AMDCC Neuropathy Phenotyping Core. Eva Feldman MD, PhD JDRF Center University of Michigan
|
|
|
- Rolf Holmes
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AMDCC Neuropathy Phenotyping Core Eva Feldman MD, PhD JDRF Center University of Michigan 1
2 Outline Define neuropathy and illustrate phenotyping Summarize current phenotyping efforts Collaborations 2
3 AMDCC Definition of Neuropathy Evidence of clinical loss of sensory function Tail flick and hind paw withdrawal latencies (TF and HP) Electrophysiological evidence of nerve impairment Sensory and motor distal latencies and nerve conduction velocity (NCV) Anatomical evidence of nerve fiber loss Intraepidermal fiber density (IEFD 3
4 Evidence of Clinical Loss of Sensory Function Tail flick and hind paw thermal testing The time from the application of the stimulus to time of withdrawal equals the latency Measured every 12 weeks and at tissue harvest Reliable and reproducible Hind paw latencies correlate well with IEFD Non-invasive 4
5 Tail Flick 5
6 Hind Paw Withdrawal 6
7 Electrophysiological Evidence of Nerve Conductions Nerve Impairment Tail motor distal latency, tail sensory and sciatic motor conduction velocity Sensitive measures of peripheral nerve function Requires anesthesia Performed at 12 weeks post-diabetes and at tissue Harvest 7
8 Tail Distal Motor Latency 8
9 Sciatic Nerve Motor Conduction Velocity 9
10 Anatomical Evidence of Nerve Fiber Loss with Skin Biopsies Intraepidermal Fiber Density PGP9.5 (ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase) Pan-axonal marker Confocal image capture and analysis Data may be expressed as number of fibers per mm of epidermis or as area of fibers per area epidermis Samples may also be examined for specific neurotransmitters 1
11 Normal Cutaneous Innervation Assessed with Skin Biopsy 11
12 SOD2+/+ Db+ E D Bar = 5 υm 12
13 SOD2+/- Dbdb E D 13
14 Current models uma/cr Every 12 weeks 24 hr urine at 24 wks or end of trial Tail Flick Hind Paw Every 8 weeks NCV Measured 12 and 24 weeks post-diabetes Glom. PAS area Measured at tissue harvest Glom. podocyte Measured at tissue harvest IEFD Measured at tissue harvest Biochemistry Measured at tissue harvest C57BLKS db/db NA X X NA NA X X GCLC +/- db/db high fat diet Ongoing X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing GLUT1 tg db/db high fat diet Nphs2 GLUT1 tg C57BLKSdb/db Nphs2 Cre// SOD2 loxp/loxp Nestin Cre// SOD2 loxp/loxp GLUT4 -/- and Nphs2 Cre// GLUT4 loxp/loxp Ongoing X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing X NA NA X Ongoing NA Ongoing X X X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing X X X X X X Ongoing GLUT4 -/- Akita Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding PDX+/- Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing 14
15 Sensory Measures BKLS Mice 1. TF HP * # 7.5 seconds seconds db+ dbdb. db+ dbdb *P <.1, #P <.1 15
16 Nerve Conduction Velocities BKLS Mice 3 TSNCV 5 TDML * meters/seconds * milliseconds db+ dbdb db+ dbdb SMNCV 5 seconds # *P <.1, #P <.1 1 db+ dbdb 16
17 Sensory Testing GCLC+/+, +/- Db/db Mice TF HP seconds seconds 1 5. wt db+ wt dbdb gclc db+ gclc dbdb wt db+ wt dbdb gclc db+ gclc dbdb No Significant Differences 17
18 Sensory Testing GLUT4-/- C57Bl/6J Mice TF HP seconds seconds wt wt DM ko ko DM. wt wt DM ko ko DM No Significant Differences 18
19 Sensory Tests GLUT1tg C57Bl/6J Mice TF HP seconds 6 4 seconds wt db+ wt dbdb tg db+ tg dbdb wt db+ wt dbdb tg db+ tg dbdb No Significant Differences 19
20 Nerve Conduction Velocity GLUT1tg C57Bl/6J Mice TSNCV TDML 25 6 meters/second milliseconds wt db+ wt dbdb tg db+ tg dbdb SMNCV wt db+ wt dbdb tg db+ tg dbdb 4 meters/second No Significant Differences wt db+ wt dbdb tg db+ tg dbdb 2
21 Sensory Testing Cre//SOD2 loxp/loxp Mice TF HP 1 5 seconds 5 seconds flox flox cre flox flox flox flox cre flox flox No Significant Differences 21
22 Nerve Conduction Velocity Cre//SOD2 loxp/loxp Mice TSNCV TDML 3 3 meters/second 2 1 milliseconds 2 1 flox flox cre flox flox flox flox cre flox flox SMNCV 4 meters/second No Significant Differences flox flox cre flox flox 22
23 Sensory Testing PDX+/+ and +/- Mice 1. TF * 4 HP seconds seconds pdx +/- pdx +/+ pdx +/- pdx +/+ * P <.4 23
24 Nerve Conduction Studies PDX +/+ and +/- Mice TSNCV TDML 3 3 meters/second 2 1 milliseconds 2 1 pdx +/+ pdx +/- pdx +/+ pdx +/- SMNCV 5 * P <.4 meters/second * pdx +/+ pdx +/- 24
25 Intraepidermal Fibers LDLRO and LDLRO ob/ob Mice 25
26 Current models uma/cr Every 12 weeks 24 hr urine at 24 wks or end of trial Tail Flick Hind Paw Every 8 weeks NCV Measured 12 and 24 weeks post-diabetes Glom. PAS area Measured at tissue harvest Glom. podocyte Measured at tissue harvest IEFD Measured at tissue harvest Biochemistry Measured at tissue harvest C57BLKS db/db NA X X NA NA X X GCLC +/- db/db high fat diet Ongoing X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing GLUT1 tg db/db high fat diet Nphs2 GLUT1 tg C57BLKSdb/db Nphs2 Cre// SOD2 loxp/loxp Nestin Cre// SOD2 loxp/loxp GLUT4 -/- and Nphs2 Cre// GLUT4 loxp/loxp Ongoing X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing X NA NA X Ongoing NA Ongoing X X X Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing X X X X X X Ongoing GLUT4 -/- Akita Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding Breeding PDX+/- Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing Ongoing 26
27 Collaborations Jan Breslow, Rockefeller University Has sent food pad biopsies to Michigan for IEFD from LDLR mice Completing phenotyping of Pdx mice (very promising model) Firouz Daneshgari, Cleveland Clinic Foundation Measures of bladder elasticity and emptying Plans to examine innervation density similar to foot pad biopsy method Timothy Kern, Case Western Reserve University Sending whole eyes from Michigan and Rockefeller mice Are able to supply eyes after terminal neuropathy phenotyping David Clemmons and Timothy Nichols, University of North Carolina Have sent ankle and hip skin, dorsal root ganglia and sciatic nerves from hypercholesterolemic pigs Continue to encounter some difficulties with IEFD antibody? 27
28 Porcine Skin 28
29 Sensory Testing PDX+/+ and +/- Mice 1. TF * 4 HP seconds seconds pdx +/- pdx +/+ pdx +/- pdx +/+ * P <.4 29
30 Porcine Skin J. Anat. 19:61-611,
31 IEFD Porcine Skin E D 31
32 Outline Respond to EAC comments Define neuropathy and illustrate phenotyping Summarize current phenotyping efforts Highlight key models Collaborations AMDCC Neuropathy Core is fully functional and can perform screening via footpads for IEFD or terminal phenotyping 32
33 IntraEpidermal Fiber Density 33
34 Animal model Background strain current status Phenotyping (begin-end) Consortium collaborators Current Models (page 1) SOD2 +/- STZ C57BL/6J phenotyping complete; no increase in neuropathy or nephropathy 3-2 to 8-3 SOD2 +/- db/db Nphs2 Cre//SOD2 loxp/loxp C57BL/6J C57BL/6J Phenotyping complete; no increase in neuropathy or nephropathy 3-3 to 9-3 phenotyping ongoing; no obvious increase nephropathy 12-3 to 12-4 Vanderbilt ROS Nphs2 Cre//SOD2 loxp/loxp C57BL/6J 129SvJ phenotyping nearing completion; no significant increase nephropathy 1-4 to 12-4 Vanderbilt nestin Cre//SOD2 loxp/loxp C57BL/6J phenotyping ongoing 3-4 to 2-5 Vanderbilt synapsin Cre//SOD2 loxp/loxp C57BL/6J Breeding complicated; phenotyping ongoing 4-4 to 4-5 Vanderbilt Po Cre// SOD2 loxp/loxp C57BL/6J receiving mice On hold 12-4 to 12-5 Vanderbilt GCLC +/- STZ C57BL/6J On hold 6-3 to 5-4 GCLC +/- db/db AR tg//sod2+/- STZ C57BL/6J C57BL/6 phenotyping virtually complete; excellent neuropathy; no increase nephropathy 7-3 to 6-4 phenotyping ongoing; increased neuropathy in diabetics with double mutation 1-4 to 12-4 GCLC +/-//SOD2 +/- STZ C57BL/6 To begin breeding On hold 12-4 to 12-5 signaling fyn -/- fyn -/- STZ fyn -/- C57BL/6J 129SvJ C57BL/6J 129SvJ 129SvJ phenotyping complete severe albuminuria in nondiabetics 6-3 to 8-3 phenotyping completed: increased albuminuria in diabetics with mutation 6-3 to 8-3 rederivation completed; phenotyping ongoing. No albuminuria in nondiabetics 9-3 to 8-4 fyn -/- and +/- STZ 129SvJ phenotyping ongoing 9-3 to 9-4 IRS-1 -/- C57BL/6J Breeding colony On hold? 34
35 Animal model Background strain current status Phenotyping (begin-end) Consortium collaborators Current Models (page 2) GLUT4 -/- STZ C57BL/6J phenotyping complete; increased nephropathy; modest increase neuropathy 11-1 to 5-4 Einstein GLUT4 -/- db/db C57BL/6J On hold 11-3 to 1-4 Einstein Nphs2 Cre //Glut4 loxp/loxp C57BL/6J phenotyping ongoing 4-4 to 12-5 Utah GLUTs GLUT1 tg C57BL/6J phenotyping ongoing; increased glomerulosclerosis in nondiabetics 7-3 to 1-5 Hopkins GLUT1 tg STZ C57BL/6J expanding lines 9-3 to 11-4 Hopkins GLUT1 tg db/db C57BL/6J phenotyping ongoing 1-3 to 1-5 Hopkins Nphs2 GLUT1 tg db/db C57BLKS Transgenic lines with overexpression established; beginning phenotyping 12-4 to 1-5 Hopkins Nestin GLUT1 tg db/db C57BLKS making construct On hold 3-4 to 1-5 Hopkins Nphs2 cre //PPARγ loxp/loxp C57BL/6J uncertain 12-4 to 8-5 UCLA conditional Nphs2 cre C57BL/6J Crossed with other lines breeding stock synapsin cre C57BL/6J crossed with other lines breeding stock nestin cre C57BL/6J crossed with other lines breeding stock db/db C57BL/6J breeding; phenotyping complete 9-3; breeding stock db/db C57BLKS breeding; increased neuropathy 2-4 to 1-4; breeding stock Selenocysteine floxed (trsp) x synapsin cre STZ C57BL/6J breeding 8-4 Selenocysteine floxed (trsp) x podocin cre STZ C57BL/6J breeding 8-4 Koenig (Michigan) Koenig (Michigan) 35
36 Phenotyping: Current Tail Flick Hind Paw Every 8 weeks NCV Measured 12 and 24 weeks post-diabetes IEFD Measured at tissue harvest C57BLKS Animals being added GCLC +/- and +/+ Dbdb and Db+ C57Bl6 Dbdb Breeder Chow nestin Cre// SOD2 LoxP/LoxP synapsin Cre// SOD2 LoxP/LoxP fyn (-/-)(+/-)(+/+) STZ treated and control X X X X X Ongoing 4 animals X (9 animals) Animals Breeding X X (9 animals) X GLUT4 (-/-) (+/+) STZ treated and control X X 36
37 General schema for evaluation STZ 5 mg/kg/day x 5 days Sensory function ±NCVs uma/creat (spot) Sensory function +NCVs uma/creat (24h) blood glc Age (months) BP harvest kidneys, nerves, blood 37
38 Nerve Conduction Velocity GCLC+/+, +/- Db/db Mice TSNCV TDML 3 4 meters/second 2 1 milliseconds wt db+ wt dbdb gclc db+ gclc dbdb wt db+ wt dbdb gclc db+ gclc dbdb SMNCV 5 meters/second No Significant Differences wt db+ wt dbdb gclc db+ gclc dbdb 38
39 C57BlKS * * * P<.1 39
40 C57BlKS : Sensory Tests * # * P<.1 # P <.5 4
41 C57BlKS : Nerve Conductions * * * * P<.1 41
AMDCC Neuropathy Core March Eva L. Feldman, M.D., Ph.D Department of Neurology JDRF Center University of Michigan
 AMDCC Neuropathy Core March 6 Eva L. Feldman, M.D., Ph.D Department of Neurology JDRF Center University of Michigan AMDCC Definition of Neuropathy Evidence of clinical loss of sensory function Tail flick
AMDCC Neuropathy Core March 6 Eva L. Feldman, M.D., Ph.D Department of Neurology JDRF Center University of Michigan AMDCC Definition of Neuropathy Evidence of clinical loss of sensory function Tail flick
Michigan/Chicago unit
 Michigan/Chicago unit Modifications in Mouse Models to Enhance Nephropathy/Neuropathy- GLUT1 overexpression Increased oxidative stress Increased glucose metabolic flux or alteration in GLUT expression
Michigan/Chicago unit Modifications in Mouse Models to Enhance Nephropathy/Neuropathy- GLUT1 overexpression Increased oxidative stress Increased glucose metabolic flux or alteration in GLUT expression
March 2005 AMDCC Progress Report. Diabetic Uropathy. Firouz Daneshgari, M.D. The Cleveland Clinic Foundation
 March 2005 AMDCC Progress Report Diabetic Uropathy Firouz Daneshgari, M.D. The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Diabetic Uropathy Ouline Further definition of diabetes- specific changes in the bladder Find
March 2005 AMDCC Progress Report Diabetic Uropathy Firouz Daneshgari, M.D. The Cleveland Clinic Foundation Diabetic Uropathy Ouline Further definition of diabetes- specific changes in the bladder Find
Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy. Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI
 Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI Group Members Mount Sinai: Phenotyping, Molecular Pathology & Validation Erwin
Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI Group Members Mount Sinai: Phenotyping, Molecular Pathology & Validation Erwin
Atherosclerosis in Insulin Resistant Hyperlipidemic Pigs R01 HL
 Atherosclerosis in Insulin Resistant Hyperlipidemic Pigs R01 HL 069364 Timothy C. Nichols, M.D. David R. Clemmons, M.D. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill AMDCC Presentation 1. Review Research Goals
Atherosclerosis in Insulin Resistant Hyperlipidemic Pigs R01 HL 069364 Timothy C. Nichols, M.D. David R. Clemmons, M.D. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill AMDCC Presentation 1. Review Research Goals
Diabetic Complications Consortium
 Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: Cathepsin S inhibition and diabetic neuropathy Principal Investigator: Nigel A Calcutt 1. Project Accomplishments: We investigated the efficacy of cathepsin
Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy. Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI
 Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI Group Members Mount Sinai: Phenotyping, Molecular Pathology & Validation Erwin
Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai / Jefferson / Einstein / Minnesota Erwin Böttinger, PI Kumar Sharma, Co-PI Group Members Mount Sinai: Phenotyping, Molecular Pathology & Validation Erwin
Epidermal Nerve Fiber and Schwann cell densities in the distal leg of Nine-banded Armadillos with Experimental Leprosy neuropathy
 Epidermal Nerve Fiber and Schwann cell densities in the distal leg of Nine-banded Armadillos with Experimental Leprosy neuropathy Gigi J Ebenezer 1 Richard Truman 2 David Scollard 2 Michael Polydefkis
Epidermal Nerve Fiber and Schwann cell densities in the distal leg of Nine-banded Armadillos with Experimental Leprosy neuropathy Gigi J Ebenezer 1 Richard Truman 2 David Scollard 2 Michael Polydefkis
AMDCC Progress Report Duke/UNC/Stanford Unit. Program Director Thomas M. Coffman, MD
 AMDCC Progress Report Duke/UNC/Stanford Unit Program Director Thomas M. Coffman, MD Susceptibility Mutation Model Development + ApoE-/- +STZ Kidney Phenotype Screen Vascular & Kidney Phenotype Screen Generate
AMDCC Progress Report Duke/UNC/Stanford Unit Program Director Thomas M. Coffman, MD Susceptibility Mutation Model Development + ApoE-/- +STZ Kidney Phenotype Screen Vascular & Kidney Phenotype Screen Generate
Endothelial PGC 1 - α 1 mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes
 Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
Animal Models of Diabetic Complications Consortium (U01 HL70524)
 Animal Models of Diabetic Complications Consortium (U01 HL70524) Annual Report (2005) Mouse Models of Diabetic Vascular Disease Rockefeller/Columbia/NYU Principal Investigator Jan L. Breslow, M.D. Rockefeller
Animal Models of Diabetic Complications Consortium (U01 HL70524) Annual Report (2005) Mouse Models of Diabetic Vascular Disease Rockefeller/Columbia/NYU Principal Investigator Jan L. Breslow, M.D. Rockefeller
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study
 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used in this study Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Rat Met 5 -aggtcgcttcatgcaggt-3 5 -tccggagacacaggatgg-3 Rat Runx1 5 -cctccttgaaccactccact-3 5 -ctggatctgcctggcatc-3
Clinical Case Presentation. Dana Assis, MD
 Clinical Case Presentation Dana Assis, MD 4.12.2016 Clinical Presentation 63 year old male with medical history AIDS (CD4 11, VL 62K), Hep C cirrhosis (never treated), DM II c/b diabetic retinopathy, HTN,
Clinical Case Presentation Dana Assis, MD 4.12.2016 Clinical Presentation 63 year old male with medical history AIDS (CD4 11, VL 62K), Hep C cirrhosis (never treated), DM II c/b diabetic retinopathy, HTN,
SURAL NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES USING ULTRASOUND-GUIDED NEEDLE
 SURAL NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES USING ULTRASOUND-GUIDED NEEDLE POSITIONING: INFLUENCE OF AGE AND RECORDING LOCATION Olivier Scheidegger, MD; Christina Kihm; Christian Philipp Kamm, MD; Kai Michael Rösler
SURAL NERVE CONDUCTION STUDIES USING ULTRASOUND-GUIDED NEEDLE POSITIONING: INFLUENCE OF AGE AND RECORDING LOCATION Olivier Scheidegger, MD; Christina Kihm; Christian Philipp Kamm, MD; Kai Michael Rösler
Chapter 17 Nervous System
 Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Chapter 17 Nervous System 1 The Nervous System Two Anatomical Divisions Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain and Spinal Cord Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) Two Types of Cells Neurons Transmit nerve impulses
Measure #1a: Essential Components of Electrodiagnostic (EDX) Evaluation for Median Neuropathy at the Wrist
 Measure #1a: Essential Components of Electrodiagnostic (EDX) Evaluation for Median Neuropathy at the Wrist Measure Description Percentage of patients referred for EDX evaluation of CTS who had adequate
Measure #1a: Essential Components of Electrodiagnostic (EDX) Evaluation for Median Neuropathy at the Wrist Measure Description Percentage of patients referred for EDX evaluation of CTS who had adequate
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy
 Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Potential for delta opioid receptor agonists as analgesics in chronic pain therapy David Kendall & Bengt von Mentzer; PharmNovo AB/UK Alex Conibear & Eamonn Kelly, University of Bristol Junaid Asghar,
Diabetic nephropathy (DN) is the major single cause of
 JASN Express. Published on November 24, 2004 as doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004080648 Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Matthew D. Breyer,* Erwin Böttinger, Frank C. Brosius, III, Thomas M. Coffman, Raymond C.
JASN Express. Published on November 24, 2004 as doi: 10.1681/ASN.2004080648 Mouse Models of Diabetic Nephropathy Matthew D. Breyer,* Erwin Böttinger, Frank C. Brosius, III, Thomas M. Coffman, Raymond C.
Role and Mechanisms of Epithelial Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy
 Animal Models of Diabetic Complications Consortium (U01 DK060905-10) Annual Report (2010) Role and Mechanisms of Epithelial Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai School of Medicine Albert Einstein
Animal Models of Diabetic Complications Consortium (U01 DK060905-10) Annual Report (2010) Role and Mechanisms of Epithelial Injury in Diabetic Nephropathy Mount Sinai School of Medicine Albert Einstein
Microneurography in Diabetic Mice. Final Report
 Microneurography in Diabetic Mice Final Report The goal of this Pilot/Feasibility study was to adapt microneurography to studies of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the mouse and measure spontaneous action
Microneurography in Diabetic Mice Final Report The goal of this Pilot/Feasibility study was to adapt microneurography to studies of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in the mouse and measure spontaneous action
DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY
 DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Dept of PM&R, College of Medicine, Korea University Dong Hwee Kim Electrodiagnosis ANS Clinical Measures QST DIAGRAM OF CASUAL PATHWAYS TO FOOT ULCERATION Rathur & Boulton.
DIAGNOSIS OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Dept of PM&R, College of Medicine, Korea University Dong Hwee Kim Electrodiagnosis ANS Clinical Measures QST DIAGRAM OF CASUAL PATHWAYS TO FOOT ULCERATION Rathur & Boulton.
Motor and sensory nerve conduction studies
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Hands-on Course 2 Assessment of peripheral nerves function and structure in suspected peripheral neuropathies
The Autonomic Nervous
 Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq System Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University LECTUR (1) Functional Anatomy & Physiology of Autonomic
Kim Chong Hwa MD,PhD Sejong general hospital, Division of endocrine & metabolism
 Kim Chong Hwa MD,PhD Sejong general hospital, Division of endocrine & metabolism st1 Classification and definition of diabetic neuropathies Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
Kim Chong Hwa MD,PhD Sejong general hospital, Division of endocrine & metabolism st1 Classification and definition of diabetic neuropathies Painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy Diabetic autonomic neuropathy
The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48: 999-1003 The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome SHN J OH, HYUN S KM, BASHRUDDN K AHMAD From the Department ofneurology,
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1985;48: 999-1003 The near-nerve sensory nerve conduction in tarsal tunnel syndrome SHN J OH, HYUN S KM, BASHRUDDN K AHMAD From the Department ofneurology,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Eremina V, Jefferson JA, Kowalewska J, et al. VEGF inhibition
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Eremina V, Jefferson JA, Kowalewska J, et al. VEGF inhibition
Compound Action Potential, CAP
 Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Stimulus Strength UNIVERSITY OF JORDAN FACULTY OF MEDICINE DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY & BIOCHEMISTRY INTRODUCTION TO NEUROPHYSIOLOGY Spring, 2013 Textbook of Medical Physiology by: Guyton & Hall, 12 th edition
Diabetes and Inflammasomes in the Bladder
 Diabetes and Inflammasomes in the Bladder J Todd Purves MD, PhD Duke University Medical Center Division of Urology Disclosures: None Introduction Diabetic Bladder Dysfunction (DBD) is the most common
Diabetes and Inflammasomes in the Bladder J Todd Purves MD, PhD Duke University Medical Center Division of Urology Disclosures: None Introduction Diabetic Bladder Dysfunction (DBD) is the most common
NGS. Search for homozygous regions. Why is there a need for a new diagnostic tool? Department of Genetics and Metabolic Diseases Hadassah, Jerusalem
 Why is there a need for a new diagnostic tool? Homozygosity mapping as a primary, new diagnostic tool ERNDIM meeting, Basel, Oct 22, 2009 Orly Elpeleg Department of Genetics and Metabolic Diseases Hadassah,
Why is there a need for a new diagnostic tool? Homozygosity mapping as a primary, new diagnostic tool ERNDIM meeting, Basel, Oct 22, 2009 Orly Elpeleg Department of Genetics and Metabolic Diseases Hadassah,
RECEIVED. W. M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, D-251 Piscataway, NJ (732)
 Principal Investigator: Dongming Sun, W. M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, D-251 Piscataway, NJ 08854 (732) 445-1832 RECEIVED NJ COMMISSION ON SPINAL CORD RESEARCH The overall
Principal Investigator: Dongming Sun, W. M. Keck Center for Collaborative Neuroscience 604 Allison Road, D-251 Piscataway, NJ 08854 (732) 445-1832 RECEIVED NJ COMMISSION ON SPINAL CORD RESEARCH The overall
Journal Club. 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal
 Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Learning Modules - Medical Gross Anatomy Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14
 Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14 Overview of the Nervous System Every minute of every day, your nervous system is sending and receiving countless messages about what is happening both inside and
Nervous System Overview - Page 1 of 14 Overview of the Nervous System Every minute of every day, your nervous system is sending and receiving countless messages about what is happening both inside and
A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch
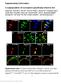 Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
Supplementary Information A subpopulation of nociceptors specifically linked to itch Liang Han 1, Chao Ma 3,4, Qin Liu 1,2, Hao-Jui Weng 1,2, Yiyuan Cui 5, Zongxiang Tang 1,2, Yushin Kim 1, Hong Nie 4,
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
Cutaneous innervation in chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy
 Because the breeder pairs, which never produced myotonic offspring in the same colony, showed the same nucleotide substitutions in the ClC-1, we concluded that these nucleotide substitutions seen in the
Because the breeder pairs, which never produced myotonic offspring in the same colony, showed the same nucleotide substitutions in the ClC-1, we concluded that these nucleotide substitutions seen in the
University of Utah. Cutaneous Nerve Evaluation. Please read through all information BEFORE scheduling patient s biopsy
 University of Utah Cutaneous Nerve Evaluation Please read through all information BEFORE scheduling patient s biopsy Now 1) Open the enclosed kit and FREEZE the cold pack for return shipment 2) Keep everything
University of Utah Cutaneous Nerve Evaluation Please read through all information BEFORE scheduling patient s biopsy Now 1) Open the enclosed kit and FREEZE the cold pack for return shipment 2) Keep everything
Title: Catheter-based distal sciatic nerve block in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease
 Author's response to reviews Title: Catheter-based distal sciatic nerve block in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease Authors: Hubert J. Schmitt (Hubert.Schmitt@kfa.imed.uni-erlangen.de) Sandra Huberth
Author's response to reviews Title: Catheter-based distal sciatic nerve block in patients with Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease Authors: Hubert J. Schmitt (Hubert.Schmitt@kfa.imed.uni-erlangen.de) Sandra Huberth
ZL ZDF ZDF + E2 *** Visceral (g) ZDF
 Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
STUDY ON COMMUNICATING BRANCHES OF SURAL NERVE: REVIEW OF LITERATURE AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS
 Original Article STUDY ON COMMUNICATING BRANCHES OF SURAL NERVE: REVIEW OF LITERATURE AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS Sherry Sharma * 1, Meenakshi Khullar 2, Harpreet Singh Gulati 3, Sunil Bhardwaj 4. ABSTRACT
Original Article STUDY ON COMMUNICATING BRANCHES OF SURAL NERVE: REVIEW OF LITERATURE AND ITS CLINICAL IMPLICATIONS Sherry Sharma * 1, Meenakshi Khullar 2, Harpreet Singh Gulati 3, Sunil Bhardwaj 4. ABSTRACT
Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic
 HISTORY OF PF-NCS Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic diagnosis remains unclear. EMG/NCV
HISTORY OF PF-NCS Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook of Pain Management Lippinott 2002; 350:382 In most cases of neck and back pain the anatomic and physiologic diagnosis remains unclear. EMG/NCV
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD
 AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM PART I: SPINAL CORD How is the organization of the autonomic nervous system different from that of the somatic nervous system? Peripheral Nervous System Divisions Somatic Nervous
9.01 Midterm Examination NAME October 27, 2003
 9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
9.01 - Neuroscience & Behavior, Fall 2003 Massachusetts Institute of Technology Instructor: Professor Gerald Schneider 9.01 Midterm Examination NAME 1) Karl Wernicke, in the 1870s, formulated a model of
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Spinal and Peripheral Nerves and Reflexes 1 This lab involves the second section of the exercise Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and the Autonomic Nervous System,
Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice
 Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice Fasted Refed GFP OGT GFP OGT Liver G6P (mmol/g) 0.03±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.60±0.04 0.42±0.10 A TGs (mg/g of liver) 20.08±5.17 16.29±0.8
Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice Fasted Refed GFP OGT GFP OGT Liver G6P (mmol/g) 0.03±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.60±0.04 0.42±0.10 A TGs (mg/g of liver) 20.08±5.17 16.29±0.8
Effect of Empagliflozin, a Selective Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, on Kidney and Peripheral Nerves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
 Brief Report Complications Diabetes Metab J Published online Apr 25, 2018 https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0095 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Effect of Empagliflozin, a
Brief Report Complications Diabetes Metab J Published online Apr 25, 2018 https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0095 pissn 2233-6079 eissn 2233-6087 DIABETES & METABOLISM JOURNAL Effect of Empagliflozin, a
REVIEWERS' COMMENTS: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Editorial Note: this manuscript has been previously reviewed at another journal that is not operating a transparent peer review scheme. This document only contains reviewer comments and rebuttal letters
Editorial Note: this manuscript has been previously reviewed at another journal that is not operating a transparent peer review scheme. This document only contains reviewer comments and rebuttal letters
A HIGH-FAT DIET ALTERS THE PHENOTYPE OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY. Brianne Lynn Guilford
 A HIGH-FAT DIET ALTERS THE PHENOTYPE OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY BY Brianne Lynn Guilford Submitted to the graduate degree program in Anatomy and Cell Biology and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas
A HIGH-FAT DIET ALTERS THE PHENOTYPE OF DIABETIC NEUROPATHY BY Brianne Lynn Guilford Submitted to the graduate degree program in Anatomy and Cell Biology and the Graduate Faculty of the University of Kansas
7/31/2009. G.Y. Prince Used Cars 10 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland Drive..later that day. Would you buy a car without taking it for a spin first?
 7/31/29 My Anna will love it! Who needs a test drive? Or a Warranty? It looked great in the lot! Do mean to say that you never actually test drove the car? G.Y. Prince Used Cars 1 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland
7/31/29 My Anna will love it! Who needs a test drive? Or a Warranty? It looked great in the lot! Do mean to say that you never actually test drove the car? G.Y. Prince Used Cars 1 am Los Angelos, CA Mullholland
Cystinosis Research Foundation Progress Report. Energy homeostasis and muscle wasting in nephropathic cystinosis. Final Report
 Cystinosis Research Foundation Progress Report Energy homeostasis and muscle wasting in nephropathic cystinosis Principle Investigator: Robert Mak, MD, PhD Institution: University of California, San Diego
Cystinosis Research Foundation Progress Report Energy homeostasis and muscle wasting in nephropathic cystinosis Principle Investigator: Robert Mak, MD, PhD Institution: University of California, San Diego
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Regents of the University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI 48109
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0463 TITLE: The Ketogenic Diet and Potassium Channel Function PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Geoffrey Murphy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Regents of the University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-13-1-0463 TITLE: The Ketogenic Diet and Potassium Channel Function PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Geoffrey Murphy CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Regents of the University of Michigan Ann Arbor,
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix
 Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
Biomechanics of Pain: Dynamics of the Neuromatrix Partap S. Khalsa, D.C., Ph.D. Department of Biomedical Engineering The Neuromatrix From: Melzack R (1999) Pain Suppl 6:S121-6. NIOSH STAR Symposium May
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Year 2004 Paper one: Questions supplied by Megan
 QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
QUESTION 47 A 58yo man is noted to have a right foot drop three days following a right total hip replacement. On examination there is weakness of right ankle dorsiflexion and toe extension (grade 4/5).
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.)
 Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Chp. 16: AUTONOMIC N.S. (In Review: Peripheral N. S.) Peripheral nerves contain both motor and sensory neurons Among the motor neurons, some of these are somatic and innervate skeletal muscles while some
Part 1 Making the initial neuron connection
 To begin, follow your teacher's directions to open the Virtual Neurons software. On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In
To begin, follow your teacher's directions to open the Virtual Neurons software. On the left side of the screen is a group of skin cells. On the right side of the screen is a group of muscle fibers. In
Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2
 NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
NAME PER DATE Chapter Six Review Sections 1 and 2 Matching: 1. afferent nerves 2. autonomic nervous system 3. cell body 4. central nervous system (CNS) 5. dendrites 6. efferent nerves 7. myelin sheath
The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
17 The Nervous System: Autonomic Nervous System Introduction The autonomic nervous system: Functions outside of our conscious awareness Makes routine adjustments in our body s systems The autonomic nervous
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
CHAPTER 15 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) regulates the activity of smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, and certain glands. B. Operation of the ANS to maintain homeostasis,
Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model. Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications. SDT fatty rats. SDT fatty rats
 Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model rats Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications rats Background and Origin In 24, Dr. Masuyama and Dr. Shinohara (Research Laboratories of Torii Pharmaceutical Co.,
Obese Type 2 Diabetic Model rats Rat Model with Early Onset of Diabetic Complications rats Background and Origin In 24, Dr. Masuyama and Dr. Shinohara (Research Laboratories of Torii Pharmaceutical Co.,
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord
 Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Lecture 14: The Spinal Cord M/O Chapters 16 69. Describe the relationship(s) between the following structures: root, nerve, ramus, plexus, tract, nucleus, and ganglion. 70. Trace the path of information
Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials
 Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials Li Zhang Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health,
Glycine-gated ion channels Converging mechanism and therapeutic potentials Li Zhang Laboratory for Integrative Neuroscience, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, National Institutes of Health,
The Lower Limb II. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
The Lower Limb II Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 3 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Tibia The larger & medial bone of the leg Functions: Attachment of muscles Transfer of weight from femur to skeleton of the foot Articulations
Somatosensation. Recording somatosensory responses. Receptive field response to pressure
 Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Somatosensation Mechanoreceptors that respond to touch/pressure on the surface of the body. Sensory nerve responds propotional to pressure 4 types of mechanoreceptors: Meissner corpuscles & Merkel discs
Mutant SOD1 Transgenic Rodents as Models of FALS
 Mutant SOD1 Transgenic Rodents as Models of FALS Transgenic mice and rats expressing mutant forms of SOD1 develop motor neuron pathology and clinical symptoms similar to those seen in patients with ALS.
Mutant SOD1 Transgenic Rodents as Models of FALS Transgenic mice and rats expressing mutant forms of SOD1 develop motor neuron pathology and clinical symptoms similar to those seen in patients with ALS.
Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor of the Chair of Human Anatomy, Candidate of Medicine
 Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
Theoretical background to the study of the autonomic nervous system. Sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. Features of the structure, function Composed by Natalia Leonidovna
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Rett Syndrome Mutation MeCP2 T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Rett Syndrome Mutation T158A Disrupts DNA Binding, Protein Stability and ERP Responses Darren Goffin, Megan Allen, Le Zhang, Maria Amorim, I-Ting Judy Wang, Arith-Ruth S. Reyes,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
Curriculum Vitae James N. Domingue, M.D.
 Page 1 of 5 Contact Information Office Address: 1245 S. College Rd. Suite 100 Lafayette, La. 70503 Office 337-269-5840 Cell 337-781-6187 Certifications American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, Neurology,
Page 1 of 5 Contact Information Office Address: 1245 S. College Rd. Suite 100 Lafayette, La. 70503 Office 337-269-5840 Cell 337-781-6187 Certifications American Board of Psychiatry and Neurology, Neurology,
35-2 The Nervous System Slide 1 of 38
 1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
1 of 38 35-2 The Nervous System The nervous system controls and coordinates functions throughout the body and responds to internal and external stimuli. 2 of 38 Neurons Neurons The messages carried by
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Supplementary Figure 1 Splenic atrophy and leucopenia caused by T3 SCI. (a) Gross anatomy of representative spleens from control and T3 SCI mice at 28 days post-injury. (b and c) Hematoxylin and eosin
Inflammatory basis of diabetic retinopathy. Tim Kern, PhD Case Western Reserve University and Stokes VA Hospital, Cleveland, OH
 Inflammatory basis of diabetic retinopathy Tim Kern, PhD Case Western Reserve University and Stokes VA Hospital, Cleveland, OH Diabetic retinopathy currently is diagnosed based on vascular abnormalities
Inflammatory basis of diabetic retinopathy Tim Kern, PhD Case Western Reserve University and Stokes VA Hospital, Cleveland, OH Diabetic retinopathy currently is diagnosed based on vascular abnormalities
Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago IL Division of Nephrology and Hypertension
 Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago IL Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Daniel Batlle MD Earle, del Greco Levin Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Northwestern University
Feinberg School of Medicine Chicago IL Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Daniel Batlle MD Earle, del Greco Levin Professor of Medicine Division of Nephrology and Hypertension Northwestern University
Chapter 16. APR Enhanced Lecture Slides
 Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Chapter 16 APR Enhanced Lecture Slides See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables pre-inserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission
Autonomic Nervous System
 Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ref: Textbook of Medical Physiology, Guyton, 12th ed: 729-738, 11th ed. P748-760, and 10th ed. p697-708. Fig.17.02 General functions Control and Adaptation
Autonomic Nervous System Autonomic Nervous System Ref: Textbook of Medical Physiology, Guyton, 12th ed: 729-738, 11th ed. P748-760, and 10th ed. p697-708. Fig.17.02 General functions Control and Adaptation
Exercise and Type 1 Diabetes
 Exercise and Type 1 Diabetes QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. 1 Characteristics of Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus ACE Mtng 2011 Rate of New Cases of Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
Exercise and Type 1 Diabetes QuickTime and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. 1 Characteristics of Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus ACE Mtng 2011 Rate of New Cases of Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects.
 Supplementary Figure 1 BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects. Boxplots show the 25% and 75% quantiles of normalized mrna expression levels
Supplementary Figure 1 BMI risk SNPs associate with increased CADM1 and CADM2 expression in the cerebellum of human subjects. Boxplots show the 25% and 75% quantiles of normalized mrna expression levels
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 2 done by: Dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer #Sacral plexus : emerges from the ventral rami of the spinal segments L4 - S4 and provides motor and
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists
 Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
Guide to the use of nerve conduction studies (NCS) & electromyography (EMG) for non-neurologists What is NCS/EMG? NCS examines the conduction properties of sensory and motor peripheral nerves. For both
A STUDY OF ASSESSMENT IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DETECTED THYROID DISORDERS IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING INSTITUTE
 A STUDY OF ASSESSMENT IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DETECTED THYROID DISORDERS IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING INSTITUTE Rajan Ganesan 1, Marimuthu Arumugam 2, Arungandhi Pachaiappan 3, Thilakavathi
A STUDY OF ASSESSMENT IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHY IN PATIENTS WITH NEWLY DETECTED THYROID DISORDERS IN A TERTIARY CARE TEACHING INSTITUTE Rajan Ganesan 1, Marimuthu Arumugam 2, Arungandhi Pachaiappan 3, Thilakavathi
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline
 Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Chapter 14 The Autonomic Nervous System Chapter Outline Module 14.1 Overview of the Autonomic Nervous System (Figures 14.1 14.3) A. The autonomic nervous system (ANS) is the involuntary arm of the peripheral
Conclusions The modified segmental palmar test is a sensitive, robust and easily applicable method in diagnosing CTS.
 Abstract Objective To test our hypothesis that comparing the sensory nerve conduction velocity of the median nerve across the wrist with that of the forearm is more sensitive than comparing it with that
Abstract Objective To test our hypothesis that comparing the sensory nerve conduction velocity of the median nerve across the wrist with that of the forearm is more sensitive than comparing it with that
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents
 Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
Central injection of fibroblast growth factor 1 induces sustained remission of diabetic hyperglycemia in rodents Jarrad M Scarlett 1,,1, Jennifer M Rojas 1,1, Miles E Matsen 1, Karl J Kaiyala 3, Darko
Effect of exercise and glycemic control on diabetic mouse (db/db) Achilles tendons
 Effect of exercise and glycemic control on diabetic mouse (db/db) Achilles tendons Peter Knoll MD, Justin Chu, Joe Cox MD, Ryan Hamilton MD, Gregory P. Boivin MD, Richard Laughlin MD Wright State University
Effect of exercise and glycemic control on diabetic mouse (db/db) Achilles tendons Peter Knoll MD, Justin Chu, Joe Cox MD, Ryan Hamilton MD, Gregory P. Boivin MD, Richard Laughlin MD Wright State University
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam
 Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
Anatomy Paper 2 Exam Monday, 4 Head Office: Level 9, 51 Druitt Street, Sydney NSW 2000, Australia Ph: +61 2 9268 9777 Fax: +61 2 9268 9799 Email: ranzcr@ranzcr.edu.au New Zealand Office: Floor 6, 142 Lambton
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain. Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic
 Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
Electrodiagnostics for Back & Neck Pain Steven Andersen, MD Providence Physiatry Clinic Electrodiagnostics Electromyography (EMG) Needle EMG exam (NEE) Nerve conduction studies (NCS) Motor Sensory Late
The Nervous System. Anatomy of a Neuron
 The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
The Nervous System Chapter 38.1-38.5 Anatomy of a Neuron I. Dendrites II. Cell Body III. Axon Synaptic terminal 1 Neuron Connections dendrites cell body terminal cell body cell body terminals dendrites
Regulation of the Urinary Bladder Chapter 26
 Regulation of the Urinary Bladder Chapter 26 Anatomy 1. The urinary bladder is smooth muscle lined internally by transitional epithelium and externally by the parietal peritoneum. Contraction of the smooth
Regulation of the Urinary Bladder Chapter 26 Anatomy 1. The urinary bladder is smooth muscle lined internally by transitional epithelium and externally by the parietal peritoneum. Contraction of the smooth
Internship Research Paper. Locomotion and Motor Neuron Plasticity after Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury. Completed at St.
 Internship Research Paper Locomotion and Motor Neuron Plasticity after Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Completed at St. Joseph s Hospital Barrow Neurological Institute Dr. Thomas Hamm By Anivarya Kumar Introduction
Internship Research Paper Locomotion and Motor Neuron Plasticity after Incomplete Spinal Cord Injury Completed at St. Joseph s Hospital Barrow Neurological Institute Dr. Thomas Hamm By Anivarya Kumar Introduction
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (January 2018) Vol. 70 (12), Page 2172-2177 Blockage of HCN Channels with ZD7288 Attenuates Mechanical Hypersensitivity in Rats Model of Diabetic Neuropathy Hussain
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome. and Type-2 Diabetes
 A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
Evaluation of nerve conduction abnormalities in type 2 diabetic patients
 Original article: Evaluation of nerve conduction abnormalities in type 2 diabetic patients 1Kannan K, 2 Sivaraj M 1Asst Professor, Dept of Physiology, kilpauk Medical College, Kilpauk, Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
Original article: Evaluation of nerve conduction abnormalities in type 2 diabetic patients 1Kannan K, 2 Sivaraj M 1Asst Professor, Dept of Physiology, kilpauk Medical College, Kilpauk, Chennai, Tamil Nadu,
Ethanol-mediated long-lasting adaptations of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum
 Article Addendum Channels 5:3, 205-209; May/June 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience Article Addendum Ethanol-mediated long-lasting adaptations of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum
Article Addendum Channels 5:3, 205-209; May/June 2011; 2011 Landes Bioscience Article Addendum Ethanol-mediated long-lasting adaptations of the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors in the dorsomedial striatum
Short Communication. In vivo recording of nerve conduction velocity of spinal CNS fibers in the. mouse
 1 Short Communication In vivo recording of nerve conduction velocity of spinal CNS fibers in the mouse Payam Dibaj 1, Eike D. Schomburg 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Experimental Medicine, Göttingen,
1 Short Communication In vivo recording of nerve conduction velocity of spinal CNS fibers in the mouse Payam Dibaj 1, Eike D. Schomburg 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Experimental Medicine, Göttingen,
EVALUATION OF HYPERPOLARIZATION POTENTIALS AND NERVE CONDUCTION PARAMETERS IN AXONAL NEUROPATHIC PATIENTS
 EVALUATION OF HYPERPOLARIZATION POTENTIALS AND NERVE CONDUCTION PARAMETERS IN AXONAL NEUROPATHIC PATIENTS Muhammad Abdul Azeem, Nabeeh Ibrahim Ali Rakkah, Muhammad Amir Mustufa, Anwar Ali *, Najamuddin
EVALUATION OF HYPERPOLARIZATION POTENTIALS AND NERVE CONDUCTION PARAMETERS IN AXONAL NEUROPATHIC PATIENTS Muhammad Abdul Azeem, Nabeeh Ibrahim Ali Rakkah, Muhammad Amir Mustufa, Anwar Ali *, Najamuddin
Diabetic Complications Consortium
 Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: PTEN KNOCKDOWN: A NOVEL STRATEGY TO REVERSE DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Principal Investigator: Douglas W. Zochodne. 1. Project Accomplishments: The role of
Diabetic Complications Consortium Application Title: PTEN KNOCKDOWN: A NOVEL STRATEGY TO REVERSE DIABETIC NEUROPATHY Principal Investigator: Douglas W. Zochodne. 1. Project Accomplishments: The role of
Angelman Syndrome: Research landscape. Ben Philpot, Ph.D., University of North Carolina Stormy Chamberlain, Ph.D., University of Connecticut
 Angelman Syndrome: Research landscape Ben Philpot, Ph.D., University of North Carolina Stormy Chamberlain, Ph.D., University of Connecticut OUTLINE Research Biochemistry Mouse studies Other models Therapeutic
Angelman Syndrome: Research landscape Ben Philpot, Ph.D., University of North Carolina Stormy Chamberlain, Ph.D., University of Connecticut OUTLINE Research Biochemistry Mouse studies Other models Therapeutic
Diabetic Neuropathy: Discordance between Symptoms and Electrophysiological Testing in Saudi Diabetics
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.1, March 2002 Diabetic Neuropathy: Discordance between Symptoms and Electrophysiological Testing in Saudi Diabetics Daad H Akbar, FRCP(UK), Arab Board, Saudi Board
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol.24, No.1, March 2002 Diabetic Neuropathy: Discordance between Symptoms and Electrophysiological Testing in Saudi Diabetics Daad H Akbar, FRCP(UK), Arab Board, Saudi Board
Electrodiagnosis of the carpal tunnel syndrome
 J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 23-27 FRANK KEMBLE From the Department of Neurology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In the carpal tunnel syndrome median nerve motor conduction may be delayed
J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiat., 1968, 31, 23-27 FRANK KEMBLE From the Department of Neurology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Birmingham In the carpal tunnel syndrome median nerve motor conduction may be delayed
