Table S4A- GOBP functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes common between CO
|
|
|
- Brianne Cannon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Table S4A- GOBP functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes common between CO Terms ListHits ListTotal PopulationHits cell proliferation cell cycle DNA replication and chromosome cycle DNA replication response to DNA damage stimulus response to endogenous stimulus DNA repair DNA metabolism response to stress cellular physiological process cell growth and/or maintenance nucleobase/, nucleoside/, nucleotide and nucleic acid metabolism DNA-dependent DNA replication metabolism regulation of cell cycle regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter transcription from Pol II promoter ER to Golgi transport cytokinesis ubiquitin cycle G1 phase of mitotic cell cycle mitotic cell cycle nuclear division traversing start control point of mitotic cell cycle DNA replication initiation M phase regulation of biological process RNA catabolism physiological process sister chromatid segregation mitotic sister chromatid segregation positive regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter regulation of I-kappaB kinase/nf-kappab cascade protein modification G1/S transition of mitotic cell cycle pyridine nucleotide biosynthesis keratinocyte differentiation glycerophospholipid metabolism regulation of DNA replication water-soluble vitamin metabolism mitotic anaphase deoxyribonucleotide metabolism water-soluble vitamin biosynthesis Golgi vesicle transport nucleotide metabolism dtmp biosynthesis regulation of sister chromatid cohesion DNA synthesis during DNA repair deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate biosynthesis
2 deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate metabolism pyrimidine deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate metabolism pyrimidine deoxyribonucleoside monophosphate biosynthesis trna catabolism viral intracellular protein transport trna 5'-leader removal host cell protein transport mitotic spindle positioning or orientation positive regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition negative regulation of sister chromatid cohesion dtmp metabolism regulation of viral protein levels dermatan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthesis/, polysaccharide chain bios cell cycle arrest vitamin biosynthesis phosphoinositide biosynthesis protein localization lipid metabolism cell death translational initiation death telomerase-dependent telomere maintenance regulation of cellular process I-kappaB kinase/nf-kappab cascade meiosis carboxylic acid metabolism organic acid metabolism G2/M transition of mitotic cell cycle telomere maintenance phosphoinositide metabolism apoptosis programmed cell death base-excision repair positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/nf-kappab cascade nucleotide biosynthesis mrna capping seryl-trna aminoacylation biotin metabolism G1-specific transcription in mitotic cell cycle pyrimidine nucleoside monophosphate metabolism pyrimidine nucleoside monophosphate biosynthesis pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis RNA capping negative regulation of transcriptional preinitiation complex formation glucocorticoid receptor signaling pathway positive regulation of cell cycle positive regulation of mitosis negative regulation of proteolysis and peptidolysis glycerophospholipid catabolism dermatan sulfate proteoglycan biosynthesis chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthesis/, polysaccharide chain bio cellular process
3 vitamin metabolism DNA recombination protein transport meiotic recombination translation response to unfolded protein mitosis glycerophospholipid biosynthesis protein secretion secretory pathway positive regulation of signal transduction M phase of mitotic cell cycle meiosis I meiotic prophase I pyridine nucleotide metabolism cysteinyl-trna aminoacylation male meiosis deoxyribonucleotide biosynthesis UV protection malate metabolism regulation of mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition bile acid catabolism retrograde protein transport/, ER to cytosol establishment of protein localization dermatan sulfate proteoglycan metabolism base-excision repair/, DNA ligation DNA ligation during DNA repair macromolecule metabolism chromosome segregation intracellular protein transport receptor mediated endocytosis pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis regulation of DNA metabolism regulation of metabolism oxidoreduction coenzyme metabolism nitrogen metabolism bile acid biosynthesis mitotic metaphase/anaphase transition arachidonic acid metabolism myoblast differentiation endothelial cell differentiation chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan biosynthesis cofactor metabolism negative regulation of transcription from Pol II promoter vesicle-mediated transport positive regulation of transcription/, DNA-dependent lipid biosynthesis cell organization and biogenesis amino acid transport regulation of transcription from Pol III promoter imprinting glycosaminoglycan catabolism
4 deoxyribonucleoside diphosphate metabolism response to UV NAD biosynthesis negative regulation of catabolism acidic amino acid transport L-glutamate transport organic acid catabolism NAD metabolism ER-associated protein catabolism misfolded or incompletely synthesized protein catabolism unfolded protein response phosphatidylinositol biosynthesis carboxylic acid catabolism aminoglycan catabolism chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan metabolism regulation of protein secretion negative regulation of metabolism regulation of cell proliferation regulation of nucleobase/, nucleoside/, nucleotide and nucleic acid meta RNA metabolism amine transport cell cycle checkpoint cellular morphogenesis sister chromatid cohesion parturition DNA ligation nucleoside diphosphate metabolism regulation of transcriptional preinitiation complex formation phosphatidylinositol metabolism transcriptional preinitiation complex formation positive regulation of cell proliferation regulation of physiological process regulation of translational initiation intracellular transport membrane lipid metabolism coenzyme biosynthesis cofactor biosynthesis transcription regulation of cyclin dependent protein kinase activity pyrimidine nucleotide metabolism RNA processing transcription/, DNA-dependent regulation of signal transduction regulation of cell size cell growth ER-nuclear signaling pathway plasma membrane organization and biogenesis lipopolysaccharide metabolism lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis urea cycle cortical cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis cortical actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis
5 arginine catabolism phospholipid metabolism protein amino acid dephosphorylation chromosome organization and biogenesis (sensu Eukaryota) negative regulation of transcription dephosphorylation pyrimidine deoxyribonucleotide metabolism organic acid transport carboxylic acid transport nuclear organization and biogenesis protein folding positive regulation of apoptosis positive regulation of programmed cell death GPI anchor metabolism GPI anchor biosynthesis dicarboxylic acid transport galactose metabolism initiation of viral infection estrogen receptor signaling pathway viral entry steroid catabolism negative regulation of nucleobase/, nucleoside/, nucleotide and nucleic carbohydrate biosynthesis regulation of transcription/, DNA-dependent trna processing regulation of transcription fatty acid metabolism phospholipid biosynthesis angiogenesis bile acid metabolism membrane protein ectodomain proteolysis response to hormone stimulus beta-amyloid metabolism steroid metabolism ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolism modification-dependent protein catabolism nucleotide-excision repair response to radiation negative regulation of transcription/, DNA-dependent blood vessel development regulation of gene expression/, epigenetic phosphorus metabolism phosphate metabolism protein kinase cascade regulation of cell growth DNA packaging insulin receptor signaling pathway phospholipid catabolism L-amino acid transport regulation of proteolysis and peptidolysis NLS-bearing substrate-nucleus import DNA unwinding
6 sulfur metabolism tricarboxylic acid cycle intermediate metabolism integrin-mediated signaling pathway nuclear transport positive regulation of transcription chloride transport protein metabolism vesicle docking during exocytosis histone deacetylation fatty acid beta-oxidation proteoglycan biosynthesis cell fate determination regulation of cell migration spindle assembly mitotic spindle assembly vesicle docking regulation of secretion coenzyme metabolism regulation of apoptosis regulation of growth glutamine family amino acid metabolism regulation of programmed cell death growth prostaglandin metabolism Notch signaling pathway response to nutrients cell fate commitment prostanoid metabolism trna metabolism nucleocytoplasmic transport positive regulation of nucleobase/, nucleoside/, nucleotide and nucleic a cholesterol metabolism microtubule stabilization protein amino acid deacetylation response to stimulus viral life cycle membrane lipid biosynthesis organic acid biosynthesis carboxylic acid biosynthesis calcium-mediated signaling circadian rhythm chromosome condensation membrane lipid catabolism biological_process unknown trna aminoacylation for protein translation amino acid activation trna aminoacylation lipid transport energy coupled proton transport/, down electrochemical gradient ATP synthesis coupled proton transport sterol metabolism double-strand break repair
7 ceramide metabolism secretion cell migration protein-nucleus import/, docking response to extracellular stimulus covalent chromatin modification histone modification microtubule cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis protein-nucleus import nuclear import protein ubiquitination actin cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis nicotinamide metabolism M phase specific microtubule process sphingoid metabolism nucleoside phosphate metabolism ATP biosynthesis trna modification RNA splicing regulation of catabolism membrane organization and biogenesis regulation of actin filament length transcription from Pol III promoter glutamine family amino acid catabolism glutamine metabolism induction of programmed cell death induction of apoptosis protein lipidation fatty acid oxidation lipoprotein biosynthesis polysaccharide biosynthesis arginine metabolism establishment and/or maintenance of chromatin architecture ATP metabolism actin filament-based process glycerol metabolism endosome transport porphyrin biosynthesis response to drug urea cycle intermediate metabolism nitric oxide metabolism proteoglycan metabolism nitric oxide biosynthesis heterocycle metabolism regulation of translation cell-matrix adhesion polyol metabolism steroid hormone receptor signaling pathway maintenance of fidelity during DNA-dependent DNA replication axon guidance mismatch repair RNA modification
8 rhythmic behavior intracellular receptor-mediated signaling pathway B-cell activation endosome organization and biogenesis amino acid metabolism lipid catabolism positive regulation of metabolism phosphorylation intracellular signaling cascade glycosaminoglycan metabolism membrane fusion complement activation\, classical pathway nucleoside monophosphate biosynthesis porphyrin metabolism aminoglycan metabolism nucleoside monophosphate metabolism regulation of development Ras protein signal transduction triacylglycerol metabolism negative regulation of cell cycle purine nucleoside triphosphate biosynthesis purine ribonucleoside triphosphate biosynthesis ribonucleoside triphosphate biosynthesis tricarboxylic acid cycle group transfer coenzyme metabolism nucleoside triphosphate biosynthesis organic anion transport neutral lipid metabolism glycerolipid metabolism induction of apoptosis by extracellular signals acylglycerol metabolism glycerol ether metabolism mrna-nucleus export mrna transport amine metabolism RNA splicing/, via transesterification reactions with bulged adenosine as RNA splicing/, via transesterification reactions nuclear mrna splicing/, via spliceosome ribonucleoside triphosphate metabolism purine ribonucleoside triphosphate metabolism purine nucleoside triphosphate metabolism nucleoside metabolism icosanoid metabolism chromatin modification chromatin assembly or disassembly regulation of protein kinase activity cyclic nucleotide metabolism nucleoside triphosphate metabolism proton transport hydrogen transport regulation of mitosis iron ion transport
9 oxidative phosphorylation anti-apoptosis RNA localization RNA-nucleus export nucleic acid transport RNA transport complement activation biosynthesis amino acid and derivative metabolism viral infectious cycle axonogenesis lipoprotein metabolism JNK cascade nuclear export negative regulation of apoptosis purine ribonucleotide biosynthesis negative regulation of programmed cell death mrna processing fertilization (sensu Metazoa) protein amino acid phosphorylation non-covalent chromatin modification chromatin remodeling nucleobase/, nucleoside/, nucleotide and nucleic acid transport translational elongation purine nucleotide biosynthesis purine ribonucleotide metabolism fertilization organelle organization and biogenesis ribonucleotide biosynthesis humoral defense mechanism (sensu Vertebrata) protein complex assembly regulation of protein biosynthesis carbohydrate metabolism purine nucleotide metabolism regulation of enzyme activity neurogenesis sphingolipid metabolism ribonucleotide metabolism regulation of biosynthesis polysaccharide metabolism exocytosis mrna metabolism amino acid catabolism fatty acid biosynthesis transition metal ion transport amine catabolism negative regulation of cell proliferation development alcohol metabolism regulation of GTPase activity transcription initiation macromolecule biosynthesis
10 reproductive physiological process small GTPase mediated signal transduction digestion protein targeting cell differentiation response to oxidative stress macromolecule catabolism endocytosis epidermis development cytoplasm organization and biogenesis glycoprotein metabolism lymphocyte activation hemopoiesis steroid biosynthesis cytoskeleton organization and biogenesis ectoderm development humoral immune response immune cell activation cell activation catabolism antimicrobial humoral response (sensu Vertebrata) oxygen and reactive oxygen species metabolism antimicrobial humoral response microtubule-based process blood coagulation cellular defense response behavior sexual reproduction reproduction inflammatory response hemostasis sodium ion transport response to wounding response to abiotic stimulus cell-cell signaling histogenesis circulation regulation of body fluids central nervous system development response to pest/, pathogen or parasite transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway morphogenesis innate immune response coagulation response to chemical substance nucleosome assembly protein amino acid glycosylation response to external biotic stimulus male gamete generation spermatogenesis transport localization
11 glycoprotein biosynthesis carbohydrate catabolism cell motility di-/, tri-valent inorganic cation transport cell adhesion synaptic transmission main pathways of carbohydrate metabolism monovalent inorganic cation transport neuromuscular physiological process transmission of nerve impulse gametogenesis anion transport enzyme linked receptor protein signaling pathway protein biosynthesis hexose metabolism energy pathways proteolysis and peptidolysis monosaccharide metabolism cation transport protein catabolism second-messenger-mediated signaling signal transduction inorganic anion transport potassium ion transport energy derivation by oxidation of organic compounds response to biotic stimulus organogenesis immune response metal ion transport electron transport perception of smell organismal movement response to external stimulus cell communication ion transport defense response sensory perception of chemical stimulus neurophysiological process sensory perception organismal physiological process detection of external stimulus cell surface receptor linked signal transduction G-protein coupled receptor protein signaling pathway
12 OX-2 expressers and non-expressers PopulationTotal Fisher Exact P-Values TermID E-10 GO: E-09 GO: E-09 GO: E-08 GO: E-08 GO: E-08 GO: E-07 GO: E-06 GO: E-06 GO: E-06 GO: E-05 GO: E-05 GO: E-04 GO: E-04 GO: E-04 GO: E-04 GO: E-04 GO: E-04 GO: E-04 GO: E-04 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-03 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO:
13 E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO:
14 E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO:
15 E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: GO: GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
16 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: E-02 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
17 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
18 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
19 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
20 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
21 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
22 GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO: GO:
Module C CHEMISTRY & CELL BIOLOGY REVIEW
 Module C CHEMISTRY & CELL BIOLOGY REVIEW Note: This module is provided for A&P courses that do not have a prerequisite class which includes chemistry and cell biology. Content covered by required prerequisite
Module C CHEMISTRY & CELL BIOLOGY REVIEW Note: This module is provided for A&P courses that do not have a prerequisite class which includes chemistry and cell biology. Content covered by required prerequisite
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 3 The Cellular Level of Organization Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Introduce the parts of a cell 2. Discuss the importance
LIX1 APOD RRM2 FAIM2 MGST1 UHRF1 PPIA BEX1
 C2orf80 1 C2orf80 A2M ANXA1 APOD ARL4A BEX1 C1S C3 CD44 CHI3L1 CHI3L2 CLU DPYD DSCAM EMP3 FN1 GBP1 GEM GLIPR1 GRIA2 IDH1 LIX1 MAP2 MDK MGST1 MIR3917 NAMPT PCMTD2 PPIA PTN PTPRZ1 S100B SCG3 SERPINA3 TCF12
C2orf80 1 C2orf80 A2M ANXA1 APOD ARL4A BEX1 C1S C3 CD44 CHI3L1 CHI3L2 CLU DPYD DSCAM EMP3 FN1 GBP1 GEM GLIPR1 GRIA2 IDH1 LIX1 MAP2 MDK MGST1 MIR3917 NAMPT PCMTD2 PPIA PTN PTPRZ1 S100B SCG3 SERPINA3 TCF12
Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds
 Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds Objectives: 1) List the major groups of inorganic chemicals common in cells. 2) Describe the functions of various types of inorganic chemicals in cells.
Chapter 2 Part 3: Organic and Inorganic Compounds Objectives: 1) List the major groups of inorganic chemicals common in cells. 2) Describe the functions of various types of inorganic chemicals in cells.
Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed after two rounds
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Fah + hepatocytes in a Fah -/- mouse transplanted with sorted cells. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1 Fah + hepatocytes in a Fah -/- mouse transplanted with sorted cells. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded sections of liver from a recipient mouse sacrificed
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function
 Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Ch. 3 CELLS AND TISSUES Generalized Cell All cells: Human cells have three basic parts: Plasma membrane flexible outer boundary Cytoplasm intracellular fluid containing organelles Nucleus control center
Identification of Tissue-Specific Protein-Coding and Noncoding. Transcripts across 14 Human Tissues Using RNA-seq
 Identification of Tissue-Specific Protein-Coding and Noncoding Transcripts across 14 Human Tissues Using RNA-seq Jinhang Zhu 1, Geng Chen 1, Sibo Zhu 1,2, Suqing Li 3, Zhuo Wen 3, Bin Li 1, Yuanting Zheng
Identification of Tissue-Specific Protein-Coding and Noncoding Transcripts across 14 Human Tissues Using RNA-seq Jinhang Zhu 1, Geng Chen 1, Sibo Zhu 1,2, Suqing Li 3, Zhuo Wen 3, Bin Li 1, Yuanting Zheng
Cells and Tissues. Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues
 2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
2 Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1: Molecules of Life Lesson 2.2: Cells Lesson 2.3: Tissues Chapter 2: Cells and Tissues Lesson 2.1 Molecules of Life Molecules of Life carbohydrates proteins lipids nucleic
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1
 Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3: Cells 3-1 Introduction: A. Human body consists of 75 trillion cells B. About 260 types of cells that vary in shape & size yet have much in common B. Differences in cell shape make different
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis!
 Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
Chapter 3 Part 2! Pages 65 89 (10 th and 11 th eds.)! The Cellular Level of Organization! Cellular Organelles and Protein Synthesis! The Cell Theory! Living organisms are composed of one or more cells.!
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified
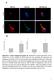 Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Suppl. Figure 1. T 3 induces autophagic flux in hepatic cells. (A) RFP-GFP-LC3 transfected HepG2/TRα cells were visualized and cells were quantified for RFP-LC3 puncta (red dots) representing both autolysosomes
Structures in Cells. Cytoplasm. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being A Eukaryote. Eukaryotic Cells. Basic eukaryotes have:
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BRIEF CONTENTS COPYRIGHTED MATERIAL III METABOLIC AND DEVELOPMENTAL INTEGRATION COMPARTMENTS CELL REPRODUCTION PLANT ENVIRONMENT AND AGRICULTURE
 BRIEF CONTENTS I COMPARTMENTS 1 Membrane Structure and Membranous Organelles 2 2 The Cell Wall 45 3 Membrane Transport 111 4 Protein Sorting and Vesicle Traffic 151 5 The Cytoskeleton 191 II CELL REPRODUCTION
BRIEF CONTENTS I COMPARTMENTS 1 Membrane Structure and Membranous Organelles 2 2 The Cell Wall 45 3 Membrane Transport 111 4 Protein Sorting and Vesicle Traffic 151 5 The Cytoskeleton 191 II CELL REPRODUCTION
Cells and Tissues 3PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College Cells and Tissues 3PART A Cells and Tissues Carry out all chemical activities needed to sustain life
Structures in Cells. Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules.
 Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
Structures in Cells Lecture 5, EH1008: Biology for Public Health, Biomolecules Limian.zheng@ucc.ie 1 Cytoplasm Nucleus Centrioles Cytoskeleton Cilia Microvilli 2 Cytoplasm Cellular material outside nucleus
The Study of Cells The diversity of the cells of the body The following figure shows the proportion of cell size of the variety of cells in the body
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 2 Foundations: The Cell Introduction There are trillions of cells in the body Cells are the structural building blocks of all plants and animals Cells
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition
 McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition Chapter 01: Cellular Biology Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a lack of a distinct nucleus, whereas prokaryotic cells have intracellular
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition Chapter 01: Cellular Biology Test Bank TRUE/FALSE 1. Eukaryotic cells are characterized by a lack of a distinct nucleus, whereas prokaryotic cells have intracellular
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz )
 Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Published on Second Faculty of Medicine, Charles University (http://www.lf2.cuni.cz ) Biochemistry Submitted by Marie Havlová on 8. February 2012-0:00 Syllabus of Biochemistry Mechanisms of enzyme catalysis.
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with. unipartite and bipartite structure. Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2
 Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry
 1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
1. Fluid mosaic describes. A. Tertiary structure of proteins B. Ribosomal subunits C. DNA structure D. Plasma membrane structure NBCE Mock Board Questions Biochemistry 2. Where in the cell does beta oxidation
October 26, Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12
 Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Name: Date: Block: Biology 12 Provincial Exam Review: Cell Processes and Applications January 2003 Use the following diagram to answer questions 1 and 2. 1. Which labelled organelle produces most of the
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide
 Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
Chemistry 107 Exam 4 Study Guide Chapter 10 10.1 Recognize that enzyme catalyze reactions by lowering activation energies. Know the definition of a catalyst. Differentiate between absolute, relative and
levels of genes were separated by their expression levels; 2,000 high, medium, and low
 Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Figure S1. Histone modification profiles near transcription start sites. The overall histone modification around transcription start sites (TSSs) was calculated. Histone modification levels of genes were
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Membrane transport D. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
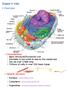 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Propagation of the Signal
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
OpenStax-CNX module: m44452 1 Propagation of the Signal OpenStax College This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section,
6 functions of membrane proteins integral & peripheral proteins Membrane Junctions
 Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Cell cycle and apoptosis
 Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Cell cycle and apoptosis Cell cycle Definition Stages and steps Cell cycle Interphase (G1/G0, S, and G2) Mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, karyokinesis, cytokinesis) Control checkpoints
Week 1 Multiple Choice Questions: 1. A substrate molecule may be bound to the active site of an enzyme by all of the following EXCEPT
 WEEK 1: Chemistry of Life (7%) Week 1 Concepts: How do the unique chemical and physical properties of water make life on earth possible? What is the role of carbon in the molecular diversity of life? How
WEEK 1: Chemistry of Life (7%) Week 1 Concepts: How do the unique chemical and physical properties of water make life on earth possible? What is the role of carbon in the molecular diversity of life? How
Chapter 3 Review Assignment
 Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Class: Date: Chapter 3 Review Assignment Multiple Choice 40 MC = 40 Marks Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which of the following organelles produces transport
Cell Structure and Function
 C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
C h a p t e r 3 Cell Structure and Function PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris 3-1 The study of cells provides the foundation for understanding human physiology
Levels of organization
 The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
The Chemical Level of Organization
 2 The Chemical Level of Organization PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Table 2-1 Principal Elements in the Human Body Table 2-1 Principal Elements
2 The Chemical Level of Organization PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris Table 2-1 Principal Elements in the Human Body Table 2-1 Principal Elements
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Structure & Function of Cells
 Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Anatomy & Physiology 101-805 Unit 4 Structure & Function of Cells Paul Anderson 2011 Anatomy of a Generalised Cell Attached or bound ribosomes Cilia Cytosol Centriole Mitochondrion Rough endoplasmic reticulum
The Structure and Function of Biomolecules
 The Structure and Function of Biomolecules The student is expected to: 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
The Structure and Function of Biomolecules The student is expected to: 9A compare the structures and functions of different types of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
What are the molecules of life?
 Molecules of Life What are the molecules of life? Organic Compounds Complex Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Organic Compounds Carbon- hydrogen based molecules From Structure to Function Ø Carbon
Molecules of Life What are the molecules of life? Organic Compounds Complex Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Organic Compounds Carbon- hydrogen based molecules From Structure to Function Ø Carbon
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney
 BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
BCHM3972 Human Molecular Cell Biology (Advanced) 2013 Course University of Sydney Page 2: Immune Mechanisms & Molecular Biology of Host Defence (Prof Campbell) Page 45: Infection and Implications for Cell
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
CHAPTER II PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 CHAPTER II PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Structure of cell: Human body develops from a single cell zygote which results from fusion of the ovum andd the spermatozoan.
CHAPTER II PDL 101 HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. Structure of cell: Human body develops from a single cell zygote which results from fusion of the ovum andd the spermatozoan.
6/15/2015. Biological Molecules. Outline. Organic Compounds. Organic Compounds - definition Functional Groups Biological Molecules. What is organic?
 Biological Molecules Biology 105 Lecture 3 Reading: Chapter 2 (pages 29 39) Outline Organic Compounds - definition Functional Groups Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids and Proteins Nucleotides
Biological Molecules Biology 105 Lecture 3 Reading: Chapter 2 (pages 29 39) Outline Organic Compounds - definition Functional Groups Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Lipids Amino Acids and Proteins Nucleotides
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 2.1 Using Figure 2.1, match the following: 1) Rough endoplasmic reticulum 1) 2) Nucleolus 2) 3)
An Introduction to Genetics. 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Genetics. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid
 An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
An Introduction to Genetics 9.1 An Introduction to Genetics DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid Information blueprint for life Reproduction, development, and everyday functioning of living things Only 2% coding
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
Chapter 2 Adapted from Tortora 10 th ed LECTURE OUTLINE A. A Generalized Cell (p. 25) 1. A human cell consists of three major parts (see Table 2.2 on p. 42): a. Plasma membrane b. Cytoplasm which includes
(impermeable; freely permeable; selectively permeable)
 BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
BIOL 2457 CHAPTER 3 Part 1 SI 1 1. A is the basic structure of life. 2. The gelatinous inside of the cell is called the. 3. Name the structure that increases the cell s surface area? 4. Name the structure
Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units
 Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Cell Theory Chaffey College: Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 3: Cells - The Living Units The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life Organismal activity depends on individual and collective
Activity: Biologically Important Molecules
 Activity: Biologically Important Molecules AP Biology Introduction We have already seen in our study of biochemistry that the molecules that comprise living things are carbon-based, and that they are thought
Activity: Biologically Important Molecules AP Biology Introduction We have already seen in our study of biochemistry that the molecules that comprise living things are carbon-based, and that they are thought
Cell Physiology
 Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
Cell Physiology 21-10-2018 1 The two major parts of a typical cell are the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is separated from the cytoplasm by a nuclear membrane, and the cytoplasm is separated from
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell Biology. A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division
 The Cell Cell Biology 1 A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division Tight connection with 1. Molecular biology 2. Biochemistry Cell theory 2 1838, 1839 Theodor Schwann
The Cell Cell Biology 1 A discipline of biology: 1. Cell structure 2. Cellular processes 3. Cell division Tight connection with 1. Molecular biology 2. Biochemistry Cell theory 2 1838, 1839 Theodor Schwann
Levels of organization
 The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
The Cell 1.The cell the basic structural and functional unit of living organisms 2.Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells 3.Cellular organization: external morphology cell size, shape and color internal structure
Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION
 Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION It is within the cell where the functions of the body occur. We are going to look at structure, function and reproduction of cells in this chapter. Cytology
Unit 1 Lecture 2 THE CELLULAR LEVEL OF ORGANIZATION It is within the cell where the functions of the body occur. We are going to look at structure, function and reproduction of cells in this chapter. Cytology
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? An understanding of chemistry is essential to understand cellular structure and function, which are paramount for your understanding
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? An understanding of chemistry is essential to understand cellular structure and function, which are paramount for your understanding
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism . Anabolism
 If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
BIOCHEMISTRY. How Are Macromolecules Formed? Dehydration Synthesis or condensation reaction Polymers formed by combining monomers and removing water.
 BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Anatomy Chapter 2 - Cells
 Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Cells Cells are the basic living structural, functional unit of the body Cytology is the branch of science that studies cells The human body has 100 trillion cells 200 different cell types with a variety
Human Epithelial Cells
 The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
The Cell Human Epithelial Cells Plant Cells Cells have an internal structure Eukaryotic cells are organized Protective membrane around them that communicates with other cells Organelles have specific jobs
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
A Tour of the Cell. Ch. 7
 A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
A Tour of the Cell Ch. 7 Cell Theory O All organisms are composed of one or more cells. O The cell is the basic unit of structure and organization of organisms. O All cells come from preexisting cells.
The Cell. Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62)
 The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
The Cell Biology 105 Lecture 4 Reading: Chapter 3 (pages 47 62) Outline I. Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic II. Eukaryotic A. Plasma membrane transport across B. Main features of animal cells and their functions
Chapter 8. Metabolism. Topics in lectures 15 and 16. Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Chapter 12. living /non-living? growth repair renew. Reproduction. Reproduction. living /non-living. fertilized egg (zygote) next chapter
 Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Summary of Endomembrane-system
 Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
Summary of Endomembrane-system 1. Endomembrane System: The structural and functional relationship organelles including ER,Golgi complex, lysosome, endosomes, secretory vesicles. 2. Membrane-bound structures
The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions
 Chemistry of Life Revision: The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions Atoms exchange electrons with other elements to form
Chemistry of Life Revision: The further from the nucleus, the higher the electron s energy Valence shell electrons participate in biological reactions Atoms exchange electrons with other elements to form
The questions for oral part of exam from Medical Biochemistry. 1. Energetic metabolism and metabolism of nutrients
 The questions for oral part of exam from Medical biochemistry for students of general medicine are divided into three parts: Contents 1. Energetic metabolism and metabolism of nutrients... 1 2. General
The questions for oral part of exam from Medical biochemistry for students of general medicine are divided into three parts: Contents 1. Energetic metabolism and metabolism of nutrients... 1 2. General
2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November
 Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Class: Date: 2015 AP Biology Unit #4 Test Cell Communication, Cancer, Heredity and The Cell Cycle Week of 30 November Multiple Choice 1 point each Identify the choice that best completes the statement
Genetics Unit Bell Work September 27 & 28, 2016
 Name: Date: Genetics Unit Bell Work September 27 & 28, 2016 nswer the following questions about the process shown above. 1. What are the reactants in this process? 2. What are the products in this process?
Name: Date: Genetics Unit Bell Work September 27 & 28, 2016 nswer the following questions about the process shown above. 1. What are the reactants in this process? 2. What are the products in this process?
1- Which of the following statements is TRUE in regards to eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells?
 Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Name: NetID: Exam 3 - Version 1 October 23, 2017 Dr. A. Pimentel Each question has a value of 4 points and there are a total of 160 points in the exam. However, the maximum score of this exam will be capped
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis - Pre-Lab Exercises
 A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis - Pre-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of
A&P 1 Cellular Anatomy, Division & Mitosis - Pre-Lab Exercises Have someone in your group read the following out loud, while the others read along: In this "Pre-lab Guide", we will be going over some of
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester
 BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Cell Biology. a review! Cell Theory & Cell Structures
 Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Cell Biology Cell Theory & a review! Cell Structures Cell Theory refers to the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Cells are either prokaryotic or eukaryotic
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together. Packet #5
 Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
Organelles of the Cell & How They Work Together Packet #5 Developed by Mr. Barrow 2018 1 Introduction Organization of cells is basically similar in all cells. Additionally, most cells are tiny Ranging
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Biological Molecules. Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids
 Biological Molecules Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules Always contain Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) Carbon is missing four electrons Capable of forming 4 covalent bonds
Biological Molecules Carbohydrates, Proteins, Lipids, and Nucleic Acids Organic Molecules Always contain Carbon (C) and Hydrogen (H) Carbon is missing four electrons Capable of forming 4 covalent bonds
Chapter 3: Cytology. Cytology is the study of cells. Cells are the basic units of life. We are made up of trillions of cells.
 PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
PLEASE NOTE THAT THE ITEMS IN THE TEXT THAT ARE HIGHLIGHTED IN YELLOW ARE THOSE THAT ARE TOUCHED ON IN THE READING ASSIGNMENT (PAGES 90-99) AND IN THE LECTURE. ESPECIALLY KNOW THIS MATERIAL FOR THE FIRST
Exam 2 fall 2015 Page 1
 xam 2 fall 2015 Page 1 Name: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium for
xam 2 fall 2015 Page 1 Name: 1 ll of the following are composed of eukaryotic cells XPT animals plants fungi bacteria 2 The function of the cytoplasm is to keep the cell contents wet provide a medium for
Lesson Overview. Carbon Compounds. Lesson Overview. 2.3 Carbon Compounds
 Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
Lesson Overview 2.3 The Chemistry of Carbon What elements does carbon bond with to make up life s molecules? Carbon can bond with many elements, including Hydrogen, Oxygen, Phosphorus, Sulfur, and Nitrogen
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways
 Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
Protein Trafficking in the Secretory and Endocytic Pathways The compartmentalization of eukaryotic cells has considerable functional advantages for the cell, but requires elaborate mechanisms to ensure
General Principles of Endocrine Physiology
 General Principles of Endocrine Physiology By Dr. Isabel S.S. Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong The major human endocrine glands Endocrine glands and hormones
General Principles of Endocrine Physiology By Dr. Isabel S.S. Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong The major human endocrine glands Endocrine glands and hormones
