THE FALL AND RISE OF FIBROSARCOMA. Cyril Fisher MD DSc FRCPath. Royal Marsden Hospital/Institute of Cancer Research London UK
|
|
|
- Stuart Logan
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE FALL AND RISE OF FIBROSARCOMA Cyril Fisher MD DSc FRCPath Royal Marsden Hospital/Institute of Cancer Research London UK Bullet points Fibrosarcoma was a common diagnosis until the 1960s. It became a diagnosis of exclusion as evolving techniques facilitated recognition of other sarcoma subtypes. Pleomorphic forms became categorized as malignant fibrous histiocytoma. From the 1990s, several clinicopathologic subtypes of fibrosarcoma were characterized by cellular morphology or stromal patterns. Fibrosarcomas can be differentiated or pleomorphic. Pleomorphic fibrosarcoma subsumes many tumors previously characterized as malignant fibrous histiocytoma or undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma. A variable proportion of myofibroblasts can be found in some types of fibrosarcoma. Fibrosarcomas are defined by electron microscopy and identifiable by light microscopy. Immunohistochemistry is useful mainly to exclude other sarcomas. Some subtypes of fibrosarcoma have specific and consistent genetic abnormalities which are of diagnostic value.
2 Historical Introduction The definition and classification of fibrosarcoma are related to its stroma. Fibrosarcoma was defined by Rokitansky (1842) as a tumor with varieties dependent on the form and arrangement of the fibers, and Mallory (1908) defined the fibroblast by its production of extra-cellular fibers. 1 Fibrosarcoma was included in subsequent classifications by Wilks (1849) (as fibroplastic) and Borst (1902)(as fibroma sarcomatosum) 2. Later, following the views of Ewing (1922) 3 and of Quick and Cutler (1927) 4, many deeply located fibrogenic spindle cell sarcomas were assumed to be of nervous origin; neurogenic sarcoma became a common diagnosis, though no specific criteria were given. Indeed, Warren and Sommer (1936) 5 considered 63/118 (53%) of their fibrosarcomas to be of neurogenic origin because of their herringbone and interlacing patterns. Stout dismissed neurogenic sarcoma as a term with as little meaning as spindle cell sarcoma. In Cancer vol 1 (1948), he defined fibrosarcoma as a tumor composed of spindle shaped fibroblasts and connective tissue fibers which are wrapped around all the cells rather than forming long wires 6, but emphasized that before rendering a diagnosis of fibrosarcoma it was necessary to exclude all other diagnoses especially in cellular, fiber-deficient tumors. Stout found a low metastatic rate of 8% in fibrosarcoma but 76% of his cases were well-differentiated and included many examples of dermatofibrosarcoma. In the first AFIP Fascicle on soft tissue tumors (1953), the term non-metastasizing fibrosarcoma appears under the heading of fibromatosis, and dermatofibrosarcoma under fibrosarcoma. Both were removed from these headings in the 2nd edition (1966). By this time, the concept of the facultative fibroblast had taken hold: and Stout pointed out (p 101) that after the so-called differentiated fibrosarcomas have been set aside, and malignant tumors of other types composed of cells acting as facultative fibroblasts, are omitted, the number of true malignant fibroblastic tumors capable of metastasizing shrinks very markedly. Gabbiani described the myofibroblast in Subsequently, with the recognition of fibromatosis and numerous benign fibroblastic/myofibroblastic lesions, the identification of specific sarcoma subtypes such as monophasic synovial sarcoma, and the categorization of many pleomorphic sarcomas as malignant fibrous histiocytoma (see below), fibrosarcoma became a rare diagnosis. In the last decade, however, the advent of newer techniques and methods of investigations has led to the definition of several fibrosarcoma subtypes and to the reassessment of the roles of the fibroblast and myofibroblast in pleomorphic sarcomas. Fibroblastic Sarcomas Adult fibrosarcoma in dermatofibrosarcoma in solitary fibrous tumor Infantile fibrosarcoma Myxofibrosarcoma Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma/hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with rosettes
3 Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma Pleomorphic fibrosarcoma (MFH) Adult fibrosarcoma Classical fibrosarcoma can be seen as a component of other subtypes of fibrosarcoma but its incidence as a pure tumor is rare; it probably accounts for around 1% of adult sarcomas. It is most common in middle-aged and older adults with equal sex incidence. 8 Fibrosarcomas involve deep tissues of extremities, trunk, and head & neck; reports of occurrences in visceral organs and retroperitoneum are questionable. Some arise following therapeutic irradiation, and rarely following implantation of foreign material but the nature of these tumors is not always certaiin. The typical fibrosarcoma has sweeping herringbone fascicles of spindle-shaped cells with tapered darkly staining nuclei, small nucleoli, and scanty cytoplasm with variable mitotic activity. The cells have prominent rough endoplasmic reticulum and absence of myofilaments, external lamina or intercellular junctions, and (apart from vimentin) usually lack markers except focal CD34 9 and SMA in some cases. An occasional cell has peripheral filament bundles suggestive of myofibroblastic differentiation; tumors in which this is prominent are myofibrosarcomas. 10 Inflammatory fibrosarcoma is currently included with inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor, although it might properly be applied to malignant variants of the latter. Higher-grade tumors have more densely staining nuclei, and can display focal round cell change and multinucleated cells, but sarcomas with marked pleomorphism are classified as malignant fibrous histiocytomas. The stroma varies from a delicate intercellular network to paucicellular areas with diffuse or keloid-like sclerosis or hyalinization, or fibromatosis-like foci. Myxoid change and osteochondroid metaplasia can occur. Fibrosarcomas metastasize to lungs and bone, especially the axial skeleton, and rarely to lymph nodes. Metastasis occurs in 9-63% of patients and is time- and gradedependent. 5 year survival is 39-54% 11, 12. Poor prognostic factors include high grade, high cellularity with minimal collagen, mitotic rates >20/10hpf, necrosis, and little collagen. Fibrosarcoma can arise in dermatofibrosarcoma both de novo and in recurrent lesions. It is characterized by greater cellularity with fascicular architecture and increased mitotic activity. CD34 can be positive or negative in the fibrosarcomatous area. The fibrosarcomatous component behaves more aggressively, with local recurrence in >50% and metastasis in 15% of cases. Adequate local control of DFS with fibrosarcomatous changes, with clear surgical margins, can reduce both local recurrence and the incidence of metastasis. The reciprocal translocation of DFSP, t(17;22)(q22;q13) (with a supernumerary ring chromosome), resulting in fusion of the genes COL1A (17q21-22) and PDGFB1(22q13), has also been shown in FS-DFSP. COL1A1-PDGFB fusion transcripts have also been detected in four of six superficial adult fibrosarcomas (but not deep ones) without a component of DFSP, implying possible origin from DFSP. 13
4 Myxofibrosarcoma The term myxosarcoma was originally applied to myxoid change in fibrosarcoma (Warren and Sommer illustrate this labelled edema - in their Fig 7 5 ) but Stout did not regard this as a separate entity and opposed the use of the term 6. The modern concept of myxofibrosarcoma was introduced in studies from Sweden in Higher grades of myxofibrosarcoma were considered to be equivalent to the contemporaneously described myxoid MFH 17, and there have been recent large clinicopathological series 18, 19. Although Merck (1983) 20 suggested that myxofibrosarcoma was fibrohistiocytic, most utrastructural and immunohistochemical studies have suggested that myxofibrosarcoma is a fibroblastic (not myofibroblastic) lesion. In fact, the term myxoid fibrosarcoma would be more appropriate as it would then be in line with myxoid liposarcoma, chondrosarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, etc. The proportion of myxoid change required to define this tumor has not been agreed. It has varied between >10% of tumor area 19, >30% of the whole tumor (or <20% of solid areas) 18, at least half of the tumor 21, and wholly or almost wholly myxomatous 20 ; the current WHO classification refers to variably myxoid stroma. 22 Myxofibrosarcoma occurs mostly in the limbs of older subjects, and has a tendency to superficial location, as a multinodular subcutaneous unencapsulated mass which is usually slowly-growing. Within the myxoid nodules, spindle-shaped cells with hyperchromatic nuclei are irregularly dispersed. Nuclear pleomorphism is always present at least focally, but this is highly variable, and in areas the cells can look remarkably bland. Mitotic figures are usually found relatively easily, especially in the pleomorphic areas, and abnormal forms are seen. Higher grade lesions have an increasing proportion of non-myxoid tumor and pleomorphism as in storiform-pleomorphic MFH. These initially form solid cellular areas between the myxoid nodules, and can be fibrous, hemorrhagic or necrotic. Vessels are typically fairly numerous, short, separate, curved and relatively thick-walled rather than delicate; a plexiform vascular pattern is lacking and the tumor cells are not closely related to the blood vessels. A few scattered cells can be actin-positive, implying possible myofibroblastic differentiation and there is sometimes focal immunoreactivity for the fibroblastic marker CD34. Ultrastructurally, there are fibroblasts, with myofibroblastic differentiaton appearing in higher grade or pleomorphic areas. The genetic abnormalities vary; some tumors are polyploidy with complex kaytotypes, and other have ringn chromosomes, 6p-or 9q+ or 12q+. This lesion was originally defined as having four grades of which the lower ones are relatively bland angiomyxoid lesions, while higher ones have features of pleomorphic sarcomas. Prognostic factors include size (for metastasis, but not recurrence - 60% recur locally, often with grade progression), and depth: tumors in subcutis may recur but do not metastasize, whereas those involving deep fascia or muscle are more likely to recur and metastasize. The likelihood of metastasis is inversely proportional to the amount of myxoid change.
5 Low grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (LGFMS) 23, 24 This was first described by Evans with 2 cases in 1987 and 10 more in It occurs in deeper soft tissues of young adults (with a subset located superficially 25 ) and is characterised by benign-looking histology, but a prolonged history of multiple recurrences and eventual metastasis. Histologically, the neoplasm shows predominantly fibrous and focally myxoid areas with a swirling or loosely whorled growth pattern. The appearance of fibrous areas and abrupt myxoid whorls is characteristic. Cellularity is low to moderate, and the stromal cells are bland with very rare mitoses, although there is focally minimal nuclear pleomorphism. The nuclei are not tapered but are ovoid or rectangular in places. The stroma is not markedly vascular, but tumor cells sometimes aggregate around vessels and a plexiform vascular pattern is occasionally seen. Subsequent recurrences are more cellular and mitotically active, and ultimately pleomorphic. The cases described by Evans recurred one to several times, usually over a period of many years, and eventually metastasized, most frequently to lung. Hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes (HSCT) was described in , as a painless, slowly growing, deeply situated mass of the proximal extremities (age years, mean 38; 68% in males). 14 tumors were in skeletal muscle, and three in subcutis and most were circumscribed with occasional infiltrative borders microscopically. Histologically, they are composed of short fascicles of bland fusiform to spindled cells with minimal mitotic activity, situated in a hyalinized to myxoid stroma, often with cracking artefact in the collagen. In places there are more cellular areas sometimes with atypia. A characteristic feature is scattered large rosette-like structures that often merge with serpiginous areas of dense hyalinization. The rosettes, which vary from from few and inconspicuous to multiple and prominent, consist of a central collagenous core surrounded by an irregular rim of rounded cells morphologically and immunophenotypically different from the cells of the spindled stroma. Lane et al suggested that this entity was similar to low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma and a larger study from the same group 27 of 73 cases of LGFMS and HSCT, supported this view and widened the spectrum of LGFMS. Epithelioid areas were present in 45% and rosettes in 30%. A number of LGFMS were also found to possess inconspicuous collagen rosettes indicating that these two tumors form a common spectrum. In fact, a specific chromosomal translocation, t(7;16)(q34;p11) resulting in a fusion gene FUS-BBF2H7 (also known as CREB3L2, or CREB3L1 in some cases), has recently been described in both LGFMS and HSCT, proving their identity and their nature as a distinct entity The spindle cells are immunoreactive in some examples for EMA 25 and rarely for SMA and S100pr. The cells around the rosettes can express S-100 protein NSE and Leu 7 (11/13), and occasionally CD34. Ultrastructurally, both cell types appear fibroblastic with rare focal myofibroblastic differentiation. 31 Follow up (54 cases; range, mos; median, 24 mos; mean, 38 mos) showed 5 recurrences, 3 metastases, and 1 death. 27 Two of the metastatic tumors were LGFMS and one was a HSCT. HSCT, like LGFMS, are low-grade sarcomas with metastatic potential. The presence of focal areas of intermediate- to high-grade sarcoma does not relate to a worse outcome in the short term. LGFMS was initially reported to have a higher
6 metastatic rate than HSCT. However, Evans cases of LGFMS were initially selected because they eventuated in metastasis (and have frequently been misdiagnosed as fibromatosis), whereas in the large series of HSCT many cases were diagnosed prospectively as sarcomas and treated aggressively. Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma This was described in and occurs in deep muscle, around fascia or periosteum in the lower limb, trunk, shoulder and neck. Around 60 cases have now been reported. The tumors are circumscribed and can be up to 14.5 cm in diameter. They are sometimes multinodular, and cyst formation and calcification can be seen. Histologically, there are carcinoma-like nests or cords of rounded, epithelioid or fusiform cells, many of which have angulated nuclei within clear cytoplasm. Foci of more typical fibrosarcoma, with spindle cells in fascicles can be present elsewhere in the tumor. The cells are usually bland but can be pleomorphic, with mitoses up to 4/10 hpf and sometimes necrosis. The stroma has myxohyaline areas with metaplastic bone/cartilage, and a focal pericytomatous pattern. Some show positivity for CK, EMA, S100 protein, and bcl2, and the ultrastructure is interpreted as fibroblastic. Amplification of 12q13 and 12q15 sequences has been described in one case. Antonescu et al (2001) 33 described a further series of 16 cases (3 of which had previously been reported) (6M, 10F, mean age 40) involving limbs and girdles, penis, chest wall and head and neck, with tumors between 3.7 and 22 cm. Only vimentin was expressed (though 5/12 had weak focal EMA), and again the ultrastructure was fibroblastic. These authors also describe some overlap with other fibrosarcoma patterns, including fascicular, and low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. The tumor was initially described as low grade with 75% 5 year survival, but 53% persisted/recurred and 43% metastasised to lung or bone. In the series of Antonescu et al, the tumor appears to be of higher grade malignancy, with persistent disease or LR in 50% and metastasis in 86%, and 57% dead of disease 16 to 86 months after diagnosis. The aggregate of published cases indicates persistent/recurrent disease in 40%, and metastasis in 47% of cases. Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma/inflammatory myxohyaline tumor This is a low-grade fibrosarcoma described from three centers in 1998, which arises in digits, wrist, and ankle regions, and predominantly in the subcutis. Montgomery et al 34 described 51 cases, which occurred over a wide age range (4 81 years) and affected the sexes equally. 35 were in fingers, hand, wrist or arm, and 13 in toe, foot or lower leg. Many of the patients were treated aggressively but recurrences were noted in six of twenty-seven patients with follow-up. Almost simultaneously, a series of 44 apparently similar tumors in patients aged between 20 and 91 years was reported as acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma 35. These authors also noted a relation to tendon sheaths and joints in some cases. There was local recurrence in two thirds (67%) and several patients required amputation after repeated local recurrences. There was histologic documentation of metastasis to lymph node in one case. 5 tumors of the hand reported as inflammatory myxoid tumor of the soft parts with bizarre giant cells by Michal, also in 1998, appear to be the same entity 36. There are now about 132 published cases, including 7 non-acral examples.
7 These tumors form infiltrative multinodular masses characterized by dense inflammation merging with myxoid to collagenous stroma. The myxoid zones contain (multi)vacuolated lipoblast-like fibroblasts, as seen in other myxoid fibroblastic lesions and representing stromal mucin within dilated RER. The inflammatory zones have scattered bizarre cells with vesicular nuclei and large inclusion-like nucleoli with abundant focally vacuolated cytoplasm, reminiscent of Reed-Sternberg cells or virocytes, some of which contain phagocytosed neutrophils. Other components include eosinophils, neutrophils, lymphocytes, plasma cells, Touton giant cells and siderophages, and fibrosis (including sclerosed and hyalinized areas). Normal and atypical mitoses are seen among the bizarre cells, and some cases displayed focal necrosis. Immunostains are positive for vimentin and negative for CD30, CD15, and S100 protein; 4 of 13 cases were cytokeratin positive, but this was focal and weak and interpreted as aberrant. PCR for EBV was negative in 6/10 cases and positive at low levels (suggesting latent rather than active viral infection in 4). In the Swedish series, 7 of 25 were CD34 positive, 2 were SMA positive in occasional bizarre cells, and Ki67 labeling index was less than one per cent. 35 Ultrastructural studies in this series demonstrated fibroblastic characteristics, and the ganglion-like cells are interpreted as modified fibroblasts. Clonal chromosome changes have been described in one case, which showed a complex karyotype with a reciprocal translocation t(1;10) (p22;q24) in addition to the loss of chromosomes 3 and Of the 132 published cases, 40% have recurred but only 3 have metastasized. Of the 4 non-acral cases with follow up information, only one has recurred (after 5 years). Pleomorphic Fibrosarcoma and Myofibrosarcoma Pleomorphic sarcomas have been subject to numerous revisions. Until the 1960s, they were categorized as pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma, fibrosarcoma, or undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma. At this time, based on tissue culture studies, it was considered that histiocytes of the reticuloendothelial system could under the correct circumstances become facultative fibroblasts. In 1963 Stout and coworkers examined a heterogeneous collection of soft tissue tumors (supposedly histiocytomas and fibrous xanthomas) with tissue culture and concluded that the fibroblastic elements were derived from histiocytes. The term malignant fibrous histiocytoma (MFH) was formalized as a type of malignant histiocytic tumor in the 1967 AFIP fascicle. A clinico-pathologic series of MFH, published in 1972, was soon followed by studies defining further morphologic types of MFH: giant cell, inflammatory, myxoid and angiomatoid. MFH became the most common diagnosis among adult soft tissue sarcomas, and pleomorphic fibrosarcoma essentially disappeared. The fibrohistiocytic concept was later challenged and rebutted by the sequential application of new investigative modalities. Immunohistochemistry showed absence of marrow-derived histiocytic antigens and presence of antigens associated with mesenchymal cells, including intermediate filaments. 38 Careful morphologic observation combined with immuno-histochemical and genetic studies allow separation of other
8 pleomorphic sarcomas such as pleomorphic liposarcoma or dedifferentiated liposarcoma. 39 The residual tumors (synonym: MFH) formed a genetically heterogeneous group of fascicular or storiform neoplasms composed of atypical spindle and polygonal cells which show no specific line of differentiation. In fact, the consitutent cells, whether fusiform or plump and histiocyte-like, have ultrastructural features of fibroblasts, with much rough endoplasmic reticulum. In addition, myofibroblastic differentiation has been observed since electron microscopy was first employed on examples of MFH. 40 Typically, there are subplasmalemmal aggregates of cytoplasmic filaments, and a neoplastic cell with a fibronexus has been recorded in a pleomorphic myofibrosarcoma of bone. The proportion of pleomorphic sarcomas which display myofibroblastic differentiation increases with sample size and length of search. In one study, 56% of MFH of all types had detectable myofibroblasts, with a mean of 3% (range 0-22%) of myofibroblasts per case. 41 Some low-or intermediate-grade myofibrosarcomas have recurred as pleomorphic tumors. Pleomorphic MFH and pleomorphic myofibrosarcoma are morphologically indistinguishable but the latter (like pleomorphic sarcomas with myogenic differentiation) have a worse outcome in the relatively few cases with clinical and follow up data. Immunohistochemically, both SMA and desmin have been described in pleomorphic sarcomas with ultrastructurally confirmed myofibroblastic differentiation. 42 None of the pleomorphic myofibrosarcomas examined expressed h-caldesmon, which implies that they are not merely poorly differentiated leiomyosarcomas. However, both actin and desmin have been demonstrated in pleomorphic sarcomas without ultrastructural features of myofibroblastic or smooth muscle differentiation. Ultrastructural examination reveals variable myofibroblastic differentiation. As recently suggested 43, 44, pleomorphic MFH, since it is primarily composed of fibroblasts with or without myofibroblastic modulation, can be regarded as the pleomorphic form of fibrosarcoma. Conclusions Fibrosarcomas can be cellular or modified by stromal changes They can be differentiated or pleomorphic. Pleomorphic fibrosarcoma subsumes many tumors previously characterized as malignant fibrous histiocytoma or undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma. They can contain a variable proportion of myofibroblasts They are defined by EM and identifiable by LM. Immunohistochemistry is chiefly of value in excluding other tumors. Some have specific and consistent genetic abnormalities which are of diagnostic use. References 1. Mallory FB. The results of the application of special histological methods to the study of tumors. J Exp Med 1908;10: Borst M. Die Lehre von den Geschwulsten mit einem mikroskopischen Atlas. Wiesbaden: Bergmann, 1902.
9 3. Ewing J. Neoplastic Diseases. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co, Quick D, Cutler M. Neurogenic sarcoma: a clinical and pathological study. Ann Surg 1927;86: Warren S, Sommer GNJ. Fibrosarcoma of the soft parts with special reference to recurrence and metastasis. Ann Surg 1936;33: Stout AP. Fibrosarcoma. The malignant tumor of fibroblasts. Cancer 1948;1: Gabbiani G, Ryan GB, Majno G. Presence of modified fibroblasts in granulation tissue and their possible role in wound contraction. Experientia 1971;27: Fisher C, van den Berg E, Molenaar WM. Adult fibrosarcoma. In Fletcher CD, Unni K, Mertens F eds. in WHO classification of tumours. Pathology and Genetics. Tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC Press, 2002; Fisher C. Low-grade sarcomas with CD34-positive fibroblasts and low-grade myofibroblastic sarcomas. Ultrastruct Pathol 2004;28: Fisher C. Myofibrosarcoma. Virchows Arch 2004;445: Pritchard DJ, Soule EH, Taylor WF et al. Fibrosarcoma--a clinicopathologic and statistical study of 199 tumors of the soft tissues of the extremities and trunk. Cancer 1974;33: Scott SM, Reiman HM, Pritchard DJ et al. Soft tissue fibrosarcoma. A clinicopathologic study of 132 cases. Cancer 1989;64: Sheng WQ, Hashimoto H, Okamoto S et al. Expression of COL1A1-PDGFB fusion transcripts in superficial adult fibrosarcoma suggests a close relationship to dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans. J Pathol 2001;194: Angervall L, Kindblom LG, Merck C. Myxofibrosarcoma. A study of 30 cases. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand [A] 1977;85A: Kindblom LG, Merck C, Angervall L. The ultrastructure of myxofibrosarcoma. A study of 11 cases. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol 1979;381: Kindblom LG, Merck C, Svendsen P. Myxofibrosarcoma: a pathologicoanatomical, microangiographic and angiographic correlative study of eight cases. Br J Radiol 1977;50: Weiss SW, Enzinger FM. Myxoid variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Cancer 1977;39: Huang HY, Lal P, Qin J et al. Low-grade myxofibrosarcoma: A clinicopathologic analysis of 49 cases treated at a single institution with simultaneous assessment of the efficacy of 3-tier and 4-tier grading systems. Hum Pathol 2004;35: Mentzel T, Calonje E, Wadden C et al. Myxofibrosarcoma. Clinicopathologic analysis of 75 cases with emphasis on the low-grade variant. Am J Surg Pathol 1996;20: Merck C, Angervall L, Kindblom LG et al. Myxofibrosarcoma. A malignant soft tissue tumor of fibroblastic-histiocytic origin. A clinicopathologic and prognostic study of 110 cases using multivariate analysis. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand Suppl 1983;282: Weiss SW, Enzinger FM. Myxoid variant of malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Cancer 1977;39:
10 22. Mentzel T, van den Berg E, Molenaar WM. Myxofibrosarcoma. In Fletcher C, Unni KK, Mertens F eds. in WHO Classification of Tumours. Pathology and Genetics. Tumours of soft tissue and bone. Lyon: IARC Press, 2002; Evans HL. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. A report of two metastasizing neoplasms having a deceptively benign appearance. Am J Clin Pathol 1987;88: HL E. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. A report of 12 cases. Am J Surg Pathol 1993;17: Billings SD, Giblen G, Fanburg-Smith JC. Superficial low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma (Evans tumor): a clinicopathologic analysis of 19 cases with a unique observation in the pediatric population. Am J Surg Pathol 2005;29: Lane KL, Shannon RJ, Weiss SW. Hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes - A distinctive tumor closely resembling low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21: Folpe AL, Lane KL, Paull G et al. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma and hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes: a clinicopathologic study of 73 cases supporting their identity and assessing the impact of high-grade areas. Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24: Mertens F, Fletcher CD, Antonescu CR et al. Clinicopathologic and molecular genetic characterization of low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma, and cloning of a novel FUS/CREB3L1 fusion gene. Lab Invest 2005;85: Panagopoulos I, Storlazzi CT, Fletcher CD et al. The chimeric FUS/CREB3l2 gene is specific for low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2004;40: Reid R, de Silva MV, Paterson L et al. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma and hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes share a common t(7;16)(q34;p11) translocation. Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27: Dobashi Y, Noguchi T, Nasuno S et al. Hyalinizing spindle cell tumor with giant rosettes: report of a case showing remarkable myofibroblastic differentiation. Pathol Res Pract. 2001;197: Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG, Enzinger FM. Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma. A variant of fibrosarcoma simulating carcinoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19: Antonescu CR, Rosenblum MK, Pereira P et al. Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma: a study of 16 cases and confirmation of a clinicopathologically distinct tumor. Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25: Montgomery EA, Devaney KO, Giordano TJ et al. Inflammatory myxohyaline tumor of distal extremities with virocyte or Reed-Sternberg-like cells: a distinctive lesion with features simulating inflammatory conditions, Hodgkin's disease, and various sarcomas. Mod Pathol 1998;11: Meis-Kindblom JM, Kindblom LG. Acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma: a low-grade tumor of the hands and feet. Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22: Michal M. Inflammatory myxoid tumor of the soft parts with bizarre giant cells. Pathol Res Pract 1998;194:
11 37. Lambert I, Debiec-Rychter M, Guelinckx P et al. Acral myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcoma with unique clonal chromosomal changes. Virchows Arch 2001;438: Lawson CW, Fisher C, Gatter K. An immunohistochemical study of differentiation in malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Histopathology 1987;11: Fletcher CD. Pleomorphic malignant fibrous histiocytoma: fact or fiction? A critical reappraisal based on 159 tumors diagnosed as pleomorphic sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol 1992;16: Fu Y-S, Gabbiani G, Kaye GI et al. Malignant soft tissue tumours of probable histiocytic origin (malignant fibrous histiocytomas): general considerations and electron microscopic and tissue culture studies. Cancer 1975;35: Fukuda T, Tsuneyoshi M, Enjoji M. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma of soft parts: an ultrastructural quantitative study. Ultrastruct Pathol 1988;12: Montgomery E, Fisher C. Myofibroblastic differentiation in malignant fibrous histiocytoma (pleomorphic myofibrosarcoma): a clinicopathological study. Histopathology 2001;38: Antonescu CR, Erlandson RA, Huvos AG. Primary fibrosarcoma and malignant fibrous histiocytoma of bone--a comparative ultrastructural study: evidence of a spectrum of fibroblastic differentiation. Ultrastruct Pathol 2000;24: Erlandson RA, Antonescu CR. The rise and fall of malignant fibrous histiocytoma. Ultrastruct Pathol 2004;28:
Newer soft tissue entities
 Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
Newer soft tissue entities Examples among fibroblastic tumors Turku, May 6, 2010 Markku Miettinen, M.D. AFIP, Washington, DC Fibroblastic neoplasms Solitary fibrous tumor /Hemangiopericytoma Low-grade
A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen
 May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
May 2016 A 25 year old female with a palpable mass in the right lower quadrant of her abdomen Contributed by: Paul Ndekwe, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Department of Pathology and
Evening Specialty Conference Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology. Diagnostic pitfalls in bone and soft tissue pathology
 Evening Specialty Conference Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology. Case 1 Elizabeth G Demicco, MD, PhD Mount Sinai Hospital, New York Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners
Evening Specialty Conference Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology. Case 1 Elizabeth G Demicco, MD, PhD Mount Sinai Hospital, New York Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships USCAP requires that all planners
Soft Tissue Tumor Specimens
 More Than a Diagnosis: How the Surgical Pathologist Should Deal with a Soft Tissue Tumor. Andrew E. Rosenberg, MD. James Homer Wright Laboratories Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital
More Than a Diagnosis: How the Surgical Pathologist Should Deal with a Soft Tissue Tumor. Andrew E. Rosenberg, MD. James Homer Wright Laboratories Department of Pathology Massachusetts General Hospital
Diplomate of the American Board of Pathology in Anatomic and Clinical Pathology
 A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
A 33-year-old male with a left lower leg mass. Contributed by Shaoxiong Chen, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Indiana University School of Medicine/ IU Health Partners Department of Pathology and Laboratory
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis
 Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Selected Pseudomalignant Soft Tissue Tumors of the Skin and Subcutis Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN folpe.andrew@mayo.edu 2016 MFMER slide-1
Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma
 AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
AKA Myxo-inflammatory Fibroblastic sarcoma Acral Myxoinflammatory fibroblastic sarcomaam.j.surg.path1998; 22; 911-924 Inflammatory myxoid tumour of soft parts with bizarre giant cells [Pathol.Res.Pract.
Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology
 Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine 1921 Original
Slide Seminar Spanish Society of Pathology John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine 1921 Original
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors
 The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
The Relevance of Cytologic Atypia in Cutaneous Neural Tumors Recent Findings - New Developments New Problems Zsolt B. Argenyi, M.D. Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Director of Dermatopathology Department
أملس عضلي غرن = Leiomyosarcoma. Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5
 Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Leiomyosarcoma 1 / 5 EPIDEMIOLOGY Exact incidence is unknown, but older studies suggest that leiomyosarcomas comprise approximately 3 percent of soft-tissue sarcomas. Superficial leiomyosarcoma occurs
Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts
 Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Update On Lipomatous Tumors: Old Standbys and New Concepts John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Anatomic Pathology Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Conceptual Evolution of Soft Tissue Tumors Classification
 Conceptual Evolution of Soft Tissue Tumors Classification Angelo P. Dei Tos M.D. Departments of Pathology & Oncology Treviso, Italy How WHO classification was reshaped Pathologists and Cytogeneticists
Conceptual Evolution of Soft Tissue Tumors Classification Angelo P. Dei Tos M.D. Departments of Pathology & Oncology Treviso, Italy How WHO classification was reshaped Pathologists and Cytogeneticists
Part 1. Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013
 Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Part 1 Slides 1-38, Rita Alaggio Soft tissue tumors Trondheim 14. mars 2013 Pediatric Pathology Soft Tissue Tumors AN UPDATE Rita Alaggio Azienda Ospedaliera Università di Padova Soft Tissue Tumors More
Spindle Cell Lesions Of The Breast. Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology and Consultant Pathologist
 Spindle Cell Lesions Of The Breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology and Consultant Pathologist * SCLs comprise a wide spectrum of diseases, ranging from reactive processes to aggressive malignant
Spindle Cell Lesions Of The Breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology and Consultant Pathologist * SCLs comprise a wide spectrum of diseases, ranging from reactive processes to aggressive malignant
Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor
 C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
C H A P T E R 120 Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumor Currently, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) is the most commonly used generic name for the neoplasms known in the past as neurosarcoma,
3/27/2017. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
Ophthalmic Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2017 5 th March, 2017 Mukul K. Divatia, MD Assistant Professor Department of Pathology & Genomic Medicine Weill Cornell Medical College Houston Methodist
SOFT TISSUE TUMOR PATHOLOGY: AN UPDATE
 SOFT TISSUE TUMOR PATHOLOGY: AN UPDATE Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD July 18, 2013 Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA I have no disclosures. New Soft
SOFT TISSUE TUMOR PATHOLOGY: AN UPDATE Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD July 18, 2013 Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, MA, USA I have no disclosures. New Soft
5/10. Pathology Soft tissue tumors. Farah Bhani. Mohammed Alorjani
 5/10 Pathology Soft tissue tumors Mohammed Alorjani Farah Bhani Slides are included in this sheet. Objectives: Soft tissue tumors 1. Describe soft tissue tumors. 2. Understand the classification of soft
5/10 Pathology Soft tissue tumors Mohammed Alorjani Farah Bhani Slides are included in this sheet. Objectives: Soft tissue tumors 1. Describe soft tissue tumors. 2. Understand the classification of soft
Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma : A Case Report
 영남의대학술지제24권제2호 Yeungnam Univ. J. of Med. Vol.24 No.2 p315-321, Dec. 2007 증례 Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma : A Case Report Joon Hyuk Choi, Woo Jung Sung, Nam Hyuk Lee* Department of Pathology, and *Department
영남의대학술지제24권제2호 Yeungnam Univ. J. of Med. Vol.24 No.2 p315-321, Dec. 2007 증례 Angiomatoid Fibrous Histiocytoma : A Case Report Joon Hyuk Choi, Woo Jung Sung, Nam Hyuk Lee* Department of Pathology, and *Department
Desmoplastic Melanoma R/O BCC. Clinical Information. 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o BCC
 R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
R/O BCC Sabine Kohler, M.D. Professor of Pathology and Dermatology Dermatopathology Service Stanford University School of Medicine Clinical Information 74 y.o. man with lesion on left side of neck r/o
CASE REPORT Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumour resembling schwannoma
 Malaysian J Pathol 2014; 36(3) : 217 221 CASE REPORT Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumour resembling schwannoma Thejasvi KRISHNAMURTHY MD and SR NIVEDITHA MD, DNB Department of Pathology,
Malaysian J Pathol 2014; 36(3) : 217 221 CASE REPORT Benign epithelioid peripheral nerve sheath tumour resembling schwannoma Thejasvi KRISHNAMURTHY MD and SR NIVEDITHA MD, DNB Department of Pathology,
57th Annual HSCP Spring Symposium 4/16/2016
 An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
An Unusual Malignant Spindle Cell Lesion to Involve the Breast Erinn Downs-Kelly, D.O. Associate Professor of Pathology University of Utah & ARUP Laboratories No disclosures Case 39 y/o female with no
The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the. Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue
 The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue Tumors of the Head and Neck Joaquín J. García MD and Andrew L. Folpe MD Department
The Impact of Advances in Molecular Genetic Pathology on the Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Selected Soft Tissue Tumors of the Head and Neck Joaquín J. García MD and Andrew L. Folpe MD Department
International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences
 International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR) IJAMSCR Volume 2 Issue 4 Oct-Dec- 2014 Case report Medical research Myxofibrosarcoma of the male breast An infrequent neoplasm:
International Journal of Allied Medical Sciences and Clinical Research (IJAMSCR) IJAMSCR Volume 2 Issue 4 Oct-Dec- 2014 Case report Medical research Myxofibrosarcoma of the male breast An infrequent neoplasm:
Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 10 Number 1 Atypical Palisaded Myofibroblastoma of Lymph Node: Report of a rare case. V Kinnera, R Nandyala, M Yootla, K Mandyam Citation V Kinnera, R
21/07/2017. Hobnail endothelial cells are not the same as epithelioid endothelial cells
 UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
UPDATE IN CUTANEOUS VASCULAR S DERMATOPATHOLOGY SESSION BELFAST PATHOLOGY JUNE 21/2017 Dr E Calonje St John s Institute of Dermatology, London, United Kingdom THE FAMILY OF VASCULAR S WITH EPITHELIOID
USCAP 2011: ASDP companion meeting. Steven D. Billings 1
 USCAP 2011: ASDP companion meeting. Steven D. Billings (billins@ccf.org) 1 Spindle cell tumors that make you say, Oh $*&%! This lecture will focus on examples of cutaneous tumors that present particular
USCAP 2011: ASDP companion meeting. Steven D. Billings (billins@ccf.org) 1 Spindle cell tumors that make you say, Oh $*&%! This lecture will focus on examples of cutaneous tumors that present particular
Case 1 10/2/17. Myxoid Soft Tissue Tumors & Tumor-like Lesions. Myxofibro- or Fibromyxo-?: Myxoid Soft Tissue Tumours We Are All Mixed Up About
 Myxoid Soft Tissue Tumors & Tumor-like Lesions Myxofibro- or Fibromyxo-?: Myxoid Soft Tissue Tumours We Are All Mixed Up About Rajiv M. Patel, M.D. RCPA NZ ASM 2017 (4:15-5:00pm, Saturday, 23-09-17) Heterogenous
Myxoid Soft Tissue Tumors & Tumor-like Lesions Myxofibro- or Fibromyxo-?: Myxoid Soft Tissue Tumours We Are All Mixed Up About Rajiv M. Patel, M.D. RCPA NZ ASM 2017 (4:15-5:00pm, Saturday, 23-09-17) Heterogenous
1/10/2018. Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation. Overview. Desmoplastic/ Spindle Cell Melanoma
 2016 MFMER slide-1 2016 MFMER slide-2 2016 MFMER slide-3 Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
2016 MFMER slide-1 2016 MFMER slide-2 2016 MFMER slide-3 Soft Tissue Tumors Showing Melanocytic Differentiation Andrew L. Folpe, M.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic, Rochester,
Contents Part I Introduction 1 General Description 2 Natural History: Importance of Size, Site, Histopathology
 Contents Part I Introduction 1 General Description... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Incidence and Prevalence... 5 1.3 Predisposing and Genetic Factors... 8 References... 16 2 Natural History: Importance
Contents Part I Introduction 1 General Description... 3 1.1 Introduction... 3 1.2 Incidence and Prevalence... 5 1.3 Predisposing and Genetic Factors... 8 References... 16 2 Natural History: Importance
Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Analysis Of 19 Cases
 Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Analysis Of 19 Cases Katharine A. Downes, M.D., John R. Goldblum, M.D., Elizabeth A. Montgomery, M.D., Cyril Fisher, M.D., F.R.C.Path. Departments of Anatomic
Pleomorphic Liposarcoma: A Clinicopathologic Analysis Of 19 Cases Katharine A. Downes, M.D., John R. Goldblum, M.D., Elizabeth A. Montgomery, M.D., Cyril Fisher, M.D., F.R.C.Path. Departments of Anatomic
Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1637 Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors Sridevi. V*., Susruthan Muralitharan., and Thanka. J Dept of Pathology, SriMuthukumaran Medical
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/APALM.1637 Diagnostic Value of Immunohistochemistry in Soft Tissue Tumors Sridevi. V*., Susruthan Muralitharan., and Thanka. J Dept of Pathology, SriMuthukumaran Medical
Special slide seminar
 Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
Special slide seminar Tomáš Rozkoš The Fingerland Department of Pathology Charles University Medical Faculty and Faculty Hospital in Hradec Králové Czech Republic Case history, 33 years old resistance
Cellular Neurothekeoma
 Cellular Neurothekeoma Scott W Binder, MD Pritzker Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Sr. Vice Chair Director, Pathology Clinical Services Chief, Dermatopathology Geffen/UCLA School of Medicine Clinical
Cellular Neurothekeoma Scott W Binder, MD Pritzker Professor of Pathology & Dermatology Sr. Vice Chair Director, Pathology Clinical Services Chief, Dermatopathology Geffen/UCLA School of Medicine Clinical
GUT-C 11/30/2017. Debasmita Das, M.D. PGY-1 Danbury Hospital
 GUT-C 11/30/2017 Debasmita Das, M.D. PGY-1 Danbury Hospital CLINICAL SUMMARY 8/2017 59 year old female Presented to the ED with 1 month history of general malaise, fever and weight loss PMH: Significant
GUT-C 11/30/2017 Debasmita Das, M.D. PGY-1 Danbury Hospital CLINICAL SUMMARY 8/2017 59 year old female Presented to the ED with 1 month history of general malaise, fever and weight loss PMH: Significant
Tumors of Adipose Tissue Tumors Epidemiology Clinical Features. Morphology. Mature Adipocytes Separated by delicate fibrous septa
 Tumors of Adipose Tissue Lipoma Liposarcoma Most commonly happens in female The most common soft tissue tumor o Originates from matured Adipocytes Most commonly happes at the 4 th and 5 th decade of life
Tumors of Adipose Tissue Lipoma Liposarcoma Most commonly happens in female The most common soft tissue tumor o Originates from matured Adipocytes Most commonly happes at the 4 th and 5 th decade of life
Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON
 Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Presentation outline Background and epidemiology of sarcomas Sarcoma classification Sarcoma
Pathology of Sarcoma ELEANOR CHEN, MD, PHD, ASSISTANT PROFESSOR DEPARTMENT OF PATHOLOGY UNIVERSITY OF WASHINGTON Presentation outline Background and epidemiology of sarcomas Sarcoma classification Sarcoma
I n a previous study,
 666 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Expression of smooth muscle markers in so called malignant fibrous histiocytomas T Hasegawa, F Hasegawa, T Hirose, T Sano, Y Matsuno... See end of article for authors affiliations...
666 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Expression of smooth muscle markers in so called malignant fibrous histiocytomas T Hasegawa, F Hasegawa, T Hirose, T Sano, Y Matsuno... See end of article for authors affiliations...
ACCME/Disclosures ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS. Tumor types with ALK rearrangements. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase. Jason L.
 Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Companion Meeting of the International Society of Bone and Soft Tissue Pathology The Evolving Concept of Mesenchymal Tumors ALK FUSION-POSITIVE MESENCHYMAL TUMORS Jason L. Hornick, MD, PhD March 13, 2016
Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors. Thomas Brenn
 Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors Thomas Brenn Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumours Wide morphological and biological spectrum Myofibroblastic, smooth muscle, neural, vascular, apidocytic, undifferentiated;
Update on Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumors Thomas Brenn Cutaneous Mesenchymal Tumours Wide morphological and biological spectrum Myofibroblastic, smooth muscle, neural, vascular, apidocytic, undifferentiated;
SMOOTH MUSCLE TUMOURS
 SMOOTH MUSCLE TUMOURS NORMAL SMOOTH MUSCLE Cytology Immunohistochemistry Ultrastructure Masson Trichrome Smooth Muscle Ultrastructure Many myofilaments running parallel to the long axis of the smooth
SMOOTH MUSCLE TUMOURS NORMAL SMOOTH MUSCLE Cytology Immunohistochemistry Ultrastructure Masson Trichrome Smooth Muscle Ultrastructure Many myofilaments running parallel to the long axis of the smooth
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology. Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport
 From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
From Morphology to Molecular Pathology: A Practical Approach for Cytopathologists Part 1-Cytomorphology Songlin Zhang, MD, PhD LSUHSC-Shreveport I have no Conflict of Interest. FNA on Lymphoproliferative
ESS: Pathologic Insights
 GEIS XVI INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM Seville 4th October 2018 ESS: Pathologic Insights Sílvia Bagué The Royal Marsden Hospital London (United Kingdom) I have no conflicts of interest Endometrial stromal sarcoma
GEIS XVI INTERNATIONAL SYMPOSIUM Seville 4th October 2018 ESS: Pathologic Insights Sílvia Bagué The Royal Marsden Hospital London (United Kingdom) I have no conflicts of interest Endometrial stromal sarcoma
Morphologically Benign Lesions of Soft Tissue and Bone Which Metastasize - What Can We Do?
 Andrew L. Folpe, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN ISBSTP Handout 2010 Morphologically Benign Lesions of Soft Tissue and Bone Which Metastasize - What Can We Do? Introduction Over the past several decades
Andrew L. Folpe, MD Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN ISBSTP Handout 2010 Morphologically Benign Lesions of Soft Tissue and Bone Which Metastasize - What Can We Do? Introduction Over the past several decades
Endometrial Stromal Tumors
 Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Endometrial Stromal Tumors WHO Categories: Endometrial Stromal Nodule (ESN) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, low grade (LGESS) Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma, high grade (HGESS) Undifferentiated Uterine Sarcoma
Case Presentation. Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD. Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan
 Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Case Presentation Maha Akkawi, MD, Fatima Obeidat, MD, Tariq Aladily, MD Department of Pathology Jordan University Hospital Amman, Jordan The 25th Annual Congress of the ADIAP The 8/11/2013 1 5th International
Klinisch belang van chromosomale translocatie detectie in sarcomen
 Translocations in sarcomas Klinisch belang van chromosomale translocatie detectie in sarcomen Judith V.M.G. Bovée, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Leiden University Medical Center RNA binding DNA binding
Translocations in sarcomas Klinisch belang van chromosomale translocatie detectie in sarcomen Judith V.M.G. Bovée, M.D., Ph.D. Department of Pathology Leiden University Medical Center RNA binding DNA binding
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology
 IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
IN THE NAME OF GOD Dr. Kheirandish Oral and maxillofacial pathology ORAL FOCAL MUCINOSIS Uncommon Tumorlike Cutaneous myxoid cyst Overproduction of hyaluronic acid by firoblasts Young adults Female Gingiva
Soft Tissue Perineurioma
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2009; 43: 266-70 DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.266 Soft Tissue Perineurioma - A Case Report - Jun Mo Kim Joon Hyuk Choi Department of Pathology, Yeungnam University
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2009; 43: 266-70 DOI: 10.4132/KoreanJPathol.2009.43.3.266 Soft Tissue Perineurioma - A Case Report - Jun Mo Kim Joon Hyuk Choi Department of Pathology, Yeungnam University
Classification (1) Classification (3) Classification (2) Spindle cell lesions. Spindle cell lesions of bladder (Mills et al.
 Non-epithelial tumours and nonepithelial tumour-like lesions of the bladder Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Classification (1) Myofibroblastic proliferations and
Non-epithelial tumours and nonepithelial tumour-like lesions of the bladder Dr Jonathan H Shanks The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Manchester, UK Classification (1) Myofibroblastic proliferations and
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare
 Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
Enterprise Interest Nothing to declare Diagnoses one would not like to miss in soft tissue pathology early in your career Marta Sbaraglia, MD Department of Pathology Hospital of Treviso University of Padua
Prognostic Significance of Grading and Staging Systems using MIB-1 Score in Adult Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma of the Extremities and Trunk
 843 Prognostic Significance of Grading and Staging Systems using MIB-1 Score in Adult Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma of the Extremities and Trunk Tadashi Hasegawa, M.D. 1 Seiichiro Yamamoto, Ph.D. 2
843 Prognostic Significance of Grading and Staging Systems using MIB-1 Score in Adult Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma of the Extremities and Trunk Tadashi Hasegawa, M.D. 1 Seiichiro Yamamoto, Ph.D. 2
Immunohistochemical Staining for Claudin-1 Can Help Distinguish Meningiomas From Histologic Mimics
 Anatomic Pathology / CLAUDIN-1 IN MENINGIOMAS Immunohistochemical Staining for Claudin-1 Can Help Distinguish Meningiomas From Histologic Mimics Hejin P. Hahn, MD, PhD, Elizabeth A. Bundock, MD, PhD, and
Anatomic Pathology / CLAUDIN-1 IN MENINGIOMAS Immunohistochemical Staining for Claudin-1 Can Help Distinguish Meningiomas From Histologic Mimics Hejin P. Hahn, MD, PhD, Elizabeth A. Bundock, MD, PhD, and
No financial or other disclosures
 Case 2014-5 Esther N. Bit-Ivan, DO Northwestern University Jason Wang, MD Jason Park, MD Korgun Koral, MD Children s Medical Center Charles Timmons, MD Veena Rajaram, MD No financial or other disclosures
Case 2014-5 Esther N. Bit-Ivan, DO Northwestern University Jason Wang, MD Jason Park, MD Korgun Koral, MD Children s Medical Center Charles Timmons, MD Veena Rajaram, MD No financial or other disclosures
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1
 A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
A case of giant cell tumour of soft parts in a horse Francesco Cian 1, Sarah Whiteoak 2, Jennifer Stewart 1 1 Animal Health Trust, Newmarket, UK 2 608 Equine and Farm Vets, Rowington, UK Signalment: Horse,
Case 27 Male 42. Painless, static, well-circumscribed, subcutaneous nodule right lower leg,?lipoma. The best diagnosis is:
 Case 27 Male 42. Painless, static, well-circumscribed, subcutaneous nodule right lower leg,?lipoma. The best diagnosis is: A. Angiosarcoma B. Haemangiopericytoma C.Myopericytoma D.Myofibroma E. Angioleiomyoma
Case 27 Male 42. Painless, static, well-circumscribed, subcutaneous nodule right lower leg,?lipoma. The best diagnosis is: A. Angiosarcoma B. Haemangiopericytoma C.Myopericytoma D.Myofibroma E. Angioleiomyoma
Case 2. Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset
 Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Case 2 Dr. Sathima Natarajan M.D. Kaiser Permanente Medical Center Sunset History 24 year old male presented with a 3 day history of right flank pain, sharp in nature Denies fever, chills, hematuria or
Fun with Fat. General Rules. Case
 Fun with Fat General Rules Imaging: location (deep vs. superficial) Superficial lesions are seldom liposarcomas Deep lesions may be benign or malignant Myxoid stroma is common in benign and malignant lesions
Fun with Fat General Rules Imaging: location (deep vs. superficial) Superficial lesions are seldom liposarcomas Deep lesions may be benign or malignant Myxoid stroma is common in benign and malignant lesions
S clerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma is a rare tumour
 90 CASE REPORT Primary sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma of the sacrum: a case report and review of the literature L T C Chow, Y H Lui, S M Kumta, P W Allen... Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma is
90 CASE REPORT Primary sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma of the sacrum: a case report and review of the literature L T C Chow, Y H Lui, S M Kumta, P W Allen... Sclerosing epithelioid fibrosarcoma is
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Fibrosarcomatous Variant of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: An Aggressive Tumor - A Case Report Swati Sharma
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Case Report Fibrosarcomatous Variant of Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans: An Aggressive Tumor - A Case Report Swati Sharma
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors
 Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Diagnostic problems in uterine smooth muscle tumors Marina Kos Ljudevit Jurak Clinical Department of Pathology, Clinical Hospital Center Sestre milosrdnice, Zagreb Institute of Pathology, University of
Financial disclosures
 Mesenchymal Neoplasms with Melanocytic Differentiation By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel
Mesenchymal Neoplasms with Melanocytic Differentiation By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center Geisel
Chondroid lipoma: A rare recently described benign lipomatous tumor
 Al-Malki et al. 7 case report peer Reviewed open OPEN ACCESS Chondroid lipoma: A rare recently described benign lipomatous tumor Salman T. Al-Malki, Abdullah S. Al-Khamiss Abstract Introduction: lipomatous
Al-Malki et al. 7 case report peer Reviewed open OPEN ACCESS Chondroid lipoma: A rare recently described benign lipomatous tumor Salman T. Al-Malki, Abdullah S. Al-Khamiss Abstract Introduction: lipomatous
Case of Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma of the Eyelid Treated with Micrographic Surgery and Secondary Intention Healing
 JI Kim, et al pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 5, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.5.632 CASE REPORT Case of Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma of the Eyelid Treated with Micrographic
JI Kim, et al pissn 1013-9087ㆍeISSN 2005-3894 Ann Dermatol Vol. 28, No. 5, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.5.632 CASE REPORT Case of Pleomorphic Dermal Sarcoma of the Eyelid Treated with Micrographic
Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case
 Journal of Cancer Research Updates, 2013, 2, 135-139 135 Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case Justin Kerstetter 1, Mia Perez
Journal of Cancer Research Updates, 2013, 2, 135-139 135 Hemangioendothelioma with a Prominent Lymphoid Infiltrate Mimicking Follicular Dendritic Cell Tumor: Report of a Case Justin Kerstetter 1, Mia Perez
3/24/2017 DENDRITIC CELL NEOPLASMS: HISTOLOGY, IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, AND MOLECULAR GENETICS. Disclosure of Relevant Financial Relationships
 DENDRITIC CELL NEOPLASMS: HISTOLOGY, IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, AND MOLECULAR GENETICS Jason L. Hornick, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Surgical Pathology and Immunohistochemistry Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor
DENDRITIC CELL NEOPLASMS: HISTOLOGY, IMMUNOHISTOCHEMISTRY, AND MOLECULAR GENETICS Jason L. Hornick, M.D., Ph.D. Director of Surgical Pathology and Immunohistochemistry Brigham and Women s Hospital Professor
Pleomorphic Sarcoma of Breast: A Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature
 CASE REPORT Pleomorphic Sarcoma of Breast: A Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature Anju Bansal, Manveen Kaur, and Varsha Dalal Department of Pathology, National Institute of Pathology (ICMR), Safdarjang
CASE REPORT Pleomorphic Sarcoma of Breast: A Report of Two Cases and Review of Literature Anju Bansal, Manveen Kaur, and Varsha Dalal Department of Pathology, National Institute of Pathology (ICMR), Safdarjang
A case of pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma
 Jichi Medical University Journal Chio Shuto Kuniyasu Soda Takayoshi Yoshida Fumio Konishi Abstract We report a very rare case of a pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma in the parietal peritoneum of the
Jichi Medical University Journal Chio Shuto Kuniyasu Soda Takayoshi Yoshida Fumio Konishi Abstract We report a very rare case of a pedunculated intraperitoneal leiomyoma in the parietal peritoneum of the
Surgical Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2015
 Surgical Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2015 John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Surgical Pathology Evening Specialty Conference USCAP 2015 John R. Goldblum, M.D. Chairman, Department of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Professor of Pathology, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
HOW MAY THE CLASSIFICATION OF SOFT TISSUE TUMORS EVOLVE?
 Spanish Society of Pathology Zaragoza, May 2011 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SYMPOSIUM HOW MAY THE CLASSIFICATION OF SOFT TISSUE TUMORS EVOLVE? Christopher D.M. Fletcher, M.D., FRCPath Brigham and Women s Hospital
Spanish Society of Pathology Zaragoza, May 2011 ARTHUR PURDY STOUT SYMPOSIUM HOW MAY THE CLASSIFICATION OF SOFT TISSUE TUMORS EVOLVE? Christopher D.M. Fletcher, M.D., FRCPath Brigham and Women s Hospital
Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma
 Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(3):229 233 Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma CARMEN ARDELEANU 1, 2), MARIA COMĂNESCU 3), VIOLETA COMĂNESCU 4), F. ANDREI 1) 1)
Romanian Journal of Morphology and Embryology 2005, 46(3):229 233 Uncommon pattern in soft tissues epithelioid sarcoma CARMEN ARDELEANU 1, 2), MARIA COMĂNESCU 3), VIOLETA COMĂNESCU 4), F. ANDREI 1) 1)
Molecular pathology in soft tissue tumors. Sylvia Höller Pathologie
 Molecular pathology in soft tissue tumors Sylvia Höller Pathologie When do we perform molecular testing? Morphology and IHC are not clearly fitting with an entity some translocations are entity specific
Molecular pathology in soft tissue tumors Sylvia Höller Pathologie When do we perform molecular testing? Morphology and IHC are not clearly fitting with an entity some translocations are entity specific
Molecular Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Tumors: Avoid Pitfalls
 Molecular Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Tumors: Avoid Pitfalls Cristina Antonescu, MD Department of Pathology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Overview I. When should we rely on the help of
Molecular Diagnosis of Soft Tissue Tumors: Avoid Pitfalls Cristina Antonescu, MD Department of Pathology Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Overview I. When should we rely on the help of
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, :30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY
 SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
SESSION 1: GENERAL (BASIC) PATHOLOGY CONCEPTS Thursday, October 16, 2008 9:30am - 11:30am FACULTY COPY GOAL: Describe the basic morphologic (structural) changes which occur in various pathologic conditions.
CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. CYSTIC NEPHROMA
 Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Page 1 CYSTIC TUMORS OF THE KIDNEY JOHN N. EBLE, M.D. Department of Pathology & Laboratory Medicine Phone (317) 274-4806 Medical Science A-128 FAX: (317) 278-2018 635 Barnhill Drive jeble @iupui.edu Indianapolis,
Rhabdomyomas and Rhabdomyosarcomas (RMS) David M. Parham, MD Chief of Anatomic Pathology
 Rhabdomyomas and Rhabdomyosarcomas (RMS) David M. Parham, MD Chief of Anatomic Pathology Tumors of skeletal muscle: Rhabdomyomas and rhabdomyosarcomas Embryonal muscle 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Rhabdomyoma Benign
Rhabdomyomas and Rhabdomyosarcomas (RMS) David M. Parham, MD Chief of Anatomic Pathology Tumors of skeletal muscle: Rhabdomyomas and rhabdomyosarcomas Embryonal muscle 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Rhabdomyoma Benign
Grading of Bone Tumors
 Grading of Bone Tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D. Department of Pathology College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Introduction to grading system of bone tumor used at Mayo Clinic WHO Histologic Classification
Grading of Bone Tumors Joon Hyuk Choi, M.D. Department of Pathology College of Medicine, Yeungnam University Introduction to grading system of bone tumor used at Mayo Clinic WHO Histologic Classification
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling
 Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Case 8 Soft tissue swelling 26-year-old female presented with a swelling on the back of the left knee joint since the last 6 months and chronic pain in the calf and foot since the last 2 months. Pain in
Lung Tumor Cases: Common Problems and Helpful Hints
 Lung Tumor Cases: Common Problems and Helpful Hints Brandon T. Larsen, MD, PhD Senior Associate Consultant Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Arizona Society of Pathologists
Lung Tumor Cases: Common Problems and Helpful Hints Brandon T. Larsen, MD, PhD Senior Associate Consultant Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic Arizona Arizona Society of Pathologists
LAC + USC.
 Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
Jeff McDavit,, M.D. LAC + USC mcdavit@usc.edu Clinical History 55 year old male with large, deep, non- tender left thigh mass. Seen at LAC+USC Med Ctr FNA clinic No h/o trauma or radiation Vimentin
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report
 Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
Low-Grade Periductal Stromal of Breast: a case report Rosanna Nenna 1 Cosimo Damiano Inchingolo 1 Domenico Palmieri 2 Annalisa De Lucia 1 Giusy Elicio 1 Pina Miscioscia 1 ( 1 ) U.O.C. di Anatomia Patologica,
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor
 Gastrointestinal stromal tumor 영남의대병리학교실 최준혁 Classification of gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumor Gastrointestinal stromal tumor(gist) Smooth muscle tumors : leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma Neurogenic tumors
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor 영남의대병리학교실 최준혁 Classification of gastrointestinal mesenchymal tumor Gastrointestinal stromal tumor(gist) Smooth muscle tumors : leiomyoma, leiomyosarcoma Neurogenic tumors
CHAPTER 3. So-called Fibrohistiocytic Tumours
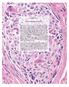 CHPTER 3 So-called Fibrohistiocytic Tumours Over the past 10 years, the concept of fibrohistiocytic differentiation has been challenged and is now regarded as a poorly defined morphological descriptor
CHPTER 3 So-called Fibrohistiocytic Tumours Over the past 10 years, the concept of fibrohistiocytic differentiation has been challenged and is now regarded as a poorly defined morphological descriptor
Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia
 Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Case Report Sarcomatoid (spindle cell) carcinoma of the cricopharynx presenting as dysphagia Jagtap Sunil V. 1, Shukla Dhirajkumar B. 2, Jagtap Swati S. 3, Havle Abhay D. 4 1 Associate Professor, Department
Disclosure. Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None. Off Label Usage None MFMER slide-1
 Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
Disclosure Relevant Financial Relationship(s) None Off Label Usage None 2013 MFMER slide-1 Case Presentation A 43 year old male, with partial nephrectomy for a right kidney mass 2013 MFMER slide-2 2013
The Genetics of Myoepithelial Tumors: salivary glands, soft tissue and bone
 The Genetics of Myoepithelial Tumors: salivary glands, soft tissue and bone Cristina Antonescu, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Nothing to declare Disclosure Spectrum of Myoepithelial
The Genetics of Myoepithelial Tumors: salivary glands, soft tissue and bone Cristina Antonescu, MD Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, New York Nothing to declare Disclosure Spectrum of Myoepithelial
59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain
 December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
December 2016 59 yo male with past medical history of prostate carcinoma, presented with upper abdominal pain Contributed by: Divya Sharma, MD. Fellow, Gastrointestinal Pathology, Department of Pathology
Keywords solitary fibrous tumor, dedifferentiation, dedifferentiated solitary fibrous tumor, STAT6, GRIA2, cytokeratin, rhabdomyosarcomatous
 758452IJSXXX10.1177/1066896918758452International Journal of Surgical PathologyCreytens et al research-article2018 Pitfalls in Pathology Multifocal Cytokeratin Expression in a Dedifferentiated Solitary
758452IJSXXX10.1177/1066896918758452International Journal of Surgical PathologyCreytens et al research-article2018 Pitfalls in Pathology Multifocal Cytokeratin Expression in a Dedifferentiated Solitary
Synovial Sarcoma with Massive Myxoid Feature
 The Korean Journal of Pathology 2005; 39: 273-7 Synovial Sarcoma with Massive Myxoid Feature - Case Report - Joon Hyuk Choi Young Ran Shim Young Kyung ae Mi Jin Kim Duk Seop Shin 1 Kil Ho Cho 2 Departments
The Korean Journal of Pathology 2005; 39: 273-7 Synovial Sarcoma with Massive Myxoid Feature - Case Report - Joon Hyuk Choi Young Ran Shim Young Kyung ae Mi Jin Kim Duk Seop Shin 1 Kil Ho Cho 2 Departments
A Cooperative Approach to Diagnosis of Rare Diseases: Primitive Myxoid Mesenchymal Tumor of Infancy
 310 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org A Cooperative Approach to Diagnosis of Rare Diseases: Primitive Myxoid Mesenchymal Tumor of Infancy David W Cuthbertson 1, Kevin Caceres 1, John Hicks 2, and
310 Available online at www.annclinlabsci.org A Cooperative Approach to Diagnosis of Rare Diseases: Primitive Myxoid Mesenchymal Tumor of Infancy David W Cuthbertson 1, Kevin Caceres 1, John Hicks 2, and
Case: The patient is a 24 year- old female who was found to have multiple mural nodules within the antrum. Solid and cystic components were noted on
 Case: The patient is a 24 year- old female who was found to have multiple mural nodules within the antrum. Solid and cystic components were noted on imaging. There is no significant past medical history.
Case: The patient is a 24 year- old female who was found to have multiple mural nodules within the antrum. Solid and cystic components were noted on imaging. There is no significant past medical history.
Case Report Myxoid dermatofibroma on a great toe: a case report
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):7605-7609 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008464 Case Report Myxoid dermatofibroma on a great toe: a case report Ahrim Moon 1*, Nara Yoon 2*, Hyun-Soo Kim 3 1 Department
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(6):7605-7609 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0008464 Case Report Myxoid dermatofibroma on a great toe: a case report Ahrim Moon 1*, Nara Yoon 2*, Hyun-Soo Kim 3 1 Department
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement
 Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Cutaneous Mesenchymal Neoplasms with EWSR1 Rearrangement By Konstantinos Linos MD, FCAP, FASDP Bone, Soft Tissue and Dermatopathology Assistant Professor of Pathology Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors. James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon
 Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
Introduction to Musculoskeletal Tumors James C. Wittig, MD Orthopedic Oncologist Sarcoma Surgeon www.tumorsurgery.org Definitions Primary Bone / Soft tissue tumors Mesenchymally derived tumors (Mesodermal)
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck. Kevin Harrington
 Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
Update on Sarcomas of the Head and Neck Kevin Harrington Overview Classification and incidence of sarcomas Clinical presentation Challenges to treatment Management approaches Prognostic factors Radiation-induced
Spontaneous Rat Malignant Tumors of Fibrohistiocytic Origin: An Ultrastructural Study
 Vet. Pathol. 19: 497-505 (1982) Spontaneous Rat Malignant Tumors of Fibrohistiocytic Origin: An Ultrastructural Study P. GREAVES, J.-M. MARTIN, and M.-T. MASSON Centre de Recherche, Laboratoires Pfizer,
Vet. Pathol. 19: 497-505 (1982) Spontaneous Rat Malignant Tumors of Fibrohistiocytic Origin: An Ultrastructural Study P. GREAVES, J.-M. MARTIN, and M.-T. MASSON Centre de Recherche, Laboratoires Pfizer,
Other New entities in soft tissue tumors.
 Other New entities in soft tissue tumors. Angelo Paolo Dei Tos MD Departments of Pathology and Oncology General Hospital of Treviso, Italy Introduction During the past decade classification schemes have
Other New entities in soft tissue tumors. Angelo Paolo Dei Tos MD Departments of Pathology and Oncology General Hospital of Treviso, Italy Introduction During the past decade classification schemes have
Division of Pathology
 Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
Case 38 Adult woman with a 35mm right breast lump at the 10 o clock position. Excision performed. (Case contributed by Dr Mihir Gudi, KKH) Division of Pathology Merlion, One Fullerton Singapore Diagnosis
PROBLEMS OF PROGNOSTICATION IN SOFT TISSUE TUMOURS. Christopher D.M. Fletcher Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA
 PROBLEMS OF PROGNOSTICATION IN SOFT TISSUE TUMOURS Christopher D.M. Fletcher Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Dr. Fletcher has no conflict of interest or disclosures to
PROBLEMS OF PROGNOSTICATION IN SOFT TISSUE TUMOURS Christopher D.M. Fletcher Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard Medical School Boston, MA Dr. Fletcher has no conflict of interest or disclosures to
Notice of Faculty Disclosure
 Mesenchymal Tumors of the Vulva: Old, New, Something(s) Different Napa Valley Conference Pathology Education Partners Inc May 15, 2018 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University,
Mesenchymal Tumors of the Vulva: Old, New, Something(s) Different Napa Valley Conference Pathology Education Partners Inc May 15, 2018 Teri A. Longacre, M.D. longacre@stanford.edu Stanford University,
