Radiological Imaging in pneumonia and its complications
|
|
|
- Earl Murphy
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Radiological Imaging in pneumonia and its complications Cornelia Schaefer-Prokop Meander Medical Center Amersfoort Radboud University Nijmegen Netherlands
2 Outline Radiographic patterns Infections in immunocompromised patients Complications
3 Radiographic Classification Bronchopneumonia Lobar pneumonia (alveolar) Interstitial pneumonia (interstitial) Cave: OVERLAP
4 Bronchopneumonia The most common pattern Lobular Pneumonia Multifocal and centered around inflamed airway, involving some acini and sparing others Patchy consolidation and no air bronchogram, they may confluent and resemble lobar pneumonia Organisms: Staphylococcus aureus, gram-negative organisms, anaerobic bacteria, Mycoplasma, Legionella
5 Lobular (Broncho)pneumonia (Staphylococcus aureus)
6 Bronchopneumonia (Mycoplasma)
7 Lobar pneumonia Inflammation starts in the distal air ways and expands over Kohn sche pores Homogeneous, non-segmental consolidation with air bronchogram, complete / incomplete lobe Organisms: Streptococcus pneumoniae, Klebsiella, Legionella, Mycoplasma pneumoniae
8 Lobar pneumonia
9 Interstitial Pneumonia Extended bilateral peribronchial thickening and reticulo-nodular shadows CT: ground glass, micro-nodular, tree in bud Organisms: Viral, Mycoplasma, Pneumocystis
10 HIV-positive, Pneumocystis pneumonia
11 Role of Imaging CXR: diagnosis and/or assessment of - presence and extent of opacification - differentiation between bronchitis vs. pneumonia - prognosis esp. in high risk patients - therapy control CT: diagnosis and/or assessment of - alternative diagnosis (e.g., PE) - underlying malignancy - complications: empyema, BPF
12 Risk Stratification Pneumonia severity index clinical prediction rule for morbidity/mortality in CAP Curb 65 (Brit. Soc of pulmonologists) Confusion of new onset Urea greater than 7 mmol/l (19 mg/dl) Respiratory rate of 30 breaths per minute or greater Blood pressure < 90 mmhg systolic or diastolic blood pressure <60 mmhg age 65 or older Independent risk factors for treatment failure and inhospital mortality: liver disease, leucopenia, multilobar CAP, pleural effusion, and cavitation Menendez R et al. Thorax 2004, 59, 960
13 Definitions CAP = community acquired pneumonia pneumonia in an out-patient Nosocomial pneumonia pneumonia in an in-patient (> 48 hours) Opportunistic pneumonia pneumonia in an immunocompromised patient Atypical pneumonia CAP, which requires spec. antibiotics (macrolide and tetracycline) Legionella, Mycoplasma, Chlamydia, Protozoa
14 Specific Patient Groups Elderly patient Children COPD Smoker Cardiac patient Mild immune -deficiency less symptoms but higher risk aspecific symptoms exacerbation of chr. bronchitis exclusion of an underlying malignancy comorbidity causes higher risk Diabetes, alcoholism, malnutrition
15 Specific agents.. radiologic pattern
16 2 out-patients, high fever, consult the family doctor Xray Streptococcus pneumoniae
17 Elderly lady, very dyspnoic, admission to the ER What is your differential diagnosis?
18 Pneumococcus Pneumonia Air bronchogram Bulging fissure Positive angiogram sign
19 Take-home points The presence of air bronchogram indicates a pulmonary origin of the opacification Lack of an airbronchogram does not necessarily mean that the opacification is non-pulmonary Atelectasis of almost the complete lung causes mediastinal shift
20 Legionellaires Disease DD: lobar pneumonia 2-25% of CAP, requires hospitalization In elderly, patients with malignancies Lobar pneumonia Fast bilateral spread Legionella test
21 Klebsiella DD: lobar pneumonia 1-5% of CAP but more common in alcoholism and chr. bronchopulm. disease Bulging fissure (30%) Pleural effusion (60%) Abscess, cavitation and empyema
22 Bronchopneumonia: Mycoplasma DD: lobular pneumonia
23 Bronchiolitis: Mycoplasma
24 Lobular Pattern in HRCT Random Tb Perilymphatic Sarcoidosis Tree-in-bud Bronchiolitis
25 Chlamydia vs. Mycoplasma acinar nodules ground glass consolidations centrilobular nodules bronchial wall thickening From Okada F et al. JCAT 2005,29(5):626
26 Haemophilus influenzae gram neg coccobacillus Up to 20% of CAP Risk factors: diabetes, acoholism, COPD 60% bronchopneumonia 40% lobar pneumonia In > 50% effusion Cavitation in up to 15% Rarely empyema
27 Take home points: CAP Str Pneumoniae 40% lobar pneumonia H Influenza 25% COPD, bronchopn. Atypical 20% in young adults (mycoplasma, bronchopn, but also chlamydia) confluent Klebsiella 5% predisposition, abcess Legionella 2-20% fast spread, ill!
28 Pneumonia in the immunocompromised Patient
29 The Immuno-compromised Patient bone marrowtransplantation organ transplantation chemotherapy immunosuppressive therapy splenectomy diabetes sarkoidosis malnutrition alcoholism renal/liver insufficiency HIV
30 The Immuno-compromised Patient 1. Granulozytopenia / dysfunction neutropenia, sarkoid, alcohol, diabetes, SLE Staph, gram-neg bacteries, Aspergillus 2. T-cell-dysfunction HIV, BM-Tx, Thymus aplasia, steroids, PcP, CMV, Tb, Aspergillus, Nocardia 3. B-cell-dysfunction organ-tx, nephrot. syndrome, splenectomy, lymphoma Strept pneum. Hemoph. Infl.
31 Role of Imaging Chest radiograph Screening, first imaging but not very sensitive (in 40% negative) HRCT more sensitive pattern analysis is helpful for classification differential diagnosis follow-up / therapy control complications
32 Bacterial Infections Lobular/ lobar consolidations Air bronchogram but with bad immune status only ground glass Staph. aureus, gramneg. bact, Klebsiella >>> S. pneumoniae, H. Influenzae Frequently mixed infections
33 Septic Emboli (endocarditis, drug addict)
34 Take home points In immune-incompetent patients - any bacterial infection is possible - may present atypically - increased risk for gramnegative bacteries and complications - opportunistic infections
35 Fungal infections Patients with... - neutropenia (under chemotherapy) - Cortison therapy - GVHD - AIDS - BM-Tx
36 Angio-invasive Aspergillus Halo Consolidations Air crescent
37 Neutropenic patient: aspergillus??
38 It may start small
39 There has to be an adequate clinical situation! Multiple opacifications Halo???? Bacterial bronchopneumonia in a COPD patient
40 Endobronchial Aspergillus more rare!
41 Fungal infection...but not aspergillus... Candida sepsis
42 Fungal Infections Take home points 1. Aspergillus the most frequent one 2. Halo / bronchovascular distribution / air crescent sign 3. Cave: endobronchial fungal infection with bronchiolitis (Tree-in bud) 4. Look at extrapulmonary findings
43 Crytococcus Infection Congenital immunedeficiency, back pain
44 Role of Imaging: Caveats There might be a delay of several hours (12h) between onset of symptoms and presence of opacifications In up to 10% negative CXR despite clinical symptoms, in immunoincomptetent patients negative CXR in up to 40%. No or delayed opacification in patients with reduced immune competence (diabetes, alcohol, neutropenia) Atypical pattern in patients with pre-exisiting lung disease (emphysema, fibrosis)
45 Role of preexisting lung disease Pneumococcus Pn. in emphysema Idiopathic fibrosis (UIP)
46 Pneumonia: Complications Empyema Abcess Bronchopleural fistulal
47 HIV pos patient: more imaging needed?
48 The importance of CT for complications HIV+, Bacteroides
49 Pleural Fluid Collections Uncomplicated that resolve with conservative therapy transudative effusions small free-flowing exudative effusions Complicated do not resolve without drainage moderate to large unilocular or multilocular parapneumonic effusions Empyema malignant effusions hematothoraces
50 Complicated Pleural Effusion
51 Pleural Infection in CT Pleural enhancement / thickening (split pleura sign) Increased extrapleural fat with increased attenuation Pleural adhesions / (fibrious septations) Loculations (air bubbles) DD pulmonary abscess from pleural empyema
52 Which one is the empyema? A: Hemato thorax B: empyema C: pulm. abscess D: chr effusion in RA
53 Anaerobic Bacteria typically after aspiration 20-35% of CAP, requires hospitalization In > 30% of nosocomial infection Risk: impaired consciousness Bronchopneumonia posterior upper lobe and apical lower lobe In 20-60% abscess formation, In 50% effusion and empyema
54 Day 1 day 2
55 Day 7
56 Nosocomial Pneumonia Infection > 48 h after hospitalization IC: 10-65%, of which 20-55% fatal ARDS: in 55% complicated by sec. infection Aspiration: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Anaeroben Septic emboli: Staphylococcus aureus
57 Aspiration pneumonia ARDS
58 Conclusion Overlap of radiologic pattern and underlying type of infectious agents Differentiation between bacterial vs. fungal vs. viral infection under immunosuppression Role of imaging is to sort out differential diagnosis and to look for complications
Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients
 Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D.
 Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Eun-Young Kang, M.D., Jae Wook Lee, M.D., Ji Yung Choo, M.D., Hwan Seok Yong, M.D., Ki Yeol Lee, M.D., Yu-Whan Oh, M.D. Department of Radiology, Korea University Guro Hospital, College of Medicine, Korea
Pathology of Pneumonia
 Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
Pathology of Pneumonia Dr. Atif Ali Bashir Assistant Professor of Pathology College of Medicine Majma ah University Introduction: 5000 sq meters of area.! (olympic track) Filters >10,000 L of air / day!
PULMONARY EMERGENCIES
 EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
EMERGENCIES I. Pneumonia A. Bacterial Pneumonia (most common cause of a focal infiltrate) 1. Epidemiology a. Accounts for up to 10% of hospital admissions in the U.S. b. Most pneumonias are the result
Pneumonia. Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial
 Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
Pneumonia Definition of pneumonia Infection of the lung parenchyma Usually bacterial Epidemiology of pneumonia Commonest infectious cause of death in the UK and USA Incidence - 5-11 per 1000 per year Worse
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Resident Case Review CHEST. Daria Manos CAR 2016
 Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Resident Case Review CHEST CAR 2016 Daria Manos Disclosure Speakers bureau, Roche CAR 2016 Daria Manos 1. Recognize common and critical chest radiograph and computed tomography signs and use these clues
Pneumonia. Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine
 Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Key messages. CXR interpretation in TB/HIV setting. Training course
 Key messages CXR interpretation in TB/HIV setting Training course Normal CXR Front view and lateral view Good notions of technical conditions to obtain a good CXR Good knowledge of criteria for quality
Key messages CXR interpretation in TB/HIV setting Training course Normal CXR Front view and lateral view Good notions of technical conditions to obtain a good CXR Good knowledge of criteria for quality
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Respiratory Pathology. Kristine Krafts, M.D.
 Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
Respiratory Pathology Kristine Krafts, M.D. Normal lung: alveolar spaces Respiratory Pathology Outline Acute respiratory distress syndrome Obstructive lung diseases Restrictive lung diseases Vascular
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99. Presented by: Jesicca Andrews
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
Chapter 10 Respiratory System J00-J99 Presented by: Jesicca Andrews 1 Respiratory System 2 Respiratory Infections A respiratory infection cannot be assumed from a laboratory report alone; physician concurrence
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Uses, limitations and interpretation of CT in pulmonary infections: A practical approach
 Uses, limitations and interpretation of CT in pulmonary infections: A practical approach Canadian Association of Radiologists 2013 DISCLOSURES Speakers honorarium, Siemens Canada Objectives 1. Recognize
Uses, limitations and interpretation of CT in pulmonary infections: A practical approach Canadian Association of Radiologists 2013 DISCLOSURES Speakers honorarium, Siemens Canada Objectives 1. Recognize
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH. Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch
 ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
Community Acquired Pneumonia. Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP
 Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Community Acquired Pneumonia Abdullah Alharbi, MD, FCCP A 68 y/ male presented to the ED with SOB and productive coughing for 2 days. Reports poor oral intake since onset due to nausea and intermittent
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD
 TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
TB Intensive Tyler, Texas June 2-4, 2010 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David Finlay, MD June 3, 2010 2stages stages- Tuberculosis 1. primary infection 2. reactivation, or post primary disease 2 1 Primary
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN. IAP UG Teaching slides
 PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
PNEUMONIA IN CHILDREN 1 INTRODUCTION 156 million new episodes / yr. worldwide 151 million episodes developing world 95% in developing countries 19% of all deaths in children
Tuberculosis: The Essentials
 Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Tuberculosis: The Essentials Kendra L. Fisher, MD, PhD THORACIC TUBERCULOSIS: THE BARE ESSENTIALS Kendra Fisher MD, FRCP (C) Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Medical Center TUBERCULOSIS ()
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
POLICY FOR TREATMENT OF LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT INFECTIONS
 POLICY F TREATMENT OF LOWER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2018 Approved by: The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date: July 2018 Implementation
POLICY F TREATMENT OF LOWER RESPIRATY TRACT INFECTIONS Written by: Dr M Milupi, Consultant Microbiologist Date: June 2018 Approved by: The Drugs & Therapeutics Committee Date: July 2018 Implementation
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT
 How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
How to Analyse Difficult Chest CT Complex diseases are:- - Large lesion - Unusual or atypical pattern - Multiple discordant findings Diffuse diseases are:- - Numerous findings in both sides 3 basic steps
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Sheet: Patho-Pulmonary infections Done by: Maen Faoury
 Sheet: Patho-Pulmonary infections Done by: Maen Faoury Pneumonitis : might be an infection or not. Chemical Pneumonitis : not an infection. Parenchyma : an infection.( تندرج تحت ال pneumonitis) Lung Parenchyma
Sheet: Patho-Pulmonary infections Done by: Maen Faoury Pneumonitis : might be an infection or not. Chemical Pneumonitis : not an infection. Parenchyma : an infection.( تندرج تحت ال pneumonitis) Lung Parenchyma
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA
 KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
To Study The Cinico-Radiological Features And Associated Co-Morbid Conditions
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 7 Ver. 16 (July. 2018), PP 58-62 www.iosrjournals.org To study the clinico-radiological features
Pulmonary Pathology II. William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU
 Pulmonary Pathology II William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Goals and Objectives Comprehend the etiology, pathogenesis/pathopysiology and consequences of pulmonary hypertension Distinguish
Pulmonary Pathology II William Bligh-Glover M.D. Department of Anatomy, CWRU Goals and Objectives Comprehend the etiology, pathogenesis/pathopysiology and consequences of pulmonary hypertension Distinguish
Bacterial pneumonia with associated pleural empyema pleural effusion
 EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
EMPYEMA Synonyms : - Parapneumonic effusion - Empyema thoracis - Bacterial pneumonia - Pleural empyema, pleural effusion - Lung abscess - Complicated parapneumonic effusions (CPE) 1 Bacterial pneumonia
Pneumonia. Introduction. The Different Faces of Pneumonia. Immunocompetent Host. Elisa Franquet, MD
 Pneumonia Elisa Franquet, MD Introduction Pneumonia continues to be a significant global health problem, remaining among the top 10 causes of death globally and in the US, 1 especially among elderly patients.
Pneumonia Elisa Franquet, MD Introduction Pneumonia continues to be a significant global health problem, remaining among the top 10 causes of death globally and in the US, 1 especially among elderly patients.
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
and localized ground glass opacities, or bronchiolar focal or multifocal micronodules;
 E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
PBL RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DR. NATHEER OBAIDAT
 PBL RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DR. NATHEER OBAIDAT Dr started to talk about his specialty at the hospital which is (ICU-Pulmonary-Internal Medicine). Pulmonary medical branch is a subspecialty of internal medicine.
PBL RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DR. NATHEER OBAIDAT Dr started to talk about his specialty at the hospital which is (ICU-Pulmonary-Internal Medicine). Pulmonary medical branch is a subspecialty of internal medicine.
HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review.
 HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review. Poster No.: C-0836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, P. Trallero, L. Berrocal Morales, S. Medrano, S. 1
HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review. Poster No.: C-0836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, P. Trallero, L. Berrocal Morales, S. Medrano, S. 1
Interstitial syndrome
 Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
Interstitial syndrome Ground-glass attenuation Miliary and nodular images linear images Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
The Pulmonary Pathology of Iatrogenic Immunosuppression. Kevin O. Leslie, M.D. Mayo Clinic Scottsdale
 The Pulmonary Pathology of Iatrogenic Immunosuppression Kevin O. Leslie, M.D. Mayo Clinic Scottsdale The indications for iatrogenic immunosuppression Autoimmune/inflammatory disease Chemotherapy for malignant
The Pulmonary Pathology of Iatrogenic Immunosuppression Kevin O. Leslie, M.D. Mayo Clinic Scottsdale The indications for iatrogenic immunosuppression Autoimmune/inflammatory disease Chemotherapy for malignant
Pulmonary Computed Tomography Findings in 39 Cases of Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pulmonary Computed Tomography Findings in 39 Cases of Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumonia Attiya Haroon 1, Futoshi Higa 1, Jiro Fujita 1, Akira Watanabe 2, Nobuki Aoki 3, Yoshihito Niki
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Pulmonary Computed Tomography Findings in 39 Cases of Streptococcus pneumoniae Pneumonia Attiya Haroon 1, Futoshi Higa 1, Jiro Fujita 1, Akira Watanabe 2, Nobuki Aoki 3, Yoshihito Niki
Acute Respiratory Infection. Dr Anthony Gibson
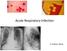 Acute Respiratory Infection Dr Anthony Gibson Range of Conditions Upper tract Common Cold coryza Sore Throat- Pharyngitis Sinusitis Epiglottitis Range of Conditions Lower Acute Bronchitis Acute Exacerbation
Acute Respiratory Infection Dr Anthony Gibson Range of Conditions Upper tract Common Cold coryza Sore Throat- Pharyngitis Sinusitis Epiglottitis Range of Conditions Lower Acute Bronchitis Acute Exacerbation
66YM Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease annual review. H Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
 Supplementary materials Table S1. Read codes to define COPD Read code Medical code Clinical event Read term 66YM.00 11287 382901 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease annual review H3...00 1001 338812
Supplementary materials Table S1. Read codes to define COPD Read code Medical code Clinical event Read term 66YM.00 11287 382901 Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease annual review H3...00 1001 338812
Bronchitis/Pneumonia Core Content Keith Conover, M.D., FACEP /15/02 Clinical Spectrum Chest pain, shoulder pain, neck pain, abdominal pain,
 Bronchitis/Pneumonia Core Content Keith Conover, M.D., FACEP 1.0 10/15/02 Clinical Spectrum Chest pain, shoulder pain, neck pain, abdominal pain, headache Links with smoking, pollen count, FH of asthma
Bronchitis/Pneumonia Core Content Keith Conover, M.D., FACEP 1.0 10/15/02 Clinical Spectrum Chest pain, shoulder pain, neck pain, abdominal pain, headache Links with smoking, pollen count, FH of asthma
Pulmonary Morning Report. Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January,
 Pulmonary Morning Report Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January, 8 2015 Pleural Effusion Unilateral versus Bilateral Associated symptoms Transudate versus Exudate Light s Criteria: Pleural protein: Serum protein
Pulmonary Morning Report Ashley Schmehl D.O. PGY-3 January, 8 2015 Pleural Effusion Unilateral versus Bilateral Associated symptoms Transudate versus Exudate Light s Criteria: Pleural protein: Serum protein
Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics)
 Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
Page 1 of 8 Official reprint from UpToDate www.uptodate.com 2014 UpToDate Patient information: Pneumonia in adults (Beyond the Basics) Authors Thomas J Marrie, MD Thomas M File, Jr, MD Section Editor John
David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Diagnosis of TB: Radiology David E. Griffith, MD March 13, 2015 TB for Pulmonologist March 13, 2015 Phoenix, AZ EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION David E. Griffith, MD has the following disclosures to make:
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Acute pneumonia Simple complement
 Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
Acute pneumonia Simple complement 1. Clinical variants of acute pneumonia in children are, except: A. Bronchopneumonia B. Lobar confluent pneumonia C. Viral pneumonia D. Interstitial pneumonia E. Chronic
Chapter 16. Lung Abscess. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 Lung Abscess 1 EDA PM C AFC RB A B Figure 16-1. Lung abscess. A, Cross-sectional view of lung abscess. B, Consolidation and (C) excessive bronchial secretions are common secondary anatomic alterations
Chapter 16 Lung Abscess 1 EDA PM C AFC RB A B Figure 16-1. Lung abscess. A, Cross-sectional view of lung abscess. B, Consolidation and (C) excessive bronchial secretions are common secondary anatomic alterations
Community-Acquired Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: Initial Chest Radiographic Findings and Follow-up CT Findings in Helping Predict Patient Outcome
 Community-Acquired Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: Initial Chest Radiographic Findings and Follow-up CT Findings in Helping Predict Patient Outcome Jeong Joo Woo, Dong Hyun Lee, Jin Kyung An Department
Community-Acquired Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: Initial Chest Radiographic Findings and Follow-up CT Findings in Helping Predict Patient Outcome Jeong Joo Woo, Dong Hyun Lee, Jin Kyung An Department
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Case 1 : Question. 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random
 Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Interstitial Syndrome Ground glass attenuation miliary and nodular images Linear images
 Interstitial Syndrome Ground glass attenuation miliary and nodular images Linear images Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology
Interstitial Syndrome Ground glass attenuation miliary and nodular images Linear images Dr Etienne Leroy-Terquem Centre hospitalier de Meulan les Mureaux. France French-cambodian association for pneumology
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
May. Pathology #2. part. Rahaf Al-yousef. Mohammad Al-Qudah
 8 th May Pathology #2 nd Pneumonias 2 part Mohammad Al-Qudah Rahaf Al-yousef In the first part of our lectures today, we will define pneumonia clinically and pathologically(which is an infection of the
8 th May Pathology #2 nd Pneumonias 2 part Mohammad Al-Qudah Rahaf Al-yousef In the first part of our lectures today, we will define pneumonia clinically and pathologically(which is an infection of the
Community acquired pneumonia
 Community acquired pneumonia definition Symptoms of an acute LRTI New focal signs on chest examination At least one systemic feature New radiographic shadow Defination{Crofton} IT IS A SYNDROME CAUSED
Community acquired pneumonia definition Symptoms of an acute LRTI New focal signs on chest examination At least one systemic feature New radiographic shadow Defination{Crofton} IT IS A SYNDROME CAUSED
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Charles Krasner, M.D. University of NV, Reno School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Medical Center
 Charles Krasner, M.D. University of NV, Reno School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Medical Center Kathy Peters is a 63 y.o. patient that presents to your urgent care office today with a history
Charles Krasner, M.D. University of NV, Reno School of Medicine Sierra NV Veterans Affairs Medical Center Kathy Peters is a 63 y.o. patient that presents to your urgent care office today with a history
X-Rays. Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady
 X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
X-Rays Prepared by Prof.Dr. Magda Hassab Allah Assist.lecturer Marwa Al Hady CHEST X-RAYS Normal Chest X-ray Comments on chest X ray includes examination of 1- Bony cage (ribs,clavicles &vertebral column
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Clinical and Etiological Profile of Unresolving Pneumonia Cases Attending Government Chest Hospital, Visakhapatnam
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2015), PP 56-61 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical and Etiological Profile of
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 7 Ver. VII (July. 2015), PP 56-61 www.iosrjournals.org Clinical and Etiological Profile of
A Study of Prognosis and Outcome of Community Acquired Pneumonia in a Tertiary Care Centre
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 8 (2015) pp. 763-769 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A Study of Prognosis and Outcome of Community Acquired Pneumonia in a Tertiary Care Centre Bhadra Reddy
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 8 (2015) pp. 763-769 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article A Study of Prognosis and Outcome of Community Acquired Pneumonia in a Tertiary Care Centre Bhadra Reddy
Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Teenager with persistent fever and cough. Pneumonia diagnosed 1 week ago. Diagnosis Pleural Empyema Additional Clinical Surgery-Clear fluid with
Pleural Empyema Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/19/2010 History Teenager with persistent fever and cough. Pneumonia diagnosed 1 week ago. Diagnosis Pleural Empyema Additional Clinical Surgery-Clear fluid with
Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia
 Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Difference Between Pleural Effusion and Pneumonia www.differencebetween.com Key Difference - Pleural Effusion vs Pneumonia Pleural effusion and pneumonia are two conditions that affect our respiratory
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, et al. Hydrocortisone therapy for
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Sprung CL, Annane D, Keh D, et al. Hydrocortisone therapy for
PNEUMONIA. I. Background 6 th most common cause of death in U.S. Most common cause of infection related mortality
 Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Page 1 of 8 September 4, 2001 Donald P. Levine, M.D. University Health Center Suite 5C Office: 577-0348 dlevine@intmed.wayne.edu Assigned reading: pages 153-160; 553-563 PNEUMONIA the most widespread and
Index. B Biological factors, 2 Brain stem encephalitis, Burkitt s lymphoma, 83, 105
 Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) abdomen gallbladder complications, 97, 107 109 gastrointestinal complications, 96, 105 106 liver complications, 97, 107 109 neoplasm, 99, 110 111 pancreas
Index A Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) abdomen gallbladder complications, 97, 107 109 gastrointestinal complications, 96, 105 106 liver complications, 97, 107 109 neoplasm, 99, 110 111 pancreas
Respiratory System Disorders 3
 Respiratory System Disorders 3 Lecture 25 Pathology and Clinical Science 1 (BIOC211) Department of Bioscience Text Reference: Porth s Pathophysiology: Concepts of Altered Health States Sheila C. Grossman
Respiratory System Disorders 3 Lecture 25 Pathology and Clinical Science 1 (BIOC211) Department of Bioscience Text Reference: Porth s Pathophysiology: Concepts of Altered Health States Sheila C. Grossman
Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD
 Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Pulmonary Cryptococcosis in Patients Without HIV Infection* Judith A. Aberg, MD; Linda M. Mundy, MD; and William G. Powderly, MD Purpose: To further elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches
Chapter. Imaging of Pneumonia in Children. Introduction. Chest X-ray and Common Infective Agents. School Age Children
 content Chapter 11 Winnie CW Chu Introduction Chest X-ray and Common Infective Agents School Age Children Computed Tomography and Common Infective Agents Utility of Computed Tomography Evaluation of Persistent
content Chapter 11 Winnie CW Chu Introduction Chest X-ray and Common Infective Agents School Age Children Computed Tomography and Common Infective Agents Utility of Computed Tomography Evaluation of Persistent
Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia.
 Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Joseph Garland, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD. Round Pneumonia. Joseph Garland, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman, MD
 Round Pneumonia Joseph Garland, HMS IV Case 1: Mr. H Mr. H is a 45-year-old man who presents with a 4 day history of full-body myalgias, headaches and fever to 103 F. He also complains of sharp leftsided
Round Pneumonia Joseph Garland, HMS IV Case 1: Mr. H Mr. H is a 45-year-old man who presents with a 4 day history of full-body myalgias, headaches and fever to 103 F. He also complains of sharp leftsided
HRCT of pulmonary infections in patients post solid organ transplantation
 HRCT of pulmonary infections in patients post solid organ transplantation Poster No.: C-2100 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Sulkowska, P. D. Palczewski, M. Golebiowski, K. Mucha,
HRCT of pulmonary infections in patients post solid organ transplantation Poster No.: C-2100 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Sulkowska, P. D. Palczewski, M. Golebiowski, K. Mucha,
Immune-mediated lung disease. Ian Sabroe
 Immune-mediated lung disease Ian Sabroe It s all immune? Diseases that doesn t have immune involvement? The processes of response to injury and tissue repair are key homeostatic pathways involved in all
Immune-mediated lung disease Ian Sabroe It s all immune? Diseases that doesn t have immune involvement? The processes of response to injury and tissue repair are key homeostatic pathways involved in all
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Pneumonia Coding. Let s Breathe Some Life Into It. Karen L. Bucci, RHIA Sandy Frey, RHIT, CCS
 Pneumonia Coding Let s Breathe Some Life Into It Karen L. Bucci, RHIA Sandy Frey, RHIT, CCS Agenda Lung Anatomy and Function Pneumonia Types Coding Guidelines Pneumonia and COPD Pneumonia and Influenza
Pneumonia Coding Let s Breathe Some Life Into It Karen L. Bucci, RHIA Sandy Frey, RHIT, CCS Agenda Lung Anatomy and Function Pneumonia Types Coding Guidelines Pneumonia and COPD Pneumonia and Influenza
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Epidemiology of Infectious Complications of H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection
 Epidemiology of Infectious Complications of H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection Lyn Finelli, DrPH, MS Lead, Influenza Surveillance and Outbreak Response Epidemiology and Prevention Branch Influenza Division
Epidemiology of Infectious Complications of H1N1 Influenza Virus Infection Lyn Finelli, DrPH, MS Lead, Influenza Surveillance and Outbreak Response Epidemiology and Prevention Branch Influenza Division
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
 May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
Residents Section Pattern of the Month
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gosset et al. Tree-In-Bud Pattern Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Natacha Gosset 1 Alexander A. Bankier Ronald L. Eisenberg Gosset N,
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gosset et al. Tree-In-Bud Pattern Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Natacha Gosset 1 Alexander A. Bankier Ronald L. Eisenberg Gosset N,
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Life-threatening infections. Frank Bowden October 5, 2018
 Life-threatening infections Frank Bowden October 5, 2018 David Sackett Evidence Based Medicine is the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. The Golden Rules
Life-threatening infections Frank Bowden October 5, 2018 David Sackett Evidence Based Medicine is the integration of best research evidence with clinical expertise and patient values. The Golden Rules
Interpretation of Chest Radiographs Paul Christensen, MD 10/21/09. Diagnostic Evaluation. Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation.
 Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis?
 Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Excavated pulmonary nodule: steps to diagnosis? Poster No.: C-1044 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit W. Mnari, M. MAATOUK, A. Zrig, B. Hmida, M. GOLLI; Monastir/ TN Metastases,
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Pleural Effusion. Exudative pleural effusion - Involve an increase in capillary permeability and impaired pleural fluid resorption
 Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Pleural Effusion Definition of pleural effusion Accumulation of fluid between the pleural layers Epidemiology of pleural effusion Estimated prevalence of pleural effusion is 320 cases per 100,000 people
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
