4/14/2017. Unknown Case #1 Intramedullary Lesion
|
|
|
- Molly Brown
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 4/14/2017 Intradural, Intramedullary Tumor or Mimic Intradural, Extramedullary Tumor or Mimic Extradural Tumor or Mimic Unknown Case #1 Intramedullary Lesion Unknown Case #1 -POST - MAG AXIAL Cranial Caudal Patient: 57 year old male diagnosed with multiple sclerosis in 1999, has had progressive left sided weakness and tingling over many years Unknown Case #2 Intradural, Extramedullary Lesion - MAG PRE -POST Unknown Case #2 INTRADURAL, EXTRAMEDULLARY LESION Patient: 31 year old female with history of chronic pain secondary to pelvic chondrosarcoma 1
2 Unknown Case #3 Extradural Lesion -POST CORONAL AXIAL Unknown Case #3 EXTRADURAL LESION Patient: 25 year old male with sporadic lower back pain Case #1 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Cord expansion and edema, mass with solid/polar cystic components; foci of hypointense hemorrhage on axial; syringomyelia extending to thoracic spine AXIAL C3 LEVEL Case #1 AXIAL C6 LEVEL Patient: 34 year old male with 3 months of neck pain, mild upper extremity numbness, found on initial MRI Case #1 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Nodular enhancement at caudal aspect of tumor -POST Case #1 Ependymoma, WHO Grade II Arises from central canal ependymal lining Well circumscribed mass with symmetric cord expansion Cervical spine most common, followed by thoracic spine, then conus Majority enhance 2
3 Case #1 Ependymoma, WHO Grade II Hemorrhage hyperintensity; focal hypointensity corresponding to hemosiderin; * GRE hypointensity Cap Sign: cranial/caudal margin hemosiderin Cysts: tumoral cysts (necrosis), rostral/caudal polar cysts, syrinx beyond tumor margins Rare: intradural, extramedullary Which of the following statements about spinal ependymomas is NOT true? A: Ependymomas are less common than spinal astrocytomas in adults B: Associated with neurofibromatosis type II C: Most commonly occur between age 35 and 45 D: Low risk of local and intracranial recurrence after surgical resection Case #2 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Cord expansion and edema with cystic change and thoracic syrinx STIR AXIAL AT T5 LEVEL Case #2 AXIAL AT T7 LEVEL Patient: 41 year old male from Tucson who is referred to neurology clinic for the evaluation of upper and lower extremity weakness Case #2 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: No intrinsic hyperintensity or post-gadolinium enhancement Case #2 Coccidioidomycosis Coccidioides immitis fungus -POST Endemic to soil of southwest USA, Mexico, Central America, and South America Primary pulmonary infection from inhaled spores 1-5% get disseminated disease more common in pregnant or immunocompromised 3
4 Case #2 Coccidioidomycosis Lammering et al. (AJR June 2013) - retrospective imaging review of 23 patients with proven coccidioidal CNS meningitis (CSF and blood antibody titers) 23/23 patient had intracranial abnormalities 91% leptomeningeal enhancement predominately in basal cisterns 78% hydrocephalus (moderate/severe in 72% of those patients, 61% had transependymal flow of CSF) 90% enhancement in MCA cisterns 26% had acute infarcts Case #2 Coccidioidomycosis 19/22 (86%) patients had concomitant intraspinal disease 84% of those patients leptomeningeal enhancement 63% of those patients arachnoiditis (nerve root clumping/thickening) 37% of those patients intramedullary hyperintense signal abnormalities 42% of those patients focal extramedullary intradural lesions 47% patients who underwent myelogram complete spinal blocks? Snowbird in Arizona Snowbird in Utah 300k a year estimated in Arizona alone: Retired folk who escape from their cold native habitats to the warm and dry desert of Arizona from November-April every year. While local shopkeepers, innkeepers, and other employees of the service industry may tell them that their dollar is welcome, every native son and daughter of the desert prays for the day the temperature gets above 90 degrees. That is the point that people from the regions known as the Midwest, Canada, and the East Coast board their land barges, manufactured by companies such as Buick, Lincoln, and Winnebago and begin their trek back to the colder lands. Urban dictionary definition Case #3 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Cord expansion and edema; hypointense ring shaped capsule; ring enhancement of the capsule POST Case #3 Patient: 51 year old immunocompromised male with history of streptococcal endocarditis 4
5 Case #3 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Left frontal lobe ring enhancing lesion with hypointense capsule and surrounding vasogenic edema AXIAL AXIAL POST Case #3 Spinal Cord Abscess Very rare entity, commonly delayed diagnosis Often present with signs of structural cord lesion as opposed to infection Idiopathic, iatrogenic, or hematogenous seeding Can be from extension/rupture of epidural abscess Case #3 Spinal Cord Abscess Dysraphism or dermal sinus tract usually present in children with spinal abscess High mortality/morbidity persistent neurologic deficit common Additional imaging: Diffusion + Case #4 Patient: 44 year old male with PMH of head and neck cancer with 12 month history of right leg weakness Case #4 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: hyperintense lesion along dorsal cord with serpentine flow voids; long segment cord edema above lesion AXIAL T9 LEVEL Case #4 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Homogeneous enhancement associated with lesion along dorsal thoracic cord -POST AXIAL -POST T9 LEVEL 5
6 Case #4 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: DSA for preoperative embolization; sequential images from right to left demonstrate intense prolonged vascular stain associated with lesion Case #4 Hemangioblastoma WHO Grade I Low grade, capillary rich neoplasm (WHO I) Sporadic (2/3) or associated with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome (1/3) Mean age: 30 y/o, younger if VHL Thoracic spine most common, then cervical Sensory > motor deficits Image whole axis in VHL, assess for multiple Case #4 Hemangioblastoma WHO Grade I Subpial location, posterior aspect of spinal cord Subpial enhancing nodule Intraspinal cyst common Serpentine vascular flow voids if large Syrinx common, +/- long segment edema Small percentage extramedullary Which of the following is TRUE regarding spinal hemangioblastomas? A: Rarely undergo malignant transformation B: Second most common intramedullary neoplasm C: Associated VHL gene is located on chromosome 5 D: 75% of patients with VHL have a spinal hemangioblastoma Case #5 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: heterogeneous lesion, no significant cord edema, hypointense rim on axial imaging; susceptibility artifact on SWI SWI AXIAL AT C4 LEVEL Case #5 AXIAL AT C4 LEVEL Patient: 36-year-old female, with acute episode of waking up with neck pain and pins and needles sensation in her right arm 6
7 Imaging Findings: Lesion demonstrates regions of intrinsic hyperintensity with mild regions of enhancement Case #5 Intramedullary Lesion POST AXIAL POST Case #5 Cavernous Malformation Lobulated vascular channels without neural tissue Spinal cord uncommon location (<5%), thoracic most common / heterogeneous from blood locules of varying ages ( popcorn ) with fluid-fluid levels -hypointense rim (hemosiderin) Edema if recent hemorrhage Minimal or no enhancement Blooming on * GRE Case #5 Cavernous Malformation May regress or progress conservative follow-up if asymptomatic Multiple (familial) cavernous malformation syndrome (20%) high hemorrhage risk Brain MRI is indicated to assess for additional lesions What is the average risk of bleeding of a spinal cavernous malformation? A: % per lesion per year B: % per lesion per year C: % per lesion per year D: % per lesion per year Case #6 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Cord expansion with beaded, cystic dilatation of the cord; cord atrophy above level of cystic dilatation AXIAL AT C4 LEVEL Case #6 Patient: 61 year old female with remote history of gun shot wound STIR AXIAL AT C6 LEVEL 7
8 Case #6 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: No enhancing mass associated with cystic dilatation POST Case #6 Syringomyelia Expansion of the spinal cord with dilated, sacculated, or beaded cystic activity Etiologies: including post-traumatic, Chiari I/II, spondylosis, neoplasms, arachnoiditis Theories: 1) CSF driven from abnormal subarachnoid space through perivascular spaces syrinx enlargement 2) Cord destruction from primary process cavitation Case #6 Syringomyelia Hydromyelia cystic central cord canal dilatation (lined by ependyma) Syringomyelia paracentral cystic cavity that is not contiguous with central cord canal Syringobulbia syrinx in brainstem Pre-syrinx state reversible spinal cord edema from CSF flow dynamic alteration Timpone (AJR May 2015) 87 patients with syrinx Complete syrinx imaged on and post-contrast Imaging markers independently determined by two board-certified neuroradiologists blinded to clinical and imaging report information GOAL: assess for mass underlying syrinx on only Pathology: 23 mass lesions 11 Chiari malformations 3 chronic spinal cord contusions 50 cases were idiopathic (no underlying cause determined). Timpone (AJR May 2015) Timpone (AJR May 2015) 55/87 cases readers detected no suspicious syrinx associated mass on axial/sagittal ONLY 100% sensitivity 100% NPV Inter-reader agreement (κ = 0.88) 32/87 cases readers detected suspicious syrinx associated mass on axial/sagittal ONLY 23 true positives, 9 false positives Dominant imaging feature: Syrinx nodularity mass lesion present in 88% of cases Spinal cord signal intensity or mass separate from syrinx mass lesion present in 82% of cases Syrinx septation: mass lesion present in 0% of cases Syrinx diameter Mean associated with mass: 8.1 mm Mean associated without mass: 4.1 mm Association with > syrinx size and spinal cord mass Size threshold of 5 mm No neoplastic lesion present when axial diameter < 5 mm (except cav. mal. & AVM) 8
9 Case #7 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Patchy long-segment cervical and thoracic /STIR cord signal abnormality STIR AXIAL AT LEVEL Case #7 AXIAL AT C6 LEVEL Patient: 51 year old female with history of lupus with positive anti-phospholipid antibodies, progressive lower extremity weakness Case #7 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Regions of abnormal cord signal associated with enhancement; no intrinsic hyperintensity POST AXIAL PRE AT T4 Case #7 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Subcortical white matter FLAIR hyperintense, enhancing lesions; enhancement of the right optic nerve AXIAL FLAIR AXIAL POST AXIAL POST AXIAL POST AT T4 Case #7 Neuromyelitis Optica Autoimmune inflammatory disorder affects myelin of spinal cord and optic nerves possible targeting of transmembrane channel protein for water transport (aquaorin-4) Acute transverse myelopathy spectrum Inflammatory (acute transverse myelitis) Radiation, paraneoplastic, vascular disease, or idiopathic causes of cord dysfunction Longitudinal, enhancing hyperintensity which usually involves entire cord cross section + optic nerve enhancement Case #7 Neuromyelitis Optica Revised diagnostic neurology criteria: Optic neuritis + myelitis and 2 of 3 supportive criteria (99% sensitive, 90% specific) 1. Cord lesion 3 or more segments 2. NMO-IgG seropositivity 3. Initial brain MRI non-diagnostic for MS Annual relapse rate of 1.3% Increased relapse risk during pregnancy IV steroids first line of treatment 9
10 NMO Longitudinal, cross section Outcome worse than MS Older age of onset than MS Oligoclonal bands in 20-30% Cannot be distinguished from ADEM on first attack NMO vs. MS vs. ADEM Nuggets Multiple Sclerosis Typical periventricular white matter lesions < 1 vertebral segment (more focal), multiple lesions Cord periphery Oligoclonal bands in 85% Relapsing as opposed to ADEM ADEM Para/Postinfectious Associated encephalopathy Monophasic (2-4 weeks) Thalamic involvement Cranial nerve involvement indicates ADEM over MS What is the sensitivity and specificity of NMO-IgG seropositivity for NMO? A: Sensitivity: 25%, Specificity: 80% B: Sensitivity: 57%, Specificity: 75% C: Sensitivity: 76%, Specificity: 94% D: Sensitivity: 99%, Specificity: 99% Case #8 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: /STIR hyperintense expansile mass lesion involving nearly the complete cord cross section, no syrinx STIR AXIAL AT C6-C7 LEVEL Case #8 Patient: 40 year old male who noticed mild left lower extremity weakness, having difficulty raising his left leg to put his socks and ski boots on Case #8 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Very mild enhancement associated with this lesion -POST Case #8 Astrocytoma Slow onset myelopathy most commonly Most common intramedullary tumor in young adults and children Overall ependymomas are more common accounting for all ages Fusiform cord expansion which commonly spans less than 4 segments Eccentricity in the cord more common Can be multisegmental or holocord 10
11 Case #8 Astrocytoma Majority of lesions enhance and are hyperintense Partial and mild enhancement more common Cervical spine most common +/- cyst, less likely to hemorrhage 80-90% low grade (WHO I or II) Which of the following is NOT more common in spinal astrocytomas compared to ependymomas? A: Astrocytomas are often longer and more eccentric within the cord B: Bony remodeling and scoliosis C: Ill defined margins D: Most common primary spinal neoplasm in kids Case #9 Cauda Equina Lesion Imaging Findings: Diffuse fusiform enlargement of cauda equina nerve roots AXIAL AT L4 LEVEL Case #9 CAUDA EQUINA LESION Patient: 47 year old female with history of multiple sclerosis and developing worsening lower extremity weakness Imaging Findings: Symmetric enlargement and enhancement of nerve roots Case #9 Cauda Equina Lesion POST AXIAL POST AT L3 & L5-S1 LEVELS Case #9 Cauda Equina Lesion Imaging Findings: Cranial nerve enhancement in the internal auditory canals and cisternal trigeminal nerve segments AXIAL POST 11
12 Case #9 Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) Clinical diagnosis: Sensory/motor neuropathy, usually symmetric, developing over greater than 8 weeks Monophasic, progressive, or relapsing Responsive to steroid therapy EMG abnormal Nerve biopsy if unclear Case #9 Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) Enlarged, hyperintense nerve roots (extraforaminal > intradural), peripheral nerves, or plexi enhancement Lumbar > thoracic/cervical > cranial nerves Guillain-Barré (AIDP): similar nerve root enlargement/enhancement more acute ascending paralysis onset more sensory preservation Non-imaging findings described with CIDP include the following, EXCEPT? A: Onion bulb formation on nerve biopsy B: Decrease in F-wave conduction velocities on EMG C: Increase in CSF total protein D: Mixed sensorimotor neuropathy E: All of the above are actually true Case #10 INTRADURAL, EXTRAMEDULLARY LESION Patient: 30 year old male with slowly increasing lower extremity sensory loss Case #10 Intradural, Extramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Ovoid, / hyperintense mass with saturation on STIR sequence, no enhancement was noted PRE STIR Case #10 Intradural Lipoma Presentation: Slow ascending mono- or paraparesis, spasticity, sensory loss. Symptomatic patients unlikely to improve without intervention. May grow dramatically during infancy. Can shrink with weight loss. Intradural location: Thoracic (30%) > cervicothoracic (24%) > cervical > lumbosacral Dorsal (73%) > lateral/anterolateral > anterior 12
13 Case #10 Intradural Lipoma / hyperintense, fat suppression, no enhancement +/- dysraphism Terminal lipoma associated with distal cord/filum insertion may extend into subq fat through defect cord tethering and syrinx Back to Unknown Case #1 Unknown Case #1 Intramedullary Lesion Imaging Findings: Cord signal abnormality at and levels with associated contour abnormality of the dorsal aspect of the cord - MAG Unknown Case Arachnoid Web Arachnoid webs: intradural, extramedullary transverse bands of tissue that can extend to spinal cord pial surface Presence of dorsal subarachnoid space web alteration of CSF flow dynamics pre-syrinx state versus syringomyelia Unknown Case Arachnoid Web Reardon et al. (AJNR May 2013) 14 patients (ages years) described with scalpel sign on MRI or myelogram 10/13 patients who underwent MRI showed cord hyperintensity 7/13 patients demonstrated syringomyelia 7 patients underwent surgery 5 demonstrated arachnoid web as cause of dorsal indentation on pre-operative imaging all patients symptoms improved post-operatively MAYBE IM NOT A TUMOR? Unknown Case #2 INTRADURAL, EXTRAMEDULLARY LESION Patient: 31 year old female with history of chronic pain secondary to pelvic chondrosarcoma 13
14 Unknown Case #2 Intradural, Extramedullary Lesion Intrathecal catheter tip granuloma: hypointense enhancing focus at the tip of the intrathecal catheter; inflammatory granulomas can cause pump-catheter dysfunction (increased pain/withdrawal) PRE -POST Iatrogenic Companion Case History is key Presented to outside facility with post-lumbar puncture headache Received epidural blood patch hypointense, hyperintense nonenhancing intrathecal mass Presumably an iatrogenic thrombus risk of arachnoiditis Unknown Case #3 Extradural Lesion Imaging Findings: / hypointense lesion along the superior endplate with avid post-gadolinium enhancement; shows partially ossified nidus and reactive zone -POST CORONAL AXIAL Unknown Case #3 EXTRADURAL LESION Patient: 25 year old male with sporadic lower back pain Unknown Case #3 Osteoid Osteoma Benign osteoid-producing tumor < 1.5 cm in size (larger lesion = osteoblastoma) 10% occur in spine, neural arch; lumbar > cervical > thoracic Can case focal scoliosis with concavity towards the side of the tumor Night pain treatment aspirin or NSAIDS Unknown Case #3 Osteoid Osteoma Central nidus: Usually lucent on with variable ossification MRI: low signal, variable signal, enhancement Reactive zone: Dense sclerosis and edema surrounding the nidus High STIR/ signal, low signal, enhances May have soft tissue mass or pleural thickening/effusion if near the lung 14
15 THANK YOU 15
Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Imaging the Spinal Cord & Intradural Disease John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spinal Cord Diseases Tumors Syringohydromyelia Trauma Ischemia / Infarction
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 51. Primary Neoplasms
 51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
51. Primary Neoplasms As with spinal central canal neoplasms in other regions, those of the lumbar spine may be classified as extradural, intradural extramedullary, and medullary. If an extradural lesion
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses)
 Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
Pediatric Spine Tumors (and other masses) Francisco A Perez, MD, PhD Assistant Professor Neuroradiology and Pediatric Radiology Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington, Seattle Commercial
Spinal cord tumours Luc van den Hauwe et al.
 overview spinal cord tumours L. van den Hauwe 1,2, D. Balériaux 3, J.W. Van Goethem 2, C. Venstermans 2, F. De Belder 2, P.M. Parizel 2 introduction imaging spinal tumour classification spinal cord tumours
overview spinal cord tumours L. van den Hauwe 1,2, D. Balériaux 3, J.W. Van Goethem 2, C. Venstermans 2, F. De Belder 2, P.M. Parizel 2 introduction imaging spinal tumour classification spinal cord tumours
Spinal Vascular Lesions
 Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal Vascular Lesions Spinal cord infarction Hemangioblastoma Cavernous malformation Vascular malformations (Type 1-4) Spinal artery aneurysm Troy Hutchins, MD Assistant Professor
Spinal Neoplasms. First Things First!! Localize the Lesion!! Ependymomas. Common Intramedullary Lesions
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXIII, nº 90, pág. 101-114, Abr.-Jun., 2011 Spinal Neoplasms Bruno A Policeni University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Assistant Professor of Radiology Disclosure of Commercial
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XXIII, nº 90, pág. 101-114, Abr.-Jun., 2011 Spinal Neoplasms Bruno A Policeni University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Assistant Professor of Radiology Disclosure of Commercial
A Journey Down The Canal
 A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
A Journey Down The Canal Radiological Assessment of Spinal Cord Masses John Berry-Candelario HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Objectives Patient review Anatomy of the spine Imaging techniques Classification
NEURORADIOLOGY. Part III. Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology
 NEURORADIOLOGY Part III Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders inflammatory processes
NEURORADIOLOGY Part III Angela Csomor University of Szeged Department of Radiology DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders inflammatory processes
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine. John J. McCormick MD
 Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Spinal Imaging. Bearbeitet von Herwig Imhof. 1. Auflage Taschenbuch. 312 S. Paperback ISBN Format (B x L): 12,5 x 19 cm
 Spinal Imaging Bearbeitet von Herwig Imhof 1. Auflage 2007. Taschenbuch. 312 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 144071 6 Format (B x L): 12,5 x 19 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Sonstige Medizinische Fachgebiete
Spinal Imaging Bearbeitet von Herwig Imhof 1. Auflage 2007. Taschenbuch. 312 S. Paperback ISBN 978 3 13 144071 6 Format (B x L): 12,5 x 19 cm Weitere Fachgebiete > Medizin > Sonstige Medizinische Fachgebiete
Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center. 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Guerbet Outline Acute neck and back pain Acute
Kathleen R. Fink, MD Virginia Mason Medical Center 6 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course 2017 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Guerbet Outline Acute neck and back pain Acute
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
PMH: No medications; Immunizations UTD No hospitalizations or surgeries Speech Delay. Birth Hx: 24 WGA, NICU x6 months
 HPI: 6 months of weakness and parathesias- originally in both feet x 2-3 months, then resolved. Now with parathesias and weakness in fingers x 1 week. Seen by podiatrist and given custom in-soles 1 month
HPI: 6 months of weakness and parathesias- originally in both feet x 2-3 months, then resolved. Now with parathesias and weakness in fingers x 1 week. Seen by podiatrist and given custom in-soles 1 month
MRI in Differential Diagnosis. CMSC, June 2, Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE
 MRI in Differential Diagnosis CMSC, June 2, 2016 Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC Disclosures Speaking, consulting, and/or
MRI in Differential Diagnosis CMSC, June 2, 2016 Jill Conway, MD, MA, MSCE Director, Carolinas MS Center Clerkship Director, UNCSOM-Charlotte Campus Charlotte, NC Disclosures Speaking, consulting, and/or
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Intrinsic Spinal Cord Lesions: A Pictorial Review
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Intrinsic Spinal Cord Lesions: A Pictorial Review Award: Guerbet Best Registrar Exhibit Prize Poster No.: R-0024 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Intrinsic Spinal Cord Lesions: A Pictorial Review Award: Guerbet Best Registrar Exhibit Prize Poster No.: R-0024 Congress: RANZCR ASM 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Non-Traumatic Neuro Emergencies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Nontraumatic Neuroemergencies 1. Acute focal neurological deficit 2. Worst headache of
Paraparesis. Differential Diagnosis. Ran brauner, Tel Aviv university
 Paraparesis Differential Diagnosis Ran brauner, Tel Aviv university Definition Loss of motor power to both legs Paraparesis (paraplegia) refers to partial (- paresis) or complete (-plegia) loss of voluntary
Paraparesis Differential Diagnosis Ran brauner, Tel Aviv university Definition Loss of motor power to both legs Paraparesis (paraplegia) refers to partial (- paresis) or complete (-plegia) loss of voluntary
Difficult Diagnosis: Case History. 7 months prior, she happened to have undergone a C-spine MRI after a car accident
 Relevant Disclosures: None Difficult Diagnosis: Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD Assistant Professor UCSF Neuroinflammation and MS Center UCSF Department of Neurology Case History
Relevant Disclosures: None Difficult Diagnosis: Recent Advances in Neurology 2013 Jeffrey M. Gelfand, MD Assistant Professor UCSF Neuroinflammation and MS Center UCSF Department of Neurology Case History
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN. Scalp, Skull. Anatomically Based Differentials. Skull Normal Variants. Scalp Mass, Child.
 Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
Table of Contents: SKULL AND BRAIN Scalp, Skull Skull Normal Variants Scalp Mass, Child Scalp Mass, Adult Congenital Anomalies of Skull Base Sellar/Parasellar Mass With Skull Base Invasion "Hair on End"
New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Study New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People Sergio Carmona 1, Sandra Barbosa 1 and Maria Laura Ortube 2 * 1 Department of Neuro-ophthalmology, Hospital
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC OPHTHALMOLOGY Case Study New Insights on Optic Neuritis in Young People Sergio Carmona 1, Sandra Barbosa 1 and Maria Laura Ortube 2 * 1 Department of Neuro-ophthalmology, Hospital
Pediatric Spinal Anomalies
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Pediatric Spinal Anomalies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spine Embryogenesis 1. Primitive streak 2. Proliferation of cells at primitive pit (Hensen's
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Pediatric Spinal Anomalies John R. Hesselink, M.D. Spine Embryogenesis 1. Primitive streak 2. Proliferation of cells at primitive pit (Hensen's
Neuromyelitis optica (NMO), or Devic s disease, is a rare
 Case Report Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) Abstract NMO is a is a rare entity which involves the central nervous system acting as an inflammatory process by attacking the optic nerve (ON) and longitudinally
Case Report Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) Abstract NMO is a is a rare entity which involves the central nervous system acting as an inflammatory process by attacking the optic nerve (ON) and longitudinally
Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância. Silvia Tenembaum
 Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância Silvia Tenembaum Acquired CNS inflammatory/demyelinating disorders: Background information More frequent in children than
Actualização no diagnóstico e tratamento das doenças desmielinizantes na infância Silvia Tenembaum Acquired CNS inflammatory/demyelinating disorders: Background information More frequent in children than
Intradural spinal tumours and their mimics: a review of radiographic features
 Department of Radiology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, Victoria, Australia Correspondence to Dr Sara Wein, Radiology Department, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Grattan Street, Parkville, VIC 3050, Australia;
Department of Radiology, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Parkville, Victoria, Australia Correspondence to Dr Sara Wein, Radiology Department, Royal Melbourne Hospital, Grattan Street, Parkville, VIC 3050, Australia;
1/9/2013 EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE. Introduction. Classification for Extramedullary Tumors
 EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE Eugene Wang 1/20/12 Dent Neurologic Institute Introduction 2/3 of all intraspinal tumors of childhood are extramedullary 50% Extradural 10-15% Intradural Back
EXTRAMEDULLARY TUMORS OF THE PEDIATRIC SPINE Eugene Wang 1/20/12 Dent Neurologic Institute Introduction 2/3 of all intraspinal tumors of childhood are extramedullary 50% Extradural 10-15% Intradural Back
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours. Colin Kennedy March 2015
 Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Optic Pathway Gliomas, Germinomas, Spinal Cord Tumours Colin Kennedy March 2015 Glioma of the optic chiasm. T1-weighted MRI with gadolinium enhancement, showing intense irregular uptake of contrast. The
Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens
 2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
2015 Kenneth M. Earle Memorial Neuropathology Review Pathologic Analysis of CNS Surgical Specimens Peter C. Burger, MD Interdisciplinary Quality Control Familiarity with entities Use of diagnostic algorithm
NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics. Disclosures. Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor 4/14/2017
 Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants
 1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
1 Normal Anatomy and Variants 1.1 Normal Anatomy MR Technique. e standard MR protocol for a routine evaluation of the spine always comprises imaging in sagittal and axial planes, while coronal images are
Myelitis. Case 2. History. Examination. Mahtab Ghadiri
 Case 2 Myelitis Mahtab Ghadiri History A 42-year-old man presented to the emergency department with altered sensation in the lower limbs and difficulty ambulating. He first noted paresthesia in his feet
Case 2 Myelitis Mahtab Ghadiri History A 42-year-old man presented to the emergency department with altered sensation in the lower limbs and difficulty ambulating. He first noted paresthesia in his feet
MRI of chronic spinal cord injury
 The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
The British Journal of Radiology, 76 (2003), 347 352 DOI: 10.1259/bjr/11881183 E 2003 The British Institute of Radiology Pictorial review MRI of chronic spinal cord injury 1 K POTTER, FRCR and 1 A SAIFUDDIN,
Magnetic resonance imaging of intramedullary spinal cord lesions
 Magnetic resonance imaging of intramedullary spinal cord lesions Poster No.: C-1762 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Abdelkafi, H. Derbel, H. Abid, S. Haddar, B. Souissi, N. 1 1
Magnetic resonance imaging of intramedullary spinal cord lesions Poster No.: C-1762 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Abdelkafi, H. Derbel, H. Abid, S. Haddar, B. Souissi, N. 1 1
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Seema Sikka, MD January 18, 2014 TRANSVERSE MYELITIS: A CLINICAL OVERVIEW
 Seema Sikka, MD January 18, 2014 TRANSVERSE MYELITIS: A CLINICAL OVERVIEW DISCLOSURES I have no industry relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off-label use. OBJECTIVES: TRANSVERSE MYELITIS Review
Seema Sikka, MD January 18, 2014 TRANSVERSE MYELITIS: A CLINICAL OVERVIEW DISCLOSURES I have no industry relationships to disclose. I will not discuss off-label use. OBJECTIVES: TRANSVERSE MYELITIS Review
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome
 A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
The central nervous system
 Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
Sectc.qxd 29/06/99 09:42 Page 81 Section C The central nervous system CNS haemorrhage Subarachnoid haemorrhage Cerebral infarction Brain atrophy Ring enhancing lesions MRI of the pituitary Multiple sclerosis
The Neurology of HIV Infection. Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University
 The Neurology of HIV Infection Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University HIV/AIDS Epidemiology World-wide pandemic, 40 million affected U.S.- Disproportionate
The Neurology of HIV Infection Carolyn Barley Britton, MD, MS Associate Professor of Clinical Neurology Columbia University HIV/AIDS Epidemiology World-wide pandemic, 40 million affected U.S.- Disproportionate
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
11 May Disclosure. + Outline: Acute Spine Emergencies
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet K Fink Nordic
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet K Fink Nordic
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Benign brain lesions
 Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Benign brain lesions Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology Hung-Wen Kao Department of Radiology, Tri-Service General Hospital, National Defense Medical Center Computed tomography Hounsfield unit (HU)
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases
 Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Peripheral neuropathies, neuromuscular junction disorders, & CNS myelin diseases Peripheral neuropathies according to which part affected Axonal Demyelinating with axonal sparing Many times: mixed features
Myelitis. Myelitis. Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Acute demyelinating syndrome (ADS) Indictions for spinal cord MRI in MS.
 Myelitis Myelitis Majda M Thurnher Professor of Radiology Medical University of Vienna University Hospital Vienna Department of Biomedical Imaging and Image-Guided Therapy Vienna Austria Acute demyelinating
Myelitis Myelitis Majda M Thurnher Professor of Radiology Medical University of Vienna University Hospital Vienna Department of Biomedical Imaging and Image-Guided Therapy Vienna Austria Acute demyelinating
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome)
 J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 45-50 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome) Chien-Chuan Huang Tai-Yuan Chen Tai-Ching Wu Yu-Kun Tsui Te-Chang Wu Wen-Sheng Tzeng Chien-Jen Lin Department
J Radiol Sci 2012; 37: 45-50 Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic s Syndrome) Chien-Chuan Huang Tai-Yuan Chen Tai-Ching Wu Yu-Kun Tsui Te-Chang Wu Wen-Sheng Tzeng Chien-Jen Lin Department
Spectrum of Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings in infective intra spinal complications of dermal sinus and associated inclusion cysts
 Spectrum of Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings in infective intra spinal complications of dermal sinus and associated inclusion cysts Poster No.: C-1443 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Spectrum of Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings in infective intra spinal complications of dermal sinus and associated inclusion cysts Poster No.: C-1443 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
MRI Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica
 July 2009 MRI Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica Jenna Nolan, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Our Patient: Initial Presentation J.H. is a 29 year-old woman who presents with acute vision
July 2009 MRI Imaging of Neuromyelitis Optica Jenna Nolan, Harvard Medical School Year III Gillian Lieberman, MD Our Patient: Initial Presentation J.H. is a 29 year-old woman who presents with acute vision
Spine and spinal cord
 NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
NEURORADIOLOGY Spine and spinal cord Erika Vörös University of Szeged Department of Radiology SZEGED DISEASES OF SPINE AND SPINAL CORD I. Non-tumourous diseases developmental anomalies vascular disorders
MYELITIS. A Mochan Neurology
 MYELITIS A Mochan Neurology ATM MS LETM NMOSD ATM LETM MS NMOSD Acute Transverse Myelitis Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis Multiple Sclerosis Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders ATM ADEM
MYELITIS A Mochan Neurology ATM MS LETM NMOSD ATM LETM MS NMOSD Acute Transverse Myelitis Longitudinally Extensive Transverse Myelitis Multiple Sclerosis Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorders ATM ADEM
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
How to Think like a Neurologist Review of Exam Process and Assessment Findings
 Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Lehigh Valley Health Network LVHN Scholarly Works Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist 2013 Neurology Update for the Non-Neurologist Feb 20th, 5:10 PM - 5:40 PM How to Think like a Neurologist Review
Imaging of Hearing Loss
 Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
Contemporary Imaging of Sensorineural Hearing Loss Imaging of Hearing Loss Discussion Outline (SNHL) Imaging Approaches Anatomic Relationships Lesions: SNHL KL Salzman, MD University of Utah School of
22110 vertebral segment; cervical vertebral segment; thoracic vertebral segment; lumbar
 The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
The following codes are authorized by Palladian Health for applicable product lines. Visit palladianhealth.com to request authorization and to access guidelines. Palladian Musculoskeletal Program Codes
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases
 Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Mayo Clinic College of
Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Common Pitfalls in Multiple Sclerosis and CNS Demyelinating Diseases Case-Based Learning Mayo Clinic College of
Pediatric CNS Tumors. Disclosures. Acknowledgements. Introduction. Introduction. Posterior Fossa Tumors. Whitney Finke, MD
 Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Pediatric CNS Tumors Disclosures Whitney Finke, MD Neuroradiology Fellow PGY-6 University of Utah Health Sciences Center Salt Lake City, Utah None Acknowledgements Introduction Nicholas A. Koontz, MD Luke
Neurosurgery. Neurosurgery
 Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Telephone Numbers: Appointment: 202-476-3020 Fax: 202-476-3091 Administration: 202-476-3020 Evenings and Weekends: 202-476-5000 Robert Keating, MD, Chief The Division
Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Neurosurgery Telephone Numbers: Appointment: 202-476-3020 Fax: 202-476-3091 Administration: 202-476-3020 Evenings and Weekends: 202-476-5000 Robert Keating, MD, Chief The Division
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Ependymoma of the spine
 Ependymoma of the spine Tenny Zhang, MS-3 Harvard Medical School 1 Case presentation: history and exam HPI: A 30-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents with one week of bilateral
Ependymoma of the spine Tenny Zhang, MS-3 Harvard Medical School 1 Case presentation: history and exam HPI: A 30-year-old man with no significant past medical history presents with one week of bilateral
Brain and Spine Tumors
 Brain and Spine Tumors Andrew J. Fabiano, MD FAANS Associate Professor of Neurosurgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute SUNY at Buffalo School of Medicine Brain Tumors Brain Tumor Basics Types of Tumors Cases
Brain and Spine Tumors Andrew J. Fabiano, MD FAANS Associate Professor of Neurosurgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute SUNY at Buffalo School of Medicine Brain Tumors Brain Tumor Basics Types of Tumors Cases
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties:
 Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Introduction to Neurosurgical Subspecialties: Pediatric Neurosurgery Brian L. Hoh, MD 1 and Gregory J. Zipfel, MD 2 1 University of Florida, 2 Washington University Pediatric Neurosurgery Pediatric neurosurgeons
Neuroimaging. spine / spinal cord
 Neuroimaging spine / spinal cord Spine & spinal cord imaging methodology Plain x-ray of spine Computed tomography CT - traditional ( normal CT) - reconstructions - myelo-ct Magnetic resonance MR - standard
Neuroimaging spine / spinal cord Spine & spinal cord imaging methodology Plain x-ray of spine Computed tomography CT - traditional ( normal CT) - reconstructions - myelo-ct Magnetic resonance MR - standard
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks
 Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
Vascular Malformations of the Brain: A Review of Imaging Features and Risks Comprehensive Neuroradiology: Best Practices October 27-30, 2016 Sudhakar R. Satti, MD Associate Director Neurointerventional
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves
 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward and downward travel
RSR RSR RSR RSR RSR. ElisaRSR AQP4 Ab RSR. Aquaporin-4 Autoantibody Assay Kit
 To aid diagnosis of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) and NMO spectrum disorder (NMOSD) To confirm diagnosis before initial treatment of patients with demyelinating inflammatory disease NMO, NMOSD and AQP4 Elisa
To aid diagnosis of Neuromyelitis Optica (NMO) and NMO spectrum disorder (NMOSD) To confirm diagnosis before initial treatment of patients with demyelinating inflammatory disease NMO, NMOSD and AQP4 Elisa
Overview. Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord. Anatomy of the dura. Anatomy of the arachnoid. Anatomy of the spinal meninges
 European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
European Course in Neuroradiology Module 1 - Anatomy and Embryology Dubrovnik, October 2018 Spinal Anatomy Spaces & Meninges Spinal Cord Johan Van Goethem Overview spinal meninges & spaces spinal cord
IMAGING OF SPINE TUMORS
 IMAGING OF SPINE TUMORS Laszlo Mechtler, MD, FAAN, FASN SUMMARY Historic classification of spine tumors based on computed tomography myelopgraphy. (A) Normal, (B) extradural extramedullary, (C) intradural
IMAGING OF SPINE TUMORS Laszlo Mechtler, MD, FAAN, FASN SUMMARY Historic classification of spine tumors based on computed tomography myelopgraphy. (A) Normal, (B) extradural extramedullary, (C) intradural
Contrast Guidelines for Common CT/CTA & MRI/MRA
 Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Contrast Guidelines for Common /A & /MRA Body Imaging Gastrointestinal CLINICAL GUIDELINES EXAM DESCRIPTION /A CPT CODES EXAM DESCRIPTION /MRA CPT CODES Abdominal mass Abdomen & Pelvis w 74177 Abdomen
Imaging in neurofibromatosis type 1: An original research article with focus on spinal lesions
 Original Research Article Imaging in neurofibromatosis type 1: An original research article with focus on spinal lesions Kalpesh Patel 1*, Siddharth Zala 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 1
Original Research Article Imaging in neurofibromatosis type 1: An original research article with focus on spinal lesions Kalpesh Patel 1*, Siddharth Zala 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 1
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS
 IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
IMAGING OF INTRACRANIAL INFECTIONS Dr Carolina Kachramanoglou LYSHOLM DEPARTMENT OF NEURORADIOLOGY NATIONAL HOSPITAL FOR NEUROLOGY AND NEUROSURGERY Plan Introduce MR sequences that are useful in the diagnosis
Surgery. Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes. Anatomy. See online here
 Surgery Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes See online here Conus medullaris and cauda equina syndromes are spinal cord injuries that involve injury to the lumbosacral segment of the spinal cord.
Surgery Conus medullaris and Cauda Equina Syndromes See online here Conus medullaris and cauda equina syndromes are spinal cord injuries that involve injury to the lumbosacral segment of the spinal cord.
References 1. Feng S et al. Journal of Thoracic Oncology 2017; 12: Spain L et al. Annals of Oncology 2017; 28:
 Maulik Shah, MD February 15, 2019 Patient Presentation: Progressive Sensory Disturbance In early 2018, this 57 year old man was sent to the Emergency Department after complaining in the oncology clinic
Maulik Shah, MD February 15, 2019 Patient Presentation: Progressive Sensory Disturbance In early 2018, this 57 year old man was sent to the Emergency Department after complaining in the oncology clinic
CNS TUMORS. D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria)
 CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
CNS TUMORS D r. Ali Eltayb ( U. of Omdurman. I ). M. Path (U. of Alexandria) CNS TUMORS The annual incidence of intracranial tumors of the CNS ISmore than intraspinal tumors May be Primary or Secondary
Lumbosacral plexus lesion Lumbosacral plexus disorders G54.1 Neuralgic amyotrophy Neuralgic amyotrophy G
 ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM NEUROMUSCULAR DIAGNOSIS CODES Focal Neuropathy ICD-9-CM ICD-10-CM Mononeuropathy G56.00 Carpal tunnel syndrome 354.00 Other median nerve lesion 354.10 Lesion of ulnar nerve 354.20
Intraspinal Seeding from Intracranial Tumors in Children
 805 Intraspinal Seeding from Intracranial Tumors in Children Philip Stanley 1 Melvin O. Senac, Jr. Hervey D. Segall Cerebrospinal fluid-borne metastases were demonstrated by metrizamide myelography in
805 Intraspinal Seeding from Intracranial Tumors in Children Philip Stanley 1 Melvin O. Senac, Jr. Hervey D. Segall Cerebrospinal fluid-borne metastases were demonstrated by metrizamide myelography in
Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal Cord without Evidence of Spinal Cord Herniation or an Intradural Mass
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Emergency Neurological Life Support Spinal Cord Compression
 Emergency Neurological Life Support Spinal Cord Compression Version: 2.0 Last Updated: 19-Mar-2016 Checklist & Communication Spinal Cord Compression Table of Contents Emergency Neurological Life Support...
Emergency Neurological Life Support Spinal Cord Compression Version: 2.0 Last Updated: 19-Mar-2016 Checklist & Communication Spinal Cord Compression Table of Contents Emergency Neurological Life Support...
Disclosures None. Common Neurosurgical Problems Seen in Office Encounters. Macrocephaly Low Back Pain Sacral Dimple Concussion Chiari Malformation
 Common Neurosurgical Problems Seen in Office Encounters When to Manage, When to Refer Andrew Jea MD FAAP Professor and Chief of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Indiana University School
Common Neurosurgical Problems Seen in Office Encounters When to Manage, When to Refer Andrew Jea MD FAAP Professor and Chief of Pediatric Neurosurgery Riley Hospital for Children Indiana University School
The dura is sensitive to stretching, which produces the sensation of headache.
 Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
Dural Nerve Supply Branches of the trigeminal, vagus, and first three cervical nerves and branches from the sympathetic system pass to the dura. Numerous sensory endings are in the dura. The dura is sensitive
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Spine Pain Management Program
 Spine Pain Management Program Please complete the following information: Patient Name: Patient ID Number: Patient DOB: The procedure being requested: Epidural Injection Please check the indication (reason)
Spine Pain Management Program Please complete the following information: Patient Name: Patient ID Number: Patient DOB: The procedure being requested: Epidural Injection Please check the indication (reason)
SPINAL CORD DISEASE IN DOGS PART TWO: MOST LIKELY CAUSES
 Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk SPINAL CORD DISEASE IN DOGS PART TWO: MOST LIKELY CAUSES Author : RITA GONÇALVES Categories : Vets Date : April 7, 2014 RITA
Vet Times The website for the veterinary profession https://www.vettimes.co.uk SPINAL CORD DISEASE IN DOGS PART TWO: MOST LIKELY CAUSES Author : RITA GONÇALVES Categories : Vets Date : April 7, 2014 RITA
Key words: Brain, Cysticercosis, Neurocysticercosis, Parasites, Spinal Cord.
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(2):438-442 Disseminated Spinal Cysticercosis: A Rare Intramedullary Ring Enhancing Lesion Avanti Gulhane, Sushil Kumar Kale Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Mahatma Gandhi
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2015;5(2):438-442 Disseminated Spinal Cysticercosis: A Rare Intramedullary Ring Enhancing Lesion Avanti Gulhane, Sushil Kumar Kale Department of Radio-Diagnosis, Mahatma Gandhi
Chiari malformations. A fact sheet for patients and carers
 A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
A fact sheet for patients and carers Chiari malformations This fact sheet provides information on Chiari malformations. It focuses on Chiari malformations in adults. Our fact sheets are designed as general
Adult - Cerebrovascular. Adult - Cranio-Cervical Junction. Adult - Epilepsy. Adult - Hydrocephalus
 list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
list for SET and IMG Neurosurgery Adult - Cerebrovascular Aneurysm - Clipping: Anterior circulation Aneurysm - Clipping: Posterior circulation AVM excision Carotid endarterectomy Carotid trapping Cavernoma
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
The CNS Part II pg
 The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The CNS Part II pg. 455-474 Protection of the Brain Objectives Describe how the meninges, cerebrospinal fluid, and the blood brain barrier protect the CNS. Explain how Cerebrospinal fluid is formed, and
The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis
 September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
MR imaging of acute non-traumatic spinal cord syndrome
 MR imaging of acute non-traumatic spinal cord syndrome Poster No.: C-0872 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Ripoll, N. Sarbu, A. Lopez, S. Capurro, L. Oleaga Zufiría; Barcelona/ES
MR imaging of acute non-traumatic spinal cord syndrome Poster No.: C-0872 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Ripoll, N. Sarbu, A. Lopez, S. Capurro, L. Oleaga Zufiría; Barcelona/ES
CONTINUING EDUCATION MRI OF MYELITIS* JBR BTR, 2012, 95: J. Hodel 1,2, O. Outteryck 3, P. Jissendi 1, M. Zins 2, X. Leclerc 1, J.-P.
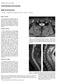 JR TR, 2012, 95: 270-276. ONTINUING EDUTION MRI OF MYELITIS* J. Hodel 1,2, O. Outteryck 3, P. Jissendi 1, M. Zins 2, X. Leclerc 1, J.-P. Pruvo 1 MRI of myelitis The diagnosis of myelitis relies on MRI.
JR TR, 2012, 95: 270-276. ONTINUING EDUTION MRI OF MYELITIS* J. Hodel 1,2, O. Outteryck 3, P. Jissendi 1, M. Zins 2, X. Leclerc 1, J.-P. Pruvo 1 MRI of myelitis The diagnosis of myelitis relies on MRI.
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
General: Brain tumors are lesions that have mass effect distorting the normal tissue and often result in increased intracranial pressure.
 1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
1 Lecture Objectives Know the histologic features of the most common tumors of the CNS. Know the differences in behavior of the different tumor types. Be aware of the treatment modalities in the various
