Intracranial extension of a non-striated embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit
|
|
|
- Imogene Miller
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brit. j. Ophthal. (I969) 53 i8o Intracranial extension of a non-striated embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit D. SEVEL Department of Ophthalmology, University of Cape Town, Groote Schuur Hospital, South Africa The subject of embryonal sarcomata of the orbit has already been adequately reviewed by Calhoun and Reese (I942), Frayer and Enterline (I959), Porterfield and Zimmerman (I962), Howard and Casten (I963), Reese (I963), Wybar (I964), and Ashton and Morgan (I965). A further case is presented to emphasize the necessity and value of detailed neurological examination (including carotid angiography and brain-scan) even in the absence of symptoms and signs of intracranial extension. This is the first time that a brain-scan has been used to demonstrate the spread of an embryonal sarcoma. Case report A coloured boy aged 6 years was first seen on May i9, i967, when he gave a history of having fallen 3 weeks previously and of "injuring his left eye". He was feverish and generally unwell but there was no neurological deficiency and no evidence of cerebral involvement or other symptoms. X ray of chest was normal. Examination The left eye was proptosed (24 mm.) centrally, the lids were swollen and oedematous, and the conjunctiva was markedly chemotic and congested (Fig. i). Total internal and external ophthalmoplegia, together with complete ptosis, was noted on this side. The fundus showed venous congestion and retinal oedema. The visual acuity was counting fingers at i metre. The right eye and its adnexa were normal. A fluctuant soft tissue swelling filled the left temporal fossa. The left cheek was swollen and a purulent bloody discharge was noted in the left nostril. Detailed X rays of the skull showed a large soft tissue mass which eroded the medial wall of the left orbit, filled the nasal cavity, deviating the septum to the right and filling the maxillary sinus (Fig. 2). Basal views of the skull showed erosion of the left petrous temporal bone. The inferior and superior orbital fissures were enlarged and the left side of the middle cranial fossa was markedly expanded. Exploration On May 26, i967, under general anaesthesia, an oto-laryngologist found that the left nostril was filled with friable tumour material which also occupied the left aural aperture, and involved the entire soft palate and the posterior aspect of the hard palate. Biopsies were taken from both the tumour in the left choanal aperture and from the soft tissue mass in the left temporal fossa. Histological examination showed the features of an undifferentiated embryonal sarcoma consisting of primitive mesenchymal cells. Pleomorphism was a prominent feature and mitoses were common. While occasional rhabdomyoblasts were identified, cross-striations were not noted in the abundant cytoplasm of these strap-like cells (Figs 3 and 4). The enlargement of the superior orbital fissure indicated possible intracranial extension of the orbital tumour. On June 6, I967, left carotid angiography revealed marked upward displacement of the left middle cerebral artery. The anterior cerebral artery filled only with gross compression. Received for publication May 6, I968 Address for reprints: Department of Ophthalmology, University of Cape Town, Groote Schuur Hospital, Observatory, Cape Town, Republic of South Africa
2 Rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit FIG. I Left eye proptosed and the temporal fossa FIG. 2 Skull x-ray (postero-anterior view), showfilled by a soft tissue mass. The left cheek is swollen ing a soft tissue massfilling the left maxillary antrum, and a discharge is notedfrom the left nostril extending into the nasal cavity, and deviating the nasal septum to the right F I G. 3 Biopsy showing ovoid, round, and spindle cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm. Haematoxylin and eosin. x i8 F I G. 4 High-power view offig. 3, showing straplike cells. Cross-striations are not present. Haematoxylin and eosin. x 48 There was upward and backward displacement of the carotid syphon and a tumour blush was noted in the left temporal region of the brain (Fig. 5, overleaf). Brain-scan On June io, 1967, the intracranial extension of the embryonal sarcoma was confirmed with the aid of brain-scan using Technetium 99 (Fig. 6a and b, overleaf). Three days before the procedure the patient was given IO minims of Lugol's iodine three times a day to reduce the thyroid uptake activity of the Technetium 99. On the day of the test, I mc. I8I
3 182 Technetium 99 was injected intravenously one hour before the scan. to chart the brain fields. D. Sevel A positron scanner was used G Left carotid angiogram (lateral vtew), showing upward displacement of the middle cerebral artery and upward and backward displacement of the carotid siphon. There is a tumour blush in the left temporal region Outcome The patient's general condition deteriorated, he refused to eat, and became weak. As there was extensive spread of the embryonal sarcoma it was decided that a mutilating surgical operation was not indicated as a primary procedure. Deep x-ray and cytotoxic therapy was contemplated, to be followed, if possible, by an exenteration, but the child's parents took him home and refused further hospital treatment. The general practitioner who originally referred the case to hospital confirmed that he died on July 5, I967. A post mortem examination was not performed. Discussion Rhabdomyosarcomata are classified according to the degree of differentiation attained by the tumour: (a) Embryonal sarcoma, completely undifferentiated; (b) Non-striated embryonal rhabdomyosarcomata; rhabdomyoblasts may be recognized but no cross-striations are found; (c) Striated embryonal rhabdomyosarcomata; cross-striations are noted. The histological features of this case were those of category b as true striated rhabdomyoblasts were not noted. The clinical features (rapid development, galloping spread, and retrogression with death only 3 months after the onset) are in keeping with the embryonal nature of the tumour. At no stage during the clinical examination was there any indication of the extensive intracranial spread of the embryonal sarcoma. The spread of orbital embryonal sarcomata into the cranial cavity has already been recognized (Krayenbuhl, I962; Wybar, I964; Ashton and Morgan, I965), but the diagnosis has always been made at operation or post mortem. The advantage of carotid angiography with orbital tumours has been indicated by Krayenbuhl (I962) but the value of the brain-scan to assess the spread of such tumours has not been adequately considered. The brain-scan is a simple procedure
4 Rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit tiftts;tti t liis 1* ftsl p^ ii1il btwl E RIbX I.4 'I 4 ; l J II : I 1 I1i ~~~~~~~I~~~~~ IH1$S....U Ij ilji t \ H^ 5 : 'V :+/ FIG. 6a Brain-scan (Technetium 99), antero-posterior view, showing abnormal area of intracranial activity in temporal region (E.A.M.-External auditory meatus, O.P.-occipital protuberance) W. h ij 4tf of ni I ft ji 111 I. IPf IIV"1ffIWI j ft,fti I83 Br J Ophthalmol: first published as /bjo on 1 March Downloaded from FIG. 6b Brain-scan (Technetium 99), lateral view, showing abnormal area of intracranial activity in left temporal region (E.A.M.-External auditory meatus, O.P.- occipital protuberance) not requiring a general anaesthetic and causing minimal discomfort to the patient. Angiography does not alter the uptake of the radioisotope (Brinkman, 1966). Moore (1948) first proposed the use of radioisotopes for the diagnosis and localization of intracranial lesions. The radioisotopes which have been considered and evaluated are arsenic 74 on 15 January 2019 by guest. Protected by
5 x84 D. Sevel (Botterell, Lougheed, Morley, Tasker, and Paul, 196i), bismuth206, copper64 (Bagnall, Benda, Brownell, and Sweet, I958), gallium68, mercury197, mercury203, iodine124, iodine131, and technetium99. The advantage of the last is its rather short half-life. Localization of the isotope depends on the alteration of the blood-brain barrier in the area of disease or in the tissue immediately adjacent thereto (Sweet, Ojemann, Aronow, and Brownell, 1966). This permits a greater concentration of isotope than in the surrounding normal brain and overlying skull and scalp. In the patient under consideration, the radioactive isotope brain-scan was invaluable, as it determined the extent of the intracranial spread of the tumour and hence the proposed subsequent treatment. Summary A case of a non-striated embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit is described where there was no clinical evidence of gross intracranial extension. The value of carotid angiography and brain-scan in such cases is emphasized. I wish to thank Dr. R. P. van Heerden of Bredasdorp, Cape Province, for referring the patient to the Eye Department at Groote Schuur Hospital and for the follow-up, Dr. J. Marais for the E.N.T. opinion, and Dr. P. le Roux for the neurosurgical investigations. This investigation was financed by the Gratitude Fund of Ophthalmology, University of Cape Towvn. References ASHTON, N., and MORGAN, G. (I965) J. clin. Path., i8, 699 BAGNALL, H. J., BENDA, P., BROWNELL, G. L., and SWEET, W. H. (I958) J. Neurosurg., 15, 411 BOTTERELL, E. H., LOUGHEED, W. M., MORLEY, T. P., TASKER, R. R., andpaul, W. (196I) Canad. med. Ass. J., 85, 132 I BRINKMAN, C. A. (I966) In "Neurological Diagnostic Techniques", I3th Annual Houston Neurological Scientific Symposium, I965, ed. W. S. Fields, p Thomas, Springfield, Ill. CALHOUN, F. P., and REESE, A. B. (1942) Arch. Ophthal. (Chicago), 27, 558 FRAYER, W. C., and ENTERLINE, H. T. (1959) A.M.A. Arch. Ophthal., 6.k, 203 HOWARD, G. M., and CASTEN, V. G. (I963) Arch. Ophthal. (Chicago), 70, 319 KRAYENBUHL, H. (I962) J. Jfeurosurg., 19, 289 MOORE, G. E. (1948) Science, 107, 569 PORTERFIELD, J. F., and ZIMMERMAN, L. E. (I962) Virchows Arch. Path. Anat., 335, 329 REESE, A. B. (I963) "Tumors of the Eye", 2nd ed., p. 44I. Hoeber, New York SWEET, W. H., OJEMANN, R. G., ARONOW, S., and BROWNELL, G. L. (I966) In "Neurological Diagnostic Techniques", ed. W. S. Fields, p. I90. Thomas, Springfield, Ill. WYBAR, K. (I964) Proc. roy. Soc. Med., 57, 738
MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMOURS OF THE
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 279. MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMOURS OF THE NASAL SINUSES AND EXOPHTHALMOS* BY ALY MORTADA Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine Cairo University, Egypt TUMOURS
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 279. MALIGNANT SALIVARY GLAND TUMOURS OF THE NASAL SINUSES AND EXOPHTHALMOS* BY ALY MORTADA Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine Cairo University, Egypt TUMOURS
_~~~~~~~~~~~~~~... I~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~...x'..'.i ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA*
 '..,S''''. t ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. g.# lgl,~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.%. : Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 164. ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA* BY ALY MORTADA Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
'..,S''''. t ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~. g.# lgl,~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~.%. : Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 164. ORBITAL BENIGN HAEMANGIO ENDOTHELIOMATA* BY ALY MORTADA Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University,
SUPERVOLTAGE X-IURADIATION OF EPITHELIAL TUMOURS
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 601. SUPERVOLTAGE X-IURADIATION OF EPITHELIAL TUMOURS OF THE LACRIMAL GLAND* BY ALY MORTADA Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Egypt HOGAN
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 601. SUPERVOLTAGE X-IURADIATION OF EPITHELIAL TUMOURS OF THE LACRIMAL GLAND* BY ALY MORTADA Department of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine, Cairo University, Egypt HOGAN
Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 2 2013 Malignant growth Maxilla management an analysis *Balasubramanian Thiagarajan *Geetha Ramamoorthy *Stanley Medical College Abstract: Malignant tumors involving maxilla
METASTATIC MALIGNANT SCHWANNOMA OF ORBIT: A CASE REPORT
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 41 No. 4 December 1986 METASTATIC MALIGNANT SCHWANNOMA OF ORBIT: A CASE REPORT FATHILAH JAAIS S. SIVANESAN SUMMARY A case of metastatic malignant schwannoma of the right orbit is
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 41 No. 4 December 1986 METASTATIC MALIGNANT SCHWANNOMA OF ORBIT: A CASE REPORT FATHILAH JAAIS S. SIVANESAN SUMMARY A case of metastatic malignant schwannoma of the right orbit is
NEUROBLASTOMA* retroperitoneal area; occasionally other abdominal sites and the mediastinum
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 48. NEUROBLASTOMA* BY W. J. LEVY Moorfields Branch, Moorfields Westminster and Central Eye Hospital, London A SURVEY of the literature reveals that about five hundred cases
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1957) 41, 48. NEUROBLASTOMA* BY W. J. LEVY Moorfields Branch, Moorfields Westminster and Central Eye Hospital, London A SURVEY of the literature reveals that about five hundred cases
Orbital cellulitis. Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9,
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 833 FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t BY P. W. R. M. ALBERTI, H. F. MARSHALL, AND J. I. MUNRO BLACK Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 833 FRONTO-ETHMOIDAL MUCOCOELE AS A CAUSE OF UNILATERAL PROPTOSIS*t BY P. W. R. M. ALBERTI, H. F. MARSHALL, AND J. I. MUNRO BLACK Royal Victoria Infirmary, Newcastle upon Tyne
Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma
 Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
Brit. 1. Ophthal. (I 971) 55, 6oo Diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma GWYN MORGAN Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University of London The term "diffuse infiltrating retinoblastoma"
ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 473. ANGIOGRAPHY OF THE NORMAL OPHTHALMIC ARTERY AND CHOROIDAL PLEXUS OF THE EYE* BY P. H. SCHURR From the Department of Neurosurgery, Radcliffe Infirmary, Oxford THE ophthalmic
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 251 CEREBRAL ANEURYSMS PRESENTING WITH VISUAL FIELD DEFECTS* BY University Department of Ophthalmology and Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh ANEURYSMS occur more frequently within
Orbital cellulitis. Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9,
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 143-148 Orbital cellulitis D. P. MARTIN-HIRSCH, S. HABASHI, A. H. HINTON & B. KOTECHA University Department of ENT Surgery, Manchester Royal Infirmary, Manchester
Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 823 Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma F. H. STEFANI AND ELISABETH ROTHEMUND From the University Eye Clinic and the Max Planck Institute ofpsychiatry, Munich, Federal Republic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I974) 58, 823 Intracranial optic nerve angioblastoma F. H. STEFANI AND ELISABETH ROTHEMUND From the University Eye Clinic and the Max Planck Institute ofpsychiatry, Munich, Federal Republic
OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 242. OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS* BY J. R. HUDSON Institute of Ophthalmology, London HAEMOCHROMATOSIS is a rare condition, the chief clinical features of which are
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1953) 37, 242. OCULAR FINDINGS IN HAEMOCHROMATOSIS* BY J. R. HUDSON Institute of Ophthalmology, London HAEMOCHROMATOSIS is a rare condition, the chief clinical features of which are
Anatomic Relations Summary. Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh
 Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Anatomic Relations Summary Done by: Sohayyla Yasin Dababseh Anatomic Relations Lecture 1 Part-1 - The medial wall of the nose is the septum. - The vestibule lies directly inside the nostrils (Nares). -
Benign melanoma of the choroid
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 621 Benign melanoma of the choroid Recognition of malignant change using clinical photographic techniques E. S. ROSEN* AND A. GARNERt Manchester Roval Eye Hospital* and the
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I969) 53, 621 Benign melanoma of the choroid Recognition of malignant change using clinical photographic techniques E. S. ROSEN* AND A. GARNERt Manchester Roval Eye Hospital* and the
B-Scon. T4vI55)SOi}i)ii5 IFIG. I Schematic diagram comparing A- and B- scan ocular ultrasonograms. The B-scan is an
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 193 B-scan ultrasonography of orbital lymphangiomas D. JACKSON COLEMAN, ROBERT L. JACK, AND LOUISE A. FRANZEN From the Ultrasound Laboratory, Edward S. Harkness Eye Institute,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 193 B-scan ultrasonography of orbital lymphangiomas D. JACKSON COLEMAN, ROBERT L. JACK, AND LOUISE A. FRANZEN From the Ultrasound Laboratory, Edward S. Harkness Eye Institute,
Primary optic nerve meningioma
 Primary optic nerve meningioma British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 553-558 J. E. WRIGHT, N. B. CALL,* AND S. LIARICOSt From the Orbital Clinic, Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London ECJ V
Primary optic nerve meningioma British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1980, 64, 553-558 J. E. WRIGHT, N. B. CALL,* AND S. LIARICOSt From the Orbital Clinic, Moorfields Eye Hospital, City Road, London ECJ V
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
ADRENERGIC BLOCKING AGENTS*t A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL IN THE TREATMENT OF THE EYE SIGNS OF THYROID DISORDER
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 616 ADRENERGIC BLOCKING AGENTS*t A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL IN THE TREATMENT OF THE EYE SIGNS OF THYROID DISORDER BY A. L. CROMBIE+ Professorial Unit, Eye Department, Royal Infirmary,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 616 ADRENERGIC BLOCKING AGENTS*t A DOUBLE-BLIND TRIAL IN THE TREATMENT OF THE EYE SIGNS OF THYROID DISORDER BY A. L. CROMBIE+ Professorial Unit, Eye Department, Royal Infirmary,
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the skull is divided into
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
CHOROIDAL HAEMANGIO-ENDOTHELIOMA*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 215. CHOROIDAL HAEMANGIO-ENDOTHELIOMA* BY Moorfields Eye Hospital, and Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon HAEMANGIO-ENDOTHELIOMATA have
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1963) 47, 215. CHOROIDAL HAEMANGIO-ENDOTHELIOMA* BY Moorfields Eye Hospital, and Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon HAEMANGIO-ENDOTHELIOMATA have
Anatomy and Physiology. Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 6 DRO Bones, Sutures, Teeth, Processes and Foramina of the Human Skull Name: Period: Bones of the Human Skull Bones of the Cranium: Frontal bone: forms the forehead and the
Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
 Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
Acta Radiologica ISSN: 0001-6926 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaro20 Chapter XII: Temporal Expanding Processes, Including Those in the Sylvian Fissure and the Insula
CASE REPORT SEVERE GUMMATOUS ULCERATION OF FACE AND AURICULAR REGION
 III CASE REPORT SEVERE GUMMATOUS ULCERATION OF FACE AND AURICULAR REGION By E. T. BURKE IN these days of modern diagnosis and free treatment, gummatous ulceration of a severe type is relatively rarely
III CASE REPORT SEVERE GUMMATOUS ULCERATION OF FACE AND AURICULAR REGION By E. T. BURKE IN these days of modern diagnosis and free treatment, gummatous ulceration of a severe type is relatively rarely
AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY-
 TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
TX: primary tumor cannot be assessed T0: no evidence of primary tumor Tis: carcinoma in situ. T1: tumor is 2 cm or smaller AJCC Staging of Head & Neck Cancer (7 th edition, 2010) -LIP & ORAL CAVITY- T2:
Juvenile Angiofibroma
 Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
Juvenile Angiofibroma Disclaimer The pictures used in this presentation have been obtained from a number of sources. Their use is purely for academic and teaching purposes. The contents of this presentation
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
surgery Macular puckers after retinal detachment and loss of the macular reflex with a greyish appearance of the macula
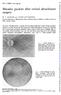 Brit. J. Ophthal. (97 ) 55, 451 Macular puckers after retinal detachment surgery W. S. HAGLER AND UPAL ATURALYA* From the Department of Ophthalmology, Emory University School of Medicine, and Emory University
Brit. J. Ophthal. (97 ) 55, 451 Macular puckers after retinal detachment surgery W. S. HAGLER AND UPAL ATURALYA* From the Department of Ophthalmology, Emory University School of Medicine, and Emory University
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
Treatment of diabetic maculopathy by
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 85 Treatment of diabetic maculopathy by argon-laser S. MERIN, L. YANKO, AND M. IVRY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Hadassah University Hospital, Jerusalem, Israel Diabetic
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1974) 58, 85 Treatment of diabetic maculopathy by argon-laser S. MERIN, L. YANKO, AND M. IVRY From the Department of Ophthalmology, Hadassah University Hospital, Jerusalem, Israel Diabetic
Lecture 07. Lymphatic's of Head & Neck. By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC
 Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
Lecture 07 Lymphatic's of Head & Neck By: Dr Farooq Amanullah Khan PMC Dated: 28.11.2017 Lymphatic Vessels Of the 800 lymph nodes in the human body, 300 are in the Head & neck region. The lymphatic vessels
R,;habdomyosarcoma, the most common
 Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Fine-structural classification of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma Arnold J. Kroll Six cases of orbital rhabdomyosarcoma were studied with the electron microscope. Tumor cells (rhabdomyoblasts) could be classified
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14
 Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
Principles Arteries & Veins of the CNS LO14 14. Identify (on cadaver specimens, models and diagrams) and name the principal arteries and veins of the CNS: Why is it important to understand blood supply
NAEVUS OF OTA* naevus" occurring in the skin areas supplied by the ophthalmic and maxillary
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 364 NAEVUS OF OTA* BY G. P. GUPTA AND D. N. GANGWAR From the Muslim University Institute of Ophthalmology and Gandhi Fye Hospital, Aligarh, India THE naevus of Ota is characterized
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1965) 49, 364 NAEVUS OF OTA* BY G. P. GUPTA AND D. N. GANGWAR From the Muslim University Institute of Ophthalmology and Gandhi Fye Hospital, Aligarh, India THE naevus of Ota is characterized
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas
 External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
External carotid blood supply to acoustic neurinomas Report of two cases HARVEY L. LEVINE, M.D., ERNEST J. FERmS, M.D., AND EDWARD L. SPATZ, M.D. Departments of Radiology, Neurology, and Neurosurgery,
Corneal blood staining after hyphaema
 Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
Brit. J_. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 589 after hyphaema J. D. BRODRICK Sheffield has been described as a rare complication of contusion injury in which a hyphaema of relatively long duration and a raised intraocular
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
NECROGRANULOMATOUS SCLERITIS* EFFECTS ON THE SCLERA OF VASCULAR DEPRIVATION
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 453 NECROGRANULOMATOUS SCLERITIS* EFFECTS ON THE SCLERA OF VASCULAR DEPRIVATION BY DAVID SEVELt Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1968) 52, 453 NECROGRANULOMATOUS SCLERITIS* EFFECTS ON THE SCLERA OF VASCULAR DEPRIVATION BY DAVID SEVELt Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE
Experience with malignant tumours of the maxillary sinus in the Department of Otolaryngology Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 44 No. 1 March 1989 Experience with malignant tumours of the maxillary sinus in the Department of Otolaryngology Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur S. Lokman, MD (UKMalaysia)
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 44 No. 1 March 1989 Experience with malignant tumours of the maxillary sinus in the Department of Otolaryngology Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur S. Lokman, MD (UKMalaysia)
Investigations. The blood count was normal with an erythrocyte. sedimentation rate of 5 mm. ist hr, and negative Waaler-
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I975) 59, 149 Tolosa-Hunt syndrome The dangers of an eponym T. J. FOWLER, C. J. EARL, V. L. McALLISTER, AND W. I. McDONALD From the Institute of Neurology, National Hospitalfor Nervous
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 737. UNIQUE CHANGES IN THE RETINAL VEINS OF A DIABETIC PATIENT* BY Nuffield Laboratory of Ophthalmology, Oxford, and Cape Town, Union of South Africa THis paper illustrates
Orbital Tumors - A Clinico Pathological Study
 Orbital Tumors - A Clinico Pathological Study Radha. J. DO, Ani Sreedhar. MS. Little Flower Hospital, Angamaly, Kerala ORIGINAL ARTICLES Abstract: Aim. To study the clinical and histopathological profiles
Orbital Tumors - A Clinico Pathological Study Radha. J. DO, Ani Sreedhar. MS. Little Flower Hospital, Angamaly, Kerala ORIGINAL ARTICLES Abstract: Aim. To study the clinical and histopathological profiles
Structure Location Function
 Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Frontal Bone Cranium forms the forehead and roof of the orbits Occipital Bone Cranium forms posterior and inferior portions of the cranium Temporal Bone Cranium inferior to the parietal bone forms the
Bones of the skull & face
 Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
Bones of the skull & face Cranium= brain case or helmet Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. The cranium is composed of eight bones : frontal Occipital
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula
 A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
A Case of Carotid-Cavernous Fistula By : Mohamed Elkhawaga 2 nd Year Resident of Ophthalmology Alexandria University A 19 year old male patient came to our outpatient clinic, complaining of : -Severe conjunctival
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
The Nose External Nose Nasal Cavity External Nose Blood and Nerve Supplies of the External Nose Blood Supply of the External Nose The skin of the external nose Branches of the ophthalmic and the maxillary
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
Temporal arteritis. Occurrence of ocular complications 7 years after diagnosis. University of Edinburgh, and Royal Infirmary of Edinburgh
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 584 Temporal arteritis Occurrence of ocular complications 7 years after diagnosis JAMES F. CULLEN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Edinburgh, and Royal Infirmary
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 972) 56, 584 Temporal arteritis Occurrence of ocular complications 7 years after diagnosis JAMES F. CULLEN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Edinburgh, and Royal Infirmary
PITUITARY AND PARAPITUITARY TUMOURS* VALUE OF PERIMETRY IN DIAGNOSIS
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 590. PITUITARY AND PARAPITUITARY TUMOURS* VALUE OF PERIMETRY IN DIAGNOSIS BY J. F. CULLEN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Edinburgh THE occurrence of pallor of the
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1964) 48, 590. PITUITARY AND PARAPITUITARY TUMOURS* VALUE OF PERIMETRY IN DIAGNOSIS BY J. F. CULLEN Department of Ophthalmology, University of Edinburgh THE occurrence of pallor of the
Pharyngeal Apparatus. Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel
 Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
Pharyngeal Apparatus Pouches Endoderm Grooves Ectoderm Arch Neural Crest Somitomeres Aortic Arch - Vessel Segmental Organization Humans: Arch 1-4 prominent Arch 5 absent Arch 6 - transient First Arch Face
EXTRACRANIAL MENINGIOMA PRESENTING AS INFRATEMPORAL FOSSA MASS: A CASE SERIES
 Case Series EXTRACRANIAL MENINGIOMA PRESENTING AS INFRATEMPORAL FOSSA MASS: A CASE SERIES Sunil Mathew * 1, Reddy Ravikanth 2, Vijaykishan B 3. ABSTRACT Extradural meningioma occurs as extracranial extension
Case Series EXTRACRANIAL MENINGIOMA PRESENTING AS INFRATEMPORAL FOSSA MASS: A CASE SERIES Sunil Mathew * 1, Reddy Ravikanth 2, Vijaykishan B 3. ABSTRACT Extradural meningioma occurs as extracranial extension
Ocular toxocariasis in adults
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1976) 6o, 365 Ocular toxocariasis in adults E. R. RAISTRICK AND J. C. DEAN HART From the Department of Ophthalmology, Bristol Eye Hospital, Bristol The larva of the nematode Toxocara
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1976) 6o, 365 Ocular toxocariasis in adults E. R. RAISTRICK AND J. C. DEAN HART From the Department of Ophthalmology, Bristol Eye Hospital, Bristol The larva of the nematode Toxocara
Blindness due to aneurysm of anterior communicating artery
 Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I 970) 54, I 70 Blindness due to aneurysm of anterior communicating artery * le With recovery following carotid ligation J. H. J. DURSTON AND B. G. PARSONS-SMITH The 14est End Hospital
Brit. 7. Ophthal. (I 970) 54, I 70 Blindness due to aneurysm of anterior communicating artery * le With recovery following carotid ligation J. H. J. DURSTON AND B. G. PARSONS-SMITH The 14est End Hospital
TISSUE* ABERRANT INTRA-OCULAR LACRIMAL GLAND. of the left eye of a full-term infant of 2 weeks; the tumour was globular and
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 619. ABERRANT INTRA-OCULAR LACRIMAL GLAND TISSUE* BY W. S. HUNTERt Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE occurrence of aberrant lacrimal
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 619. ABERRANT INTRA-OCULAR LACRIMAL GLAND TISSUE* BY W. S. HUNTERt Department of Pathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, University oflondon THE occurrence of aberrant lacrimal
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
Brit. J. Ophthal., 35, 119. AQUEOUS VEINS IN RABBITS* BY D. P. GREAVES AND E. S. PERKINS Institute of Ophthalmology, London Director of Research, Sir Stewart Duke-Elder IN the course of investigations
UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1962) 46, 51. UNIOCULAR APLASIA OF THE OPTIC NERVE* BY FROMA SOMERVILLE London APLASIA of the optic nerve occurring as an isolated abnormality in an eye of normal external appearance
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 5 Positioning for Exams of the Cranium, Sinuses, and Mandible. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 5-1 through 5-9. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able
Chapter 7: Head & Neck
 Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Chapter 7: Head & Neck Osteology I. Overview A. Skull The cranium is composed of irregularly shaped bones that are fused together at unique joints called sutures The skull provides durable protection from
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
A PLEA FOR LATERAL ORBITOTOMY WITH CERTAIN MODIFICATIONS*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 718. A PLEA FOR LATERAL ORBITOTOMY WITH CERTAIN MODIFICATIONS* BY H. B. STALLARD London THE frontiers of human interest and work are often disputed and, there is no exception
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1960) 44, 718. A PLEA FOR LATERAL ORBITOTOMY WITH CERTAIN MODIFICATIONS* BY H. B. STALLARD London THE frontiers of human interest and work are often disputed and, there is no exception
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM
 LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
LECTURE 4 SKULL NEUROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM VISCEROCRANIUM CRANIUM NEUROCRANIUM (protective case around brain) VISCEROCRANIUM (skeleton of face) NASOMAXILLARY COMPLEX MANDIBLE (DESMOCRANIUM)
CASE REPORT Adult onset sinonasal rhabdomyosarcoma - a rare case report with cytohistological features
 Malaysian J Pathol 2016; 38(2) : 169 173 CASE REPORT Adult onset sinonasal rhabdomyosarcoma - a rare case report with cytohistological features Neelam SOOD MD Pathology and Nisha SEHRAWAT MD Pathology
Malaysian J Pathol 2016; 38(2) : 169 173 CASE REPORT Adult onset sinonasal rhabdomyosarcoma - a rare case report with cytohistological features Neelam SOOD MD Pathology and Nisha SEHRAWAT MD Pathology
CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID*
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
Brit. J. Ophthal. (1966) 50, 409 CASE OF CONGENITAL CYSTIC EYE AND ACCESSORY LIMB OF THE LOWER EYELID* BY N. S. C. RICE Department ofpathology, Institute of Ophthalmology, London, AND S. P. MINWALLA AND
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
cellulitis and paranasal sinusitis
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, I 33 Gas in the orbit associated with orbital cellulitis and paranasal sinusitis *D. SEVEL, *B. TOBIAS, ts. L. SELLARS, AND +A. FORDER From the Departments of *Ophthalmology,
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I 973) 57, I 33 Gas in the orbit associated with orbital cellulitis and paranasal sinusitis *D. SEVEL, *B. TOBIAS, ts. L. SELLARS, AND +A. FORDER From the Departments of *Ophthalmology,
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board
 THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
THE NASAL TIP IN BILATERAL HARE LIP By J. POTTER, F.R.C.S.Ed. Plastic Surgeon, Middlesbrough General Hospital, Stockton Children's Hospital, Newcastle Regional Hospital Board IN the problem of the bilateral
Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report
 Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
Romanian Journal of Rhinology, Volume 8, No. 30, April-June 2018 CASE REPORT Sphenoid rhinosinusitis associated with abducens nerve palsy Case report Lucian Lapusneanu 1, Marlena Radulescu 1, Florin Ghita
HEAD/NECK VESSELS. Objectives
 Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Objectives Arterial Supply to Head and Neck Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain Common carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External carotid arteries Arteries to Head Surrounding Brain External
Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion
 Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Brit. J. Ophthal. (I973) 57, 766 Blood vessels of the ciliary ganglion in man M. ELIJKOVA Institute of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Charles University, Prague, Czechoslovakia Many authors, including Egorov
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir. HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi
 Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Professor Dr.Muhammad Ajmal Dr.Tehmina Nazir HOLY FAMILY HOSPITAL Rawalpindi SCHEME OF PRESENTATION PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI CONCLUSION IMAGING MODALITIES PLAIN X-RAYS CT SCAN MRI OCCIPITOMENTAL/WATER
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines
 Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
Michele Long Division of Otorhinolaryngology Faculty of Health Sciences Tygerberg Campus, University of Stellenbosch Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Departmental guidelines Anatomy- cavernous sinus 2cm in
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔. 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機
 Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
Bisection of Head & Nasal Cavity 頭部對切以及鼻腔 解剖學科馮琮涵副教授 分機 3250 E-mail: thfong@tmu.edu.tw Outline: The structure of nose The concha and meatus in nasal cavity The openings of paranasal sinuses Canals, foramens
04 Development of the Face and Neck. Development of the Face Development of the neck
 04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
04 Development of the Face and Neck Development of the Face Development of the neck Development of the face Overview of facial development The fourth week ~ the twelfth week of prenatal development Between
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102-6102 1 The Palate The palate forms the roof of the mouth and the floor of the nasal cavity. It is divided into two
Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1984, 68, 128-134 Ophthalmoplegia in carotid cavernous sinus fistula T. J. K. LEONARD, I. F. MOSELEY, AND M. D. SANDERS From the Departments ofneuro-ophthalmology and
Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic Veins K Kragha Citation K Kragha. Cryptogenic Enlargement Of Bilateral Superior Ophthalmic
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa. Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine
 Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Maxilla, ORBIT and infratemporal fossa Neophytos C Demetriades MD, DDS, MSc Associate professor European University of Cyprus School of Medicine MAXILLA Superior, middle, and inferior meatus Frontal sinus
Fracture of the Temporal Bone: A Tomographic V/S Autopsy Study
 Fracture of the Temporal Bone: A Tomographic V/S Autopsy Study * Dr. Mukesh Kumar Goel, ** Dr. Rashmi Goel, *** Dr. Shiv R Kochar, **** Dr. M. R. Goel, *Asst Proff, Department of Forensic Medicine, People,s
Fracture of the Temporal Bone: A Tomographic V/S Autopsy Study * Dr. Mukesh Kumar Goel, ** Dr. Rashmi Goel, *** Dr. Shiv R Kochar, **** Dr. M. R. Goel, *Asst Proff, Department of Forensic Medicine, People,s
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Congenital ocular palsy
 Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 356 Congenital ocular palsy C. G. KEITH Queen Elizabeth Hospitalfor Children, Hackney Road, London Three patients with severe restriction of the ocular movements in one eye
Brit. j. Ophthal. (1972) 56, 356 Congenital ocular palsy C. G. KEITH Queen Elizabeth Hospitalfor Children, Hackney Road, London Three patients with severe restriction of the ocular movements in one eye
Orbital facia. Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia
 Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
Anatomy Orbital facia Periororbital facia Orbital septum Bulbar facia Muscular facia Physiology of symptoms 1) Proptosis ( exophthalmos) Pseudoproptosis Axial Non axial Pulsating Positional Intermittent
