Supplementary Table 8. Genes from supplementary table 4 ordered in the way in which they occur in the heatmap in Figure 4b of the main text.
|
|
|
- Lynn Snow
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supplementary Table 8. Genes from supplementary table 4 ordered in the way in which they occur in the heatmap in Figure 4b of the main text. gene name protein name reference name strand start positend positi log2 fold change log10 p valog10 FDRGO category B7LAF3 Zinc transporter zitb TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGV1 Cell volume regulation protein A TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L4D2 Putative amino acid sodium/proton trty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L5A9 Zinc transport protein ZntB TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGF1 Membrane spanning protein in TonB TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGF2 Membrane spanning protein in TonB TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8H2 Iron enterobactin transporter subunitty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L4T5 Ferrous iron transporter, protein A TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LHJ8 Membrane spanning protein in TonB TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L4T8 Fused ferrous iron transporter, protei TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L5T0 Nickel transporter subunit ; membranty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L5T1 Nickel transporter subunit ; membranty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8G9 Enterobactin synthase multienzyme c TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LB16 Cation/acetate symporter ActP (AcetaTY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LDV1 Iron dicitrate transporter subunit ; mety 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L777 Glutamate transporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LDV0 Iron dicitrate transporter subunit ; mety 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGL3 Iron hydroxamate transporter subuni TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LDV3 Iron dicitrate transporter subunit ; pe TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LFC5 Proline:sodium symporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8H6 Isochorismate synthase 1 (EC ) TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8H8 Isochorismatase (EC ) TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L7A3 Putative monovalent cation:proton anty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LDV4 Ferric citrate outer membrane transpoty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L668 Cytochrome o ubiquinol oxidase subu TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LDU9 Iron dicitrate transporter subunit ; ATTY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LHJ6 Voltage gated potassium channel TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8G6 Iron enterobactin outer membrane tr TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGI2 Zinc transporter ZupT TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L9X6 Putative uncharacterized protein yohlty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LCE3 Manganese transport protein mnth TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LB62 Melibiose:sodium symporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L7A9 Copper transporter (EC ) TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8H7 2,3 dihydroxybenzoate AMP ligase coty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LC88 Putative TonB dependent iron outer mty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LAH7 Ferric iron catecholate outer membraty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LBU7 L lysine 6 monooxygenase (Lysine N(6TY 2482_chromosome cation transport
2 B7L8H9 2,3 dihydro 2,3 dihydroxybenzoate dety 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LDV2 RNA polymerase sigma factor TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8H5 Iron enterobactin transporter subunitty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LD40 Putative transport protein YbjL TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGL2 Ferrichrome outer membrane transpoty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8H3 Iron enterobactin transporter subunitty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8H1 Iron enterobactin transporter subunitty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGL4 Iron hydroxamate transporter subuni TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L5T2 Nickel transporter subunit ; ATP bindi TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L5S9 Nickel transporter subunit ; ATP bindi TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LB10 Putative cation/proton antiporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L4L4 Bacterioferritin associated ferredoxin TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGL5 Fused iron hydroxamate transporter sty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LDV5 Transmembrane signal transducer for TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8G7 Enterobactin/ferric enterobactin este TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LBE6 Putative transporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L824 Putative transport protein YidE TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L7R2 Zinc transporter subunit: membrane cty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L7V6 Ferritin iron storage protein (CytoplasTY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L888 ATP synthase subunit a (ATP synthasety 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGX9 Calcium/sodium:proton antiporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8V3 Flagellum specific ATP synthase (EC 3TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LHW2 Pantothenate:sodium symporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L8C4 Transcription termination factor Rho (TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LHY9 NAD binding component of TrK potas TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L6I3 Glutathione peroxidase TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L972 Magnesium/nickel/cobalt transporter TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LCV2 Magnesium transporter (EC ) TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7LGE1 Aldo keto reductase TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L7P3 Putative uncharacterized protein yebzty 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L7R0 Zinc transporter subunit: periplasmic TY 2482_chromosome cation transport B7L524 Putative flagellin structural protein; p TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LHG1 Flagellar system protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L7T3 Flagellar export pore protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8W2 Flagellar biosynthetic protein flir TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V5 Flagellar hook length control protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection
3 B7L8T7 Putative Flagellar hook associated proty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG16 Flagellar hook filament junction protety 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG10 Flagellar hook protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG11 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG08 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG12 Flagellar component of cell distal portty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG17 Flagellar hook filament junction protety 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V4 Flagellar protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V1 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LGV4 Flagellar brake protein YcgR (Cyclic di TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L7T2 Putative flagellar export pore protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V8 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V9 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8W0 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V6 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V0 Flagellar basal body MS ring and collaty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8T8 Flagellar protein potentiates polymerity 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V7 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LBH5 Flagella control of anti sigma factor Fl TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG07 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG09 Flagellar hook assembly protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L609 EAL domain containing protein involvety 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8W1 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7LG06 Assembly protein for flagellar basal boty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L7U2 Protein that enables flagellar motor roty 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L8V2 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome cell projection B7L6W8 Putative outer membrane lipoprotien TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7L8V2 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG06 Assembly protein for flagellar basal boty 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG13 Flagellar L ring protein (Basal body L rty 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG12 Flagellar component of cell distal portty 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG17 Flagellar hook filament junction protety 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7L8V1 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG08 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG14 Flagellar P ring protein (Basal body P TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7L8V8 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot
4 B7L8V0 Flagellar basal body MS ring and collaty 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7L8V7 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7L8V6 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG07 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG15 Muramidase TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7L8V4 Flagellar protein TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG16 Flagellar hook filament junction protety 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG10 Flagellar hook protein TY 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7LG11 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome ciliary or flagellar mot B7L8W2 Flagellar biosynthetic protein flir TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V4 Flagellar protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L7T3 Flagellar export pore protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LGV4 Flagellar brake protein YcgR (Cyclic di TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L7T2 Putative flagellar export pore protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V8 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V9 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8W0 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8T9 Flagellar protein FliT TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V1 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V6 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V0 Flagellar basal body MS ring and collaty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8T8 Flagellar protein potentiates polymerity 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V7 Flagellar motor switching and energiz TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LBH5 Flagella control of anti sigma factor Fl TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG07 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG09 Flagellar hook assembly protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V5 Flagellar hook length control protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum
5 B7L8T7 Putative Flagellar hook associated proty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG16 Flagellar hook filament junction protety 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG10 Flagellar hook protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG11 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG08 Flagellar component of cell proximal pty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG12 Flagellar component of cell distal portty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG17 Flagellar hook filament junction protety 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG06 Assembly protein for flagellar basal boty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L7U2 Protein that enables flagellar motor roty 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8V2 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L7T1 Putative uncharacterized protein flhe TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L609 EAL domain containing protein involvety 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L8W1 Flagellar biosynthesis protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7L524 Putative flagellin structural protein; p TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LG05 Anti sigma factor for FliA (Sigma 28) TY 2482_chromosome flagellum B7LHG1 Flagellar system protein TY 2482_chromosome flagellum
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function
 Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Table S9A: List of taurine regulated genes in Bp K96243 Chr 1 (up regulated >=2 fold) Cluster no GENE ID Start Stop Strand Function 1 BPSL0024 26223 26621 + LrgA family BPSL0025 26690 27412 + hypothetical
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Figure S1: Abundance of Fe related proteins in oceanic Synechococcus sp. strain WH8102 in. Ferredoxin. Ferredoxin. Fe ABC transporter
 0.004 SW nm 0.04 0.03 nm nm 0.16 0.1 nm nm 0.40 0.3 nm nm 0.80 0.5 nm 1.6 1 nm 16 10 nm 160 100 nm 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm 0.80 nm 1.6 nm 16 nm 160 nm Spectral counts 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm
0.004 SW nm 0.04 0.03 nm nm 0.16 0.1 nm nm 0.40 0.3 nm nm 0.80 0.5 nm 1.6 1 nm 16 10 nm 160 100 nm 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm 0.80 nm 1.6 nm 16 nm 160 nm Spectral counts 0 nm 0.04 nm 0.16 nm 0.40 nm
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM LAB SECTION
 BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
BIOLOGY 103 Spring 2001 MIDTERM NAME KEY LAB SECTION ID# (last four digits of SS#) STUDENT PLEASE READ. Do not put yourself at a disadvantage by revealing the content of this exam to your classmates. Your
Chem Lecture 11 Molecular Motors Part 2
 Chem 452 - Lecture 11 Molecular Motors Part 2 Question of the Day. How is the movement of bacteria like a bumper car ride? Bacterial flagella are remarkably similar to an electrical motor. 2 Bacterial
Chem 452 - Lecture 11 Molecular Motors Part 2 Question of the Day. How is the movement of bacteria like a bumper car ride? Bacterial flagella are remarkably similar to an electrical motor. 2 Bacterial
it selectively allows some molecules to pass into the organism
 Multiple Choice Quiz Procaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Choose the best answer 1. The significance of the plasma membrane is that it selectively allows some
Multiple Choice Quiz Procaryotic Cell Structure and Function Eucaryotic Cell Structure and Function Choose the best answer 1. The significance of the plasma membrane is that it selectively allows some
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers. EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3
 Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
Microbiology for Environmental Health Officers EHL0033 Prokaryotes 3 Mutualism: bacterial headlights. The glowing oval below the eye of the flashlight fish (Photoblepharon palpebratus) is an organ harboring
Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation The cheetah, whose capacity for aerobic metabolism makes it one of the fastest animals Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 1 14.4 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Chapter 14 - Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation The cheetah, whose capacity for aerobic metabolism makes it one of the fastest animals Prentice Hall c2002 Chapter 14 1 14.4 Oxidative Phosphorylation
Bacterial Structures. Capsule or Glycocalyx TYPES OF FLAGELLA FLAGELLA. Average size: µm 2-8 µm Basic shapes:
 PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
PROKARYOTIC One circular chromosome, not in a membrane No histones No organelles Peptidoglycan cell walls Binary fission EUKARYOTIC Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane Histones Organelles Polysaccharide
Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Oxidative Phosphorylation Energy from Reduced Fuels Is Used to Synthesize ATP in Animals Carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids are the main reduced fuels for the cell. Electrons from reduced fuels are
Oxidative Phosphorylation Energy from Reduced Fuels Is Used to Synthesize ATP in Animals Carbohydrates, lipids, and amino acids are the main reduced fuels for the cell. Electrons from reduced fuels are
Cell Structure. Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell. Cytoplasmic Membrane 4/6/2011. Chapter 3. Cytoplasmic membrane
 Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
Cell Structure Chapter 3 Morphology of Prokaryotic Cell Cytoplasmic membrane Delicate thin fluid structure Surrounds cytoplasm of cell Defines boundary Defines boundary Serves as a selectively permeable
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH AEROBIC RESPIRATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF AEROBIC RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is a series of reactions involving electron transfers to breakdown molecules for (ATP) 1. Glycolytic pathway: Glycolysis
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: OVERVIEW OF AEROBIC RESPIRATION Cellular respiration is a series of reactions involving electron transfers to breakdown molecules for (ATP) 1. Glycolytic pathway: Glycolysis
ORGANELLES OF THE ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM
 Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Membranes compartmentalize the interior of the cell and facilitate a variety of metabolic activities. Chloroplasts and a rigid cell wall are what distinguish a plant cell from an animal cell. A typical
Mineral Nutrition in Plants. Plant nutrition: essentiality, mechanism of absorption, role in plant metabolism.
 Mineral Nutrition in Plants Plant nutrition: essentiality, mechanism of absorption, role in plant metabolism. Mineral : An inorganic element Nutrient : A substance needed to survive or necessary for the
Mineral Nutrition in Plants Plant nutrition: essentiality, mechanism of absorption, role in plant metabolism. Mineral : An inorganic element Nutrient : A substance needed to survive or necessary for the
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Crosstalk between sugarcane and a plant-growth promoting Burkholderia species Chanyarat Paungfoo-Lonhienne, Thierry G. A. Lonhienne, Yun Kit Yeoh, Bogdan C. Donose, Richard I.
Supplementary information Crosstalk between sugarcane and a plant-growth promoting Burkholderia species Chanyarat Paungfoo-Lonhienne, Thierry G. A. Lonhienne, Yun Kit Yeoh, Bogdan C. Donose, Richard I.
Bio Microbiology - Spring 2012 Learning Guide 03.
 Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2012 Learning Guide 03 http://seemikedraw.files.wordpress.com/2007/07/biology-final.jpg Walsby's Square Bacteria Images of cells from 12 different colonies on blood agar
Bio 230 - Microbiology - Spring 2012 Learning Guide 03 http://seemikedraw.files.wordpress.com/2007/07/biology-final.jpg Walsby's Square Bacteria Images of cells from 12 different colonies on blood agar
Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTERS 20 and 21 The Electron-Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Cellular Respiration and Physiologic
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTERS 20 and 21 The Electron-Transport Chain And Oxidative Phosphorylation 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Cellular Respiration and Physiologic
Length Regulation of Flagellar Hooks and Filaments in Salmonella
 Length Regulation of Flagellar Hooks and Filaments in Salmonella J. P. Keener Department of Mathematics Length Regulation of Flagellar Hooks p.1/36 Introduction The first of many slides p.2/36 Control
Length Regulation of Flagellar Hooks and Filaments in Salmonella J. P. Keener Department of Mathematics Length Regulation of Flagellar Hooks p.1/36 Introduction The first of many slides p.2/36 Control
Microbiology: A Systems Approach
 Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
Microbiology: A Systems Approach First Edition Cowan & Talaro Chapter 4 Prokaryotic Profiles: the Bacteria and the Archaea Chapter 4 Fig. 4.1 3 3 parts flagella filament long, thin, helical structure composed
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم -Please refer to the slides from (4-20) -Slides (4, 5) -Oxidative phosphorylation consists of 2 parts: 1.electron transport chain (series of electron transport proteins much filled
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم -Please refer to the slides from (4-20) -Slides (4, 5) -Oxidative phosphorylation consists of 2 parts: 1.electron transport chain (series of electron transport proteins much filled
Mineral Nutrition. Criteria for Essentiality
 Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
Mineral Nutrition Criteria for Essentiality The element is absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction. In the absence of essential elements, plants cannot complete their life cycle
Introduction to Metal Transport Bertini et al Ch. 5 and 8
 Introduction to Metal Transport Bertini et al Ch. 5 and 8 Prof. Arthur D. Tinoco University of Puerto Rico, Rio Piedras Campus 1 Focus on Metal Transport to Cells Movement through Membranes www.nineplanets.org
Introduction to Metal Transport Bertini et al Ch. 5 and 8 Prof. Arthur D. Tinoco University of Puerto Rico, Rio Piedras Campus 1 Focus on Metal Transport to Cells Movement through Membranes www.nineplanets.org
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4. Outline. Early contributors to Understanding Cells. Cell Theory. Cell Size s Matt Schleiden & Ted Schann
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 4 Outline History of the science behind cells Cell theory & its importance Why are cells small? Microscopes Cell structure and function Prokaryotic cells Eukaryotic cells Early
PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name
 PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name Student ID # (U Number) A Before beginning this exam, please complete the following instructions: 1) Write your name and U number on the first page of this
PCB 3023 Exam 4 - Form A First and Last Name Student ID # (U Number) A Before beginning this exam, please complete the following instructions: 1) Write your name and U number on the first page of this
BIOH111. o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
BIOH111 o Cell Biology Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 Textbook
10 m Human height 1 m Length of some nerve and muscle cells eye 100 mm (10 cm) Chicken egg aid n 10 mm
 Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
Biology 112 Unit Three Chapter Four 1 Cell Sizes Smallest Bacteria Largest Bird egg Longest Giraffe s Nerve Cell Most Cells Diameter of 0.7µm to 105 µm 2 10 m 1 m 100 mm (10 cm) 10 mm (1 cm) Human height
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP SYNTHESIS (taken from Chapter 18 of Stryer)
 MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP SYNTHESIS (taken from Chapter 18 of Stryer) FREE ENERGY MOST USEFUL THERMODYNAMIC CONCEPT IN BIOCHEMISTRY Living things require an input of free energy for 3 major
MEMBRANE-BOUND ELECTRON TRANSFER AND ATP SYNTHESIS (taken from Chapter 18 of Stryer) FREE ENERGY MOST USEFUL THERMODYNAMIC CONCEPT IN BIOCHEMISTRY Living things require an input of free energy for 3 major
Membranes. Chapter 5
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain. Pavla Balínová
 Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain Pavla Balínová Mitochondria Structure of mitochondria: Outer membrane Inner membrane (folded) Matrix space (mtdna, ribosomes, enzymes of CAC, β-oxidation of FA,
Citric acid cycle and respiratory chain Pavla Balínová Mitochondria Structure of mitochondria: Outer membrane Inner membrane (folded) Matrix space (mtdna, ribosomes, enzymes of CAC, β-oxidation of FA,
f(x) = x R² = RPKM (M8.MXB) f(x) = x E-014 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.
 14 12 f(x) = 1.633186874x - 21.46732234 R² =.995616541 RPKM (M8.MXA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 RPKM (M8.MXB) 14 12 f(x) =.821767782x - 4.192595677497E-14 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.XA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14
14 12 f(x) = 1.633186874x - 21.46732234 R² =.995616541 RPKM (M8.MXA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14 RPKM (M8.MXB) 14 12 f(x) =.821767782x - 4.192595677497E-14 R² = 1 RPKM (M31.XA) 1 8 6 4 2 2 4 6 8 1 12 14
Bio10 Cell Structure SRJC
 3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
3.) Cell Structure and Function Structure of Cell Membranes Fluid mosaic model Mixed composition: Phospholipid bilayer Glycolipids Sterols Proteins Fluid Mosaic Model Phospholipids are not packed tightly
Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membrane Structure. Membranes
 Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Membrane Structure Membranes Chapter 5 The fluid mosaic model of membrane structure contends that membranes consist of: -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted in the lipid bilayer
Quiz #1. BIO200 January 11, point each
 Quiz #1 January 11, 2013 1. The primary amine group of an amino acid has a pka of 10 and the carboxylic acid group of an amino acid has a pka of 2. The side chain of the amino acid alanine is a methyl
Quiz #1 January 11, 2013 1. The primary amine group of an amino acid has a pka of 10 and the carboxylic acid group of an amino acid has a pka of 2. The side chain of the amino acid alanine is a methyl
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140. 1st Midterm Exam October 18 th, Tuesday Material covered: Lectures 1-6 & Reading
 Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam October 18 th, Tuesday Material covered: Lectures 1-6 & Reading Review session October 17 th 3500 Pacitic Hall, 6-8 pm (access code is 127895) Come with questions!
Cellular Neurobiology BIPN140 1st Midterm Exam October 18 th, Tuesday Material covered: Lectures 1-6 & Reading Review session October 17 th 3500 Pacitic Hall, 6-8 pm (access code is 127895) Come with questions!
Supplemental Information:
 SupplementalInformation: Content: FigureS1.AccessibilityoftheL.interrogansproteomebyLC MSanalysis. FigureS2.Functionalannotationoftheidentifiedproteins. FigureS3.DistributionofMS1 featureintensities. FigureS4.ComparisonoftheDDA
SupplementalInformation: Content: FigureS1.AccessibilityoftheL.interrogansproteomebyLC MSanalysis. FigureS2.Functionalannotationoftheidentifiedproteins. FigureS3.DistributionofMS1 featureintensities. FigureS4.ComparisonoftheDDA
BIOCHEMISTRY - CLUTCH REVIEW 6.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: AMINO ACID OXIDATION Urea cycle occurs in liver, removes amino groups from amino acids so they may enter the citric acid cycle 2 nitrogen enter the cycle to ultimately leave
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: AMINO ACID OXIDATION Urea cycle occurs in liver, removes amino groups from amino acids so they may enter the citric acid cycle 2 nitrogen enter the cycle to ultimately leave
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Membranes. Chapter 5. Membrane Structure
 Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Membranes Chapter 5 Membrane Structure Lipid Bilayer model: - double phospholipid layer - Gorter & Grendel: 1925 Fluid Mosaic model: consist of -phospholipids arranged in a bilayer -globular proteins inserted
Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Electron Transport Chain (overview) The NADH and FADH 2, formed during glycolysis, β- oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O 2 to H 2 O. Electron transfer occurs through
Electron Transport Chain (overview) The NADH and FADH 2, formed during glycolysis, β- oxidation and the TCA cycle, give up their electrons to reduce molecular O 2 to H 2 O. Electron transfer occurs through
CELL PART OF THE DAY. Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
 CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
CELL PART OF THE DAY Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function Cell Membrane Cell membranes are composed of two phospholipid layers. Cell membrane is flexible, not rigid The cell membrane has two major functions.
10/13/11. Cell Theory. Cell Structure
 Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Structure Grade 12 Biology Cell Theory All organisms are composed of one or more cells. Cells are the smallest living units of all living organisms. Cells arise only by division of a previously existing
Cell Membranes Valencia college
 6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
Tema 4. Electron Transport. Cap. 4 pages
 Tema 4. Electron Transport Cap. 4 pages 120-145 The generation of energy for growth-related physiological processes in respiring prokaryotes is by coupling the flow of electrons in membranes to the creation
Tema 4. Electron Transport Cap. 4 pages 120-145 The generation of energy for growth-related physiological processes in respiring prokaryotes is by coupling the flow of electrons in membranes to the creation
CELL AND PLASMA MEMBRANE CELL: BASIC UNIT OF LIFE
 CELL AND PLASMA MEMBRANE CELL: BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Approximate elementary composition of the human body (dry weight) Carbon - 50% Oxygen - 20% Hydrogen - 10% Nitrogen - 8.5% Calcium - 4% Phosphorus - 2.5%
CELL AND PLASMA MEMBRANE CELL: BASIC UNIT OF LIFE Approximate elementary composition of the human body (dry weight) Carbon - 50% Oxygen - 20% Hydrogen - 10% Nitrogen - 8.5% Calcium - 4% Phosphorus - 2.5%
2 kinds of secondary active transport Ion and solute move in the same direction = symport Example: Na + and glucose in the kidney 2 kinds of secondary
 Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Transport Across Cell Membranes We ve talked about how cells move solutes across membranes Simple diffusion Channel-mediated diffusion Carrier-mediated
Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life Transport Across Cell Membranes We ve talked about how cells move solutes across membranes Simple diffusion Channel-mediated diffusion Carrier-mediated
Cell Cell
 Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Go to cellsalive.com. Select Interactive Cell Models: Plant and Animal. Fill in the information on Plant and Animal Organelles, then Click on Start the Animation Select Plant or Animal Cell below the box.
Chapter 3: Cells. I. Overview
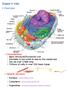 Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
Chapter 3: Cells I. Overview A. Characteristics 1. Basic structural/functional unit 2. Diameter is too small to see by the naked eye 3. Can be over 3 feet long 4. Trillions of cells in over 200 basic types
9/10/2012. The electron transfer system in the inner membrane of mitochondria in plants
 LECT 6. RESPIRATION COMPETENCIES Students, after mastering the materials of Plant Physiology course, should be able to: 1. To explain the process of respiration (the oxidation of substrates particularly
LECT 6. RESPIRATION COMPETENCIES Students, after mastering the materials of Plant Physiology course, should be able to: 1. To explain the process of respiration (the oxidation of substrates particularly
XI CLASS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 12: MINERAL NUTRITION
 XI CLASS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 12: MINERAL NUTRITION Mineral nutrition is the study of source, mode of absorption, distribution and metabolism of various inorganic substances (minerals) by plants for their growth,
XI CLASS BIOLOGY CHAPTER 12: MINERAL NUTRITION Mineral nutrition is the study of source, mode of absorption, distribution and metabolism of various inorganic substances (minerals) by plants for their growth,
SID#: Also give full SID# (w/ 9) on your computer grid sheet (fill in grids under Student Number) BIO 315 Exam I
 SID#: Also give full SID# (w/ 9) on your computer grid sheet (fill in grids under Student Number) BIO 315 Exam I Choose an answer of A,B, C, or D for each of the following Multiple Choice Questions 1-35.
SID#: Also give full SID# (w/ 9) on your computer grid sheet (fill in grids under Student Number) BIO 315 Exam I Choose an answer of A,B, C, or D for each of the following Multiple Choice Questions 1-35.
6. C-type cytochrome, soluble and membrane protein
 185 6. C-type cytochrome, soluble and membrane protein analysis of Rhodobacter sp SW2 and Rhodopseudomonas palustris TIE-1 ABSTRACT The ability to grown on Fe(II) is thought to be a primitive metabolism
185 6. C-type cytochrome, soluble and membrane protein analysis of Rhodobacter sp SW2 and Rhodopseudomonas palustris TIE-1 ABSTRACT The ability to grown on Fe(II) is thought to be a primitive metabolism
Electron Transport and Oxidative. Phosphorylation
 Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron-transport chain electron- Definition: The set of proteins and small molecules involved in the orderly sequence of transfer to oxygen within the
Electron Transport and Oxidative Phosphorylation Electron-transport chain electron- Definition: The set of proteins and small molecules involved in the orderly sequence of transfer to oxygen within the
5/12/2015. Cell Size. Relative Rate of Reaction
 Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
Cell Makeup Chapter 4 The Cell: The Fundamental Unit of Life We previously talked about the cell membrane The cytoplasm is everything inside the membrane, except the nucleus Includes Cytosol = liquid portion
4/12/17. Cells. Cell Structure. Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on. Range of Cell Sizes BIOL 100
 Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
Ch. 2 Cell Structure and Func.on BIOL 100 Cells Fundamental units of life Cell theory All living things are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells come from pre-existing
The Cell and Cellular transport
 Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
Cell theory (1838): The Cell 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells. 2. Cells are the smallest living things, the
6 functions of membrane proteins integral & peripheral proteins Membrane Junctions
 Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Cells Cells are the structural units of all living organisms ranging from unicellular to multicellular organisms. Biochemical activities of cells are dictated by cell shape and specific subcellular structures.
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval
 Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry. The cell: Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell
 Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry Cell Chapt. 10 Cell Biology and Biochemistry The cell: Lipid bilayer membrane Student Learning Outcomes: Describe basic features of typical human cell Integral transport
Module 1. Introduction. Microbial Physiology
 Module 1 Introduction to Microbial Physiology Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGY Page 2 Last time * Discussed the central dogma of molecular biology * Look at, in detail, the process of replication,
Module 1 Introduction to Microbial Physiology Module 1 INTRODUCTION TO MICROBIAL PHYSIOLOGY Page 2 Last time * Discussed the central dogma of molecular biology * Look at, in detail, the process of replication,
PETER PAZMANY CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY Consortium members SEMMELWEIS UNIVERSITY, DIALOG CAMPUS PUBLISHER
 PETER PAZMANY SEMMELWEIS CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
PETER PAZMANY SEMMELWEIS CATHOLIC UNIVERSITY UNIVERSITY Development of Complex Curricula for Molecular Bionics and Infobionics Programs within a consortial* framework** Consortium leader PETER PAZMANY
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush
 number 8 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Mamoon Mohamad Alqtamin Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 0 P a g e Oxidative phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation has 3 major aspects: 1. It involves flow of electrons
number 8 Done by Ali Yaghi Corrected by Mamoon Mohamad Alqtamin Doctor Nafeth Abu Tarboush 0 P a g e Oxidative phosphorylation Oxidative phosphorylation has 3 major aspects: 1. It involves flow of electrons
Chapter 10. 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation)
 Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Chapter 10 이화작용 : 에너지방출과보존 (Catabolism: Energy Release and Conservation) 1 Fueling Processes Respiration 1 Most respiration involves use of an electron transport chain As electrons pass through the electron
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism
 Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Chem*3560 Lecture 29: Membrane Transport and metabolism Insulin controls glucose uptake Adipose tissue and muscles contain a passive glucose transporter GluT4 which takes up glucose from blood. (This is
Cell Biology. AP1 Chapter 3
 Chapter 3: Cell Biology AP1 Chapter 3 1 Cell I. Fxns of a cell the basic unit of all living things (the smallest part of a living organism in our case humans) Shared Characteristics Plasma Membrane Outer
Chapter 3: Cell Biology AP1 Chapter 3 1 Cell I. Fxns of a cell the basic unit of all living things (the smallest part of a living organism in our case humans) Shared Characteristics Plasma Membrane Outer
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis
 Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Cell Physiology Final Exam Fall 2008
 Cell Physiology Final Exam Fall 2008 Guys, The average on the test was 69.9. Before you start reading the right answers please do me a favor and remember till the end of your life that GLUCOSE TRANSPORT
Cell Physiology Final Exam Fall 2008 Guys, The average on the test was 69.9. Before you start reading the right answers please do me a favor and remember till the end of your life that GLUCOSE TRANSPORT
Chapter 4. A Tour of the Cell. Lecture by Richard L. Myers
 Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Lecture by Richard L. Myers Introduction: Cells on the Move
Fall Name Student ID
 Name Student ID PART 1: Matching. Match the organelle to its function (11 points) 1.Proton motive force 2. Fluid Mosiac 3. Oxidative Phosphorylation 4. Pyruvate dehydrogenase 5. Electrochemical Force 6.
Name Student ID PART 1: Matching. Match the organelle to its function (11 points) 1.Proton motive force 2. Fluid Mosiac 3. Oxidative Phosphorylation 4. Pyruvate dehydrogenase 5. Electrochemical Force 6.
Autonomic Nervous System. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Autonomic Nervous System Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Peripheral Nervous System A. Sensory Somatic Nervous System B. Autonomic Nervous System 1. Sympathetic Nervous
Plasma (cell) membrane
 Plasma Membrane 1. Chemical composition of the plasmalemma 2. Models of cell membrane structure 3. Structure and functions of membrane proteins carriers (transporters) channels receptors 4. Cell coat (glycocalyx)
Plasma Membrane 1. Chemical composition of the plasmalemma 2. Models of cell membrane structure 3. Structure and functions of membrane proteins carriers (transporters) channels receptors 4. Cell coat (glycocalyx)
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
GCE BIOLOGY BY4. Cells increase in size / storage of nutrients; (iii) Population grows at an increasing rate / doubles in unit time /
 GCE BIOLOGY BY4 1. (a) (i) 8.0-13.8/13.8 OR 14./13.8; 10.9 / 103%; ( marks for correct answer) (1 mark for calculation if answer incorrect) (ii) Any from: Genes switched on; Synthesis of enzymes / protein
GCE BIOLOGY BY4 1. (a) (i) 8.0-13.8/13.8 OR 14./13.8; 10.9 / 103%; ( marks for correct answer) (1 mark for calculation if answer incorrect) (ii) Any from: Genes switched on; Synthesis of enzymes / protein
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
- Biosignaling: Signal transduction. References: chapter 8 of Lippincots chapter 1 3 of Lehningers
 Basic concepts of Metabolism Metabolism and metabolic pathway Metabolic Map Catabolism Anabolism - Regulation of Metabolism Signals from within the cell (Intracellular) Communication between cells. - Biosignaling:
Basic concepts of Metabolism Metabolism and metabolic pathway Metabolic Map Catabolism Anabolism - Regulation of Metabolism Signals from within the cell (Intracellular) Communication between cells. - Biosignaling:
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al)
 BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
BIO 5099: Molecular Biology for Computer Scientists (et al) Lecture 15: Being a Eukaryote: From DNA to Protein, A Tour of the Eukaryotic Cell. Christiaan van Woudenberg Being A Eukaryote Basic eukaryotes
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function
 Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
Chapter 4: Cell Structure and Function Robert Hooke Fig. 4-2, p.51 The Cell Smallest unit of life Can survive on its own or has potential to do so Is highly organized for metabolism Senses and responds
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
 RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
RNA (Ribonucleic acid) Structure: Similar to that of DNA except: 1- it is single stranded polunucleotide chain. 2- Sugar is ribose 3- Uracil is instead of thymine There are 3 types of RNA: 1- Ribosomal
Electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondrial transport systems
 Electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondrial transport systems JAN ILLNER Respiratory chain & oxidative phosphorylation INTERMEMBRANE SPACE ubiquinone cytochrome c ATPase Production
Electron transport chain, oxidative phosphorylation, mitochondrial transport systems JAN ILLNER Respiratory chain & oxidative phosphorylation INTERMEMBRANE SPACE ubiquinone cytochrome c ATPase Production
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture Series 4 Cellular Membranes Reading Assignments Read Chapter 11 Membrane Structure Review Chapter 21 pages 709-717 717 (Animal( Cell Adhesion) Review Chapter 12 Membrane Transport Review Chapter
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
 Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad
 23 Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad Revision of previous lectures G-proteins coupled receptors mechanism: When a hormone binds to G-protein coupled receptor, GTP
23 Leen Osama, Lujain Hamdan, Osama Mohd, Razi Kittaneh... Faisal Mohammad Revision of previous lectures G-proteins coupled receptors mechanism: When a hormone binds to G-protein coupled receptor, GTP
From zinc homeostasis in a bacterium to a vision for zinc eco-remediation (Sendai, )
 Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg Life Sciences Molecular Microbiology From zinc homeostasis in a bacterium to a vision for zinc eco-remediation (Sendai, 2013-10-28) 4. Brand-new: the ZupT story
Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg Life Sciences Molecular Microbiology From zinc homeostasis in a bacterium to a vision for zinc eco-remediation (Sendai, 2013-10-28) 4. Brand-new: the ZupT story
LECT 6. RESPIRATION COMPETENCIES. Students, after mastering materials of the present lecture, should be able:
 LECT 6. RESPIRATION COMPETENCIES Students, after mastering materials of the present lecture, should be able: 1. 2. To explain the process of respiration (the oxidation of substrates particularly carbohydrates
LECT 6. RESPIRATION COMPETENCIES Students, after mastering materials of the present lecture, should be able: 1. 2. To explain the process of respiration (the oxidation of substrates particularly carbohydrates
CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL
 AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
AP BIOLOGY CText Reference, Campbell v.8, Chapter 6 ACTIVITY1.12 NAME DATE HOUR CELL PARTS TYPICAL ANIMAL CELL ENDOMEMBRANE SYSTEM TYPICAL PLANT CELL QUESTIONS: 1. Write the name of the cell part in the
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Cell Theory states that: 1. All living things are made of cells 2. Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things 3. New cells are produced from
Scantron Instructions
 BIOLOGY 1A MIDTERM # 1 February 17 th, 2012 NAME SECTION # DISCUSSION GSI 1. Sit every other seat and sit by section number. Place all books and paper on the floor. Turn off all phones, pagers, etc. and
BIOLOGY 1A MIDTERM # 1 February 17 th, 2012 NAME SECTION # DISCUSSION GSI 1. Sit every other seat and sit by section number. Place all books and paper on the floor. Turn off all phones, pagers, etc. and
Characterization of the use of wastewater from hydrothermal liquefaction as a nitrogen source by the potential algal biofuel strain Picochlorum sp.
 Characterization of the use of wastewater from hydrothermal liquefaction as a nitrogen source by the potential algal biofuel strain Picochlorum sp. Shuyi Wang, Xinguo Shi, Fatima Foflonker, Debashish Bhattacharya,
Characterization of the use of wastewater from hydrothermal liquefaction as a nitrogen source by the potential algal biofuel strain Picochlorum sp. Shuyi Wang, Xinguo Shi, Fatima Foflonker, Debashish Bhattacharya,
) one consumes in breathing is converted to:, which of the following would be found in the oxidized state?
 MCB 102: Pantea s Sxn Chapter 19 Problem Set Answer Key 1) Page: 690 Ans: E Almost all of the oxygen (O 2 ) one consumes in breathing is converted to: A) acetyl-coa. B) carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). C) carbon
MCB 102: Pantea s Sxn Chapter 19 Problem Set Answer Key 1) Page: 690 Ans: E Almost all of the oxygen (O 2 ) one consumes in breathing is converted to: A) acetyl-coa. B) carbon dioxide (CO 2 ). C) carbon
Photosynthesis: The light Reactions. Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU
 Photosynthesis: The light Reactions Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU When Molecules Absorb or Emit Light, They Change Their Electronic State lowest-energy, or ground state higher-energy, or excited, state extremely
Photosynthesis: The light Reactions Dr. Obaidur Rahman NSU When Molecules Absorb or Emit Light, They Change Their Electronic State lowest-energy, or ground state higher-energy, or excited, state extremely
MITOCHONDRIA. Speaker: 陳玉怜 Mar. 2018
 MITOCHONDRIA Speaker: 陳玉怜 Mar. 2018 1. Structure 2. Genetic system 3. Function: ATP synthesis 4. Dysfunction: cell apoptosis eukaryotic cells mitochondrion mitochondria the specialized membranes inside
MITOCHONDRIA Speaker: 陳玉怜 Mar. 2018 1. Structure 2. Genetic system 3. Function: ATP synthesis 4. Dysfunction: cell apoptosis eukaryotic cells mitochondrion mitochondria the specialized membranes inside
The Cell Organelles. Eukaryotic cell. The plasma membrane separates the cell from the environment. Plasma membrane: a cell s boundary
 Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
Eukaryotic cell The Cell Organelles Enclosed by plasma membrane Subdivided into membrane bound compartments - organelles One of the organelles is membrane bound nucleus Cytoplasm contains supporting matrix
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Structure and Function In Biochemistry
 University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
