The Arab Board of Health Specializations Radiology And Medical Imaging Council
|
|
|
- Gilbert Greene
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 جامعة الدول العربیة مجلس وزراء الصحة العرب المجلس العربي للاختصاصات الصحیة The Arab Board of Health Specializations Radiology And Medical Imaging Council Subspecialty Fellowship Programme Arab Board Fellowship of Neuroradiology and Head & Neck Imaging 1
2 Introduction: The overall intent of the programme is to provide trainees with specific knowledge& skills of clinicalutility, interpretation, and standards of performance of neuroimaging studies.. The goals of the Neuroimaging Fellowship are to provide the trainee with the opportunity to developdiagnostic, procedural, and technical skills essential to the performance of neuroimaging, including: 1. To gain knowledge in the technical aspects of imaging 2. To gain clinical experience in interpretation of images 3. To achieve competence allowing independent performance of the specialty of neuroradiology & head & neck imaging Requirements of Institute of Training&Required Personnel: The training centre/s must be approved for training by the ArabBoard A Fellowship Director must be identified/appointed by the training institution. S/he must be a consultant radiologist with appropriate expertise in neuroimaging and with appropriate academic background Facilities: The major imaging modalities include computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT), positron emission tomography (PET), ultrasound, conventional X-ray and contrast studies and selected angiographic & neurointerventional procedures. CTA, MRA, functional imaging & spectroscopy are required PACS. Appropriate number of supervisors relative to trainees. Ideally at least two consultants should be available in the training unit. Ratio: One consultant: One trainee Volume needed for training: To obtain the appropriate breadth of exposure to the full spectrum of diseases in a specific subspecialty,in both inpatient and outpatient settings. Facilities should have asufficient volume and variety of patient material to provide training. To obtain practical experience, the suggested minimum number of studies performed and interpreted under supervision in fellowship settings will be set. A teaching file of representative cases in each modality, with case histories and images, should be available to the trainee, either from the training institution itself or on electronic media. Training should include daily interpretation sessions and clinical case discussions. Eligibility Criteria for training: The applicant Must have successfully completed The Arab Board of Radiology & Medical Imaging ( eligibility of graduates of other schemes will be re-evaluated in two years after the start of the subspecialty programme) Is licensed to practice medicine in the country/ies of training Must have completed one year of radiology practice Provide written permission from the sponsoring body allowing him/her to undertake full time training for the full one/two year programme Provides two letters of recommendation from the institute where he last worked Registers as a trainee with the Arab Board for Health Specialties 2
3 Application for Certification in Neuroradiology & Head & Neck Imaging Programme in Radiology& Medical Imaging: All applications must be completed online, and all supporting documentation must be uploaded through the online application system where requested. Fees paid. Timetable for Training: The programme is offered over two years Training guidelines and the curriculum are specified below Examination Process: The examination is held once a year in October Examination format : One hour oral examination by a panel of experts. The candidate has three chances of passing the exam Setup for the Training: Formal rotations are highly desirable where the trainee spendsdefined periods dedicated to a specific modality & which should be arranged by the fellowship director. Methods of Training: Lectures Individual interpretation session of representative cases (a teaching file). Daily self-studies of course materials and reference textbooks or papers (acquiring knowledge of basic principles, applied anatomy, pathophysiology, diagnostic criteria, and clinical applications). Daily interpretation sessions Weekly conferences with faculty (discussion of current cases, Q&A, differential diagnosis). Individual skill assessment (performing a procedure under direct supervision). Methods of Evaluation of Trainees: 1. On-going evaluation: (under the supervision of the fellowship director) Performance and interpretation skills assessment by the training personnel (daily or weekly). Interpretation skills assessment using case reviews (weekly or monthly). The trainee s professionalism, attitude to work, team work, responsibility and adherence to ethical principles in medical practice will be included in the assessment 2. Final evaluation of proficiency in interpretation (Arab Board certification examination): Individual consultants should provide written evaluation of trainees who have completed formal rotations in musculoskeletal imaging.the evaluations will be collected and endorsed by the fellowship director After finishing training, the trainee should pass the exit examination Evaluation forms required for a CME activity filled out by the trainee upon course completion. Methods of Upgrading Knowledge/CME: During the training course, trainees are required to perform self- studies of selected textbooks and papers, and participate in weekly discussions with faculty of current cases. Trainees are expected to participate in research and audit. The trainee is expected to present 10 full case conferences/lectures during each year of training. S/he is required to demonstrate ability to instruct and teach junior colleagues and medical students The trainee is expected to be cognizant of radiation protection guidelines and practice 3
4 Upon completion of the coursetrainees are expected to prepare for the Arab Board certification examination. Leave/ Vacation: The trainee is entitled to three weeks of annual leave per year One week of educational leave is available per year to attend courses/scientific meetings Core curriculum: 1. MRI/CT: A. Technical aspects of MRI/CT: X-ray production Collimation Interaction of X-ray in tissue Electricity and nuclear magnetism Radiofrequency pulse sequences MRI signals and parameters Fourier transforms MRI and CT hardware and safety Conventional spin-echo technique Gradient-echo technique Fast spin-echo and fast imaging Echo planar imaging MRA MRI and CT Contrast agents MRI and CT artifacts CTA CT perfusion MR spectroscopy Diffusion and perfusion MRI B. Clinical aspects of MRI/CT neuroimaging: I: Brain Imaging 1. Primary Tumors/Masses/Cysts Astro-Glial (Glioma) Astrocytoma Choroid plexus papilloma Ependymoma/Subependymoma Glioblastoma multiforme Gliomatosiscerebri Oligodendroglioma Germ Cell Germinoma Teratoma Maldevelopmental Craniopharyngioma Lipoma Meningeal Meningioma Mesenchymal and Lymphoreticular 4
5 Hemangioblastoma Hemangiopericytoma Lymphoma Neuronal Origin Ganglioglioma Hamartoma Neurocytoma PNET Esthesioneuroblastoma Medulloblastoma Peripheral Nervous System Neurofibroma Schwannoma (neuroma) Regional Neoplasms Pineoblastoma Pineocytoma Pituitary adenoma Non-neoplastic Cysts Arachnoid (leptomeningeal) cyst Colloid cyst Dermoid Epidermoid Neuroepithelial (neuroglial) cyst Pineal cyst Rathke s cleft Spinal tumors Intramedullary Extramedullary/intradural Extramedullary/extradural 2. Cerebrovascular Diseases Infarction Thromboembolism Watershed Infarction Lacunar syndromes Venous thrombosis Arterial Dissection MR Angiography Advanced MRI Techniques Paraventricular and Subcortical White Matter Disease 3. Vascular Lesions/Malformations Aneurysms Saccular, Giant Dolichoectasia Vascular malformations Arterioveno us malformation Cavernous Angioma Capillary Telangiectasia Venous Angioma 4. Infectious/Granulomatous Diseases Pyogenic/Bacterial 5
6 Viral Fungal Parasitic Sarcoidosis Prion-associated Myelitis 5. Hemorrhage/Trauma Intraparenchymal Hemorrhage Subdural Hemorrhage Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Intratumoral and Secondary Hemorrhage Cerebral contusions/traumatic Brain injury Spinal Hemorrhage/Spinal Trauma 6. Toxic/Metabolic Diseases Chemotherapeutic/Immunosuppressive agents Ethanol-related: Degeneration/atrophy Wernicke s encephalopathy Hallervorden-Spatz disease Hepatic failure Mitochondrial disorders Radiation injury Toxin exposure Wilson s disease 7. Degenerative Diseases Aging Alzheimer s disease Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Friedreich s ataxia Huntington s disease Parkinsonian states Pick s disease Wallerian degeneration Spinal degenerative diseases Disc herniation Spinal stenosis 8. Seizures/Epilepsy Mesial Temporal Lobe Sclerosis 9. Hydrocephalus/CSF Disorders Benign Intracranial Hypertension Hydrocephalus Noncommunicating Communicating Intracranial Hypotension 10. Neurocutaneous Syndromes Neurofibromatosis Sturge-Weber Syndrome 6
7 Tuberous sclerosis VonHippel-Lindau and Hemangioblastomas 11. Demyelinating/Inflammatory Diseases Multiple Sclerosis Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis Central Pontine Myelinolysis Myelitis 12. Metastatic Diseases Brain/spinal parenchymal metastases. Calvarial and meningeal metastases Extra-axial spinal metastases 13. Congenital Anomalies/Developmental Disorders Brain malformations Spinal cord and spinal canal malformations 14. Miscellaneous Normal tomographic imaging anatomy of head and spine Imaging of head and neck diseases relevant to neurology Brain death II. HEAD AND NECK RADIOLOGY A) Paranasal Sinuses 1)Anatomy of paranasal sinuses 2)Congenital disease Dermal sinus tract Encephalocele Choanal atresia Dacrocystocele Nasal glioma (dehiscence of anterior skull base) 3) Inflammation/Infection Acute sinusitis Chronic sinusitis - (Allergic, Fungal, Granulomatous) Polyposis Mucocele 4) Benign Sinus Tumors Osteoma Antrochoanal polyp Juvenile angiofibromainverted Papilloma Schwannoma HemangiomaMeningioma 5) Malignant Sinus Tumors Squamous cell carcinoma Esthesioneuroblastoma Adenocarcinoma Lymphoma Metastases Minor Salivary gland tumors Rhbdomyosarcoma Lethal midline granuloma B. Oral Cavity, Oropharynx, Hypopharynx 1)Anatomy, contents 2)Masses Squamous cell carcinoma Dermoid/Epidermoid Lingual thyroid Thyroglossal duct cyst 7
8 Ranula Hemangioma 3)Infection Cellulitis, tonsillitis, abscess (Ludwig s angina) Ranula C. Paraphayngeal Space 1)Location, contents, anatomy and importance in relation to other spaces 2)Pharyngeal Mucosal Space (Anatomy, contents) Infection (tonsilar abscess, adenitis) Pleomorphic adenoma (minor salivary glands) Squamous cell CA Non-Hodgkin s lymphoma Thornwaldt cyst Hemangioma 3)Masticator Space (Anatomy, contents) Tumors (mesenchymal) Infection 4)Parotid Space (Anatomy, contents) 1st Brachial cleft cyst Infection Sialadenitis Sialodochitis, ductal stricture, stone Lymphoepithelial lesions Sjogren s Pleomorphic adenoma Warthin s tumors Mucoepidermoid carcinoma Adenoid cystic carcinoma Metastases Lymphoma 5) Carotid Space (Anatomy, contents) Aneurysm Paragangliomas (Glomus tumors) Schwannoma Neurofibroma Nodal Metastases 2) Retropharyngeal Space (Anatomy, contents) Neoplastic and reactive lymph nodes Infection ( Danger space ) 6) Perineural spread D. Larynx 1) Squamous cell carcinomas Staging Supraglottic, glottic, subglottic Treatment effects (surgery and radiation) Airway obstruction 2)Trauma (laryngeal fractures) E. Thyroid 1) Masses Multinodular goiter Adenoma Cyst Carcinoma 8
9 F. Cystic Neck Masses 1)Second brachial cleft cyst 2)Thyroglossal duct cyst 3)Cystic hygroma 4)Laryngocele, internal, external 3)Abscess 4)Ranula 5)Dermoid/Epidermoid G. Lymphadenopathy 1)Graded by level and/or anatomic space. 2)Size criteria for pathologic nodes 3)Etiology HIV Lymphoma Metastases (aerodigestive carcinoma) Cat scratch fever Atypical mycobacterium Mononucleosis Castleman s disease H. Temporal bones 1)Imaging Techniques (Multi-planar CT/MR) 2)Anatomy/Embryology 3)Trauma Transverse and longitudinal fractures CSF leaks, brain herniation 4) Tumors Schwannoma Vestibular (8th) (common) Facial (7th) and trigeminal (5th) Meningioma Lipoma Dermoid/Epidermoid Metastases 5) Pulsatile Tinnitus Glomus tympanicum High riding/dehiscent jugular bulb Ectopic carotid, persistent stapedial artery AVM, AV fistula Venous tinnitus Atherosclerotic disease Dissection FMD 6) Inflammatory Diseases Otitis media Mastoiditis Cholesteatoma (acquired or congenital) Malignant external otitis Cholesterol granuloma Hemorrhage or inflammation cochlea, vestibule (labrynthitis) 7)Congenital anomalies Cochlear hypoplasia/aplasia, Mondini External ear atresia/hypoplasia (ossicular anomalies) 9
10 Enlarged vestibular/cochlea aqueducts Cochlear/vestibular aplasias-hypoplasias Internal Auditory Canal anomalies I.Mandible 1)infection 2)Trauma 3)Cystic lesions 4)Benigntumours 5)Malignanttumours III. Orbits 1)Imaging Techniques 2)Anatomy/Embryology Lesion localization based on relationship to muscle cone 3) Lacrimal Gland Tumors Epithelial Pleomorphic adenomas Carcinomas Lymphoma Dermoid Metastases 4)Extra-conal Masses Orbital wall or sinus neoplasms with extension Subperiosteal abscess/orbital cellulitis from sinusitis/osteomyelitis Metastases Lymphoma/Leukemia/Myeloma Lymphangioma/Hemangioma Rhabdomyosarcoma Histiocytosis Pseudotumor and granulomatous disease Hematoma 5) Extra-ocular Muscles (Conal) Grave s Disease Orbital myositis (Pseudotumor) Granulomatous disease Lymphoma/Leukemia Metastases Carotid cavernous fistula 6) Intra-conal lesions Related to optic nerve Glioma Meningioma Optic neuritis Increased intracranial pressure Pseudotumor Grave s disease Meningeal carcinomatosis Leukemia Separate from optic nerve (well defined) Cavernous angioma, capillary angioma Varix Neurofibroma/Schwannoma Meningioma Pseudotumor Lymphoma Separate from optic nerve (ill defined infiltrative) Infection Metastases Pseudotumor 7) Intra-ocular 10
11 Adult Melanoma Metastases Drusen Child Retinoblastoma Retrolental fibroplasia Coat s disease Primary Hypertrophic Persistent Vitreous (PHPV) Any age Metastases Retinal detachment Infection and inflammation (endopthalmitis), AIDS Phthsis bulbi 8)Trauma Fractures of the orbital wall Extra-ocular muscle entrapment Orbital emphysema Intra-orbital hematoma Penetrating soft tissue injuries Laceration of the optic nerve or muscles Ocular - Ruptured globe, intra-ocular hemorrhage, dislocated lens Foreign Body IV. Spinal Imaging A. Anatomy and Biomechanics 1.Vertebral bodies 2.Facet joints and transverse processes 3.Lamina and spinous processes 4.Support ligaments 5.Specific characteristics of cervical, thoracic, and lumbar segments 6.Cranio-vertebral and lumbo-sacral junctions 7.Normal stability and motion B. Imaging Modalities 1) Role and relative merit of non-invasive imaging studies. Plain radiography, CT, MR, nuclear medicine, PET imaging 1)Role of invasive procedures Myelography (including CT) angiography, biopsies, facet injections, nerve root blocks, discography C. Trauma 1) Mechanism of injury Flexion Extension Axial loading Compression Distraction Rotation 2) Stable fractures and ligamentous injuries Compression fracture Isolated anterior column Isolated posterior column Unilateral locked facet Hyperextension, teardrop Clay Shoveler s (Spinous process C7) 3) Unstable injuries (Involvement of the middle column and ligaments) Hyperflexionteardrop Facet joint disruption and dislocation (bilateral locked facets) Hyperflexionligamentous injury without fracture Odontoid fracture Distraction fracture (Hangman s) (C2/C3) Chance Burst 11
12 4)Traumatic disc herniation 5)Extrinsic cord compression 6)Cord contusion 7)Intra-spinal hemorrhage Epidural hematoma (EDH) Subdural hematoma (SDH) SAH Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) Cord hematoma (hematomyelia) 8) Post-traumatic abnormalities Instability with spondylolithesis Syringomyelia Arachnoiditis Pseudomeningocele and root avulsion D. Degenerative disease 1)Epidemiology 2)Disc degeneration 3)End plate degeneration 4)Disc herniation distributionimaging findings 5) Spinal stenosisdistribution Imaging findings 6) Post-operative changes Epidural scar Arachnoiditis Recurrent herniation or stenosis E. Inflammatory and Demyelinating Disease 1)Discitis/osteomyelitis Acute (Spontaneous and Post-operative) Epidural and paravertebral abscess Chronic low grade discitis 2)Vertebral body Tuberculosis (Potts Disease) 3)Meningitis (Arachnoiditis) TB, Sarcoid, CMV, AIDS 4) Spinal cord lesions Abscess, granuloma Transverse myelitis Multiple Sclerosis ADEM F. Neoplastic Disease 1)Osseous Primary tumors - Benign Hemangioma Osteoid Osteoma/Osteoblastoma Chondroid tumors Giant Cell Aneurysmal Bone Cyst (ABC) Chordoma Primary tumors Malignant Osteoid Chondroid Metastases Lymphoma Myeloma Leukemia 2) Extradural Neurofibroma Lymphoma Metastases 3) Intradural extramedullary Meningioma Schwannoma Neurofibroma Dermoid Lipoma Epidermoid 12
13 Epidermal inclusion Cyst Metastases (Carcinomatous Meningitis) Lymphoma 4) Intramedullary Ependymoma Astrocytoma Hemangioblastoma Metastases Lymphoma G. Cystic lesions 1) Extradural Meningocele Pseudo-meningocele (post-operative and post-traumatic) Root sleeve cysts (Tarlov) and terminal Meningocele 2)Intradural extramedullary Arachnoid cyst Post inflammatory and post hemorrhagic arachnoiditis 3)Intramedullary Syringomyelia/Hydromyelia Chiari malformation, post traumatic, post infectious, neoplastic H. Vascular lesions 1)Dural venous fistula 2)AVM 3)Cavernous Angioma 4)Spinal cord infarct I. Developmental Spine Disease 1)Normal embryological development of spine 2)Open dysraphisms 3)Myelomeningocele 4)Lipomyelomeningocele (tethered cord) 5)Myelocele 6)Diastemometamyelia 7)Occult spinal dysraphisms 8)Tight filum, thick filum 9)Intradural lipoma 10)Dorsal dermal sinus 2. NUCLEAR NEUROLOGY (SPECT/PET): A. Technical aspects of nuclear neurology: Physics and instrumentation Radiation Biology Radiation Dosimetry Radiation Safety Mathematics and Statistics Radionuclide Chemistry and Radiopharmacy Image Generation and Display SPECT Principles PET Principles B. Clinical aspects of nuclear neurology: 13
14 1. Tumors/Masses/Cysts Grading of primary and metastatic neoplasms Differentiation of radiation injury from tumor recurrence 2. Cerebrovascular Diseases Assessment of cerebrovascular reserve Diagnosis of ischemia and infarction Determination of stroke subtypes Vasospasm following SAH Prognosis/recovery from stroke 3. Infectious/Granulomatous Diseases Differentiation of abscess versus neoplasm Diagnosis of viral encephalitis 4. Hemorrhage/Trauma Altered brain metabolism or blood flow in posttraumatic encephalopathy 5. Toxic/Metabolic Diseases Cerebral radiation injury versus recurrent neoplasm 6. Degenerative Diseases/Aging Aging Alzheimer s disease Huntington s disease Parkinsonian states Pick s disease 7. Seizures/Epilepsy Ictal localization Interictal localization Mesial temporal sclerosis 8. Hydrocephalus/CSF Disorders Brain metabolism/perfusion pattern in hydrocephalic states including NPH Use of cisternography to diagnose hydrocephalus and CSF leakage 9. Psychiatric Disorders Mood disorders Schizophrenia Obsessive-compulsive disorders 10. Miscellaneous Normal anatomy and physiology Ligand tracer studies Brain death 3. NEUROSONOLOGY (CAROTID DOPPLER/TCD): 1. Basic principles of Doppler physics 2. Continuous wave (CW) Doppler principles 3. Pulsed wave (PW) Doppler principles 4. Physical principles of brightness-modulated (B-mode) real time ultrasound imaging 5. Principles of color Doppler imaging 14
15 6. Principles of color velocity imaging 7. Basic principles of emboli detection 8. Ultrasound artifacts 9. Ultrasound equipment/hardware 10. Ultrasound bioeffects and safety 11. Cerebrovascular hemodynamics and anatomy 12. Pulsed Doppler techniques 13. Spectral analysis 14. Pulsed Doppler interpretation principles 15. Clinical applications of duplex sonography 16. Plaque morphology 17. Duplex sonography interpretation/criteria 18. Color flow imaging techniques 19. Color flow clinical applications 20. Interpretation extracranial and transcranial color flow studies 21. Power Doppler techniques 22. Power Doppler applications 23. Techniques of adult transcranial Doppler 24. Techniques of transcranial Doppler in children with sickle cell disease 25. Interpretation of transcranial Doppler 26. Applications of transcranial Doppler 4. ANGIOGRAPHY: Clinical Aspects: 1. General Aspects of Angiography a. Principles of Angiography Interpretation b. Normal Arterial Anatomy c. Normal Venous Anatomy d. Congenital Anatomic Variants e. Congenital Anomalies 2. Cerebrovascular Disorders a. Occlusive Pathology b. Defining Degree of Stenosis c. Emergency Angiography of Ischemic Stroke d. Atherosclerotic vs. Non-Atherosclerotic Pathology e. Traumatic Injuries and Dissection f. Fibromuscular Dysplasia g. Moya-Moya h. Cerebral Aneurysms i. Cerebral Vasospasm j. Arteriovenous Malformations k. Venous Angiomas 3. Neoplastic Conditions a. Typical Angiographic Findings in Brain Tumors b. Vascularity of Brain Tumors 4. Inflammatory Conditions a. Cerebral Vasculitis b. Meningeal Infections List of References/Resources for Neuroradiology/Head & Neck Subspecialty: Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical and Biological Principles. 4 th Edition.Stewart C Bushong& Geoffrey Clarke.Elsevier
16 Advanced MR Imaging Techniques. William G Bradley & Graeme M Bydder GM, eds. St. Louis: Mosby, 1997 MRI in Practice. 4 th Edition. Catherine Westbrook, Carolyn Kaut Roth & John Talbot. Wiley Blackwell, 2011 Neuroimaging. William W Orrison.WB Saunders, Philadelphia, 2000, Osborn s brain. Anne G Osborn, Amirsys, 2012 Diagnostic & Surgical Imaging anatomy : Brain, Head & Neck, Spine. Ann G Osborn & H RicHarnsberger. Amirsys, 2006 Diagnostic Imaging : Brain. Anne G Osborn, Karen L Salzman& A James Barkovich, Amirsys, 2010 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of CNS Disease: A Teaching File.2 nd Edition. Douglas H Yock.PA Saunders, 2002 Physics in Nuclear Medicine, 4th Edition, Simon R Cherry, James Sorenson & Michael E Phelps. Elsevier, 2012 Principles and Practice of Nuclear Medicine, 2nd Edition,Oaul J Early & D Bruce Sodee, Positron Emission Tomography : Clinical Practice. Peter E Valk Ed.. Springer, 2006 Neurosonology& Neuroimaging of Stroke. Jose M Valdueza, Stephan J Schreiber, jens-eric Roehl & Randolph Klingbiel. Thieme, 2008 Cerebrovascular Ultrasound in Stroke Prevention and Treatment. 2 nd Edition. Andrei V Alexandrov Ed. Wiley-Blackwell, Interventional Neuroradiology: Strategies and Practical Techniques. J J Connors & Joan C Wojak.WBSaunders, 1999 Practical Neuroangiography. 3 rd Edition. P Pearse Morris. Wolters Kluwer Lippincott Williams and Wilkins Handbook of Cerebrovascular Disease and NeurointerventionalTechniques. 2 nd Edition. Mark R Harrigan& John P Deveikis. Humana Press,2013 Qualification Degree: Arab Board Fellowship in Neuroradiology & Head and Neck Imaging
Neuroimaging Core Curriculum
 Neuroimaging Core Curriculum Program Content The purpose of the training program is to prepare the physician for the independent practice of neuroimaging. Neuroimaging is the subspecialty of Neurology
Neuroimaging Core Curriculum Program Content The purpose of the training program is to prepare the physician for the independent practice of neuroimaging. Neuroimaging is the subspecialty of Neurology
DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY ROTATION #2
 DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY ROTATION #2 Typical Day The morning is spent with Dr. Jim Wood at the VAMC. The afternoon is spent with the Methodist Neuroradiologist as listed on the MRPC work schedule. In
DIAGNOSTIC NEURORADIOLOGY ROTATION #2 Typical Day The morning is spent with Dr. Jim Wood at the VAMC. The afternoon is spent with the Methodist Neuroradiologist as listed on the MRPC work schedule. In
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine. John J. McCormick MD
 Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
NEURORADIOLOGY. Part III. Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part III Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders inflammatory processes
NEURORADIOLOGY Part III Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders inflammatory processes
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies
 Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
Clinician s Guide To Ordering NeuroImaging Studies MRI CT South Jersey Radiology Associates The purpose of this general guide is to assist you in choosing the appropriate imaging test to best help your
NEURORADIOLOGY EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM for Radiology Residents NEURORADIOLOGY CORE CURRICULUM
 NEURORADIOLOGY EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM for Radiology Residents NEURORADIOLOGY CORE CURRICULUM Each topic to cover relevant anatomy, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, imaging strategies, differential diagnosis,
NEURORADIOLOGY EDUCATIONAL PROGRAM for Radiology Residents NEURORADIOLOGY CORE CURRICULUM Each topic to cover relevant anatomy, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, imaging strategies, differential diagnosis,
Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Neuroradiology Subspecialty Exam Study Guide
 Neuroradiology Subspecialty Exam Study Guide The exam will consist of three equal parts; Brain, Spine and Head & Neck. Pediatric cases are included within each exam section. Each section will consist of
Neuroradiology Subspecialty Exam Study Guide The exam will consist of three equal parts; Brain, Spine and Head & Neck. Pediatric cases are included within each exam section. Each section will consist of
Patients Treated with Leksell Gamma Knife
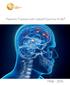 Patients Treated with Leksell Gamma Knife 1968-2016 TREATMENTS REPORTED 2016 BY REGION AND INDICATION INDICATION Asia excl. Europe Latin Middle East & Africa North Grand Total Benign Tumors 12283 9778
Patients Treated with Leksell Gamma Knife 1968-2016 TREATMENTS REPORTED 2016 BY REGION AND INDICATION INDICATION Asia excl. Europe Latin Middle East & Africa North Grand Total Benign Tumors 12283 9778
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY SPINE FELLOWSHIP CORE CURRICULUM
 AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY SPINE FELLOWSHIP CORE CURRICULUM Introduction Spine conditions affect virtually everyone at some time during their life. Surveys indicate a yearly prevalence of spine-related
AMERICAN ACADEMY OF NEUROLOGY SPINE FELLOWSHIP CORE CURRICULUM Introduction Spine conditions affect virtually everyone at some time during their life. Surveys indicate a yearly prevalence of spine-related
Neuroimaging. spine / spinal cord
 Neuroimaging spine / spinal cord Spine & spinal cord imaging methodology Plain x-ray of spine Computed tomography CT - traditional ( normal CT) - reconstructions - myelo-ct Magnetic resonance MR - standard
Neuroimaging spine / spinal cord Spine & spinal cord imaging methodology Plain x-ray of spine Computed tomography CT - traditional ( normal CT) - reconstructions - myelo-ct Magnetic resonance MR - standard
1. GOAL 2. OBJECTIVES a) KNOWLEDGE b) SKILLS c) INTEGRATION
 1. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Otorhinolaryngology is that the undergraduate student have acquired adequate knowledge and skills for optimally dealing with common disorders
1. GOAL The broad goal of the teaching of undergraduate students in Otorhinolaryngology is that the undergraduate student have acquired adequate knowledge and skills for optimally dealing with common disorders
PA SYLLABUS. Syllabus for students of the FACULTY OF MEDICINE No.2
 Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Approved At the meeting of the Faculty Council Medicine No. of Approved At the meeting of the chair of Neurosurgery No. of Dean of the Faculty Medicine No.2 PhD, associate professor M. Betiu Head of the
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Spinal Neoplasms. First Things First!! Localize the Lesion!! Ependymomas. Common Intramedullary Lesions
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXIII, nº 90, pág. 101-114, Abr.-Jun., 2011 Spinal Neoplasms Bruno A Policeni University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Assistant Professor of Radiology Disclosure of Commercial
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXIII, nº 90, pág. 101-114, Abr.-Jun., 2011 Spinal Neoplasms Bruno A Policeni University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Assistant Professor of Radiology Disclosure of Commercial
A Journey Down The Canal
 A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
Index ... Moedder et al., Direct Diagnosis in Radiology. Head and Neck Imaging (ISBN ), 2008 Georg Thieme Verlag KG
 A abscess vs. branchial cleft cyst 204 cervical 214 216 vs. cervical hematoma 207 cervical prevertebral 138 140 epidural, intraoral 159 161 paralaryngeal, vs. laryngeal edema 134 parapharyngeal 115 117
A abscess vs. branchial cleft cyst 204 cervical 214 216 vs. cervical hematoma 207 cervical prevertebral 138 140 epidural, intraoral 159 161 paralaryngeal, vs. laryngeal edema 134 parapharyngeal 115 117
Adult - Cerebrovascular. Adult - Cranio-Cervical Junction. Adult - Epilepsy. Adult - Hydrocephalus
 list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF CNS BRAIN Developmental anomalies Cerebrovascular disorders Tumours Inflammatory diseases Trauma DISEASES
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Glomus Glomus tympanicum tumor 52. Mondini Mondini malformation 64
 5 2 2 A Key to Head and Neck Imaging 3 4 6 3 9 1 16 ossicular malformation 30 aberrant internal carotid artery, partial absence of internal carotid artery 34 jugular bulb variants 36 Bezold S acute otitis
5 2 2 A Key to Head and Neck Imaging 3 4 6 3 9 1 16 ossicular malformation 30 aberrant internal carotid artery, partial absence of internal carotid artery 34 jugular bulb variants 36 Bezold S acute otitis
Spine and spinal cord
 NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
Case Studies in the Skull Base
 Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
Case Studies in the Skull Base Amy C Tsai, MD Neuroradiology Fellow Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah, USA No disclosures related
European Board of Head and Neck Radiology Diploma
 European Board of Head and Neck Radiology Diploma Aim(s) and target group Fee structure Eligibility Criteria Knowledge base Examination Structure Terminology Appendix 1-3 Aim(s) and target group The diploma
European Board of Head and Neck Radiology Diploma Aim(s) and target group Fee structure Eligibility Criteria Knowledge base Examination Structure Terminology Appendix 1-3 Aim(s) and target group The diploma
Neckmasses in infancy and childhood: Clinical and radiological classification and imaging approaches M. Mearadji
 Neckmasses in infancy and childhood: Clinical and radiological classification and imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Neck masses are a frequent
Neckmasses in infancy and childhood: Clinical and radiological classification and imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Introduction Neck masses are a frequent
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses)
 Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
Contrast Guidelines for Common CT/CTA & MRI/MRA
 Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Appendix 2 (as supplied by the authors): ICD codes to identify high-risk children
 Appendix 2 (as supplied by the authors): ICD codes to identify high-risk children ICD-9 codes to identify high risk children in physician claims database Category of condition Condition ICD-9 code Bacterial
Appendix 2 (as supplied by the authors): ICD codes to identify high-risk children ICD-9 codes to identify high risk children in physician claims database Category of condition Condition ICD-9 code Bacterial
Imaging of Hearing Loss
 Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease
 Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
Imaging of Cerebrovascular Disease A Practical Guide Val M. Runge, MD Editor-in-Chief of Investigative Radiology Institute for Diagnostic, Interventional, and Pediatric Radiology Inselspital, University
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
UNMH Neurosurgery Clinical Privileges
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 02/20/2015 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees effective: 02/20/2015 INSTRUCTIONS Applicant: Check off the "Requested" box for each privilege requested.
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center
 Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Neurosurgery Student Clerkship Guide 2017 2018 Introduction Welcome to LSUHSC New Orleans neurosurgery rotation. Our department is dedicated
Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center Department of Neurosurgery Student Clerkship Guide 2017 2018 Introduction Welcome to LSUHSC New Orleans neurosurgery rotation. Our department is dedicated
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography
 Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
Medical Review Guidelines Magnetic Resonance Angiography Medical Guideline Number: MRG2001-05 Effective Date: 2/13/01 Revised Date: 2/14/2006 OHCA Reference OAC 317:30-5-24. Radiology. (f) Magnetic Resonance
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Dosimetry, see MAGIC; Polymer gel dosimetry. Fiducial tracking, see CyberKnife radiosurgery
 Subject Index Acoustic neuroma, neurofibromatosis type 2 complications 103, 105 hearing outcomes 103, 105 outcome measures 101 patient selection 105 study design 101 tumor control 101 105 treatment options
Subject Index Acoustic neuroma, neurofibromatosis type 2 complications 103, 105 hearing outcomes 103, 105 outcome measures 101 patient selection 105 study design 101 tumor control 101 105 treatment options
I. TECHNIQUE AND INDICATIONS
 FOURTH YEAR (R4) Date last updated: 12/11/17 Should also review everything in the R1 R3 curriculum I. TECHNIQUE AND INDICATIONS 1. Review to ensure independent proficiency (R4 1 a. Obtaining informed consent
FOURTH YEAR (R4) Date last updated: 12/11/17 Should also review everything in the R1 R3 curriculum I. TECHNIQUE AND INDICATIONS 1. Review to ensure independent proficiency (R4 1 a. Obtaining informed consent
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Background Principles and Technical Development
 Contents Part I Background Principles and Technical Development 1 Introduction and the Nature of Radiosurgery... 3 Definitions of Radiosurgery... 5 Consequences of Changing Definitions of Radiosurgery...
Contents Part I Background Principles and Technical Development 1 Introduction and the Nature of Radiosurgery... 3 Definitions of Radiosurgery... 5 Consequences of Changing Definitions of Radiosurgery...
C. Douglas Phillips MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical College/NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital
 C. Douglas Phillips MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical College/NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor any family members have any pertinent financial relations
C. Douglas Phillips MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical College/NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor any family members have any pertinent financial relations
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions
 CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
CT & MRI Evaluation of Brain Tumour & Tumour like Conditions Dr. Anjana Trivedi 1, Dr. Jay Thakkar 2, Dr. Maulik Jethva 3, Dr. Ishita Virda 4 1 M.D. Radiology, Professor and Head, P.D.U. Medical College
Sample page. Radiology. Cross Coder. Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS
 Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
Cross Coder 2018 Radiology Essential links from CPT codes to ICD-10-CM and HCPCS POWER UP YOUR CODING with Optum360, your trusted coding partner for 32 years. Visit optum360coding.com. Contents Introduction...
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck
 "The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
"The Space Between Us:" A Radiographic Review of Common and Uncommon Pathologic Findings within the Deep Spaces of the Neck Poster No.: C-2457 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. K.
C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital
 C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital Objectives Review basics of head and neck imaging Discuss our spatial approach
C. Douglas Phillips, MD FACR Director of Head and Neck Imaging Weill Cornell Medical Center NewYork Presbyterian Hospital Objectives Review basics of head and neck imaging Discuss our spatial approach
CONTENTS. Section 1 Bilateral Predominantly Symmetric Abnormalities. Cases. Other Relevant Cases
 Edited by,, and List of contributors xi List of abbreviations xii Preface xv Section 1 Bilateral Predominantly Symmetric Abnormalities 1 Hepatic Encephalopathy 2 2 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 UBOs 4 3 Carbon
Edited by,, and List of contributors xi List of abbreviations xii Preface xv Section 1 Bilateral Predominantly Symmetric Abnormalities 1 Hepatic Encephalopathy 2 2 Neurofibromatosis Type 1 UBOs 4 3 Carbon
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales
 28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
28th Annual In-Training Examination for Diagnostic Radiology Residents Rationales Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology February 3, 2005 The American
The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego The Temporal Bone Anatomy & Pathology John R. Hesselink, M.D. Temporal Bone Axial View Temporal Bone Coronal View Longitudinal Fracture The Temporal
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
 EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
EXPERT DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Sellar Region Anne G. Osborn, M.D. DISCLOSURE: Published RSNA 2008 SELLA, PITUITARY: Normal Gross, 3T Anatomy SELLA, PITUITARY: Anatomically-Based Differential Diagnoses
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011
 Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
Job Task Analysis for ARDMS Abdomen Data Collected: June 30, 2011 Reported: Analysis Summary for: Abdomen Examination Survey Dates 06/13/2011-06/26/2011 Invited Respondents 6,000 Surveys with Demographics
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services
 CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
CMS Limitations Guide MRA Radiology Services Starting July 1, 2008, CMS has placed numerous medical necessity limits on tests and procedures. This reference guide provides you with all of the latest changes.
DEPARTMENT OF NEUROSURGERY. Records, Archival Collection - AC 13. Boston Children s Hospital Archives
 DEPARTMENT OF NEUROSURGERY Records, 1929-1999 Archival Collection - AC 13 Boston Children s Hospital Archives Contact Information: 300 Longwood Avenue Hospital Library Boston, MA 02135 Phone: 617-355-5286
DEPARTMENT OF NEUROSURGERY Records, 1929-1999 Archival Collection - AC 13 Boston Children s Hospital Archives Contact Information: 300 Longwood Avenue Hospital Library Boston, MA 02135 Phone: 617-355-5286
Pediatric Spinal Anomalies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Pediatric Spinal Anomalies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spine Embryogenesis 1. Primitive streak 2. Proliferation of cells at primitive pit (Hensen's
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Pediatric Spinal Anomalies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spine Embryogenesis 1. Primitive streak 2. Proliferation of cells at primitive pit (Hensen's
Orbital facia. Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia
 Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3
 PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
PTA 106 Unit 1 Lecture 3 The Basics Arteries: Carry blood away from the heart toward tissues. They typically have thicker vessels walls to handle increased pressure. Contain internal and external elastic
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography
 Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Clinical indications for positron emission tomography Oncology applications Brain and spinal cord Parotid Suspected tumour recurrence when anatomical imaging is difficult or equivocal and management will
Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center. 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Guerbet Outline Acute neck and back pain Acute
Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Guerbet Outline Acute neck and back pain Acute
Clinical Policy: Evoked Potential Testing
 Clinical Policy: Evoked Potential Testing Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.134 Last Review Date: 09/18 Effective Date: 09/18 Coding Implications Revision Log Description Evoked potentials evaluate electrical
Clinical Policy: Evoked Potential Testing Reference Number: PA.CP.MP.134 Last Review Date: 09/18 Effective Date: 09/18 Coding Implications Revision Log Description Evoked potentials evaluate electrical
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region. Child thirsty, increased urination. Imaging. Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) No Disclosures
 Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
Case Studies in Sella/Parasellar Region No Disclosures 2018 Head and Neck Imaging Conference Child thirsty, increased urination Suprasellar Germ Cell Tumor (Germinoma) Midline Pineal >> Suprasellar > Other
Radiation Oncology Study Guide
 Radiation Oncology Study Guide For the Initial CertificationQualifying (Computer-Based) Examination General and Radiation Oncology This examination is designed to assess your understanding of the entire
Radiation Oncology Study Guide For the Initial CertificationQualifying (Computer-Based) Examination General and Radiation Oncology This examination is designed to assess your understanding of the entire
Introduction to Neuroimaging Aaron S. Field, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology Neuroradiology Section University of Wisconsin Madison
 Introduction to Neuroimaging Aaron S. Field, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology Neuroradiology Section University of Wisconsin Madison Updated 7/17/07 Neuroimaging Modalities Radiography (X-Ray)
Introduction to Neuroimaging Aaron S. Field, MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology Neuroradiology Section University of Wisconsin Madison Updated 7/17/07 Neuroimaging Modalities Radiography (X-Ray)
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline
 Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Overview. Call: You will not be assigned to be on call during this rotation. Overall Objectives
 Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Anatomical Pathology and Radiology Rotation Resident PGY5 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton, McMaster Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) Overview
Goals and Objectives for the Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Anatomical Pathology and Radiology Rotation Resident PGY5 St. Joseph s Healthcare Hamilton, McMaster Hospital (1 four-week rotational block) Overview
Neck mass Evaluation & Management OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY
 Neck mass Evaluation & Management MOHAMMED ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR CONSULTANT OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY KSU, MEDICAL CITY & KKUH Objectives Obtain map overview in neck
Neck mass Evaluation & Management MOHAMMED ALESSA MBBS,FRCSC ASSISTANT PROFESSOR CONSULTANT OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK SURGICAL ONCOLOGY KSU, MEDICAL CITY & KKUH Objectives Obtain map overview in neck
UNMH Radiology Clinical Privileges. Name: Effective Dates: From To
 All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees, effective April 28, 2017: Initial Privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of Privileges (reappointment)
All new applicants must meet the following requirements as approved by the UNMH Board of Trustees, effective April 28, 2017: Initial Privileges (initial appointment) Renewal of Privileges (reappointment)
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
NEURORADIOLOGY Part I Vörös Erika University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED BRAIN IMAGING METHODS Plain film radiography Ultrasonography (US) Computer tomography (CT) Magnetic resonance imaging
Manual of Head and Neck Imaging. Prashant Raghavan Sugoto Mukherjee Mark Jameson Max Wintermark
 Manual of Head and Neck Imaging Prashant Raghavan Sugoto Mukherjee Mark Jameson Max Wintermark 123 Manual of Head and Neck Imaging Prashant Raghavan Sugoto Mukherjee Mark J. Jameson Max Wintermark Manual
Manual of Head and Neck Imaging Prashant Raghavan Sugoto Mukherjee Mark Jameson Max Wintermark 123 Manual of Head and Neck Imaging Prashant Raghavan Sugoto Mukherjee Mark J. Jameson Max Wintermark Manual
Spinal cord tumours Luc van den Hauwe et al.
 overview spinal cord tumours L. van den Hauwe 1,2, D. Balériaux 3, J.W. Van Goethem 2, C. Venstermans 2, F. De Belder 2, P.M. Parizel 2 introduction imaging spinal tumour classification spinal cord tumours
overview spinal cord tumours L. van den Hauwe 1,2, D. Balériaux 3, J.W. Van Goethem 2, C. Venstermans 2, F. De Belder 2, P.M. Parizel 2 introduction imaging spinal tumour classification spinal cord tumours
Neoplasms that present as a swelling in the neck may be either
 Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
Problems in otolaryngology Inflammatory swellings Viral and bacterial infection are frequent causes of swellings in the neck. Enlargement of the cervical lymph nodes is most likely but a dormant branchial
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS. Kim Learned, MD
 PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
PITUITARY PARASELLAR LESIONS Kim Learned, MD DIFFERENTIALS Pituitary Sella Clivus, Sphenoid Sinus Suprasellar Optic chiasm, Hypothalamus, Circle of Willis Parasellar Cavernous Sinus Case 1 17 YEAR-OLD
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire
 Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List: Radiology & Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 93451 Right heart catheterization 93452 Left heart catheterization 93453 Combined right and left
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST
 HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
HEALTHFIRST 2011 RADIOLOGY PROGRAM CODE LIST Outpatient Radiology utilization call Carecore at 1-877-773-6964 Modality CPT CODE Description CT SCANS 70450 CT HEAD/BRAIN W/O CONTRAST CT SCANS 70460 CT HEAD/BRAIN
Deepak M. Sampathu MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Deepak M. Sampathu MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Recognize benign masses and masslike lesions of the neck and skull base Understand the imaging
Deepak M. Sampathu MD, PhD Assistant Professor of Clinical Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Recognize benign masses and masslike lesions of the neck and skull base Understand the imaging
Neuro-MRI Exam Ordering Guide
 Neuro-MRI Exam Ordering Guide Dear Colleague, This list is meant to assist you when placing an order for a Neuro-MRI examination. The list includes common indications for neuro-mri as well as recommendations
Neuro-MRI Exam Ordering Guide Dear Colleague, This list is meant to assist you when placing an order for a Neuro-MRI examination. The list includes common indications for neuro-mri as well as recommendations
Notifiable Medical Conditions
 Notifiable Medical Conditions A Acoustic neuroma Addison s disease Agoraphobia AIDS Alcohol problems Alzheimer s disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis - see Motor Neurone Disease Amputations Aneurysm Angina
Notifiable Medical Conditions A Acoustic neuroma Addison s disease Agoraphobia AIDS Alcohol problems Alzheimer s disease Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis - see Motor Neurone Disease Amputations Aneurysm Angina
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013
 Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
Anthem Blue Cross and Blue Shield Virginia Advanced Imaging Procedures Requiring Precertification Revised 02/13/2013 Modality and CT Head CTA Head: Cerebrovascular MRI Head MRA Head: Cerebrovascular Functional
secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma.
 Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
Neuroimaging of vascular/secondary secondary effects and sequelae of head trauma. Andrès Server Alonso Department of Neuroradiology Division of Radiology Ullevål University Hospital Oslo, Norway. Guidelines
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus. Disclosures. Pulsatile Tinnitus: Differential Diagnosis. Pulsatile Tinnitus
 Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
Advanced Vascular Imaging: Pulsatile Tinnitus Patrick Turski MD, Zach Clark MD, Tabby Kennedy MD The Objectives of this presentation are to: Review the differential diagnosis of pulsatile tinnitus Discuss
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
2012 CPT Codes Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o 74160 CT abdomen; with 74170 CT abdomen; w/o followed by Chest 71250 CT thorax; w/o 71260 CT thorax; with 71270
AMERICAN IMAGING MANAGEMENT
 2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
2010 BCBS of Georgia CPT Codes With Grouper Numbers Computerized Tomography (CT) CPT Description Abdomen 74150 CT abdomen; w/o contrast 6 74160 CT abdomen; with contrast 74170 CT abdomen; w/o contrast
Ependymoma of the spine
 Ependymoma of the spine Tenny Zhang, MS-3 Harvard Medical School 1 Case presentation: history and exam HPI: A 30-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents with one week of bilateral
Ependymoma of the spine Tenny Zhang, MS-3 Harvard Medical School 1 Case presentation: history and exam HPI: A 30-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents with one week of bilateral
Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation
 American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]
![PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center] PRIVILEGE APPLICATION FORM - [Mercy Medical Center]](/thumbs/89/98821167.jpg) Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
Current Privilege Status Key Practitioner's Current Privilege status is signified in ( ) preceding each privilege. G = W = Withdrawn T = Temporary P = With Proctor A = Assist with C = With Consult E =
INFECTION. HIV Infection DWI
 HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management. Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP
 Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS BACKGROUND: Incidence: Third most common pediatric tumor type (leukemia, neuroblastoma,
Pediatric Brain Tumors Pre, Intra & Post Op Evaluation and Management Timothy M. George, MD, FACS, FAAP PEDIATRIC BRAIN TUMORS BACKGROUND: Incidence: Third most common pediatric tumor type (leukemia, neuroblastoma,
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire
 Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
Diagnostic Imaging Utilization Management and Consultation Management Programs Imaging Code Listing for Connecticut, Maine and New Hampshire The grid below contains the CPT * codes that are subject to
13/02/1440 بسم ا هلل ا لرحمن ا لر حيم
 بسم ا هلل ا لرحمن ا لر حيم 1 Slowly progressive versus rapidly progressive proptosis by Ali M ISMAIL professor of ophthalmology @SOHAG U H Occuloplastic fellow @NNUH Occuloplastic fellow @Cambridge UH
بسم ا هلل ا لرحمن ا لر حيم 1 Slowly progressive versus rapidly progressive proptosis by Ali M ISMAIL professor of ophthalmology @SOHAG U H Occuloplastic fellow @NNUH Occuloplastic fellow @Cambridge UH
