SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
|
|
|
- Evan Jennings
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 doi: /nature05772 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental figure 1. Enrichment facilitates learning. a. Images showing a home cage and a cage used for environmental enrichment (EE). For EE up to 4 mice were constantly housed in a large cage that contained various toys and running wheels (1 wheel/2 mice). All toys were changes on daily basis. b. C57BL6J mice (n=8/group) were subjected to EE for 2 weeks and trained in the contextual fear conditioning paradigm. Enriched mice showed significantly more freezing behavior during the memory test performed 24h later, when compared to the home cage group (P<0.0001), indicating facilitated associative learning. c. Left: Similar results were obtained in the Morris water maze paradigm (P< control vs. enrichment). 1
2
3 Supplemental figure 2. Enrichment facilitates synaptic plasticity. C57BL6J mice (n=3/group) were subjected to EE for 2 weeks and subsequently used for analysis. a. Representative images showing increased MAP-2 immunoreactivity (IR) in the hippocampus and anterior cingulate cortex (b) of enriched mice. c. Representative images of the hippocampal and anterior cingulate cortex (d) region of enriched and non-enriched mice showing staining of the synaptic marker protein synaptophysin (SVP). Confocal images (1µm) were scanned and subjected to three-dimensional reconstruction. Pictures are displayed as seen from the x-axis. LSMeta10 software was used to calculate the mean SVP intensity. Brain sections with the strongest intensity were scanned first. All other images included in the analysis where scanned using the same microscope setting. Enriched mice displayed significantly increased hippocampal SVP (IR) when compared to non-enriched mice. e. Representative immunoblots from the hippocampus and cortex of enriched and non-enriched mice. Several markers for synaptic plasticity and integrity were increased in enriched when compared to non-enriched mice, indicating facilitated synaptic plasticity (P<0.0001). **P< py, pyramidal cell layer; oriens; rad, stratum radiatum; Lmol, molecular layer; mol, lower molecular layer; GrDG, granula cell layer of the dentate gyrus, DG, dentate gyrus; CA1, hippocamapl regions CA1; cg, cingulate cortex. 3
4
5 Supplemental figure 3. Effects of enrichment or sodiumbutyrate treatment on plasticity factors in CK-p25 Tg mice that developed severe neurodegeneration. a-d. Enrichment of CK-p25 TG mice a. p25 was induced in 11 month old CK-p25 Tg mice for 6 weeks. Afterwards p25 expression was repressed as described previously 3 and one group of CK-p25 Tg mice was subjected to EE. Representative pictures showing immunostaining for NeuN in the hippocampal region confirm similar degree of hippocampal neuronal loss in enriched and non-enriched CK-p25 Tg mice. b. Brain sections from the same mice used in the experiment described under (a) were immunostained for the dendritic marker protein MAP-2. Note the increased MAP-2 immunoreactivity of enriched CK-p25 Tg mice when compared to the non-enriched group. Similar results are observed in other brain regions such as the anterior cingulated cortex (c). d. Representative immunoblots from cortical lysates of control mice, enriched and non-enriched CK-p25 Tg mice. Although NeuN levels were decreased to similar levels in enriched and nonenriched CK-p25 Tg mice, several markers for synaptic plasticity and integrity were increased in enriched when compared to non-enriched CK-p25 Tg mice. *P<0.05 vs. non enriched group, n=3. e-h. Sodiumbutyrate treatment of CK-p25 Tg mice e. P25 was induced in 11 month old CK-p25 Tg mice for 6 weeks. Afterwards p25 expression was repressed and one group of CK-p25 Tg mice was subjected to daily sodiumbutyrate (SB) injection (1.2g/kg) for 4 weeks, whereas the other group received saline injection. Representative images showing hippocampal NeuN staining confirming that SB and vehicle injected CK-p25 mice displayed hippocampal neuronal loss to the same degree. f. Representative images showing hippocampal MAP-2 staining. Note the increased MAP-2 immunoreactivity of CK-p25 Tg mice treated with SB when compared to the vehicle group. g. Representative images showing NeuN 5
6 staining of the ACC. While SB and vehicle-injected CK-p25 Tg mice displayed similar levels of neuronal loss in the ACC (red, NeuN staining) MAP-IR was increased in SB treated when compared to vehicle treated CK-p25 Tg mice. h. Representative immunoblots from the hippocampus and cortex of all groups. Although NeuN levels were decreased to similar levels in SB and vehicle injected CK-p25 Tg mice, several markers for synaptic plasticity and integrity were increased in SB-injected when compared to vehicle injected CK-p25 Tg mice. *P<0.05 vs. vehicle group, n=3. py, pyramidal cell layer; rad, stratum radiatum; Lmol, molecular layer; mol, lower molecular layer; GrDG, granula cell layer of the dentate gyrus, DG, dentate gyrus; CA1, hippocamapl regions CA1; cg, cingulate cortex. 6
7
8 Supplemental figure 4. The effect of sodiumbutyrate injection on learning, basal anxiety, explorative behavior and brain plasticity. a. C57BL/6J mice were subjected to fear conditioning and injected intraperitoneally [ip] with 1.2g/kg sodiumbutyrate (SB, n=8) or saline (vehicle; n=8) immediately afterwards. SB injected mice displayed significantly more freezing behavior during the memory test performed 24h later (P<0.0001). b. C57BL/6J mice were implanted with microcannulae into the lateral brain ventricles (icv) and injected with either 100ng SB, 50 ng TSA or vehicle immediately after fear conditioning (n=8/group). SB or TSA injected mice displayed more freezing behavior than vehicle injected mice during the memory test performed 24h later (P<0.0001). c. C57BL/6J were daily injected [ip] with SB or saline (n=8/group) for 4 weeks before all mice were subjected the elevated plus maze and open field test. No significant group difference was observed indicating that SB- treatment did not affect basal anxiety or explorative behavior. d. Representative images showing increased MAP-2 immunoreactivity (IR) in the hippocampus of wild type mice injected with SB for 4 weeks, when compared to vehicle injected mice. e. Representative immunoblots (n=3/group) from hippocampal lysates of wild type mice injected with SB or vehicle for 4 weeks. Immunoblots were quantified relative to the optical density of the vehicle-group (set to 1). Several markers for brain plasticity were increased in SB injected mice. f. Representative images showing increased SVP IR in the hippocampus of mice injected with SB for 4 weeks, when compared to vehicle injected mice (P=0.0243). The analysis was performed as described under figure 1f. g. Representative immunoblots (n=3/group) from hippocampal lysates of wild type mice subjected to environmental enrichment for 3h or 4 weeks and mice injected with SB or vehicle for 4 weeks. Interestingly, activity (as determined by phosphorylation) and total levels of ERK-1/2 were neither affected by enrichment or SB treatment. py, pyramidal cell layer; or, oriens; rad, stratum radiatum; Lmol, molecular layer; mol, lower molecular layer; GrDG, granula 8
9 cell layer of the dentate gyrus, DG, dentate gyrus; CA1, hippocamapl regions CA1; cg, cingulate cortex. 9
10 .
11 Supplemental figure 5. Evidence that enrichment and sodiumbutyrate injection lead to the recovery of spatial memories. a. CK-p25 Tg mice in which p25 expression was repressed and control mice were trained in the water maze paradigm until all mice reliably found the hidden platform. Afterwards all mice were returned to their home cages for 4 weeks to allow the consolidation of hippocampus independent long-term memories. b. Afterwards p25 expression was induced for 6 weeks, followed by p25 repression. In pilot studies we found that a probe test, commonly used to analyze memory retrieval in the water maze paradigm, was not a reliable read out to analyze long-term memory retrieval. In fact, without extensive re-training even wild type mice showed no significant preference for the target quadrant when tested 10 weeks after the training in a probe test (data not shown). To measure the retrieval of long-term memory mice were instead exposed to only 2 reminder-training sessions on a single day. The mean escape latency during this remindertraining sessions was compared to control mice that did not receive the initial training. Using this approach we found that control mice that did not receive the initial training (n=7) showed a significantly longer escape latency than trained control mice, suggesting that this difference reflects spatial long-term memory in trained control mice. Notably, 6-week induced trained CKp25 Tg mice (n=8) showed significantly longer escape latency than trained control mice (n=8) during the reminder-training session. These data indicate that 6 weeks of p25 expression causes loss of spatial memory. c. The experiment was performed as described under (a). However, after 6 weeks of p25 expression mice were either subjected to EE or returned to their home cages for 4 weeks. When the memory test was performed as described under (b) non-enriched CK-p25 Tg mice (n=8) showed significantly reduced escape latency when compared to the trained control group (n=8). However, the escape latency of enriched CK-p25 Tg mice was significantly shorter when compared to non-enriched CK-p25 Tg mice. Enriched control mice that did not receive the 11
12 initial training served as a control to delineate learning from long-term memory retrieval. These data provide evidence that spatial long-term memories can recover upon EE. d. The experiment was performed as described under (c) but instead of EE one group of CK-p25 Tg mice (n=10) received daily injection of SB, whereas the other group was injected with vehicle (n=10). Similar to the data described under (c), the results provide evidence that spatial long-term memories recover after neuronal loss upon injection of SB. *P<0.001 vs. CK-p25 vehicle or no p25 no training groups. 12
13
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioural effects of ketamine in non-stressed and stressed mice. Naive C57BL/6 adult male mice (n=10/group) were given a single dose of saline vehicle or ketamine (3.0 mg/kg,
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma
 Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma Paper: Abraham, Wickliffe C., and Anthony Robins. "Memory retention the synaptic stability versus plasticity dilemma." Trends in neurosciences
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.2275
 Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Figure S1. The presence of MeCP2 in enriched primary glial cultures from rat or mouse brains is not neuronal. Western blot analysis of protein extracts from (a) rat glial and neuronal cultures.
Supplementary Fig. 1
 PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
PDK1-dependent quenching of TACE shedding activity in prion and Alzheimer s diseases Mathéa Pietri, Caroline Dakowski, Samia Hannaoui, Aurélie Alleaume-Butaux, Julia Hernandez-Rapp, Audrey Ragagnin, Sophie
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models. From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Rodent Behavioral Learning and Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, 2 nd Edition by J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron of Mice and Rats Figure 1 Open Field Apparatus Open Field Behavior
Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2+ cells in different brain regions.
 Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
Hip SVZ OB Cere Hypo Supplementary Fig. 1: TBR2 + cells in different brain regions. Three weeks after the last tamoxifen injection, TBR2 immunostaining images reveal a large reduction of TBR2 + cells in
mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci.; doi:1.138/nn.3351 mtorc2 controls actin polymerization required for consolidation of long-term memory Wei Huang, Ping Jun Zhu, Shixing Zhang, Hongyi Zhou, Loredana Stoica,
GABA from reactive astrocytes impairs memory in mouse models of Alzheimer disease
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION from reactive astrocytes impairs memory in mouse models of Alzheimer disease Seonmi Jo *, Oleg Yarishkin *, Yu Jin Hwang, Ye Eun Chun, Mijeong Park, Dong Ho Woo, Jin Young Bae,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION from reactive astrocytes impairs memory in mouse models of Alzheimer disease Seonmi Jo *, Oleg Yarishkin *, Yu Jin Hwang, Ye Eun Chun, Mijeong Park, Dong Ho Woo, Jin Young Bae,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2566 Figure S1 CDKL5 protein expression pattern and localization in mouse brain. (a) Multiple-tissue western blot from a postnatal day (P) 21 mouse probed with an antibody against CDKL5.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
The Timing of Differentiation of Adult Hippocampal Neurons Is Crucial for Spatial Memory
 The Timing of Differentiation of Adult Hippocampal Neurons Is Crucial for Spatial Memory PLoS BIOLOGY Stefano Farioli-Vecchioli 1[, Daniele Saraulli 2,3[, Marco Costanzi 2,3[, Simone Pacioni 4[, Irene
The Timing of Differentiation of Adult Hippocampal Neurons Is Crucial for Spatial Memory PLoS BIOLOGY Stefano Farioli-Vecchioli 1[, Daniele Saraulli 2,3[, Marco Costanzi 2,3[, Simone Pacioni 4[, Irene
Limbic system outline
 Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
Limbic system outline 1 Introduction 4 The amygdala and emotion -history - theories of emotion - definition - fear and fear conditioning 2 Review of anatomy 5 The hippocampus - amygdaloid complex - septal
SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material. Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN
 SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN Jana Husse, Xunlei Zhou, Anton Shostak, Henrik Oster and Gregor Eichele SOM Husse et al.,
SOM Husse et al. Supplementary online material Synaptotagmin10-Cre, a driver to disrupt clock genes in the SCN Jana Husse, Xunlei Zhou, Anton Shostak, Henrik Oster and Gregor Eichele SOM Husse et al.,
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Doubly Phosphorylated Peptide Vaccines to Protect Transgenic P301S Mice against Alzheimer s Disease Like Tau Aggregation
 , 1-11 manuscripts; doi:10.3390/vaccines20x000x Article OPEN ACCESS vaccines ISSN 2076-393X www.mdpi.com/journal/vaccines Doubly Phosphorylated Peptide Vaccines to Protect Transgenic P301S Mice against
, 1-11 manuscripts; doi:10.3390/vaccines20x000x Article OPEN ACCESS vaccines ISSN 2076-393X www.mdpi.com/journal/vaccines Doubly Phosphorylated Peptide Vaccines to Protect Transgenic P301S Mice against
Methylphenidate improves the behavioral and cognitive deficits of neurogranin knockout mice
 Genes, Brain and Behavior (2012) 11: 794 805 doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00825.x Methylphenidate improves the behavioral and cognitive deficits of neurogranin knockout mice F. L. Huang and K.-P. Huang
Genes, Brain and Behavior (2012) 11: 794 805 doi: 10.1111/j.1601-183X.2012.00825.x Methylphenidate improves the behavioral and cognitive deficits of neurogranin knockout mice F. L. Huang and K.-P. Huang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal AMPAR-mediated fepsp input-output curve in CA3-Psen cdko mice. Input-output curves, which are plotted initial slopes of the evoked fepsp as function of the amplitude of the
PERSPECTIVES. Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety
 OPINION Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety David M. Bannerman, Rolf Sprengel, David J. Sanderson, Stephen B. McHugh, J. Nicholas P. Rawlins, Hannah Monyer and Peter H. Seeburg
OPINION Hippocampal synaptic plasticity, spatial memory and anxiety David M. Bannerman, Rolf Sprengel, David J. Sanderson, Stephen B. McHugh, J. Nicholas P. Rawlins, Hannah Monyer and Peter H. Seeburg
Zhu et al, page 1. Supplementary Figures
 Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
Zhu et al, page 1 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1: Visual behavior and avoidance behavioral response in EPM trials. (a) Measures of visual behavior that performed the light avoidance behavior
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A. Hippocampus. Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D.
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A Hippocampus Jaime A. Pineda, Ph.D. Common (Distributed) Model of Memory Processes Time Course of Memory Processes Long Term Memory DECLARATIVE NON-DECLARATIVE Semantic Episodic Skills
DNA and Histone Methylation in Learning and Memory
 EXPERIMENTAL BIOLOGY ANNUAL MEETING April 2010 DNA and Histone Methylation in Learning and Memory J. David Sweatt Dept of Neurobiology McKnight Brain Institute UAB School of Medicine The Molecular Basis
EXPERIMENTAL BIOLOGY ANNUAL MEETING April 2010 DNA and Histone Methylation in Learning and Memory J. David Sweatt Dept of Neurobiology McKnight Brain Institute UAB School of Medicine The Molecular Basis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
Multiple memory trace theory Duncan, 1949
 Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 5: Memory Consolidation Multiple memory trace theory Duncan, 1949 McGaugh, 2 Squire: retention of TV shows after ECS At least 2 kinds
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory Prof. Stephan Anagnostaras Lecture 5: Memory Consolidation Multiple memory trace theory Duncan, 1949 McGaugh, 2 Squire: retention of TV shows after ECS At least 2 kinds
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
From Rapid Place Learning to Behavioral Performance: A Key Role for the Intermediate Hippocampus
 From Rapid Place Learning to Behavioral Performance: A Key Role for the Intermediate Hippocampus Tobias Bast 1,2*, Iain A. Wilson 1, Menno P. Witter 3,4, Richard G. M. Morris 1 PLoS BIOLOGY 1 Centre for
From Rapid Place Learning to Behavioral Performance: A Key Role for the Intermediate Hippocampus Tobias Bast 1,2*, Iain A. Wilson 1, Menno P. Witter 3,4, Richard G. M. Morris 1 PLoS BIOLOGY 1 Centre for
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 Second midterm is next Tuesday!! Covers lectures 7-12 (Synaptic transmission, NT & receptors, intracellular signaling & synaptic plasticity). Review session is on Monday (Nov
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 Second midterm is next Tuesday!! Covers lectures 7-12 (Synaptic transmission, NT & receptors, intracellular signaling & synaptic plasticity). Review session is on Monday (Nov
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory. David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology
 Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
Neuronal Plasticity, Learning and Memory David Keays Institute of Molecular Pathology http://keayslab.org Structure 1. What is learning and memory? 2. Anatomical basis 3. Cellular basis 4. Molecular
Endogenous IL-1 in Cognitive Function and Anxiety: A Study in IL-1RI 2/2 Mice
 Endogenous IL-1 in Cognitive Function and Anxiety: A Study in IL-1RI 2/2 Mice Carol L. Murray 1, Pauline Obiang 1, David Bannerman 2, Colm Cunningham 1 * 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology & Trinity
Endogenous IL-1 in Cognitive Function and Anxiety: A Study in IL-1RI 2/2 Mice Carol L. Murray 1, Pauline Obiang 1, David Bannerman 2, Colm Cunningham 1 * 1 School of Biochemistry and Immunology & Trinity
Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Terminology. Bromodeoxyuridine
 Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Kateřina Náměstková, Zuzana Šimonová, Eva Syková Behavioural Brain Research Bromodeoxyuridine : Doublecortin : DCX Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein : GFAP Trace eye blink conditioning 1 Volume 163 : pp.
Durham Research Online
 Durham Research Online Deposited in DRO: 19 December 2014 Version of attached le: Accepted Version Peer-review status of attached le: Peer-reviewed Citation for published item: Bannerman, D.M. and Sprengel,
Durham Research Online Deposited in DRO: 19 December 2014 Version of attached le: Accepted Version Peer-review status of attached le: Peer-reviewed Citation for published item: Bannerman, D.M. and Sprengel,
CREB Binding Protein Is Required for Both Short-Term and Long-Term Memory Formation
 13066 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 29, 2010 30(39):13066 13077 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive CREB Binding Protein Is Required for Both Short-Term and Long-Term Memory Formation Guiquan Chen, 1
13066 The Journal of Neuroscience, September 29, 2010 30(39):13066 13077 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive CREB Binding Protein Is Required for Both Short-Term and Long-Term Memory Formation Guiquan Chen, 1
<student name> Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal
 Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Undergraduate Research Grant Proposal A. Project Description Objective of research: The objective of this study is to determine if hippocampal dopamine D1 receptors facilitate novel object
Anatomy of the Hippocampus
 Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Anatomy of the Hippocampus Lecture 3.2 David S. Touretzky September, 2015 Human Hippocampus 2 Human Hippocampus 3 Hippocampus Means Seahorse Dissected human hippocampus next to a specimen of hippocampus
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment
 Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Short- and long-lasting consequences of in vivo nicotine treatment on hippocampal excitability Rachel E. Penton, Michael W. Quick, Robin A. J. Lester Supplementary Figure 1. Histogram showing the maximal
Mecanismo de acción de Souvenaid: nuevos datos preclínicos
 Mecanismo de acción de Souvenaid: nuevos datos preclínicos Dra. Sagrario Manzano Coordinadora del Grupo de Neurología de la Conducta y Demencias de la SEN. Hospital Universitario Infanta Cristina. Parla.
Mecanismo de acción de Souvenaid: nuevos datos preclínicos Dra. Sagrario Manzano Coordinadora del Grupo de Neurología de la Conducta y Demencias de la SEN. Hospital Universitario Infanta Cristina. Parla.
Persistent improvement in synaptic and cognitive functions in an Alzheimer mouse model after rolipram treatment
 Persistent improvement in synaptic and cognitive functions in an Alzheimer mouse model after rolipram treatment Bing Gong,, Michael Shelanski, Ottavio Arancio J Clin Invest. 2004;114(11):1624-1634. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci22831.
Persistent improvement in synaptic and cognitive functions in an Alzheimer mouse model after rolipram treatment Bing Gong,, Michael Shelanski, Ottavio Arancio J Clin Invest. 2004;114(11):1624-1634. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci22831.
Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a)
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Microglia do not show signs of classical immune activation following MD a-b. Images showing immunoreactivity for MHCII (a) and CD45 (b) in fixed sections of binocular visual cortex
Supplementary Materials
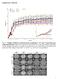 Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Materials Fig. S1. Weights of full-dose treatment groups comparing 1 st, 2 nd, and 3 rd generation gene replacement therapy. Mice were treated at p1 with 4x10 11 GC of the three different
Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from WT and Adcy1 KO mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody.
 ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
ADCY1 13 kda β-actin 45 kda Supplementary Figure 1. Western blot of hippocampal lysates from and mice demonstrates the specificity of the ADCY1 antibody. a DHPG perk1/2 ERK1/2 Relative level min 1.6 *
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature09667 A critical role for IGF-II in memory consolidation and enhancement Dillon Y. Chen, Sarah A. Stern, Ana Garcia-Osta, Bernadette Saunier-Rebori, Gabriella Pollonini, Dhananjay Bambah-Mukku,
doi:10.1038/nature09667 A critical role for IGF-II in memory consolidation and enhancement Dillon Y. Chen, Sarah A. Stern, Ana Garcia-Osta, Bernadette Saunier-Rebori, Gabriella Pollonini, Dhananjay Bambah-Mukku,
Cdk5 Is Required for Memory Function and Hippocampal Plasticity via the camp Signaling Pathway
 Cdk5 Is Required for Memory Function and Hippocampal Plasticity via the camp Signaling Pathway Ji-Song Guan 1,2,3,4., Susan C. Su 1,2,3,4., Jun Gao 1,2,3,4, Nadine Joseph 1,2,3,4, Zhigang Xie 1,2, Ying
Cdk5 Is Required for Memory Function and Hippocampal Plasticity via the camp Signaling Pathway Ji-Song Guan 1,2,3,4., Susan C. Su 1,2,3,4., Jun Gao 1,2,3,4, Nadine Joseph 1,2,3,4, Zhigang Xie 1,2, Ying
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
S100B+ Cell Density day Spine Formation (%)
 b * CP * HC CP Th DAPI S100B ** 50 40 30 * 20 10 0-10 -20 * * ** 9 6 3 0 0-50 50-100 100-150 150-200 Distance from Prism Face (um) 1-day Spine Formation (%) 1-day Spine Elimination (%) 12 Distance from
b * CP * HC CP Th DAPI S100B ** 50 40 30 * 20 10 0-10 -20 * * ** 9 6 3 0 0-50 50-100 100-150 150-200 Distance from Prism Face (um) 1-day Spine Formation (%) 1-day Spine Elimination (%) 12 Distance from
Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive
 6230 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 7, 2006 26(23):6230 6237 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Environmental Enrichment Enhances Neurogranin Expression and Hippocampal Learning and Memory But Fails to Rescue
6230 The Journal of Neuroscience, June 7, 2006 26(23):6230 6237 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Environmental Enrichment Enhances Neurogranin Expression and Hippocampal Learning and Memory But Fails to Rescue
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females
 The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
The Effects of Chemotherapy on Cognitive Behavior and Neurogenesis in an Animal Model of Pre- and Post- Menopausal Females Samantha Pavlock (Medical Student) Pradeep Bhide and Deirdre McCarthy (Faculty
Rescue of neurological deficits in a mouse model for Angelman Syndrome by reduction of αcamkii inhibitory phosphorylation
 Rescue of neurological deficits in a mouse model for Angelman Syndrome by reduction of αcamkii inhibitory phosphorylation Geeske M van Woerden 1, Karen D Harris 2, Mohammad Reza Hojjati 1, Richard M Gustin
Rescue of neurological deficits in a mouse model for Angelman Syndrome by reduction of αcamkii inhibitory phosphorylation Geeske M van Woerden 1, Karen D Harris 2, Mohammad Reza Hojjati 1, Richard M Gustin
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission
 Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior. James L. McClelland Stanford University
 Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
Memory: Computation, Genetics, Physiology, and Behavior James L. McClelland Stanford University A Playwright s Take on Memory What interests me a great deal is the mistiness of the past Harold Pinter,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4642
 Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Supplementary Figure 1 Recording sites and example waveform clustering, as well as electrophysiological recordings of auditory CS and shock processing following overtraining. (a) Recording sites in LC
Dissected tissues were minced and lysed in lysis buffer (1x Tris buffered saline (TBS), 1% NP-40,
 Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Data Supplement for Dincheva et al., Effect of Early-Life Fluoxetine on Anxiety-Like Behaviors in BDNF Val66Met Mice. Am J Psychiatry (doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2017.15121592) Contents Supplemental Methods
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II
 Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Introduction to Physiological Psychology Learning and Memory II ksweeney@cogsci.ucsd.edu cogsci.ucsd.edu/~ksweeney/psy260.html Memory Working Memory Long-term Memory Declarative Memory Procedural Memory
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning.
 Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Supplementary Figure 1 ACx plasticity is required for fear conditioning. (a) Freezing time of conditioned and control mice before CS presentation and during CS presentation in a new context. Student s
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury
 Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Assessing mouse behaviors: Modeling pediatric traumatic brain injury Bridgette Semple Ph.D. Postdoctoral Fellow, Noble Laboratory Department of Neurological Surgery, UCSF Pediatric Traumatic Brain Injury
Ng et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration (2016) 11:71 DOI /s x
 Ng et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration (216) 11:71 DOI 1.1186/s1324-16-136-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Chronic adiponectin deficiency leads to Alzheimer s disease-like cognitive impairments and pathologies
Ng et al. Molecular Neurodegeneration (216) 11:71 DOI 1.1186/s1324-16-136-x RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Chronic adiponectin deficiency leads to Alzheimer s disease-like cognitive impairments and pathologies
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour
 Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Environmental influences on brain and behaviour Abdul H. Mohammed Dept. of Neurotec Karolinska Institutet Stockholm, Sweden IBRO African Neuroscience School, Nairobi, 2005 Environmental interventions affecting
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Hippocampal protein kinase C signaling mediates the short-term memory
 Hippocampal protein kinase C signaling mediates the short-term memory impairment induced by delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol Arnau usquets-garcia* 1,2, Maria Gomis-González* 1, Victòria Salgado-Mendialdúa 1,
Hippocampal protein kinase C signaling mediates the short-term memory impairment induced by delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol Arnau usquets-garcia* 1,2, Maria Gomis-González* 1, Victòria Salgado-Mendialdúa 1,
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior
 Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Modeling of Hippocampal Behavior Diana Ponce-Morado, Venmathi Gunasekaran and Varsha Vijayan Abstract The hippocampus is identified as an important structure in the cerebral cortex of mammals for forming
Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by
 Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Nakano et al. Supplementary information 1. Supplementary Figure 2. Methods 3. References Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improve diabetes-induced cognitive impairment by exosome transfer into
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic
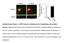 Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Single Enrichment Variables Differentially Reduce Age-Related Memory Decline in Female Mice
 Behavioral Neuroscience Copyright 2007 by the American Psychological Association 2007, Vol. 121, No. 4, 679 688 0735-7044/07/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.121.4.679 Single Enrichment Variables Differentially
Behavioral Neuroscience Copyright 2007 by the American Psychological Association 2007, Vol. 121, No. 4, 679 688 0735-7044/07/$12.00 DOI: 10.1037/0735-7044.121.4.679 Single Enrichment Variables Differentially
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Acetylcholine again! - thought to be involved in learning and memory - thought to be involved dementia (Alzheimer's disease)
 Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Free recall and recognition in a network model of the hippocampus: simulating effects of scopolamine on human memory function Michael E. Hasselmo * and Bradley P. Wyble Acetylcholine again! - thought to
Lisa M. Giocomo & Michael E. Hasselmo
 Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Mol Neurobiol (2007) 36:184 200 DOI 10.1007/s12035-007-0032-z Neuromodulation by Glutamate and Acetylcholine can Change Circuit Dynamics by Regulating the Relative Influence of Afferent Input and Excitatory
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition. From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D.
 Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Chapter 6: Hippocampal Function In Cognition From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Grid Cell The Hippocampus Serves a Role in Multimodal Information Processing and Memory
Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory
 Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory Anna Smith Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Background in Memory Models Models of Consolidation The Hippocampus Competitive Trace Theory
Prior Knowledge and Memory Consolidation Expanding Competitive Trace Theory Anna Smith Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Background in Memory Models Models of Consolidation The Hippocampus Competitive Trace Theory
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
International Journal of. Peptides. Hindawi Publishing Corporation. Submit your manuscripts at. Anatomy Research International
 Directions in Science TheScientificWorld (2001) 1, 530 533 ISSN 1532-2246; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2001.259 Calcineurin, Synaptic Plasticity, and Memory Carl Weitlauf and Danny Winder Vanderbilt University School
Directions in Science TheScientificWorld (2001) 1, 530 533 ISSN 1532-2246; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2001.259 Calcineurin, Synaptic Plasticity, and Memory Carl Weitlauf and Danny Winder Vanderbilt University School
Session Goals. Principles of Brain Plasticity
 Presenter: Bryan Kolb Canadian Centre for Behavioural Neuroscience University of Lethbridge Date: January 12, 2011 The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and
Presenter: Bryan Kolb Canadian Centre for Behavioural Neuroscience University of Lethbridge Date: January 12, 2011 The FASD Learning Series is part of the Alberta government s commitment to programs and
Metformin Activates an Atypical PKC-CBP Pathway to Promote Neurogenesis and Enhance Spatial Memory Formation
 rticle formin ctivates an typical PKC-CBP Pathway to Promote Neurogenesis and Enhance Spatial Memory Formation Jing Wang, 1,2 Denis Gallagher, 1,2,4,9 Loren M. DeVito, 3,9 Gonzalo I. Cancino, 1,2 David
rticle formin ctivates an typical PKC-CBP Pathway to Promote Neurogenesis and Enhance Spatial Memory Formation Jing Wang, 1,2 Denis Gallagher, 1,2,4,9 Loren M. DeVito, 3,9 Gonzalo I. Cancino, 1,2 David
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Model of Sleep Deprivation Effects on camp Signaling In our work, we have used electrophysiological, biochemical and pharmacological studies to reveal that sleep deprivation alters camp signaling in the
Model of Sleep Deprivation Effects on camp Signaling In our work, we have used electrophysiological, biochemical and pharmacological studies to reveal that sleep deprivation alters camp signaling in the
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation
 Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
Why do we have a hippocampus? Short-term memory and consolidation So far we have talked about the hippocampus and: -coding of spatial locations in rats -declarative (explicit) memory -experimental evidence
THE ORGANIZATION OF RECENT AND REMOTE MEMORIES
 THE ORGANIZATION OF RECENT AND REMOTE MEMORIES Paul W. Frankland* and Bruno Bontempi Abstract A fundamental question in memory research is how our brains can form enduring memories. In humans, memories
THE ORGANIZATION OF RECENT AND REMOTE MEMORIES Paul W. Frankland* and Bruno Bontempi Abstract A fundamental question in memory research is how our brains can form enduring memories. In humans, memories
TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement
 Supplementary Information Title: TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement Authors: Allison R. Bialas and Beth Stevens Supplemental Figure 1. In vitro characterization
Supplementary Information Title: TGF-β Signaling Regulates Neuronal C1q Expression and Developmental Synaptic Refinement Authors: Allison R. Bialas and Beth Stevens Supplemental Figure 1. In vitro characterization
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003
 Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
Psychology 320: Topics in Physiological Psychology Lecture Exam 2: March 19th, 2003 Name: Student #: BEFORE YOU BEGIN!!! 1) Count the number of pages in your exam. The exam is 8 pages long; if you do not
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) (B) (C) (D) (E)
 Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
Supplementary Figure 1: Validation of labeling specificity of immature OSNs and presynaptic terminals. (A) Confocal images of septal olfactory epithelium of an adult Gγ8-sypGFP-tdTom mouse showing colocalization
An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration
 An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration Sabrina M. Lehmann, Christina Krüger, Boyoun Park, Katja Derkow, Karen Rosenberger, Jan Baumgart, Thorsten
An unconventional role for mirna: let-7 activates Toll-like receptor 7 and causes neurodegeneration Sabrina M. Lehmann, Christina Krüger, Boyoun Park, Katja Derkow, Karen Rosenberger, Jan Baumgart, Thorsten
Neurotrophin receptor p75 NTR mediates Huntington s disease associated synaptic and memory dysfunction
 The Journal of Clinical Investigation Neurotrophin receptor p75 NTR mediates Huntington s disease associated synaptic and memory dysfunction Verónica Brito, 1,2,3 Albert Giralt, 1,2,3 Lilian Enriquez-Barreto,
The Journal of Clinical Investigation Neurotrophin receptor p75 NTR mediates Huntington s disease associated synaptic and memory dysfunction Verónica Brito, 1,2,3 Albert Giralt, 1,2,3 Lilian Enriquez-Barreto,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Ch 8. Learning and Memory
 Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Ch 8. Learning and Memory Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga,, R. B. Ivry,, and G. R. Mangun,, Norton, 2002. Summarized by H.-S. Seok, K. Kim, and B.-T. Zhang Biointelligence
Supplemental Table I
 Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001
 Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Brain and Cognitive Sciences 9.96 Experimental Methods of Tetrode Array Neurophysiology IAP 2001 An Investigation into the Mechanisms of Memory through Hippocampal Microstimulation In rodents, the hippocampus
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse
 Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
Supplemental figure legends Supplemental Figure 1. Intracranial transduction of a modified ptomo lentiviral vector in the mouse hippocampus targets GFAP-positive but not NeuN-positive cells. (A) Stereotaxic
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience
 CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
CISC 3250 Systems Neuroscience Levels of organization Central Nervous System 1m 10 11 neurons Neural systems and neuroanatomy Systems 10cm Networks 1mm Neurons 100μm 10 8 neurons Professor Daniel Leeds
Theories of memory. Memory & brain Cellular bases of learning & memory. Epileptic patient Temporal lobectomy Amnesia
 Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Cognitive Neuroscience: The Biology of the Mind, 2 nd Ed., M. S. Gazzaniga, R. B. Ivry, and G. R. Mangun, Norton, 2002. Theories of Sensory, short-term & long-term memories Memory & brain Cellular bases
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Early Influences: Seizures During Infancy Influence Behavior in Young Adult Mice
 Early Influences: Seizures During Infancy Influence Behavior in Young Adult Mice Current Literature In Basic Science Early-Life Seizures Result in Deficits in Social Behavior and Learning. Lugo JN, Swann
Early Influences: Seizures During Infancy Influence Behavior in Young Adult Mice Current Literature In Basic Science Early-Life Seizures Result in Deficits in Social Behavior and Learning. Lugo JN, Swann
Mind bomb-1 is an essential modulator of long-term memory and synaptic plasticity via the Notch signaling pathway
 Yoon et al. Molecular Brain 2012, 5:40 RESEARCH Open Access Mind bomb-1 is an essential modulator of long-term memory and synaptic plasticity via the Notch signaling pathway Ki-Jun Yoon 1, Hye-Ryeon Lee
Yoon et al. Molecular Brain 2012, 5:40 RESEARCH Open Access Mind bomb-1 is an essential modulator of long-term memory and synaptic plasticity via the Notch signaling pathway Ki-Jun Yoon 1, Hye-Ryeon Lee
HISTOLOGY AND HISTOCHEMISTRY OF LIMBIC HIPPOCAMPUS IN THE INDIAN BUFFALOES
 HISTOLOGY AND HISTOCHEMISTRY OF LIMBIC HIPPOCAMPUS IN THE INDIAN BUFFALOES A. Kumaravel*, Geetha Ramesh, S. Rajathi and S. Muthukrishnan Department of Veterinary Anatomy, Veterinary College and Research
HISTOLOGY AND HISTOCHEMISTRY OF LIMBIC HIPPOCAMPUS IN THE INDIAN BUFFALOES A. Kumaravel*, Geetha Ramesh, S. Rajathi and S. Muthukrishnan Department of Veterinary Anatomy, Veterinary College and Research
Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back
 Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back Matt Bellizzi, MD PhD Department of Neurology University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Rochester, NY "I can walk down the hall just fine,
Research Development: Bedside to Bench and Back Matt Bellizzi, MD PhD Department of Neurology University of Rochester School of Medicine and Dentistry Rochester, NY "I can walk down the hall just fine,
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
