بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
|
|
|
- Helena Flowers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم **As we remember from the last lecture: The arterial supply which comes from the single branches of the aorta drains in the portal vein (venous drainage of the gut = portal vein). Now we will start with the portal vein.. as usual we want to know (beginning, course, end and tributaries just clinical importance of them ) 1.Begining : it begins as the union of splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein (from the intestine). Note : the inferior mesenteric vein drains the blood from the descending colon and it joins the splenic vein. 2. Course: it enters the liver from an opening which called porta hepatis. Be aware: it s important to know the site of formation of the portal vein let us remember the C shaped organ (duodenum) in its concavity we find the pancreas which divides into head, neck, body and tail. The portal vein forms behind the neck of the pancreas. 1
2 So the portal vein forms posterior to the neck of the pancreas as the union of the superior mesenteric and splenic veins 3. End: it enters the liver and divides to give its branches 4. Clinical importance: the portal circulation is a separate circulation which takes the venous drainage of the gut but it s not completely separate from the systemic venous circulation of the body, they are united at 3 regions (anastomosis between the portal and the systemic venous circulation portosystemic anastomosis ): 1. the union between the upper part of the stomach and the lower part of the esophagus (at the beginning of the portal) 2. at the anal canal (the end of the gut, the end of the portal) 3. around the umbilicus (superficial veins at the anterior abdominal wall) A short story: If we have a disease in the liver either we can fix it or not it leads at the end to liver cirrhosis (that means we have a fibrous tissue deposited in the passage ways between the cells which leads these passages to close or to narrow ), then the portal vein when it empties its contents it will find it difficult to do that and the blood will accumulate in the portal circulation, by the time the pressure in the portal circulation (portal hypertension) will increase but the veins will not rapture it will compress at the sites of the anastomosis because of the low pressure there (portosystemic anastomosis: the 3 regions that we have already mentioned) this leads these veins to be: 1. Filled with blood. 2. Dilated(because the wall does not contain muscles it can dilate easily). 3.turtous. these 3 signs are signs of the varices: 1. esophageal varices. 2. The veins that are at the anal canal will cause hemorrhoids. 3. The veins that are radiating around the umbilicus will cause caput medusa (you can see that like the sun under the skin with a bluish color). 2
3 when I found these 3 signs I know that the patient has portal hypertension which is a result of liver cirrhosis. The danger of these things is that the walls of the veins are very thin with the increased abdominal pressure they will rapture which causes bleeding until death, and usually who dies from that he will suffer from hematemesis (vomiting of blood) because of the rapture of the esophageal varices. **Why does alcohol causes cirrhosis?? Because it cause inflammation in the liver and this inflammation cannot be treated so actually around 100% it will lead to cirrhosis, also any inflammation in the body we did not treat, we treat in a wrong way or we take antibiotics for a short period this inflammation will disappear and convert into fibrous tissue. Now stop for a second and take a deep breath. we have to know some things about the liver, pancreas and spleen then we will finish this course, so let us continue The liver: 1 st. The largest gland all over the body which secretes the bile (it is NOT the gallbladder it is the liver which secretes the bile), the bile will be concentrated in the gallbladder which will be secreted from the biliary system. 3
4 2 nd. the site of the liver: it is located in the first row of the abdominal nine regions (right hypochondrium, epigastric and a part of the left hypochondrium). 3 rd. the orientation of the liver: it is pyramidal in shape, it is lying on its side (like the heart),and has: apex (directed to the left side), base(directed to the right) & 4 surfaces (according to their position or direction: superior, inferior, anterior and posterior). **How to differentiate between the posterior surface and the inferior surface?? At the posterior aspect we have an opening which called porta hepatis (where we observe that the vessels enter and exit the liver) we put there a horizontal line, above this line we find the posterior surface and below it there is the inferior surface (this is the best way to differentiate between them). 4 th. the lobes of the liver: it is composed of 2 large lobes and 2 small lobes. the large lobes: right lobe at the right side and left smaller lobe. **How to differentiate between the right site and the left side?? We look for a complete circle around the liver(it is obvious on the 4 surfaces) and we put our hands on it then everything at the right side is a part of the right lobe also everything at the left side is a part of the left lobe. In this circle at the superior and anterior surfaces we find a ligament, using the line of attachment of this ligament we can differentiate between the right lobe and the left lobe at the superior and anterior surfaces. 4
5 From where did this ligament arise?? It arose from the peritoneum (sac of the abdomen) which gave fold (ligament) that attach to the liver to fix it on the anterior abdominal wall. Because this ligament is crescent in shape we call it falciform ligament. Now, from posterior and inferior surfaces: at this aspect of the liver we find 2 groves one above the line that we have already mentioned in the posterior surface and one below in the inferior surface, in the first groove (above) we will find a ligament called ligamentum venosum and in the other one (below) we will find a ligament called ligamentum teres A way to memorize them: وفق.. venosum تتح.. teres From where did these ligament arise?? When we was at the intrauterine life we used to have umbilical artery and umbilical vein which is important for the exchange of blood between the mother and the fetus and after delivery we do not need that, we breath and we can oxygenate our blood, then they will experience obliteration and fibrosis, then they will form these ligaments as remnants from those vessels. 5 th. relations of the liver: A. Superior surface: 1. Diaphragm which separates the liver from the following organs: 5
6 2. Right lung and right pleura. 3. Left lung and left pleura. 4. Heart and pericardium. B. Anterior surface: we will divide it into two parts: 1. Upper part related to the diaphragm. 2. Lower part related to the anterior abdominal wall muscles (external oblique, internal oblique, transversus abdominis and rectus abdominis) C. Right side (roughly at the mid axillary line): 1. Related directly to the diaphragm which separates the liver from the following structures: 2. The ribs from the 7 th to the 11 th rib. 3. Right lung and right pleura. D. The most important surfaces are the posterior and the inferior because the posterior lies on the posterior abdominal wall and the inferior is related to the viscera (here we will learn the parts + the boundaries and we will start from right to the left): 6
7 1. First of all the dull area (not glistering like the others) we call it the bare area of the liver (not covered by peritoneum). Remember: the liver is one of the organs that will grow largely and it will be completely covered by the peritoneum except one area (the bare area). 2. When we proceed to the left side we find a groove for the great vein that lies on the posterior abdominal wall (inferior vena cava). 3. Then we find the third lobe of the liver (caudate lobe). Boundaries of this lobe: a. at the right side: inferior vena cava. b. at the left side: fissure for ligamentum venosum. c. superiorly: upper surface of the liver. d. inferiorly: porta hepatis. 4. Then we proceed to the left lobe which lies on the stomach that means we have a gastric impression on the liver at this site (back of the left lobe). 5. Then we will go downward then we will return to the right side crossing the ligamentum teres then we will find the 4 th lobe of the liver (quadrate lobe). Boundaries of this lobe: a. at the left side: ligamintum teres. b. at the right side: gallbladder. c. upwards: porta hepatis. d. downwards: inferior border of the liver. Remember: the stomach ends at the pylorus to continue as the duodenum. So the first part of duodenum is related to the upper part of the quadrate lobe. also the transverse colon is located there.. So it s related to the lower part of this lobe. 6. Then we proceed to reach the gallbladder which consist of three parts: Fundus (the head), body (the largest part), neck (the constriction). 7. Then we proceed to reach the colic impression which is made by the right colic flexure (hepatic flexure; because it is related to the liver) 7
8 Remember: the ascending colon turns to the left and continues as the transverse colon which causes the formation of the right colic flexure. 8. Then we go upwards to reach another impression (renal impression) which lies on the right kidney and the right suprarenal. 6 th. An important note: the portal vein and the hepatic artery, when they enters the liver they will divide into two branches one for the right lobe and the other is for the left lobe. BUT we have an exception : the caudate and the quadrate lobe are anatomically part of the right lobe but functionally they are related to the left side (they take blood supply from the left hepatic artery and the left portal vein and they drains in the left hepatic vein also anything they secrete goes to the left side) 7 th. The porta hepatis consists of: 1. Bile duct (the most anterior in position and carries the bile that is secreted from the liver). 2. Intermediate in position we have the hepatic artery which is a branch from the celiac trunk (it s derived from the foregut). 3. The most posterior in position is the portal vein. 8 th. the blood supply of the liver (the portal vein and the hepatic artery): 1. The portal vein provides the liver with 75%-80% of its needs (most important) 2. The hepatic artery provides the liver with oxygen. 8
9 As they enter the liver they divides into right and left branches then they divides more and more, the liver then takes its needs and the other things drains in the hepatic vein which will drain in the inferior vena cava (the last tributaries to the inferior vena cava before it enters the central tendon to drain in the heart). 9 th. the biliary system: The bile is secreted by the liver cells then it will continue into two ducts (right hepatic duct from the right lobe and left hepatic duct from the left lobe), both hepatic ducts unites to form the common hepatic duct (which sends the bile to the gallbladder to be concentrated there) then the bile will leave the fundus, body and neck through the cystic duct which unite with the common hepatic duct to form the common bile duct which also unite with the pancreatic duct to enter the duodenum from the postromedial aspect at the midpoint of the second part. قال اإلمام الشافعي رحمه هللا : ولما قسى قلبي وضاقت مذاهبي...جعلت الرجا مني لعفوك سلما تعاظمني ذنبي فلما قرنته بعفوك...ربي كان عفوك أعظما وما زلت ذا عفو عن الذنب لم تزل...تجود وتعفو منة وتكرما إليك إله الخلق أرفع رغبتي... وإن كنت يا ذا المن والجود مجرما 9 وأخيرا أعتذر عن اي اخطاء وردت اثن اء الكتابة فالخطأ من طبيعة البشر
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER
 Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
The Spleen. Dr Fahad Ullah
 The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Anatomy of Liver and Spleen
 Anatomy of Liver and Spleen Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Anatomy of Liver and Spleen Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Done by: nisreen obeidat
 Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
Sheet: liver and pancreas Done by: nisreen obeidat Embryology of the liver The liver develops in the ventral mesentery of the foregut and divides the ventral mesentery :into 1)lesser omentum (between the
بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم
 MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
-12. -Renad Habahbeh. -Dr Mohammad mohtasib
 -12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
-12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II
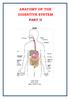 ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Omran Saeed. Mohammad Al-muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
ABDOMEN - GI. Duodenum
 TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
Cardiovascular System Anatomy & Embryology
 بسم رلاهللا Cardiovascular System Anatomy & Embryology Portal circulation: Portal vessel: a vessel or a vein running between two sets of capillaries, the portal vein of the liver starts from a set of capillaries
بسم رلاهللا Cardiovascular System Anatomy & Embryology Portal circulation: Portal vessel: a vessel or a vein running between two sets of capillaries, the portal vein of the liver starts from a set of capillaries
Mousa Salah. Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib. 1 P a g e
 8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE. Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC
 Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
Liver o The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety of functions. - It s an accessory organ of GIT
 بسم رلاهللا You don t need to refer to the slides, we included everything here In this lecture we will talk about Liver & Gallbladder Liver o The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety
بسم رلاهللا You don t need to refer to the slides, we included everything here In this lecture we will talk about Liver & Gallbladder Liver o The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai
 Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 21.12.2017 Internal surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall The internal ( posterior ) surface of the anterolateral
Lecture 01 Internal surface of anterolateral abdominal wall BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 21.12.2017 Internal surface of the anterolateral abdominal wall The internal ( posterior ) surface of the anterolateral
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Posterior Abdominal wall-
 Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Common Bile Duct (CBD)
 Liver Last time we talked about the liver and the doctor started by revising some information about it: It has five surfaces. It reaches the 5 th intercostal space ; some books write that it reaches the
Liver Last time we talked about the liver and the doctor started by revising some information about it: It has five surfaces. It reaches the 5 th intercostal space ; some books write that it reaches the
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
The Whipple Operation Illustrations
 The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
The peritoneum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website:
 The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
-the stones will obstruct the common bile duct and it might also be precancerous. -so the best treatment is chlolycyctoctomy.
 At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3-
 1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
1 2 The sinus venosus represent the venous end of the heart It receives 3 veins: 1- Common cardinal vein body wall 2- Umbilical vein from placenta 3- Vitelline vein from yolk sac 3 However!!!!! The left
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Basic Abdominal Sonography
 24S Basic Abdominal Sonography Procedural Overview JOHN FATCHETT II, RDMS is provided. Patient preparation (i.e., fasting) scanning techniques, spleen, transducer. evaluation of abdominal anatomy in the
24S Basic Abdominal Sonography Procedural Overview JOHN FATCHETT II, RDMS is provided. Patient preparation (i.e., fasting) scanning techniques, spleen, transducer. evaluation of abdominal anatomy in the
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures. The Large Arteries. The Aorta. Ascending aorta
 Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Chapter 5: Other mediastinal structures The Large Arteries The Aorta The aorta is the main arterial trunk of the systemic circulation and in the healthy state its wall contain a large amount of yellow
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
In the name ofgod. Abdomen 3. Dr. Zahiri
 In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries. Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through them.
 Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Artery 1 Head and Thoracic Arteries 1. Given the following parts of the aorta: 1. abdominal aorta 2. aortic arch 3. ascending aorta 4. thoracic aorta Arrange the parts in the order blood flows through
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer
 Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
Done by: Dina Sawadha & Mohammad Abukabeer The stomach *the stomach is a dilated part of the gastro intestinal tract, it's "J" shape. *the lower surface of the stomach ( the greater curvature ) reaches
DEVELOPMENT OF THE LIVER
 THE LIVER DEVELOPMENT OF THE LIVER THE LIVER The hepa-c diver-culum develops as an outgrowth of the endoderm of the foregut in the region of the second por-on of duodenum. This diver-culum enters the ventral
THE LIVER DEVELOPMENT OF THE LIVER THE LIVER The hepa-c diver-culum develops as an outgrowth of the endoderm of the foregut in the region of the second por-on of duodenum. This diver-culum enters the ventral
Mediastinum It is a thick movable partition between the two pleural sacs & lungs. It contains all the structures which lie
 Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
Dr Jamila EL medany OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Define the Mediastinum. Differentiate between the divisions of the mediastinum. List the boundaries and contents of
UNIVERSITY DEVELOPMENT CENTER. Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department 29/12/2015
 Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the spleen. Oluwadiya KS
 Anatomy of the spleen Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The spleen is an ovoid, usually purplish, pulpy mass about the size and shape of one's fist. It is the largest lymphoid tissue in the body
Anatomy of the spleen Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The spleen is an ovoid, usually purplish, pulpy mass about the size and shape of one's fist. It is the largest lymphoid tissue in the body
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination. (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax)
 1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH
 ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
ORAL CAVITY, ESOPHAGUS AND STOMACH 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture you should be able to: Describe the anatomy the oral cavity, (boundaries, parts, nerve supply). Describe the anatomy of the palate,
THE ORAL CAVITY
 THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
THE ORAL CAVITY WALL OF ABDOMEN (ANTERIOR) The paraumbilical vein drains into the portal vein and then through the liver. This is an important clinical connection. THE ABDOMINAL VISCERA The small
10/14/2018 Dr. Shatarat
 2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
2018 Objectives To discuss mediastina and its boundaries To discuss and explain the contents of the superior mediastinum To describe the great veins of the superior mediastinum To describe the Arch of
Liver. Function of the liver
 Liver & Gallbladder Liver The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety of functions Weight: 1/50 of body weight in adult & 1/20 of body weight in infant It is exocrine(bile) & endocrine
Liver & Gallbladder Liver The liver is the largest gland in the body and has a wide variety of functions Weight: 1/50 of body weight in adult & 1/20 of body weight in infant It is exocrine(bile) & endocrine
Which Artery am I? I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm.
 I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm. A. I supply blood to the head and neck. I am large and will branch into two smaller arteries.
I am one of two smaller arteries that arise from the brachial. I supply blood to the medial aspect of the forearm. A. I supply blood to the head and neck. I am large and will branch into two smaller arteries.
Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder
 Connexions module: m49293 1 Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Donna Browne Based on Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and
Connexions module: m49293 1 Digestive System Module 6: Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and Gallbladder Donna Browne Based on Accessory Organs in Digestion: The Liver, Pancreas, and
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
YOU MUST BRING GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
EFSUMB Course Book, 2 nd Edition
 Ultrasound of the liver. 11.04.2018 10:01 1 EFSUMB Course Book, 2 nd Edition Editor: Christoph F. Dietrich Ultrasound of the liver Christoph F. Dietrich, Carla Serra 2, Maciej Jedrzejczyk 3 1 Caritas-Krankenhaus
Ultrasound of the liver. 11.04.2018 10:01 1 EFSUMB Course Book, 2 nd Edition Editor: Christoph F. Dietrich Ultrasound of the liver Christoph F. Dietrich, Carla Serra 2, Maciej Jedrzejczyk 3 1 Caritas-Krankenhaus
slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments
 Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Done By : Rahmeh Alsukkar Date : 26 /10/2017 slide 23 The lobes in the right and left lungs are divided into segments,which called bronchopulmonary segments Each segmental bronchus passes to a structurally
Development of the Liver and Pancreas
 Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Development of the Liver and Pancreas Professor Alfred Cuschieri Department of Anatomy University of Malta Three glandular buds arise from the distal end of the foregut during the fourth week Day 22 -The
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
CT Basics: Cross-sectional Anatomy of the Chest, Abdomen and Pelvis Module 9
 Module 9 Transcript For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions.
Module 9 Transcript For educational and institutional use. This transcript is licensed for noncommercial, educational inhouse or online educational course use only in educational and corporate institutions.
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
Dana Alrafaiah. - Moayyad Al-Shafei. -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 - 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
- 6 - Dana Alrafaiah - Moayyad Al-Shafei -Mohammad H. Al-Mohtaseb 1 P a g e Quick recap: Both lungs have an apex, base, mediastinal and costal surfaces, anterior and posterior borders. The right lung,
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Anatomy. Ruba Mahafzah 18/11/2015. Mohammad Allouh. 1 P a g e
 Anatomy Ruba Mahafzah 18/11/2015 Mohammad Allouh 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we started speaking about the liver. We said that the liver is composed of 2 main surfaces: 1. Convex diaphragmatic surface
Anatomy Ruba Mahafzah 18/11/2015 Mohammad Allouh 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we started speaking about the liver. We said that the liver is composed of 2 main surfaces: 1. Convex diaphragmatic surface
VESSELS: GROSS ANATOMY
 ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
ACTIVITY 10: VESSELS AND CIRCULATION OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 23, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Observe and sketch histology slide
Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract
 HPB, 2008; 10: 7276 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract DENIS CASTAING Centre hépato-biliaire, Hôpital Paul Brousse, Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Paris XI, Paris,
HPB, 2008; 10: 7276 REVIEW ARTICLE Surgical anatomy of the biliary tract DENIS CASTAING Centre hépato-biliaire, Hôpital Paul Brousse, Assistance Publique- Hôpitaux de Paris, Université Paris XI, Paris,
Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings
 Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings Poster No.: C-3193 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular
Spontaneous portosystemic venous shunts in liver cirrhosis: Anatomy, pathophysiology, hemodynamic changes and imaging findings Poster No.: C-3193 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Vascular
