KNES 260: MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE
|
|
|
- Lee Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
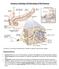
1 KNES 260: MIDTERM STUDY GUIDE ANATOMY: MEDIASTINUM & HEART & CARDIOVASCULAR CIRCULATION Arteries: Walls f arteries have three layers I. II. Tunica Adventitia (uter layer) Tunica Media (middle smth muscle layer) III. This layer maintains the artery s rund shape Elastic lamina helps maintain the shape f the artery alng with the Tunica Media Tunica Intima (inner layer) There is a smth inner lumen Carries bld frm heart t tissue Carries bld away frm the heart! Decreasing size f vessels ges frm arteries arteriles capillaries All three sizes f vessels all have smth muscle There are three types f arteries: I. Elastic Are largest in size Allw fr high degree f expansin between heart beats Example: thracic and abdminal arta II. Muscular Distributing arteries It regulates bld flw t different parts f the bdy Example: femral arteries III. Arteriles Has a narrw lumina (narrw pening)
2 Thick muscular walls Bld pressure is regulated by degree f muscular tne Examples: tributaries Veins: Veins carry bld frm tissue t heart I. Veins return bld t heart! Increasing size f vessels g frm capillaries venules veins Three types f veins: I. II. III. Large (Inferir Vena Cava) Have wide bundles f smth muscles Well develped Tunica Adventitia (uter layer) Medium (Great Saphenus Vein) Cntains vessels that maintain bld flw in the right directin Muscles must cntract in rder t pump bld int the next cmpartment (musculvenus pump) Small (Venules) Unite t frm the venus plexuses Desn t cntain nticeable amunts f smth muscle (thus the shape isn t like the shape f an artery) Structure f the vein is similar t the structure f arteries hwever: Walls are thinner due t a lwer bld pressure There is a prly develped muscular layer There are accmpanying (cmmunicating) vein fr extremity arteries Larger f the valves have valves in them Capillaries: Simple endthelial tubes D nt have tunica layers These vessels have the diameter f a red bld cell
3 Are arranged in netwrks called capillary beds Nutrients and ther materials are exchanged thrugh diffusin (example: O2, CO2) Mediastinum: (I need a better explanatin fr this, I am ttally lst nt exactly sure where it is?) It is the middle space Middle septum ccupied by tissue between tw pulmnary cavities Cvered n each side by the mediastinal pleura Tissues untied by lse cnnective tissue and infiltrated by fat (it separates the heart and lungs) Allws fr accmmdatin t changes in mvement, vlume, and pressure Heart: Pericardium: a duble walled fiberus sac enclsing the heart Outer Fiberus Pericardium: it stabilizing and prevents ver dilatin Serus Pericardium: it lies within and directly cvers the heart Visceral Layer Partial Layer Pericardial cavity is a space filled with fluid that allws the heart t beat in a frictinless envirnment There is a duble self adjusting muscular pump Right side f heart receives and sends dexygenated bld Left side f heart receives and sends xygenated bld Three tissue layers f the heart: Endcardium: internal layer f prtectin Mycardium: thick middle layer fr cntractin (the heart is mainly cmprised f this layer) Epicardium: thin external layer fr lubricatin Summary f the layers frm mst external t mst internal: Pericardium: a fiberus sac enclsing the heart Epicardium: utermst tissue layer f the heart that prvides lubricatin Mycardium: middle tissue layer f the heart, it is the thickest and it is fr cntractin Endcardium: innermst layer f the heart, prvides prtectin
4 when ventricles cntract, they prduce a wringing (squeezing, twisting) mtin due t spiral rientatin f cardiac muscle this prpels bld ut the muscle fibers are anchred t fibrus skeletn f dense cllagen the fibrus skeletn prevents: ver dilatin prvides attachment frms and electrical insulatr Cardiac Cycle: Dexygenated bld enters thrugh the right atrium and exits thrugh right ventricle int the lung, xygenated bld enters thrugh the left atrium and thrugh the right ventricle and exits int the ascending arta. Perid f relaxatin (diastle): is relaxatin f the ventricles and filling f atria ( lub sund) Perid f cntractin (systle): is perid f cntractin f the ventricles ( dub sund) Sunds are prduced by the snapping shut f ne way valves Atrium: Smth thin walled interir Musculi pectinati (small ridges f muscle) fr cntractin and mvement f bld t ventricles Atria dn t require a lt f muscle, they require a lt f rm. Interatrial septum between atria (it s a wall that separates the tw atria) Fssa valis (framen vale) The framen vale is an pening between the tw atria that clses up after birth and frms the fssa valis. Ventricles: Muscular elevatin are called trabeculae carnae Tendinus (sinewy) crds extend frm the papillary muscles t the chrdae tendinae They prduce vigrus cntractin Chrdae Tendinae prevents bld frm back flwing thrugh the ne way valve Interventricular septum separates the tw ventricles
5 Cardivascular Circulatin: Dexygenated Bld: Dexygenated bld frm the Superir Vena Cava, Inferir Vena Cava, and Crnary Sinus dump int the right atrium The bld travels thrugh the tricuspid valve int the right ventricle Bld then ges thrugh the pulmnary semi lunar valve int the pulmnary trunk The pulmnary trunk bifurcates int the right and left pulmnary arteries which then travel t each lung Oxygenated Bld: Oxygenated bld frm the pulmnary veins enter the left atrium It travels thrugh the bicuspid valve t the left ventricle Frm the left ventricle, bld travels thrugh the artic semi lunar valve and up t the ascending arta where bld then enters general circulatin Heart will first take bld via crnary artery befre it enters the ascending arta Diagram: Dexygenated bld frm Superir Vena Cava, Inferir Vena Cava, Crnary Sinus Right Atrium Tricuspid Valve Right Ventricle Pulmnary Semi Lunar Valve Pulmnary Trunk Pulmnary Arteries Lungs Pulmnary Veins Left Atrium Bicuspid Valve Left Ventricle Artic Semi Lunar Valve Ascending Arta General Circulatin Values: Valves serve t prevent back flw f bld thrugh ne way valves They are held in place by fiberus cnnective tissue Venus Return: (What exactly is systemic circulatin it s a dumb questin, I knw ) All systemic circulatin dumps int the right atrium Cardiac circulatin is attached t systemic circulatin Systemic system is when bld is transprted frm the heart t ther parts f the bdy and back Veins drain int crnary sinus, which dumps int the right atrium (s, let me get this straight: all bld frm the SVC and IVC all g int the crnary sinus, which then ges int the right atrium?) Bypass Surgery: Uses either the great saphenus vein r the internal thracic artery t replace Bypass = when crnary arteries are blcked
6 Duble bypass = when tw crnary arteries are blcked SUMMARY:
7 ANATOMY: THORACIC AND ABDOMINAL CIRCULATION: Brain must have 8% f bld supply at all times Entire digestin system ges t liver, kidney desn t have anything t d with it Cstal Grve: Cntains intercstal artery, vein, and nerve neurvascular bundle Runs n the psterir aspect f each rib Mst f the red bld cells are made by the ribs Intercstals help with inhalatin and exhalatin Arteries f the Thrax: Thracic arta Axillary artery
8 Subclavian artery Azygs Venus System: Venus return via the intercstal vein Mst psterir intercstal vein dumps int the Azygs system (when yu say mst psterir, are yu saying the MOST psterir as in there are anterir intercstal veins and ther parts f the psterir vein, r is it that MOST OF THE psterir intercstal vein dumps int the Azygs system?) Azygs venus system is a pathway between the Superir Vena Cava and the Inferir Vena Cava in an effrt t nt ver dilate the heart Azygs vein = drains right side f psterir thrax Hemiazygs vein = drains left lwer psterir thrax Accessry hemiazygs = drains left upper psterir thrax Circulatin t the Abdmen: Abdminal arta Frm thracic descending arta Passes thrugh artic hiatus f diaphragm Branches f the Abdminal Arta: Celiac trunk I. Distal t artic hiatus Splenic artery Supplies bld t the spleen, pancreas, and greater curvature f the stmach The artery is curly t lengthen the rute t the spleen because the spleen cannt handle the pressure I. Cmmn hepatic artery Supplies liver, gallbladder, stmach, pancreas, and dudenum Supplies the liver! Gastrdudenal Supplies bld t the stmach, pancreas, and prximal dudenum
9 II. Left gastric artery Superir mesenteric artery Supplies bld t part f the gastrintestinal (GI) tract Renal arteries Supplies distal esphagus and lesser curve f the stmach Supplies bld t kidneys Inferir mesenteric Supplies the lwer part f the GI tract Iliac arteries It is the bifurcatin f the abdminal arta Venus Return: Fur imprtant veins: Superir Mesenteric Splenic Inferir Mesenteric Prtal Fetal Circulatin: (SO LOST) All embrytic nutritinal needs are prvided by diffusin acrss the placenta Umbilical arteries bring dexygenated bld t placenta frm internal iliac arteries Fetal hemglbin has a higher attractin fr O2 and thus, allws diffusin f O2 frm mther t fetus Dexygenated bld frm fetus t placenta Bld returned xygenated via umbilical vein Umbilical vein: brings bld frm placenta t the fetus Placenta acts as a liver and a lung Difference in fetal and infant circulatin: Bld returning via umbilical veins bypass liver t inferir vena cava
10 Since pressure in right atrium exceeds that f the left atrium, framen vale allws bld t bypass right ventricle Ductus aterisus takes bld frm right ventricle t the arta Clamping f the umbilical crd: Umbilical veins becme ligamentum teres Umbilical arteries t becme ligaments With first breath: Ductus Aterisus cnstricts and becmes ligamentum arterisum Ductus arterisus = bld frm right ventricle ges t the arta (nly pen in uter) Ductus vensus cntricts and becmes ligamentum vensum Increased pressure in left atrium and decreased right atrium pressure causes framen vale t clse and becme fssa valis SUMMARY: ANATOMY: PERIPHERAL CIRCULATION Arteries: Artic arch: Brachicephalic trunk Right subclavian Right cmmn cartid Left cmmn cartid Left subclavian
11 Arteries in the arm: Subclavian artery Axillary artery Brachial artery Ulnar Radial Arteries ging int the neck: Cmmn cartid Internal cartid brain External cartid face and scalp Arteries in the leg: Cmmn iliac Internal stays in the pelvic basin External Femral artery Ppliteal artery Veins: Veins in the arms: Subclavian Axillary Basilic Cephalic Median cubital Median antebrachial? Veins in the legs: Psterir tibial Anterir tibial Perneal
12 Bld in legs must return t femral vein Greater saphenus Lesser saphenus If the lesser saphenus vein is blcked, can bld still return t the femral artery? Yes, because the greater saphenus vein SUMMARY: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY: HEART: Anatmy f the Circulatry System: Pulmnary system heart t the lung It has a lw pressure circuit Left ventricle pumps mre Systemic system heart t everywhere else n the bdy There is a very strng pump Heart anatmy: Left ventricle is a lt thicker than the right ventricle because it has t pump mre bld Heart Muscle and Electrical Excitatin: Cardiac muscle: Is striated (has A bands, I bands, M lines, Z lines, etcetera) Has a T Tubule system Has trpnin (calcium activated and remves trpmysin frm mysin) Must have calcium ins activate trpnin t achieve crss bridge cycle Cells are cnnected by gap junctins (mlecular tunnels that allw fr faster electrical cnductin) and desmsmes (hlds the cardiac cells tgether) at the intercalated discs Electrical Excitatin:
13 Sin atrial nde (SA Nde) It is fund at the functin between the Superir Vena Cava and the right atrium Primary pacemaker Primary pacemaker because it underges spntaneus deplarizatin fastest It is muscle nt nerve tissue Impulses f the SA ndes are cnducted thrugh the atria rapidly due t the gap junctins and the wave f excitatin causes the atrial cells t cntract SA nde is autrhythmic Atrial ventricular nde (AV Nde) Fund at the junctin f the right atrium and right ventricle Secndary pacemaker It is muscle nt nerve tissue The pacemaker ptential als ccurs in the AV nde, hwever because it is much slwer, the SA nde is the primary pace maker AV nde is als autrhythmic Main jb f the AV nde is t allw atria t cntract and then the ventricles t cntract, this is very imprtant! It receives the wave f excitatin frm the SA nde but then it delays the signal t the ventricles by 100ms. (the AV Ndal Delay) Pacemaker Ptential: The slw rise in membrane ptential (deplarizatin) prir t an actin ptential in the SA nde. Summary f the Pacemaker Ptential: K+ in channel clses N+ in channel pens and Na+ in rush int cell T type calcium channels pen and the membrane ptential rushes twards threshld T type calcium channels are transient and clse quickly Threshld is passed T type calcium channels clse and L type calcium channels pen L type are lng lasting calcium channels
14 Causes deplarizatin and an actin ptential L type channels clses and K+ channels pen and K+ ins rush ut, causing the SA nde cells t return t nrmal and becme replarized again Series f events repeats itself and thus, the SA nde is autrhythmic The waves f excitatin travel rapidly dwn the left and right branches f the Bundle f His and the Purkinje Fiber System Changes membrane ptential away frm threshld t threshld that ccurs prir actin ptential Steeper pacemaker ptential = heart beats faster Shallwer pacemaker ptential = heart beasts slwer Heart Muscle Electrical Excitatin Memberane Ptential (mv) 2 3 1
15 Pacemaker Ptential Time (ms) 1. Pacemaker Ptential: K+ channels clse Na+ cntinues t leak inwards T type calcium channels pen arund 55 t 50 mv Calcium leaks int cell These channels are transient (which means they dn t stay pen fr lng) 2. Threshld is reached: L type calcium channels pen These are lng lasting calcium channels This causes rapid deplarizatin and an actin ptential 3. Replarizatin: L type calcium channels clse K+ (rectifier/crrecter) channel pens and allws K+ ins t leave cells f the SA nde, thus replarizing it Ventricular Muscle Actin Ptential: Events: There is n pacemaker ptential Perid f deplarizatin is much lnger Actin ptential is ms in length Stage 1: At rest, membrane ptential is 90 mv It is permeable t K+ ins
16 Impermeable t Ca++ and Na+ ins A wave f excitatin causes the membrane t becme permeable t Na+ ins and K+ channels t clse Membrane ptential rises t abut 30 mv Stage 2: Na+ inactivatin Opening f L type Ca++ channels which an influx f Ca++ ins ccurs This prlngs deplarizatin and thus, a plateau ccurs Stage 3: L type in channels clse and K+ channels pen K+ efflux which causes replarizatin Mycardial Muscle Cntractin: lk this ver! 20% f calcium cmes frm extracellular fluid Calcium frm extracellular fluid stimulates release f calcium frm sarcplasmic reticulum Steps t Mycardial Muscle Cntractin: Current spreads frm ne cntractile (autrhythmic cell) cell t anther thrugh gap junctins Actin ptential travels dwn plasma membrane and T Tubules Ca2+ channels pen in plasma membrane and sarcplasmic reticulum Ca2+ that cmes frm the extracellular fluid induces sarcplasmic reticulum t release Ca2+ Crss bridge cycle begins Ca2+ is actively being transprted back t the extracellular fluid and sarcplasmic reticulum Trpmysin blck mysin binding sites and the muscle fiber relaxes ECG: Electrcardigram R P 1 2 T 3
17 S P wave = caused by atrial deplarizatin that is initiated by the SA nde 1 = plateau caused by the impulse delayed at the AV nde Q & R & S wave = ventricular deplarizatin that begins at the apex and atrial replarizatin ccurs 2 = ventricular deplarizatin is cmplete T wave = Ventricular replarizatin that begins at the apex 3 = ventricular replarizatin is cmplete Cardiac Cycle: Wigger s Diagram Steps t the Cardiac Cycle: 1. Bld returns t the atria (bth atria) and fill it. The pressure against the atriventricular valves frce the valves upn 2. Ventricles fill with bld and as they fill, the flaps f the atriventricular valves (tricuspid and bicuspid) hang pen in the ventricles. 3. Atria cntract and frce mre bld int the ventricles. 4. Ventricles cntract. 5. The bld pushes against the atriventricular valves frcing them clse 6. The papillary muscles cntract and the chrdae tendinae tighten and prevent the valve flaps frm pening.
18 7. The pressure frm the ventricles cntracting frces the semi lunar valves t pen. 8. As the ventricles relax, bld flws back dwn the artery and it fills the cusps f the semi lunar valves, thus, clsing them. THIS IS FOR THE LEFT SIDE OF THE HEART, right side wuld be different Pressure: Green line: pressure in the arta Greater amunt f pressure in the arta as the ventricle is cntracting and pushing bld int the arta The dicrtic ntch ccurs because the arta is very elastic and it bulges utward befre rebunding Blue line: left ventricle Great pressure in the left ventricle as it is cntracting and pushing bld Purple line: Atrial systle Ventricular Vlume: black line Increases as atrium fills and atriventricular valves pen and increases even mre as atria cntract. Then decreases as ventricles cntract. Autnmic Cntrl f Cardiac Output: Cardiac utput: the amunt f bld ejected frm the left r right ventricle per minute
19 Cardiac utput = strke vlume X heart rate CO = SV x HR Autnmic cntrl f the heart parasympathetic and sympathetic cntrl f the heart Parasympathetic (resting) Input: the Sa and Av ndes are cntrlled by the input frm the parasympathetic nervus system via the Vagus nerve Actin: Chlmergic muscarinic receptrs (metabtrpic) stimulates G prtein Inhibits camp Increases K+ efflux Decreases Na+ influx during pacemaker ptential Decreases heart rate Sympathetic Cntrl: Effects the SA and Av ndes, and Bundle f His / Purkinje SA Nde: Nrepinephrine acts n beta adrenergic receptrs increase in camp prductin (via actin G prteins) Decreases K+ efflux Increases Na+ influx Thus, increases heart rate AV Nde: Reduces AV ndal delay Bundle f His / Purkinje Fibers: Faster cnductin Sympathetic effect f mycardium: Nrepinephrine and epinephrine act n beta 1 adrenergic receptrs activates acetylate cyclase which increases camp pens mre L type calcium channels Increases the frce f the cntractins Increases strke vlume Frank Starling Law f the Heart: (Bldy cnfused)
20 Intrinsic cntrl f strength f mycardial cntractin Skeletal muscle has an ptimal length tensin where the maximum tensin is prduced Cardiac muscle desn t have ptical psitin f actin and mysin at rest This allws filling f bld during exercise and excitement The greater the end diastle vlume the greater the strke vlume The greater the prelad (the amunt f filling) the greater the stretch f the mycardium and then the greater the frce f cntractin. What affects strke vlume? Venus return (mre bld = mre strke vlume) Parasympathetic changes heart rate Sympathetic nervus system changes rate f cntractin Heart Metablism: Heart muscles are highly xidative It has an abundance f mitchndria and myglbin Its main energy sres is fatty acids Relies n crnary circulatin Crnary Circulatin: Mst f the crnary bld flw take place during diastle VASCULATURE: Circulatin: Bld is mainly kept in the venus return during rest Capillary endthelium: Endthelial cells can prevent bld flw Nt all endthelial cells are created equal Sme are mre leaky than thers Types f vessels: Artery muscular and highly elastic
21 Arteriles muscular and well innervated Capillaries thin walled and highly permeable Venules thin walled and cntains smth muscle Veins thin walled, fairly muscular, highly distensible (expandable) Hemdynamics: The flw f bld is thrugh the vessels (F) is dependent n the pressure gradient alng the vessel (DP) and resistance t the flw. F= P L mm Hg = = R min mm Hg/ L/min Flw will increase if pressure gradient is increased Flw will increase if resistance t flw is reduced (r bth!) What if: Pressure gradient is increased and resistance is kept cnstant Resistance is increased and pressure gradient is kept cnstant Flw wuld increase Flw wuld decrease Changing the size f the vessel has a great effect n resistance because it is inversely prprtinal t radius t the 4th pwer R 1 r4 What if: Pressure remains cnstant and resistance decreased by 16 fld. Arteriles underg the greatest amunt f radius change and thus the radius change in resistance Radius is cntrlled by the sympathetic nervus system and epinephrine Nrepinephrine is released nt alpha 1 adrenergic receptrs which causes vascnstrictin Which is a reductin in vessel radius and thus, it increases the resistance t bld flw Epinephrine released frm adrenal medulla results in beta 2 type adrenergic receptrs being activated which causes vasdilatin
22 Summary: Alpha 1 adrenergic receptrs causes vascnstrictin Beta 2 adrenergic receptrs causes vasdilatin Cntrlled by lcal chemical factrs in tissues supplied by arteriles Dilates: Include NO (Nitric Oxide) prduced by vascular endthelium Dilates: Histamine released by immune system due t an allergic reactin Beta receptrs are mainly fund in the heart Alpha receptrs are mainly fund in the GI tract Active Hyperemia: Increases bld flw in active skeletal muscle (withut sympathetic cntrl) due t accumulatin f metablites which dilates (expands) the arteries Metablites include: increase in CO2, decrease O2, increase in lactic acid Micrcirculatin and Exchange acrss Capillary Walls: Meta arteriles are shunts, mst bld at rest will g thrugh meta arteriles Mst capillary beds in muscle tissue are clsed at rest Bld is pushed (shunted) thrugh meta arteriles t venules when the pre capillary sphincters are clsed The pre capillary sphincters pen when: There is an increase in CO2 in tissue There is a decrease in O2 in tissue There is an increase in lactic acid in tissue Capillaries: where the exchange f nutrients and waste prducts f metablism and xygen and carbn dixide ccurs Mvement acrss the capillary: Simple diffusin: a slute mves dwn the cncentratin gradient (Dn t exactly get this) Bulk flw: mvement f water and the slutes disslved in the water acrss the endthelial later thrugh pres due t the differences in pressure between capillary and interstitial fluid Capillary bld pressure: frces fluid ut f capillary Interstitial bld pressure: frces fluid int capillary
23 Plasma cllid smtic pressure: frce that favurs mvement f water int capillary Interstitial fluid cllid smtic pressure: frce that favurs mvement f water ut f capillary Example f mvement acrss the capillary: There is high amunts f xygen in bld xygen will diffuse int interstitial fluid Capillary Filtratin and Reabsrptin: Lymph System: The small amunt f fluid that is nt reabsrbed by the capillaries is taken up by the lymphatic system And then it is returned t the bld eventually when the lymphatic duct dumps int a majr vein This prevents build up f fluid in the interstitium which culd cause tissue swelling Smth muscle arund the lympathatics cntract and frce the lymph int back int the circulatin and skeletal muscle cntractin frces the fluid int venus circulatin There are valves which prevent back flw Veins: Can stre abut 60% f the large vlume f bld at rest (capacitance) Veins are expandable, thin walled, with little smth muscle r elastin Venus return is facilitated by: Venus values which prevent back flw Stimulated by the sympathetic nervus system which can cntrl capacitance Skeletal muscle pumping which squeezes veins and frces bld int the next cmpartment Cntrl f Bld Pressure: Cntrlled by: Cardiac utput Heart rate is cntrlled by parasympathetic and sympathetic nervus system Strke vlume cntrlled by sympathetic nervus system Arterilar resistance Cntrlled by the sympathetic nervus system
24 Bld vlume Cntrlled by the kidneys Shrt term cntrl: Regulatin is maintained by adjustments t the cardiac utput and arterilar resistance SUMMARY: ANATOMY: PULMONARY SYSTEM Functins f the Respiratry System: Gas exchange between air and circulating bld Mving air frm the exchange surface f the lungs Prtectin f the respiratry surfaces Prductin f sund Prvisin f lfactry sensatin Thracic Cage: It is frmed by:
25 A sternum 12 pairs f ribs Cstal cartilage 12 pairs f thracic vertebrae Surrunds the thracic cavity and supprts the pectral girdle Prvides prtectin fr the thracic and abdminal cntents (heart and lungs) Organizatin f the Respiratry System: Upper respiratry system: Nse, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx Lwer respiratry system: Larynx, trachea, brnchi, brnchiles, alveli Pharynx: Psterir t nasal and ral cavities Purpse is t supply air t larynx and trachea Part f digestive and respiratry system There are three parts t the pharynx (NOL): Naspharynx Functin is respiratry It warms and mistens the air It is a psterir extensin f the nasal cavities Extends t sft palate Orpharynx Is frm the sft palate t the epiglttis (the functin f the epiglttis is t prevent chcking) Has a digestive functin Laryngpharynx Digestive functin Lies psterir t the larynx
26 Epiglttis t cricid cartilage Larynx: It is a cmplex rgan fr vice prductin Cnnects pharynx t trachea It is cmpsed f nine cartilages It changes in size and length f cartilage t affect vcalizatin Laryngeal Prminence = Adam s Apple Three main cartilages: Thyrid cartilage this is the largest Arytenid cartilage Lies superir and psterir t the cricid Lks like a hk Frms cricarytenid jint fr attachment f vcal ligament Cricid cartilage thicker and strnger It is the nly cmplete ring f cartilage Vcalizatin: Glttis is the vcal apparatus f larynx Rima glttdis is the aperture/pening between the vcal flds Shape f rima varies accrding t the vcalizatin desired. Vcal Flds: True Vcal Flds: Cntrls sund prductin Cnsists f vcal ligament and vcalis muscle False Vcal Flds: Vestibular fld Prtective functin Extend between thyrid and arytenid cartilages
27 The space between the false and true vcal wrds is the ventricle f the larynx Trachea: Fibrcartilagenus tube frm larynx t T4 / T5 It is supprted by incmplete cartilaginus tracheal rings The psterir gap f the rings is cvered by smth muscle Cmmn cartid artery and thyrid gland lie laterally It is arund 2.5 cm in diameter in adults Trachestmy: A surgery where an incisin is made between tracheal rings and a tube is inserted t maintain airways Opening is made between either rings 1 2 r rings 2 4 Esphagus: Muscular tube after the laryngpharynx Cnsists f: Upper 1/3 being vluntary Middle 1/3 being a mixture f bth vluntary and smth muscle Lwer 1/3 being smth muscle Travels psterir t trachea and pierces diaphragm t enter stmach Fd mves dwn the stmach via parastalsis (which is the invluntary squishing f fd) Trachea and Brnchi: Trachea bifurcates int tw primary brnchi Each primary brnchi is supprted by hyaline cartilage Each primary brnchi branches t frm a brnchial tree that ges int a lbe Primary brnchi divide t becme lbar brnchi (secndary brnchi) that g int each lbe Tw n the left side Three n the right side Lbar brnchi divide int terminal brnchiles which divide int respiratry brnchiles Thracic Viscera: (rgans lying in the thracic cage)
28 Tw lateral cmpartments which cnsist f the lungs and pleurae Pleurae f the lungs: Each lung is enclsed in a serus sac Has tw cntinuus membrane: Visceral cannt be separated frm the lungs Parietal lines the pulmnary cavity One central cmpartment which cnsists f the heart, great vessels, esphagus, trachea, thymus (a special rgan f the immune system) Lungs: Organs f respiratin Separated frm each ther by the heart, great vessels, and viscera Attached t the heart and trachea by structures cmprise the rt f the lung (pulmnary arteries, pulmnary veins, and brnchile structures) Lung has three surfaces: Cstal surface Mediastinal surface Diaphragmatic surface Lung als has three brders Anterir where cstal and mediastinal meet anterirly Psterir where cstal and mediastinal meet psterirly Inferir circumscribes the diaphragmatic surface Right Lung: Larger, wider, shrter, and heavier than the left lung Cause the left lung as the liver in the way And the heart is als partially in the way t Has three lbes: Superir Middle Inferir
29 Superir and inferir lbes are separated by the blique fissure Superir and middle lbes are separated by hrizntal fissures Left Lung: Left heart has a deep cardiac ntch that indents the anterir brder f the superir lbe Has tw lbes: Superir anterir brder has an indent called the cardiac impressin Inferir Lbes are separated by the blique fissure Thracic Diaphragm: Main muscle f inspiratin 3 penings g thrugh the diaphragm fr three imprtant structures: Artic hiatus Esphageal hiatus Caval framen When thracic diaphragm cntracts, the dme mves inferirly (during inhalatin) This is Byle s Law Decreased pressure = increased vlume Increased pressure = decreased vlume Pushes abdminal viscera dwn (inferirly) Mechanisms f Breathing: Quiet breathing: eupnea Invlve diaphragm, internal and external intercstals Frced breathing: hyperpnea Invlves accessry muscles as well Alveli: Final gaseus exchange ccurs in the alvelar sacs
30 SUMMARY: Intimately lcated next t the brnchial capillaries which bring dexygenated bld frm heart via pulmnary arteries Are efficient because there is a lt f surface area and: There is a difference in partial pressure There is a small diffusin distance The gas exchange invlves gasses that are lipid sluble Crdinatin f bld flw and airflw
31 ANATOMY: LYMPHATIC SYSTEM Lymphatic system: Vast netwrk f lymphatic vessels that are cnnected t lymph ndes Lymph ndes = masses f lymphatic tissue It s the secnd circulatry system It s jb is t cllect surplus tissue fluid (lymph) and send it back t the heart Parts f the lymph system include: spleen, bne marrw, thymus, ndes, and vessels Functins: Drainage f tissue fluid Cllectin f lymph frm tissue spaces Transprtatin f lymph t the venus return system the lymph drains int the subclavian vein Absrptin and transprtatin f fat Defense mechanism f the bdy as it transprts antibdies and lymphcytes t fight pathgens Lymph either enters the: Right lymphatic duct (where the lymph frm the right side f the bdy and head enter) Thracic duct (where lymph frm the rest f the bdy enter) Lymph re enters venus circulatry system Lymphid Organs: Lymph ndes: Tnsils, dense cnnective tissue thrugh the bdy Functin is t filter lymph befre it enters the venus circulatin Usually the first t react t pathgens and thus, strategically placed Fixed macrphages Thymus: It is psterir t the sternum Imprtant rle in grwth and develpment f the immune system Grws until puberty hits and then the thymus degrades (atrphy) int fat
32 Cntinues t prduce T lymphcytes in adulthd Spleen: It is a nn vital rgan Largest f the lymphatic rgans The splenic artery is large due t the large amunt f bld vlume Functin: Bld is mnitred fr pathgens by T cells Macrphages swallw and digest debris in bld cells Lymphcytes: Three type f lymphcytes: T cells (thymus dependant) 80% f the lymphcytes are T cells Fur types f T cells Helper T cells Cyttxic T cells Memry T cells B cells (bne marrw) NK cells (natural killer) Supresses the respnse after initial respnse These cells ward ff cancer cells These cells are bigger than the T cells and the B cells Defense Mechanisms: Nn specific defense: Creates a memry fr fllwing expsures t the same pathgen Suppressr T cells Stimulate further cell mediated and anti bdy mediated immunity Desn t distinguish pathgens
33 Examples: fever, skin, phagcytes, inflammatin NK cells Mast cells, basphils Neutrphils, esinphils, macrphages Specific defenses: It depends n the activity f lymphcytes Example: T cell that is manufactured fr a specific bacteria Immune Respnses: Innate immunity (which is nn specific) Dn t need previus expsure t pathgens t attack it Magnitude f respnse is always the same Acquired Immunity (which is specific): Learns t recgnize the pathgen and munts a larger attack the secnd time arund Cell mediated immunity: (which is ne cell signals anther cell) Helper T cell recgnizes pathgens antigen Helper T cells activate cyttxic T cells Cyttxic t cell tracks and destrys the cell with that specific antigen Anti bdy mediated immunity: (antibdy signals the prductin f mre antibdies) B cell recgnizes freign antigen And then the b cell divides int plasma cells and memry B cells The plasma cells can prduce antibdies Memry b cells creates a memry fr fllwing expsures When the antibdy cmes in cntact with the antigen: Neutralizatin can happen (antibdies prevent the antigen frm ding any harm) Enhances phagcytsis Agglutinatin can happen (antibdies bring tgether all the antigens and stick them tgether) Enhances phagcytsis
34 Precipitatin can ccur (antibdies slubafy the antigen?) Enhances phagcytsis Cmplement can ccur (NEED EXPLANATION!) Leads t cell lysis (explsin!) SUMMARY: ANATOMY: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Cmpnents f the System: Accessry structures Subcutaneus layer Functins f the System: Prtectin (primary functin) Excretin Temperature maintenance Nutrient strage Vitamin D3 synthesis (when expsed t UV rays) Sensry detectin (thermreceptrs, mechanreceptrs, chemreceptrs) Cutaneus membrane Epidermis: Cmpsed f layer f keratincytes Thin skin = fur layers Thick skin = five layers
35 Prvides mechanical prtectin Prevents fluid ls Keeps micrrganisms frm invading the bdy Cells accumulate keratin and eventually are shed Epidermal ridges are interlcked with dermal papillae which imprves gripping ability (and causes fingerprint) Langerhans cells (immunity) Merkel cells (sensitivity) Epidermal cells: Synthesize vitamin D3 when expsed t the UV Respnd t epidermal grwth factr This determines hw fast ur hair, skin, and nails grw, repair, and secrete Dermis: Papillary layer: Cntains bld vessels, lymphatic vessels, sensry nerves f the epidermis Reticular layer: Cntains netwrk f cllagen and elastic fibers t resists tensin This give skin its elasticity, nt t anchr it t anything Stretch marks ccur because it is an excessive stretching f the dermis It leaves patterns f cllagen and elastic fibers frm lines f cleavage It is red because it is an accumulatin f red bld cells Lines f cleavage are naturally ccurring and allws fr mvement Cutaneus plexus arteries fund in subcutaneus layer / papillary dermis Cutaneus sensry receptrs (light tuch, pressure) Hypdermis: Reticular layer gets stretched and thus, papillary layer gets damaged and vessels rupture Keratin: Cnnects skin t underlying tissue (underlying tissue = adipse r fascia)
36 Fibrus structural prtein Key material in epidermis, nails, and hair Callus frmatin Epithelial cells becme crnified with keratin (which makes skin waterprf) Skin clur: Depends upn: Bld supply Hw much melanin we have Cartene Epidermal pigmentatin Hair fllicles: Hair riginates in the fllicle Cmpsed f rts and shaft Rt (papilla) surrunded by bulb and plexus Sft medulla and hard crtex Cuticle is the superficial dead prtective layer Glands: Sebaceus: Tied t the lymphatic system Discharge waxy sebum nt hair shaft Sudriferus: Give yu yur distinct dr Apcrine sweat glands Mercrine sweat glands: Prduce dr Perspiratin Mammary: Structurally similar t apcrine sweat glands
37 Ceruminus: In ear, it prduces waxy cerumen t prtect the ear Nails: Nail bdy cvers the nail bed Nail prductin ccurs at the rts Cuticle (epnychium) lies ver the rt Injury and Repair: Regenerates easily Regeneratin prcess includes: Scabbing Granulatin tissue Scar tissue SUMMARY: PHYSIOLOGY: PULMONARY PHYSIOLOGY Anatmical Features f the Pulmnary System: Airways: There is an increase in the amunt f smth muscle we see in the airways Parasympathetic nervus system stimulus f the smth muscle results in cnstrictin f the brnchiles Sympathetic nervus system stimulus f the smth muscle results in dilatin f the brnchiles Alvelar Sac: a cluster f alveli with a cmmn pening Alveli: The alvelar wall is cmpsed f tw types f cells:
38 Type I: smetimes are called pavement cells Usually make up the alvelar wall Are thin and flat Type II: prduce pulmnary surfactant Surfactant is a type f phsphlipid Because water cats bth type I and type II surfactant breaks the water mlecule bnd in rder fr the alveli t expand Type tw is thicker and isn t as cmmn as type I Alvelar macrphage attacks any bacteria r virus The thin walls f the alveli and high surface area allw high permeability fr gas diffusin Pleural sac: Visceral Pleura: This is cnnective tissue surrunding the lung This layer cannt be separated frm the lung Parietal Pleura: Cnnective tissue lining the inside f the thrax Intrapleural Space: Thin and fluid filled This is lubricatin and glue The visceral and parietal pleura are in very clse prximity, the nly thing separating the tw is the intrapleural space which is filled with the intrapleural fluid Respiratry Mechanics: Pressures: Atmspheric Pressure: pressure f the atmsphere, decreases as elevatin increases Intra alvelar Pressure / Intra pulmnary pressure: pressure inside each alveli Intra pleural Pressure: pressure inside pleural space, this is always belw the atmspheric pressure Why is intrapleural pressure belw the atmspheric pressure? (r sub atmspheric) If the pressure is equal r greater than the atmspheric pressure then the lung wuldn t expand
39 Because f the tendency fr the thrax t expand utwards Because f the tendency f lung t recil inward (cllapse) These tw frces try frce the lung apart, but the thin layer f intrapleural fluid between the tw layers prevents it frm ccurring Pneumthrax: The pressure inside the intra pleural space is negative, and thus, it frces the tw pleural tgether and prevents it frm separating Lung wuld cllapse! Trans pulmnary Pressure: difference between intra alvelar (intra pulmnary) pressure and the intra pleural pressure Inhalatin / Inspiratin: Cntractin f: (which results in the thrax having vlume) External intercstal muscles ribs mve up and ut Diaphragm mves dwn Changes in Pressure: Intra pulmnary: pressure decreases as yu inhale because the external intercstal muscles and diaphragm mves ut f the way Trans pulmnary: stays relatively the same due t the fact that the intra pulmnary pressure decrease s des the intra pleural pressure Intra pleural pressure: decreases, but then the pressure is relatively mre negative t the atmspheric which frces the tw pleura tgether and prevents the separatin Summary: Inhalatin: Increase in vlume (Byle s Law: increase in vlume = decrease in pressure) Decrease in intra pleural pressure Exhalatin / expiratin: Relaxatin f: (which results in mre pressure) External intercstal muscles Diaphragm
40 The intra pulmnary pressure is greater r equal t the atmspheric pressure Intrapleural pressure returns t nrmal Cmpliance: Change in alvelar vlume is nt nly a functin f the change in thracic pressure, but als in the cmpliance f the alveli Cmpliance: Ease f filling f the alveli Change in vlume f the alveli / unit change in pressure What affects cmpliance? Thickness f the alvelar wall (thinner the better) The thinner the better Size f the alveli at the start f inhalatin (larger the alveli the better) The smaller the alveli at the start f inspiratin the harder it is t fill the alveli The larger the alveli the better Surface tensin f alveli (less surface tensin is better) The less surface tensin the better Lung Vlume: Definitins: Respiratin (ventilatin) rate: number f breaths taken per minute breaths ( f min ) Tidal vlume: amunt f air mved in and ut f lungs per minute ut f lungs ( amunt f air ) breath Minute ventilatin: tidal vlume times respiratry rate breaths ut f lungs amunt f air ( f min ) ( amunt f airbreath )= min Dead space: amunt f air in the airway that desn t underg gas exchange
41 Alvelar ventilatin: Tidal vlume minus dead space times the respiratry rate ( Tidal vlume dead space ) x breaths vlume ( f min )= min Vital capacity: max expiratin fllwing a max inspiratin Gas Exchange: All abut the mvement f xygen and CO2 the alvelar air, bld, and tissues It is based upn the partial pressure f gasses in these cmpartments Gas always mves frm an area f high partial pressure t an area f lw partial pressure Partial pressure = fractin f a gas in the atmsphere x the atmspheric pressure Partial pressure in the atmsphere is different frm the partial pressure in the alveli Fractin f xygen = 21% (PN2) Fractin f nitrgen = 79% (PO2) Fractin f carbn dixide and ther gases: less than 1% (PCO2) Gases als exert a partial pressure n liquid It depends upn the partial pressure f the gas n tp f the liquid r mixed in with the liquid When a liquid is expsed t the atmsphere, it will eventually reach the same pressure as the atmsphere Oxygen: PO2 in dry air versus at sea level is different because: Due t the mixing f air in the dead space and fresh air during inhalatin Dead space air = lw in xygen Fresh air = high in xygen Thus, there is a reductin in the PO2 levels Humidificatin f air during inhalatin Reduces fractin f xygen in the alveli Reduces PO2 We will assume that we are at sea level under resting cnditins which means that the PO2 levels in alvelar air is 100 mmhg Carbn dixide: PO2 levels in alvelar air is 40mmHg at sea level because:
42 Mixing f fresh air with dead space Rate f which CO2 is delivered t the lung frm the bld Fick s Law f Diffusin: Rate f diffusin f gases acrss the alveli is gverned by Fick s Law ( Surface area increase = gd Partial pressure increases = gd Thickness f alveli increases = bad kxax =rate f diffusin ( P P D )) 2 1 K = diffusin cefficient f gas A = surface area D = thickness f the barrier P2 P1 = partial pressure gradient fr gas Gas Transprtatin: Vast majrity f xygen carried in bld is carried by hemglbin fund in red bld cells It can carry 20mL xygen/100 ml Because cardiac utput cannt deliver amunt f bld desired Binding f xygen t hemglbin: Hemglbin is made up f fur prtein subunits called glbulins 2 Alpha 2 Beta All fur have a prplyrin ring (a heme grup) that cntains ferrus irn which is the nly irn capable f transprting xygen. The curve is S shaped (it is called sigmidal curve)
43 Cperativity: the binding f ne xygen mlecule facilities the rapid binding f ther xygen mlecules Full saturatin f hemglbin ccurs arund 60 mmhg Hemglbin nly unlads abut 25% 30% f its xygen t diffuse int the tissue We usually still have 20% t 40% f xygen left in the hemglbin at all times (unless yu are dead) Bhr s Shift: The rightward shift f the sigmidal curve due t the increase f carbn dixide levels helps unlad mre xygen at the tissue level It desn t affect the ability t saturate at the level f the lung Only helps t unlad the xygen at the tissue level Things that affect affinity f hemglbin t xygen: Increased CO2 levels Lwer ph Increase in temperature Increase in 2,3 diphsphglycerate ccurs when expsed t high altitudes CO2 can be in three different frms in the bld: Disslved in the bld plasma In the frm f bicarbnate (mst f the CO2 in the bld is in this frm) CO2 bund t hemglbin At the tissue level, xygen is released and carbn dixide is picked up At the alvelar level, xygen is picked up and carbn dixide is released Cntrl f Ventilatin: Cntrl is centered in the medulla blngata and pns regin f the brain stem
44 Medullary Respiratry Center: 1. Drsal Respiratry Grup: Passive Cntrls quiet breathing during rest Cntrls the intercstal neurns (external intercstal muscles) and the phrenic neurns (diaphragm) 2. Ventral Respiratry Grup: Active Active during time f increased needs fr ventilatin (exercise) Stimulates internal intercstal and abdminal muscles during frced expiratin Cntrl f Inspiratin and Expiratin: 1. Central Pattern Generatr Cells: Sends cmmands t regulate frequency fr firing f Drsal Regulatin Grup cells These cells are called pre Btzinger cells 2. Pntine Respiratry Center: Fine tunes perid f inhalatin and exhalatin via signals t the Drsal regulatin Grup cells 3. Pulmnary Stretch Receptrs and Hering Breuer (stretch) reflex: Hering Breuer (stretch) reflex if there is an ver inflatin f the lung, then it signals the Drsal Regulatin Grup t stp further inhalatin 4. Chemreceptrs: Peripheral: cartid bdies and artic bdies Faster t react than central chemreceptrs Central: it nly mnitrs the cerebral spinal fluid ph They are a lt mre sensitive t the changes t the PCO2 Hw they wrk: CO2 can crss the bld brain barrier and it wuld enter the cerebral spinal fluid Carbn dixide + water in the cerebral spinal fluid carbnic acid Carbnic acid HCO 3 + H+ H+ stimulates cntrl chemreceptrs which increases ventilatin Pulmnary Pathphysilgy: Hypxia: reduced availability f xygen at the tissue level
45 Fur types f hypxia: 1. Hypxic hypxia: Due t a lack f xygen in the atmsphere 2. Anemic hypxia: Due t anemia which is a reductin in hemglbin 3. Circulatry hypxia: Due t pr circulatin 4. Histtxic hypxia: Due t the inability t use xygen in the cells (ex. cyanide pisning) Pulmnary bstructins: All pulmnary bstructins result in the same effect n ventilatin, which is reduced ability t frcefully exhale due t either: 1. Increased airway resistance 2. Reduced elastic recil Type f Obstructins: 1. Chrnic Brnchitis: narrwing f airways due t mucus 2. Asthma: narrwing f airway due t the cntractin f smth muscles arund airway 3. Emphysema: due t the breaking dwn f the alvelar walls which is due t an enzyme that is released that destry elastin SUMMARY:
Chapter 20 The Heart
 Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Chapter 20 The Heart ANATOMY OF THE HEART The adult heart is apprximately the size f. The heart is lcated in the cavity, between. Base is directed, and the apex is directed. The membrane surrunding and
Materials Dissecting pan, dissecting kit, safety glasses, lab apron, pig heart, & gloves
 Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
Heart Dissectin Intrductin Mammals have fur-chambered hearts and duble circulatin. The heart f a bird r mammal has tw atria and tw cmpletely separated ventricles. The dublelp circulatin is similar t amphibians
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: Identify the cmpnents f the cardivascular
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Proenza
 CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
CV 03-20-17 08AM CVPR Overview-Anatmy - Prenza CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM: OVERVIEW & ANATOMY Cathy Prenza catherine.prenza@ucdenver.edu Recmmended Reading Lilly p 1-12 Other learning resurces: http://www.cvphysilgy.cm/
Exercise Physiology CardioRespiratory Trimester 2. Exercise Physiology Cardiorespiratory Study Guide
 Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
Exercise Physilgy CardiRespiratry Trimester 2 Cardivascular System Exercise Physilgy Cardirespiratry Study Guide 1. Be able t label the structures f the heart (chambers, vessels, valves) and the pattern
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
INTRODUCTION TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM What des bld d? 5. What makes this pssible? : In rder fr there t be an efficient exchange f xygen, waste and nutrients there must be a high surface area between the
Name: Date: Period: Notes: The Blood and Lymphatic System
 Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Name: Date: Perid: Cmpsitin f Bld and their Functins Red Bld Cells (aka ) Structure Ntes: The Bld and Lymphatic System D nt have a like ther cells d Cntain a specialized prtein called Hemglbin cntains
Topic 11: Nervous System
 Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Tpic 11: Nervus System Functin: Imprtant Definitins Neurns: Stimulus: anything that causes a nerve impulse t be sent Ex: Receptrs: sense rgans that detect Impulse: change alng the neurn Effectrs: any structure
Biology 30S Unit Test Review: Digestion
 Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Bilgy 30S Unit Test Review: Digestin Test utline: Multiple Chice: 10 Questins, 1 mark each. Shrt Answer: 5 Questins (answer 3 f them), 5 marks each. Lng Answer: 2 Lng Answer Questins, 10 marks each. Tasks
Autonomic. Nervous System
 Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Autnmic Nervus System Cmpiled by Campbell M Gld (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgld.cm IMPORTANT The health infrmatin cntained herein is nt meant as a substitute fr advice frm yur physician, r ther
Bio 103 Tissues and Skin 35
 Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
Bi 103 Tissues and Skin 35 Lecture Outline: Tissues & Skin [Chapters 5, 6, 12 (p. 440441)] Chapter 5: Tissues Def.: Tissue = Fur basic tissue types 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial Tissues General Characteristics
BROCKTON AREA MULTI-SERVICES, INC. MEDICAL PROCEDURE GUIDE. Date(s) Reviewed/Revised:
 Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
Page 1 f 6 Subject: Range f Mtin Exercises Date Develped: 4/2010 PROTOCOL FOR: All trained staff PURPOSE: Range f Mtin (ROM) exercises are very imprtant if an individual has t stay in bed r in a wheelchair.
b. Responses/Reflexes Food bulk stretches the fundus of stomach, activating mechanoreceptors GI peptides activate chemoreceptor s o o o
 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 2 GASTRIC PHASE OF DIGESTION DIGESTIVE SYSTEM CHAPTER 21 I. ENTERIC NERVOUS SYSTEM a. Defined and Crrelatin with Shrt Reflexes Fund in walls f LUMEN Invlved in shrt reflexes
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System:
 Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Chapter 37 The Skeletal and Muscular System: 3.5 Learning Objectives 3.5. Respnses in the human 1. Descriptin f the structure and functins f the skeletn. 2. Label the cmpnent parts f the axial and appendicular
Cairns Base Hospital Emergency Department Part 1 FACEM MCQs
 airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
airns ase Hspital mergency epartment Part 1 FM MQs 1 ncerning the cardiac actin ptential Phase 1 is due t rapid sdium influx Resting membrane ptential is typically -90mV Phase 2 results frm slw prlnged
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
Cardiovascular System I. Structure of the Heart A. Average adult heart is 14 cm long and 9 cm wide. B. Lies in the mediastinum. C. Enclosed in the pericardium. 1. Fibrous pericardium- Outer, tough connective
1A Human Biology Food, Digestion and Associated Body Systems
 1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
1A Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Human Bilgy Fd, Digestin and Assciated Bdy Systems Fd Fd is ne f the basic human needs and the digestive system enables the bdy t cnvert it int a frm
AP Biology Immune System. Pathogens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability to avoid disease when invaded by a pathogen
 AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
AP Bilgy Pathgens: agents that cause disease Immunity: the ability t avid disease when invaded by a pathgen Innate Immunity: nnspecific First line f defense Barriers such as skin Hard fr bacteria t penetrate
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Function
 Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
Chapter 18 The Urinary System Renal Functin Chapter Outline Functins f the Urinary System Anatmy f the Urinary System Basic Renal Exchange Prcesses Reginal Specializatin f the Renal Tubules Excretin 18.1.
HUMAN HEART. Learn the following structures on the heart models.
 HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
HUMAN HEART Learn the following structures on the heart models. The human heart has four chambers that consist of the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are smaller
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
NSB603 Introduction to Cardiothoracic Nursing
 NSB603 Intrductin t Cardithracic Nursing Lecture 1a HEART OBJECTIVES Describe pathphysilgy f heart failure, CAD, angina/mi List Rx fr angina/mi Evaluate effectiveness f interventins HEART PATHWAY Frm Bdy
NSB603 Intrductin t Cardithracic Nursing Lecture 1a HEART OBJECTIVES Describe pathphysilgy f heart failure, CAD, angina/mi List Rx fr angina/mi Evaluate effectiveness f interventins HEART PATHWAY Frm Bdy
Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 CEREBRAL BLOOD CIRCULATION Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: List the cerebral arteries. Describe
CEREBRAL BLOOD CIRCULATION Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University Schl f Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end f the lecture, students shuld be able t: List the cerebral arteries. Describe
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 18. Bdy Fluids and Circulatin Bld: A special cnnective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system f man and ther vertebrates cnsisting f fluid matrix, plasma and frmed elements.
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 18. Bdy Fluids and Circulatin Bld: A special cnnective tissue that circulates in principal vascular system f man and ther vertebrates cnsisting f fluid matrix, plasma and frmed elements.
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Test 3 Study Guide: Photosynthesis, Respiration, and the Cell Membrane
 Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
Name Blck Date Test 3 Study Guide: Phtsynthesis, Respiratin, and the Cell Membrane Test Dates: December 13 (1 st and 7 th blck) and 12 (6 th blck) SOL: BIO.2d, 3d-e Related Ntes Phtsynthesis Respiratin
The Digestive System. May 16, The Digestive System.notebook
 3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
3 The Digestive System.ntebk The Digestive System THE BASIC CONCEPTS Animals btain energy by breaking fd mlecules int smaller pieces. The basic fuel mlecules are amin acids, lipids and carbhydrates. The
The Heart. The Heart A muscular double pump. The Pulmonary and Systemic Circuits
 C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
C H A P T E R 19 The Heart The Heart A muscular double pump circuit takes blood to and from the lungs Systemic circuit vessels transport blood to and from body tissues Atria receive blood from the pulmonary
The Excretory System. 4 The Excretory System.notebook. May 24, 2017
 4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
4 The Excretry System.ntebk The Excretry System OSMOREGULATION (WATER BALANCE) Mst marine invertebrates are smcnfrmers, meaning the cncentratin f slutes in their bdy fluid is equal t that f their envirnment.
Topic 12: Endocrine System. Function: Group of glands that produces regulatory chemicals ( )
 Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
Tpic 12: Endcrine System Functin: Grup f glands that prduces regulatry chemicals ( ) Hrmnes: Chemical messengers released directly int the bldstream that regulate: *May have wide-spread effects r nly affect
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Division
 The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
The Cell Cycle & Cellular Divisin Name: Perid: Date: I. Cell Divisin: All are derived frm preexisting cells (Cell Thery) is the prcess by which cells prduce new cells Cells grw in number, NOT in Smaller
Can exert forces from a fraction of an ounce to > 70 lbs
 Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Anatmy & Physilgy Chapter 9 Ntes: Muscles and Muscle Tissue Name Muscle Cell = My / Mys = Sarc = Muscle Cell Plasma Membrane = Muscle Celly Cytplasm = Three types f muscle tissue: 1. 2. 3. Skeletal Muscle
Cellular Neurophysiology Membrane Ionic Gradients Concentration gradients and diffusion Membrane transport:
 Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Cellular Neurphysilgy Membrane Inic Gradients Fluid-msaic mdel f plasma membrane: lipid bilayer separating intracellular and extracellular fluids Biplar phsphlipids Hydrphilic head grups and hydrphbic
Group Members: Date Period
 Dissectin Kit Number: Grup Members: Date Perid Dissectins Objective: In this tw-week investigatin, we will be lking at an invetebrate (grasshpper) and a vertebrate (frg). Yu will be fcusing n the external
Dissectin Kit Number: Grup Members: Date Perid Dissectins Objective: In this tw-week investigatin, we will be lking at an invetebrate (grasshpper) and a vertebrate (frg). Yu will be fcusing n the external
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
11/10/2014. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
Anemia. There are three types of Anemia that effect EB patients. They are Iron Deficiency, Chronic Inflammatory and Nutritional.
 Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
Anemia Mst patients with Recessive Dystrphic Epidermlysis Bullsa are als Anemic. Anemia in EB is caused by many factrs and can becme very severe if nt treated. Anemia means nt having enugh red cells and
BIOLOGY 101. CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Function: Life at the Edge
 BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
BIOLOGY 101 CHAPTER 7: Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge Membrane Structure and Functin: Life at the Edge CONCEPTS: 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid msaics f lipids and prteins 7.2 Membrane
ANAT2011 Anatomy Notes
 ANAT2011 Anatmy Ntes Mdule 1: Hw t Speak Anatmy... 2 Mdule 2: Nervus System... 4 Mdule 3: Sniff, Swallw, Speak!... 14 Mdule 4: Just Breathe... 35 Mdule 5: Wh are the Great 8?... 43 Mdule 6: N Guts, N Glry...
ANAT2011 Anatmy Ntes Mdule 1: Hw t Speak Anatmy... 2 Mdule 2: Nervus System... 4 Mdule 3: Sniff, Swallw, Speak!... 14 Mdule 4: Just Breathe... 35 Mdule 5: Wh are the Great 8?... 43 Mdule 6: N Guts, N Glry...
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES.! BIOL1040 University of Queensland
 CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
CELLS TO ORGANISMS LECTURE NOTES BIOL1040 University f Queensland BIOL1040 Cells t rganisms Lecture Ntes Cntents Mdule 1 Principles f Cell Functin... 2 Lecture 1: Membrane Structure and Functin 1... 2
Human Senses. Touch. Fingerprint. Vidhya Peetham i-school. The skin in our fingers is very sensitive. The skin in our back is not very sensitive.
 Vidhya Peetham i-schl Human Senses Humans have five senses. They are hearing, sight, smell, taste and tuch. Often, we use mre than ne sense at the same time. All the five senses wrk with the brain and
Vidhya Peetham i-schl Human Senses Humans have five senses. They are hearing, sight, smell, taste and tuch. Often, we use mre than ne sense at the same time. All the five senses wrk with the brain and
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE. All Systems, GO! Lesson #3
 ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
ITQ ARTS AND SCIENCE INTEGRATION GRADE 5 DANCE AND LIFE SCIENCE All Systems, GO! Lessn #3 FOSS Califrnia, Grade 5, Living Systems, Investigatin 1, Part 3 CONTENT STANDARDS Dance Grade 5 2.1 Create, memrize
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
Science. Human Biology. New Jersey Quality Single Accountability Continuum (NJQSAC) Department: Course Title
 New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
New Jersey Quality Single Accuntability Cntinuum (NJQSAC) Department: Curse Title Human Bilgy Textbk(s): Fundamentals f Anatmy and Physilgy Essential Questin(s): Cntent Unit 1, September 1. What are Anatmy
Anatomy, Histology, & Embryology of the Pancreas
 Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
Anatmy, Histlgy, & Embrylgy f the Pancreas *Pancreas is secndary retrperitneal, with the exceptin f the tail, the fregut. Anatmy f Pancreas Lcatin: Within the curve f the dudenum, lcated in the epigastric
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
POINTS TO REMEMBER : 20. Lcmtin and Mvement Types f Mvement : Amebid mvement: This mvement takes place in phagcytes where leuccytes and macrphages migrate thrugh tissue. It is affected by pseudpdia frmed
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Chapter 20 (1) The Heart Learning Objectives Describe the location and structure of the heart Describe the path of a drop of blood from the superior vena cava or inferior vena cava through the heart out
Human Anatomy, First Edition
 Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley & O'Loughlin Chapter 22 : Heart 1 Functions of the Heart Center of the cardiovascular system, the heart. Connects to blood vessels that transport blood between the
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
Cardiovascular Anatomy Dr. Gary Mumaugh Location of Heart Approximately the size of your fist Location o Superior surface of diaphragm o Left of the midline in mediastinum o Anterior to the vertebral column,
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
Virginia Western Community College BIO 142 Human Anatomy and Physiology II
 Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Virginia Western Cmmunity Cllege BIO 142 Human Anatmy and Physilgy II Prerequisites BIO 141 r equivalent: an ENG 111 placement recmmendatin, c-enrllment in ENF 3/ENG 111, r successful cmpletin f all develpmental
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
2. right heart = pulmonary pump takes blood to lungs to pick up oxygen and get rid of carbon dioxide
 A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
A. location in thorax, in inferior mediastinum posterior to sternum medial to lungs superior to diaphragm anterior to vertebrae orientation - oblique apex points down and to the left 2/3 of mass on left
Topic 1: Cell Biology (Student) Essential Idea: Eukaryotes have a much more complex cell structure that prokaryotes.
 Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Tpic 1: Cell Bilgy (Student) 1.2 Essential Idea: Eukarytes have a much mre cmplex cell structure that prkarytes. 1.2 Intrductin t Cells i. Prkarytes have a simple cell structure withut cmpartmentalizatin.
Cardiovascular System. Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessel anatomy Physiology & regulation Path of blood flow Aorta Arteries Arterioles Capillaries Venules Veins Vena cava Vessel anatomy: 3 layers Tunica externa (adventitia):
Finding the right 90 people in 90 days and what to do with them:
 Finding the right 90 peple in 90 days and what t d with them: Wh can yu give the 3 packets (with instructins) t? Current Preferred Custmers nt currently n the Daily Essentials Packets. Friends and Family
Finding the right 90 peple in 90 days and what t d with them: Wh can yu give the 3 packets (with instructins) t? Current Preferred Custmers nt currently n the Daily Essentials Packets. Friends and Family
Chapter 18 - Heart. I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity)
 Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Chapter 18 - Heart I. Heart Anatomy: size of your fist; located in mediastinum (medial cavity) A. Coverings: heart enclosed in double walled sac called the pericardium 1. Fibrous pericardium: dense connective
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
Cardiovascular System The Heart Cardiovascular System The Heart Overview What does the heart do? By timed muscular contractions creates pressure gradients blood moves then from high pressure to low pressure
10/23/2017. Muscular pump Two atria Two ventricles. In mediastinum of thoracic cavity 2/3 of heart's mass lies left of midline of sternum
 It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
It beats over 100,000 times a day to pump over 1,800 gallons of blood per day through over 60,000 miles of blood vessels. During the average lifetime, the heart pumps nearly 3 billion times, delivering
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART B The Heart: Cardiac Output Cardiac output (CO) Amount of blood pumped
I Before You Read. I Read to Learn. What is an arthropod? How does an exoskeleton provide protection?
 I Befre Yu Read Have yu seen a drawing r picture f a knight in armr? What is the purpse f armr? On the lines belw list the advantages and disadvantages f wearing a heavy suit f armr. As yu read this sectin
I Befre Yu Read Have yu seen a drawing r picture f a knight in armr? What is the purpse f armr? On the lines belw list the advantages and disadvantages f wearing a heavy suit f armr. As yu read this sectin
Module 2. Chapter 4 Anatomy of the Cell
 Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
Mdule 2 Chapter 4 Anatmy f the Cell The Prkarytic and Eukarytic Cells Prkarytic cells and eukarytic cells Cmpsed f carbhydrates, prteins, nucleic acids, lipids Perfrm f chemical reactins Differences are
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
Chapter 13. Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Chapter 13 Cardiovascular System 1 Introduction A. The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and vessels (arteries, capillaries and veins.) B. A functional cardiovascular system is vital for supplying
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1
 Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
Unit 11 - The Cardiovascular System 1 I. Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System A. The Cardiovascular System 1. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels a) The heart pumps blood b) Blood vessels allow
The Cardiovascular System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Cardiovascular System 11PART A The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood
Understanding and Recognizing Anxiety
 Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Understanding and Recgnizing Anxiety Mst peple d nt recgnize their anxiety fr what it is, and instead think there is smething mre serius ging n. Myth: Reading, thinking, and learning abut anxiety will
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels
 MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
MODULE 2: CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ANTOMY An Introduction to the Anatomy of the Heart and Blood vessels The cardiovascular system includes a pump (the heart) and the vessels that carry blood from the heart
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Biology 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reproductive Systems ANSWERS
 Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
Bilgy 12 Review sheet Urinary and Reprductive Systems ANSWERS 1. What is the main excretry rgan? Kidneys 2. What are the functins f the kidney? helps maintain hmestasis thrugh regulatin f H 2O and ins
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters
 Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
Test Review Circulatory System Chapters 13-2010 1. The tissue that forms the tight fitting sac around the heart is the a. parietal pericardium c. myocardium b. visceral pericardium d. endocardium 2. Which
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Part 1
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Part 1 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Blood Heart Blood vessels What is the function of this system? What other systems does it affect? CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Functions Transport gases,
Circulatory and Respiratory
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Animals are complex multicellular organisms that require a mechanism for transporting nutrients throughout their bodies and removing wastes. The
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Downloaded from
 POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
POINTS TO REMEMBER : Dwnladed frm www.studiestday.cm 19. Excretry Prducts and Their Eliminatin Ammntelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste in the frm f ammnia.(fish) Uretelic: eliminatin f nitrgenus waste
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distribution
 Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
Lecture 9 PCL201 Drug Distributin Where d drugs distribute? Drug distributin (and ptentially cncentratin) will depend n bld flw and the physichemical prperties f the chemical Lipid and water slubility
the Cardiovascular System I
 the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
the Cardiovascular System I By: Dr. Nabil A Khouri MD, MsC, Ph.D MEDIASTINUM 1. Superior Mediastinum 2. inferior Mediastinum Anterior mediastinum. Middle mediastinum. Posterior mediastinum Anatomy of
Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column,
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Approximately the size of your fist Location Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline in mediastinum Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Posteriorly the
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
The HEART. What is it???? Pericardium. Heart Facts. This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep
 This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
This muscle never stops working It works when you are asleep The HEART It works when you eat It really works when you exercise. What is it???? Located between the lungs in the mid thoracic region Apex
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart -
 Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Ch 19: Cardiovascular System - The Heart - Give a detailed description of the superficial and internal anatomy of the heart, including the pericardium, the myocardium, and the cardiac muscle. Trace the
Close to spine/ point of attachment
 Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Terms, Tissues and Imaging INTRODUCTION TO ANATOMY AND ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY 1. Anatmical Facts; islated bservatins r statements abut structures (bdy parts) r events (happenings) Anatmical cncepts; structures
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease
 Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
Section 5.1 The heart and heart disease Mammals are too large to rely on diffusion. They need a circulatory system to move substances around the body. Blood moves down pressure gradients, from high to
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Extension: Flexion: Motor neurons: o Only excitatory neurons release acetylcholine (ACh)
 Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
Interneurn -> A nerve cell fund entirely within the central nervus system that acts as a link between sensry neurns and mtr neurns Infrmatin sent frm brain t perfrm a gal, has a purpse Tw Types f Mtr Behavir:
The Cardiovascular System. Preview of Heart Action. The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
 The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
The Cardiovascular System BIO 250 Human Anatomy & Physiology Preview of Heart Action http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d3zdj gfddk0&nr=1 The CV system provides oxygen & nutrients to tissues-removes wastes.
Collin County Community College. ! BIOL Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5. The Heart
 Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
The Heart. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
C h a p t e r 20 The Heart PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings Introduction
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System
 Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
Unit 11: The Cardiovascular System I. The Cardiovascular System A. A closed system of the heart and blood vessels 1. The heart pumps blood 2. Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the
