FUNCTION: It COORDINATES movement HOW IT WORKS
|
|
|
- Eileen Farmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
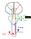
1 CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences other components of the motor system Understand the general scheme of information flowing to the cerebellum and leaving the cerebellum Have a general understanding of the functions and pathways of the vestibulo-, spino-, cerebro- cerebellum Understand the effects/symptoms of lesions of each unit of the cerebellum and the CNS areas where lesions produce cerebellar symptoms Describe the clinical tests used to assess cerebellar function I) FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS: Function Component Deficits Start Basal Ganglia Spontan movements Move Cerebral Cortex/ Weak/Paralyzed Brainstem/SpCord Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjusts Cerebellum Ataxia Balance/EyeMove Cerebellum Falling/ nystagmus Desire to move originates in motor cortical areas. Subsequently, the cerebellum cooperates in planning the movement (which muscles will be activated and in what sequence). When the movement starts, its progress is monitored continuously by sensory and motor feedback to adjust the movement to achieve its goal. Balance is also monitored by cerebellum to ensure postural steadiness. FUNCTION: It COORDINATES movement HOW IT WORKS Thalamus Cerebral Cortex Basal Ganglia Cerebellum head muscles Brainstem body muscles Spinal Cord How does the cerebellum influence movement: 1) by influencing corticospinal and corticobulbar neurons in the cerebral cortex 2) by influencing the descending brainstem pathways that project to the spinal cord. There are NO direct efferent projections from the cerebellum to the spinal cord. SYMPTOMS of cerebellar disease: uncoordinated movement ataxia, nystagmus BIG PICTURE: the cerebellum controls 3 functions relating to coordination of movement (planning, adjusting, balance/eye movements) these 3 functions are controlled by 3 specific areas of the cerebellum the cerebellum affects movement by regulating UMN activity (cortex and brainstem) damage to the cerebellum or its pathways causes ataxia Not so Simple: how the cerebellum is able to perform these functions and the pathways it uses to do it. 1
2 II) Cerebellar Anatomy -cerebellum is composed of 2 lateral hemispheres joined by a central portion called vermis. -Fissures separate the cerebellum into 3 lobes: primary fissure separates anterior lobe and posterior lobes; posterolateral fissure separates post. lobe from flocculonodular lobe. -there are 4 pairs of deep nuclei within the cerebellum: Fastigial, Interpositus, and Dentate. -all fibers going to or coming from the cerebellum travel via the cerebellar peduncles: Inferior (restiform body), Middle (brachium pontis), Superior (brachium conjunctivum). -review cerebellar anatomy in your text and lab manual. superior surface anterior surface Deep Nuclei III) Functional subdivisions of cerebellum Vestibulocerebellum, Spinocerebellum Cerebrocerebellum Functional Unit 1.Vestibulocerebellum Structure Flocculus, nodulus Inputs from Vestib Nuc&Nerve To Deep Nuclei (Vestibular Nuc) 2a.Spinocerebellum Vermis. Fastigial Nuc 2b.Spinocerebellum Lateral hemisphere (Intermediate zone) Lateral hemisphere Spinal cord (Vest.nuc,, visual, auditory, face) Spinal cord Cerebral Cortex via pons Dentate Nuc. 3.Cerebrocerebellum (or Pontocerebellum Interpositus Function Balance & eye movements adjust movement of axial musc adjust movement of distal musc motor planning IV) Cerebellar Pathways Sensory or Motor info Brainstem UMNs Cerebral Cortex UMNs (via thalamus) Cerebellum Control Axial/Proximal muscles Control Distal limb muscles Vestibulospinal Tracts Reticulospinal Tracts Lateral Corticospinal Tract Rubrospinal Tract Abbreviations SCP- superior cerebellar peduncle MCP- middle cerebellar peduncle ICP- inferior cerebellar peduncle DSCT- dorsal spinocerebellar tract VSpCerT- ventral spinocerebellar t. 2
3 Cerebellum uses multiple pathways to affect movement, but all are based on above scheme. Afferent (sensory and motor) info arises from spinal cord, vestibular nuclei, cerebral cortex (via pontine nuclei), and brainstem nuclei. ALL fibers leaving the cerebellum arise from the deep nuclei, except for axons from the flocculonodular cortex to the vestibular nuclei. V) FLOCCULUS and NODULUS Vestibulocerebellum How it works: cerebellum uses vestibular information to control balance and eye movements. It does this by controlling the vestibular nuclei. Sensory or Motor info ICP Cerebellum ICP UMNs Vestibular system Vestibular nuclei: Vestibulospinal Ts MLF Flocculus/Nodulus Role of Vestibulospinal Tracts (UMNs) in Motor System Antigravity fighters! - provide excitatory activity to LMNs controlling antigravity muscles (predominantly extensors) to maintain balance and posture. controlled by cerebellum via the vestibular nuclei UMN LVST Tactile fibers + +/ Extensor LMN + Info to and from vestibulocerebellum via ICP. Lesions: loss of balance and consequent gait problems (ataxia); nystagmus, vertigo, nausea. 3
4 VI) VERMIS Spinocerebellum WHAT: coordinates axial/trunk muscles for postural stability HOW: The vermis communicates with the spinal cord. The cerebellum uses ( unconscious ) proprioceptive and motor information from limbs. Vermis controls trunk (axial musculature). Sensory or Motor info ICP/SCP Cerebellum ICP/SCP UMNs Ipsilateral effects For trunk (axial) control Spinal cord Vestibular nuc, Reticular Form, Motor Cortex Vestibulospinal T Reticulospinal T VCST VERMIS Fastigial nucleus Pathways from spinal cord to Vermis/spinocerebellum (2-neuron chains): transmit proprioceptive, tactile, and motor information from the upper and lower body 1. Cuneocerebellar tract diverted from fasciculus cuneatus 2. Dorsal spinocerebellar tract diverted from fasciculus gracilis 3. Ventral spinocerebellar tract From dorsal columns for Unconscious proprioception Body Region 1 neuron Relay Nucleus Tract Peduncle Side Upper Fasc. Cuneatus Lateral Cuneate Nuc Cuneocerebellar Inferior ipsilateral Lower Fasc. Gracilis Nucleus Dorsalis (T1-L2) Dorsal spinocerebellar Inferior ipsilateral Lower Spinal Border Cells Ventral spinocerebellar Superior ipsilateral 4
5 Axons from the vermis use the fastigial nucleus as relay on their way to the brainstem. Lesions of vermis cause trunkal/gait ataxia (uncoordinated proximal leg movements during walking) VCST VL fastigial vermis ICP/SCP 5
6 VII) CEREBELLAR HEMISPHERES (Spino and Cerebrocerebellum) WHAT: control movements of the upper and lower limbs assists in adjusting and planning movements. Adjusting movement involves correcting the speed, direction, and force of intended movement. HOW: cerebellar hemispheres communicate with both the spinal cord and cerebral cortex. Sensory or Motor info MCP Cerebellum SCP UMNs Spinal Cord Motor Cortex Brainstem Red Nucleus Motor Cortex - LCST 1. Spinal cord Cerebellar Hemisphere Nuc Interpositus Red Nucleus upper Limb flexors 2. Cerebral cortex LATERAL HEMISPHERES Interpositus and Dentate nucleus This pathway demonstrates a general feature of the cerebellum the cerebellum influences ipsilateral body movement because most of its pathways cross the CNS twice. Lesions: cause distal limb ataxia (difficulty controlling the smoothness and accuracy of arm and leg movements) and decreased muscle tone. 6
7 VIII) Cerebellar Cortex and Motor Learning consists of 3 layers: granular, purkinje cell, molecular all afferents entering cerebellar cortex are known as Climbing fibers or Mossy fibers. 1. Climbing fibers originate in contralateral inferior olivary nuclei and travel in ICP. 2. All other afferents to cerebellar cortex are mossy fibers that enter cerebellum through all 3 peduncles. Cerebellum plays a important role in motor learning. New movements are made automatic by action of the cerebellum with the motor cortex. Inferior olivary nucleus and its climbing fibers play a big role in this as a relay between motor cortex and cerebellum. PET studies indicate that the cerebellum also participates in cognitive functions, but we don t understand yet the basis for this. IX) Symptoms of Cerebellar lesions Flocculus/Nodulus (Vestibulocerebellar) Signs Loss of balance Ataxic Gait caused by loss of balance Nystagmus Vermis (Spinocerebellar) Signs Ataxic Gait due to uncoordinated trunk/proximal lower limb movements Cerebellar Hemisphere (spinocerebellar/cerebrocerebellar) Signs all related to uncoordinated upper and lower limb movements: Ataxia/Asynergia/Decomposition of movements - lack of coordinated contractions of agonist and antagonist muscles Dysmetria- inaccurate movement range or direction Hypermetria- excessive movement amplitude (overshoot) Hypometria- insufficient movement amplitude (movement falls short) Dysdiadochokinesia- inability to perform fine, repetitive movements(e.g. rapid pronation and supination of the hand) Tremor (kinetic or intention) - occurs during muscle contraction or during performance of a voluntary task. Lack of Check inability to readjust limb position when movement is disturbed Inappropriate force Delayed initiation of movement Hypotonia (due to decreased influence of LVST) Dysarthria- uncoordinated, slurred, or slow speech (word use is unaffected) XI) SUMMARY and General Principles of Cerebellar Pathways (be able to distinguish these) Floccululas/Nodulus Vestibular signs Falling Nystagmus Ataxic Gait 4 th ventricle tumor, MS Vermis Trunkal ataxia Postural instability ataxic gait Alcohol, MS, tumors Cerebellar Hemispheres Upper/lower limb ataxia Ataxic gair Intention Tremor Uncoordinated motion MS, tumors, infarcts 1. Cerebellar symptoms are caused by damage to cerebellum, its peduncles, or its CNS pathways. 2. Lesions of any cerebellar peduncle cause limb ataxia, because each peduncle contains axons that connect with the cerebellar hemispheres. 3.. Lesions produce IPSILATERAL motor deficits. Two clinical tests to assess limb coordination (cerebellar hemisphere): finger-to-nose test and heel-to-shin test. These tests are easy to perform and reveal tremor and ataxia with cerebellar impairment. 7
8 Recognizing Cerebellar Signs IMPORTANT! Cerebellar Signs basically fall into 2 categories: 1) Vestibular Symptoms: falling, nystagmus, ataxic gait. Subsequent analysis must be used to determine whether these result from lesions of the vestibular system or flocculus/nodulus. 2) Ataxia vermis trunk/proximal lower limbs ataxic gait cerebellar hemispheres (including intermediate zone) upper and lower limbs tremor and other symptoms of uncoordinated movement. Summary Table for Cerebellar Peduncles (for clarification not memorization) Peduncle Input Output Function Inferior Dorsal spinocerebellar tract Vestibular Nuclei vestibulo and Cuneocerebellar tract Reticular Formation spinocerebellum Vestibular nerve/nuclei CN V, IX, XII (coordination) Inferior Olivary Nucleus Middle Cerebral cortex via pontine nuclei none cerebrocerebellum Superior Ventral spinocerebellar tract Red Nucleus spino and cerebro- VL of Thalamus cerebellum Reticular Formation 8
9 CASE 1: A mother brought her 6-year-old son to a physician because he had been falling frequently and vomiting over the past 3 weeks, but he had no fever. On examination, the boy complained that he had a stiff neck. He lost his balance easily when he stood unsupported and nystagmus was observed. Ocular exam revealed papilledema. Solution: The symptoms are falling, vomiting, nystagmus, which are signs of vestibular problems. The absence of fever (no infection) and presence of papilledema suggest increased intracranial pressure tumor. Medulloblastoma arises in roof of 4th ventricle; affects cerebellar nodulus/ vestibulocerebellum; is most common in children. CASE 2: A 70-year-old man with a long history of alcohol dependency was brought to the ED because he had fallen in the street and was unconscious. On examination, he stood with a broad base and exhibited a truncal tremor. His walking was wide-based and unsteady. Even when supported, his steps were irregular and uncoordinated. Solution: the cerebellar vermis is especially sensitive to chronic alcohol intoxication. As part of the spinocerebellum, it controls trunk muscles necessary for standing and walking. Damage to the vermis causes truncal tremor and gait ataxia. To compensate, patients stand/walk with their legs widely separated. His uncoordinated steps even while supported indicate that his ataxia in not due just to loss of balance (vestibulocerebellum). Acute alcohol intoxication impairs cerebellar function, causing trunk and limb ataxia. CASE 3: A 45-year-old women with a history of multiple sclerosis visited her physician because she had difficulty controlling her left arm. She complained that when she eats, her arm shakes as she tries to bring her fork towards her mouth and that she often misses her mouth with her left hand and injures her cheek. Her left arm and leg muscles were hypotonic. The finger-to-nose test showed a gross inaccuracy in her ability to touch her nose with her left hand and she developed a severe left hand tremor as her finger approached her nose. Findings were similar for the heel-to-shin test on the left. It was also difficult for her to perform rapid alternating movements with her left hand. Her speech was slurred, but there was no problem with comprehension, word use, or capacity to vocalize. 9
10 Solution: The symptoms indicate ataxia affecting limb movements: arm shaking during movement - intention tremor finger to nose inaccuracy/tremor dysmetria/intention tremor of upper limb heel to shin deficits dysmetria/intention tremor of lower limb difficulty with rapid alternating movements (dysdiadochokinesia) uncoordinated movements slurred speech without difficulty in comprehension/capacity to vocalize (dysarthria) uncoordinated tongue, laryngeal, jaw muscles used for vocalization. All are symptoms of damage to the lateral cerebellar hemisphere or cerebrocerebellar pathway that lead to ataxia in movements of the limbs. 10
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Abdullah AlZibdeh. Dr. Maha ElBeltagy. Maha ElBeltagy
 19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
Connection of the cerebellum
 CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T!
 CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
CN V! touch! pain! Touch! P/T! Visual Pathways! L! R! B! A! C! D! LT! E! F! RT! G! hypothalamospinal! and! ALS! Vestibular Pathways! 1. Posture/Balance!!falling! 2. Head Position! 3. Eye-Head Movements
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Medial View of Cerebellum
 Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum. Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
The Cerebellum. The Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
Functional Distinctions
 Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Functional Distinctions FUNCTION COMPONENT DEFICITS Start Basal Ganglia Spontaneous Movements Move UMN/LMN Cerebral Cortex Brainstem, Spinal cord Roots/peripheral nerves Plan Cerebellum Ataxia Adjust Cerebellum
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
THE CEREBELLUM SUDIVISIONS, STRUCTURE AND CONNECTIONS
 THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Cerebellum. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications. Dr. Stuart Inglis
 Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
Spinal Cord: Clinical Applications Dr. Stuart Inglis Tabes dorsalis, also known as syphilitic myelopathy, is a slow degeneration (specifically, demyelination) of the nerves in the dorsal funiculus of the
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
The Cerebellum. Outline. Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal:
 Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
Motor tracts Both pyramidal tracts and extrapyramidal both starts from cortex: Area 4 Area 6 Area 312 Pyramidal: mainly from area 4 Extrapyramidal: mainly from area 6 area 6 Premotorarea: uses external
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Learning Objectives.
 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the Functions/Components/Deficits of the motor system (table) 2. Explain the difference between upper and lower motoneurons 3. Describe the roles of the Basal Ganglia and
Learning Objectives 1. Describe the Functions/Components/Deficits of the motor system (table) 2. Explain the difference between upper and lower motoneurons 3. Describe the roles of the Basal Ganglia and
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Functions. Traditional view: Motor system. Co-ordination of movements Motor learning Eye movements. Modern view: Cognition
 The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana
 3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
3) Approach to Ataxia - Dr. Zana Introduction Ataxia is derived from Greek word a -not, taxis -orderly, (not orderly/ not in order) Ataxia is the inability to make smooth, accurate and coordinated movements
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives
 Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Upper and Lower Motoneurons for the Head Objectives Know the locations of cranial nerve motor nuclei Describe the effects of motor cranial nerve lesions Describe how the corticobulbar tract innervates
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum
 Outline Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum 陽明大學醫學院腦科所陳昌明副教授 Anatomy Cerebellar cortex Neuronal circuitry Cerebellar connections Vestibulocerebellum Spinocerebellum Neocerebellum Other cerebellar functions
Outline Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum 陽明大學醫學院腦科所陳昌明副教授 Anatomy Cerebellar cortex Neuronal circuitry Cerebellar connections Vestibulocerebellum Spinocerebellum Neocerebellum Other cerebellar functions
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
The NIHSS score is 4 (considering 2 pts for the ataxia involving upper and lower limbs.
 Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Neuroscience case 5 1. Speech comprehension, ability to speak, and word use were normal in Mr. Washburn, indicating that aphasia (cortical language problem) was not involved. However, he did have a problem
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
THE BACK. Dr. Ali Mohsin. Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Pathways of proprioception
 The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Autonomic Nervous Assess Prof. Fawzia Al-Rouq Department of Physiology College of Medicine King Saud University Pathways of proprioception System posterior column& Spinocerebellar Pathways https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pmeropok6v8
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum
 The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
Cerebellum 1/20/2016. Outcomes you need to be able to demonstrate. MHD Neuroanatomy Module
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Vestibular System. Dian Yu, class of 2016
 Vestibular System Dian Yu, class of 2016 Objectives 1. Describe the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? 2. Describe the vestibular
Vestibular System Dian Yu, class of 2016 Objectives 1. Describe the functions of the vestibular system: What is it? How do you stimulate it? What are the consequences of stimulation? 2. Describe the vestibular
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Dr Maha ELbeltagy THE BRAIN STEM Dr Maha ELbeltagy It includes: Midbrain - Pons - Medulla
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Dr Maha ELbeltagy THE BRAIN STEM Dr Maha ELbeltagy It includes: Midbrain - Pons - Medulla
Spinal Interneurons. Control of Movement
 Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
Control of Movement Spinal Interneurons Proprioceptive afferents have a variety of termination patterns in the spinal cord. This can be seen by filling physiologically-identified fibers with HRP, so their
The Motor Systems. What s the motor system? Plan
 The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions
 Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Neuroanatomy. Dr. Maha ELBeltagy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 THE BRAIN STEM It includes: Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Anterior view Anterior view
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 THE BRAIN STEM It includes: Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Anterior view Anterior view
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
LOCALIZATION NEUROLOGY EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS AND GAIT ATAXIA
 LOCALIZATION NEUROLOGY EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS AND GAIT ATAXIA EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS APPROACH and DIAGNOSIS 2 Cochlea and Auditory nerve Pons (superior olive) lateral lemniscus Inferior colliculus Thalamus
LOCALIZATION NEUROLOGY EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS AND GAIT ATAXIA EPISODE VI HEARING LOSS APPROACH and DIAGNOSIS 2 Cochlea and Auditory nerve Pons (superior olive) lateral lemniscus Inferior colliculus Thalamus
The Cerebellum. Physiology #13 #CNS1
 Physiology #13 #CNS1 The cerebellum consists of cortex and deep nuclei, it is hugely condensed with gray mater (condensed with neurons (1/3 of the neurons of the brain)). Cerebellum contains 30 million
Physiology #13 #CNS1 The cerebellum consists of cortex and deep nuclei, it is hugely condensed with gray mater (condensed with neurons (1/3 of the neurons of the brain)). Cerebellum contains 30 million
Organization of Motor Functions 4.
 Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
THE CEREBELLUM. - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum
 CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be?
 Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Our senses provide us with wonderful capabilities. If you had to lose one, which would it be? Neurological disorders take away sensation without a choice! http://neuroscience.uth.tmc.edu/s2/chapter04.html
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology
 Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Movement Disorders Will Garrett, M.D Assistant Professor of Neurology I. The Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia are composed of several structures including the caudate and putamen (collectively called the
Pain and Temperature Objectives
 Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
Pain and Temperature Objectives 1. Describe the types of sensory receptors that transmit pain and temperature. 2. Understand how axon diameter relates to transmission of pain and temp information. 3. Describe
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA
 MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
MODULE 6: CEREBELLUM AND BASAL GANGLIA This module will summarize the important neuroanatomical and key clinical concepts from Chapters 15 and 16 of the textbook for the course. The first part of this
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Clinical Learning Exercise #1
 Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
Clinical Learning Exercise #1 Exercise: We are going to assume nothing is wrong with the peripheral nervous system and attempt to identify the central nervous system anatomical location for the following
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Spinal Cord- Medulla Spinalis Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Spinal Column Supports the skull, pectoral girdle, upper limbs and thoracic cage by way of the pelvic girdle. Transmits body weight
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve)
 Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
OVERVIEW. Today. Sensory and Motor Neurons. Thursday. Parkinsons Disease. Administra7on. Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online
 OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
skilled pathways: distal somatic muscles (fingers, hands) (brainstem, cortex) are giving excitatory signals to the descending pathway
 L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
Reflexes. Dr. Baizer
 Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Reflexes Dr. Baizer 1 Learning objectives: reflexes Students will be able to describe: 1. The clinical importance of testing reflexes. 2. The essential components of spinal reflexes. 3.The stretch reflex.
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems
 NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
NS201C Anatomy 1: Sensory and Motor Systems 25th January 2017 Peter Ohara Department of Anatomy peter.ohara@ucsf.edu The Subdivisions and Components of the Central Nervous System Axes and Anatomical Planes
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement. Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement. Neural control of movement
 KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
KINE 4500 Neural Control of Movement Lecture #1:Introduction to the Neural Control of Movement Neural control of movement Kinesiology: study of movement Here we re looking at the control system, and what
Sheet lab 3. Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation:
 Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions
 Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
Unit VIII Problem 4 Physiology lab: Brain Stem Lesions - Motor and sensory somatotopy: Pre-central gyrus: is the motor area. Post-central gyrus: is the sensory area. Somatotopy: there is a map of thee
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
