect directly to sternum. Pairs 8 through 10 connect via common costal cartilage. Pairs
Chapter 13 Injuries to the Thorax and Abdomen Anatomy Review Thoracic cage has 12 pairs of ribs. The first 7 pairs connect directly to sternum. Pairs 8 through 10 connect via common costal cartilage. Pairs
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA: Implications for Respiratory Care
 PEDIATRIC TRAUMA: Implications for Respiratory Care 17 th Annual Rainbow Respiratory Conference - September 4, 2015 Mike Dingeldein, MD Pediatric Surgeon Pediatric Trauma Medical Director Disclosures none
PEDIATRIC TRAUMA: Implications for Respiratory Care 17 th Annual Rainbow Respiratory Conference - September 4, 2015 Mike Dingeldein, MD Pediatric Surgeon Pediatric Trauma Medical Director Disclosures none
