CCK mouse 1:5000 *Dr. G. Ohning, CURE, UCLA, USA, Code 9303 (Ohning et al., 1996)
|
|
|
- Lydia Spencer
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplemental Table 1 antibody to host dilution source CB rabbit 1:5000 Swant, Bellinzona, Switzerland, code no 38 reference of characterization and specificity labelling patterns as published with other antibodies CCK mouse 1:5000 *Dr. G. Ohning, CURE, UCLA, USA, Code 9303 (Ohning et al., 1996) rabbit 1:1000 pro-cck; Dr. G. Dockrey, Liverpool University, UK, code no L424 (Morino et al., 1994) GAD mouse 1:500 Millipore Corporation, Billerica, USA, code no MAB 351, Lot (Chang and Gottlieb, 1988) mouse 1:100 Dev.Stu.Hybr. Bank, Univ. Iowa, code GAD-6 (Chang and Gottlieb, 1988) PV mouse 1:5000 Swant,Bellinzona, Switzerland, code no 235 (Celio et al., 1988) guinea pig 1:2000 SOM mouse 1:300 Dr. K.G. Baimbridge, Dept. Physiol., Univ. British Columbia, Canada, Code no 404 Dr. A. Buchan, Dept. Physiol., Univ. Br. Columbia, Canada, code no mab Soma8 rat 1:500 Millipore Corporation, Billerica, USA, code no MAB 354 labelling patterns as published with other antibodies and K.G.B. personal communication (Vincent et al., 1985) labelling patterns as published with other antibodies VIP mouse 1: *Dr. G. Ohning, CURE, UCLA, USA, Code 55 (Wong et al., 1996) *Antibodies by CURE/Digestive Diseases Research Center, Antibody/RIA Core, UCLA, NIH Grant #DK 41301
2 Reference List Celio MR, Baier W, Scharer L, de Viragh PA, Gerday C (1988) Monoclonal antibodies directed against the calcium binding protein parvalbumin. Cell Calcium 9: Chang YC, Gottlieb DI (1988) Characterization of the proteins purified with monoclonal antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase. J Neurosci 8: Morino P, Herrera-Marschitz M, Castel MN, Ungerstedt U, Varro A, Dockray G, Hokfelt T (1994) Cholecystokinin in cortico-striatal neurons in the rat: immunohistochemical studies at the light and electron microscopical level. Eur J Neurosci 6: Ohning GV, Wong HC, Lloyd KC, Walsh JH (1996) Gastrin mediates the gastric mucosal proliferative response to feeding. Am J Physiol 271:G470-G476. Vincent SR, McIntosh CH, Buchan AM, Brown JC (1985) Central somatostatin systems revealed with monoclonal antibodies. pp Wong HC, Sternini C, Lloyd K, De GR, Walsh JH (1996) Monoclonal antibody to VIP: production, characterization, immunoneutralizing activity, and usefulness in cytochemical staining. Hybridoma 15:
3 power spectrum 6 power [m V ] 2 3 dorsal CA1 0.9 coherence power [m V ] m PFC coherence coefficient.6.3 dorsal CA1/ m PFC power [m V ] interm CA1 coherence coefficient.6.3 dorsal CA1/ interm CA power [m V ] ventral CA1 coherence coefficient.6.3 dorsal CA1/ ventral CA1 0 f [Hz].0 f [Hz] suppl Fig 1. Hartwich et al. (2008)
4 Suppl. Figure 1. Power and coherence of theta oscillations in the mpfc, dorsal, intermediate and ventral CA1 hippocampus. Bars represent mean and SD from the indicated number of recordings. A, Power spectra of the LFP in the dorsal CA1 (n=33 recordings), mpfc (n=17 recordings), intermediate CA1 (n=6 recordings) and ventral CA1 area (n=10 recordings) during theta oscillations detected in the dorsal CA1 hippocampus. Note the prominent peak at 4 Hz in the dorsal and intermediate hippocampus. In the mpfc and ventral hippocampus 4 Hz theta oscillations are present but the dominant frequency is in the 2 Hz band. B, Coherence spectrum between local field potentials in the dorsal CA1 hippocampus and mpfc (n=17 recordings), intermediate CA1 (n=6 recordings) or ventral CA1 hippocampus (n=10 recordings) during theta oscillations detected in the dorsal CA1 hippocampus. Note the prominent peak at 4 Hz in all plots. However, the coherence in the theta band is higher between the dorsal and intermediate CA1 in comparison to dorsal CA1 and mpfc or ventral CA1. Black lines indicate significance thresholds determined by shuffling as described in the Methods.
5 suppl Fig 2. Hartwich et al. (2008) A dorsal CA1 theta B dorsal CA1 theta mpfc theta trough interm. CA1 theta trough ventral CA1 theta trough probability/bin probability/bin probability/bin dorsal theta phase [ ] number of recordings with significantly modulated theta troughs dorsal theta phase [ ].20 probability/bin probability/bin probability/bin
6 Suppl. Figure 2. Theta phase relationships between the dorsal CA1 hippocampus and the mpfc, intermediate or ventral CA1 area. A, B, Upper schematic waveform indicates two dorsal CA1 theta cycles; 0 and 360 mark the troughs. A, Phase probability of troughs detected from the filtered LFP (3-6 Hz) of the mpfc (upper graph), intermediate CA1 (middle graph) and ventral CA1 (lower graph) to the dorsal CA1 theta cycle (bin size 36 ). Only those troughs with an inter-event time between and s were considered. Colored traces show examples of individual recordings. B, The grey columns and left y-axis indicate the number of recordings observed with a significant mean theta phase. The red curve and right y-axis indicate the mean trough probability of all recordings in a particular area. In the mpfc in 3 out of 26 recordings no significant modulation of the theta troughs in relation to dorsal CA1 theta oscillations could be detected. Note that theta troughs in the mpfc are slightly delayed in relation to dorsal CA1 theta oscillations and theta troughs in the intermediate CA1 area are in phase with the dorsal CA1 theta troughs. Theta troughs from individual recordings in the ventral CA1 area are phase coupled to dorsal CA1 theta oscillations. However, the preferred theta trough phase is highly heterogeneous between different recording sites. Because putative pyramidal cells in the ventral CA1 area were phase coupled to the same dorsal CA1 theta phase (peak) irrespective of the recording site, this suggests that theta oscillations in the ventral CA1 hippocampus might be strongly influenced by volume conduction due to its own curvature and the geometry of the surrounding structures, which may also oscillate at theta frequency.
7 suppl Fig 3. Hartwich et al (2008) A Neurobiotin B Neurobiotin * Calbindin Calbindin Parvalbumin
8 Suppl. Figure 3. Basket cells in the PL cortex are immunopositive for PV and CB. A, A neurobiotin labeled soma of a basket cell (K 101a) is weakly immunopositive for calbindin (arrow) compared to strong immunopositive CB cells (arrowhead) nearby. B, Immunofluorescence micrographs showing a neurobiotin labeled soma of a basket cell (K124a) weakly immunopositive for calbindin compared to a negative soma (star) and strong positive soma (arrowhead) nearby. The soma of this cell was also tested positive for PV. Scale bars: 10 µm.
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Supplementary Figure 1 Large-scale calcium imaging in vivo. (a) Schematic illustration of the in vivo camera imaging set-up for large-scale calcium imaging. (b) High-magnification two-photon image from
Fig. S4. Current-voltage relations of iglurs. A-C: time courses of currents evoked by 100 ms pulses
 Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Fig. S1. Immunohistochemical detection of iglur2 protein in single islet cells. A: α cells identified using glucagon-specific antibody express the iglur2 subtype of AMPA receptor. 24 out of 26 identified
Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive
 The Journal of Neuroscience, July 29, 2009 29(30):9563 9574 9563 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Distinct Firing Patterns of Identified Basket and Dendrite-Targeting Interneurons in the Prefrontal Cortex
The Journal of Neuroscience, July 29, 2009 29(30):9563 9574 9563 Behavioral/Systems/Cognitive Distinct Firing Patterns of Identified Basket and Dendrite-Targeting Interneurons in the Prefrontal Cortex
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex
 Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Simulating inputs of parvalbumin inhibitory interneurons onto excitatory pyramidal cells in piriform cortex Jeffrey E. Dahlen jdahlen@ucsd.edu and Kerin K. Higa khiga@ucsd.edu Department of Neuroscience
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References
 File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
File name: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures, Supplementary Table and Supplementary References File name: Supplementary Data 1 Description: Summary datasheets showing the spatial
Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu
 Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Distinct contributions of Na v 1.6 and Na v 1.2 in action potential initiation and backpropagation Wenqin Hu, Cuiping Tian, Tun Li, Mingpo Yang, Han Hou & Yousheng Shu Supplementary figure and legend Supplementary
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale
 Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Figure 1. SDS-FRL localization of CB 1 in the distal CA3 area of the rat hippocampus. (a-d) Axon terminals (t) in stratum pyramidale (b) show stronger immunolabeling for CB 1 than those in
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission
 Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Supplementary Materials for VAMP4 directs synaptic vesicles to a pool that selectively maintains asynchronous neurotransmission Jesica Raingo, Mikhail Khvotchev, Pei Liu, Frederic Darios, Ying C. Li, Denise
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields.
 Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Theta sequences are essential for internally generated hippocampal firing fields. Yingxue Wang, Sandro Romani, Brian Lustig, Anthony Leonardo, Eva Pastalkova Supplementary Materials Supplementary Modeling
Nov versus Fam. Fam 1 versus. Fam 2. Supplementary figure 1
 a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
a Environment map similarity score (mean r ).5..3.2.1 Fam 1 versus Fam 2 Nov versus Fam b Environment cofiring similarity score (mean r ).7.6.5..3.2.1 Nov versus Fam Fam 1 versus Fam 2 First half versus
Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites Supplementary Table 2. Quantitative features of EC neuron axons 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Layer distribution
Supplementary Information Supplementary Table 1. Quantitative features of EC neuron dendrites Supplementary Table 2. Quantitative features of EC neuron axons 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Layer distribution
Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis of individual mice during maze learning. a,
 Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Goal-oriented searching mediated by ventral hippocampus early in trial-and-error learning Ruediger, S, Spirig, D., Donato, F., Caroni, P. Suppl. Information Supplementary Figure 1. Strategy/latency analysis
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.4084
 Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Supplementary Figure 1: Sample IEDs. (a) Sample hippocampal IEDs from different kindled rats (scale bar = 200 µv, 100 ms). (b) Sample temporal lobe IEDs from different subjects with epilepsy (scale bar
Characterization of Sleep Spindles
 Characterization of Sleep Spindles Simon Freedman Illinois Institute of Technology and W.M. Keck Center for Neurophysics, UCLA (Dated: September 5, 2011) Local Field Potential (LFP) measurements from sleep
Characterization of Sleep Spindles Simon Freedman Illinois Institute of Technology and W.M. Keck Center for Neurophysics, UCLA (Dated: September 5, 2011) Local Field Potential (LFP) measurements from sleep
Brain Rhythms. Objectives
 Brain Rhythms Michael O. Poulter, Ph.D. Professor, Molecular Brain Research Group Robarts Research Institute Depts of Physiology & Pharmacology, Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine
Brain Rhythms Michael O. Poulter, Ph.D. Professor, Molecular Brain Research Group Robarts Research Institute Depts of Physiology & Pharmacology, Clinical Neurological Sciences Schulich School of Medicine
LORETA Coherence and Phase Differences
 LORETA Coherence and Phase Differences Robert W. Thatcher, Ph.D. 4/25/12 Example from the Neuroguide Demo from a high functioning business professional prior to right hemisphere brain damage by being struck
LORETA Coherence and Phase Differences Robert W. Thatcher, Ph.D. 4/25/12 Example from the Neuroguide Demo from a high functioning business professional prior to right hemisphere brain damage by being struck
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1 Iliopsoas and quadratus lumborum motor neurons in the L2 spinal segment. (A) IL and QL motor neurons were labeled after CTb-488 (green) muscle injections at birth. At P4, the L2
Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol.
 Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figures 1-11 Supplementary Figure 1: Kv7 currents in neonatal CA1 neurons measured with the classic M- current voltage-clamp protocol. (a), Voltage-clamp recordings from CA1 pyramidal neurons
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
Supplementary Figure 1 The average sigmoid parametric curves of capillary dilation time courses and average time to 50% peak capillary diameter dilation computed from individual capillary responses averaged
What do you notice?
 What do you notice? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5v5ebf2kwf8&t=143s Models for communication between neuron groups Communication through neuronal coherence Neuron Groups 1 and 3 send projections to
What do you notice? https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5v5ebf2kwf8&t=143s Models for communication between neuron groups Communication through neuronal coherence Neuron Groups 1 and 3 send projections to
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1. Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Supplementary Figure 1 Activity in turtle dorsal cortex is sparse. a. Probability distribution of firing rates across the population (notice log scale) in our data. The range of firing rates is wide but
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Supplementary Figure 1 Lick response during the delayed Go versus No-Go task. Trial-averaged lick rate was averaged across all mice used for pyramidal cell imaging (n = 9). Different colors denote different
Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex
 Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Information Unique functional properties of somatostatin-expressing GABAergic neurons in mouse barrel cortex Luc Gentet, Yves Kremer, Hiroki Taniguchi, Josh Huang, Jochen Staiger and Carl
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) 108 (b-c) (d) (e) (f) (g)
 Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Supplementary Figure 1 Information on transgenic mouse models and their recording and optogenetic equipment. (a) In four mice, cre-dependent expression of the hyperpolarizing opsin Arch in pyramidal cells
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Cell-Type-Specific Recruitment of Amygdala Interneurons to Hippocampal Theta Rhythm and Noxious Stimuli In Vivo
 Article Cell-Type-Specific Recruitment of Amygdala Interneurons to Hippocampal Theta Rhythm and Noxious Stimuli In Vivo Thomas C.M. Bienvenu, 1,3, * Daniela Busti, 2 Peter J. Magill, 1 Francesco Ferraguti,
Article Cell-Type-Specific Recruitment of Amygdala Interneurons to Hippocampal Theta Rhythm and Noxious Stimuli In Vivo Thomas C.M. Bienvenu, 1,3, * Daniela Busti, 2 Peter J. Magill, 1 Francesco Ferraguti,
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
Supplementary Figure 1 Hippocampal recordings. a. (top) Post-operative MRI (left, depicting a depth electrode implanted along the longitudinal hippocampal axis) and co-registered preoperative MRI (right)
Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 8-Expressing Nerve Terminals Target Subsets of GABAergic Neurons in the Hippocampus
 10520 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 9, 2005 25(45):10520 10536 Cellular/Molecular Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 8-Expressing Nerve Terminals Target Subsets of GABAergic Neurons in the Hippocampus
10520 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 9, 2005 25(45):10520 10536 Cellular/Molecular Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor 8-Expressing Nerve Terminals Target Subsets of GABAergic Neurons in the Hippocampus
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Supplementary Figure 1. Basic properties of compound EPSPs at hippocampal CA3 CA3 cell synapses. (a) EPSPs were evoked by extracellular stimulation of the recurrent collaterals and pharmacologically isolated
Informationsverarbeitung im zerebralen Cortex
 Informationsverarbeitung im zerebralen Cortex Thomas Klausberger Dept. Cognitive Neurobiology, Center for Brain Research, Med. Uni. Vienna The hippocampus is a key brain circuit for certain forms of memory
Informationsverarbeitung im zerebralen Cortex Thomas Klausberger Dept. Cognitive Neurobiology, Center for Brain Research, Med. Uni. Vienna The hippocampus is a key brain circuit for certain forms of memory
Supplemental Table I
 Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Supplemental Table I Cortex Hippocampus Age (weeks) Genotype STE 61 pste 61 STE 61 pste 61 8 100.0 ± 4.4 96.2 ± 6.0 99.8 ± 8.7 167.5 ± 7.8* 100.0 ± 7.0 90.5 ± 13.8 100.0 ± 12.8 260.4 ± 33.9** 12 100.0
Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation. Jacobs et al.
 Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation Jacobs et al. Supplementary Information Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects
Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects of human spatial memory and navigation Jacobs et al. Supplementary Information Lateralized hippocampal oscillations underlie distinct aspects
NEURAL CONTROL OF MOVEMENT: ENGINEERING THE RHYTHMS OF THE BRAIN
 NEURAL CONTROL OF MOVEMENT: ENGINEERING THE RHYTHMS OF THE BRAIN Madeleine Lowery School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Centre for Biomedical Engineering University College Dublin Parkinson s
NEURAL CONTROL OF MOVEMENT: ENGINEERING THE RHYTHMS OF THE BRAIN Madeleine Lowery School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Centre for Biomedical Engineering University College Dublin Parkinson s
Layer-Specific GABAergic Control of Distinct Gamma Oscillations in the CA1 Hippocampus
 Article Layer-Specific GABAergic Control of Distinct Gamma Oscillations in the CA1 Hippocampus Bálint Lasztóczi 1, * and Thomas Klausberger 1,2, * 1 Department of Cognitive Neurobiology, Center for Brain
Article Layer-Specific GABAergic Control of Distinct Gamma Oscillations in the CA1 Hippocampus Bálint Lasztóczi 1, * and Thomas Klausberger 1,2, * 1 Department of Cognitive Neurobiology, Center for Brain
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory
 Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary materials for: Executive control processes underlying multi- item working memory Antonio H. Lara & Jonathan D. Wallis Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Behavioral measures of
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Supplementary Figure 1 Miniature microdrive, spike sorting and sleep stage detection. a, A movable recording probe with 8-tetrodes (32-channels). It weighs ~1g. b, A mouse implanted with 8 tetrodes in
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Supplementary Figure 1 Atlas representations of the midcingulate (MCC) region targeted in this study compared against the anterior cingulate (ACC) region commonly reported. Coronal sections are shown on
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12024 entary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of the number of earned cocaine infusions in Shock-sensitive
Supplementary Materials for
 advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
advances.sciencemag.org/cgi/content/full/3/3/e1600955/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Flexible and stretchable nanowire-coated fibers for optoelectronic probing of spinal cord circuits Chi Lu, Seongjun
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
Introduction to Electrophysiology
 Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Introduction to Electrophysiology Dr. Kwangyeol Baek Martinos Center for Biomedical Imaging Massachusetts General Hospital Harvard Medical School 2018-05-31s Contents Principles in Electrophysiology Techniques
Brief Communications. The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, (40):
 The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 2008 28(40):10017 10022 10017 Brief Communications Rhythmically Active Enkephalin-Expressing GABAergic Cells in the CA1 Area of the Hippocampus Project to the Subiculum
The Journal of Neuroscience, October 1, 2008 28(40):10017 10022 10017 Brief Communications Rhythmically Active Enkephalin-Expressing GABAergic Cells in the CA1 Area of the Hippocampus Project to the Subiculum
Supplementary Figure 1
 8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
8w Pia II/III IV V VI PV EYFP EYFP PV EYFP PV d PV EYFP Supplementary Figure a Spike probability x - PV-Cre d Spike probability x - RS RS b e Spike probability Spike probability.6......8..... FS FS c f
Brain Forum, presented by Mark J. Schnitzer, HHMI / Stanford Univ.
 Imaging large-scale ensemble neural codes underlying learning and long-term memory Portable microscopy for mice Brain Forum, presented by Mark J. Schnitzer, HHMI / Stanford Univ. Imaging CA1, amygdala
Imaging large-scale ensemble neural codes underlying learning and long-term memory Portable microscopy for mice Brain Forum, presented by Mark J. Schnitzer, HHMI / Stanford Univ. Imaging CA1, amygdala
Spike timing of dendrite-targeting bistratified cells during hippocampal network oscillations in vivo
 Spike timing of dendrite-targeting bistratified cells during hippocampal network oscillations in vivo Thomas Klausberger 1, László F Márton 1,Agnes Baude 1,2,J David B Roberts 1,Peter J Magill 1 & Peter
Spike timing of dendrite-targeting bistratified cells during hippocampal network oscillations in vivo Thomas Klausberger 1, László F Márton 1,Agnes Baude 1,2,J David B Roberts 1,Peter J Magill 1 & Peter
Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
Supplementary Figure 1 Tuning properties of individual circuit components and stimulus-specificity of experience-driven changes. (a) Left, circuit schematic with the imaged component (L2/3 excitatory neurons)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Regulation of Neuronal Input Transformations by Tunable Dendritic Inhibition Matthew Lovett-Barron 1, Gergely F. Turi 1, Patrick Kaifosh 1, Peter H. Lee 2, Frédéric Bolze 3, Xiao-Hua
Supplementary Information Regulation of Neuronal Input Transformations by Tunable Dendritic Inhibition Matthew Lovett-Barron 1, Gergely F. Turi 1, Patrick Kaifosh 1, Peter H. Lee 2, Frédéric Bolze 3, Xiao-Hua
Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits
 Neuron, Volume 66 Supplemental Information Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits Yusuf Tufail, Alexei Matyushov, Nathan Baldwin, Monica L. Tauchmann, Joseph Georges, Anna Yoshihiro,
Neuron, Volume 66 Supplemental Information Transcranial Pulsed Ultrasound Stimulates Intact Brain Circuits Yusuf Tufail, Alexei Matyushov, Nathan Baldwin, Monica L. Tauchmann, Joseph Georges, Anna Yoshihiro,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
doi:1.138/nature1139 a d Whisker angle (deg) Whisking repeatability Control Muscimol.4.3.2.1 -.1 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 Performance (d') Pole 8 4-4 1 2 3 4 5 Time (s) b Mean protraction angle (deg) e Hit rate (p
Molecular and Physiological Diversity of Cortical Nonpyramidal Cells
 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 1997, 17(10):3894 3906 Molecular and Physiological Diversity of Cortical Nonpyramidal Cells Bruno Cauli, 1 Etienne Audinat, 1 Bertrand Lambolez, 1 Maria Cecilia Angulo,
The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 1997, 17(10):3894 3906 Molecular and Physiological Diversity of Cortical Nonpyramidal Cells Bruno Cauli, 1 Etienne Audinat, 1 Bertrand Lambolez, 1 Maria Cecilia Angulo,
Supplementary Material for
 Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Supplementary Material for Selective neuronal lapses precede human cognitive lapses following sleep deprivation Supplementary Table 1. Data acquisition details Session Patient Brain regions monitored Time
Predictive Features of Persistent Activity Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons
 Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons Kyriaki Sidiropoulou, Panayiota Poirazi* Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Emergence in Regular Spiking and Intrinsic Bursting Model Neurons Kyriaki Sidiropoulou, Panayiota Poirazi* Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB), Foundation for Research and Technology-Hellas
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.4335
 Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Supplementary Figure 1 Cholinergic neurons projecting to the VTA are concentrated in the caudal mesopontine region. (a) Schematic showing the sites of retrograde tracer injections in the VTA: cholera toxin
Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous inhibitory networks
 Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
Cerebellar oscillations: Anesthetized rats Transgenic animals Recurrent model Review of literature: γ Network resonance Life simulations Resonance frequency Conclusion Resonant synchronization of heterogeneous
DIPLOMARBEIT. Titel der Diplomarbeit
 DIPLOMARBEIT Titel der Diplomarbeit Interneurons in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex - Molecular Expression Profiles, Postsynaptic Targets and The Qest for Novel Molecular Markers angestrebter akademischer
DIPLOMARBEIT Titel der Diplomarbeit Interneurons in the Medial Prefrontal Cortex - Molecular Expression Profiles, Postsynaptic Targets and The Qest for Novel Molecular Markers angestrebter akademischer
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Supplementary Figure 1 Localization of virus injections. (a) Schematic showing the approximate center of AAV-DIO-ChR2-YFP injection sites in the NAc of Dyn-cre mice (n=8 mice, 16 injections; caudate/putamen,
Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses
 Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information Astrocyte signaling controls spike timing-dependent depression at neocortical synapses Rogier Min and Thomas Nevian Department of Physiology, University of Berne, Bern, Switzerland
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
Supplementary Information Title Degeneration and impaired regeneration of gray matter oligodendrocytes in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis Authors Shin H. Kang, Ying Li, Masahiro Fukaya, Ileana Lorenzini,
were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the
 Supplemental Figure 1. Quality control of CD4 + T-cell purification. CD4 + T cells were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the RosetteSep CD4 + T Cell Enrichment
Supplemental Figure 1. Quality control of CD4 + T-cell purification. CD4 + T cells were isolated from the freshly drawn blood of healthy donors and ACS patients using the RosetteSep CD4 + T Cell Enrichment
Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in primary visual cortex
 *Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript revised.docx Click here to view linked Referenc Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in
*Manuscript Click here to download Manuscript: Manuscript revised.docx Click here to view linked Referenc Electrophysiological and firing properties of neurons: categorizing soloists and choristers in
Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell
 2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
2 Supplementary Figure 1. ACE robotic platform. A. Overview of the rig setup showing major hardware components of ACE (Automatic single Cell Experimenter) including the MultiClamp 700B, Digidata 1440A,
Using Multi-electrode Array Recordings to detect unrecognized electrical events in epilepsy
 Using Multi-electrode Array Recordings to detect unrecognized electrical events in epilepsy December 1, 2012 Catherine Schevon, MD, PhD Columbia University New York, NY American Epilepsy Society Annual
Using Multi-electrode Array Recordings to detect unrecognized electrical events in epilepsy December 1, 2012 Catherine Schevon, MD, PhD Columbia University New York, NY American Epilepsy Society Annual
Assessing Functional Neural Connectivity as an Indicator of Cognitive Performance *
 Assessing Functional Neural Connectivity as an Indicator of Cognitive Performance * Brian S. Helfer 1, James R. Williamson 1, Benjamin A. Miller 1, Joseph Perricone 1, Thomas F. Quatieri 1 MIT Lincoln
Assessing Functional Neural Connectivity as an Indicator of Cognitive Performance * Brian S. Helfer 1, James R. Williamson 1, Benjamin A. Miller 1, Joseph Perricone 1, Thomas F. Quatieri 1 MIT Lincoln
Supplementary Materials for. c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration
 Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Supplementary Materials for c-abl Activation Plays a Role in α-synucleinopathy Induced Neurodegeneration Saurav Brahmachari, Preston Ge, Su Hyun Lee, Donghoon Kim, Senthilkumar S. Karuppagounder, Manoj
Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit
 CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
CORRECTION NOTICE Nat. Neurosci. 20, 449 458 (2017) Hormonal gain control of a medial preoptic area social reward circuit Jenna A McHenry, James M Otis, Mark A Rossi, J Elliott Robinson, Oksana Kosyk,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Supplementary Figure 1 Arcuate ChIEF-tdTomato neurons expressed TH These micrographs show that TH-Cre-ChIEF-tdTomato (magenta), expressed by AAV in a TH-Cre mouse, were immunostained with TH (green) in
Sleep and Movement Differentiates Actions of Two Types of Somatostatin-Expressing GABAergic Interneuron in Rat Hippocampus
 Article Sleep and Movement Differentiates Actions of Two Types of Somatostatin-Expressing GABAergic Interneuron in Rat Hippocampus Linda Katona, 1, * Damien Lapray, 1,4 Tim J. Viney, 1 Abderrahim Oulhaj,
Article Sleep and Movement Differentiates Actions of Two Types of Somatostatin-Expressing GABAergic Interneuron in Rat Hippocampus Linda Katona, 1, * Damien Lapray, 1,4 Tim J. Viney, 1 Abderrahim Oulhaj,
Supplemental Information. Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking. Activity in Early Visual Cortex. Supplemental Information Inventory:
 Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
Neuron, Volume 77 Supplemental Information Gamma and the Coordination of Spiking Activity in Early Visual Cortex Xiaoxuan Jia, Seiji Tanabe, and Adam Kohn Supplemental Information Inventory: Supplementary
High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina
 High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina Greg D. Field 1, Martin Greschner 1, Jeffrey L. Gauthier 1, Carolina Rangel 2, Jonathon Shlens 1,3, Alexander
High sensitivity rod photoreceptor input to blue-yellow color opponent pathway in macaque retina Greg D. Field 1, Martin Greschner 1, Jeffrey L. Gauthier 1, Carolina Rangel 2, Jonathon Shlens 1,3, Alexander
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Supplementary Figure 1 Diverse anorexigenic signals induce c-fos expression in CEl PKC-δ + neurons a-c. Quantification of CEl c-fos expression in mice intraperitoneal injected with anorexigenic drugs (a),
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram of BBB and brain chips.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Shock-induced termination of cardiac arrhythmias
 Shock-induced termination of cardiac arrhythmias Group members: Baltazar Chavez-Diaz, Chen Jiang, Sarah Schwenck, Weide Wang, and Jinglei Zhang Cardiac arrhythmias, also known as irregular heartbeat, occur
Shock-induced termination of cardiac arrhythmias Group members: Baltazar Chavez-Diaz, Chen Jiang, Sarah Schwenck, Weide Wang, and Jinglei Zhang Cardiac arrhythmias, also known as irregular heartbeat, occur
CORTICAL INHIBITORY NEURONS AND SCHIZOPHRENIA
 CORTICAL INHIBITORY NEURONS AND SCHIZOPHRENIA David A. Lewis*,Takanori Hashimoto* and David W. Volk* Abstract Impairments in certain cognitive functions, such as working memory, are core features of schizophrenia.
CORTICAL INHIBITORY NEURONS AND SCHIZOPHRENIA David A. Lewis*,Takanori Hashimoto* and David W. Volk* Abstract Impairments in certain cognitive functions, such as working memory, are core features of schizophrenia.
Anxiolytic Drugs and Altered Hippocampal Theta Rhythms: The Quantitative Systems Pharmacological Approach
 Anxiolytic Drugs and Altered Hippocampal Theta Rhythms: The Quantitative Systems Pharmacological Approach Péter Érdi perdi@kzoo.edu Henry R. Luce Professor Center for Complex Systems Studies Kalamazoo
Anxiolytic Drugs and Altered Hippocampal Theta Rhythms: The Quantitative Systems Pharmacological Approach Péter Érdi perdi@kzoo.edu Henry R. Luce Professor Center for Complex Systems Studies Kalamazoo
SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c
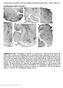 Coherent gamma oscillations couple the amygdala and striatum during learning. Popescu, Popa, Pare SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c LG LP LD R LA BL OT BM HF V HF VP RE VP CL PC d PU e 2 mm R f CP HF 2 mm GP
Coherent gamma oscillations couple the amygdala and striatum during learning. Popescu, Popa, Pare SUPPLEME TARY FIGURE 1 a b c LG LP LD R LA BL OT BM HF V HF VP RE VP CL PC d PU e 2 mm R f CP HF 2 mm GP
Temporal patterning of neural synchrony in the basal ganglia in Parkinson s disease
 Temporal patterning of neural synchrony in the basal ganglia in Parkinson s disease Shivakeshavan Ratnadurai-Giridharan 1, S. Elizabeth Zauber 2, Robert M. Worth 1,3, Thomas Witt 3, Sungwoo Ahn 1,5, Leonid
Temporal patterning of neural synchrony in the basal ganglia in Parkinson s disease Shivakeshavan Ratnadurai-Giridharan 1, S. Elizabeth Zauber 2, Robert M. Worth 1,3, Thomas Witt 3, Sungwoo Ahn 1,5, Leonid
Cytochemical Quantification of Physiologic Regulation of Oxyntic Cell Carbonic Anhydrase a
 Cytochemical Quantification of Physiologic Regulation of Oxyntic Cell Carbonic Anhydrase a A. I. VINIKb and A. A. HELDSINGER Department of Internal Medicine University of Michigan Medical School Ann Arbor,
Cytochemical Quantification of Physiologic Regulation of Oxyntic Cell Carbonic Anhydrase a A. I. VINIKb and A. A. HELDSINGER Department of Internal Medicine University of Michigan Medical School Ann Arbor,
CANON. Investigating the canonical organization of neocortical circuits for sensory integration
 Investigating the canonical organization of neocortical circuits for sensory integration Collaborators: CA Bosman, U Olcese, L Gentet, Z Somogyvári, L Négyessy The organizational principles of the brain
Investigating the canonical organization of neocortical circuits for sensory integration Collaborators: CA Bosman, U Olcese, L Gentet, Z Somogyvári, L Négyessy The organizational principles of the brain
20 2 Stomach Fig. 2.1 An illustration showing different patterns of the myenteric plexus peculiar to the regions in the guinea-pig stomach stained wit
 Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Stomach 2 The stomach is unique in that ICC have a different distribution in proximal and distal regions of the same organ. ICC-CM and ICC-LM are densely distributed throughout the thick circular and longitudinal
Oscillations: From Neuron to MEG
 Oscillations: From Neuron to MEG Educational Symposium, MEG UK 2014, Nottingham, Jan 8th 2014 Krish Singh CUBRIC, School of Psychology Cardiff University What are we trying to achieve? Bridge the gap from
Oscillations: From Neuron to MEG Educational Symposium, MEG UK 2014, Nottingham, Jan 8th 2014 Krish Singh CUBRIC, School of Psychology Cardiff University What are we trying to achieve? Bridge the gap from
Behavior-Dependent Activity and Synaptic Organization of Septo-hippocampal GABAergic Neurons Selectively Targeting the Hippocampal CA3 Area
 Article Behavior-Dependent Activity and Synaptic Organization of Septo-hippocampal GABAergic Neurons Selectively Targeting the Hippocampal Area Highlights d Rhythmically firing medial septal neurons cluster
Article Behavior-Dependent Activity and Synaptic Organization of Septo-hippocampal GABAergic Neurons Selectively Targeting the Hippocampal Area Highlights d Rhythmically firing medial septal neurons cluster
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity
 Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity Jerry L. Chen, Walter C. Lin, Jae Won Cha, Peter T. So, Yoshiyuki Kubota & Elly Nedivi SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-6 a b M
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
Desynchronization of Neocortical Networks by Asynchronous Release of GABA at Autaptic and Synaptic Contacts from Fast-Spiking Interneurons
 Desynchronization of Neocortical Networks by Asynchronous Release of GABA at Autaptic and Synaptic Contacts from Fast-Spiking Interneurons Frédéric Manseau 1, Silvia Marinelli 1, Pablo Méndez 1, Beat Schwaller
Desynchronization of Neocortical Networks by Asynchronous Release of GABA at Autaptic and Synaptic Contacts from Fast-Spiking Interneurons Frédéric Manseau 1, Silvia Marinelli 1, Pablo Méndez 1, Beat Schwaller
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
doi:10.1038/nature10353 Supplementary Figure 1. Mutations of UBQLN2 in patients with ALS and ALS/dementia. (a) A mutation, c.1489c>t (p.p497s), was identified in F#9975. The pedigree is shown on the left
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure 1 Subcellular segregation of VGluT2-IR and TH-IR within the same VGluT2-TH axon (wild type rats). (a-e) Serial sections of a dual VGluT2-TH labeled axon. This axon (blue outline) has
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals
 Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Supplementary Figure S1: Histological analysis of kainate-treated animals Nissl stained coronal or horizontal sections were made from kainate injected (right) and saline injected (left) animals at different
Nature Neuroscience doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of viral injections.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of viral injections. (a) Dorsal view of a mouse brain (dashed white outline) after receiving a large, unilateral thalamic injection (~100 nl); demonstrating that
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Supplementary Figure 1 Distribution of starter cells for RV-mediated retrograde tracing. Parcellation of cortical areas is based on Allen Mouse Brain Atlas and drawn to scale. Thick white curves, outlines
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex
 Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Ube3a is required for experience-dependent maturation of the neocortex Koji Yashiro, Thorfinn T. Riday, Kathryn H. Condon, Adam C. Roberts, Danilo R. Bernardo, Rohit Prakash, Richard J. Weinberg, Michael
Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated. reactivation during new learning
 Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
Resistance to Forgetting 1 Resistance to forgetting associated with hippocampus-mediated reactivation during new learning Brice A. Kuhl, Arpeet T. Shah, Sarah DuBrow, & Anthony D. Wagner Resistance to
