Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy. Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA
|
|
|
- Roy Davidson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Pediatric Neuroimaging in Epilepsy Bhagwan Moorjani, MD, FAAP, FAAN Hope Neurologic Center La Quinta, CA
2 Neuroimaging in Childhood Neuroimaging issues are distinct from adults Sedation/anesthesia Motion artifacts Requires knowledge of normal CNS developmental (i.e. myelin maturation) Contrast media Parental anxiety
3 Diagnostic Approach Age of onset Static versus Progressive Look for treatable causes Do not overlook abuse, Manchausen if all is negative Phenotype presence (syndromic, Head Circumference, Neurocutaneous Syndrome, systemic involvement) Predominant symptom (Epilepsy, developmental delay, weakness/motor, psychomotor regression, cognitive/dementia)
4 Neuroimaging in Epilepsy Peak incidence in childhood Occurs as a co-morbid condition in many pediatric disorders (birth injury, dysmorphism, chromosomal anomalies, developmental delays/regression) Many neurologic disorders in children have the same chief complaint
5
6 Congenital Malformation Characterized by their anatomic features Broad categories: based on embryogenesis Stage 1: Dorsal Induction: Formation and closure of the neural tube. (Weeks 3-4) Stage 2: Ventral Induction: Formation of the brain segments and face. (Weeks 5-10) Stage 3: Migration and Histogenesis: (Months 2-5) Stage 4: Myelination: (5-15 months; matures by 3 years)
7 Etiology of Epilepsy: Developmental and Genetic Classification of Cortical Dysplasia 1. Secondary to abnormal neuronal and glial proliferation/apoptosis 2. Secondary to abnormal neuronal migration 3. Secondary to abnormal cortical organization or late migration 4. Not otherwise classified IEM Other unclassified dysplasia
8 Gray Matter Heterotropia displaced masses of nerve cells (gray matter) most common: small nest adjacent to lateral ventricles Range from nodular to band heterotropia to schizencephaly, lissencephaly and polymicrogyria clinical: seizures MRI: isointense with gray matter in all sequence Subependymal heterotropia (most common) Band heterotropia (double cortex) Lissencephaly Cobblestone cortex (lis 2) Subcortical heterotropia
9 Subependymal heterotropia T1W multifocal GM nodules lining lateral ventricle, also in the frontal WM
10 Subcortical heterotropia T2W blurred curvilinear line extending from cortex to ventricular surface
11 Polymicrogyria multiple abnormal tiny indentation along brain surface (5-7mm) abnormal cortical histology can be unilateral MRI: decreased number of broad, thick, smooth gyri T2W blurring of gray white junction (open arrow) Nodular appearance
12 polymicrogyria T2W - Bilateral perisylvian/suprasylvian polymicrogyria
13 Polymicrogyria T1W irregular interface with adjacent white matter
14 Double cortex Cortex inversely proportional to band heterotropia T2W decreased sulcation primitive sylvian fissure (open arrow), Thick band of incompletely migrated cortex (arrow)
15 Double cortex T1W - asymmetry of paramedial parietal region Heterotropic Gray matter
16 Double cortex T1W - GM heterotropia right parieto-occipital region (open arrow) Thinning of overlying cortex (arrow)
17 Double cortex 6 month old with seizures T2W thin band of GM in the deep white matter
18 Pachygyria thick and more completely developed gyri commonly diffused with relative sparing of temporal lobes associated with: agenesis of CC and heterotopias clinical: microcephaly, seizures, MR, developmental delay MRI: circumferential band of high signal on T2 within the cortex
19 Lissencephaly Severe form of neuronal migration Disorder Can be seen in: Isolation Miller Dieker Syndrome TORCH infection (CMV) Clinical S/S: Mental Retardation Intractable Epilepsy Microcephaly
20 Lissencephaly Imaging Hourglass or figure of 8 Shallow sylvian fissure LIS 1: parietal-occipital X-LIS: Subfrontal/temporal 3 layers may be seen in neonates on T2W Outer layer thin, smooth Intervening cell sparse layer Deeper thick layer mimicking band heterotropia Posterior > Anterior involvement in LIS 1
21 T2W complete absence of cerebral sulcation Cerebellum is normal Hyperintensecell sparse zone separates the thin cortical ribbon from the thicker band of disorganized neurons lissencephaly
22 Miller Dieker T1W Typical midline calcification Thin outer GM layer Cell sparse WM layer Thick inner GM band
23 T2W Severe parietal-occipital involvement (Classic pattern) Cell sparse WM layer posteriorly Lis 1
24 Agyria Complete lissencephaly Smooth brain Identified by figure eight due to shallow sylvian fissures.
25 Schizencephaly Gray matter- lined cleft that extends from the ventricular ependyma to the pia. Unilateral or bilateral Two types: Closed lip (type I) Open lip (type II)
26 Schizencephaly Imaging Transmantle gray matter lining clefts Dimple in wall of ventricle if closed or narrow Frontal and Parietal lobes near central sulcus Distinction of GM lining cleft can be difficult prior to myelination DVA overlie cleft seen on MRV
27 Porencephaly Schizencephaly Differential Diagnosis Lined by gliotic white matter No dysplastic gray matter Semilobar Holoprocencephaly Can mimic bilateral open lip schizencephaly
28 Schizencephaly
29 Schizencephaly
30 Schizencephaly
31 Hemimegalencephaly Primary hamartomatous malformation Onset usually in neonatal period Catastrophic One type of onset is Tonic Seizure (Ohtahara Syndrome) Can be asymmetric and often precede or overlap with West Syndrome (IS) IS= 50%
32 Hemimegalencephaly No differences between Isolated or Syndromic type. Plain Skull Films: look for macrocrania & asymmetry. May see intracranial calcifications & bony dysplasia US: prenatal may suggest HME, may see macrocephaly, ventricular asymmetry with enlargement of lateral ventricle Postnatal: may see unilateral ventricular dilation with hemispheric enlargement
33 Hemimegalencephaly Imaging CT & MRI: Gross asymmetry 1 hemisphere enlarged Posterior falx and occipital pole displaced to contralateral side Dysplastic Cortex Asymmetry of Ventricular System 4 points of abnormal ventricle. 1. Straightened frontal horns (pointed) 2. mild-extreme dilation of lateral ventricle 3. reverse of contralateral horn (mass effect appearance) 4. colpocephaly (disproportionate developmental dilation of occipital horn of lateral ventricle) in all grades of HME
34 Hemimegalencephaly FLAIR bright signal in WM of abnormal hemisphere The only disorder that enlarges both hemisphere and ipsilateral ventricle
35 FCD with Balloon Cells Abnormal gyral pattern when large Blurring of gray-white junction Abnormal tissue: cortex to border of lateral ventricle Typically associated with TS Solitary no other TS features T2 hyperintense comet tail from cortex to ventricle Best seen on flair
36 FCD - Balloon Cell PD FSE focal thickening with increased signal of expanded gyrus
37 T2W juxtacortical signal change Thin line of signal change tracking along the expected Course of the radial glial fibers to the Subependymal margins FCD with balloon cell
38 FCD with balloon cell FLAIR gyral expansion and thin signal change extending to the ventricle
39 DNET Intractable epilepsy Focal deficits More common 2 nd and 3 rd decade Considered part of abnormal neuronal/glial proliferation - neoplastic MRI Findings: T1 hypointense T2 hyperintense Modest to no enhancement Scalloping Lack of mass effect, edema
40 DNET T2W 5 year old with seizures Multicentric bubbly DNET with involvement of body of the caudate nucleus
41 DNET FLAIR characteristic appearance Cortically based, sharply demarcated wedge shaped mass with hyperintense rim Points towards the ventricle No edema
42 DNET T1W-C+ Cystic component with multiloculated appearance No solid enhancement
43 Metabolic Epilepsies
44 MRI Features of Metabolic Diseases Common Abnormalities Atrophy Symmetry Infrequent Enhancement Myelination abnormalities Malformation
45 Neurometabolic-Degenerative Disorders Knowledge of normal myelination pattern is essential General rules: Caudal to cranial Posterior to anterior MRI provides the best imaging modality T1 matures at months T2 matures at months
46 Neurometabolic-Degenerative Disorders Type of myelination involvement Delayed myelination Demyelination Dysmyelination Nervous system involvement Brainstem involvement Cerebellar involvement Spinal Cord involvement Tissue Involvement Gray matter involvement White matter involvement
47 1 month 9 months 36 months From Alberico
48 Factors to Consider Age of Onset Degree of derangement Abnormal metabolite Deficiency or excess Stage of the disease process Phenotype
49 Leukodystrophies Abnormal signal in white matter Symmetric usually Periventricular, deep or subcortical in location Failure to achieve myelination milestones MRS abnormalities reflect neuronal loss and increased cellular turnover Some have contrast enhancement ALD: zone of active inflammation Alexander: ventricular lining, periventricular rim, frontal WM, optic chiasm, fornix, BG, thalamus, dentate nucleus
50 Leukodystrophies Differential Diagnosis Radiation and Chemotherapy injury Viral encephalitis ADEM MS In neonates: HIE Periventricular pattern
51 Head Circumference Macrocephalic Canavan Alexander Tay Sachs (GM2 gangliosidosis) L-2-hydroxyglutaric aciduria Microcephalic/Normal MLD Pelizaeus Merzbacher disease Zellweger Disease Krabbe
52 Alexander Disease Clinical S/S: macrocephaly, seizures Mutation: GFAP, Chromosome 17q21 Imaging Extensive WM changes with frontal predominance Abnormal signal in BG and thalami Enhancement: ventricular lining, periventricular rim, frontal WM, optic chiasm, fornix, BG, thalamus, dentate nucleus Give contrast to all unknown cases of hydrocephalus and abnormal WM
53 T1W-C+: Enhancement of the periventricular rim, caudate heads and putamen bilaterally Rabbit ear characteristic of Alexander Nodular appearance of frontal PV rim Alexander Disease
54 FLAIR less severe disease High signal in the anterior and posterior rims and WM with frontal predominance Alexander Disease
55 T1W-C+ - enhancement of bifrontal PV WM, PV rim and caudate head. Less intense patchy enhancement in putamen and thalamus Alexander Disease
56 T2W advanced disease Symmetric, hyperintense cerebral WM and deep gray structures Swollen caudate head and fornices Hyperintensity in external and extreme capsule claustra stands out Alexander Disease
57 Alexander Disease FLAIR large foci of cystic destruction in frontal WM and caudate head These are late findings
58 Canavan Disease Clinical S/S: Macrocephaly, hypotonia Imaging: Diffuse T2 hyperintensity preferentially involves subcortical U fibers Spares internal capsule and corpus callosum Involves thalamus, globus pallidus + dentate Spares caudate and putamen MRS shows marked elevation of NAA peak
59 T2W diffuse cerebral WM hyperintensity. Involvement of subcortical U fibers Canavan Disease
60 T2W 6 month old Diffuse increase signal cerebral WM including thalamus and right globus pallidus Sparing of internal capsule, CC and putamen Canavan Disease
61 T2W: infant Marked hyperintense signal and swelling throughout WM Striatum as island of tissue Canavan Disease
62 Canavan Disease Differential Diagnosis Maple Syrup Urine Disease Elevated branch chain AA Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease Spares GP and thalami Alexander Disease Enhances Predominantly frontal WM
63 Hypomyelination Disorder Areas to assess: internal capsule, pyramidal tracts, peripheral frontal lobe WM T1 signal reflects presence of myelin Children < 10 months Myelinated WM - hyperintense T2 reflects displacement of water Children > 10 months Mature WM - hypointense
64 Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease Clinical S/S: microcephaly, hypertonia, stridor Deficiency of proteolipid protein (PLP) Hypomyelination disorder Imaging Variable Nonspecific and symmetrical abnormality of WM Lack of myelin
65 Pelizaeus-Merzbacher Disease T2W: 13 year old absence of normal hypointense WM signal This is normal for a 6-8 month old child
66 T2W 2 year old Diffuse lack of T2 hypointense myelin in deep WM, corpus callosum and internal capsule Hypomyelination At this age nearly all WM structures should be myelinated (hypointense on T2W.
67 Metachromatic Leukodystrophy Decreased arylsulfatase A Central and peripheral demyelination Imaging Confluent butterfly-shaped increased T2 signal deep cerebral WM Spares U fibers in early disease Involves U fibers in late disease Sparing of perivenular myelin producing the tigroid appearance No enhancement of WM May have enhancement of cranial nerves and cauda equina
68 MLD FLAIR bilateral, symmetric periventricular and deep WM changes sparing U-fibers
69 MLD T2W tigroid appearance of WM Due to preservation of myelin in perivascular regions
70 Krabbe Disease aka Globoid cell leukodystrophy Clinical S/S: irritability Juvenile form: protracted course with slow rate of progression CT: hyperdensity in thalamus, BG MRI Imaging: Faint hyperintensities in thalamus and BG (T1W) Ring like appearance around dentate nucleus (T2W) PV WM hyperintensities (T2W) Initially spares U fibers Enlarged optic nerves and cranial nerves (T1W) MRS: increased choline,myoinositol, decreased NAA, lactate accumulation
71 Krabbe Disease CT Scan Faint hyperdensity in the lateral thalami, from presumed Ca++ deposits CT more sensitive than MR in early course
72 Krabbe Disease FLAIR focal symmetric hyperintensity capsular portion of corticospinal tracts.
73 Krabbe Disease FLAIR juvenile onset symmetric hyperintensity in parietal WM sparing subcortical U fibers
74 Krabbe Disease T2W advanced disease atrophy, hypointensity in BG and Thalami
75 SSPE Nonspecific leukoencephalopathy MRS: decreased NAA/Cr Increased Cho/Cr; Ins/Cr and Lac-Lip
76 Proton Density: Inhomogeneous hyperintensity bilaterally, asymmetric involving WM And cortex Biopsy - SSPE SSPE
77 Gray Matter Metabolic Disorder Leigh Disease 3-methylglutaconic aciduria Biotin dependent encephalopathy Methylmalonic acidemia
78 Leigh Syndrome Progressive neurodegenration Respiratory chain disorder Clinical S/S: psychomotor delay/regression Imaging: Bilateral symmetric increased T2/FLAIR signal Putamen>caudate>GP, periaqueductal gray, SN/STN, dorsal pons, cerebellar nuclei Restrictive diffusion in areas of acute disease MRS: increased lactate; decrease NAA, increase choline
79 Leigh Syndrome DWI reduced diffusion in thalamus T2W subtle thalamic involvement Thalamic involvement may be isolated when patient becomes symptomatic DWI shows abnormality better than T2W
80 Leigh Syndrome T2W hyperintensity in caudate head, putamen, periaqueductal GM Common site of involvement due to ETC complexes I and II
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter. Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
 Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
MALFORMATIONS OF CORTICAL DEVELOPMENT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW
 MALFORMATIONS OF CORTICAL DEVELOPMENT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW Padmaja K. Naidu, M.D. Usha D. Nagaraj, M.D. William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O. AOCR Annual Conference 2018 Scottsdale, Arizona @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad
MALFORMATIONS OF CORTICAL DEVELOPMENT: A PICTORIAL REVIEW Padmaja K. Naidu, M.D. Usha D. Nagaraj, M.D. William T. O Brien, Sr., D.O. AOCR Annual Conference 2018 Scottsdale, Arizona @CincyKidsRad facebook.com/cincykidsrad
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology
 Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology Rajan Patel, MD Director, Pediatric Neuroimaging Assistant Professor, Division of Neuroradiology DISCLOSURE No financial disclosure. LEARNING
Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology Rajan Patel, MD Director, Pediatric Neuroimaging Assistant Professor, Division of Neuroradiology DISCLOSURE No financial disclosure. LEARNING
Imaging in Epilepsy. Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015
 Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Imaging in Epilepsy Nucharin Supakul, MD Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University August 22, 2015 Nothing to disclose Outline Role of Imaging and pitfalls Imaging protocol Case scenarios Clinical & Electrophysiologic
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings.
 Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa,
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa,
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings.
 Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa 1
Malformations of cortical development. Clinical and imaging findings. Poster No.: C-2086 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Alba de Caceres, B. García-Castaño, L. Ibañez, E. Roa 1
3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures:
 3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures: Poster No.: C-1886 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. S. Alaín, E. M. DE LUCAS, J. C. Quintero Rivera, C. Pérez 1 2 3 3 3
3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures: Poster No.: C-1886 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. S. Alaín, E. M. DE LUCAS, J. C. Quintero Rivera, C. Pérez 1 2 3 3 3
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
intracranial anomalies
 Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 84 intracranial anomalies Hydrocephaly Dilatation of ventricular system secondary to an increase in the amount of CSF. Effects of hydrocephalus include flattening
MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy
 MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy Nondumiso Dlamini 1*, Vicci du Plessis 2 1. Department of Radiology, Greys' Hospital, Pietermaritzburg Metropolitan Complex, South
MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy Nondumiso Dlamini 1*, Vicci du Plessis 2 1. Department of Radiology, Greys' Hospital, Pietermaritzburg Metropolitan Complex, South
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
Supplementary Online Content Honein MA, Dawson AL, Petersen E, et al; US Zika Pregnancy Registry Collaboration. Birth Defects Among Fetuses and Infants of US Women With Laboratory Evidence of Possible
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
Nishibayashi et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2013, 7:194 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Infantile-onset Alexander disease in a child with long-term follow-up by serial magnetic
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
MRI OF THE THALAMUS. Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI
 1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD
 Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature
 Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature Agrawal Atul, Dutta Gautam, Singh Daljit, Sachdeva
Romanian Neurosurgery Volume XXXI Number 3 2017 July-September Article Hemimegalencephaly without seizures: report of a case and review of literature Agrawal Atul, Dutta Gautam, Singh Daljit, Sachdeva
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, Dr. Peter Ostrow
 Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Development of the Nervous System. Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria
 Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Genetic test for Bilateral frontoparietal polymicrogyria Daniela Pilz, Cardiff UKGTN Genetic testing for neurological conditions; London February 26 th 2013 Region-specific Polymicrogyria (PMG) bilateral
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
myelin in the CNS Multiple axons are oligodendrocyte
 Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology
 General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Gross Organization I The Brain. Reading: BCP Chapter 7
 Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Gross Organization I The Brain Reading: BCP Chapter 7 Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Located inside of bone Includes the brain (in the skull) and the spinal cord (in the backbone)
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Fetal CNS MRI. Daniela Prayer. Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology. Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA
 Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Fetal CNS MRI Daniela Prayer Division of Neuroradiology And Musculoskeletal Radiology Medical University of Vienna, AUSTRIA Methods Normal development Malformations Acquired pathology MR- methods for assessment
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN. Scalp, Skull. Anatomically Based Differentials. Skull Normal Variants. Scalp Mass, Child.
 Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics. Disclosures. Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor 4/14/2017
 Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18
 IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Publication for the Philips MRI Community Issue 46 2012/2 High spatial resolution reveals excellent detail in pediatric neuro imaging Achieva 3.0T with 32-channel SENSE Head coil has become the system
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Cortical malformations and epilepsy: role of MR imaging
 Cortical malformations and epilepsy: role of MR imaging Poster No.: C-0921 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Jerbi, O. Bradai, S. Haj Slimene, Y. Abdelhafidh, H. HAMZA; Mahdia/TN
Cortical malformations and epilepsy: role of MR imaging Poster No.: C-0921 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Jerbi, O. Bradai, S. Haj Slimene, Y. Abdelhafidh, H. HAMZA; Mahdia/TN
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere)
 Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Telencephalon (Cerebral Hemisphere) OUTLINE The Cortex - Lobes, Sulci & Gyri - Functional Subdivisions - Limbic Lobe & Limbic System The Subcortex - Basal Ganglia - White Matter (Internal Capsule) - Relations
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome
 A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center. Wednesday, 16 March 2009, 1:00p.m. 2:00p.m.
 Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
Normal CNS, Special Senses, Head and Neck TOPIC: CEREBRAL HEMISPHERES FACULTY: LECTURE: READING: P. Hitchcock, Ph.D. Department of Cell and Developmental Biology Kellogg Eye Center Wednesday, 16 March
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH
 RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
RING ENCHANCING LESION BY M.S. HEMHNATH A 21 YRS FEMALE CAME WITH H/O HEADACHE AND SEIZURE FOR THE PAST ONE MONTH. NO OTHER FOCAL NEUROLOGICAL DEFICIT. DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS For this case are Neurocysticerosis
Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) CNS Anomalies
 82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
82 Symposium: OB/GY US (Room B) 11 : 50 1 2 : 10 CNS Anomalies Brain area Midline structure S u p r a t e n t o r i a l ventricular system Cerebral hemisphere Posterior fossa Head size and shape Image
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
BIOL Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain
 BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound
 Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
Prenatal Prediction of The Neurologically Impaired Neonate By Ultrasound Robert H. Debbs, D.O.,F.A.C.O.O.G. Professor of OB-GYN Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Director, Pennsylvania
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
LIMBIC SYSTEM. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
LIMBIC SYSTEM Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy Learning Objectives Define the limbic system Identify the parts of the limbic system Describe the circulation of the limbic system
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES)
 AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
AAP ZIKA ECHO (EXTENSION FOR COMMUNITY HEALTHCARE OUTCOMES) HOUSEKEEPING ITEMS For educational and quality improvement purposes, this ECHO session will be recorded Project ECHO collects participation data
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA)
 DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
DEFICIENCY OF METABOLITE -HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA -HYPOVITAMINOSIS SELECTIVE VULNERABILITY (HYPOXIA AND HYPOGLYCEMIA) -SPECIFIC CELL TYPE NEURONS>OLIGODENDROCYTES>ASTROCYTES -SPECIFIC BRAIN REGION PYRAMIDAL
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP:
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP BRAIN LAB GROUP: Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the three dimensional structure of the brain and teach you
Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients
 Original Research Article Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients Kataria Sushma K 1, Gurjar Anoop S 2,*, Parakh Manish 3, Gurjar Manisha 4, Parakh
Original Research Article Neuro-Anatomical Study of a Rare Brain Malformation: Lissencephaly, A Report of Eleven Patients Kataria Sushma K 1, Gurjar Anoop S 2,*, Parakh Manish 3, Gurjar Manisha 4, Parakh
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
EGI Clinical Data Collection Form Cover Page
 EGI Clinical Data Collection Form Cover Page Please find enclosed the EGI Clinical Data Form for my patient. This form was completed by: On (date): _ Page 1 of 14 EGI Clinical Data Form Patient Name: Date
EGI Clinical Data Collection Form Cover Page Please find enclosed the EGI Clinical Data Form for my patient. This form was completed by: On (date): _ Page 1 of 14 EGI Clinical Data Form Patient Name: Date
1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Best Cases from the AFIP
 AFIP ARCHIVES 843 Editor s Note. Everyone who has taken the course in radiologic pathology at the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) remembers bringing beautifully illustrated cases for accession
AFIP ARCHIVES 843 Editor s Note. Everyone who has taken the course in radiologic pathology at the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) remembers bringing beautifully illustrated cases for accession
Fetal Medicine. Case Presentations. Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital. October 2003
 Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
Case Presentations Dr Ermos Nicolaou Fetal Medicine Unit Chris Hani Baragwanath Hospital October 2003 Case 1 Ms A M 22year old P0 G1 Referred from Sebokeng Hospital at 36w for polyhydramnios On Ultrasound:
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
Magnetic resonance imaging findings and Spectrum of Etiologies in children epilepsy
 Magnetic resonance imaging findings and Spectrum of Etiologies in children epilepsy Poster No.: C-2262 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Alami, L. Tazi, Z. Traoré, M. Y. Alaoui Lamrani,
Magnetic resonance imaging findings and Spectrum of Etiologies in children epilepsy Poster No.: C-2262 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. Alami, L. Tazi, Z. Traoré, M. Y. Alaoui Lamrani,
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain
 An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Disease of Myelin. Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 9, 2019
 Disease of Myelin Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 9, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES TO DECLARE. I HAVE NO
Disease of Myelin Reid R. Heffner, MD Distinguished Teaching Professor Emeritus Department of Pathology and Anatomy January 9, 2019 1 I HAVE NO CONFLICTS OF INTEREST OR DISCLOSURES TO DECLARE. I HAVE NO
BASAL GANGLIA. Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY
 BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
BASAL GANGLIA Dr JAMILA EL MEDANY OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Define basal ganglia and enumerate its components. Enumerate parts of Corpus Striatum and their important
Encephalitis. HSV Encephalitis. Encephalitis. Viral CNS Infection. WNV Encephalitis GRAY MATTER. Zoran Rumboldt
 Encephalitis Viral CNS Infection Hematogenous dissemination ( along peripheral nerves ) Zoran Rumboldt University of Rijeka Medical University of South Carolina Telemedicine Clinic MarinMed Clinic Many
Encephalitis Viral CNS Infection Hematogenous dissemination ( along peripheral nerves ) Zoran Rumboldt University of Rijeka Medical University of South Carolina Telemedicine Clinic MarinMed Clinic Many
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
Posterior fossa malformations
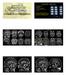 ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Hamartomas and epilepsy: clinical and imaging characteristics
 Seizure 2003; 12: 307 311 doi:10.1016/s1059 1311(02)00272-8 Hamartomas and epilepsy: clinical and imaging characteristics B. DIEHL, R. PRAYSON, I. NAJM & P. RUGGIERI Departments of Neurology, Pathology
Seizure 2003; 12: 307 311 doi:10.1016/s1059 1311(02)00272-8 Hamartomas and epilepsy: clinical and imaging characteristics B. DIEHL, R. PRAYSON, I. NAJM & P. RUGGIERI Departments of Neurology, Pathology
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings
 Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
Developmental Posterior Fossa Abnormalities with Associated Supratentorial Findings Seattle Children s Hospital Christopher J Hurt, MD Gisele E Ishak, MD Dennis W Shaw, MD Introduction Barkovich has classified
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
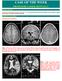 CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CLINICAL PICTURE: A 6 years old male patient presented clinically with intractable complex partial seizure. The child is mentally
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE: CLINICAL PICTURE: A 6 years old male patient presented clinically with intractable complex partial seizure. The child is mentally
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex
 Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
Pathologies of postchiasmatic visual pathways and visual cortex Optic radiation: anatomy Pathologies of the postchiamsatic visual pathways and visual cortex Characterized by homonymous hemianopsia. This
Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
Leah Militello, class of 2018 Objectives 1. Describe the general organization of cerebral hemispheres. 2. Describe the locations and features of the different functional areas of cortex. 3. Understand
Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Dean Shibata, M.D. Department of Radiology, University of Washington. White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease.
 White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease UW Radiology Review 2015 Dean Shibata, M.D Neuroradiology Department of Radiology, University of Washington MS (Multiple Sclerosis) ADEM (Acute Disseminated
White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease UW Radiology Review 2015 Dean Shibata, M.D Neuroradiology Department of Radiology, University of Washington MS (Multiple Sclerosis) ADEM (Acute Disseminated
