2012 National Science Olympiad Anatomy and Physiology Division B. Maximum Team Members: 2. Time Allotted: 50 minutes. Number of Questions: 64
|
|
|
- Aldous Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2012 National Science Olympiad Anatomy and Physiology Division B Maximum Team Members: 2 Time Allotted: 50 minutes Number of Questions: 64 Number of Tie Breaker Questions: 7 DESCRIPTION: This event encompasses the anatomy (structure and function) of the digestive and respiratory systems and the effects of aging and diseases on them. EVENT PARAMETERS: Each team may bring only one 8.5 x 11 two-sided page of notes that contain information in any form from any source and up to 2 nonprogrammable, non-graphing calculators. Exam Description: The Exam consists of 64 questions of varying types including multiple choice, true or false, matching, short answer, and labeling. Tie breaker questions are clearly identified throughout the test. These will only be used in the event of a tie and failure to answer them will not directly affect your score. Each question has only one correct answer. Please answer each question as briefly as possible (the short answer questions do not require essays!). IMPORTANT NOTICE Please record your answer to tie-breaker questions on the answer sheet in the labeled section at the end. You may write on the exam, but only the answer sheets will be graded. If you have any questions, please feel free to ask the proctor.
2 Questions 1-10: Label the following structures. BE SPECIFIC A drawing of the abdominal contents with the wall and parietal peritoneum is shown. The greater omentum is not reflected, and a window is cut into the lesser omentum, exposing the vessels, tail of the pancreas, and major ducts of the liver and gallbladder. The structures labeled include the right and left lobe of the liver, the gall bladder, the pancreas, the duodenum, the fundus, body, and antrum of the stomach, the spleen, and the greater omentum.
3 For questions 11-16, identify the labeled structure. Be Specific Shown is a drawing of the anterior trunk up through the level of the thyroid cartilage. The lungs, heart, and pleura are visible as a ghost, as well as major abdominal organs. Labeled structures include the transverse/horizontal fissure of the right lung, the middle lobe of the right lung, the pleura, the superior and inferior lobes of the left lung, and the trachea.
4 For Questions 17-20, Please Refer to the Following Story Mary is a 35 year old female who suffers from severe abdominal pain. The pain often occurs at night, and also occurs one hour after eating. Endoscopy reveals multiple ulcers in the first portion of her duodenum. Further evaluation reveals a pancreatic tumor that secretes the hormone gastrin, leading to the production of excessive amounts of stomach acid. She is first treated with medications, then a curative surgery that removes the entire tumor. 17. Where is the majority of gastrin normally produced? 18. What cells produce stomach acid? 19. The cells that produce stomach acid also produce a protein required for absorption of a water soluble vitamin. What is that vitamin? 20. Had tumor cells also been found in Mary s liver, what blood vessel would have brought them there? Tie Breaker #1 Name a potential medication that could have treated Mary prior to her surgery?(hint: this condition is usually treated with powerful antacids)
5 For Questions 21-24, Please Refer to the Following Story Jack is a 35 year old man who has been plagued with diarrhea and abdominal pain for years. One day he develops a rash that looks like small blisters and goes to see the doctor. He s surprised when the doctor s first questions are focused on his abdominal pain and diarrhea, which he didn t mention. The doctor sends Jack for some blood tests which confirm his suspicions. Jack is told that his condition is treated by avoiding foods containing gluten. 21. What disease does Jack have? 22. Gluten is a protein found in many foods. Where does protein digestion begin? 23. Jack s disease is classified as an autoimmune disease. Name another autoimmune disease that affects the gastrointestinal system. 24. People with Jack s disease often have difficulty absorbing fat and fat soluble vitamins. Name two fat soluble vitamins that Jack may be at risk of being deficient in. Tie Breaker #2 Doctors can test a person s blood for antibodies that are often produced by people with Jack s disease. Name one of those antibodies.**
6 Questions 25-35: Multiple Choice; Each question has only ONE correct answer 25. During a surgical procedure to remove a tumor of the transverse colon, the surgeon accidentally severs its major arterial supply. This vessel most commonly arises from what major artery? a. Common Hepatic Artery b. Left Renal Artery c. Inferior Mesenteric Artery d. Superior Mesenteric Artery 26. A 19 year old girl is an extremely picky eater and refuses to consume anything but toast and jelly. She is subsequently diagnosed with Kwashiorkor s disease, which results when people eat a normal amount of calories but are deficient in essential proteins. Which of the following is true about protein digestion? a. Enzymatic breakdown of protein begins in the mouth b. Bile produced by the liver is required for the absorption of protein c. Absorbed protein is first transported to the liver via the hepatic portal vein d. Protein absorption occurs in the small intestine via chylomicrons 27. A premature male infant born at 25 weeks suffers from severe respiratory distress. This occurs because the infant is unable to produce sufficient surfactant for normal breathing. Which of the following is true about surfactant production in the lungs? a. Type I pneumocytes are responsible for the majority of surfactant production b. Surfactant is produced by ciliated cells in the bronchi c. Type II pneumocytes are responsible for the majority of surfactant production d. Surfactant is not needed for the normal function of the lungs 28. A 27 year old male is involved in a skiing accident and breaks three ribs. When he arrives to the emergency room, he is taking short, rapid breaths but is unable to meet his metabolic demand for lung function. Which of the following terms correctly describes this man s breathing? a. Eupnea b. Hyperventilation c. Hypoventilation d. Apnea
7 29. Failure of the left ventricle to adequately pump blood leads to increased fluid in the lungs that interferes with breathing, particularly when the person lies down. Which of the following terms most accurately describes shortness of breath that occurs when lying down? a. Dyspnea b. Orthopnea c. Eupnea d. Hypopnea 30. People with broken ribs have severe pain when attempting to breathe. The pain limits their ability to expand their chest and take a normal breath. With this in mind, what can we conclude about chest wall mechanics in patients with broken ribs that cause pain severe enough to limit expansion? a. Chest wall compliance, Chest wall elasticity b. Chest wall compliance, Chest wall elasticity c. Chest wall compliance, Chest wall elasticity d. Chest wall compliance, Chest wall elasticity 31. Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis is a restrictive lung disease that leads to increased elasticity of the lung tissue, limiting its ability to expand. In terms of lung volumes, what would we expect to find in a person with interstitial pulmonary fibrosis relative to normal? a. Total lung capacity, Tidal volume b. Total lung capacity, Tidal volume c. Total lung capacity, Tidal volume d. Total lung capacity, Tidal volume 32. Aspirin is an acid that is capable of increasing the acidity of blood. Following ingestion of a large volume of aspirin, what would be an appropriate respiratory response to the increased acid load? a. Decrease ventilation to increase arterial CO 2 and decrease blood ph b. Decrease ventilation to increase arterial CO 2 and increase blood ph c. Increase ventilation to decrease arterial CO 2 and increase blood ph d. Increase ventilation to increase arterial CO 2 and decrease blood ph
8 For questions 33-35, please refer to the following micrograph The tissue type shown in the section below is a thin, single layer of cells. It is not adipose tissue. (A surface photomicrograph of simple squamous epithelium is shown) 33. What type of tissue is this? a. Simple squamous epithelium b. Stratified squamous epithelium c. Simple columnar epithelium d. Transitional epithelium e. None of the above 34. Where is this tissue type normally found in the respiratory system? a. Walls of the trachea b. Walls of the pharynx c. Walls of the larynx d. Walls of the alveoli e. This tissue type is not found in the respiratory system. 35. Where is this tissue type normally found in the digestive system? a. Lips b. Walls of the esophagus c. Duodenum d. Ilium e. This tissue type is not found in the digestive system.
9 For Tie-Breaker Questions 3 & 4, Please Refer to the Following Light Micrographs of the Trachea Tie Breaker #3 What part of the trachea is the arrow pointing to? Tie Breaker #4 What type of material makes up the structure at the arrow?
10 For questions 36-37, please refer to the following photomicrograph of respiratory epithelium 36. What type of epithelium lines the respiratory system? 37. What cellular structure is identified by arrow A? Tie Breaker #5 What is the effect of cigarette smoking on the structures identified by arrow A?** Tie Breaker #6 What type of cell is identified by arrow B?**
11 Questions 38-42: Short Answer 38. A 40 year old man from Africa has been experiencing a mild fever, cough, night sweats, and weight loss for the past few months. He is diagnosed with a bacterial pulmonary disease. What is the most likely bacterial species responsible for this man s disorder? For question 39 & 40 please refer to the following photograph of a lung A photograph of the right lung is shown 39. Which lung is pictured above (right or left)? 40. Why do you think it is the right or left lung?
12 41. (Please refer to the picture below) The arrows below are pointing to one of three bands that run the length of the colon. What are those bands called? A drawing of the abdominal organs with the teniae coli labeled on the ascending, transverse, and descending colon is shown.
13 42. Which of the muscles labeled in the following picture is MOST IMPORTANT for FORCED EXHALATION?
14 Tie Breaker #7: please refer to the following surgical photograph What structure is identified by the question mark (it is being compressed by a surgical instrument; both arrows are labeling the same structure)?
15 Questions 43-46: Calculations Doctors use spirometery to measure lung volumes and lung capacities in assessing disease states of the respiratory system. The following data were collected on a patient suspected of having COPD (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease) - Quiet breathing at rest: 500 ml - Maximum volume exhaled following deepest possible inhale: 2500 ml - Volume exhaled at end of normal breath: 1500 ml Using the above data, calculate the: 43. Vital Capacity (VC) 44. Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV) 45. Tidal Volume (TV) 46. Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV) 47. Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
16 Questions 47-51: True or False 48. The epiglottis is part of the nasopharynx. 49. There are 35 cartilaginous rings in the trachea. 50. Short thick membranes in the vocal cords produce low pitched sound. 51. The three anatomical regions of the pharynx are the nasopharynx, the oropharynx, and the palatopharynx. 52. The trachea bifurcates into left and right primary bronchi. Questions 52-57: Matching; Please choose the letter corresponding to the disease described in the question. There are no doubles. a. Long-term obstruction of airflow and substantial reduction in pulmonary ventilation b. Allergies trigger the release of histamine and other inflammatory mediators that lead to intense bronchoconstriction c. Alveolar walls are broken down by enzymes that reduce the surface area of the lung d. An inherited disorder that causes thick, sticky mucus to build up in the lungs and other organs such as the pancreas e. The common cold f. Inflammation of the vocal cords 53. Asthma 54. Cystic Fibrosis 55. COPD 56. Laryngitis 57. Emphysema 58. Acute Rhinitis
17 Questions 60-64: Matching; Please choose the letter corresponding to the disease described in the question. There are no doubles. a. Stomach Ulcers b. Lactose Intolerance c. Hepatitis d. GERD e. Crohn s disease f. Diarrhea 59. Inflammation of the liver 60. Loose, watery, and/or frequent stools 61. Caused by failure of the lower esophageal sphincter to prevent movement of acid into the esophagus 62. Lack of a brush border enzyme leads to diarrhea, gassiness, and abdominal discomfort following ingestion of dairy products 63. Autoimmune disorder of the digestive tract 64. Lesions of the gastric mucosa frequently associated with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori
18 1. Left lobe of the Liver 2. Right lobe of Liver 3. Gall Bladder 4. Pancreas 5. Pylorus of the Stomach_ 6. Duodenum 7. Fundus of the Stomach_ 8. Spleen 9. Body of the Stomach 10. Greater Omentum_(1/2 point for Transverse_ Colon) 11. Trachea 12. Horizontal or Transverse Fissure 13. Middle lobe of right lung_ 14. Pleura (parietal is still correct; visceral is not) 15. Superior Lobe of Left Lung_ 16. Inferior Lobe of Left Lung 17. Stomach 18. Parietal Cells 19. B Portal Vein 21. Celiac Disease 22. Stomach 23. _Many answers 24. _A, D, E, or K_(two) 25. D 26. C 27. C 28. C 29. B 30. C 31. D 32. C 33. A 34. D 35. E 36. Ciliated Pseudostratified Columnar 37. Cilia 38. Tuberculosis 39. Right Lung 40. _3 Lobes or 2 Fissures 41. _Tinea Coli 42. B ml _mL ml _mL 47. Cannot be Calculated_ 48. F 49. F 50. T 51. F 52. T 53. B 54. D 55. A 56. F 57. C 58. E 59. C 60. F 61. D 62. B 63. E 64. A Tie Breakers 1. _Proton Pump Inhibitors (end in -prazole), H2- antagonists (end in itidine), Tums or other basic substances (half credit) 2. gliadin, reticulun, or endomysial 3. Cartilaginous Ring 4. _Hyaline Cartilage 5. _Prevents them from functioning 6. _Goblet Cell 7. _Gall Bladder
19 For Question 23, correct answers include, but are not limited to: pernicious anemia, celiac disease, crohn s disease, ulcerative colitis, and autoimmune hepatitis.
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52
 Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
Organs of the Respiratory System Laboratory Exercise 52 Background The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, nasal cavity, sinuses, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchial tree, and lungs. They
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Answers may be found in 2011 Training Handout. Based on the rules.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Answers may be found in 2011 Training Handout. Based on the 2010-2011 rules. School: Total Score: Team Number: Denominator: 50 Part I: Respiratory System Section A. Fill in the blanks.
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Answers may be found in 2011 Training Handout. Based on the 2010-2011 rules. School: Total Score: Team Number: Denominator: 50 Part I: Respiratory System Section A. Fill in the blanks.
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. described: pp. 744,746 fig. 25.1, described: p. 746 fig described: p. 776 fig. 26.3
 ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
ACTIVITY 11: RESPIRATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 25 and 26, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. 2) Identify structures
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous
 I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
I. Anatomy of the Respiratory System A. Upper Respiratory System Structures 1. Nose a. External Nares (Nostrils) 1) Vestibule Stratified Squamous Epithelium b. Nasal Cartilages 1) Nasal Cavity Pseudostratified
Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human;
 Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Name Date Lab Exercise 5: Lab Exercise 6: Lab Exercise 7: Lab Exercise 8: Respiratory & Digestive Organs of the Head and Neck, Human; Histology of the Respiratory System Digestive System Models, Human
Nasal cavity. pharynx. LARYNX trachea Primary bronchi lung. Alveoli Technically its bronchioles. diaphragm
 1. Nasal cavity Alveoli Technically its bronchioles. pharynx LARYNX trachea Primary bronchi lung diaphragm 2. What are the five functions of the nose? Serves as a resonating chamber for speech gives tone
1. Nasal cavity Alveoli Technically its bronchioles. pharynx LARYNX trachea Primary bronchi lung diaphragm 2. What are the five functions of the nose? Serves as a resonating chamber for speech gives tone
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
Lab Activity 27. Anatomy of the Respiratory System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Lab Activity 27 Anatomy of the Respiratory System Portland Community College BI 233 1 Terminology Pulmonary Ventilation: aka breathing, is the movement of air into and out of the lungs External Respiration:
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9.
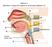 Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
NURSE-UP RESPIRATORY SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pulmonary Ventilation - Breathing Gas exchanger External Respiration between lungs and bloodstream Internal Respiration between bloodstream
Ch16: Respiratory System
 Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
Ch16: Respiratory System Function: - O2 in and CO2 out of the blood vessels in the lungs - O2 out and CO2 into the blood vessels around the cells - Gas exchange happens in - Other organs purify, humidify,
ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS
 ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS Know these endocrine organs of the cat: thymus, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes. Review and know microslides, hormones, and structures
ANATOMY AND BASIC FUNCTION OF THE ENDOCRINE GLANDS Know these endocrine organs of the cat: thymus, thyroid, pancreas, adrenal glands, ovaries, and testes. Review and know microslides, hormones, and structures
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Functions of the Respiratory System Provides extensive gas exchange surface area between air and circulating blood Moves air to and from exchange surfaces of lungs Protects respiratory
Al s 202 study guide answers Answers Respiratory System 1 External nares (nostrils) 33 Carina 2 Vestibule 34 Left primary bronchus 3 Nasal cavity 35
 Trachea & Respiratory Histology 1 Epiglottis 26 Capillary 2 Larynx 27 Alveolar sac 3 Thyroid cartilage 28 Alveoli/Alveolus 4 Cricoid cartilage 29 Basement membrane 5 Vocal folds (True vocal cords) 30 Cilia
Trachea & Respiratory Histology 1 Epiglottis 26 Capillary 2 Larynx 27 Alveolar sac 3 Thyroid cartilage 28 Alveoli/Alveolus 4 Cricoid cartilage 29 Basement membrane 5 Vocal folds (True vocal cords) 30 Cilia
The Digestive System. Chapter
 The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
The Digestive System Chapter 15.1 Functions: mechanical and chemical breakdown of food *absorption of nutrients Consists of alimentary canal and accessory organs Wall of the Alimentary Canal 15.2 Characteristics
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 9
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 9 Respiration The exchange of gases between the atmosphere, blood, and cells Pulmonary Ventilation - the exchange of air between the atmosphere and lungs External (Pulmonary)
Digestive System 7/15/2015. Outline Digestive System. Digestive System
 Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
Digestive System Biology 105 Lecture 18 Chapter 15 Outline Digestive System I. Functions II. Layers of the GI tract III. Major parts: mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine,
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion. 7/16/2015 MDufilho 1
 Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
Lab 5 Digestion and Hormones of Digestion 1 Figure 23.1 Alimentary canal and related accessory digestive organs. Mouth (oral cavity) Tongue* Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
ORGANS OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES: 1. List and describe the major activities of the digestive system. 2. Identify and give the functions of the organs in and along the digestive tract. MAJOR ACTIVITIES
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY. Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad
 SCIENCE OLYMPIAD 1 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of the test. 2. Put your TEAM NAME AND
SCIENCE OLYMPIAD 1 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS DIVISION C ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY Written by Monta Vista Science Olympiad INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Please turn in ALL MATERIALS at the end of the test. 2. Put your TEAM NAME AND
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY
 CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY Section 1: Respiratory System (65 points) 1) It provides CO 2 and O 2 exchange, enables vocalization, provides the sense of smell, helps control the
CAPTAINS TRYOUTS 2018 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ANSWER KEY Section 1: Respiratory System (65 points) 1) It provides CO 2 and O 2 exchange, enables vocalization, provides the sense of smell, helps control the
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank
 UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
UNIT 5 MAINTENANCE SYSTEMS Digestive System Test Bank Objective 5.01 Describe the basic functions of the digestive system. 1. What is the main function of the digestive system? a. Hold and receive food
Respiratory System. Functional Anatomy of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
Respiratory System Overview of the Respiratory System s Job Major Duty Respiration Other important aspects ph control Vocalization Processing incoming air Protection Metabolism (ACE) What structures allow
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Respiratory System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 23 For this lab you will use
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. - Mucosa
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Respiratory System Functions. Respiratory System Organization. Respiratory System Organization
 Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Respiratory System Functions Functions of Respiratory System Gas exchange between blood and air Move air to and from exchange surfaces Protect exchange surfaces from environmental variations and pathogens
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 15. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
The Respiratory System If you have not done so already, please print and bring to class the Laboratory Practical II Preparation Guide. We will begin using this shortly in preparation of your second laboratory
Module 2 Heartburn Glossary
 Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Absorption Antacids Antibiotic Module 2 Heartburn Glossary Barrett s oesophagus Bloating Body mass index Burping Chief cells Colon Digestion Endoscopy Enteroendocrine cells Epiglottis Epithelium Absorption
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 26 The Digestive System
 Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Chapter 26 The Digestive System Digestive System Gastroenterology is the study of the stomach and intestine. Digestion Catabolism Absorption Anabolism The actions of the digestive system are controlled
Respiratory System. BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College
 Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
Respiratory System BSC 2086 A&P 2 Professor Tcherina Duncombe Palm Beach State College Respiration Ventilation of lungs Gas exchange between air/bld and bld/tissue Use of oxygen in cellular respiration
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
SU 12 Name: This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. BIO 116 - Anatomy & Physiology II Practice Assignment 2 - The Respiratory and Cardiovascular Systems 1. The exchange of oxygen and carbon
Digestive System. Digestion Myths
 Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
Digestive System Digestion Myths Myth # 1 Ulcers: Spicy food and stress cause stomach ulcers. Myth # 2 Heartburn: Smoking a cigarette helps relieve heartburn. Myth # 3 Celiac Disease: Celiac disease is
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B.
 HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
HISTOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. Introduction A. The respiratory system provides for gas exchange between the environment and the blood. B. The human respiratory system may be subdivided into two
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
- Digestion occurs during periods of low activity - Produces more energy than it uses. 3 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
 Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Introduction Digestive System Chapter 29 Provides processes to break down molecules into a state easily used by cells - A disassembly line: Starts at the mouth and ends at the anus Digestive functions
Pepsin Chief Cells of Stomach Protein (albumin) Lipase Pancreas (pancreatine) Fats (Cream)
 Enzyme Source Substraight Reaction ph Pepsin Chief Cells of Stomach Protein (albumin) Pepsin Albumin Amino Acids 1.5 2.0 Enzyme Source Substraight Reaction ph Lipase Pancreas (pancreatine) Fats (Cream)
Enzyme Source Substraight Reaction ph Pepsin Chief Cells of Stomach Protein (albumin) Pepsin Albumin Amino Acids 1.5 2.0 Enzyme Source Substraight Reaction ph Lipase Pancreas (pancreatine) Fats (Cream)
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models.
 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM I. OVERVIEW OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM AND THORAX A. Upper respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1) Use the half-head models. Nasal cavity Pharynx (fare-rinks) B. Lower respiratory tract (Fig. 23.1)
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 11. The respiratory system. Glossary. Anthony Wheeldon
 Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Chapter 11 The respiratory system Anthony Wheeldon Glossary Accessory muscles Muscles not normally involved in respiration that can be utilised to increase inspiration. Acid base balance The mechanisms
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Soft palate elevates, closing off the nasopharynx. Hard palate Tongue Bolus Epiglottis. Glottis Larynx moves up and forward.
 The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
The Cephalic Phase Chemical and mechanical digestion begins in the mouth Saliva is an exocrine secretion Salivary secretion is under autonomic control Softens and lubricates food Chemical digestion: salivary
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
The Respiratory System Function of the Respiratory System Oversees gas exchanges (oxygen and carbon dioxide) between the blood and external environment Exchange of gasses takes place within the lungs in
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS. Mar 16 10:34 PM
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM ALIMENTARY CANAL / GI TRACT & ACCESSORY ORGANS Mar 16 10:34 PM 1 I. Digestive System Functions > Ingestion the taking in of food > Propulsion movement caused by force > Digestion breakdown
The respiratory system has multiple organs, we will begin with the nose and nasal cavity.
 Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Respiratory System (Peer reviewed and edited) Slide 1: Respiratory System Slide 2: Functions Functions of respiratory system include gas exchange, communication, olfaction, and ph regulation. Gas exchange
Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms
 131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
131 Lesson 9.1: Learning the Key Terms Directions: Place the letter of the best definition next to each key term. 1. alveolar capillary membrane 2. alveoli 3. bronchioles 4. cardiopulmonary system 5. conchae
The Respiratory System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Vince Austin Human Anatomy & Physiology FIFTH EDITION Elaine N. Marieb The Respiratory System Dr Nabil Khouri. MD, Ph.D Respiratory System Consists of a conducting
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Overview Oxygen is important to our body. The cardiovascular and respiratory system share responsibility for supplying the body with oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide. Functional
The Respiratory System Overview Oxygen is important to our body. The cardiovascular and respiratory system share responsibility for supplying the body with oxygen and disposing of carbon dioxide. Functional
Exercise. Digestive System. Digestive system function. 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc.
 Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
Exercise 7 The Digestive System NAME: DATE: INSTRUCTOR: SECTION: Digestive system function 1. Define the following terms: a. Chemical digestionb. Mechanical digestionc. Ingestiond. Digestione. Absorptionf.
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
Student Name CHAPTER 26 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM D igestion is the process of breaking down complex nutrients into simpler units suitable for absorption. It involves two major processes: mechanical
3/16/2016. Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
 Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Food--mixture of carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids Food being broken down into small molecules Takes place in the alimentary canal Complete digestive system 4 layers of tissue (in book) Lumen 1) MECHANICAL/PHYSICAL--
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23
 The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
The Respiratory System Chapter16/ 23 There are two organ systems that cooperate to supply O 2 and eliminate CO 2 : the respiratory system and the cardiovascular system. The respiratory system provides
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Karachi King s College of Nursing
 Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Karachi King s College of Nursing Badil Dass Lecturer Respiratory system Respiratory System Respiratory system consist of: Nose Pharynx (Throat) Larynx (Voice Box) Trachea (Wind Pipe) Bronchi Bronchioles
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
Packet #6 Cells: Internal Environment, part 2 (organ systems) Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: You should expect a variety of quizzes: announced, unannounced, open-notes and closed-notes. Packet
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Respiratory System Mechanics
 M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
Bio 104 Digestive System
 13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
13 Lecture Outline: Digestive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 17 & 18] General Characteristics of the Alimentary Canal A. Functions 1. Ingestion 2. Mechanical digestion 3. Chemical digestion 4. Propulsion
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS
 11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
11.3 RESPIRATORY SYSTEM DISORDERS TONSILLITIS Infection of the tonsils Bacterial or viral Symptoms: red and swollen tonsils, sore throat, fever, swollen glands Treatment: surgically removed Tonsils: in
Primary Function. 1. Ingestion: food enters the system
 Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
Digestive System Primary Function 1. Ingestion: food enters the system - Physical and enzymatic breakdown begins 2. Digestion: Further breakdown - Chemical/enzymatic 3. Absorption: Nutrients enter circulatory
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1
 Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
Unit 13 - The Respiratory System 1 I. Unit 13: The Respiratory System A. Organs of the Respiratory System 1. Nose 2. Pharynx 3. Larynx 4. Trachea 5. Bronchi 6. Lungs - alveoli B. Functions of the Respiratory
EXPLORING LIFE EXERCISE 13: THE RESPIRATORY, CIRCULATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OF THE RAT
 EXPLORING LIFE EXERCISE 13: THE RESPIRATORY, CIRCULATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OF THE RAT Exercise 13: Respiratory, Circulatory and Digestive Systems of the Rat Workbook Contents Corresponding Section
EXPLORING LIFE EXERCISE 13: THE RESPIRATORY, CIRCULATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OF THE RAT Exercise 13: Respiratory, Circulatory and Digestive Systems of the Rat Workbook Contents Corresponding Section
