Breast Calcifications: The Focal Group
|
|
|
- Myles Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Residents Section Pattern of the Month reast alcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Residents inradiology manda Demetri-Lewis 1, 2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1 Ronald L. Eisenberg 1 Demetri-Lewis, Slanetz PJ, Eisenberg RL Keywords: breast, calcification DOI: /JR Received September 6, 2010; accepted after revision June 10, Department of Radiology, eth Israel Deaconess Medical enter, Harvard Medical School, 330 rookline ve, oston, M ddress correspondence to R. L. Eisenberg (rleisenb@bidmc.harvard.edu). 2 Present address: reast are enter, York Hospital, York, ME. WE This is a Web exclusive article. JR 2012; 198:W325 W X/12/1984 W325 merican Roentgen Ray Society reast alcifications: The Focal Group reast calcifications are common findings on mammography and may reflect both benign and malignant causes (Fig. 1). The detection of breast calcifications often necessitates further imaging evaluation. Magnification mammography is the primary technique used for further analysis of calcifications in the breast. Typically, magnified mammographic views in the craniocaudal and mediolateral projections are obtained because this permits differentiation of benign milk of calcium, a form of fibrocystic change, from other worrisome deposits. Magnification mammography decreases noise and increases image sharpness, permitting clearer analysis of the morphology and the distribution of the calcifications. Evaluation of breast calcification morphology and distribution as well as assessing for any interval changes can aid in determining patient management. The morphology and size of calcifications are the most important factors in deciding whether calcifications are typically benign, indeterminate and warranting follow-up imaging or biopsy, or suspicious and requiring biopsy. Macrocalcifications are defined as larger (typically > 2 mm) calcium deposits in the breast tissue that are generally associated with a benign process, such as those related to fat necrosis, involuting fibroadenomas, radiation therapy, or plasma cell mastitis. Microcalcifications are calcific particles smaller than 0.5 mm that can be associated with a malignant process, such as ductal carcinoma in situ or invasive carcinoma. nalysis of the morphology of breast calcifications is helpful in determining the likelihood that the calcifications are benign, probably benign, or malignant (Fig. 2). The distribution of breast calcifications is also useful in differentiating benign from indeterminate and malignant causes (Fig. 3). Diffuse or scattered calcifications, most often bilateral, are distributed randomly throughout the breasts and are typically benign, such as skin TLE 1: Differential Diagnosis calcifications and calcifications associated of Focal Group of with fibrocystic change. Regional calcifications are scattered in a larger volume (> 2 enign causes alcifications cm 3 ) of breast tissue; often involve most of rtifact (ointment/antiperspirant) the breast or more than a single quadrant but not in an expected ductal distribution; and Skin calcification favor a benign cause, such as seen with sclerosing adenosis or fibrocystic change. Fibroadenoma Fibrocystic change/milk of calcium Grouped (or clustered) calcifications, which Papilloma are defined as at least five calcifications within 1 cm 3 of tissue, are most often of intermediate concern for malignancy of the breast. Sclerosing adenosis Fat necrosis Linear calcifications, which suggest deposits typia (DH, pleomorphic LIS, LH) in a duct, are suspicious for malignancy. Segmental calcifications, which are deposited in reast infarct one or more ducts and branches of a segment Malignancy or lobe, are typically suspicious for multifocal breast cancer. Invasive cancer, most commonly ductal DIS Most breast calcifications form either Note DH = atypical ductal hyperplasia, LIS = within the terminal ducts (intraductal) or lobular carcinoma in situ, LH = atypical lobular within the acini (lobular), both of which hyperplasia, DIS = ductal carcinoma in situ. JR:198, pril 2012 W325
2 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved enign Dystrophic Eggshell Fat necrosis Milk of calcium Plasma cell mastitis Popcorn Round/punctate Skin Sutural Vascular alcification Morphology Intermediate concern morphous Granular oarse heterogeneous Fig. 1 Various appearances of clustered calcifications in 54-year-old woman who had abnormal screening mammography results., Right mediolateral oblique image shows three clusters of calcifications (arrows)., Magnification mediolateral image shows cluster of pleomorphic calcifications (arrow) in superior anterior right breast, which represented biopsyproven ductal carcinoma in situ., Magnification mediolateral image shows two posterior clusters of calcifications (arrows), which represented fibroadenomas at different stages of hyalinization. Malignant Fine linear branching Fine pleomorphic Fig. 2 Flowchart shows morphology of breast calcifications. [1] W326 JR:198, pril 2012
3 reast alcifications Fig. 3 Flowchart shows calcification differentiation. alcification Distribution enign Intermediate concern Malignant Diffuse Regional Grouped Linear Segmental Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved compose the terminal duct lobular unit (TDLU), the basic functional unit of the breast. The ducts and lobules are lined by breast epithelium. onsequently, most breast disorders, including fibrocystic change and malignancies, arise from the TDLU. Lobular calcifications, which are located within the acini of the breast, tend to be uniform, homogeneous, and sharply defined and are often punctuate or round. When the acini become very large, as in cystic hyperplasia, calcium oxalate may precipitate out in the concentrated fluid contained within the distended acinus, most often referred to as milk of calcium. When there is more fibrosis, as Fig. 4 Skin ointment artifact in 63-year-old woman. and, Left mediolateral oblique () and magnification mediolateral () images from screening mammography show cluster of pleomorphic calcific densities in axilla (arrow, )., Tangential compression image with radiopaque marker on skin lesion shows calcific densities seen mammographically (arrow). Further discussion with patient revealed that she had applied zinc oxide cream to her axilla. JR:198, pril 2012 W327
4 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 5 ntiperspirant artifact in 47-year-old woman. and, Mediolateral oblique () and magnification mediolateral oblique () images of left breast show cluster of pleomorphic multiple densities in axilla (arrow, ). and D, Repeat mediolateral oblique images without () and with (D) magnification obtained after patient was called back and axilla was washed show no evidence of previous clustered densities, consistent with antiperspirant that was removed. D in sclerosing adenosis, the calcifications are usually smaller and less uniform, making them difficult to differentiate from intraductal calcifications. Lobular calcifications usually have a diffuse or scattered distribution and are often benign. Intraductal calcifications represent calcified cellular debris or secretions within the distal aspect of the TDLU and typically vary in size, density, and shape. Intraductal calcifications may form complete casts of the duct, ap- W328 JR:198, pril 2012
5 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved pearing as fine linear or branching calcifications or appearing more fragmented and irregular, both appearances suspicious for malignancy. Most breast calcifications are deposits of calcium phosphate, usually in the form of hydroxyapatite. These stain dark blue to purple on routine H and E stains. alcium phosphate is found in a spectrum of entities that includes fibrocystic changes (cysts, usual ductal hyperplasia, adenosis, and sclerosing adenosis), fibroadenomas, and in situ and invasive carcinomas. alcium oxalate crystals are much less common; colorless on H and E staining; and predominantly found in benign fibrocystic epithelium, usually accompanied by apocrine epithelial metaplasia. This type of calcification is uncommon in malignant epithelium. The remainder of this article focuses on benign and malignant causes of grouped calcifications (Table 1), which often pose a diagnostic challenge. When properly evaluated with additional mammographic views, some groups of calcifications can be definitively characterized as benign, whereas others may still require follow-up imaging or biopsy. enign Lesions Presenting as Grouped Microcalcifications rtifacts reast calcifications may be simulated by a wide array of artifacts, including radiopaque material on the skin such as antiperspirants, deodorants, powders, and salves, many of which contain metals such as aluminum, magnesium, iodine, or zinc oxide (Fig. 4). Radiopaque Fig. 6 Skin calcifications in 60-year-old woman. and, Screening craniocaudal () and mediolateral oblique () images of right breast show cluster of calcifications (arrow) in posterior inferior medial breast., Magnification craniocaudal image shows cluster of calcifications (arrow) lies within skin and some of calcifications have lucent centers. JR:198, pril 2012 W329
6 densities projecting over the axilla suggest antiperspirant on the skin, which will not persist on repeat imaging after the patient washes the axillary region (Fig. 5). Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Skin alcifications Dermal calcifications usually have lucent centers and are located along the inframammary fold, in the parasternal region, in the axilla, and around the areola (Fig. 6). Dermal calcifications may appear on mammography as a group of calcifications and simulate intraparenchymal calcifications on multiple projections. Tangential views can confirm that the calcifications lie within the skin and are therefore of no clinical concern. Fibrocystic hange Fibrocystic change refers to a constellation of benign entities in the ducts and the stroma that most commonly present as cysts and may have calcifications (Figs. 7 and 8). Sedimented calcium deposits within benign cysts are often referred to as milk of calcium (Fig. 9). Milk of calcium has a very characteristic appearance mammographically and, when present, can be readily recognized as a benign process. On the mediolateral or the lateromedial projection, milk of calcium has the characteristic appearance of crescent-shaped calcium deposits, corresponding to the calcifications conforming to the curve in the inferior aspect of the cyst. On the craniocaudal projection, the calcifications are indistinct, sometimes referred to as smudgy. Other proliferative fibrocystic changes include usual ductal hyperplasia, adenosis, and sclerosing adenosis, all of which may present as grouped calcifications on mammography. Fig. 7 Fibrocystic changes in 61-year-old woman. and, raniocaudal () and mediolateral oblique () images reveal cluster of calcifications in central upper right breast (arrow)., Spot compression magnification craniocaudal image of right breast shows predominantly punctuate group (arrow), which on biopsy were shown to be fibrocystic change. W330 JR:198, pril 2012
7 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved D Fig. 8 Fibrocystic change in 44-year-old woman who had abnormal screening mammography., raniocaudal spot compression magnification image of left breast shows cluster of calcifications medially (arrow)., luster of numerous fine pleomorphic calcifications (arrow) on this magnified craniocaudal image was considered suspicious, and stereotactic core biopsy was recommended., Image shows stereotactic core biopsy of this suspicious cluster of calcifications in left breast, which was performed with superior to inferior approach in craniocaudal projection. D, Specimen radiograph of biopsied calcifications (arrows) confirms adequate sampling and histopathology confirms fibrocystic change. Fibroadenoma Fibroadenomas are benign masses of stroma (fibroblasts and collagen) that distort the native duct epithelium. They most commonly occur in women younger than 30 years but can be seen at any age. On mammography, a fibroadenoma usually appears as an oval or lobulated mass with a density equal to that of breast parenchyma. Involution of a fibroadenoma typically leads to calcification, which initially may appear small and irregular and prompt biopsy. Eventually, the calcification progresses to a dense more popcornlike appearance that confirms its benign cause (Fig. 10). Fat Necrosis Fat necrosis may develop in patients who have sustained trauma or undergone previous surgery or radiation. Fat necrosis usually appears as rimlike or eggshell calcifications with fat-containing radiolucent centers, termed oil cysts (Fig. 11). Occasionally, fat necrosis can appear as a group of indeterminate microcalcifications that may warrant biopsy (Fig. 12). JR:198, pril 2012 W331
8 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 9 Milk of calcium in 55-year-old woman with abnormal screening mammography who presented for diagnostic workup., Two-minute delayed lateral image of left breast shows cluster of calcifications in upper breast (arrow)., Magnification image of 2-minute delayed lateral view shows layering of calcifications within tiny cysts, consistent with milk of calcium (arrow)., raniocaudal image of left breast shows same cluster of calcifications in lateral breast (arrow). D, On magnification craniocaudal image, calcifications appear rounded, fuzzy, and amorphous, typical of milk of calcium (arrow) on this projection. iopsy is not indicated. D W332 JR:198, pril 2012
9 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 10 Hyalinized fibroadenoma in 51-yearold woman who presented for annual screening mammography., raniocaudal image of right breast shows cluster of coarse calcifications in central posterior breast (arrow)., Mediolateral oblique image shows cluster in superior right breast (arrow)., On magnification mediolateral image, calcifications have popcornlike appearance that is typical of hyalinized fibroadenoma. iopsy is not indicated. Fig. 11 Oil cysts in fat necrosis in 74-year-old woman who had undergone lumpectomy for invasive ductal carcinoma., Mediolateral oblique image of right breast with lumpectomy marker and four clips shows cluster of calcifications in lumpectomy bed (arrow)., Magnification mediolateral image shows cluster of calcifications with lucent-centered calcifications in lumpectomy bed, consistent with oil cysts seen with fat necrosis. No further imaging or workup is necessary. JR:198, pril 2012 W333
10 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved E Fig. 12 Fat necrosis in 29-year-old woman who had undergone prior lumpectomy and radiation therapy for invasive ductal carcinoma and ductal carcinoma in situ and presented for annual mammography., Mediolateral oblique image of right breast shows cluster of calcifications in lumpectomy bed (arrow)., Lateral magnification compression image of lumpectomy bed confirms cluster of pleomorphic calcifications., ompression magnification craniocaudal image of same breast shows cluster of calcifications in lateral breast (arrow). D, Magnified craniocaudal view shows cluster of pleomorphic calcifications (arrow), which were considered suspicious and therefore biopsied. E, Specimen radiograph (with gray scale inverted) after stereotactic-guided core biopsy of calcifications (arrows) in lumpectomy bed confirmed calcifications in biopsy specimen. Histopathology showed fat necrosis. Diagnosis was considered concordant with imaging findings. D W334 JR:198, pril 2012
11 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 13 alcified suture material in radiated breast in 67-year-old woman with prior radiation treatment for invasive carcinoma 1 year ago who presented for annual mammography. and, raniocaudal () and mediolateral oblique () images of right breast show group of linear calcifications (arrow). and D, Magnification craniocaudal () and lateral (D) images show linear calcifications in configuration of suture material (arrow) that have knots consistent with calcified suture material, which can occur after radiation therapy and rarely after benign breast biopsy. Sutural alcifications alcifications occurring in the operative site of a resected malignancy are challenging to assess. omparing the current study with pre- and postbiopsy images and specimen radiographs can help to determine whether the calcifications represent residual tumor or a benign finding. alcifications of suture material can occur in a radiated breast and, rarely, at the site of a prior benign surgical biopsy (Fig. 13). D reast Infarct Hemorrhagic breast infarct has been described as a complication of anticoagulant therapy, during pregnancy and lactation, and after harvesting of the internal mammary artery for JR:198, pril 2012 W335
12 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 14 reast infarction in 89-year-old woman who had abnormal screening mammography., Mediolateral oblique image of left breast shows cluster of calcifications in anterior slightly superior breast (arrow)., Magnification compression craniocaudal image shows cluster of heterogeneous calcifications (arrow) in this patient, who was on anticoagulation therapy. This cluster was considered suspicious, and biopsy revealed breast infarction. coronary artery bypass grafting. Infarction of breast masses, such as fibroadenoma and phyllodes tumor, has also been reported. reast infarction may manifest mammographically as a group of calcifications that is indistinguishable from the appearance associated with malignant disease (Fig. 14). Sclerosing denosis Sclerosing adenosis is a condition characterized by lobular calcification and associated fibrosis. Lobular calcifications filling the acini are typically uniform, homogeneous, and sharply defined, appearing mammographically as punctate or round. When grouped, they can be difficult to differentiate from suspicious calcifications and thus warrant biopsy (Fig. 15). Fig. 15 Sclerosing adenosis in 77-year-old woman who presented for screening mammography., raniocaudal image of left breast shows cluster of calcifications in lateral breast (arrow)., Magnified craniocaudal image of area shows cluster of pleomorphic calcifications in lateral breast (arrow), for which biopsy was recommended. (Fig. 15 continues on next page) W336 JR:198, pril 2012
13 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 15 (continued) Sclerosing adenosis in 77-year-old woman who presented for screening mammography., Postbiopsy radiograph shows calcifications within specimen (arrows). D, Magnified specimen radiograph shows calcifications (arrow), which were shown at biopsy to represent sclerosing adenosis. Fig. 16 Papilloma in 48-year-old woman who presented with bloody nipple discharge. and, raniocaudal () and magnified craniocaudal () images of right breast show cluster of about nine rounded calcifications in retroareolar region (arrow)., Ultrasound image of area shows discrete lesion (cursors) containing calcifications (arrows), which was biopsied under ultrasound guidance and shown to be papilloma. D JR:198, pril 2012 W337
14 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved High-Risk Lesions Presenting as Grouped alcifications Papilloma Papillomas are intraductal lesions composed of a fibrovascular core capped by epithelial and fibroepithelial cells. They are often solitary, occurring in one of the large ducts within 3 cm of the nipple, and typically present with spontaneous clear or bloody discharge. Papillomas are typically not seen on mammograms because of their relatively small size, infrequently associated calcifications, and subareolar location. lmost 60% of patients with papillomas have normal mammograms. Mammographic findings associated with papillomas include benign-appearing circumscribed masses of various sizes and solitary dilated retroareolar ducts. The rare calcifications identified mammographically within a papilloma may be rounded, crescentic, coarse, or eggshell. However, calcifications associated with papillomas may have other appearances that are indistinguishable from the grouped microcalcifications seen in malignant lesions (Fig. 16). Papillomas containing calcifications are believed to have previously undergone infarction with hemorrhage. Papillary lesions of the breast with atypical ductal hyperplasia should be excised because of the significant upgrade rate to malignancy. In some centers, even benign papillomas diagnosed on core needle biopsy are surgically excised, although this is controversial. typical Ductal Hyperplasia typical ductal hyperplasia (DH) is a high-risk marker because women with atypical proliferative changes are 4 5 times more likely to develop breast cancer than those with nonproliferative changes. typical proliferative change in association with a family history of breast cancer elevates the risk to 11 times that of the general population. The risk is increased in both the ipsilateral and the contralateral breasts. Mammographically, DH may appear as a group of amorphous, indistinct, or fine granular calcifications that are difficult to differentiate from a malignant cause (Fig. 17). Fig. 17 typical ductal hyperplasia in 69-year-old woman who presented for screening mammography., Magnification compression craniocaudal image shows cluster of calcifications in left retroareolar breast (arrow)., Magnified craniocaudal image of area shows cluster of pleomorphic calcifications (arrow), which were considered suspicious. iopsy showed atypical ductal hyperplasia and excision was performed. W338 JR:198, pril 2012
15 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 18 Lobular carcinoma in situ in 43-year old woman who presented with abnormal screening mammography., Magnified craniocaudal image of left breast shows cluster of calcifications in central posterior breast (arrow)., Magnified craniocaudal image of area shows cluster of pleomorphic calcifications (arrow). ecause of patient s small breast with compression thickness of 14 mm, excisional biopsy after needle localization was performed, revealing pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ containing microcalcifications. Lobular arcinoma in Situ Lobular carcinoma in situ (LIS), also termed lobular neoplasia, is an incidental histologic diagnosis with no clinical or mammographic findings except in the pleomorphic variant where calcifications may be seen (Fig. 18). The pleomorphic variant appears to be more aggressive than conventional LIS, with up to 30% having an associated malignancy on surgical excision. For most cases in which LIS is found on a biopsy specimen obtained for grouped calcifications, most centers recommend surgical excision, although the management of LIS remains somewhat controversial. ll forms of LIS are considered a significant risk marker for the development of subsequent breast cancer in either breast, elevating the lifetime risk by 8 10 times. Fig. 19 typical lobular hyperplasia in 51-year-old woman who presented for screening mammography., raniocaudal image of right breast shows cluster of calcifications in lateral central breast (arrow)., Magnified craniocaudal image of area shows cluster of pleomorphic calcifications (arrow), which were considered suspicious. iopsy showed atypical lobular hyperplasia. JR:198, pril 2012 W339
16 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 20 Ductal carcinoma in situ (DIS) in 62-year-old woman who presented for screening mammography., Mediolateral oblique image of right breast shows cluster of linear calcifications in superior breast (arrow)., Magnification mediolateral image shows linear calcifications with associated density (arrow). iopsy showed DIS with microinvasion. Fig. 21 Ductal carcinoma in situ (DIS) in 45-year-old woman who presented for screening mammography., raniocaudal image of right breast shows cluster of calcifications in outer breast (arrow). and, Magnified craniocaudal () and lateral () images of area show suspicious cluster of coarse heterogeneous calcifications. iopsy confirmed grade 2 DIS. W340 JR:198, pril 2012
17 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved typical Lobular Hyperplasia Women with atypical lobular hyperplasia (LH) have a 4 5 times increased risk for developing breast cancer in their lifetime. Mammographically, LH is thought to be a serendipitous finding that may result when a biopsy is performed for calcifications. The management of LH is controversial. LH is considered by some to require surgical excision if found on core biopsy to exclude an associated malignancy. Others think that LH does not require surgical excision (Fig. 19). Malignant Lesions Presenting as Grouped alcifications Ductal arcinoma In Situ Ductal carcinoma in situ (DIS) is confined within the TDLU because of its intact basement membrane. The tumor grows within and along the duct, expanding the duct and assuming its D Fig. 22 Ductal carcinoma in situ (DIS) in 40-year-old woman who presented for baseline screening mammography., raniocaudal image of both breasts shows cluster of heterogeneous calcifications in lateral right breast (arrow)., ilateral mediolateral oblique image shows cluster of heterogeneous calcifications in anterior superior right breast (arrow)., Magnification compression craniocaudal image shows cluster or innumerable heterogeneous calcifications (arrow), considered suspicious and prompting biopsy. D, Magnified lateral image shows suspicious cluster of heterogeneous calcifications (arrow), shown to be DIS on stereotactic core biopsy. JR:198, pril 2012 W341
18 Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Fig. 23 Grade 1 invasive ductal carcinoma in 53-year-old woman who presented for screening mammography. and, raniocaudal () and mediolateral oblique () images of right breast show cluster of calcifications in upper outer quadrant (arrow). and D, Magnified craniocaudal () and lateromedial (D) images of area show suspicious group of calcifications. iopsy revealed grade 1 invasive ductal carcinoma. shape. alcifications form within DIS either from calcifying secretions or from cell death with necrosis. The classic appearance of DIS includes linear, branching, or fine pleomorphic calcifications in a ductal distribution. The calcifications in DIS may have a dot-dash appearance with both round and linear shapes, or they may appear as broken needles. However, DIS occasionally may present as a focal group of fine pleomorphic or coarse heterogeneous calcifications, which on histopathology reflect the rounded, tiny, and irregular calcifications that form in necrotic tumors and are most often seen in the micropapillary or cribriform subtypes (Figs ). Invasive arcinoma Most calcifications developing in breast cancer are fine pleomorphic, meaning that they vary in size, shape, and density. These calcifications are concerning for malignancy and warrant biopsy. alcifications in invasive carcinoma typically are due to cell death and necrosis, which occur as the cancer outgrows its blood supply (Fig. 23). Typically seen with invasive ductal cancer, calcifications are rarely associated with invasive lobular malignancies. D onclusions grouped distribution of calcifications carries an intermediate concern for malignancy and therefore warrants further imaging evaluation. reast calcifications should be classified W342 JR:198, pril 2012
19 reast alcifications Downloaded from by on 01/08/18 from IP address opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved on the basis of their morphology and distribution. Imaging with additional spot compression magnification views in the craniocaudal and the true lateral projections helps further characterize the morphology of calcifications within a group. Those calcifications that are thought to be definitely benign should be managed with routine yearly follow-up mammography. alcifications thought to be probably benign (< 2% chance of malignancy) should be managed with follow-up mammography in 6 months (and placed in the I-RDS 3 category). Periodic follow-up at 6 months for 2 years or follow-up imaging at 6 months, 1 year, 2 years, and 3 years can be undertaken in these probably benign calcifications if they are round or punctuate, have no malignant features, and are stable. Grouped calcifications characterized as suspicious (new, increasing in number, or pleomorphic) warrant further intervention with stereotactic core needle, vacuum-assisted ultrasound-guided, or surgical biopsy. Reference 1. Radiology ssistant Website. alcifications morphology ce38e6d1d7T-calcifications.png. ccessed December 19, 2011 Suggested Reading 1. goff SN, Lawton TJ. Papillary lesions of the breast with and without atypical ductal hyperplasia: can we accurately predict benign behavior from core needle biopsy? m J lin Pathol 2004; 122: merican ollege of Radiology. reast imaging reporting and data system (I-RDS), 4th ed. Reston, V: merican ollege of Radiology, anik S, runt. Haemorrhagic breast infarction complicating anticoagulant therapy. Postgrad Med J 1982; 58: arder PJ, Shaaban, lizadeh Y, Kumarasuwamy V, Liston J, Sharma N. Screen-detected pleomorphic lobular carcinoma in situ (PLIS): risk of concurrent invasive malignancy following a core biopsy diagnosis. Histopathology 2010; 57: De Lafontan, Daures JP, Salicru, et al. Isolated clustered microcalcifications: diagnostic value of mammography series of 400 cases with surgical verification. Radiology 1994; 190: Esserman LE, Lamea L, Tanev S, Poppiti R. Should the extent of lobular neoplasia on core biopsy influence the decision for excision? reast J 2007; 13: Kopans D. reast imaging, 3rd ed. Philadelphia, P: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2007:73 75, 443, 444, , Mahoney M, Robinson-Smith TM, Shaughnessy E. Lobular neoplasia at 11-gauge vacuum-assisted stereotactic biopsy: correlation with surgical excisional biopsy and mammographic follow-up. JR 2006; 187: Sickles E. reast calcifications: mammographic evaluation. Radiology 1986; 160: Sigfúson F, ndersson I, spegren K, Janzon L, Linell F, Ljungberg O. lustered breast calcifications. cta Radiol Diagn (Stockh) 1983; 24: Tavassoli R. Pathology of the breast, 2nd ed. Hong Kong: ppleton and Lange, 1999: Wellings SR, Jensen HM, Marcum RG. n atlas of subgross pathology of the human breast with special reference to possible precancerous lesions. J Natl ancer Inst 1975; 55: Winchester DJ, ernstein JR, Jeske JM, et al. Upstaging of atypical ductal hyperplasia after vacuum-assisted 11-gauge stereotactic core needle biopsy. rch Surg 2003; 138: Jiang Y, Nishikawa RM, Wolverton DE, et al. Malignant and benign clustered microcalcifications: automated feature analysis and classification. Radiology 1996; 198: JR:198, pril 2012 W343
Segmental Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Linear Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Lai et al. Linear reast alcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Kenny. Lai 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Lai K, Slanetz
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Lai et al. Linear reast alcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Kenny. Lai 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Lai K, Slanetz
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review
 Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
Breast calcification: Management and Pictorial Review Poster No.: C-0692 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. de Lara Bendahan, M. F. Ramos Solis, A. Amador Gil, C. 1 2 3 2 4 4 Gómez
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications. BI-RADS 5 th Edition
 UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Architectural Distortion of
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Leonard M. Glassman MD Analysis of Breast Calcifications
 Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
Importance of Calcification Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Washington DC 45% of all breast cancers present as calcification
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Evaluation of Breast Calcifications Leonard M.
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Evaluation of Breast Calcifications Leonard M.
Pictorial Essay Singapore Med J 2009; 50(9) :
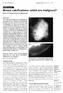 907 Pictorial Essay CME Article Breast calcifications: which are malignant? Muttarak M, Kongmebhol P, Sukhamwang N ABSTRACT Most calcifications depicted on mammograms are benign. However, calcifications
907 Pictorial Essay CME Article Breast calcifications: which are malignant? Muttarak M, Kongmebhol P, Sukhamwang N ABSTRACT Most calcifications depicted on mammograms are benign. However, calcifications
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions. Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea
 Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Cystic Masses of the Breast
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Eisenberg ystic Masses of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Neely Hines 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Hines N, Slanetz
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Eisenberg ystic Masses of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Neely Hines 1 Priscilla J. Slanetz Ronald L. Eisenberg Hines N, Slanetz
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS
 1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
1 NORMAL HISTOLOGY AND METAPLASIAS, MD Anatomy and Histology 1 Metaplasias 2 ANATOMY AND HISTOLOGY The female breast is composed of a branching duct system, which begins at the nipple with the major lactiferous
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Using T2-Weighted Sequences to More Accurately Characterize Breast Masses Seen on MRI
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Cytyc Corporation - Case Presentation Archive - March 2002
 FirstCyte Ductal Lavage History: 68 Year Old Female Gail Index: Unknown Clinical History: Negative Mammogram in 1995 6 yrs. later presents with bloody nipple discharge Subsequent suspicious mammogram Suspicious
FirstCyte Ductal Lavage History: 68 Year Old Female Gail Index: Unknown Clinical History: Negative Mammogram in 1995 6 yrs. later presents with bloody nipple discharge Subsequent suspicious mammogram Suspicious
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER
 RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER Orsolya Farkas, Gabriella Bodrogi and Gábor Szalai Department of Radiology, Pécs University Orsifarkas@yahoo.com Complex evaluation of the breast Patient history
RADIOLOGIC EVALUATION OF BREAST CANCER Orsolya Farkas, Gabriella Bodrogi and Gábor Szalai Department of Radiology, Pécs University Orsifarkas@yahoo.com Complex evaluation of the breast Patient history
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
High risk lesions of the breast : Review of the current diagnostic and management strategies
 High risk lesions of the breast : Review of the current diagnostic and management strategies Poster No.: C-1204 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Jagmohan, F. J. Pool, P. G. Pillay,
High risk lesions of the breast : Review of the current diagnostic and management strategies Poster No.: C-1204 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Jagmohan, F. J. Pool, P. G. Pillay,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast: MRI, Ultrasound, and Mammographic Appearances
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Eiada et al. Imaging Papillary Lesions of the reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.194 on 01/27/18 from IP address 37.44.198.194.
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Screen Detected Breast Carcinoma, with Coarse Calcification
 Screen Detected Breast Carcinoma, with Coarse Calcification Poster No.: R-0168 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Ebrahim, D. Abeywardhana, D. Dissanayake, C. Metcalf, E. Wylie;
Screen Detected Breast Carcinoma, with Coarse Calcification Poster No.: R-0168 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Ebrahim, D. Abeywardhana, D. Dissanayake, C. Metcalf, E. Wylie;
COMMON BENIGN DISORDERS AND DISEASES OF THE BREAST
 COMMON BENIGN DISORDERS AND DISEASES OF THE BREAST Aberrations of Normal Development and Involution (ANDI). The basic principles underlying the aberrations of normal development and involution (ANDI) classification
COMMON BENIGN DISORDERS AND DISEASES OF THE BREAST Aberrations of Normal Development and Involution (ANDI). The basic principles underlying the aberrations of normal development and involution (ANDI) classification
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Interpretation of Positron Emission Mammography: Feature Analysis and Rates of Malignancy
 Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research Deepa Narayanan 1,2 Kathleen S. Madsen 3 Judith E. Kalinyak 1 Wendie. erg 4,5 Narayanan D, Madsen KS, Kalinyak JE, erg W 1 Naviscan,
Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research Deepa Narayanan 1,2 Kathleen S. Madsen 3 Judith E. Kalinyak 1 Wendie. erg 4,5 Narayanan D, Madsen KS, Kalinyak JE, erg W 1 Naviscan,
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Imaging-Guided Core Needle Biopsy of Papillary Lesions of the Breast
 Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
Eric L. Rosen 1 Rex C. Bentley 2 Jay A. Baker 1 Mary Scott Soo 1 Received January 30, 2002; accepted after revision April 12, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Breast Imaging Division, Duke University Medical
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
The Postconservation Breast: Part 1, Expected Imaging Findings
 Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Chansakul et al. Imaging the Postconservation reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay CME SM The Postconservation reast Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.130
Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay Chansakul et al. Imaging the Postconservation reast Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay CME SM The Postconservation reast Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.192.130
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR
 BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
RSNA, /radiol Appendix E1. Methods
 RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU?
 MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
MEDICAL IMAGING AND BREAST DISEASE HOW CAN WE HELP YOU? Barbara M. Preston, M.D. SCREENING MAMMOGRAPHY AVERAGE RISK PATIENTS KAISER RECOMMENDATION: ALL WOMEN (INCLUDING TRANSGENDER FEMALES) Every 1-21
Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast as Cystic Lesions: Sonographic-Pathologic Correlation
 Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
Women s Imaging Original Research Kim et al. Breast Tumors as Cystic Lesions Women s Imaging Original Research WOMEN S IMGING Sun Mi Kim 1,2 Hak Hee Kim 1 Doo Kyung Kang 3 Hee Jung Shin 1 Nariya Cho 4
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
04/10/2018 HIGH RISK BREAST LESIONS. Pathology Perspectives of High Risk Breast Lesions ELEVATED RISK OF BREAST CANCER HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVES
 Pathology Perspectives of High Risk Breast Lesions Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head Director of Clinical Trials, Research and Development The University of Texas MD
Pathology Perspectives of High Risk Breast Lesions Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head Director of Clinical Trials, Research and Development The University of Texas MD
Atypical papillary lesions after core needle biopsy and subsequent breast carcinoma
 Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 243-248 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.031 Original article Atypical papillary lesions after core needle biopsy and subsequent breast carcinoma Tuenchit Khamapirad
Asian Biomedicine Vol. 5 No. 2 April 2011; 243-248 DOI: 10.5372/1905-7415.0502.031 Original article Atypical papillary lesions after core needle biopsy and subsequent breast carcinoma Tuenchit Khamapirad
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS
 BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Breast Disease: What PCPs Need to Know. Eunice Cho MD FACS
 Breast Disease: What PCPs Need to Know Eunice Cho MD FACS New Breast Cancer Screening Guideline for women with average risk Every other year AGE 40 AGE 45 AGE 55 AGE 55 + Talk with your doctor about when
Breast Disease: What PCPs Need to Know Eunice Cho MD FACS New Breast Cancer Screening Guideline for women with average risk Every other year AGE 40 AGE 45 AGE 55 AGE 55 + Talk with your doctor about when
Interpretation of Breast Pathology in the Era of Minimally Invasive Procedures
 Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns
 Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast
Microcalcifications detected on mammography classified as BIRADS 4 and 5 and their correlations with histopatologic findigns Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Breast
Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms
 342 Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms Ellen Shaw de Paredes, M.D. The purpose of routine screening mammography is to detect unsuspected cancer that has the potential to be cured. Abnormalities
342 Evaluation of Abnormal Screening Mammograms Ellen Shaw de Paredes, M.D. The purpose of routine screening mammography is to detect unsuspected cancer that has the potential to be cured. Abnormalities
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay
 CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
The Hot Topic for today is a biopsy from a 58-year-old woman who had worrisome mammographic calcifications on screening.
 The Hot Topic for today is a biopsy from a 58-year-old woman who had worrisome mammographic calcifications on screening. 1 My name is Dan Visscher; I am a consultant in the Division of Anatomic Pathology
The Hot Topic for today is a biopsy from a 58-year-old woman who had worrisome mammographic calcifications on screening. 1 My name is Dan Visscher; I am a consultant in the Division of Anatomic Pathology
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 52 year old female with an abnormal screening mammogram Areeg Rehman, MS 4 Nova Southeastern University Rebecca T. Sivarajah, MD Penn State University College of
One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy
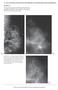 66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia and Papillomas: A Comparison of Ultrasound Guided Breast Biopsy and Stereotactic Guided Breast Biopsy Breast Cancer is the most common cancer diagnosed in women in the United
DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation.
 DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation. Poster No.: C-1560 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. B. Ibrahim, P. Morris, S. ANANDAN; Burlington, MA/US Keywords:
DCIS of the Breast--MRI findings with mammographic correlation. Poster No.: C-1560 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. B. Ibrahim, P. Morris, S. ANANDAN; Burlington, MA/US Keywords:
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ. Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Definition of DCIS WHO 2012 A neoplastic proliferation
Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Laura C. Collins, M.D. Department of Pathology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Definition of DCIS WHO 2012 A neoplastic proliferation
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
M Wani, M Khan, N Ul Gani, S Sangeen, B Singh, M Shafi, A Bilal, S Umer
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 12 Number 1 Juvenile Fibroadenoma With Fibroadenomatoid Hyperplasia M Wani, M Khan, N Ul Gani, S Sangeen, B Singh, M Shafi, A Bilal, S Umer Citation M Wani,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 12 Number 1 Juvenile Fibroadenoma With Fibroadenomatoid Hyperplasia M Wani, M Khan, N Ul Gani, S Sangeen, B Singh, M Shafi, A Bilal, S Umer Citation M Wani,
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN
 Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Index. C Calcifications fat necrosis 1, 61 fat necrosis 4, 69 nipple/peri-areolar involvement 1, 165
 A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast. Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London
 Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Proliferative Epithelial lesions of the Breast Sami Shousha, MD, FRCPath Charing Cross Hospital & Imperial College, London Amman, November2013 Proliferative Epithelial Lesions of the Breast Usual type
Papillary lesions of the breast - Imaging findings and diagnostic challenges
 Papillary lesions of the breast - Imaging findings and diagnostic challenges Poster No.: R-0146 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Jagmohan, F. J. Pool Keywords: Breast, Mammography,
Papillary lesions of the breast - Imaging findings and diagnostic challenges Poster No.: R-0146 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Jagmohan, F. J. Pool Keywords: Breast, Mammography,
Image guided core biopsies:
 Recommendations on the Surgical, Radiologic and Pathologic Approaches to Breast Disease: Using best practices based on multidisciplinary methodologies developed through the Allina Breast Committee. Image
Recommendations on the Surgical, Radiologic and Pathologic Approaches to Breast Disease: Using best practices based on multidisciplinary methodologies developed through the Allina Breast Committee. Image
Breast imaging in general practice
 Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Breast series CLINICAL PRACTICE Breast imaging in general practice Nehmat Houssami, MBBS, FAFPHM, FASBP, PhD, is Associate Clinical Director, NSW Breast Cancer Institute, Westmead Hospital, Honorary Senior
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications
 Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Sonographic Detection and Sonographically Guided Biopsy of Breast Microcalcifications Mary Scott Soo 1 Jay A. Baker Eric L. Rosen OBJECTIVE. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the ability of sonography
Guidance on the management of B3 lesions
 Guidance on the management of B3 lesions Lesion diagnosed on 14g or vacuumassisted biopsy (VAB) Risk of upgrade Recommended investigation Suggested approach for follow-up if no malignancy on VAE awaiting
Guidance on the management of B3 lesions Lesion diagnosed on 14g or vacuumassisted biopsy (VAB) Risk of upgrade Recommended investigation Suggested approach for follow-up if no malignancy on VAE awaiting
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
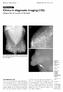 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
6/3/2010. Outline of Talk. Lobular Breast Cancer: Definition of lobular differentiation. Common Problems in Diagnosing LCIS in Core Biopsies
 Outline of Talk Lobular Breast Cancer: Common Problems in Diagnosing LCIS in Core Biopsies Definition of lobular differentiation Variants of LCIS that: carry risk for unsampled invasive cancer mimic DCIS
Outline of Talk Lobular Breast Cancer: Common Problems in Diagnosing LCIS in Core Biopsies Definition of lobular differentiation Variants of LCIS that: carry risk for unsampled invasive cancer mimic DCIS
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
Solitary Dilated Duct Identified at Mammography: Outcomes Analysis
 Women s Imaging Original Research Mammography of Solitary Dilated Duct Chang et al. Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: C. Belinda Chang 1 Natalya M. Lvoff 2 Jessica W. Leung 3 R. James Brenner
Women s Imaging Original Research Mammography of Solitary Dilated Duct Chang et al. Women s Imaging Original Research FOCUS ON: C. Belinda Chang 1 Natalya M. Lvoff 2 Jessica W. Leung 3 R. James Brenner
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Breast Evaluation & Management Guidelines
 Breast Evaluation & Management Guidelines Pamela L. Kurtzhals, M.D. F.A.C.S. Head, Dept. of General Surgery Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Objective Review screening & diagnostic guidelines Focused patient complaints
Breast Evaluation & Management Guidelines Pamela L. Kurtzhals, M.D. F.A.C.S. Head, Dept. of General Surgery Scripps Clinic, La Jolla Objective Review screening & diagnostic guidelines Focused patient complaints
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
Mammography Education, Inc.
 Mammography Education, Inc. 2018 3D image of the breast tissue BREAST SEMINAR SERIES Faculty LÁSZLÓ TABÁR, MD, FACR (Hon) Professor emeritus of Radiology Using the Multimodality Approach. A FULLY INTERACTIVE,
Mammography Education, Inc. 2018 3D image of the breast tissue BREAST SEMINAR SERIES Faculty LÁSZLÓ TABÁR, MD, FACR (Hon) Professor emeritus of Radiology Using the Multimodality Approach. A FULLY INTERACTIVE,
Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET
 Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions/Answers/Rationales/References 1. Below
Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions/Answers/Rationales/References 1. Below
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS
 7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE HISTOPATHOLOGICAL EVALUATION OF BENIGN PROLIFERATIVE BREAST LESIONS DR. VIBHUTI H. CHIHLA*, DR. N N. JAGRIT **, DR. JAYASHREE M. SHAH*** *3 rd year Pathology Resident, **Associate Professor,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY
 Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Breast Cancer. Most common cancer among women in the US. 2nd leading cause of death in women. Mortality rates though have declined
 Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Breast Cancer Most common cancer among women in the US 2nd leading cause of death in women Mortality rates though have declined 1 in 8 women will develop breast cancer Breast Cancer Breast cancer increases
Incidence and Management of Complex Fibroadenomas
 Incidence and Management of Complex Fibroadenomas Women s Imaging Original Research 214.fm 11/29/07 WOMEN S IMAGING Miri Sklair-Levy 1 Tamar Sella 1 Tanir Alweiss 2 Ilia Craciun 1 Eugene Libson 1 Bella
Incidence and Management of Complex Fibroadenomas Women s Imaging Original Research 214.fm 11/29/07 WOMEN S IMAGING Miri Sklair-Levy 1 Tamar Sella 1 Tanir Alweiss 2 Ilia Craciun 1 Eugene Libson 1 Bella
