JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 04 Page April 2018
|
|
|
- Alexis Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Impact Factor (SJIF): Index Copernicus Value: ISSN (e) x ISSN (p) DOI: A Study on Characterization of Breast Lesions Using Sonomammography and Comparing with Histopathology Authors Deepa S 1, Beena Sebastian 2, Radhamani MV 3, Divya S 4, Kiran Ravi 5 1 Senior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Govt Medical College, Kottayam 2 Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Govt Medical College, Kottayam 3 Additional Professor, Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, Govt Medical College, Kottayam 4 Assistant Professor, Department of Community Medicine, Malabar Medical College, Kozhikode 5 DNB Resident, Department of General Medicine, Baby Memorial Hospital, Kozhikode Corresponding author Beena Sebastian Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Govt. Medical College, Kottayam, Kerala deepaosler@gmail.com Abstract Introduction: The changing lifestyle practices can lead to a higher number of cancer cases. Breast cancer is the most common cancer among women in India. It is very important to identify the palpable breast lump as benign or malignant. Ultrasonography is a commonly used screening imaging modality in breast lumps. The present study aims to find out the accuracy of sonomammography by comparing with histopathology. Materials and Methods: A descriptive study was conducted among female patients for one year. It included 75 female patients above 20 years of age with palpable breast lesions and bloody discharge from the nipple. Patients with advanced carcinoma, previously treated cases and patients with history of previous breast biopsy were excluded from the study. Designed as diagnostic test evaluation, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of the variables in differentiation was calculated comparing with histolopathological diagnosis. The features of ultrasonography was analyzed by Cohen s Kappa for statistical agreement with histopathology. Results: With sonomammography, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy obtained were 83.3%, 89.7% and 86.67% respectively for detection of malignancy. Discussion and Conclusion: Sonomammography is a very useful non-invasive imaging modality having high sensitivity and specificity in diagnosing breast lesions. This study shows that ultrasonography is useful in characterization of breast masses. The requirement of biopsy for breast masses can be reduced. The kappa values for ultrasonographic diagnosis was with P value <0.001 which indicates good agreement with histopathology. Keywords: Benign, breast lesion, histopathology, malignant, sonomammography. Introduction The incidence of cancer is increasing day by day. In a developing country like India, because of the changing lifestyle practices including food habits, environmental and genetic factors, the number of breast cancer cases are higher. The most common cancer among women in India is breast cancer. (1) A palpable breast lump is a very common diagnostic problem. The most important question in the case of a breast lump is whether the lesion is benign or malignant. The field of breast imaging is undergoing a rapid revolution due to improvement in the technology. Ultrasonography is a commonly used screening imaging modality Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 26
2 in breast lumps. It can be used in pregnant females also without the risk of radiation. The development of high frequency probes allow a high degree of accuracy in characterizing breast lumps. It is important to obtain a definitive preoperative diagnosis because the surgical approach is different in malignant and benign lesions. Breast cancer screening helps to detect cancers at an earlier, more treatable stage, and is an important clinical procedure because approximately one in eight women will develop breast cancer over their lifetimes. The various characteristics studied are as follows: The characteristics suggestive of benign lesions are: Ellipsoid shape - Most of the small fibroadenomas have smooth, well circumscribed ellipsoid shape, suggesting benignity. Echogenecity- Hyperechoic masses are generally benign and are confined to subcutaneous fat. Capsule - Thin, well-circumscribed, echogenic capsule around a solid nodule suggest a benign nature of the lesion. Breast calcifications are small calcium deposits that develop in a woman's breast tissue. Certain types of breast calcifications may suggest early breast cancer. Most of the breast calcifications encountered by radiologists are benign. Radiologists must be able to identify typically benign breast calcifications that do not require biopsy to prevent unnecessary procedures and to reduce patient anxiety (2-5). The characteristics suggestive of malignant lesions are: Greater anteroposterior diameter- when the lesion is taller than broader (AP diameter more than the transverse diameter), as explained by the fact that generally the benign lesion propagate along the tissue plane whereas the malignant lesion propagate perpendicular to the tissue plane. Echogenecity -Presence of markedly hypo echoic nodule is characteristic of malignant lesion. Margins -Angular margins refer to the contour of the junction between the nodule and surrounding tissue. It has highest sensitivity of the individual findings suggesting malignancy. Presence of many microlobulations on the surface of a solid breast nodule is suggestive of malignancy. Distal shadowing - Shadowing is due to fibroelastic host response elements within the tumor. It is common with scirrhous carcinoma. Calcifications - Presence of punctate calcifications is suggestive of malignancy although large nodular calcifications are seen in benign lesions like calcified fibroadenoma. Lucent-centered calcifications may be spiculated, with local thickening, branching, rod-like or angular. In early stages of development, calcifications in the wall of an oil cyst may simulate malignancy (6) Large rod like calcifications may have lucent centers if the ductal secretions undergo peripheral calcification. In general, these calcifications are coarser and larger (usually > 1 mm in diameter) than malignant calcifications. Round and punctate calcifications- Punctate calcifications are spherical calcifications that have well-defined margins. Punctate calcifications usually measure less than 0.5 mm in diameter. Round calcifications are benign spherical calcifications that may vary in size. Distribution of breast calcifications- Breast calcifications are described in terms of type and distribution and categorized according to the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BIRADS) of the American College of Radiology (ACR). Invasive ductal carcinoma is the most common type of breast cancer. Ductal carcinomas elicit a desmoplastic reaction that produces fibrosis. In such cases, a hard, palpable mass is commonly found at examination. At US, invasive ductal carcinoma typically manifests as an irregular, hypoechoic mass with or without posterioracoustic shadowing. The second most common type of breast cancer is invasive lobular carcinoma, which accounts for 5% 10% of all malignant breast tumors (7). Invasive lobular carcinoma is thought to arise from the terminal ductules of a breast lobule and invades the normal Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 27
3 breast parenchyma in a single file pattern (8). Due to this pattern of invasion, the tumor often manifests as a subtle area of distortion or asymmetry. Tubular carcinoma is a low grade, welldifferentiated form of ductal breast cancer. Lesions are of ductal origin and are characterized by ductal cells invading normal breast tissue and forming groups in the shape of tubules (9). Although these lesions are occasionally palpable, they more frequently go undetected until a screening test is performed. Fibroadenoma- Fibroadenoma is one of the commonest benign breast lumps and results from excess proliferation of connective tissue. They characteristically contain glandular and fibrous connective tissue. Fibroadenomas have a spectrum of features from the well circumscribed discrete mass, to the multilobulated mass. They may contain popcorn calcification. Calcification may also present as microcalcification which makes differentiation from malignancy very difficult. On ultrasound they are typically seen as a wellcircumscribed, round to ovoid, or macrolobulated mass with generally uniform hypoechogenicity. Intramammary lymph nodes- are lymph nodes within the breast tissue. In breast imaging, they generally fall into BIRADS II lesions. On ultrasound it is usually detected as a solid reniform lesion which is hypoechoic to the remainder of the breast tissue. A hyperechoic central area resulting from the hilar fat may be seen. Sometimes a nearby blood vessel may be seen with some flow entering the hilum on colour Doppler. Enlargement of the nodes may result from dermatitis, hyperplasia, breast cancer or metastasis (10,11). Lipoma- On ultrasound it is most often seen as a rounded lesion that is iso-echoic or at times slightly hyperechoic to surrounding fat. Circumscribed carcinoma- On sonography, lesion appear as hypoechoic oval or round lesion with varying degree of attenuation usually less than that of spiculated carcinoma, some of lesion show internal cystic spaces (12). Margins are usually well defined but some of margins are irregular or illdefined, such a lesion should be suspicious for malignancy. Sonographic evaluation reveals area projecting from the wall of the cyst (13,14). USS finding are nonspecific, as they are identical to those from an intracystic papilloma and a blood clot in a cyst (13). Lymphoma- Primary lymphoma of the breast is rare and secondary involvement is more frequent. The sonographic appearance is most often that of a solid hypoechoic mass which is again non specific and both radiologic and clinical appearance is similar to carcinoma. Metastasis to the breast- Lymphoma and other hematologic malignancies, melanoma and lung cancer are the three most common blood-borne hematologic sources followed by ovarian cancer, soft tissue sarcomas and other gastrointestinal and genitourinary cancer (15). Breast abscess- Sonographic features suggestive of a breast abscess include hypoechoic collection, mostly multiloculated, no vascularity within the collection, acoustic enhancement due to fluid content, an echogenic, vascular rim. Mammographic appearance can mimic carcinoma. Carcinoma- A very few studies have been conducted regarding sonomammographic findings of benign and malignant breast lesions and assessing how accurately it can be used by comparing them with the findings of the gold standard technique, histopathology. This study is an attempt to evaluate the accuracy of ultrasonogam in characterizing breast lumps and comparing them with clinical findings and correlate them with histopathology results. It is very important to understand the accuracy of sonomammogram as unnecessary and several biopsy can be avoided which itself can be a risk factor for breast cancer. This study has been taken up to study the accuracy of sonomammogram in differentiating benign and malignant lesions on comparing with histopathology. Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 28
4 Aim The aim of the study was to characterize the clinically palpable breast masses into benign and malignant, based on sonomammographic findings and to assess the accuracy by comparing with histopathology, as the gold standard. Objectives To determine the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, of sonomammography in differentiating benign from malignant breast lesion by comparing with histopathology Material and Methods A descriptive study was conducted among female patients with breast lesions at the Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Thiruvananthapuram for one year from July 2013 to July The study sample consisted of patients referred to Department of Radiodiagnosis for ultrasonogram for evaluation of breast lesions. All female patients above 20 years of age with palpable breast lesions and bloody discharge from the nipple were included for the study. Patients with advanced carcinoma(stage III and IV), previously treated cases, those who have not given consent for the study and with history of previous breast biopsy were excluded. Consecutive sampling method was used for data collection using a pre-tested structured questionnaire. There were 75 patients satisfying the inclusion criteria during the study period. After obtaining the proper history, clinical examination and consent, the patients were subjected to ultrasound and compared with histopathology which is the gold standard test. The need and aim of study were explained to the patients and informed written consent was obtained before including the subject in the study. Data Collection Patients who satisfied the inclusion criteria were 75 and were subjected to undergo USS with 17mHz linear array probes and confirmed the findings with FNAC or biopsy reports. Data collection was started after obtaining the Institutional Research and Ethical Committee Clearance. Benign criteria studied with ultrasonography are 1. Hyperechoic 2. Ellipsoid 3. <3 or few lobulations 4. Thin echogenic capsules and the malignant criteria were: 1. Anteroposterior diameter more than transverse 2. Angular margins 3. Markedly hypo echoic 4. Distal acoustic shadowing Data Analysis Data was analysed using SPSS 16.0 (Statistical Package for Social Sciences, version16) and Microsoft Excel has been used to generate graph and tables. Sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, and accuracy of sonomammogram for detection of benign and malignant breast lesions were worked out considering FNAC as the gold standard. It is derived from 2x2 table with rows representing ultrasonography positive and negative cases as well as columns representing FNAC positive and negative cases. The features of ultrasonography was analyzed by Cohen s Kappa for statistical agreement between these and histopathology. Results Table 1. Distribution of study population according to age and type according to FNAC Age(in years) Characterisation( FNAC) Malignant n(%) Benign n(%) Total n(%) (5.6%) 5(12.8%) 7 (9.3) (11.1%) 10(25.6%) 14 ( 18.7) (33.3%) 8(20.5%) 20 (26.7) (38.9%) 11(28.2%) 25 (33.3) (11.1%) 5(12.8%) 9 (12) Total 36(100%) 39(100%) 75 (100) The youngest patient was 23 year old and the oldest was 67 year. Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 29
5 Number of patients JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 04 Page April 2018 Table 2: Distribution of patients according to clinical and FNAC diagnosis Clinical diagnosis Malignant N(%) FNAC diagnosis Benign N(%) Total N(%) Benign 0(0) 27(69.2) 27(36) Malignant 27(75) 1(2.6) 28(37.3) Indeterminate 9(25) 11(28.2) 20(26.7) Total 36(100) 39(100) 75(100) P< o.oo1 Table 3 : Distribution of benign and malignant cases according to margin Margin FNAC findings Total N(%) Malignant n(%) Benign n(%) Smooth 1(2.8) 28(71.8) 29(38.7) Irregular 8(22.2) 10(25.6) 18(24) Spiculated 27(75) 1(2.6) 28(37.3) Total 39(100) 36(100) 75(100) Graph 1: Distribution of benign and malignant lesions according to shape with HPR correlation P value < Distribution according to shape and HPR 35(97.2%) 26(66.7%) 12(30.8%) 0 1(2.8%) 1(2.8%) Ellipsoid Lobulated Angular Shape Malignant Benign Table 4: Distribution of benign and malignant lesions according to thin echogenic capsule Thin echogenic capsule FNAC findings Total N(%) Malignant n(%) Benign n(%) Absent 27(75) 4(10.3) 31(41.3) Present 9(25) 35(89.7) 44(58.7) Total 36(100) 39(100) 75(100) P<0.001 Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 30
6 Absent Present Smooth Irregular Spiculated Hypoechoic Hyperechoic Absent Present Number of patients JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 04 Page April 2018 Graph 2: Distribution of benign and malignant lesions according to AP> Transverse diameter, margin, echogenicity and distal shadowing (92.3%) 29(80.6%) 28(71.8%) 34(94.4%) 29(74.4%) 27(75%) 36(92.3%) 29(80.6%) (19.4%) 10(25.6%) 8(22.2%) 3(7.7%) 1(2.8%) 1 10(25.6%) 7(19.4%) 2(5.6%) 3(7.7%) Malignant Benign 0 AP>Transverse Margin Echogenicity Distal shadowing Malignant criteria Table 5: Distribution of benign and malignant lesions according to BIRADS BIRADS FNAC findings Total n(%) Malignant n(%) Benign n (%) 2 0(0) 31(79.5) 31(41.3) 3 3(8.3) 3(7.7) 6(8) 4 11(30.6) 5(12.8) 16(21.3) 5 22(61.1) 0(0) 22(29.3) Total 36(100) 39(100) 75(100) P<0.001 Table 6: Distribution according to benign criteria and negative predictive value of each characteristic in ultrasonography Criteria FNAC findings Total n(%) Specificity NPV Malignant n(%) Benign n (%) Hyperechoic 2(5.6) 10(25.6) 12(16) Ellipsoid 0(0) 26(66.7) 26(34.7) Lobulated(3 or fewer 1(2.8) 12(30.8) 13(17.3) lobulations) Thin echogenic capsule 9(25) 35(89.7) 44(58.7) Table 7: Distribution according to malignant criteria and positive predictive value of each characteristic in ultrasonography Criteria FNAC findings Total n(%) Sensitivity PPV Malignant n(%) Benign n (%) Angular margins(spiculated) 35(97.2) 1(2.6) 36(48) Distal shadowing 29(80.6) 3(7.7) 32(42.7) Hypoehoic 34(94.4) 29(74.4) 63(84) AP> Transverse 29(80.6) 3(7.7) 32(42.7) Table 8: Distribution according to ultrasonographic diagnosis(2 or more ultrasonographic features) and Histopathology Diagnosis ultrasonographic diagnosis n(%) Histopathology n(%) Benign 41(54.7) 39(52) Malignant 34(45.3) 36(48) Total 75(100) 75(100) Of the 34 sonologically malignant lesions, 30 were malignant histopathologically. Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 31
7 Table 9: Sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of ultrasonography USS findings FNAC findings Total n(%) Malignant n(%) Benign(%) Malignant (based on the presence of atleast 2 of 30(83.3) 4(10.3) 34(45.3) the malignant criteria in ultrasonography) Benign 6(16.7) 35(89.7) 41(54.7) Total 36(100) 39(100) 75(100) Measure of agreement Kappa= P < For detecting malignancy, with sonomammography, the sensitivity, specificity and accuracy obtained were 83.3%, 89.7% and 86.67% respectively for detection of malignancy;with PPV: 88.2% and NPV 85.3% Discussion The maximum number of breast lumps was in the age group of years irrespective of benign or malignant nature. The most common benign lesion observed in the index study was fibroadenoma which was present in 16 patients (21 % of study population). Studies showed fibroadenoma is common before 40 years. In our study 10 out of 16 patients were below 40 years (62.5%). The youngest patient with malignancy was 23 years old and the oldest patient was 67 years old. Above 60 years age, 4 out of 9 patients were malignant (44.5%) and rest were benign cases which consisted of oil cysts, simple cysts and breast abscesses. Here, only 44.5% in the age group above 60 years were malignant. There is higher chance of malignancy in a breast lump in patients older than 60 years. This may be due to the advanced stage of presentation which was an exclusion criterion here. According to histopathology, 39 lesions were benign and 36 lesions were malignant. Benign lesions that came across the study were simple cysts, breast abscess, galactocele and fibrocystic breast disease. Among the 6 cases of simple cyst, 3 were in the age group of years and 3 in years. According to literature, cysts are common in years. According to the malignant criteria for ultrasonography, 4 cases which were diagnosed as malignant by USS came out to be benign on histopathology. AP diameter was equal to transverse diameter in one of the case. Two lesions were hypoechoic and had angular margins (satisfying malignant criteria in ultrasonography) of which two turned out to be post-operative scar and other two turned to be benign epithelial hyperplasia. According to benign criteria for ultrasonography 90% were benign. 6 cases which were diagnosed benign on ultrasonography came out to be malignant on histopathology. 2 were lobular carcinoma histologically. One was comedocarcinoma and 3 were invasive ductal carcinoma. Early malignancy may appear benign and can show well differentiated and smooth margins on ultrasonography. Benign criteria for USS were hyperechogenecity, ellipsoid shape, fewer lobulations and thin echogenic capsule (presence of 2 or more criteria). The NPV of each were 62, 75, 70 and 60 respectively. Malignant criteria for ultrasound were angular margins, distal shadowing, marked hypo echogenicity and larger anteroposterior diameter (presence of 2 or more criteria). Positive predictive value were 97 for angular margins, 90 for distal shadowing, 54 for hypo echogenicity and 91 for larger AP diameter. With sonomammography, the sensitivity, specificity, PPV and accuracy obtained were 83.3%, 89.7%, 88% and 86.67% respectively for detection of malignancy which is similar to that of another study showed sensitivity: 97%, specificity: 97% and positive predictive value: 85% (16). Conclusion This study shows that ultrasonography is useful in characterization of breast masses. When judiciously used the requirement of biopsy for Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 32
8 breast masses can be reduced when strict sonographic criteria for benignity are present. The sensitivity, specificity, PPV and NPV of ultrasonography were calculated. Together these imaging modalities can be reassuring if follow up is planned when the physical examination is not highly suspicious and unnecessary breast biopsy can be avoided. The kappa values for USS was with P value <0.001 which indicates good agreement with histopathology. The possible clinical implications of the current study is that ultrasonography can be a useful diagnostic armamentarium for the clinician. Limitation of the Study Even though we have done ultrasonography, doppler evaluation of breast masses was not done which would have helped in better characterization of breast lesions into benign and malignant. Also it is a hospital based study, the result may not be representative of the general population. No sources of support in the form of grants References 1. Ghoncheh M, Momenimovahed Z, Salehiniya H. Epidemiology, incidence and mortality of breast cancer in Asia. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17: Borecky N, Rickard M. Preoperative diagnosis of carcinoma within fibroadenoma on screening mammograms. J Med Imaging Radiat Oncol Feb;52(1): Lehman CD, Rutter CM, Eby PR, White E, Buist DS, Taplin SH. Lesion and patient characteristics associated with malignancy after a probably benign finding on community practice mammography. AJR Am J Roentgenol Feb;190(2): Rosenberg RD, Yankaskas BC, Abraham LA, Sickles EA, Lehman CD, Geller BM, et al. Performance benchmarks for screening mammography. Radiology Oct;241(1): Sickles EA, Miglioretti DL, Ballard- Barbash R, Geller BM, Leung JW, Rosenberg RD, et al. Performance benchmarks for diagnostic mammography. Radiology Jun;235(3): Bassett LW, Gold RH, Mirra JM. Nonneoplastic breast calcifications in lipid cysts: development after excision and primary irradiation. AJR Am J Roentgenol Feb;138(2): Sastre-Garau X, Jouve M, Asselain B, Vincent-Salomon A, Beuzeboc P, Dorval T, et al. Infiltrating lobular carcinoma of the breast. Clinicopathologic analysis of 975 cases with reference to data on conservative therapy and metastatic patterns.cancer Jan 1;77(1): Helvie MA, Paramagul C, Oberman HA, Adler DD. Invasive lobular carcinoma. Imaging features and clinical detection. Invest Radiol Mar;28(3): Moezzi M, Melamed J, Vamvakas E, Inghirami G, Mitnick J, Quish A, et al. Morphological and biological characteristics of mammogram-detected invasive breast cancer. Hum Pathol Sep;27(9): Kopans DB, Meyer JE, Murphy GF. Benign lymph nodes associated with dermatitis presenting as breast masses. Radiology Oct;137(1 Pt 1): Paulus DD. Benign diseases of the breast. Radiol Clin North Am Mar;21(1): Meyer JE, Amin E, Lindfors KK, Lipman JC, Stomper PC, Genest D. Medullary carcinoma of the breast: mammographic and US appearance. Radiology Jan;170(1 Pt 1): Estabrook A, Asch T, Gump F, Kister SJ, Geller P. Mammographic features of intracystic papillary lesions. Surg Gynecol Obstet Feb;170(2): Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 33
9 14. Reuter K, D'Orsi CJ, Reale F. Intracystic carcinoma of the breast: the role of ultrasonography. Radiology Oct;153(1): Paulus DD, Libshitz HI.Metastasis to the breast. Radiol Clin North Am Sep;20(3): Yang WT, Mok CO, King W, Tang A, Metreweli C. The role of high frequency ultrasonography in the evaluation of palpable breast masses in Chinese women: alternative to mammography? J Ultrasound in Med, Vol. 15, Issue Deepa S et al JMSCR Volume 06 Issue 04 April 2018 Page 34
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal
 Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Original article 21 Mammographic evaluation of palpable breast masses with pathological correlation: a tertiary care centre study in Nepal G. Gurung, R. K. Ghimire, B. Lohani Department of Radiology and
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN
 Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions
 Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions Poster No.: C-1870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Aouini, I. Megdiche, D. Ben Hammadi, N. BEN MAMI, I. Attia, R. Neila, A. Zidi;
Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions Poster No.: C-1870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Aouini, I. Megdiche, D. Ben Hammadi, N. BEN MAMI, I. Attia, R. Neila, A. Zidi;
Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds
 215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
215 Table 1. Classification of US Features Based on BI-RADS for US in Benign and Malignant Breast Lesions US Features Benign n(%) Malignant n(%) Odds ratio 719 (100) 305(100) Shape Oval 445 (61.9) 019
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.182 Analyzing the Role of Spectral Indices
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU?
 MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER
 RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER Orsolya Farkas, Gabriella Bodrogi and Gábor Szalai Department of Radiology, Pécs University Orsifarkas@yahoo.com Complex evaluation of the breast Patient history
RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER Orsolya Farkas, Gabriella Bodrogi and Gábor Szalai Department of Radiology, Pécs University Orsifarkas@yahoo.com Complex evaluation of the breast Patient history
Solid Breast Nodules: Use of Sonography to Distinguish between Benign and Malignant Lesions
 A. Thomas Stavros, MD #{149} David Thickman, MD #{149} Cynthia L. Rapp, RT, RDMS Mark A. Dennis, MD #{149} Steve H. Parker, MD #{149} Gale A. Sisney, MD Solid Breast Nodules: Use of Sonography to Distinguish
A. Thomas Stavros, MD #{149} David Thickman, MD #{149} Cynthia L. Rapp, RT, RDMS Mark A. Dennis, MD #{149} Steve H. Parker, MD #{149} Gale A. Sisney, MD Solid Breast Nodules: Use of Sonography to Distinguish
Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management
 Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University,
Sonographic Features of Thyroid Nodules & Guidelines for Management Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University,
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr Kumud Julka
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(2A):568-573 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(2A):568-573 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
M Wani, M Khan, N Ul Gani, S Sangeen, B Singh, M Shafi, A Bilal, S Umer
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 12 Number 1 Juvenile Fibroadenoma With Fibroadenomatoid Hyperplasia M Wani, M Khan, N Ul Gani, S Sangeen, B Singh, M Shafi, A Bilal, S Umer Citation M Wani,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 12 Number 1 Juvenile Fibroadenoma With Fibroadenomatoid Hyperplasia M Wani, M Khan, N Ul Gani, S Sangeen, B Singh, M Shafi, A Bilal, S Umer Citation M Wani,
and verbal and/or written consent was obtained from each of the patient at each visit during which their database was
 Imaging Characteristics of Triple Receptor Negative versus Triple Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Dr. Abdullateef Aliasghar M.B.CH.B., C.A.B.M.S-RAD, Lecturer, National Cancer Research Center, Baghdad
Imaging Characteristics of Triple Receptor Negative versus Triple Receptor Positive Breast Cancer Dr. Abdullateef Aliasghar M.B.CH.B., C.A.B.M.S-RAD, Lecturer, National Cancer Research Center, Baghdad
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
Mimickers of breast malignancy
 Mimickers of breast malignancy Poster No.: C-0477 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast Authors: S. H. Park, H.-Y. Choi; Incheon/KR Keywords: mimickers, breast malignancy, ultrasound
Mimickers of breast malignancy Poster No.: C-0477 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast Authors: S. H. Park, H.-Y. Choi; Incheon/KR Keywords: mimickers, breast malignancy, ultrasound
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS)
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Abbreviated Key Title: Sch. J. App. Med. Sci. Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher A Unit of Scholars Academic and Scientific Society, India www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Abbreviated Key Title: Sch. J. App. Med. Sci. Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher A Unit of Scholars Academic and Scientific Society, India www.saspublisher.com
Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; December 2016: Vol.-6, Issue- 1, P
 Original article: DIAGNOSTIC EFFICACY OF COMBINED MAMMOGRAPHY AND ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS WITH PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION AND BIRADS ASSESSMENT Dr. G Harini*, Dr. S Shrinuvasan, Dr.
Original article: DIAGNOSTIC EFFICACY OF COMBINED MAMMOGRAPHY AND ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS WITH PATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION AND BIRADS ASSESSMENT Dr. G Harini*, Dr. S Shrinuvasan, Dr.
BI-RADS and Breast MRI. Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018
 BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Radiological Appearances of Male Breast Disease
 Radiological Appearances of Male Breast Disease Poster No.: C-1916 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VALDIVIELSO, A. Guma Martinez, R. Ortega Martinez, L. 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 Perez tapia,
Radiological Appearances of Male Breast Disease Poster No.: C-1916 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. VALDIVIELSO, A. Guma Martinez, R. Ortega Martinez, L. 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 Perez tapia,
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Thyroid in a Nutshell Dublin Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer ULHT
 Thyroid in a Nutshell Dublin 2017 Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer ULHT Acknowledgements Dr. Steve Colley Dr. Rhodri Evans Dr. Rhian Rhys Dr. Andrew McQueen Aims Anatomy & Physiology Incidence
Thyroid in a Nutshell Dublin 2017 Catherine Kirkpatrick Consultant Sonographer ULHT Acknowledgements Dr. Steve Colley Dr. Rhodri Evans Dr. Rhian Rhys Dr. Andrew McQueen Aims Anatomy & Physiology Incidence
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of breast lesions with USG and colour Doppler Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler Falguni Shah 1, Hemangi Patel 2*, Nila Gandhi 3, Sudhir Singh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Evaluation of breast lesions with USG and colour Doppler Evaluation of breast lesions with ultrasonography and colour doppler Falguni Shah 1, Hemangi Patel 2*, Nila Gandhi 3, Sudhir Singh
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY
 Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Validation of the fifth edition BI-RADS ultrasound lexicon with comparison of fourth and fifth edition diagnostic performance using video clips
 Validation of the fifth edition BI-RADS ultrasound lexicon with comparison of fourth and fifth edition diagnostic performance using video clips Jung Hyun Yoon 1, Min Jung Kim 1, Hye Sun Lee 2, Sung Hun
Validation of the fifth edition BI-RADS ultrasound lexicon with comparison of fourth and fifth edition diagnostic performance using video clips Jung Hyun Yoon 1, Min Jung Kim 1, Hye Sun Lee 2, Sung Hun
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Correlation between Sonomammography and Mammography in the Evaluation of Breast Lesions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 13-20 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation between Sonomammography
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 13-20 www.iosrjournals.org Correlation between Sonomammography
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
Optimizing Breast Sonography
 Optimizing Breast Sonography Cindy Rapp BS, RDMS, FSDMS, FAIUM Denver, Colorado Breast Sonography general goal to make a more specific diagnosis than can be made with clinical and mammographic findings
Optimizing Breast Sonography Cindy Rapp BS, RDMS, FSDMS, FAIUM Denver, Colorado Breast Sonography general goal to make a more specific diagnosis than can be made with clinical and mammographic findings
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Breast imaging in general practice
 Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology
 Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging
 Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Diagnostic Dilemmas of Breast Imaging Common Causes of Error in Breast Cancer Detection By: Jason Cord, M.D. Mammography: Initial Imaging The standard for detection of breast cancer Screening mammography
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features
 Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Pure and Mixed Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Differential Features Hee Jung Shin, MD 1 Hak Hee Kim, MD 1 Sun Mi Kim, MD 1 Dae Bong Kim, MD 1 Ye Ri Lee, MD 1 Mi-Jung Kim,
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging. Medical University of South Carolina Charleston
 Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Leonard M. Glassman MD Analysis of Breast Calcifications
 Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Principal Site Investigator ENHANCE (Evaluation of Thyroid FNA Genomic Signature) study: An IRB approved study with funding to Rochester Regional
 October 20 th 2018 Principal Site Investigator ENHANCE (Evaluation of Thyroid FNA Genomic Signature) study: An IRB approved study with funding to Rochester Regional Health from Veracyte Review ultrasound
October 20 th 2018 Principal Site Investigator ENHANCE (Evaluation of Thyroid FNA Genomic Signature) study: An IRB approved study with funding to Rochester Regional Health from Veracyte Review ultrasound
The radiological spectrum of thyroid malignancy
 The radiological spectrum of thyroid malignancy Poster No.: C-2575 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Cortis, W. Scicluna, A. Mizzi ; Rabat/MT, Birkirkara/MT Keywords: Ultrasound-Colour
The radiological spectrum of thyroid malignancy Poster No.: C-2575 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Cortis, W. Scicluna, A. Mizzi ; Rabat/MT, Birkirkara/MT Keywords: Ultrasound-Colour
Evaluation of breast mass and applicability of histopathology and sonomamography for accurate diagnosis of malignant masses
 Original Research Article Evaluation of breast mass and applicability of histopathology and sonomamography for accurate diagnosis of malignant masses Naseer Khan 1, Samiullah Khan 2* 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article Evaluation of breast mass and applicability of histopathology and sonomamography for accurate diagnosis of malignant masses Naseer Khan 1, Samiullah Khan 2* 1 Assistant Professor,
Role of Elastography in the Evaluation of Breast Lesions
 Original Article Radiology Section DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/26510:2392 Role of Elastography in the Evaluation of Breast Lesions Annapurna Srirambhatla, Deepthi S, Balaji Vara Prasad, Prashanth Kumar KS
Original Article Radiology Section DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/26510:2392 Role of Elastography in the Evaluation of Breast Lesions Annapurna Srirambhatla, Deepthi S, Balaji Vara Prasad, Prashanth Kumar KS
Index words: Breast US Breast neoplasm Breast cancer
 Index words: Breast US Breast neoplasm Breast cancer 125 47.. 53. (),, taller than wide. 50.. 126 Table 1. + 34 24-106 145,, + 139 167-1 2 + 65 37-75 132 47. duct extension. 127 taller than wide + 62 95-78
Index words: Breast US Breast neoplasm Breast cancer 125 47.. 53. (),, taller than wide. 50.. 126 Table 1. + 34 24-106 145,, + 139 167-1 2 + 65 37-75 132 47. duct extension. 127 taller than wide + 62 95-78
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
Combined mammographic and sonographic evaluation of breast masses
 International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Combined mammographic and sonographic evaluation of breast masses Ramakrishna Narra*, Naganarasimha Raju Jukuri, Bhimeswarao Pasupaleti,
International Journal of Sciences & Applied Research www.ijsar.in Combined mammographic and sonographic evaluation of breast masses Ramakrishna Narra*, Naganarasimha Raju Jukuri, Bhimeswarao Pasupaleti,
Margaret Ann Mays, M.D. Clinical Instructor in Radiology Vanderbilt University Medical Center Tennessee Radiological Society February 25, 2017
 Breast Imaging in Adolescents and Young Women Margaret Ann Mays, M.D. Clinical Instructor in Radiology Vanderbilt University Medical Center Tennessee Radiological Society February 25, 2017 Disclosures
Breast Imaging in Adolescents and Young Women Margaret Ann Mays, M.D. Clinical Instructor in Radiology Vanderbilt University Medical Center Tennessee Radiological Society February 25, 2017 Disclosures
BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1
 Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Susan G. Orel, MD Nicole Kay, BA Carol Reynolds, MD Daniel C. Sullivan, MD BI-RADS Categorization As a Predictor of Malignancy 1 Index terms: Breast, biopsy, 00.1261 Breast neoplasms, localization, 00.125,
Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification. Alex Tessnow, MD, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Associate Professor of Medicine Dallas, Texas
 Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification Alex Tessnow, MD, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Associate Professor of Medicine Dallas, Texas Which of the following is true? A. All echogenic foci
Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification Alex Tessnow, MD, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Associate Professor of Medicine Dallas, Texas Which of the following is true? A. All echogenic foci
Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification and FNA Guidelines
 Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification and FNA Guidelines Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University, College
Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification and FNA Guidelines Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University, College
Is Probably Benign Really Just Benign? Peter R Eby, MD, FSBI Virginia Mason Medical Center Seattle, WA
 Is Probably Benign Really Just Benign? Peter R Eby, MD, FSBI Virginia Mason Medical Center Seattle, WA Disclosures: CONSULTANT FOR DEVICOR MEDICAL ARS Question 1 Is probably benign really just benign?
Is Probably Benign Really Just Benign? Peter R Eby, MD, FSBI Virginia Mason Medical Center Seattle, WA Disclosures: CONSULTANT FOR DEVICOR MEDICAL ARS Question 1 Is probably benign really just benign?
Papillary lesions of the breast - Imaging findings and diagnostic challenges
 Papillary lesions of the breast - Imaging findings and diagnostic challenges Poster No.: R-0146 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Jagmohan, F. J. Pool Keywords: Breast, Mammography,
Papillary lesions of the breast - Imaging findings and diagnostic challenges Poster No.: R-0146 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Jagmohan, F. J. Pool Keywords: Breast, Mammography,
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Sonographic Differentiation of Thyroid Nodules With Eggshell Calcifications
 Article Sonographic Differentiation of Thyroid Nodules With Eggshell Calcifications Byung Moon Kim, MD, Min Jung Kim, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Ki Hwang
Article Sonographic Differentiation of Thyroid Nodules With Eggshell Calcifications Byung Moon Kim, MD, Min Jung Kim, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Ki Hwang
Thyroid Nodule Risk Stratification and FNA Guidelines
 Thyroid Nodule Risk Stratification and FNA Guidelines Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University, College of Medicine
Thyroid Nodule Risk Stratification and FNA Guidelines Mark A. Lupo, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid & Endocrine Center of Florida Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine Florida State University, College of Medicine
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS. Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions
 SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
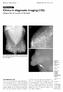 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
Observer Agreement Using the ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)-Ultrasound, First Edition (2003)
 Observer Agreement Using the ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)-Ultrasound, First Edition (2003) Chang Suk Park, MD 1 Jae Hee Lee, MD 2 Hyeon Woo Yim, MD 3 Bong Joo Kang, MD 4 Hyeon
Observer Agreement Using the ACR Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS)-Ultrasound, First Edition (2003) Chang Suk Park, MD 1 Jae Hee Lee, MD 2 Hyeon Woo Yim, MD 3 Bong Joo Kang, MD 4 Hyeon
JMSCR Vol 4 Issue 02 Page February 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.45 Combined Mammographic and Sonographic Evaluation
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i02.45 Combined Mammographic and Sonographic Evaluation
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology
 American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
American Journal of Oral Medicine and Radiology e - ISSN - XXXX-XXXX ISSN - 2394-7721 Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajomr ULTRASONOGRAPHIC EVALUATION OF ADNEXAL MASSES Nageswar Rao* Professor,
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
Case-based discussion:
 Case-based discussion: Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University There are many guidelines for managing thyroid nodules Two important guidelines: 2015 American
Case-based discussion: Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University There are many guidelines for managing thyroid nodules Two important guidelines: 2015 American
Imaging findings of malignancies arising within benign breast lesions
 Imaging findings of malignancies arising within benign breast lesions Poster No.: C-0194 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit F. Can 1, Ö. S. Okcu 2, A. Oktay 2, I. G. Bilgen 3 ; 1 Kutahya/TR,
Imaging findings of malignancies arising within benign breast lesions Poster No.: C-0194 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Educational Exhibit F. Can 1, Ö. S. Okcu 2, A. Oktay 2, I. G. Bilgen 3 ; 1 Kutahya/TR,
Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorder Unit Regina Apostolorum Hospital
 Enrico Papini Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorder Unit Regina Apostolorum Hospital Albano Laziale, Italy The Following Faculty have provide no information regarding significant relationship with commercial
Enrico Papini Endocrinology and Metabolic Disorder Unit Regina Apostolorum Hospital Albano Laziale, Italy The Following Faculty have provide no information regarding significant relationship with commercial
Cystic Masses of the Breast
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Eisenberg ystic Masses of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Neely Hines 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Hines N, Slanetz
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Eisenberg ystic Masses of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Neely Hines 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Hines N, Slanetz
Fat Necrosis: A Grand Imposter
 Fat Necrosis: A Grand Imposter Poster No.: C-0751 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. C. Flores Salinas, Y. A. Ramirez Galvan, A. Garza Báez, C. M. Ferrara Chapa; Monterrey/MX Keywords:
Fat Necrosis: A Grand Imposter Poster No.: C-0751 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. C. Flores Salinas, Y. A. Ramirez Galvan, A. Garza Báez, C. M. Ferrara Chapa; Monterrey/MX Keywords:
BR 1 Palpable breast lump
 BR 1 Palpable breast lump Palpable breast lump in patient 40 years of age or above MMG +/- spot compression or digital breast tomosynthesis over palpable findings Suspicious or malignant findings (BIRADS
BR 1 Palpable breast lump Palpable breast lump in patient 40 years of age or above MMG +/- spot compression or digital breast tomosynthesis over palpable findings Suspicious or malignant findings (BIRADS
Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer:
 Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlation with Histologic Grade 1 Joo Hee Cha, M.D., Woo Kyung Moon, M.D. 2, Nariya Cho, M.D. 2, Sun Mi Kim, M.D. 2, Seung Ja Kim, M.D. 2, Seong Ho Park,
Ultrasound Assessment of Invasive Breast Cancer: Correlation with Histologic Grade 1 Joo Hee Cha, M.D., Woo Kyung Moon, M.D. 2, Nariya Cho, M.D. 2, Sun Mi Kim, M.D. 2, Seung Ja Kim, M.D. 2, Seong Ho Park,
BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases?
 BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases? Poster No.: B-0966 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Etxano Cantera, I. Simon-Yarza, G.
BI-RADS 3 category, a pain in the neck for the radiologist which technique detects more cases? Poster No.: B-0966 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: J. Etxano Cantera, I. Simon-Yarza, G.
Thyroid Nodules and Ultrasound. Patrick Vos Department of Radiology St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC
 Thyroid Nodules and Ultrasound Patrick Vos Department of Radiology St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC No Financial Disclosures Patrick Vos Department of Radiology St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC Acknowledgements
Thyroid Nodules and Ultrasound Patrick Vos Department of Radiology St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC No Financial Disclosures Patrick Vos Department of Radiology St. Paul s Hospital Vancouver, BC Acknowledgements
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines. Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
 Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting Approved by Council June 2018 Approved: June 2018 Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting Approved by Council June 2018 Approved: June 2018 Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications. BI-RADS 5 th Edition
 UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features.
 Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
Digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) occult breast cancers: clinical, radiological and histopathological features. Poster No.: C-1707 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Vinci 1, A. Iqbal
UNC Breast Imaging Division July 2018
 UNC Breast Imaging Division July 2018 This module is to educate residents on ACR BI-RADS Atlas 2 nd edition Ultrasound Sonomammographic anatomy Sonographic features most associated with malignancy Clinical
UNC Breast Imaging Division July 2018 This module is to educate residents on ACR BI-RADS Atlas 2 nd edition Ultrasound Sonomammographic anatomy Sonographic features most associated with malignancy Clinical
Papillary Tu m o rs of the Breast: US Findings
 Papillary Tu m o rs of the Breast: US Findings of the Benign and Malignant Lesions 1 Chang-Seok Lee, M.D., Shin-Ho Kook, M.D., Hyun-Ja Shin, M.D. 2, Woo-Kyung Moon, M.D. 3, Eun-Joo Ko, M.D. 4, Young-Uk
Papillary Tu m o rs of the Breast: US Findings of the Benign and Malignant Lesions 1 Chang-Seok Lee, M.D., Shin-Ho Kook, M.D., Hyun-Ja Shin, M.D. 2, Woo-Kyung Moon, M.D. 3, Eun-Joo Ko, M.D. 4, Young-Uk
challenge is to distinguish the few clinically significant malignant nodules from many benign ones (Table 1).
 Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2015, pp- 71-76 IndianJournals.com A product of Diva Enterprises Pvt. Ltd. DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2015.00018.7 Original Research Ultrasound
Indian Journal of Mednodent and Allied Sciences Vol. 3, No. 2, June 2015, pp- 71-76 IndianJournals.com A product of Diva Enterprises Pvt. Ltd. DOI : 10.5958/2347-6206.2015.00018.7 Original Research Ultrasound
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM am am : Clinician s requirements from breast imaging
 Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms
 342 Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms Ellen Shaw de Paredes, M.D. The purpose of routine screening mammography is to detect unsuspected cancer that has the potential to be cured. Abnormalities
342 Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms Ellen Shaw de Paredes, M.D. The purpose of routine screening mammography is to detect unsuspected cancer that has the potential to be cured. Abnormalities
Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions A. Zulfiqar, MMed* v. Param, DMRD** F.A. Meah, FRACS* s. Nair, FRCS** M.A. Siti-Aishah, DCP* A. N orizan, DCP** * Departments of Radiology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prebiopsy Localization of Nonpalpable Breast Lesions A. Zulfiqar, MMed* v. Param, DMRD** F.A. Meah, FRACS* s. Nair, FRCS** M.A. Siti-Aishah, DCP* A. N orizan, DCP** * Departments of Radiology,
