Nervous system NEURON. Nervous system divisions. TYPES OF NEURONS (morfological division) Body (perikaryon)
|
|
|
- Nicholas Bell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nervous system Nervous system 1) Sensory function changes in the internal and external environment 2) Integrative function analyse, store and compare informations 3) Motor function responds to stimuli by initiating contraction and glandular secretion Receptor CNS analyzing Efector Striated muscles Smooth muscles Myocardium Glands Sensor (afferent, centripetal neurons) Motor (efferent, centrifugal neurons) Nervous system divisions 1) Centran Nervous System (CNS) brain, spinal cord 2) Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) cranial nerves (I-XII), spinal nerves (31 pairs), vegetative (visceral or autonomic) system NEURON Body (perikaryon) Dendrits (denritic zone) neurit (axon) inicial segment Schwann s covering Myelin covering Schwann cells with fat (PNS) Oligodendrocytes (CNS) Ranvier nodes internodal segments GLIAL CELLS TYPES OF NEURONS (morfological division) multipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar, unipolar Makroglia (astrocytes) transport of substances between capillary and neuron Oligodendroglia covering of axons in CNS Schwann cells covering of axons in PNS Mikroglia fagocytation activity Ependym cover ventricles 1
2 1. SENSORIC (ascendent, aferent, centripetal) Somatosensoric (proprioception, exteroception) Viscerosensoric (interoception) 2. MOTOR Somatomotor (striated muscles) Visceromotor sympaticus, parasympaticus vegetativ, autonomic (smooth muscles, heart, glands) 3. INTERNEURONS TYPES OF NEURONS (functional division) DIVISION OF NERVOUS SYSTEM 1. Central (CNS) spinal cord, brain Gray matter bodies of neurons (cortex, nuclei) White matter myelinated nerve fibres 2. Peripheral spinal, cranial and autonomic nerves (sensoric, motor, mixed) plexuses Central nervous system Spinal cord (medulla spinalis) Brain (cerebrum, encephalon) Medulla oblongata Pons (pons Varoli) Cerebellum Midbrain (mesencephalon) Hindbrain (diencephalon) Telencephalon Spinal cord (medulla spinalis) Decussatio pyramidum, spinal nerves C1 Cerical Saccus durae matris Thoracic Lumbar Sacral L 1-2 adults, L 3-4 newborns SEGMENTS 2
3 Dura mater Arachnoidea CAUDA EQUINA ROOTS, MENINGES Dorsal root Ventral root Dorsal root ganglion SPINAL NERVE ROOTS SEGMENTS GANGLION SPINALE Lumbar puncture 3
4 BRAIN STEM Medulla oblongata Pons (pons Varoli) Midbrain (mesencephalon) Hindbrain (diencephalon) Medulla oblongata spinal cord continuation (20 25mm) (bulbus medullae spinalis) from 1. pair of spinal nervesu (decussatio pyramidum) to pons Varoli sulcus bulbopontinus (VI., VII., VIII.) sulcus lateralis anterior (XII.) sulcus lateralis posterior (IX., X., XI.) pyramis medullae oblongatae (Corticospinal tract) Fossa rhomboidea Bottom of the fourth ventricle (dorsal side of brain stem) 1. pars superior (mesencephalon) 2. pars intermedia (pons Varoli) 3. pars inferior (medulla oblongata) between pedunculi cerebellares inf. sulcus medianus sulci limitantes (eminentia medialis) trigonum nervi hypogloossi trigonum nervi vagi (fovea inferior) Pons Varoli sulcus basilaris (a. basilaris) sulcus bulbopontinus VI. nervus abducens VII. nervus facialis VIII. nervus vestibulocochlearis pedunculi cerebellares medii V. nervus trigeminus Lateral side of pons Varoli pedunculus cerebellaris medius nervus trigeminus 4
5 Midbrain (mesencephalon) Between pons Varoli and kem (asi 30 mm) Dorsal side of pons Varoli Middle portion of fossa rhomboidea crura (pedunculi) cerebri fossa interpeduncularis sulcus nervi oculomotorii n. III. (nervus oculomotorius) Dorsal side of midbrain corpora quadrigemina (lamina tecti) Pars superior fossae rhomboideae colliculi superiores (optic-motor reflexes) colliculi inferiores (akustic motor reflexes) Connected with hindbrain (CGL, CGM) pedunculi cerebellares superiores velum medullare superius frenulum veli medullaris superioris n. IV. nervus trochlearis Cerebellum Posterior cranial fossa (fossae cerebellares) On the dorsal side of brain stem Boundaires of the fourth ventricle fissura transversa cerebri (tentorium cerebelli) separates the cerebellum from the occipital lobes 5
6 Cerebellum g Vermis cerebelli Hemispheria cerebelli Margo anterior (incisura cerebelli ant.) Margo posterior (incisura cerebelli post.) Pedunculus flocculi Flocculus Sulci cerebelli Folia cerebelli Connected with brain stem by three peduncles: 1. Pedunculi cerebellares sup. (midbrain) velum medullare sup. 2. Pedunculi cerebellares med. (pons Varoli) 3. Pedunculi cerebellares inf. (medulla oblongata) fastigium velum medullare inf. Functional division of cerebellum: 1. vestibular (archicerebellum) lingula, pars nodulofloccularis 2. spinal (palaeocerebellum) medial and paramedial zone lobus anterior and posterior 3. cerebral (neocerebellum) lateral zone lobus anterior and posterior 1. balance 2. tonus 3. coordination lenghth estimation Archi - palleo neo CEREBELLUM fylogenetic and functional division Diencephalon (hindbrain) Thalamencephalon Thalamus Epithalamus Metathalamus sulcus hypothalamicus ( sulcus limitans ) GRAY MATTER cortex cerebelli on the surface of hemispheria and vermis Hypothalamus a subthalamus nuclei cerebelli (ncll. fastigii, ncl. globosi, ncl. emboliformis, ncl. dentatus) WHITE MATTER arbor vitae (tree of life) 6
7 ROSTRAL SIDE OF DIENCEPHALON BASAL SIDE OF DIENCEPHALON Chiasma opticum Hypophysis cerebri Corpora mamillaria Lamina terminalis (between commisura anterior and chiasma opticum) DORSAL SIDE OF DIENCEPHALON Thalamus Tuberculum thalami anterius Epithalamus Pulvinar thalami Stria terminalis (vena thalamostriata) Taenia choroidea (tela choroidea ventriculi lateralis) Corpus pineale (epiphysis) CHANGING OF THE DAY AND NIGHT Stria medullaris thalami (tela choroidea ventriculi tertii) Epithalamus MEDIAL SIDE OF DIENCEPHALON Metathalamus corpus geniculatum mediale (auditory tract) corpus geniculatum laterale (optic tract) lateral side of III. ventricle sulcus hypothalamicus (foramen interventriculare - aquaductus cerebri) adhesio interthalamica 7
8 LATERAL SIDE OF DIENCEPHALON TELENCEPHALON Connected with structures of telencephalon (capsula interna, nucleus caudatus) Hemisphaeria cerebri Fissura longitudinalis cerebri Cortex cerebri Sulci cerebri Gyri cerebri Polus frontalis Polus occipitalis Polus temporalis Hemispheria cerebri Lobes of telencephalon: Sulcus lateralis ramus ant., ascen., post. Sulcus centalis Sulcus parietooccipitalis facies superolateralis (convexa) Incisura praeoccipitalis (impresio petrosa) Lobus frontalis facies medialis facies inferior margo superior margo inferior margo medialis Lobus parietalis Lobus occipitalis Lobus temporalis Lobus insulae Facies superolateralis cerebri gyruses Facies inferior cerebri sulci et gyri 8
9 Facies medialis cerebri sulci et gyri Lobus insulae Corpus callosum Operculum frontale parietale temporale Basal ganglia Gray matter with hemispheres Corpus amygdaloideum Globus pallidus Nucleus caudatus Putamen Claustrum 9
10 Ventricles of the brain Ventriculi laterales foramen interventriculare Ventriculus tercius aqueductus mesencephali Ventriculus quartus canalis centralis THE FOURTH VENTRICLE Between the brain stem and cerebellum Fossa rhomboidea sulcus medianus sulci limitantes eminentia medialis pars superior, intermedia, inferior Tegmen ventriculi quarti velum medullare superius fastigium velum medullare inferius Pars superior fovea superior (n. V.) locus coeruleus Pars intermedia stria medullaris, recessus lat. colliculus facialis (n. VI.) area vestibularis tuberculum acusticum Pars inferior trigonum nervi hypogloossi trigonum nervi vagi (fovea inferior) THE THIRD VENTRICLE In the midline between both hemispheres Lateral wall: Thalamus adhesio interthalamica sulcus hypothalamicus foramen interventriculare Hypothalamus Basal wall: Hypothalamus Recessus opticus Recessus infundibularis Anterior wall: lamina terminalis commisura ant. pars libera columnae fornicis Posterior wall: recessus suprapinealis commisura habenularum recessus pinealis commisura posterior aquaeductus cerebri Roof: tela choroidae ventriculi III. (stria medullaris thalami, trigonum habenulae, commisura habenularum) recessus suprapinealis 10
11 LATERAL VENTRICLE Cornu anterius (frontal lobe): Septum pellucidum Corpus callosum Ncl. caudatus Pars centralis: Corpus callosum Ncl. caudatus Stria terminalis Cornu anterius (lobus frontalis), pars centralis (lobus parietalis), cornu posterius (lobus occipitalis), cornu inferius (lobus temporalis VENTRICULUS LATERALIS Cornu posterius (occipital lobe): Corpus callosum Trigonum collaterale Calcar avis Cornu inferius (temporal lobe): Corpus callosum Ncl. caudatus Stria terminalis (tela choroidea ventriculi lat.) Fimbria hippocampi Hippocampus (pes hippoc.) Eminentia collateralis MENINGES Spatium epidurale (spinal cord!) Dura mater (encephali, spinalis) Spatium subdurale Arachnoidea Spatium subachanoidale (liquor cerebrospinalis) Pia mater DURA MATER ENCEPHALI LEPTOMENINX ENCEPHALI Falx cerebri (fissura longit. cerebri) Falx cerebelli (incisura cerebelli post.) Tentorium cerebelli (fissura transv. cerebri) incisura tentorii Diaphragma sellae Cavum trigeminale Vagina nervi optici Sinus durae matris Arachnoidea Granulationes arachnoidales Spatium subarachnoidale Liquor cerebrospinalis Cisternae subarachnoidales Pia mater encephali Tela choroidea ventriculorum Plexus choroidei (liquor cerebrospinalis) 11
12 MENINGES MEDULLA SPINALIS Cisternae subarachnoidales cerebellomedullaris, fossae lateralis cerebri, interpeduncularis, chiasmatis, ambiens, lumbalis Endorhachis Arachnoidea spinalis (S 2 ) Spatium epidurale (plexus venosi vertebrales int.) Pia mater spinalis (ligamentum denticulatum) Saccus durae matris (S 2-3, filum durae matris) Spatium subarachnoidale (cisterna lumbalis cauda equina) LIQUOR CEREBROSPINALIS ml ( per day) ARTERIES OF THE BRAIN Arteria carotis interna Plexus choroideus ventriculi lateralis (ventriculi III., IV.) Arteria ophthalmica Arteria choroidea ant. foramen interventriculare (ventriculus III.) aqueductus cerebri (ventriculus IV.) canalis centralis (medulla spinalis) apertura mediana, later. ventriculi IV. (spatium subarachnoidale) sinus sagittalis superior vv. radiculares Arteria communicans posterior (circulus arteriosus cerebri) Arteria cerebri media (circulus arteriosus cerebri) Arteria cerebri anterior (circulus arteriosus cerebri) Arteria vertebralis r. spinalis a. basilaris CIRCULUS ARTERIOSUS CEREBRI Arteriae cerebri anteriores Arteria cerebri anterior Arteria communicans anterior Arteria cerebri media Arteriae cerebri mediae Arteria cerebri posterior Arteria communicans posterior Arteriae cerebri posteriores 12
13 ARTERIES OF THE SPINAL CORD rr. spinales (branches of the adjacent arteries) aa. radiculares ant. aa. radiculares post. a. spinalis ant. (fissura mediana ant.) 2 aa. spinales post. (sulcus medianus post.) SINUS DURAE MATRIS Sinus sagittalis sup., inf. Sinus occipitalis Sinus rectus Sinus sigmoideus Sinus cavernosus (sinus intercavernosi) Sinus sphenoparietalis Sinus transversus Sinus petrosus sup., inf. Plexus basilaris DEEP VEINS OF THE BRAIN Vena septi pellucidi + Vena choroidea + Vena thalamostriata Vena cerebri interna Vena cerebri magna Sinus rectus SUPERFICIAL VEINS OF THE BRAIN Vv. cerebri superiores (sinus sagittalis superior) V. cerebri media superficialis (sinus sphenoparietalis nebo sinus cavernosus) Vena anastomatica sup. Vena anastomatica inf. V. cerebri media profunda (vena basalis) Vv. cerebri inferiores (sinus transversus) Vv. cerebri inferiores form vena basilaris (v. cerebri magna) VENOUS PLEXUS OF THE SPINAL CANAL 13
Ventricles, meninges and vessels of the CNS
 Ventricles, meninges and vessels of the CNS Lateral ventricle (ventriculus lateralis) Third ventricle (ventriculus tertius) Fourth ventricle (ventriculus quartus) Central canal (canalis centralis) Fourth
Ventricles, meninges and vessels of the CNS Lateral ventricle (ventriculus lateralis) Third ventricle (ventriculus tertius) Fourth ventricle (ventriculus quartus) Central canal (canalis centralis) Fourth
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Laboratory Manual for Comparative Anatomy and Physiology Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
 Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
The spinal cord - Medulla spinalis
 The spinal cord - Medulla spinalis The development of the neural tube in the area of the spinal cord The spinal cord - Medulla spinalis length 40 50 cm, thickness 1cm weight circa 30g it is located within
The spinal cord - Medulla spinalis The development of the neural tube in the area of the spinal cord The spinal cord - Medulla spinalis length 40 50 cm, thickness 1cm weight circa 30g it is located within
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
Model 3-50B or 3-88 III VIII. Olfactory Nerve. Optic Nerve. Oculomotor Nerve. Trochlear Nerve. Trigeminal Nerve. Abducens Nerve.
 Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Bogomolets National Medical University
 Bogomolets National Medical University The Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic Subject HUMAN ANATOMY Matter Module 2 Content module No. 11 The theme of the lesson Midbrain et diencepahalon
Bogomolets National Medical University The Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic Subject HUMAN ANATOMY Matter Module 2 Content module No. 11 The theme of the lesson Midbrain et diencepahalon
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
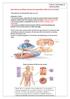 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal
 I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 13
 I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
I. embryonic development of the CNS A. neurulation is the formation of the CNS in the embryo invagination of dorsal ectoderm (outer layer of embryo cells) this process is induced (caused) by the notochord
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES NERVOUS SYSTEM TISSUES: HISTOLOGY SLIDES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
Chapter 13 Lecture Outline *
 Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
Anatomy and Physiology, Seventh Edition Rod R. Seeley Idaho State University Trent D. Stephens Idaho State University Philip Tate Phoenix College Chapter 13 Lecture Outline * *See PowerPoint Image Slides
Dissection of the Sheep Brain
 Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Dissection of the Sheep Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: 1. Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those of the human brain.
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Primary pouches: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon Secondary pouches: telencephalon diencephalon
 Telencephalon Ontogenic development of CNS Primary pouches: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon Secondary pouches: telencephalon diencephalon mesencephalon metencephalon ---- pons (pons Varoli),
Telencephalon Ontogenic development of CNS Primary pouches: prosencephalon, mesencephalon, rhombencephalon Secondary pouches: telencephalon diencephalon mesencephalon metencephalon ---- pons (pons Varoli),
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Human Anatomy. Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Human Anatomy Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 Brain and Cranial Nerves An adult brain weighs between 1.35 and 1.4 kilograms (kg) (around 3 pounds) and has a volume of about 1200 cubic centimeters (cc). Brain
Human Anatomy Brain and Cranial Nerves 1 Brain and Cranial Nerves An adult brain weighs between 1.35 and 1.4 kilograms (kg) (around 3 pounds) and has a volume of about 1200 cubic centimeters (cc). Brain
Brain ميهاربا لض اف دمح ا د The Meninges 1- Dura Mater of the Brain endosteal layer does not extend meningeal layer falx cerebri tentorium cerebelli
 .احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
.احمد د فاضل ابراهيم Lecture 15 Brain The Meninges Three protective membranes or meninges surround the brain in the skull: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater 1- Dura Mater of the Brain
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System. Lecture 4
 Nervous System Lecture 4 Neurons Functional unit of the nervous system Also called the nerve cell Soma or body Axon Dendrites Neuroglial cells support cells Schwann cells produce myelin in PNS Oligodendrocytes
Nervous System Lecture 4 Neurons Functional unit of the nervous system Also called the nerve cell Soma or body Axon Dendrites Neuroglial cells support cells Schwann cells produce myelin in PNS Oligodendrocytes
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7
 The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
The Brain Worksheet Sections 5-7 1. neuroglia 2. autonomic nervous system 3. sensory neurons 4. oligodendrocytes 5. ascending tracts 6. descending tracts 7. saltatory propagation 8. continuous propagation
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
The Brain. Brain. Spinal Cord. Cauda Equina
 The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain. MDL231 Principle of Anatomy
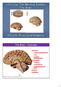 Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Student Lab #: Date. Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System)
 Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Lab: Gross Anatomy of Brain Sheep Brain Dissection Organ System: Nervous Subdivision: CNS (Central Nervous System) Student Lab #: Date 1 Objectives: 1. Learn the main components making up a motor neuron.
Embryonic Brain Development
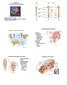 Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
Chapter 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Largest organ in the body? Brain functions in sensations, memory, emotions, decision making, behavior 19-1 19-2 Embryonic Brain Development Principal Parts of the
stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is also the center for intellect, emotions, behavior, and memory.
 Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
Chapter 14 - Outline I. INTRODUCTION A. The brain is the center for registering sensations, correlating them with one another and with stored information, making decisions, and taking action. 1. It is
Chapter 5: Fetal Central Nervous System 71
 71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
71 Chapter 5 Fetal Central Nervous System Embryology NEURULATION begins with the formation of the neural plate, the neural folds and their ultimate fusion and closure as the NEURAL TUBE. NEURAL PLATE -
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
GUIDELINES. Module 2 Content module 11. brain. The formation and ways of cerebrospinal fluid circulation. Medical1,2,3,4, military.
 Bogomolets National Medical University Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic Subject Matter HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Content module 11 Theme of the lesson The meninges of spinal cord and brain.
Bogomolets National Medical University Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic Subject Matter HUMAN ANATOMY Module 2 Content module 11 Theme of the lesson The meninges of spinal cord and brain.
The Nervous System. PowerPoint Lecture Slides C H A P T E R 7. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College C H A P T E R 7 The Nervous System NERVOUS SYSTEM OVERVIEW Essential Question: What are the primary functions
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF
 Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Brain Meninges, Ventricles and CSF Lecture Objectives Describe the arrangement of the meninges and their relationship to brain and spinal cord. Explain the occurrence of epidural, subdural and subarachnoid
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Neurology. Dr. Mohd. Zahirul Islam Khan DVM, MS, Ph.D, Postdoc.
 Neurology By, 1. Central Nervous System: a) Brain of different animals. b) Spinal cord. 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): a) Cranial Nerves b) Spinal Nerves and ganglia 3. Autonomic Nervous System (PNS)
Neurology By, 1. Central Nervous System: a) Brain of different animals. b) Spinal cord. 2. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS): a) Cranial Nerves b) Spinal Nerves and ganglia 3. Autonomic Nervous System (PNS)
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Lab Photo Review Sheet
 9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
9 8 0. Posterior Median Sulcus. Central Canal. Dorsal (Posterior) Horn. Ventral (Anterior) Horn. Grey Matter. White Matter. Anterior Median Fissure 8. Ventral (Anterior) Root (ramus) 9. Dorsal (Posterior)
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17. By: Joseline
 PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
PSY 302: CHAPTER 3 NOTES THE BRAIN (PART II) - 9/5/17 By: Joseline Left 3 MAJOR FISSURES : 2HEMISPHERES Right Lateral Ventricle Central Fissure Third Ventricle Sulcus Lateral Fissure Gyros Fissure- Fissures
BIOL Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain
 BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
BIOL 2401 Dissection of the Sheep and Human Brain Laboratory Objectives After completing this lab, you should be able to: Identify the main structures in the sheep brain and to compare them with those
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
If I Only Had a Brain
 If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
If I Only Had a Brain A Heart. (The Nerve!) Regions of the Brain Cerebral hemisphere Diencephalon Cerebellum (b) Adult brain Brain stem Regions of the Brain: Cerebrum Precentral gyrus Frontal lobe Central
Neuroanatomy. Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan Dr Maha ELBeltagy
 Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
Neuroanatomy Dr. Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Development of the Central Nervous System Development of the nervous system Development
1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS)
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 1 Sept 9 th to 11 th TA: Jürgen Germann; e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. The basic anatomy of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Cells of the CNS 3.
Developmental sequence of brain
 Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
Cerebellum Developmental sequence of brain Fourth week Fifth week Location of cerebellum Lies above and behind the medullar and pons and occupies posterior cranial fossa Location of cerebellum External
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
Central Nervous System: Part 2
 Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Central Nervous System: Part 2 1. Meninges 2. CSF 3. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves Explain spinal cord anatomy, including gray and white matter and meninges (give the general functions of this organ).
Neuroanatomy lecture (1)
 Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Neuroanatomy lecture (1) Introduction: Neuroanatomy has two parts: the central and peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system is composed of brain and spinal cord. The brain has the following
Divisions of the Nervous System
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Lecture 19 1 Divisions of the Nervous System You are here CNS PNS 3 Brain Embryology & Overview Table & Figure From:
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System Lecture 19 1 Divisions of the Nervous System You are here CNS PNS 3 Brain Embryology & Overview Table & Figure From:
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
THE ANATOMY OF THE BRAIN R.H.WHITEHEAD.
 THE ANATOMY OF THE BRAIN R.H.WHITEHEAD. ilv t? IWSTITWTO»i»TOif '-'"TKOLOfllC* o* r«evl«aui DO- MCI:,. t CIRWRQIA I* PAULO, KAXII DEDALUS - Acervo - FM BIBUOTHECAdai'/-OL0AD;de,^W0?N/ DE SAO PAL K Cy
THE ANATOMY OF THE BRAIN R.H.WHITEHEAD. ilv t? IWSTITWTO»i»TOif '-'"TKOLOfllC* o* r«evl«aui DO- MCI:,. t CIRWRQIA I* PAULO, KAXII DEDALUS - Acervo - FM BIBUOTHECAdai'/-OL0AD;de,^W0?N/ DE SAO PAL K Cy
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Unit 7: The Nervous System
 Unit 7: The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System A. Sensory input gathering information 1. To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body 2. Changes = stimuli B. Integration 1. To
Unit 7: The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System A. Sensory input gathering information 1. To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body 2. Changes = stimuli B. Integration 1. To
Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1
 Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1 I. Unit 7: The Nervous System A. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input - gathering information a) To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body b) Changes
Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1 I. Unit 7: The Nervous System A. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input - gathering information a) To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body b) Changes
Stanley Pruisinger 1980's
 Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Neuroanatomy Prion disease cerebellum chapter b/c cerebellar ataxia here as a warning for obvious reasons. Creutzfeldt - Jakob Disease (CJD) "Spongiform" (brain turns to sponge) Jews in Lybia who ate
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Dispose of debris Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Ependymal cells Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord Circulate cerebrospinal fluid Nervous
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg Three Main Regions of the Brain. Forebrain
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
Sectional Anatomy Head Practice Problems
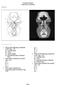 1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
1. Which of the following is illustrated by #3? (Fig. 5-42) A) maxillary sinus B) vomer C) septal cartilage D) perpendicular plate of ethmoid bone 2. What number illustrates the cornea? (Fig. 5-42) A)
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN
 Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Sheep Brain Dissection Guide Page 1 DISSECTION OF THE SHEEP'S BRAIN Introduction The purpose of the sheep brain dissection is to familiarize you with the threedimensional structure of the brain and teach
Development of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Diencephalon -interbrain ( ) -diencephalons, thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus -hollow space =
 Week 2 -neural plate Development of the Central Nervous System (CNS) Week 3 -neural groove Week 4 -neural tube (ice cream cone view) 1. Prosencephalon - 2. Mesencephalon - 3. Rhombencephalon - Week 5 -brain
Week 2 -neural plate Development of the Central Nervous System (CNS) Week 3 -neural groove Week 4 -neural tube (ice cream cone view) 1. Prosencephalon - 2. Mesencephalon - 3. Rhombencephalon - Week 5 -brain
Group D: Central nervous system yellow
 Group D: Central nervous system yellow Central nervous system 1. General structure of nervous system (neuron, glia, synapsis, mediators, receptors) Main points: types of neurons and glial cells, synapses,
Group D: Central nervous system yellow Central nervous system 1. General structure of nervous system (neuron, glia, synapsis, mediators, receptors) Main points: types of neurons and glial cells, synapses,
3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th
 3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th week differentiates into the CNS = brain development begins
3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th week differentiates into the CNS = brain development begins
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
PSY 215 Lecture #5 (01/26/2011) (Anatomy of the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96
 Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
