PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
|
|
|
- Osborne Page
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER The Project has been realised with the support of the European Union and has been co-financed by the European Social Fund *** **Molekuláris bionika és Infobionika Szakok tananyagának komplex fejlesztése konzorciumi keretben ***A projekt az Európai Unió támogatásával, az Európai Szociális Alap társfinanszírozásával valósul meg TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
2 Peter Pazmany Catholic University Faculty of Information Technology BEVEZETÉS A FUNKCIONÁLIS NEUROBIOLÓGIÁBA INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY By Imre Kalló Contributed by: Tamás Freund, Zsolt Liposits, Zoltán Nusser, László Acsády, Szabolcs Káli, József Haller, Zsófia Maglóczky, Nórbert Hájos, Emilia Madarász, György Karmos, Miklós Palkovits, Anita Kamondi, Lóránd Erőss, Róbert Gábriel, Zoltán Kisvárdai, Zoltán Vidnyánszky TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
3 Cerebellum: its structure and neuronal network Imre Kalló & Miklós Palkovits Pázmány Péter Catholic University, Faculty of Information Technology I. Macroscopic and microscopic structure II. Functonal characterization of afferent and efferent connections III. Cerebellar neuronal network TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
4 Role of the cerebellum in the central organisation of movement It occupies a determinative site in the hierarchy of movement regulation Its basic function: - initiation, coordination, execution, learning of movement - ongoing control of posture It is in close relationship with the sensory and motor systems it receives information from - muscles and joints through the spinal cord - special neurons of the spinal cord - motor areas of the cerebral cortex - neurons of the brainstem (oliva inferior, formatio reticularis) - vestibular system - visual- and auditory system - associative cortical areas it provides information to - the ascending and descending motor systems TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
5 Primary motor cortex TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
6 Descending lateral corticospinal pathway Ref: Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed. Edited by Eric R. Kandel, James H. Schwartz, and Thomas M. Jessell. New York, McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing, TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
7 Site of motor planning and generation of motor programs A Motor planning B Motor programs Ref: Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed. Edited by Eric R. Kandel, James H. Schwartz, and Thomas M. Jessell. New York, McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing, TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
8 Subdivisions of thalamus with motor functions thalamus sma = supplementer motor area pma = premotor area VA-VL = Ventral anterior and lateral nuclei VP = Ventral posterior complex VPLo = Ventral posterolateral nucleus, pars oralis TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
9 Basic neuronal connections TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
10 Regulatory circuits VLo = Ventral lateral nucleus, pars oralis VLc = Ventral lateral nucleus, pars caudalis TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
11 Location and gross anatomy of the cerebellum (rat) TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
12 The cerebro-cerebellar circuit Brainstem Spinal cord Ref: Principles of Neural Science, 4th ed. Edited by Eric R. Kandel, James H. Schwartz, and Thomas M. Jessell. New York, McGraw-Hill Professional Publishing, TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
13 Location and gross anatomy of the cerebellum (human) TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
14 Phylogenetic subdivisions of the cerebellum ARCHICEREBELLUM - posture PALEOCEREBELLUM - muscle tone NEOCEREBELLUM - regulated movement TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
15 Functional anatomical subdivisions of the cerebellum VESTIBULOCEREBELLUM = archicerebellum FLOCCULO-NODULAR LOBE (balance, eyemovement) SPINOCEREBELLUM = paleocerebellum MEDIAL (VERMIS) + INTERMEDIATE CORTEX (execution of movement) CEREBROCEREBELLUM = neocerebellum LATERAL CORTEX (planning and control of movement) TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
16 Structure of the cerebellum Macroscopic structure - vermis, hemispheres, lobes, folia - peduncles - nuclei TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
17 Microscopic anatomy of the cerebellum: structure of the vermis and the cerebellar lobes are similar vermis TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
18 Cerebellar lobes, peduncles and deep nuclei TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
19 Microscopic anatomy of the cerebellum: middle cerebellar peduncle TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
20 Deep cerebellar nuclei TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
21 Microscopic anatomy of the cerebellum: Deep cerebellar nuclei TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
22 Cerebellar nuclei FASTIGIUS EMBOLIFORMIS GLOBOSUS LATERALIS (MEDIALIS) (ANTERIOR INTERPOSITUS) (POSTERIOR INTERPOSITUS) (DENTATUS) TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
23 Functional anatomical subdivisions of cerebellum TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
24 Structure of the cerebellum MACROSCOPIC STRUCTURE - vermis, hemispheres, lobes, folia - pedunculi - nuclei MICROSCOPIC STRUCTURE - cerebellar cortex - layers - cell types TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
25 Layers of the cerebellar cortex: 1-3 Medulla: TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
26 Cell types of the cerebellar cortex: Note the size, and the number of cells in the different layers TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
27 CELL TYPES Cerebellar cortex Purkinje cell - granule cell + basket cell - Golgi cell - stellate cell - glial cells White matter glial cells Cerebellar nuclei neuron + glial cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
28 Characteristics of the cerebellar neurons Cell types Layers Function Innervated neurons Projection neuron Purkinje cells Purkinje inhibitory Deep cerebellar and vestibular nuclei Interneurons Granule cells Granule cell excitatory Purkinje-, stellate- basket and Golgi cells Basket cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Stellate cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Golgi cells Granule cell inhibitory Granule cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
29 M Cell types of the cerebellar cortex: location of different cell types P G TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
30 Two types of cerebellar afferents: mossy fibers and climbing fibers Cerebellar glomerulus TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
31 Purkinje cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
32 Neuronal connections of the Purkinje cells afferents efferents TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
33 Neuronal connections of the Purkinje cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
34 Characteristics of the cerebellar neurons Cell types Layers Function Innervated neurons Projection neuron Purkinje cells Purkinje inhibitory Deep cerebellar and vestibular nuclei Interneurons Granule cells Granule cell excitatory Purkinje-, stellate- basket and Golgi cells Basket cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Stellate cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Golgi cells Granule cell inhibitory Granule cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
35 Neuronal connections of the granule cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
36 Structure of the cerebellar glomerulus TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
37 Neuronal connections of the granule cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
38 Activation of Purkinje cells by the axons of granule cells (paralell fibers) Red: Dendritic trees of Purkinje cells innervated by granule cells Green and Blue: Dendritic trees of Purkinje cells innervated by inferior olive neurons located in different subdivisions of the nucleus TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
39 Characteristics of the cerebellar neurons Cell types Layers Function Innervated neurons Projection neuron Purkinje cells Purkinje inhibitory Deep cerebellar and vestibular nuclei Interneurons Granule cells Granule cell excitatory Purkinje-, stellate- basket and Golgi cells Basket cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Stellate cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Golgi cells Granule cell inhibitory Granule cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
40 Distribution of basket cells in the cerebellar cortex Basket cells are marked by cjun-immunoreactivity TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
41 M The cell body of basket cells are in the Purkinje cell layer G TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
42 Lateral inhibition by basket cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
43 Characteristics of the cerebellar neurons Cell types Layers Function Innervated neurons Projection neuron Purkinje cells Purkinje inhibitory Deep cerebellar and vestibular nuclei Interneurons Granule cells Granule cell excitatory Purkinje-, stellate- basket and Golgi cells Basket cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Stellate cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Golgi cells Granule cell inhibitory Granule cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
44 Localization and connectivity of stellate cells in the cerebellar cortex TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
45 Characteristics of the cerebellar neurons Cell types Layers Function Innervated neurons Projection neuron Purkinje cells Purkinje inhibitory Deep cerebellar and vestibular nuclei Interneurons Granule cells Granule cell excitatory Purkinje-, stellate- basket and Golgi cells Basket cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Stellate cells Molecular inhibitory Purkinje cells Golgi cells Granule cell inhibitory Granule cells TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
46 Localization and connectivity of Golgi cells in the cerebellar cortex TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
47 Pathways of the cerebellum: the afferent connections Pathways: cerebrum (cortico-ponto-cerebellar) spinal cord (spino-cerebellar) oliva inferior (olivo-cerebellar) formatio reticularis (reticulo-cerebellar) vestibular system (vestibulo-cerebellar) mossy fibers mossy fibers climbing fibers mossy fibers mossy fibers TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
48 The cerebro-ponto-cerebellar pathway TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
49 The cerebrocerebellum TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
50 Information processing in the cerebro-cerebellar pathway TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
51 Pathways of the cerebellum: the afferent connections Pathways: cerebrum (cortico-ponto-cerebellar) spinal cord (spino-cerebellar) oliva inferior (olivo-cerebellar) formatio reticularis (reticulo-cerebellar) vestibular system (vestibulo-cerebellar) mossy fibers mossy fibers climbing fibers mossy fibers mossy fibers TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
52 Structure, location and function of the spinocerebellar pathway TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
53 Spinocerebellum TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
54 Origin of spinocerebellar tracts TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
55 Pathways of the cerebellum: the afferent connections Pathways: cerebrum (cortico-ponto-cerebellar) spinal cord (spino-cerebellar) oliva inferior (olivo-cerebellar) formatio reticularis (reticulo-cerebellar) vestibular system (vestibulo-cerebellar) mossy fibers mossy fibers climbing fibers mossy fibers mossy fibers TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
56 The olivocerebellar tract TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
57 Pathways of the cerebellum: the afferent connections Pathways: cerebrum (cortico-ponto-cerebellar) spinal cord (spino-cerebellar) oliva inferior (olivo-cerebellar) formatio reticularis (reticulo-cerebellar) vestibular system (vestibulo-cerebellar) mossy fibers mossy fibers climbing fibers mossy fibers mossy fibers TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
58 The reticulo-cerebellar tract TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
59 Pathways of the cerebellum: the afferent connections Pathways: cerebrum (cortico-ponto-cerebellar) spinal cord (spino-cerebellar) oliva inferior (olivo-cerebellar) formatio reticularis (reticulo-cerebellar) vestibular system (vestibulo-cerebellar) mossy fibers mossy fibers climbing fibers mossy fibers mossy fibers TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
60 The vestibulocerebellum TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
61 cortico-pontin afferents spinal cord and brainstem afferents Termination fields of the afferent pathways in the cerebellum vestibular afferents TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
62 Pathways of the cerebellum: the efferent connections Cerebello-cerebral pathway: Purkinje cell cerebellar nuclei thalamo-cortical rubro-spinal Cerebello-vestibular pathway: Purkinje cell vestibular nuclei vestibulo-spinal TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
63 Ventral motor nuclei of the thalamus Execution of motor impulses Integration of informations deriving from the cerebellum and basal ganglia Modulation of motor impulses Co-ordination of motor impulses TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
64 Dentato-thalamic and dentato-rubral pathways TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
65 Pathways of the cerebellum: the efferent connections Cerebello-cerebral pathway: Purkinje cell cerebellar nuclei thalamo-cortical rubro-spinal Cerebello-vestibular pathway: Purkinje cell vestibular nuclei vestibulo-spinal TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
66 Pathways of the cerebellum: the efferent connections Cerebello-cerebral pathway: Purkinje cell cerebellar nuclei thalamo-cortical rubro-spinal Cerebello-vestibular pathway: Purkinje cell vestibular nuclei vestibulo-spinal TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
67 Structure, location and function of the cerebellovestibular pathway TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
68 Anatomical Incoming Relay Termination field Function regions informations nucleus Spinocerebellum vermis vestibular fastigial medial system: coordination of labyrinth, vestibularis nucleus, movements spinal cord reticular formation, (upper part motor cortex of the body) cranial nerves (head, neck) intermediate spinal cord interpositus lateral system: coordination of cortex (lower part nucleus ruber (magno- movements of the body) cellular), distal motor cortex Cerebrocerebellum lateral cortex cerebral dentate integrative system: initiation of cortex nucleus ruber (parvo- movements, cellular), planning and premotor cortex temporal-tuning (area 6) of movements Vestibulocerebellum flocculonodular vestibular lateral medial system: posture, lobe labyrinth vestibular motoneurons vestibular reflexes TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
69 Cerebellar network model Activation of Purkinje cells - climbing fibers - stimulation of single Purkinje cells - Golgi cell, inhibition by basket cells - mossy fibers - glomerulus activation by T-axons TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
70 Cerebellar network model TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
71 Cerebellar network model TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
72 Cerebellar network model TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
73 Cerebellar network model Activation of Purkinje cells (signal divergence) - climbing fibers - stimulation of single Purkinje cells - Golgi cell, inhibition by basket cells -mossy fibers - glomerulus activation by T-axons - Output signal originating from Purkinje cells (signal convergence) - cerebellar nuclei efferent pathways TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
74 Cerebellar network model TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
75 Cerebellar network model TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
76 Planning and programing Basal ganglia Cerebellar Cerebellar network network model model Sensory associative cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Execution Movement Cerebellum Motor cortex Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Receptors Feedback signals Peripheral receptors TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
77 Cerebellar network model Planning and programing Basal ganglia Sensory association cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Cerebellum Motor cortex Execution Movement Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Peripheral receptors Spinocerebellum Receptors Feedback signals TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
78 Cerebellar network model Planning and programing Basal ganglia Sensory association cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Cerebellum Motor cortex Execution Movement Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Peripheral receptors Spinocerebellum Receptors Feedback signals TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
79 Cerebellar network model Planning and programing Basal ganglia Sensory association cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Cerebellum Motor cortex Execution Movement Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Peripheral receptors Spinocerebellum Receptors Feedback signals TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
80 Cerebellar network model Planning and programing Basal ganglia Sensory association cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Cerebellum Motor cortex Execution Movement Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Peripheral receptors Spinocerebellum Receptors Feedback signals TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
81 Cerebellar network model Planning and programing Basal ganglia Sensory association cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Cerebellum Motor cortex Execution Movement Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Peripheral receptors Spinocerebellum Receptors Feedback signals TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
82 Cerebellar network model Planning and programing Basal ganglia Sensory association cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Cerebellum Motor cortex Execution Movement Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Peripheral receptors Spinocerebellum Receptors Feedback signals TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
83 Cerebellar network model Planning and programing Basal ganglia Sensory association cortex Premotor cortical areas Cerebrocerebellum Cerebellum Motor cortex Execution Movement Motoneurons Sensory cortical areas Sensory signals Peripheral receptors Spinocerebellum Receptors Feedback signals TÁMOP /2/A/KMR
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline.
 The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
The Cerebellum Cerebellum Located below tentorium cerebelli within posterior cranial fossa. Formed of 2 hemispheres connected by the vermis in midline. Gray matter is external. White matter is internal,
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Abdullah AlZibdeh. Dr. Maha ElBeltagy. Maha ElBeltagy
 19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
19 Abdullah AlZibdeh Dr. Maha ElBeltagy Maha ElBeltagy Introduction In this sheet, we discuss the cerebellum; its lobes, fissures and deep nuclei. We also go into the tracts and connections in which the
Medial View of Cerebellum
 Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Meds 5371 System Neuroscience D. L. Oliver CEREBELLUM Anterior lobe (spinal) Posterior lobe (cerebral) Flocculonodular lobe (vestibular) Medial View of Cerebellum 1 Ventral View of Cerebellum Flocculus
Connection of the cerebellum
 CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
CEREBELLUM Connection of the cerebellum The cerebellum has external layer of gray matter (cerebellar cortex ), & inner white matter In the white matter, there are 3 deep nuclei : (a) dentate nucleus laterally
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum
 Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
Unit VIII Problem 5 Physiology: Cerebellum - The word cerebellum means: the small brain. Note that the cerebellum is not completely separated into 2 hemispheres (they are not clearly demarcated) the vermis
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Cerebellum. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
Cerebellum Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Anatomy of the Cerebellum The cerebellum has approximately half of all the neurons in the central nervous system. The cerebellum
The Cerebellum. The Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
The Cerebellum The Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture PhD Candidate Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum - its lobes, their input and output connections
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
The Cerebellum. Outline. Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley. Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
The Cerebellum Lu Chen, Ph.D. MCB, UC Berkeley 1 Outline Overview Structure Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum The cerebellum and motor learning 2 Overview Little brain 10% of the total volume of the brain,
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
CASE 48. What part of the cerebellum is responsible for planning and initiation of movement?
 CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
CASE 48 A 34-year-old woman with a long-standing history of seizure disorder presents to her neurologist with difficulty walking and coordination. She has been on phenytoin for several days after having
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D.
 Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
Cerebellum John T. Povlishock, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To identify the major sources of afferent inputs to the cerebellum 2. To define the pre-cerebellar nuclei from which the mossy and climbing fiber systems
The Cerebellum. Little Brain. Neuroscience Lecture. Dr. Laura Georgescu
 The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
The Cerebellum Little Brain Neuroscience Lecture Dr. Laura Georgescu Learning Objectives 1. Describe functional anatomy of the cerebellum- its lobes, their input and output connections and their functions.
Motor System Hierarchy
 Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
Motor Pathways Lectures Objectives Define the terms upper and lower motor neurons with examples. Describe the corticospinal (pyramidal) tract and the direct motor pathways from the cortex to the trunk
The Cerebellum. Outline. Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning
 The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
The Cerebellum P.T Ji Jun Cheol Rehabilitation Center 1 HansarangAsan Hospital. Outline Overview Structure (external & internal) Micro-circuitry of the cerebellum Cerebellum and motor learning 2 1 Cerebellum
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo
 Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Motor systems III: Cerebellum April 16, 2007 Mu-ming Poo Population coding in the motor cortex Overview and structure of cerebellum Microcircuitry of cerebellum Function of cerebellum -- vestibulo-ocular
Copy Right- Hongqi ZHANG-Department of Anatomy-Fudan University. Systematic Anatomy. Nervous system Cerebellum. Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 )
 Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Systematic Anatomy Nervous system Cerebellum Dr.Hongqi Zhang ( 张红旗 ) Email: zhanghq58@126.com 1 The Cerebellum Cerebellum evolved and developed with the complication of animal movement. Key points about
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1
 Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
Strick Lecture 3 March 22, 2017 Page 1 Cerebellum OUTLINE I. External structure- Inputs and Outputs Cerebellum - (summary diagram) 2 components (cortex and deep nuclei)- (diagram) 3 Sagittal zones (vermal,
THE CEREBELLUM SUDIVISIONS, STRUCTURE AND CONNECTIONS
 THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
THE CEREBELLUM Damage to the cerebellum produces characteristic symptoms primarily with respect to the coordination of voluntary movements. The cerebellum receives information from the skin, joints, muscles,
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Basal Nuclei (Ganglia)
 Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
Doctor said he will not go deep within these slides because we will take them in physiology, so he will explain the anatomical structures, and he will go faster in the functions sheet in yellow Basal Nuclei
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cerebellum Dr. Abbas Anatomy of the cerebellum Cerebellum Configurations External - located in posterior cranial fossa - communicate with other structure via
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
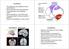 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Organization of Motor Functions 4.
 Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Organization of Motor Functions 4. Dr. Attila Nagy 2018 Sensory-motor system Limbic cortex Structure Subcortical Motivational sub areas Frontal cortex Task Motivation Sequence Plan Tim e Ascending system
Cerebellum: little brain. Cerebellum. gross divisions
 Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
Cerebellum The anatomy of the cerebellum and its gross divisions Its principal input and output pathways The organization of the cerebellar cortex Role of climbing vs. mossy fibre input The parallel-fibre/
FUNCTION: It COORDINATES movement HOW IT WORKS
 CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
CEREBELLUM Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo Objectives: Describe the anatomy of the cerebellum, its 3 functions and associated regions Describe how the cerebellum influences
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement
 Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Basal nuclei, cerebellum and movement MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 9 Department of Myotherapy Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Basal Nuclei (Ganglia) Role: Predict the effects of various actions, then make
Cerebellum 1/20/2016. Outcomes you need to be able to demonstrate. MHD Neuroanatomy Module
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex
 Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
Motor Functions of Cerebral Cortex I: To list the functions of different cortical laminae II: To describe the four motor areas of the cerebral cortex. III: To discuss the functions and dysfunctions of
A3.1.7 Motor Control. 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla
 A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
A3.1.7 Motor Control 10 November 2016 Institute of Psychiatry,Psychology and Neuroscience Marinela Vavla marinela.vavla@kcl.ac.uk Learning objectives Motor systems: components & organization Spinal cord
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
1/2/2019. Basal Ganglia & Cerebellum a quick overview. Outcomes you want to accomplish. MHD-Neuroanatomy Neuroscience Block. Basal ganglia review
 This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
This power point is made available as an educational resource or study aid for your use only. This presentation may not be duplicated for others and should not be redistributed or posted anywhere on the
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
Lecture : Basal ganglia & Cerebellum By : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem Some notes in the beginning : #1 : there is a slides file contains the sheet info as notes for those who love slides more than word papers. #2
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Voluntary Movement. Ch. 14: Supplemental Images
 Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
Voluntary Movement Ch. 14: Supplemental Images Skeletal Motor Unit: The basics Upper motor neuron: Neurons that supply input to lower motor neurons. Lower motor neuron: neuron that innervates muscles,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Neurophysiology of systems
 Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Neurophysiology of systems Motor cortex (voluntary movements) Dana Cohen, Room 410, tel: 7138 danacoh@gmail.com Voluntary movements vs. reflexes Same stimulus yields a different movement depending on context
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Neuroanatomy. Dr. Maha ELBeltagy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 THE BRAIN STEM It includes: Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Anterior view Anterior view
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 THE BRAIN STEM It includes: Midbrain Pons Medulla oblongata Anterior view Anterior view
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Dr Maha ELbeltagy THE BRAIN STEM Dr Maha ELbeltagy It includes: Midbrain - Pons - Medulla
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Dr Maha ELbeltagy THE BRAIN STEM Dr Maha ELbeltagy It includes: Midbrain - Pons - Medulla
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
THE CEREBELLUM. - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum
 CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
CHAPTER THE CEREBELLUM Key Terms - anatomy of the cerebellum cerebellar nuclei cerebellar inputs and neuronal structure of the Purkinje cells outputs cerebellum cerebellar disorders Figure 14.9 For each
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2
 Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Nervous System C H A P T E R 2 Input Output Neuron 3 Nerve cell Allows information to travel throughout the body to various destinations Receptive Segment Cell Body Dendrites: receive message Myelin sheath
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum
 Outline Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum 陽明大學醫學院腦科所陳昌明副教授 Anatomy Cerebellar cortex Neuronal circuitry Cerebellar connections Vestibulocerebellum Spinocerebellum Neocerebellum Other cerebellar functions
Outline Subcortical Motor Systems: cerebellum 陽明大學醫學院腦科所陳昌明副教授 Anatomy Cerebellar cortex Neuronal circuitry Cerebellar connections Vestibulocerebellum Spinocerebellum Neocerebellum Other cerebellar functions
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Motor systems.... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington
 Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Motor systems... the only thing mankind can do is to move things... whether whispering or felling a forest. C. Sherrington 1 Descending pathways: CS corticospinal; TS tectospinal; RS reticulospinal; VS
Cortical Control of Movement
 Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Strick Lecture 2 March 24, 2006 Page 1 Cortical Control of Movement Four parts of this lecture: I) Anatomical Framework, II) Physiological Framework, III) Primary Motor Cortex Function and IV) Premotor
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum
 The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
The Embryology and Anatomy of the Cerebellum Maryam Rahimi Balaei, Niloufar Ashtari, and Hugo Bergen Abstract The cerebellum is an important structure in the central nervous system that controls and regulates
Motor control. Proprioception and movement
 Motor control Proprioception and movement 2/24 in general we are not aware of information coming from proprioceptors though they belong to somatosensory receptors these receptors detect stretching of the
Motor control Proprioception and movement 2/24 in general we are not aware of information coming from proprioceptors though they belong to somatosensory receptors these receptors detect stretching of the
CNS MCQ 2 nd term. Select the best answer:
 Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Select the best answer: CNS MCQ 2 nd term 1) Vestibular apparatus: a) Represent the auditory part of the labyrinth. b) May help in initiating the voluntary movements. c) Contains receptors concerned with
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function. Dr Z Akbari
 Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
Brain Stem and cortical control of motor function Dr Z Akbari Brain stem control of movement BS nuclear groups give rise to descending motor tracts that influence motor neurons and their associated interneurons
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Duus' Topical Diagnosis in Neurology
 Duus' Topical Diagnosis in Neurology Anatomy - Physiology - Signs - Symptoms Bearbeitet von Michael Frotscher 1. Auflage 2005. Taschenbuch. 532 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 612804 6 Format (B x L): 19 x
Duus' Topical Diagnosis in Neurology Anatomy - Physiology - Signs - Symptoms Bearbeitet von Michael Frotscher 1. Auflage 2005. Taschenbuch. 532 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 612804 6 Format (B x L): 19 x
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS
 SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
SENSORY (ASCENDING) SPINAL TRACTS Dr. Jamila El-Medany Dr. Essam Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student will be able to: Define the meaning of a tract. Distinguish between the different
1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas:
 DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
DENT/OBHS 131 2009 Take-home test 4 Week 6: Take-home test (2/11/09 close 2/18/09) 1. The cerebellum coordinates fine movement through interactions with the following motor-associated areas: Hypothalamus
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve)
 Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Functions. Traditional view: Motor system. Co-ordination of movements Motor learning Eye movements. Modern view: Cognition
 The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
The Cerebellum Involved in motor coordination and timing Is simple and well documented Only has one type of output cell (Purkinje) The cerebellum influences motor activity through inhibition The Cerebellum
The Motor Systems. What s the motor system? Plan
 The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
The Motor Systems What s the motor system? Parts of CNS and PNS specialized for control of limb, trunk, and eye movements Also holds us together From simple reflexes (knee jerk) to voluntary movements
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions
 Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
Role of brainstem in somatomotor (postural) functions (vestibular apparatus) The muscle tone and its regulation VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Equilibrium) Receptors: Otolith organs Semicircular canals Sensation (information):
Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning
 1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
1 Computational cognitive neuroscience: 8. Motor Control and Reinforcement Learning Lubica Beňušková Centre for Cognitive Science, FMFI Comenius University in Bratislava 2 Sensory-motor loop The essence
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Chapter 21 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Overview of Sensations (p. 652) 1. Sensation is the conscious or subconscious awareness of external or internal stimuli. 2. For a sensation
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
skilled pathways: distal somatic muscles (fingers, hands) (brainstem, cortex) are giving excitatory signals to the descending pathway
 L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
L15 - Motor Cortex General - descending pathways: how we control our body - motor = somatic muscles and movement (it is a descending motor output pathway) - two types of movement: goal-driven/voluntary
CEREBRAL CORTEX CHAPTER. caudate nucleus. nucleus. Key Terms. Chapter 13 in a Nutshell REB RAL RES
 caudate nucleus CHAPTER Key Terms anatomy of the cortex hemisphere asymmetry Brodmann areas motor and premotor areas rnotor body maps corticospinal tract neuronal population studies cortical inputs and
caudate nucleus CHAPTER Key Terms anatomy of the cortex hemisphere asymmetry Brodmann areas motor and premotor areas rnotor body maps corticospinal tract neuronal population studies cortical inputs and
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU)
 Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? 1 Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU) Cerebellum The Little Brain 2 The Cerebellum takes ~10% of the Brain in Volume Small but Hefty
Cerebellum, motor and cognitive functions: What are the common grounds? 1 Eyal Cohen, PhD (Engineering, BIU) Cerebellum The Little Brain 2 The Cerebellum takes ~10% of the Brain in Volume Small but Hefty
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Brainstem: Midbrain. 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain:
 Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Brainstem: Midbrain 1. Midbrain gross external anatomy 2. Internal structure of the midbrain: cerebral peduncles tegmentum tectum (guadrigeminal plate) Midbrain Midbrain general features location between
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Histology of the CNS
 Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Histology of the CNS Lecture Objectives Describe the histology of the cerebral cortex layers. Describe the histological features of the cerebellum; layers and cells of cerebellar cortex. Describe the elements
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Neural Basis of Motor Control. Chapter 4
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
Neural Basis of Motor Control Chapter 4 Neurological Perspective A basic understanding of the physiology underlying the control of voluntary movement establishes a more comprehensive appreciation and awareness
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Fundamental Neuroscience (2 nd Edition): Section V. MOTOR SYSTEMS Chapter 32: Cerebellum James C. Houk and Enrico Mugnaini
 Fundamental Neuroscience (2 nd Edition): Section V. MOTOR SYSTEMS Chapter 32: Cerebellum James C. Houk and Enrico Mugnaini The cerebellum (Latin for little brain ) is a strategic part of the nervous system.
Fundamental Neuroscience (2 nd Edition): Section V. MOTOR SYSTEMS Chapter 32: Cerebellum James C. Houk and Enrico Mugnaini The cerebellum (Latin for little brain ) is a strategic part of the nervous system.
