DEFINATION Growth was concieved by an anatomist, born to a biologist, delivered by a physician, left on a chemist doorstep, and adopted by a physiolog
|
|
|
- Jacob Sharp
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 DEFINATION Growth was concieved by an anatomist, born to a biologist, delivered by a physician, left on a chemist doorstep, and adopted by a physiologist.at an early age- she eloped with a statistician, divorced him for a psycologist, and is now wooed, alternatively and concurrently, by an endrocrinologist, a biochemist,a physicist, a mathematician, an orthodontist, a eugenicist and the children s bureau.
3 Growth and development of an indiviual is divided into two periods- Prenatal period Post natal period
4 THE PRENATAL LIFE IS DIVIDED INTO THREE PERIODS 1.PERIOD OF THE OVUM 2.PERIOD OF THE EMBRYO 3.PERIOD OF THE FETUS
5 PRE NATAL GROWTH PHASE About the fourth week of intrauterine life, the pharyngeal arches are laid down The first arch is called the mandibular arch and the second arch the hyoid arch.
6 Each of these five arches contain - 1. A central cartilage rod that form the skeleton of the arch. 2. A muscular component termed as bronchomere 3. A vascular component. 4. A neural element.
7 INTRAMEMBRANOUS BONE The first structure to develop in the primodium of the lower jaw is the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve that precedes the mesenchymal condensation forming the first [mandibular] arch. FORMATION
8 At around days of intrauterine life there is ectomesenchymal condensation Some mesenchymal cells enlarges, acquire a basophilic cytoplasm and form osteoblasts These osteoblasts secrete a gelatinous matrix called osteoid and result in ossification of an osteogenic membrane.
9 The resulting intramembranous bone lies lateral to meckel s cartilage of first [mandibular ] arch. In the sixth week of the intrauterine life a single ossification centre for each half of the mandible arises in the bifurcation of inferior alveolar nerve into mental and incisive branches
10 During seventh week of intrauterine life bone begin to develop lateral to meckel s cartilage & continues until the posterior aspect is covered with bone Between eigth & tewelth week of intrauterine life mandibular growth accelerate, as a result mandibular length increses.
11 Ossification stops at a piont, which later become mandibular lingula, the remaining part of meckels cartilage continues to form sphenomandibular ligament & spinous process of sphenoid. Secondary accseeory cartilage appear between tenth & fourteenth week of intrauterine life to form head of condyle, part of coronoid process & mental protuberance
12 ENDROCHONDRAL BONE FORMATION Endrocondral bone formation is seen in 3 areas of mandible- 1) The condylar process 2) The coronoid process 3) The mental process
13 THE CONDYLAR PROCESS- At fifth week of intruterine life, an area of mesenchymal condensation is seen above the ventral part of developing mandible. At about tenth week it develops in cone shaped cartilage. It migrate inferior & fuses with mandibular ramus at about 4 month.
14 This cone shaped cartilage is replaced by bone but its upper end persists acting as growth cartilage & articular cartilage.
15 THE CORONOID PROCESS- Secondary accessory cartilage appear in region of coronoid process at about week of intrauterine life. This cartilage become incorporated into expanding intramembranous bone of ramus & dissapear before birth.
16 THE MENTAL REGION- In mental region, on either side of symphysis, one or two small cartilage appear and ossify in seventh week of intrauterine life to become mental ossicles. These ossicles become incorporated into intramembranous bone when symphysis ossify completely.
17 POST NATAL GROWTH PHASE At birth the two rami of the mandible are short, condylar development is minimum and there is no articular eminence in glenoid fossa. A thin layer of fibrocartilage & connective tissue exists at the midline of symphysis to separate right & left mandibular bodies. At fourth month of age and end of first year symphysial cartilage is replaced by bone
18 During first year of life appositional growth is active at alveolar border, at distal & superior surfaces of the ramus, at the condyle, along the lower border of mandible and on its lateral surface.
19 After first year of life these changes occurs - Mandibular growth become more selective, condyle shows considerable activities, mandible moves and grows downward & forward. Appositional growth occurs on posterior border of the ramus and on the alveolar process. Resorption occurs along the anterior border of ramus lenthening the alveolar border & maintaining the anterior- posterior dimension of ramus.
20
21 Gonial angle changes after little muscle activity. Transverse dimension is mainly due to growth at posterior border in an expanding V pattern.
22
23 The two rami also diverge outward from below to above so that additive growth at coronoid notch, coronoid process &condyle also increses the superior inter-ramus ramus dimension. Alveolar process of mandible grows upward & outward on an expanding arc. This permit dental arc to accommodate the larger permanent teeth.
24 Scott divides the mandible into three basic types of bone 1) Basal 2) Muscular 3) Alveolar Basal portion is tube like central foundation running from condyle to the symphysis. Muscular portion [gonial angle &coronoid process] is under influence of masseter, internal pterygoid & temporal muscle. They determine the ultimate form of the mandible in these areas.
25 Alveolar portion exists to hold the teeth & gradually resorbed in the event of tooth loss. Reduced muscular activity would account for flattening of gonial angle and reduction of the coronoid process.
26 MOSS say that the mandible as a group of microskeleton unit Coronoid process as one skeleton unit under influence of temporalis. Gonial angle is another skeleton unit under influence of massetor & internal pterygoid muscles. Alveolar process is under the influence of the dentition. Basal tubular portion of mandible serves as protection for the mandibular canal and follows a logarithim spiral in its downward & forward movement from beneath the cranium.
27 THE CHIN Enlow & harris feel that chin is associated with a generalised cortical recession in the flattened regions positioned between the canine teeth. The process involves a mechanism of endosteal cortical growth. On lingual surface, behind the chin heavy periosteal growth occurs, with the dense lamellar bone merging and overlaping on the labial side of the chin.
28 In male, the apposition of the bone at symphysis seems to be about the last change in shape during the growing period. This change is much less apparent in the females.
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
Temporomandibular Joint. Dr Noman ullah wazir
 Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Upper arch. 1Prosthodontics. Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi. Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth
 1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
1Prosthodontics Lecture 2 Dr.Bassam Ali Al-Turaihi Basic anatomy & & landmark of denture & mouth Upper arch Palatine process of maxilla: it form the anterior three quarter of the hard palate. Horizontal
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology. Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity
 Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
Essentials in Head and Neck Embryology Part 3 Development of the head, face, and oral cavity Outline General overview of prenatal development Embryonic period phase 1 Formation of bilaminar disk Formation
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Skeletal System: Skull.
 Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Skeletal System: Skull www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Bones of the Skull SPLANCHNOCRANIUM Nasal (2) Maxilla (2) Lacrimal (2) Zygomatic (2) Palatine (2) Inferior concha (2) Vomer Mandible NEUROCRANIUM Frontal
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton
 Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Human Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 07: The Skeletal System Axial Skeleton Question No. 1 of 10 Which of the following statements about the axial skeleton is correct? Question #01 A. The axial
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement
 Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
Introduction to Occlusion and Mechanics of Mandibular Movement Dr. Pauline Hayes Garrett Department of Endodontics, Prosthodontics, and Operative Dentistry University of Maryland, Baltimore Assigned reading
Interactions of the endocrine system, bone and oral health
 Interactions of the endocrine system, bone and oral health All bones are not equal! Dense high proportion of cortical bone High proportion of trabecular bone Mandible Functions: mastication, respiration,
Interactions of the endocrine system, bone and oral health All bones are not equal! Dense high proportion of cortical bone High proportion of trabecular bone Mandible Functions: mastication, respiration,
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
Oral cavity landmarks
 By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
By: Dr. Ahmed Rabah Oral cavity landmarks The knowledge of oral anatomy and physiology will help the operator and provides enough landmarks to act as positive guide during denture construction. This subject
Muscles of mastication [part 1]
![Muscles of mastication [part 1] Muscles of mastication [part 1]](/thumbs/76/73586850.jpg) Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Anatomy and physiology of Temporomandibular Joint
 Anatomy and physiology of Temporomandibular Joint Temporomandibular joint (TMJ): It is the articulation of the condyle of the mandible, and the inter-articular disc; with the mandibular fossa (glenoid
Anatomy and physiology of Temporomandibular Joint Temporomandibular joint (TMJ): It is the articulation of the condyle of the mandible, and the inter-articular disc; with the mandibular fossa (glenoid
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Temporomandibular Joint
 6 Temporomandibular Joint Most human bones are joined with one another. These connections of bones to each other are termed articulations or joints. Some joints are immovable as in the articulations of
6 Temporomandibular Joint Most human bones are joined with one another. These connections of bones to each other are termed articulations or joints. Some joints are immovable as in the articulations of
Chapter 7. Skeletal System
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Skull A. The skull is made up of 22 bones: 8 cranial bones, 13 facial bones, and the mandible. B. The Cranium encloses and protects the brain, provides attachments for muscles,
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki
 Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Dr.Sepideh Falah-kooshki MAXILLA Premaxillary/median palatal suture (radiolucent). Incisive fossa and foramen (radiolucent). Nasal passages (radiolucent). Nasal septum (radiopaque). Anterior nasal spine
Osteology. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Osteology Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions of the Skeletal System: Support Movement Protection Hemopoiesis Electrolyte balance (Ca ++ /PO -3 4 ) Acid-base balance Storage
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton
 Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Chapter 7 Part A The Skeleton Why This Matters Understanding the anatomy of the skeleton enables you to anticipate problems such as pelvic dimensions that may affect labor and delivery The Skeleton The
Cranium Facial bones. Sternum Rib
 Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
Figure 7.1 The human skeleton. Skull Thoracic cage (ribs and sternum) Cranium Facial bones Sternum Rib Bones of pectoral girdle Vertebral column Sacrum Vertebra Bones of pelvic girdle (a) Anterior view
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL
 AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
AXIAL SKELETON SKULL CRANIAL BONES (8 total flat bones w/ 2 paired) 1. Frontal forms forehead & upper portion of eyesocket (orbital) 2. Parietal paired bones; form superior & lateral walls of cranium 3.
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
Chapter 7: Skeletal System: Gross Anatomy I. General Considerations A. How many bones in an average adult skeleton? B. Anatomic features of bones are based on II. Axial Skeleton A. Skull 1. Functionally
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Sheets 16&17. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Sheets 16&17 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ossification (formation of bone) - Osteoblasts are responsible for producing the extracellular matrix of the bone and these osteoblasts
Skeletal System -Axial System. Chapter 7 Part A
 Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skeletal System -Axial System Chapter 7 Part A Skeleton Learn: Names of the s. Identify specific landmarks that allow: Bones to fit into each other, Organs to fit into the cavities, Muscles to attach,
Skull basic structures. Neurocranium
 Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Assoc. Prof. Květuše Lovásová, M.V.D., PhD. Skull basic structures Skull consists of two groups of bones: neurocranium (bones forming the brain box) splanchnocranium (bones forming the facial skeleton)
Important Parts of Bones
 Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Important Parts of Bones For 2015 Know: Humerus (posterior) Clavical Femur (Anterior) Foot Hand Mandible Os Coxa Scapula Skull (Anterior, Inferior, Lateral) Sternum Humerus (posterior) A. olecranon fossa
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream
 1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
1! Larynx - cartilaginous structure holding the vocal folds which protrude into airstream 2! Flow increase - like thumb over garden hose Pressure drop - narrower space forces pressure drop due to speed
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
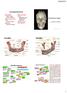 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm
 Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
Development of face Remember from the first year embryology Trilaminar disc has 3 layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm The ectoderm forms the neural groove, then tube The neural tube lies in the mesoderm
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Focus on the Skull
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Focus on the Skull Review Anatomical Terms Anterior/Posterior Dorsal/Ventral Medial/Lateral Superior/Inferior Bone Markings - Review Projections for attachment of muscles, ligaments
Pharyngeal apparatus. - At the third week, it is a 3 layered structure: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. This is called trilaminar disc
 Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
Pharyngeal apparatus Remember from the first year embryology - The embryo was disc shaped in the second week of development (this is called embryonic disc) and it is a 2 layered disc (composed of two layers)---bilaminar
YOU MUST BRING YOUR OWN GLOVES FOR THIS ACTIVITY.
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
Lips and labial mucosa
 Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
Lips and labial mucosa External portion of the lips: the vermilion border and the skin Vermilion border : the exposed red portion of the lip, covered by mucous membrane, no mucous glands Boundary: the
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION COW BONE DISSECTION
 ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
ACTIVITY 3: AXIAL SKELETON AND LONG BONE DISSECTION Objectives: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 7, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Learning the meanings
DOWNLOAD PDF GROWTH AND DEVELOPMENT OF MAXILLA AND MANDIBLE
 Chapter 1 : Mandible Development authorstream DEVELOPMENT OF MAXILLA Maxilla forms within the maxillary prominences extending ventrally from the dorsal aspect of a much larger mandibular swelling. Ossification
Chapter 1 : Mandible Development authorstream DEVELOPMENT OF MAXILLA Maxilla forms within the maxillary prominences extending ventrally from the dorsal aspect of a much larger mandibular swelling. Ossification
Biology 218 Human Anatomy. Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division
 Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Adapted from Martini Human Anatomy 7th ed. Chapter 6 The Skeletal System: Axial Division Introduction The axial skeleton: Composed of bones along the central axis of the body Divided into three regions:
Oral Embryology and Histology
 Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Oral Embryology and Histology Chapter 8 Copyright 2018, Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. 1 Learning Objectives Lesson 8.1: Oral Embryology 1. Pronounce, define, and spell the key terms. 2. Define embryology
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
FORMATION OF BONE. Intramembranous Ossification. Bone-Lec-10-Prof.Dr.Adnan Albideri
 FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
FORMATION OF BONE All bones are of mesodermal origin. The process of bone formation is called ossification. We have seen that formation of most bones is preceded by the formation of a cartilaginous model,
A Cephalometric Study
 Craniofacial Growth in Juvenile Macaca mulatta: A Cephalometric Study JOSE C. ELGOYHEN,2%3 MICHAEL L. RIOLO,3 LEE W. GRABER,3 ROBERT E. MOYERS4 AND JAMES A. McNAMARA, JR.5 3 Center for Human Growth and
Craniofacial Growth in Juvenile Macaca mulatta: A Cephalometric Study JOSE C. ELGOYHEN,2%3 MICHAEL L. RIOLO,3 LEE W. GRABER,3 ROBERT E. MOYERS4 AND JAMES A. McNAMARA, JR.5 3 Center for Human Growth and
 Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal
Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal apparatus. Drawings illustrating the human pharyngeal
Lab Activity 11: Group I
 Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group I Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Anatomy and Physiology II. Review Spine and Neck
 Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Anatomy and Physiology II Review Spine and Neck Spine regions How many cervical vertibrae are there? 7 The curvature is the cervical region posterior? Concave posterior How many thoracic? And curvature?
Oral Surgery. Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia. A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia:
 Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Oral Surgery Lecture: 9 Dr. Saif Saadedeen Basic Techniques of Dental Local Anesthesia A variety of techniques used in administration and deposition of local anesthesia: 1. Topical anesthesia 2. Infiltration
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible
 Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
Techniques of local anesthesia in the mandible The technique of choice for anesthesia of the mandible is the block injection and this is attributed to the absence of the advantages which are present in
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 09/11/2013 No. of Questions: (50) Time: 1hour Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
APPENDICULAR SKELETON 126 AXIAL SKELETON SKELETAL SYSTEM. Cranium. Skull. Face. Skull and associated bones. Auditory ossicles. Associated bones.
 SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
SKELETAL SYSTEM 206 AXIAL SKELETON 80 APPENDICULAR SKELETON 26 Skull Skull and associated s 29 Cranium Face Auditory ossicles 8 4 6 Associated s Hyoid Thoracic cage 25 Sternum Ribs 24 Vertebrae 24 column
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
E. VERTEBRAL COLUMN 1. The vertebral column extends from the skull to the pelvis and forms the vertical axis of the skeleton. 2. The vertebral column is composed of vertebrae that are separated by intervertebral
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Saba Alfayoumi. Heba Kalbouneh
 11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
11 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Saba Alfayoumi Heba Kalbouneh 2- Bone Bone tissue is also classified into primary bone and secondary bone. In the beginning, the first bone that is deposited by the osteoblasts is
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
Development of occlusion
 Development of occlusion The development of dentition is an important part of craniofacial growth as the formation, eruption, exfoliation and exchange of teeth take place during this period. Term occlusion
Development of occlusion The development of dentition is an important part of craniofacial growth as the formation, eruption, exfoliation and exchange of teeth take place during this period. Term occlusion
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Basic Functional Anatomy of the Gnathostomatic System and its Clinical Implications. Eugene Santucci DDS, MA, FACD
 Basic Functional Anatomy of the Gnathostomatic System and its Clinical Implications Eugene Santucci DDS, MA, FACD NOTHING IS MORE FUNDAMENTAL TO TREATING PATIENTS THAN KNOWING ANATOMY Jeffery P. Okeson
Basic Functional Anatomy of the Gnathostomatic System and its Clinical Implications Eugene Santucci DDS, MA, FACD NOTHING IS MORE FUNDAMENTAL TO TREATING PATIENTS THAN KNOWING ANATOMY Jeffery P. Okeson
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Vertebral Column. Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions. Cervical
 Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Vertebral Column Backbone consists of 26 vertebrae. Five vertebral regions Cervical vertebrae (7) in the neck. Thoracic vertebrae (12) in the thorax. Lumbar vertebrae (5) in the lower back. Sacrum (5,
Oral Histology. Alveolar bone or process: Functions of alveolar bone: Chemical composition: Development of the alveolar process: Dr.
 Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Oral Histology Lec.12 Alveolar bone or process: Dr. Nada Al-Ghaban Alveolar bone is a specialized part of the mandibular and maxillary bones that forms the primary support structure for teeth. Although
Panoramic Radiology. Seminars on Maxillofacial Imaging and Interpretation. Bearbeitet von Allan G Farman
 Panoramic Radiology Seminars on Maxillofacial Imaging and Interpretation Bearbeitet von Allan G Farman 1. Auflage 2007. Buch. xiv, 232 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 46229 3 Format (B x L): 19,3 x 27 cm Gewicht:
Panoramic Radiology Seminars on Maxillofacial Imaging and Interpretation Bearbeitet von Allan G Farman 1. Auflage 2007. Buch. xiv, 232 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 46229 3 Format (B x L): 19,3 x 27 cm Gewicht:
Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System. Cornelius CP, Kunz C, Prein J, Audigé L. Mandibular fractures Level-2 system (cases 1 to 18)
 Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System Cornelius CP, Kunz C, Prein J, Audigé L Mandibular fractures Level-2 system (cases 1 to 18) Case 1: Body fracture traversing anterior transition zone Imaging:
Comprehensive AOCMF Classification System Cornelius CP, Kunz C, Prein J, Audigé L Mandibular fractures Level-2 system (cases 1 to 18) Case 1: Body fracture traversing anterior transition zone Imaging:
Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of Anatomy
 5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
5-Sep Introduction and Anatomy Review 12-Sep Neurophysiology and Pain 19-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 1 26-Sep Physiology and Pharmacology part 2 Introduction to Local Anesthesia and Review of
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
BONE CHALLENGE DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD Bone Basic functions? A. support B. protection C. movement assistance in D. RBC formation-hemopoiesis E. mineral homeostasis +importance of calcium F. energy supply -yellow
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
University of Palestine. Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade:
 [ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
[ Course No: DNTS2208 Course Title: Head and Neck Anatomy Date: 17/11/1024 No. of Questions: (52) Time: 2hours Using Calculator (No) University of Palestine Midterm Exam 2013/2014 Total Grade: Instructor
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
 19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
Skeletal System. It s all about the bones!!!
 Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
Skeletal System It s all about the bones!!! The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=icwllrqkv cg&list=plzile25upgebvru0jneppcabh0fhktgt Q 1. FYI 5
External Acoustic Meatus. Mastoid Process. Zygomatic Process. Temporal Bone
 Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
Bone lab review 1. Frontal Bone 2. Supra-Orbital Foramen 3. Orbit (Orbital Cavity) 4. Superior Orbital Fissure 5. Inferior Orbital Fissure 6. Zygomatic Bone 7. Infra-Orbital Foramen 8. Maxilla 9. Mandible
529-A Treatment and Management of the Edentulous Patient. Upon completion of this course the student should be able to:
 Course & Title: Session & Topic: 529-A Treatment and Management of the Edentulous Patient Jaw Relations General Goal: To understand the principles of orientational, horizontal and vertical jaw relations
Course & Title: Session & Topic: 529-A Treatment and Management of the Edentulous Patient Jaw Relations General Goal: To understand the principles of orientational, horizontal and vertical jaw relations
-Ibrahim Al-Naser. -Dr Al- Muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 -1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
-1 -Ibrahim Al-Naser - -Dr Al- Muhtaseb 1 P a g e The Digestive System The doctor started the lecture by talking about the class rules. The GI system is an organ system, it is divided into: The Alimentary
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Horizontal jaw relations: The relationship of mandible to maxilla in a
 Horizontal relations Horizontal jaw relations: The relationship of mandible to maxilla in a horizontal plane (in anteroposterior and side to side direction). a- Protruded or forward relation. b-lateral
Horizontal relations Horizontal jaw relations: The relationship of mandible to maxilla in a horizontal plane (in anteroposterior and side to side direction). a- Protruded or forward relation. b-lateral
LECTURE -I. Intercostal Spaces & Its Content. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Date:
 LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development. Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L.
 Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
Fundamental & Preventive Curvatures of Teeth and Tooth Development Lecture Three Chapter 15 Continued; Chapter 6 (parts) Dr. Margaret L. Dennis Proximal contact areas Contact areas are on the mesial and
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust
 Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: SC-287 Original Specimen Near-complete human skeleton with 28 teeth. Osteological Observations: This is a clean,
Human Male Asian Skeleton, Robust Product Number: Specimen Evaluated: Skeletal Inventory: SC-287 Original Specimen Near-complete human skeleton with 28 teeth. Osteological Observations: This is a clean,
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1. Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology, Centro
SKELETAL SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1,2 1 Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines 2 Department of Biological Sciences, School of Science and Technology, Centro
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil khouri
 Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Dr. Nabil khouri Appendicular Skeleton The appendicular skeleton is made up of the bones of the upper and lower limbs and their girdles Two girdles: Pectoral girdles attach the upper limbs to the body
Horizontal Jaw Relation
 Horizontal Jaw Relation Horizontal Jaw Relation It is the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla in a horizontal plane. It can also be described as the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla
Horizontal Jaw Relation Horizontal Jaw Relation It is the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla in a horizontal plane. It can also be described as the relationship of the mandible to the maxilla
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System
 Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
Exercise Science Section 2: The Skeletal System An Introduction to Health and Physical Education Ted Temertzoglou Paul Challen ISBN 1-55077-132-9 Role of the Skeleton Protection Framework Attachments for
The Role of Muscles in Movement
 The Role of Muscles in Movement Muscles can t push, they can only pull as they contract, so most often body movements are the result of the activity of pairs or teams of muscles acting together or against
The Role of Muscles in Movement Muscles can t push, they can only pull as they contract, so most often body movements are the result of the activity of pairs or teams of muscles acting together or against
The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM The embryonic endoderm initially is widely connected with the yolk sac. As a consequence of cephalocaudal and lateral folding, a portion of the endoderm-lined yolk sac cavity is incorporated
