The CD46 and Jagged1 interaction is critical for human adaptive T H
|
|
|
- Buck Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The CD46 and Jagged1 interaction is critical for human adaptive T H 1 immunity Gaëlle Le Friec, Devon Sheppard, Pat Whiteman, Christian M. Karsten, Salley Al-Tilib Shamoun, Adam Laing, Laurence Bugeon, Margaret J. Dallman, Teresa Melchionna, Chandramouli Chillakuri, Richard A. Smith, Christian Drouet, Lionel Couzi, Veronique Fremeaux-Bacchi, Jörg Köhl, Simon N. Waddington, James M. McDonnell, Alastair Baker, Penny A. Handford, Susan M. Lea and Claudia Kemper. Supplementary Figures 1 to 6 and Supplementary Tables 1 and 2 Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
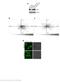
2 a Supplementary Figure 1 b Notch1 Notch2 Notch3 Notch4 N Extracellular domain Cytoplasmic membrane Intracellular domain EGF like domain RAM domain ANK domain PEST sequence Cysteine rich LIN domain NLS TAD domain c Jagged1 Jagged2 d J 1 DSL EGF3 J-1DSL-EGF3 Extracellular domain Delta like1 Delta like3 Delta like4 Cytoplasmic membrane Intracellular domain DSL domain EGF like domain Cysteine rich domain Transmembrane domain PDZ domain Supplementary Figure 1. Schematic of CD46, Notch receptors and Notch ligands including their protein modules and domains. (a) CD46 protein structure. The four major isoforms of CD46 all contain CCPs 1 to 4 at the N-terminus followed by an alternatively spliced extracellular BC region and mutually exclusive usage of the CYT1 or CYT2 cytoplasmic domains. Indicated are the Jagged1 (red) and the C3b/C4b binding sites (green). (b) Structures of the Notch receptors. The protein domain expressed and used in this study (N ) has been marked by a red box. (c) Structures of the Notch ligand family members. The J-1 DSL-EGF3 domain used in this study is marked with a red box. (d) CD46 12 with residues involved in Jagged1 interface (red) is on the left, in complex with adenovirus knob protein 11 (3O8E.pdb), with adenovirus knob protein 21 (3L89.pdb), with measles virus haemagglutinin (3INB.pdb), and non-complexed (1CKL.pdb) from top to bottom, highlighting the reorientation of CCP2 with respect to CCP1 in presenting distinctive contiguous binding surfaces for each virus. Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
3 Supplementary Figure 2a and b a Media MFI: 28.9 MFI: 6.6 MFI: 49.8 MFI: 8.8 MFI: 15.1 MFI: 2.9 MFI: 24.9 MFI: 37. -secretase inhibitor MFI: 2.3 MFI: 16.7 MFI: 36.6 MFI: 78.7 Marimastat MFI: 11.1 MFI: 22. MFI: 55. MFI: 95.8 TAPI-2 Events CD46 Notch1 b IFN- (ng/ml) nd nd nd nd nd 8 7 IL-1 (ng/ml) CD28 +CD46 +CD28 +CD46 +CD28 +CD46 +CD28 +CD46 Media + -secret. + Marim. + TAPI-2 inhibitor Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
4 c Supplementary Figure 2c and d Jurkat Jurkat BC1 Jurkat BC2 Events Isotype MFI 3 Jurkat MFI 2 MFI 13 Jurkat BC1 MFI 31 Jurkat BC2 Isotype ctrl Jurkat Jurkat BC1 Jurkat BC2 Events MFI 2 MFI 12 MFI 18 MFI 7 MFI 13 MFI 21 MFI 1 MFI 9 MFI 19 Isotype ctrl CD46-GFP Notch1 d IFN- (pg/ml) Jurkat Jurkat BC1 Jurkat BC2 ** ** 7 IL-1 (pg/ml) ** * ** * CD3/CD46 CD3/CD46 CD3/CD46 + a-cd anti Notch sol Notch + Media + -Notch + sn Supplementary Figure 2. Interference with Notch signalling disturbs CD46-mediated T H 1 induction and regulation. (a) Interference with ADAM or -secretase activity deregulates CD46 and Notch processing on CD3+CD46-activated purified T cells. Cells were activated as indicated and then analysed by FACS for CD46 and Notch expression. Note that the usually observed Notch surface down-regulation upon direct Notch stimulation with activating antibodies is also impaired in the presence of TAPI-2 or Marimastat (data not shown). Data represent one of three similarly performed experiments. (b) Interference with ADAM or -secretase activity deregulates IFN- and IL-1 secretion. Secretion of IFN- and IL-1 by purified CD4 + T cells (measured using the CBA assay) activated for 36h with the depicted immobilized antibody combinations (and 5 U/ml rhil-2) with or without a presenilin/γ-secretase inhibitor or the broad-spectrum matrix metalloproteinases inhibitors TAPI-2 or Marimastat. (c) Non-manipulated Jurkat T cells express negligible surface CD46 while Jurkat T cells stably transfected with BC1 (Jurkat BC1) or BC2 (Jurkat BC2) CD46 isforms express comparable surface levels of CD46 (upper panel). All Jurkat T cells express similar levels of Notch1 (lower three panels). Note that these data have been observed consistently over time, the protein expression levels are therefore stable. (d) CD46 CYT-1 and Notch1 signals are required for IFN- and IL-1 production. IFN- and IL-1 production by Jurkat, Jurkat BC1 or Jurkat BC2 cells activated for 4d with depicted immobilized stimulating antibodies with or without either 2 g/ml anti- Notch (function blocking) or 1 g/ml soluble N Data are representative of five independent experiments. *, p <.5; **, p <.1 when compared to CD3+CD46-activated Jurkat T cells without addition of -Notch or sn Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
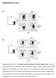
5 Supplementary Figure 3 Resting CD4+ T cell Activated CD4+ T cell TCR Notch1 T CD4+ CD46 Delta-like1 Jagged1 DC 1 - C3b production DC + IL-2 + IL C3b binds to CD CD46 engagement induces: CD46 downregulation and IL-2 secretion CD46 mediated signalling events 4 - Modulation of Notch system expression: Upregulation Notch1 and Jagged1 Downregulation Delta like1 + IL-2 + IL-2 + IL-2 + IL T cell / T cell interactions Notch system transactivation Supplementary Figure 3. Model suggestion for the CD46 and Notch system crosstalk in T H 1 regulation. On resting CD4 + T cells, CD46 binds Jagged1 thereby limiting potential Jagged1 and Notch1 interactions (as the CD46 and Jagged1 interaction is of higher affinity compared to the Jagged and Notch1 interaction). This may favour a Notch1 and DLL1 cis interaction, which has been shown to inhibit T cell activation. Thus, similarly to DLL1, in the absence of T cell activation conditions, CD46 expression on the T cell surface may function as stop signal. In antigen presence or infection and TCR engagement, T cells and APCs generate the CD46 ligand C3b. Binding of C3b to CD46 initiates CD46-mediated signalling events including T cell migratory capacity and cluster formation, substantial CD46 and DLL1 down-regulation while maintaining Notch1 and Jagged1 surface availability. This change in surface expression of CD46 and Notch receptors and ligands may release the brake and allow for Notch1 and DLL1 interaction in trans (which generates IFN- ) as well as for Notch1 and Jagged1 binding in cis or trans (necessary for IL-1 induction). The exact role of IL-2 in this model, which is required for CD3+CD46-mediated IFN- to IL-1 switching, awaits clarification. In line with this model is our observation that both IFN- and IL-1 production is blocked substantially when T cell migration and cluster formation is inhibited by function-blocking antibodies to CCL5, RANTES or CCR1 (data not shown). Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454 IFN- IL-1
6 Supplementary Figure 4a - d a IP: + GSI - CD3 Isot. b Activation: + + (kda) CD46, BC1 + BC2 85 CD46, C1 + C2 44 Detection: -E-catenin (kda) Detection: -E-catenin c d Isotype control CD3-activated CD3 + CD46-activated Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
7 Supplementary Figure 4e and f e f IFN- (ng/ml) Ctrl. sir -E-catenin sir * Events DLL1 Jur.BC1 mock Jur.BC1 mock Jur.BC1 Ctrl shr Jur.BC1 DDL1 shr 5 IL-1 (ng/ml) CD28 * Change in IL-1 secretion (%) Jurkat mock Jur.BC1 mock Jur.BC1 ctrl.r * Jur.BC1 DLL1R + Supplementary Figure 4. -E-catenin interacts with CD46. (a) -E-catenin interacts with the intracellular domain(s) of CD46 in resting human CD4 + T cells. -E-catenin was identified in a yeast-two-hybrid screen as CD46 CYT-2 interacting protein. To assess for a CD46 and -E-catenin interaction in human CD4 + T cells, cell lysates of nonactivated () or CD3 or CD3+CD46-activated CD4 + T cells were either left untreated or used for immunoprecipitation (IP) with a CD46-specific mab, an CD3-specific mab or isotype control (Isot.) mab. Immunoblotting of the IP eluates with an anti- -E-catenin antibody revealed an association between CD46 and -E-catenin. Note that in CD3+CD46- activated T cells, the -E-catenin and CD46 IP is less efficient, likely because CD46 CYT1 and -2 are processed by - secretase complex upon T cell activation. In line with this, activation of T cells in presence of a -secretase inhibitor (GSI) increased -E-catenin pull-down. Data are representative of two similarly performed experiments. (b) -E-catenin protein knock down in CD4 + T cells via sir. CD4 + T cells were transfected with Cy 3 -labeled sir targeting -E-catenin and transfection efficiency assessed via FACS 12h post transfection (left panel). Protein knockdown was measured via FACS 36h post transfection (right panel). Cell viability was routinely above 8% (not shown). Shown is one representative result of six independently performed experiments. Transfection efficiency and protein knock down reached statistical significance when the mean fluorescence intensities (MFI) of the histograms in each experiment were compared. (c) -Ecatenin protein knockdown reduces CD46 down-regulation (top left FACS panel) but (d) does not affect CD3, CD25, CD28 or CD69 expression and (e) impedes IFN- secretion and IL-1 induction in CD3+CD46+IL-2-activated CD4 + T cells. Mean ± SD (n = 4). (f) DLL1 protein knockdown in CD46-BC1-transfected Jurkat T cells increases CD46- mediated IL-1 production. Upper panel, decreased expression of DLL1 on the cell surface of Jurkat-BC1 cells (Jur.BC1) after DLL1 shr transfection and CD3+CD46 activation ( cells have barely detectable DLL1 expression, not shown). Lower panel, IL-1 secretion at d5 by Jurkat cells and Jurkat-BC1 cells treated as depicted. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). *, p <.1 when compared to control sir-treated cells. Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
8 Supplementary Figure 5a a + -CD CD28 + Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
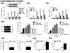
9 Supplementary Figure 5b - d b a 1 8" 6" 4" 2" " Human CD45 + cells (%) 1" Mouse A = HD1 T cells Mouse B = HD2 T cells Mouse C = HD3 T cells Mouse D = CD46-1 T cells cb IFN- (ng/ml) " d2 d7 d14 d2 d7 d14 1" 8" 8 6" 6 4" 4 2" 2 Mouse A = HD1 T cells Mouse B = HD2 T cells Mouse C = HD3 T cells Mouse D = CD46-1 T cells d c 1 Weight change (%) d d3 d5 d7 d12 d15 d21 Mouse A = HD1 T cells Mouse B = HD1 T cells Mouse C = HD1 T cells Mouse D = CD46-1 T cells Supplementary Figure 5. CD4 + T cells from CD46-deficient patient present with defective expression regulation of Jagged1, CD46, CD127 or CD132 and fail to induce GvHD. (a) T cells isolated from freshly-drawn blood of two healthy donors (HD3 and 4) and three patients with CD46 mutations (CD46-1 to CD46-3) were either left non-activated () or activated with immobilized antibodies to CD3 and CD46 in the presence of 25 U/ml rhil-2. Depicted surface maker expression was measured by FACS analysis 36h post activation. Each experimental condition was performed and analysed in duplicate with differences in measured mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) < 4% in all cases. The MFI value for the isotype control (Isot.) in each experiment is shown as range observed over all experiments performed. Note, that the marker profile of the two HDs shown are representative of twelve age- and gender-matched individuals assessed through the course of the study. (b-d) PBMCs from three different healthy donors (HD 1 to HD3) or from Patient CD46-1 wereactivated72hwithimmobilizedantibodiestocd3andcd28and1x1 7 of expanded T cells injected into NOD- SCID- 2M / mice. (b) Human T cell engraftment was assessed via presence of hcd45-positive cells at time points indicated as well as by measurement of (c) hifn- in serum. Disease onset and progression was monitored by assessing (d) the weight change until sacrifice of the animals and confirmed using immunohistological analysis of intestinal tissue (data not shown)., Mouse B was sacrificed at day 15 at humane end point. Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
10 Supplementary Figure 6a a Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
11 Supplementary Figure 6b - d ba Human CD45 + cells (%) Mouse A = HD1 T cells Mouse B = HD2 T cells Mouse C = AP1-1 T cells Mouse D = AP3-1 T cells Mouse E = AP3-2 T cells IFN- (ng/ml) nd nd nd nd nd nd nd 1 nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd nd d7 d14 d25 D46 b c 7 Mouse A = HD1 T cells 6 Mouse B = HD2 T cells 5 Mouse C = AP1-1 T cells 4 Mouse D = AP3-1 T cells Mouse E = AP3-2 T cells 3 2 d7 d14 d25 D46 dc Weight change (%) d d3 d7 d14 d25 d34 d46 d5 Mouse A = HD1 T cells Mouse B = HD2 T cells Mouse C = AP1-1 T cells Mouse D = AP3-1 T cells Mouse E = AP3-2 T cells Supplementary Figure 6. Alagille Syndrome patients present with defective expression regulation of Jagged1, CD46, CD127 or CD132 and fail to induce GvHD. (a) T cells isolated from freshly-drawn blood of two healthy age-matched donors (HD1 and 2) and four Alagille Syndrome patients (AP1 to AP4) were either left non-activated () or activated with immobilized antibodies to CD3 and CD46 in the presence of 25 U/ml rhil2. Depicted surface marker expression was measured by FACS at 36h post activation. Each experimental condition was performed and analysed in duplicate with differences in measured mean fluorescence intensities (MFIs) < 4% in all cases. The MFI value for the isotype control (Isot.) in each experiment is shown as range observed over all experiments performed. (b-d) PBMCs from two healthy donors (HD1 and HD2, one animal each) or Patients AP1 (two animals) and AP3 (one animal) were activated 72h with immobilizedantibodiestocd3andcd28and1x1 7 of expanded T cells injected into NOD-SCID-IL2RG / mice (one animal per healthy donor and two animals per patient). (b) Human T cells engraftment was assessed via presence of hcd45-positive cells at time point indicated as well as measurement of (c) hifn- in serum. Disease onset and progression was monitored by assessing (d) the weight change until sacrifice of the animals and confirmed using immunohistological analysis of intestinal tissue (data not shown). Note, that for logistic reasons, we were unable to utilize the NOD-SCID- 2M / mouse strain used previously for the injection of T cells from the CD46-deficient and GvHD onset and progression follows distinct kinetics between the two mouse strains. nd, not detectable;, Mouse A was sacrificed at day 49 at humane end point. Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
12 Supplementary Table 1. Features of CD46-deficient patients that participated in this study HD3 HD4 dcd46-1 a dcd46-2 b dcd46-3 Gender Female Male Female Male Male Age (years) Ethnicity Cauc Cauc Cauc Cauc Cauc Mutation Exon 2; 1. Splice site alteration IVS2+2T>G leading to deletion of c144/p48 in frame with residual WT sequence. Homozygous Heterozygous < 1% protein expression on T cells Exon 2; 1. Splice site alteration IVS2+1G>C leading to three aberrant mr transcripts. < 1% T cells positive for protein Exon 2; 1. Missense Cys1Tyr 2. Nonsense Arg25X. No detectable protein on T cells Homozygous Homozygous Compound heterozygous HUS Infections No hospital record of recurrent infections Recurrent infections (chest) until IVIG Recurrent infections (chest) until IVIG a, see reference [1]; b, see reference [11]; Cauc, Caucasian; HD, healthy donor; HUS, Hemolytic uremic syndrome; IVIG, Intravenous Immunoglobulin therapy; X, Stop. Note that the lymphocyte compartment (B cells, CD4 + and CD8 + T cells) is within normal range in patients CD46-1 a, CD46-2 b and CD46-3 (data not shown) Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
13 Nature Immunology: doi:1.138/ni.2454
Pearson r = P (one-tailed) = n = 9
 8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
8F4-Specific Lysis, % 1 UPN1 UPN3 8 UPN7 6 Pearson r =.69 UPN2 UPN5 P (one-tailed) =.192 4 UPN8 n = 9 2 UPN9 UPN4 UPN6 5 1 15 2 25 8 8F4, % Max MFI Supplementary Figure S1. AML samples UPN1-UPN9 show variable
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs
 Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplemental Figure 1. CD69 antigen-response curves of CAR engrafted Jurkat T cells. Supplemental Figure 2.
 Supplemental Figure 1. CD69 antigen-response curves of CAR engrafted Jurkat T cells. To evaluate the antigen sensitivity of mutant CARs transduced Jurkat T cells were stimulated with varying concentrations
Supplemental Figure 1. CD69 antigen-response curves of CAR engrafted Jurkat T cells. To evaluate the antigen sensitivity of mutant CARs transduced Jurkat T cells were stimulated with varying concentrations
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
sirna pool: Control Tetherin -HA-GFP HA-Tetherin -Tubulin Supplementary Figure S1. Knockdown of HA-tagged tetherin expression by tetherin specific sirnas. HeLa cells were cotransfected with plasmids expressing
Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ).
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Figure 1 Trim29 gene-targeting strategy. (a) Genotyping of wildtype mice (+/+), Trim29 heterozygous mice (+/ ) and homozygous mice ( / ). (b) Immunoblot analysis of TRIM29 in lung primary
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1! a! b! Nfatc1!! Nfatc1"! P1! P2! pa1! pa2! ex1! ex2! exons 3-9! ex1! ex11!!" #" Nfatc1A!!" Nfatc1B! #"!" Nfatc1C! #" DN1! DN2! DN1!!A! #A!!B! #B!!C! #C!!A!
Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel
 Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
Supplementary Figures 1-8 Crucial role for human Toll-like receptor 4 in the development of contact allergy to nickel Marc Schmidt 1,2, Badrinarayanan Raghavan 1,2, Verena Müller 1,2, Thomas Vogl 3, György
The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: An Immunodeficiency due to a defective cytoskeleton
 The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: An Immunodeficiency due to a defective cytoskeleton Raif Geha Children s Hospital, Boston Harvard Medical School Clinical features Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome An X-linked PID
The Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome: An Immunodeficiency due to a defective cytoskeleton Raif Geha Children s Hospital, Boston Harvard Medical School Clinical features Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome An X-linked PID
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-10. Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald,
 Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
Human and mouse T cell regulation mediated by soluble CD52 interaction with Siglec-1 Esther Bandala-Sanchez, Yuxia Zhang, Simone Reinwald, James A. Dromey, Bo Han Lee, Junyan Qian, Ralph M Böhmer and Leonard
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3866
 Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Nature Immunology: doi:10.1038/ni.3866 Supplementary Figure 1 The effect of TIPE2 on chemotaxis. a, The expression of TIPE2 in dhl-60c, dhl-60t, TIPE2-expressing and 15/16Q-expressing dhl-60t neutrophils
Vpu Reduces Innate Sensing of HIV-1-infected cells by PDCs via a BST2-dependent process
 Vpu Reduces Innate Sensing of HIV-1-infected cells by PDCs via a -dependent process Mariana G. Bego, Édouard Bérubé-Côté, Johanne Mercier, and Éric A. Cohen Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal.
Vpu Reduces Innate Sensing of HIV-1-infected cells by PDCs via a -dependent process Mariana G. Bego, Édouard Bérubé-Côté, Johanne Mercier, and Éric A. Cohen Institut de Recherches Cliniques de Montréal.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Tbk1-TKO! DN cells (%)! 15! 10!
 a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
a! T Cells! TKO! B Cells! TKO! b! CD4! 8.9 85.2 3.4 2.88 CD8! Tbk1-TKO! 1.1 84.8 2.51 2.54 c! DN cells (%)! 4 3 2 1 DP cells (%)! 9 8 7 6 CD4 + SP cells (%)! 5 4 3 2 1 5 TKO! TKO! TKO! TKO! 15 1 5 CD8
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection
 Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
Bead Based Assays for Cytokine Detection September 27, 2014 6 th EFIS-EJI South East European Immunology School SEEIS 2014 Timisoara, Romania The Cells of the Immune System The Immune Reaction (Th2) (Th1)
ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1
 ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
ZH, Li et al, page 1 ECM1 controls T H 2 cell egress from lymph nodes through re-expression of S1P 1 Zhenhu Li 1,4,Yuan Zhang 1,4, Zhiduo Liu 1, Xiaodong Wu 1, Yuhan Zheng 1, Zhiyun Tao 1, Kairui Mao 1,
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table
 Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures and Supplementary Table Title of file for HTML: Peer Review File Description: Innate Scavenger Receptor-A regulates
Page 39 of 44. 8h LTA & AT h PepG & AT h LTA
 Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary material. VAMP7 controls T cell activation by regulating recruitment and phosphorylation of vesicular
 Supplementary material VAMP7 controls T cell activation by regulating recruitment and phosphorylation of vesicular Lat to the TCR activation sites. Paola Larghi, David J Williamson, Jean-Marie Carpier,
Supplementary material VAMP7 controls T cell activation by regulating recruitment and phosphorylation of vesicular Lat to the TCR activation sites. Paola Larghi, David J Williamson, Jean-Marie Carpier,
Supplementary Fig. 1 No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells.
 Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
Supplementary Fig. 1 Supplementary Figure S1: No relative growth advantage of Foxp3 negative cells. itreg were induced from WT (A) or FIR (B) CD4 + T cells. FIR itregs were then removed from the TCR signal
W/T Itgam -/- F4/80 CD115. F4/80 hi CD115 + F4/80 + CD115 +
 F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
F4/8 % in the peritoneal lavage 6 4 2 p=.15 n.s p=.76 CD115 F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + F4/8 hi CD115 + F4/8 + CD115 + MHCII MHCII Supplementary Figure S1. CD11b deficiency affects the cellular responses
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the T H 17 cell it reg cell balance Rajatava Basu 1,5, Sarah K.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL IL-1 signaling modulates activation of STAT transcription factors to antagonize retinoic acid signaling and control the T H 17 cell it reg cell balance Rajatava Basu 1,5, Sarah K.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
doi: 1.138/nature775 4 O.D. (595-655) 3 1 -ζ no antibody isotype ctrl Plated Soluble 1F6 397 7H11 Supplementary Figure 1 Soluble and plated anti- Abs induce -! signalling. B3Z cells stably expressing!
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: (A) (B)
 SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
SUPPLEMENT Supplementary Figure 1: CD4 + naïve effector T cells (CD4 effector) were labeled with CFSE, stimulated with α-cd2/cd3/cd28 coated beads (at 2 beads/cell) and cultured alone or cocultured with
Notch signaling. Ramray Bhat 6/09/2017
 Notch signaling Ramray Bhat 6/09/2017 Lecture 1 introduction, signaling fundamentals, receptor ligand structure, cleavage Lecture 2 Introduction to non canonical signaling, Notch signaling in development:
Notch signaling Ramray Bhat 6/09/2017 Lecture 1 introduction, signaling fundamentals, receptor ligand structure, cleavage Lecture 2 Introduction to non canonical signaling, Notch signaling in development:
supplemental Figure 1
 supplemental Figure 1 A T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv B T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv C T cell BW1/6 anti-cea CDζ CH/CH scfv supplemental Figure 1.79.9.87
supplemental Figure 1 A T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv B T cell T1 anti-ny-eso-117-16/hla-a*:1 CDζ CH/CH scfv C T cell BW1/6 anti-cea CDζ CH/CH scfv supplemental Figure 1.79.9.87
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplementary Information mediates STAT3 activation at retromer-positive structures to promote colitis and colitis-associated carcinogenesis Zhang et al. a b d e g h Rel. Luc. Act. Rel. mrna Rel. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1
 Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
Supplemental Figure 1 1a 1c PD-1 MFI fold change 6 5 4 3 2 1 IL-1α IL-2 IL-4 IL-6 IL-1 IL-12 IL-13 IL-15 IL-17 IL-18 IL-21 IL-23 IFN-α Mut Human PD-1 promoter SBE-D 5 -GTCTG- -1.2kb SBE-P -CAGAC- -1.kb
TITLE: The Role of Constitutively Active Prolactin Receptors in the Natural History of Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0448 TITLE: The Role of Constitutively Active Prolactin Receptors in the Natural History of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kuang-tzu Huang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-06-1-0448 TITLE: The Role of Constitutively Active Prolactin Receptors in the Natural History of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kuang-tzu Huang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Nature Medicine: doi: /nm.3922
 Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Title: Glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-related protein co-stimulation facilitates tumor regression by inducing IL-9-producing helper T cells Authors: Il-Kyu Kim, Byung-Seok Kim, Choong-Hyun
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
Supplementary Material accompanying the manuscript Interleukin 37 is a fundamental inhibitor of innate immunity Marcel F Nold, Claudia A Nold-Petry, Jarod A Zepp, Brent E Palmer, Philip Bufler & Charles
A Slfn2 mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence
 Supplementary Information A Slfn mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence Michael Berger, Philippe Kres, Karine Crozat, Xiaohong Li, Ben A. Croker, Owen
Supplementary Information A Slfn mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence Michael Berger, Philippe Kres, Karine Crozat, Xiaohong Li, Ben A. Croker, Owen
X P. Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Nilotinib LSK LT-HSC. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus
 a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. EBV-gB 23-431 mainly exists as trimer in HEK 293FT cells. (a) Western blotting analysis for DSS crosslinked FLAG-gB 23-431. HEK 293FT cells transfected
Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide
 Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide pulsed T2 cells. clone avidity by 4-hour 51 Cr-release assay 50% lysis at E:T 10:1 [LML peptide, M] #24
Supplementary Table 1. Functional avidities of survivin-specific T-cell clones against LML-peptide pulsed T2 cells. clone avidity by 4-hour 51 Cr-release assay 50% lysis at E:T 10:1 [LML peptide, M] #24
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by. activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b
 Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
Integrin CD11b negatively regulates TLR-triggered inflammatory responses by activating Syk and promoting MyD88 and TRIF degradation via cbl-b Chaofeng Han, Jing Jin, Sheng Xu, Haibo Liu, Nan Li, and Xuetao
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
doi:10.1038/nature11095 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of the binding between Angptls and various Igdomain containing receptors as determined by flow cytometry analysis. The results were summarized from
NOTCH SIGNALING INHIBITED BY IKAROS1 IN HUMAN T-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC LEUKEMIA
 Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 8-2014 NOTCH SIGNALING INHIBITED BY IKAROS1 IN HUMAN T-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC
Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 8-2014 NOTCH SIGNALING INHIBITED BY IKAROS1 IN HUMAN T-CELL ACUTE LYMPHOBLASTIC
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol. absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1
 The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The clathrin adaptor Numb regulates intestinal cholesterol absorption through dynamic interaction with NPC1L1 Pei-Shan Li 1, Zhen-Yan Fu 1,2, Ying-Yu Zhang 1, Jin-Hui Zhang 1, Chen-Qi Xu 1, Yi-Tong Ma
The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens
 1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
1 The T cell receptor for MHC-associated peptide antigens T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymporphic residues of self MHC molecules, and they also recognize residues of peptide
Importance of minor TP53 mutated clones in the clinic
 Importance of minor TP53 mutated clones in the clinic Davide Rossi, M.D., Ph.D. Hematology IOSI - Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland IOR - Institute of Oncology Reserach Bellinzona - Switzerland
Importance of minor TP53 mutated clones in the clinic Davide Rossi, M.D., Ph.D. Hematology IOSI - Oncology Institute of Southern Switzerland IOR - Institute of Oncology Reserach Bellinzona - Switzerland
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
Endothelial PGC 1 - α 1 mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes
 Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Supplementary Figure 1. Supernatants electrophoresis from CD14+ and dendritic cells. Supernatants were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Supernatants electrophoresis from CD14+ and dendritic cells. Supernatants were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. One µg/ml recombinant human (rh) apo-e
Supplementary Figure 1. Supernatants electrophoresis from CD14+ and dendritic cells. Supernatants were resolved by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie brilliant blue. One µg/ml recombinant human (rh) apo-e
S1a S1b S1c. S1d. S1f S1g S1h SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1. - si sc Il17rd Il17ra bp. rig/s IL-17RD (ng) -100 IL-17RD
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 0 20 50 80 100 IL-17RD (ng) S1a S1b S1c IL-17RD β-actin kda S1d - si sc Il17rd Il17ra rig/s15-574 - 458-361 bp S1f S1g S1h S1i S1j Supplementary Figure 1. Knockdown of IL-17RD enhances
Figure S1. Gating strategy used in NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes coculture An example of flow cytometry analysis shows the gating of NK cells and γδ
 Figure S1. Gating strategy used in NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes coculture An example of flow cytometry analysis shows the gating of NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes used in all NK activation and cytotoxicity
Figure S1. Gating strategy used in NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes coculture An example of flow cytometry analysis shows the gating of NK cells and γδ T lymphocytes used in all NK activation and cytotoxicity
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 A LN Cell count (1 ) 1 3 1 CD+ 1 1 CDL lo CD hi 1 CD+FoxP3+ 1 1 1 7 3 3 3 % of cells 9 7 7 % of cells CD+ 3 1 % of cells CDL lo CD hi 1 1 % of CD+ cells CD+FoxP3+ 3 1 % of CD+ T
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 A LN Cell count (1 ) 1 3 1 CD+ 1 1 CDL lo CD hi 1 CD+FoxP3+ 1 1 1 7 3 3 3 % of cells 9 7 7 % of cells CD+ 3 1 % of cells CDL lo CD hi 1 1 % of CD+ cells CD+FoxP3+ 3 1 % of CD+ T
Supplementary Figure 1
 d f a IL7 b IL GATA RORγt h HDM IL IL7 PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM Foxp Foxp Ilra R7 HDM HDM Ilra R7 HDM. 9..79. CD + FOXP + T reg cell CD + FOXP T conv cell PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM CD + FOXP
d f a IL7 b IL GATA RORγt h HDM IL IL7 PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM Foxp Foxp Ilra R7 HDM HDM Ilra R7 HDM. 9..79. CD + FOXP + T reg cell CD + FOXP T conv cell PBS Ilra R7 PBS HDM Ilra R7 HDM CD + FOXP
A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass
 Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
Supplementary material Figure S1. Interaction between UBL5 and FANCI A. List of selected proteins with high SILAC (H/L) ratios identified in mass spectrometry (MS)-based analysis of UBL5-interacting proteins,
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
ONCO-HU TM MICE FOR IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC DRUG DISCOVERY. Brian W. Soper, Ph.D. Senior Technical Information Scientist
 ONCO-HU TM MICE FOR IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC DRUG DISCOVERY Brian W. Soper, Ph.D. Senior Technical Information Scientist Presentation Outline Capabilities Humanization Hu-NSG TM versus Hu-NSG TM -SGM3 Immuno-oncology
ONCO-HU TM MICE FOR IMMUNOTHERAPEUTIC DRUG DISCOVERY Brian W. Soper, Ph.D. Senior Technical Information Scientist Presentation Outline Capabilities Humanization Hu-NSG TM versus Hu-NSG TM -SGM3 Immuno-oncology
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Supplementary Information. Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional assay of the hcas9-2a-mcherry construct (a) Gene correction of a mutant EGFP reporter cell line mediated by hcas9 or
Fluorochrome Panel 1 Panel 2 Panel 3 Panel 4 Panel 5 CTLA-4 CTLA-4 CD15 CD3 FITC. Bio) PD-1 (MIH4, BD) ICOS (C398.4A, Biolegend) PD-L1 (MIH1, BD)
 Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Haematopoietic stem cells
 Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
Haematopoietic stem cells Neil P. Rodrigues, DPhil NIH Centre for Biomedical Research Excellence in Stem Cell Biology Boston University School of Medicine neil.rodrigues@imm.ox.ac.uk Haematopoiesis: An
LPS LPS P6 - + Supplementary Fig. 1.
 P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
P6 LPS - - - + + + - LPS + + - - P6 + Supplementary Fig. 1. Pharmacological inhibition of the JAK/STAT blocks LPS-induced HMGB1 nuclear translocation. RAW 267.4 cells were stimulated with LPS in the absence
Journal Club. 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal
 Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Journal Club 03/04/2012 Lama Nazzal NOTCH and the kidneys Is an evolutionarily conserved cell cell communication mechanism. Is a regulator of cell specification, differentiation, and tissue patterning.
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure 1 Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression during muscle regeneration (a) Analysis of CR3CR1 mrna expression by real time-pcr
 Supplementary Figure 1 Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression during muscle regeneration (a) Analysis of CR3CR1 mrna expression by real time-pcr at day 0, 1, 4, 10 and 21 post- muscle injury. (b)
Supplementary Figure 1 Chemokine and chemokine receptor expression during muscle regeneration (a) Analysis of CR3CR1 mrna expression by real time-pcr at day 0, 1, 4, 10 and 21 post- muscle injury. (b)
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Insulin Resistance. Biol 405 Molecular Medicine
 Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
Insulin Resistance Biol 405 Molecular Medicine Insulin resistance: a subnormal biological response to insulin. Defects of either insulin secretion or insulin action can cause diabetes mellitus. Insulin-dependent
The Dynamic Processing of CD46 Intracellular Domains Provides a Molecular Rheostat for T Cell Activation
 The Dynamic Processing of CD46 Intracellular Domains Provides a Molecular Rheostat for T Cell Activation Siobhan Ni Choileain 1,2, Nathan J. Weyand 3., Christian Neumann 1,2., Joelle Thomas 4, Magdalene
The Dynamic Processing of CD46 Intracellular Domains Provides a Molecular Rheostat for T Cell Activation Siobhan Ni Choileain 1,2, Nathan J. Weyand 3., Christian Neumann 1,2., Joelle Thomas 4, Magdalene
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4
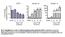 Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
Fig. S1. Upregulation of K18 and K14 mrna levels during ectoderm specification of hescs. Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of mrna levels of OCT4 (n=3 independent differentiation experiments for each
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder I Nakaya, Kousik
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-19 T H 2 response to cysteine-proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS mediated signaling Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-19 T H 2 response to cysteine-proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS mediated signaling Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder
FOCiS. Lecture outline. The immunological equilibrium: balancing lymphocyte activation and control. Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1
 1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
1 Immunological tolerance and immune regulation -- 1 Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Principles of immune regulation Self-tolerance; mechanisms of central and peripheral tolerance Inhibitory
Supplementary Data Table of Contents:
 Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
Supplementary Data Table of Contents: - Supplementary Methods - Supplementary Figures S1(A-B) - Supplementary Figures S2 (A-B) - Supplementary Figures S3 - Supplementary Figures S4(A-B) - Supplementary
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test
 FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
Eosinophils are required. for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow
 Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
Eosinophils are required for the maintenance of plasma cells in the bone marrow Van Trung Chu, Anja Fröhlich, Gudrun Steinhauser, Tobias Scheel, Toralf Roch, Simon Fillatreau, James J. Lee, Max Löhning
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS
 Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Supplementary Figure 1. Prevalence of U539C and G540A nucleotide and E172K amino acid substitutions among H9N2 viruses. Full-length H9N2 NS nucleotide sequences (a, b) or amino acid sequences (c) from
Chapter 5. Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors
 Chapter 5 Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors Structural variation in Ig constant regions Isotype: different class of Ig Heavy-chain C regions are encoded in separate genes Initially, only two of
Chapter 5 Generation of lymphocyte antigen receptors Structural variation in Ig constant regions Isotype: different class of Ig Heavy-chain C regions are encoded in separate genes Initially, only two of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
Supplemental Figure 1. Protein L
 Supplemental Figure 1 Protein L m19delta T m1928z T Suppl. Fig 1. Expression of CAR: B6-derived T cells were transduced with m19delta (left) and m1928z (right) to generate CAR T cells and transduction
Supplemental Figure 1 Protein L m19delta T m1928z T Suppl. Fig 1. Expression of CAR: B6-derived T cells were transduced with m19delta (left) and m1928z (right) to generate CAR T cells and transduction
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
doi: 10.1038/nature05732 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplemental Data Supplement Figure Legends Figure S1. RIG-I 2CARD undergo robust ubiquitination a, (top) At 48 h posttransfection with a GST, GST-RIG-I-2CARD
Principles of Adaptive Immunity
 Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Principles of Adaptive Immunity Chapter 3 Parham Hans de Haard 17 th of May 2010 Agenda Recognition molecules of adaptive immune system Features adaptive immune system Immunoglobulins and T-cell receptors
Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection
 Supplementary Information Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection Noah S. Butler, Jacqueline Moebius, Lecia L. Pewe, Boubacar Traore, Ogobara K.
Supplementary Information Therapeutic PD L1 and LAG 3 blockade rapidly clears established blood stage Plasmodium infection Noah S. Butler, Jacqueline Moebius, Lecia L. Pewe, Boubacar Traore, Ogobara K.
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, MD 21205
 AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: DAMD7---7 TITLE: Development of Artificial Antigen Presenting Cells for Prostate Cancer Immunotherapy PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jonathan P. Schneck, M.D., Ph.D. Mathias Oelke, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas
 Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Test Bank for Basic Immunology Functions and Disorders of the Immune System 4th Edition by Abbas Chapter 04: Antigen Recognition in the Adaptive Immune System Test Bank MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Most T lymphocytes
Supplemental Information. CD4 + CD25 + Foxp3 + Regulatory T Cells Promote. Th17 Cells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance
 Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Immunity, Volume 34 Supplemental Information D4 + D25 + + Regulatory T ells Promote Th17 ells In Vitro and Enhance Host Resistance in Mouse andida albicans Th17 ell Infection Model Pushpa Pandiyan, Heather
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic
 Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
Supplementary Figure 1: Expression of NFAT proteins in Nfat2-deleted B cells (a+b) Protein expression of NFAT2 (a) and NFAT1 (b) in isolated splenic B cells from WT Nfat2 +/+, TCL1 Nfat2 +/+ and TCL1 Nfat2
