Men and women are affected Male and Female larger amounts of intracranial CSF
|
|
|
- Liliana Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Male and Female Sensitivity to Alcohol-Induced Brain Damage Daniel W. Hommer, M.D. are more vulnerable than men to many of the medical consequences of alcohol use. Although research has shown that male alcoholics generally have smaller brain volumes than nonalcoholic males, the few studies that have compared brain structure in alcoholic men and women have had mixed results. To adequately compare brain damage between alcoholic women and men, it is necessary to control for age and to have separate control groups of nonalcoholic men and women. Although the majority of studies suggest that women are more vulnerable to alcohol-induced brain damage than men, the evidence remains inconclusive. KEY WORDS: AODR (alcohol and other drug related) structural brain damage; AOD sensitivity; gender differences; AODR biological markers; cerebrospinal fluid; hippocampus; corpus callosum; cerebral cortex; brain imaging and women are affected Male and Female larger amounts of intracranial CSF differently by many diseases, Vulnerability to Alcohol- than control subjects did, indicating including alcohol-related Induced Brain Damage greater brain shrinkage among alcoholics conditions. For at least a quarter cen- of both genders; alcoholic women also tury researchers have recognized that As reviewed in this issue of Alcohol reported about half as many years of many of the medical consequences of Research & Health (see the article by excessive drinking as the alcoholic men. Rosenbloom and colleagues), many excessive alcohol consumption develop In addition to this evidence for excessive brain shrinkage among alcoholic studies have found small but usually more rapidly among women than statistically significant differences in the among men (Ashley et al. 1977). For women, there is also evidence that the brain volumes of male alcoholics comexample, alcoholic women develop degree of cognitive dysfunction in alco pared with those of nonalcoholics. In cirrhosis (Loft et al. 1987), alcoholholic women is similar to that in alco contrast, few studies have directly comholic men despite fewer years of heavy induced weakening of the heart muscle pared brain structure between alcoholic drinking on the part of the women (i.e., cardiomyopathy) (Fernandez-Sola men and alcoholic women. Two early (Nixon et al. 1995). These results suget al. 1997), and nerve damage in the computerized tomography studies body s extremities (i.e., peripheral neuro- (Jacobson 1986; Mann et al. 1992) gested that the central nervous system pathy) (Ammendola et al. 2000) after compared brain shrinkage, a common (CNS) in women, like other organ marker of brain damage, in alcoholic systems, is more vulnerable to alcoholfewer years of heavy drinking than men and women by measuring the induced damage than the CNS in men. alcoholic men. Studies comparing increase in the fluid surrounding the men s and women s sensitivity to alcohol- brain (i.e., cerebrospinal fluid [CSF]), DANIEL W. HOMMER, M.D., is chief of induced brain damage, however, have which is an indication of the size of the Section of Brain Electrophysiology yielded inconsistent results. This article the lateral ventricle (a CSF-filled cavity and Imaging, Laboratory of Clinical reviews the research and the factors inside the brain that increases in size as Studies, Division of Intramural Clinical other than alcoholism that can affect the brain shrinks). and Biological Research, at the National gender-based comparisons of brain Both studies reported that male Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, structure. and female alcoholics had significantly Bethesda, Maryland. Vol. 27, No. 2,
2 Subsequent studies have not universally confirmed women s greater vulnerability to alcohol-induced brain damage. For example, Kroft and colleagues (1991), using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), failed to detect that the fluid-filled chambers in the brain (i.e., cerebral ventricles) were larger in alcoholic women than nonalcoholic women, although other researchers have found MRI evidence for ventricular enlargement among alcoholic men (Pfefferbaum et al. 1993). Two recent reports that appeared side by side in the American Journal of Psychiatry contradicted each other on the question of gender-related vulnerability to brain shrinkage in alcoholism (Hommer et al. 2001; Pfefferbaum et al. 2001). It would seem that whether alcoholic women experience greater brain damage than alcoholic men could be determined by comparing the sizes of the brains of alcoholic men and women with the brain sizes of nonalcoholics of each gender. However, details such as how different investigators measure brain size and damage or how they select alcoholic subjects may make a big difference in the results of each study. Because relatively few studies have compared alcoholic men and women, it is possible to review the measurement methods and population characteristics used in each study to determine if these factors explain the inconsistent results. Before examining these studies on alcoholism, however, it is useful to describe factors independent of alcoholism, such as age (Gur et al. 2002; Xu et al. 2000), that affect gender differences in brain structure. Factors Affecting Gender-Based Differences in Brain Structure To illustrate the factors that influence brain size, figures 1, 2, and 3 compare the brains of healthy nonalcoholic men and women. The data shown were collected using full volumetric MRI scans that were automatically segmented into gray matter, white matter, and CSF (Momenan et al. 1997). Gray matter is the tissue of the nervous system that appears grayish because of the relatively high proportion of nerve cell bodies it contains. White matter is made up of Intracranial Volume (ml) Brain/Intracranial Volume (ml) Height (cm) Age (Years) Figure 2 The ratio of brain to intracranial volume (a measure of the maximum size to which the brain grows) decreases as a function of age, among healthy nonalcoholic men and women. The brain shrinks as we age. Figure 1 Intracranial volume (a measure of the maximum size to which the brain grows) increases as a function of height among healthy nonalcoholic men and women. Most of the difference in intracranial volume between healthy nonalcoholic women and men is explained by height. 182 Alcohol Research & Health
3 Gender and Alcoholic Brain Damage fibers that extend from the nerve cell bodies and carry information between them. have smaller bodies than men, and this difference in body size extends to the head, skull, and brain. As shown in figure 1, most of the difference in intracranial volume (a measure of the maximum size to which the brain grows) between healthy nonalcoholic women and men is explained by height. However, several studies have shown that even when height is taken into account, women still have smaller brains than men (Breedlove 1994; Kretschmann et al. 1979; Swaab and Hofman 1984). In addition to height, age is another factor influencing brain size. The amount that the brain shrinks with age can be measured by examining the ratio of brain volume to intracranial volume. In this way, brain shrinkage can be measured independent of the initial size of the brain. Among both men and women the ratio of brain volume to intracranial volume decreases with age, as shown in figure 2. Several researchers Gray Matter Volume/ Intracranial Volume Gray Matter Volume have reported that the rate of brain shrinkage during aging may be slightly higher among men (Gur et al. 2002; Xu et al. 2000). Some investigators have found that women s proportion of gray matter appears to be slightly, but significantly, greater than men s (Gur et al. 1999). Other researchers have suggested that this difference is secondary to overall brain size and not specifically related to gender (Luders et al. 2002). Figure 3 shows that, among healthy nonalcoholic control subjects, women have proportionally more gray matter than men; it also appears that the proportion of the inside of the skull occupied by gray matter decreases with aging similarly in men and women. However, analyses of gray-matter volume were conducted to remove the influence of overall brain size, the differences in gray matter between the genders were no longer significant. This suggests that the greater proportion of gray matter observed among women is caused by Age (Years) Figure 3 The proportion of intracranial volume occupied by gray matter decreases as healthy nonalcoholic men and women age, but, at any age, women have proportionally more gray matter than men. differences in brain size between men and women and not by gender itself. The results summarized in the three figures indicate that to adequately compare brain damage between alcoholic women and men, researchers should control for age and have separate control groups of nonalcoholic women and men. Separate control groups are needed, for example, because differences in height account for most of the difference in brain size between men and women. Controlling for the amount of lifetime alcohol consumption also is necessary because several studies have shown that alcohol consumption, independent of age, predicts brain shrinkage (Bjork et al. in press; Pfefferbaum et al. 1998). Studies of Brain Size in Alcoholic and Only one study has compared the volumes of specific brain structures of alcoholic and nonalcoholic men and women (Agartz et al. 2003). This study measured the volume of the hippocampus, a structure critical for memory function, and found that alcoholic women had smaller right and left hippocampi than nonalcoholic women; alcoholic men only had smaller right hippocampi in comparison with nonalcoholic men. The alcoholic women reported fewer years of heavy drinking, a later age of onset, and lower estimated lifetime alcohol consumption compared with the alcoholic men. DeBellis and colleagues (2000) also reported smaller hippocampal volumes (both right and left) in a small group of adolescent alcoholics compared with their nonalcoholic peers. The authors did not report the results by gender. Two studies examined the size of the corpus callosum, a large fiber bundle connecting the two cerebral hemispheres, which is essential for communication between the hemispheres. Reduction in the size of the corpus callosum may be a marker for damage to long white-matter tracts connecting the two hemispheres, and thus an indicator of the overall health of the brain s white matter. One study showed that after controlling for brain size, alcoholic women had significantly smaller corpus callosum areas Vol. 27, No. 2,
4 than both nonalcoholic women and alcoholic men (Hommer et al. 1996). However, other research has failed to find significant differences between alcoholic and nonalcoholic women in corpus callosum area (Pfefferbaum et al. 2002). The methods used to measure corpus callosum size were similar in these studies, and the severity of alcoholism in the two samples did not differ. The reason for the inconsistent results is not clear. Subsequent studies, however, using more sensitive measures to evaluate white-matter microstructure (i.e., diffusion tensor imaging [DTI], described in the article in this issue by Rosenbloom and colleagues) have reported evidence for brain damage among alcoholic women when compared with female control subjects matched for brain size (Pfefferbaum and Sullivan 2002). It is possible that the white-matter damage in female alcoholics may be better detected using DTI than conventional MRI techniques. Only two studies have compared total cerebral volume among alcoholic and nonalcoholic men and women (Agartz et al. 2003; Hommer et al. 2001). Both studies used high-resolution, fullvolumetric MRI scanning techniques and found strong evidence for greater brain shrinkage among alcoholic women compared with alcoholic men, even though the alcoholic women started heavy drinking later in life and had consumed less alcohol in their lifetimes. (However, in both studies, alcoholic women drank as much as or more than alcoholic men in the 6 months immediately preceding the scan, suggesting that brain volume may be more influenced by recent alcohol consumption than by earlier alcohol use.) In another approach, Pfefferbaum and colleagues (2001) used an MRI method that sampled a block of tissue made up of a set of axial slices (i.e., tissue sliced along the horizontal plane) comprising approximately 25 percent of total brain volume. This study found less brain shrinkage among alcoholic women than men. The inconsistency between the results obtained by Pfefferbaum and colleagues and the results from the previously described studies (Agartz et al. 2003; Studies of Gender Differences in Alcohol-Induced Brain Damage Study Findings Imaging Method Jacobson 1986 Mann et al Kroft et al Pfefferbaum et al Hommer et al Pfefferbaum et al Agartz et al Male and female alcoholics had significantly more cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) than did control subjects. Alcoholic women had shorter histories of heavy drinking and less average daily consumption than did alcoholic men. Cerebral ventricles in alcoholic women were not larger than those in nonalcoholic women. Cerebral ventricles in alcoholic men were larger than those in nonalcoholic men. Strong evidence indicated greater brain shrinkage among alcoholic women compared with alcoholic men, even though the alcoholic women started heavy drinking later in life and had consumed less alcohol in their lifetimes. Less brain shrinkage was found among alcoholic women than among alcoholic men (few subjects had a history of hospitalization). Greater global brain shrinkage and smaller hippocampi were found among alcoholic women than among alcoholic men (although women had a later onset of heavy drinking). computerized tomography computerized tomography MRI MRI full volumetric MRI scans that automatically segmented gray/white matter and CSF MRI that sampled axial slices of tissue (25 percent of total brain volume) full volumetric MRI scans that automatically segmented gray/white matter and CSF; hippocampi outlined by hand Hommer et al Pfefferbaum et al Pfefferbaum and Sullivan 2002 Schweinsburg et al When brain size was controlled, alcoholic women had significantly smaller corpus callosums than did nonalcoholic women or alcoholic men. No significant differences were found between alcoholic and nonalcoholic women in corpus callosum area. An evaluation of white-matter microstructure found evidence for brain damage in alcoholic women but not female control subjects. Both male and female alcoholics had reductions in frontal lobe white-matter N-acetylaspartate (a marker for neuronal activity), but only alcoholic females had reduction in graymatter N-acetylaspartate. MRI; corpus callosum outlined by hand MRI; corpus callosum outlined by hand diffusion tensor imaging magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to measure concentrations of N-acetylaspartate. 184 Alcohol Research & Health
5 Gender and Alcoholic Brain Damage Hommer et al. 2001) does not appear to be accounted for by differences in lifetime alcohol consumption between the samples of alcoholic women, although few of the women in the Pfefferbaum study had a history of hospitalization for alcoholism, and all of the women in the other two studies had been hospitalized at some point. It is possible that differences in imaging methods contributed to the different results, because Pfefferbaum s study measured only a portion of the cerebrum, and the other studies measured the volume of the entire cerebrum. In addition to the studies of brain structure reviewed above, one study using magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to compare male and female alcoholics (Schweinsburg et al. 2003) found that, in frontal lobe gray matter but not frontal lobe white matter, alcoholic women had a significantly greater deficit in concentrations of N-acetylaspartate (a marker for neuronal integrity) than alcoholic men. These MRS findings are consistent with the report by Hommer and colleagues (2001) that gray-matter damage distinguishes alcoholic women and men to a greater extent than white-matter damage. Conclusion Compared with alcoholic men, alcoholic women have received little research attention. This is particularly unfortunate because there is good evidence that many of the behavioral aspects of alcoholism progress more rapidly among women than among men. It is important to determine what role, if any, alcoholism-related brain damage plays in the progression of alcoholism. Although most of the recent studies suggest that women are more vulnerable to alcohol-induced brain damage than men, it would be premature to state this conclusively. Nearly all the recent studies of gender differences in this area have been conducted by only two research groups, one of which (Hommer and colleagues) has consistently found evidence for greater brain damage among alcoholic women, whereas the other group (Pfefferbaum and colleagues) has not. The field of gender studies in alcoholism needs more investigators to join in this work in order to resolve the conflicting results that currently characterize this field. References AGARTZ, I.; SHOAF, S.; RAWLINGS, R.R.; ET AL. CSF monoamine metabolites and MRI brain volumes in alcohol dependence. Psychiatry Research: Neuroimaging 122:21 35, AMMENDOLA, A.; GEMINI, D.; IANNACCONE, S.; ET AL. Gender and peripheral neuropathy in chronic alcoholism: A clinical-electroneurographic study. Alcohol and Alcoholism 35:368 71, ASHLEY, M.J.; OLIN, J.S.; LE RICHE, W.H.; ET AL. Morbidity in alcoholics. Evidence for accelerated development of physical disease in women. Archives of Internal Medicine 137: , BJORK, J.; GRANT, S.; AND HOMMER, D. Crosssectional volumetric analysis of brain atrophy in alcoholics: Effects of drinking history and comorbid substance use disorder. American Journal of Psychiatry, in press. BREEDLOVE, S.M. Sexual differentiation of the human nervous system. Annual Review of Psychology 45: , DEBELLIS, M.D.; CLARK, D.B.; BEERS, S.R.; ET AL. Hippocampal volume in adolescent-onset alcohol use disorders. American Journal of Psychiatry 157: , FERNANDEZ-SOLA, J.; ESTRUCH, R.; NICOLAS, J.M.; ET AL. Comparison of alcoholic cardiomyopathy in women versus men. American Journal of Cardiology 80: , GUR, R.C.; TURETSKY, B.I.; MATSUI, M.; ET AL. Sex differences in brain gray and white matter in healthy young adults: Correlations with cognitive performance. Journal of Neuroscience 19: , GUR, R.C.; GUNNING-DIXON, F.M.; TURETSKY, B.I.; ET AL. Brain region and sex differences in age association with brain volume: A quantitative MRI study of healthy young adults. American Journal of Geriatric Psychiatry 10:72 80, HOMMER, D.; MOMENAN, R.; RAWLINGS, R.; ET AL. Decreased corpus callosum size among alcoholic women. Archives of Neurology 53: , HOMMER, D.W.; MOMENAN, R.; KAISER, E.; AND RAWLINGS, R.R. Evidence for a gender-related effect of alcoholism on brain volumes. American Journal of Psychiatry 158: , JACOBSON, R. The contributions of sex and drinking history to the CT brain scan changes in alcoholics. Psychological Medicine 16: , KRETSCHMANN, H.J.; SCHLEICHER, A.; WINGERT, F.; ET AL. Human brain growth in the 19th and 20th century. Journal of Neurological Science 40: , KROFT, C.L.; GESCUK, B.; WOODS, B.T.; ET AL. Brain ventricular size in female alcoholics: An MRI study. Alcohol 8:31 34, LOFT, S.; OLESEN, K.L.; AND DOSSING, M. Increased susceptibility to liver disease in relation to alcohol consumption in women. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 22: , LUDERS, E.; STEINMETZ, H.; AND JANCKE, L.C.A. Brain size and grey matter volume in the healthy human brain. Neuroreport 13: , MANN, K.; BATRA, A.; GUNTHNER, A.; AND SCHROTH, G. Do women develop alcoholic brain damage more readily than men? Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 16: , MOMENAN, R.; HOMMER, D.; RAWLINGS, R.; ET AL. Intensity adaptive segmentation of single echo T 1 -weighted magnetic resonance images. Human Brain Mapping 5: , NIXON, S.; TIVIS, R.; AND PARSONS, O. Behavioral dysfunction and cognitive efficiency in male and female alcoholics. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 19: , PFEFFERBAUM, A., AND SULLIVAN, E.V. Microstructural but not macrostructural disruption of white matter in women with chronic alcoholism. NeuroImage 15: , PFEFFERBAUM, A.; SULLIVAN, E.V.; ROSENBLOOM, M.J.; ET AL. Increase in brain cerebrospinal fluid volume is greater in older than in younger alcoholic patients: A replication study and CT/MRI comparison. Psychiatry Research 50: , PFEFFERBAUM, A.; SULLIVAN, E.V.; ROSENBLOOM, M.J.; ET AL. A controlled study of cortical gray matter and ventricular changes in alcoholic men over a 5-year interval. Archives of General Psychiatry 55: , PFEFFERBAUM, A.; ROSENBLOOM, M.; DESHMUKH, A.; AND SULLIVAN, E. Sex differences in the effects of alcohol on brain structure. American Journal of Psychiatry 158: , PFEFFERBAUM, A.; ROSENBLOOM, M.; SERVENTI, K.L.; AND SULLIVAN, E.V. Corpus callosum, pons, and cortical white matter in alcoholic women. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research 26: , SCHWEINSBURG, B.; ALHASSOON, O.; TAYLOR, M.; ET AL. Effects of alcoholism and gender on brain metabolism. American Journal of Psychiatry 160: , SWAAB, D.F., AND HOFMAN, M.A. Sexual differentiation of the human brain. A historical perspective. Progress in Brain Research 61: , XU, J.; KOBAYASHI, S.; YAMAGUCHI, S.; ET AL. Gender effects on age-related changes in brain structure. American Journal of Neuroradiology 21: , Vol. 27, No. 2,
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry
 2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
2003 KHBM DTI in Psychiatry Diffusion Tensor Imaging in Psychiatry KHBM 2003. 11. 21. 서울대학교 의과대학 정신과학교실 권준수 Neuropsychiatric conditions DTI has been studied in Alzheimer s disease Schizophrenia Alcoholism
The Brain Studying & Structures. Unit 3
 The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
The Brain Studying & Structures Unit 3 Modified PowerPoint from: Aneeq Ahmad -- Henderson State University. Worth Publishers 2007 Learning Objectives Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and
Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
 American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
American Psychiatric Association San Diego, CA 24 May 2017 Use of Multimodal Neuroimaging Techniques to Examine Age, Sex, and Alcohol-Related Changes in Brain Structure Through Adolescence and Young Adulthood
Psychology, 3 Department of Anatomy, Histology and Embryology,
 PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 115 124) QUANTITATIVE CEREBRAL ANATOMY
PROCEEDINGS OF THE BALKAN SCIENTIFIC CONFERENCE OF BIOLOGY IN PLOVDIV (BULGARIA) FROM 19 TH TILL 21 ST OF MAY 2005 (EDS B. GRUEV, M. NIKOLOVA AND A. DONEV), 2005 (P. 115 124) QUANTITATIVE CEREBRAL ANATOMY
Differences in brain structure and function between the sexes has been a topic of
 Introduction Differences in brain structure and function between the sexes has been a topic of scientific inquiry for over 100 years. In particular, this topic has had significant interest in the past
Introduction Differences in brain structure and function between the sexes has been a topic of scientific inquiry for over 100 years. In particular, this topic has had significant interest in the past
Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders
 Psychiatric Disorder Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders JMAJ 45(12): 538 544, 2002 Yoshio HIRAYASU Associate Professor, Department of Neuropsychiatry Kyorin University School of Medicine
Psychiatric Disorder Neuroimaging for Diagnosis of Psychiatric Disorders JMAJ 45(12): 538 544, 2002 Yoshio HIRAYASU Associate Professor, Department of Neuropsychiatry Kyorin University School of Medicine
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
The Central Nervous System
 The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
The Central Nervous System Cellular Basis. Neural Communication. Major Structures. Principles & Methods. Principles of Neural Organization Big Question #1: Representation. How is the external world coded
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy. Components of a Nervous System
 Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Biology 3201 Nervous System #2- Anatomy Components of a Nervous System In any nervous system, there are 4 main components: (1) sensors: gather information from the external environment (sense organs) (2)
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
The incidence of alcohol abuse and dependence among
 FOCUS ON THE BRAIN: HIV INFECTION AND ALCOHOLISM COMORBIDITY EFFECTS ON BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Margaret J. Rosenbloom, M.A., Edith V. Sullivan, Ph.D., and Adolf Pfefferbaum, M.D. Both HIV infection
FOCUS ON THE BRAIN: HIV INFECTION AND ALCOHOLISM COMORBIDITY EFFECTS ON BRAIN STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION Margaret J. Rosenbloom, M.A., Edith V. Sullivan, Ph.D., and Adolf Pfefferbaum, M.D. Both HIV infection
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2
 Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Brain tissue and white matter lesion volume analysis in diabetes mellitus type 2 C. Jongen J. van der Grond L.J. Kappelle G.J. Biessels M.A. Viergever J.P.W. Pluim On behalf of the Utrecht Diabetic Encephalopathy
Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]
![Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1] Organization of the nervous system. [See Fig. 48.1]](/thumbs/90/103926552.jpg) Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Nervous System [Note: This is the text version of this lecture file. To make the lecture notes downloadable over a slow connection (e.g. modem) the figures have been replaced with figure numbers as found
Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
Cerebral Cortex 1. Sarah Heilbronner
 Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Cerebral Cortex 1 Sarah Heilbronner heilb028@umn.edu Want to meet? Coffee hour 10-11am Tuesday 11/27 Surdyk s Overview and organization of the cerebral cortex What is the cerebral cortex? Where is each
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Living Brain
 1 of 20 10/10/2011 10:36 AM SITE SEARCH Back to: NIAAA Home > Publications Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Living Brain Evidence for Brain Degeneration Among Alcoholics and Recovery With Abstinence Margaret
1 of 20 10/10/2011 10:36 AM SITE SEARCH Back to: NIAAA Home > Publications Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Living Brain Evidence for Brain Degeneration Among Alcoholics and Recovery With Abstinence Margaret
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
Supplementary Online Content Hooshmand B, Magialasche F, Kalpouzos G, et al. Association of vitamin B, folate, and sulfur amino acids with brain magnetic resonance imaging measures in older adults: a longitudinal
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype
 MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
MAGNETOM Flash (68) 2/207 33 Assessing Brain Volumes Using MorphoBox Prototype Alexis Roche,2,3 ; Bénédicte Maréchal,2,3 ; Tobias Kober,2,3 ; Gunnar Krueger 4 ; Patric Hagmann ; Philippe Maeder ; Reto
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES
 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 Biocomputer Wired for Action MWABBYH CTBIR LOBES 100
Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT
 Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT ? Spectrum of Neurocognitive disorders The adult literature on HIV related CNS damage supports a spectrum
Imaging in Pediatric `neurohiv Dr Jackie Hoare Head of Liaison Psychiatry Groote Schuur Hospital, UCT ? Spectrum of Neurocognitive disorders The adult literature on HIV related CNS damage supports a spectrum
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE
 THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
ALCOHOLISM: CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH Vol. **, No. * ** 2012
 ALCOHOLISM: CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH Vol. **, No. * ** 2012 Drinking History Associations with Regional White Matter Volumes in Alcoholic Men and Women Susan Mosher Ruiz, Marlene Oscar-Berman,
ALCOHOLISM: CLINICAL AND EXPERIMENTAL RESEARCH Vol. **, No. * ** 2012 Drinking History Associations with Regional White Matter Volumes in Alcoholic Men and Women Susan Mosher Ruiz, Marlene Oscar-Berman,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
The Human Brain. I Think Therefore I am
 The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
The Human Brain I Think Therefore I am The Beginning The simplest creatures have very simple nervous systems made up of nothing but a bunch of nerve cells They have neural nets, individual neurons linked
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Shape Modeling of the Corpus Callosum for Neuroimaging Studies of the Brain (Part I) Dongqing Chen, Ph.D.
 The University of Louisville CVIP Lab Shape Modeling of the Corpus Callosum for Neuroimaging Studies of the Brain (Part I) Dongqing Chen, Ph.D. Computer Vision & Image Processing (CVIP) Laboratory Department
The University of Louisville CVIP Lab Shape Modeling of the Corpus Callosum for Neuroimaging Studies of the Brain (Part I) Dongqing Chen, Ph.D. Computer Vision & Image Processing (CVIP) Laboratory Department
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures
 III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
III. Studying The Brain and Other Structures 1. Accidents (case study) In 1848, a railroad worker named Phineas Gage was involved in an accident that damaged the front part of his brain. Gage s doctor
BIOL Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain
 BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
Stereotactic Diffusion Tensor Tractography For Gamma Knife Stereotactic Radiosurgery
 Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Disclosures The authors of this study declare that they have no commercial or other interests in the presentation of this study. This study does not contain any use of offlabel devices or treatments. Stereotactic
Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 793 797 www.ics-elsevier.com Visualization strategies for major white matter tracts identified by diffusion tensor imaging for intraoperative use Ch. Nimsky a,b,
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic?
 Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
Current Literature In Clinical Science Is DTI Increasing the Connectivity Between the Magnet Suite and the Clinic? Spatial Patterns of Water Diffusion Along White Matter Tracts in Temporal Lobe Epilepsy.
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1
 PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
PSYC& 100: Biological Psychology (Lilienfeld Chap 3) 1 1 What is a neuron? 2 Name and describe the functions of the three main parts of the neuron. 3 What do glial cells do? 4 Describe the three basic
Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity
 Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity ISMRM 2017: http://submissions.mirasmart.com/ismrm2017/viewsubmissionpublic.aspx?sei=8t1bikppq Jeroen
Fibre orientation dispersion in the corpus callosum relates to interhemispheric functional connectivity ISMRM 2017: http://submissions.mirasmart.com/ismrm2017/viewsubmissionpublic.aspx?sei=8t1bikppq Jeroen
IV. The Divisions of the Brain. Slide # 1
 IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
IV. The Divisions of the Brain Slide # 1 The Hindbrain Hindbrain, located at the rear base of the skull, controlling automatic functions Contains: Cerebellum (balance & coordination) Medulla (heartbeat,
A new Method on Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection
 2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 1 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology A new Method on Brain MRI Preprocessing for Tumor Detection ABSTRACT D. Arun Kumar
2015 IJSRSET Volume 1 Issue 1 Print ISSN : 2395-1990 Online ISSN : 2394-4099 Themed Section: Engineering and Technology A new Method on Brain MRI Preprocessing for Tumor Detection ABSTRACT D. Arun Kumar
Bio11: The Nervous System. Body control systems. The human brain. The human brain. The Cerebrum. What parts of your brain are you using right now?
 Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
Bio11: The Nervous System Body control systems Nervous system Quick Sends message directly to target organ Endocrine system Sends a hormone as a messenger to the target organ Can target several organs
International Journal of Research (IJR) Vol-1, Issue-6, July 2014 ISSN
 Developing an Approach to Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection Mr. B.Venkateswara Reddy 1, Dr. P. Bhaskara Reddy 2, Dr P. Satish Kumar 3, Dr. S. Siva Reddy 4 1. Associate Professor, ECE Dept,
Developing an Approach to Brain MRI Image Preprocessing for Tumor Detection Mr. B.Venkateswara Reddy 1, Dr. P. Bhaskara Reddy 2, Dr P. Satish Kumar 3, Dr. S. Siva Reddy 4 1. Associate Professor, ECE Dept,
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. CT ASSESSMENT OF BRAIN VENTRICULAR SIZE BASED ON AGE AND SEX: A STUDY OF 112 CASES Vinoo Jacob 1, A.S.
 CT ASSESSMENT OF BRAIN VENTRICULAR SIZE BASED ON AGE AND SEX: A STUDY OF 112 CASES Vinoo Jacob 1, A.S. Krishna Kumar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Vinoo Jacob, A.S. Krishna Kumar. CT Assessment of Brain
CT ASSESSMENT OF BRAIN VENTRICULAR SIZE BASED ON AGE AND SEX: A STUDY OF 112 CASES Vinoo Jacob 1, A.S. Krishna Kumar 2 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Vinoo Jacob, A.S. Krishna Kumar. CT Assessment of Brain
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7)
 Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Brain and behaviour (Wk 6 + 7) What is a neuron? What is the cell body? What is the axon? The basic building block of the nervous system, the individual nerve cell that receives, processes and transmits
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Fetal CNS MRI. Daniela Prayer. Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology. Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA
 Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Effects of Alcohol and HIV Infection on the Central Nervous System. Dieter J. Meyerhoff, Ph.D.
 Effects of Alcohol and HIV Infection on the Central Nervous System Dieter J. Meyerhoff, Ph.D. Many people at risk for or infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are heavy drinkers. Both HIV
Effects of Alcohol and HIV Infection on the Central Nervous System Dieter J. Meyerhoff, Ph.D. Many people at risk for or infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) are heavy drinkers. Both HIV
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Goal: To identify the extent to which different aspects of brain structure and brain processes might offer explanations for different forms of
 Goal: To identify the extent to which different aspects of brain structure and brain processes might offer explanations for different forms of psychopathology The human brain If genetics play a role, it
Goal: To identify the extent to which different aspects of brain structure and brain processes might offer explanations for different forms of psychopathology The human brain If genetics play a role, it
FORENSIC SCIENCE NEWSLETTER Forensic Pathology and Neuropathology. William A. Cox, M.D., FCAP.
 NEUROPATHOLOGY FORENSIC SCIENCE NEWSLETTER Forensic Pathology and Neuropathology William A. Cox, M.D., FCAP www.forensicjournals.cm May 15, 2016 This issue of the Forensic Science Newsletter will address
NEUROPATHOLOGY FORENSIC SCIENCE NEWSLETTER Forensic Pathology and Neuropathology William A. Cox, M.D., FCAP www.forensicjournals.cm May 15, 2016 This issue of the Forensic Science Newsletter will address
Announcements. Exam 1. VII. Imaging techniques of the brain. Anatomical/Structural Scans. Structural Scans: CT. Structural Scans: CT 2/17/2014
 Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 None at the moment! Announcements Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Fetal Brains Suffer Badly From Effects of Alcohol
 November 4, 2003 Fetal Brains Suffer Badly From Effects of Alcohol By LINDA CARROLL hirty years ago, scientists linked prenatal alcohol exposure with a perplexing pattern of birth defects including neurological
November 4, 2003 Fetal Brains Suffer Badly From Effects of Alcohol By LINDA CARROLL hirty years ago, scientists linked prenatal alcohol exposure with a perplexing pattern of birth defects including neurological
Exam 1. Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6%
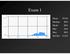 Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
Exam 1 Mean 78.0% Median 80% Mode 86% Min 26% Max 98% Std Dev 12.6% None at the moment! Announcements VII. Imaging techniques of the brain A. CT: anatomical B. MRI: anatomical C. fmri: functional D. SPECT
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Supplementary appendix
 Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Schiller R, IJsselstijn H, Hoskote A, et al.
Supplementary appendix This appendix formed part of the original submission and has been peer reviewed. We post it as supplied by the authors. Supplement to: Schiller R, IJsselstijn H, Hoskote A, et al.
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
Goal: To identify the extent to which different aspects of brain structure and brain processes might offer explanations for different forms of
 Key Dates TH Apr 6 Unit 21 TU Apr 11 Unit 22; Biological Perspective Assignment TH Apr 13 Begin Psychological Perspectives, Unit IIIB and 23; Term Paper Step 3 (only if Step 2 approved) TU Apr 18 Unit
Key Dates TH Apr 6 Unit 21 TU Apr 11 Unit 22; Biological Perspective Assignment TH Apr 13 Begin Psychological Perspectives, Unit IIIB and 23; Term Paper Step 3 (only if Step 2 approved) TU Apr 18 Unit
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity
 Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
Post Stroke Brain Plasticity François CHOLLET MD, PhD Neurology Department: Stroke Unit Toulouse University Hospital (CHU) Neurosciences Institute of Toulouse CNRS, INSERM, University, CHU Versailles le
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
The human brain weighs roughly 1.5 kg and has an average volume of 1130 cm 3. A sheep s brain weighs in however at kg.
 Sheep Brain Dissection Objectives: 1. List and describe the principal structures of the sheep brain 2. Identify important parts of the sheep brain in a preserved specimen Materials: Dissection tools, lab
Sheep Brain Dissection Objectives: 1. List and describe the principal structures of the sheep brain 2. Identify important parts of the sheep brain in a preserved specimen Materials: Dissection tools, lab
LIMBIC SYSTEM. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
Quantitative Neuroimaging- Gray and white matter Alteration in Multiple Sclerosis. Lior Or-Bach Instructors: Prof. Anat Achiron Dr.
 Quantitative Neuroimaging- Gray and white matter Alteration in Multiple Sclerosis Lior Or-Bach Instructors: Prof. Anat Achiron Dr. Shmulik Miron INTRODUCTION Multiple Sclerosis general background Gray
Quantitative Neuroimaging- Gray and white matter Alteration in Multiple Sclerosis Lior Or-Bach Instructors: Prof. Anat Achiron Dr. Shmulik Miron INTRODUCTION Multiple Sclerosis general background Gray
FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK
 07 June, 2018 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 365.11 KB 0 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK I recently had a MRI last week with
07 June, 2018 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 365.11 KB 0 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK I recently had a MRI last week with
Brain anatomy tutorial. Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics
 Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
Brain anatomy tutorial Dr. Michal Ben-Shachar 459 Neurolinguistics The human brain Left hemisphere Right hemisphere http://www.brainmuseum.org/ Zoom out Zoom in Types of Brain Tissue Gray Matter: Cell
MRI-Based Classification Techniques of Autistic vs. Typically Developing Brain
 MRI-Based Classification Techniques of Autistic vs. Typically Developing Brain Presented by: Rachid Fahmi 1 2 Collaborators: Ayman Elbaz, Aly A. Farag 1, Hossam Hassan 1, and Manuel F. Casanova3 1Computer
MRI-Based Classification Techniques of Autistic vs. Typically Developing Brain Presented by: Rachid Fahmi 1 2 Collaborators: Ayman Elbaz, Aly A. Farag 1, Hossam Hassan 1, and Manuel F. Casanova3 1Computer
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Paul Moes, Professor of Psychology - Neuroscience and Education Group - Christian Perspectives in Science - Education Program
 Paul Moes, Professor of Psychology - Neuroscience and Education Group - Christian Perspectives in Science - Education Program Thesis: Secret to the brain is Unity The problem: focused on parts A sample
Paul Moes, Professor of Psychology - Neuroscience and Education Group - Christian Perspectives in Science - Education Program Thesis: Secret to the brain is Unity The problem: focused on parts A sample
November/December 2008 The Brain Unveiled A new imaging method offers a spectacular view of neural structures. By Emily Singer
 November/December 2008 The Brain Unveiled A new imaging method offers a spectacular view of neural structures. By Emily Singer A new imaging method that offers an unprecedented view of complex neural structures
November/December 2008 The Brain Unveiled A new imaging method offers a spectacular view of neural structures. By Emily Singer A new imaging method that offers an unprecedented view of complex neural structures
Imaging in Epilepsy. Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015
 Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Central Nervous System Practical Exam. Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells. 1. Please identify the flagged structure.
 Central Nervous System Practical Exam Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells 1. Please identify the flagged structure. 2. Please identify the flagged structure. 3. Please identify the flagged structure. 4. A
Central Nervous System Practical Exam Chapter 12 Nervous System Cells 1. Please identify the flagged structure. 2. Please identify the flagged structure. 3. Please identify the flagged structure. 4. A
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
action potential afferent neuron Weblike; specifically, the weblike middle layer of the three meninges. arachnoid astrocytes autonomic nervous system
 action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
action potential A large transient depolarization event, including polarity reversal, that is conducted along the membrane of a muscle cell or a nerve fiber. afferent neuron Nerve cell that carries impulses
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Neuroimaging of TBI: Current Clinical Guidelines and Future Direction Brain Injury Alliance of Colorado 2017
 Neuroimaging of TBI: Current Clinical Guidelines and Future Direction Brain Injury Alliance of Colorado 2017 Peter E. Ricci, M.D. Staff Neuroradiologist Radiology Imaging Associates OBJECTIVES 1. Understand
Neuroimaging of TBI: Current Clinical Guidelines and Future Direction Brain Injury Alliance of Colorado 2017 Peter E. Ricci, M.D. Staff Neuroradiologist Radiology Imaging Associates OBJECTIVES 1. Understand
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
CNS Tour (Lecture 12)
 A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
A. Introduction CNS Tour (Lecture 12) There are to a chemical pathways in the nervous system. These pathways also form different neurological structures B. Spinal Cord Receives sensory neurons from skin
