RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice
|
|
|
- Jody Gordon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION RNA interference induced hepatotoxicity results from loss of the first synthesized isoform of microrna-122 in mice Paul N Valdmanis, Shuo Gu, Kirk Chu, Lan Jin, Feijie Zhang, Elizabeth M Munding, Yue Zhang, Yong Huang, Huban Kutay, Kalpana Ghoshal, Leszek Lisowski, & Mark A Kay
2 Supplementary Figure 1 shrna reads specifically compete with mir-122 in Ago2- immunoprecipitated (Ago2-IP) small RNA fractions. (a) Mature and precursor raav8-u6- haat-shrnas and raav8-h1-haat-shrnas of various stem lengths in the presence (+) or absence ( ) of Dicer1 in HEK293 cells. (b) Serum haat levels for raavs expressing all combined U6-sh-hAAT-shRNAs or H1-sh-hAAT-shRNAs compared to controls (n = 9 mice per treatment except for controls where n = 3). Data are mean ± s.e.m. (c) Serum alanine transaminase (ALT) levels for each shrna construct. Values and analysis are as in (b). (d) The profile of other small RNAs in the Ago2-IP small RNA seq fraction (n = 3 mice per condition except for control where n = 1). Data are mean ± s.e.m. (e) The proportion of reads mapping to shrnas and micrornas in Ago2-IP small RNA seq fractions of mouse livers (n = 3 mice per condition except for control where n = 1). Data are mean ± s.e.m.
3 Supplementary Figure 2 Analysis of isoform biogenesis for mir-122 and other micrornas. (a) Isoforms of mir-122-5p in normal human and mouse liver samples. (b) Analysis of deposited small RNA deep sequencing data (GEO submission GSE57381) 1 of human liver samples indicates that the most predominant isoform of mir-122-5p is 22-nt in length. Mouse liver controls are from Fig. 2b (n = 4 for human liver, n = 3 for mouse). Data are mean ± s.d. (c) Quantification of reads that arise from mir-122-3p isoforms relative to total mir-122-3p reads in mouse livers receiving U6-sh-hAAT-shRNAs, H1-sh-hAAT-shRNAs or controls (n = 3 mice per condition). Data are mean ± s.e.m. (d) Rank order of the 22-nt to 21-nt ratios for micrornas that express both 22-nt and 21-nt isoforms. The position of mir-122 and other micrornas with similar isoform ratios is noted. (e) Northern blot levels of mir-107 in mouse livers do not have an obvious isoform difference of mature mir-107. (f) Northern blot analysis of mouse liver samples receiving additional U6-shRNA constructs that mimic mir-30 or target the hepatitis C virus (HCV). (g) Northern blot quantification of the mir-122-5p bands from control mouse livers and those expressing various U6-sh-RNAs. Data are mean ± s.e.m.
4 Supplementary Figure 3 The 23 rd nucleotide of mir-122-5p is added post-transcriptionally. (a) Top, mir-122-5p isoform distribution from small RNA seq after delivery of CMV-driven mir- 122 in HEK293 cells. Site directed mutagenesis of the 23 rd nucleotide to a cytosine in transfected plasmids (23U > C) still generates post-transcriptional addition of an adenine or uracil at this position. Bottom, mature mir-122-5p isoforms generated by delivered constructs that include a modified internal residue (green). (b) Small RNA seq reads corresponding to mir p after CMV-driven mir-122 delivery in HEK293 cells. Replicate numbers are the sum of samples from different time points in (a). Data are mean ± s.e.m.
5 Supplementary Figure 4 RNA seq of shrna toxic livers reveals concordant dysregulation of mrna targets. (a) Heatmap clustering of liver RNA seq samples by Fragments Per Kilobase of transcript per Million mapped reads (FPKM) values receiving either no shrnas (Liver), H1-shhAAT-shRNAs or U6-sh-hAAT-shRNAs (n = 2 mice per condition). (b) Heatmap clustering of liver RNA seq FPKM values of five additional mice receiving various U6-shRNAs and one control. (c) Ingenuity pathway analysis pathways most significantly (FDR < 0.001) altered when combining all seven U6-shRNA RNA seq samples relative to five H1-shRNA and controls. (d) RNA seq expression of major urinary protein (Mup) family member levels. (e) Combined foldchange expression of FPKM values of validated targets of mir-122-5p (n = 73) that are derepressed in mouse livers receiving U6-shRNAs. *** P < by two-tailed Student s t test.
6 Supplementary Figure 5 Loss of mir-122 leads to functional metabolic consequences including loss of Aldob expression and intolerance to a fructose rich diet. (a) Electron micrograph image reveals glycogen rich deposits (arrow) and lipid accumulation in mouse livers receiving U6-sh-hAAT-shRNAs. (b) qpcr analysis reveals that Aldoa levels increase in liver samples with reduced mir-122 levels, with a corresponding decrease in Aldob levels, commensurate with an inverse expression pattern of Aldoa and Aldob (and mir-122) in the developing liver 2-4. (c) Correlation between serum ALT levels and percent Aldob mrna expression in the liver of seven mice receiving different U6-driven shrna constructs and one control mouse. Data represent mean ± s.e.m. of 3 independent experiments in triplicate of one
7 individual mouse per condition. (d) Luciferase expression of mouse Aldoa and human ALDOA 3 UTRs and the human ALDOA 3 UTR with site directed mutagenesis of the mir-122-5p binding site. Both the 22-nt and 21-nt isoforms of mir-122-5p target this region equally. (e) Serum ALT activity showed that diets rich in fructose (60%) and glucose (60% with no fructose) corresponded to increases in ALT levels and liver toxicity (n = 5 mice per condition). (f) Mouse body weight changes following fructose rich or glucose rich diets and raav administration (n = 5 mice per condition). (g) Small RNA northern blot of mir-122-5p isoforms in mouse liver samples receiving fructose or glucose rich diets with and without U6-sh-hAAT-shRNAs. Data are mean ± s.e.m.
8 Supplementary Figure 6 Analysis of small RNA sequencing reads derived from shrnas compared to micrornas at later time points post-raav transduction. (a) The proportion of reads from U6-sh-miR-122-shRNAs and micrornas from mouse livers 8 weeks post-raav transduction. Controls are from Fig. 1f (n = 3 mice per condition). Data are mean ± s.e.m. (b) Proportion of reads from shrnas and micrornas from various raav vectors in mir-122 knockout mouse livers 3 weeks post-transduction (n = 2 mice per condition except for U6-sh- HCV where n = 1). (c) Percent of shrna reads at indicated times relative to maximum ALT levels measured over 1 month (n = 3 mice for U6-sh-miR-122 and 2 for sh-haat and sh-hcv). ULN, upper limit normal. The vertical dashed line indicates the maximum tolerated threshold of 12% in normal mouse livers. (d) Percent shrna expression in mouse liver samples 7 days after raav transduction relative to maximum serum ALT levels measured over 1 month (n = 3 mice for U6-sh-miR-122 and WT U6-sh-hAAT, n = 2 for heterozygous (het) mice and n = 1 mouse for the remaining samples). U6-sh-hAAT-25nt and U6-sh-HCV in normal liver are included from Fig. 1d for comparison purposes. Data are mean ± s.e.m. (e) Northern blot probing for mir-122 and haat shrnas in mouse livers at various time points post-raav-shrna transduction; 122ko = Mir122 knockout. (f) Proportion of reads from shrnas and micrornas in livers at indicated time points for various raav-u6-shrna constructs in mice heterozygous for Mir122.
9 Supplementary Figure 7 Model of proposed mechanism. raavs expressing U6-shRNAs compete with the first synthesized 22-nt isoform of mir-122-5p for available RNA-induced silencing complexes (RISC). This may de-repress newly synthesized mrnas that would otherwise be targeted by mir-122 leading to liver toxicity. Other micrornas are largely unaffected in this process.
10 Supplementary Figure 8 mir-122 isoforms after antisense inhibition and mrna profiles in mir-122 knockout mice (a) mir-122-5p isoform proportions in mouse liver after delivery of mir-122 or let-7 tough decoy RNAs (TuD). Data is extracted from GEO accession # GSE In each case, reads were counted for the four most abundant mir-122 isoforms and expressed as a relative percentage. mir-122 TuDs specifically diminished the 23-nt isoform of mir-122-5p leaving the 22-nt isoform relatively unchanged. (b) Mir122 knockout mice retain embryonic gene expression profiles. qrt-pcr quantification of mrna transcripts typically expressed in embryonic but not adult mouse liver (n = 14 for Mir122 knockout, n = 11 for control). *** P < by two-tailed Student s t test.
11 Supplementary Table 1 Top expressing micrornas relative to small hairpin RNA read counts. microrna U6 total average mir shrna mir mir-let-7a mir-let-7c mir-let-7f mir mir-let-7c mir-let-7f mir-let-7b mir-let-7d mmu-mir mir-let-7g mir-29a mir-26b mir mir mir U6 95% CI ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) H1 total average H1 total 95% CI ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) U6 Ago2- IP average U6 Ago2- IP 95% CI ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) H1 Ago2- IP average H1 Ago2- IP 95% CI ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) ( ) Values are presented as normalized reads per million mapped micrornas and shrnas. U6 samples include U6-sh-hAAT-21nt and U6-sh-hAAT-25nt (n = 6); H1 samples include all H1- sh-haat samples (n = 9). IP, immunoprecipitated; CI, confidence interval.
12 Supplementary Table 6 Serum lipid and glucose levels for mice receiving fructose or gluctose rich diets with or without U6-sh-hAAT-25nt shrnas. low fructose + U6- shrna high fructose + U6- shrna Chow + U6-shmiR-30 Chow + U6- shhaat- Test Referenc e range Units low fructose high fructose con Glucose mg / dl Cholesterol mg / dl Triglycerides mg / dl HDL mg / dl LDL mg / dl HDL : LDL BUN mg / dl Creatinine mg / dl Total Protein g / dl HDL, high-density lipoprotein; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; con, control.
13 Supplementary Table 7 List of primers used for shrna cloning, luciferase cloning and small RNA sequence alignment. sh-haat-19nt-s sh-haat-19nt-a sh-haat-21nt-s sh-haat-21nt-a sh-haat-25nt-s sh-haat-25nt-a sh-mir-122-s sh-mir-122-a sh-hcv-21-s sh-hcv-21-a sh-hcv-29-s sh-hcv-29-a sh-hcv-29b-s sh-hcv-29b-a sh-mir s sh-mir a sh-mir s sh-mir a sh- mir-30-24b-s sh-mir-30-24b-a CACCGAAGCGTTTAGGCATGTTTTCAAGAGAAACATGCCT AAACGCTTC AAAAGAAGCGTTTAGGCATGTTTCTCTTGAAAACATGCCT AAACGCTTC CACCGAAGCGTTTAGGCATGTTTAATCAAGAGTTAAACAT GCCTAAACGCTTC AAAAGAAGCGTTTAGGCATGTTTAACTCTTGATTAAACAT GCCTAAACGCTTC CACCGAAGCGTTTAGGCATGTTTAACATCTCAAGAGGATG TTAAACATGCCTAAACGCTTC AAAAGAAGCGTTTAGGCATGTTTAACATCCTCTTGAGATG TTAAACATGCCTAAACGCTTC CACCGAACGCCATTATCACACTCTATACCTGACCCATATG GAGTGTGAGAATGGTGTTTTTTGTAC AAAAACACCATTCTCACACTCCATATGGGTCAGGTATAGA GTGTGATAATGGCGTTC GATCGACTTATCCAGTTGGTTCACTCCTGACCCAAGTGAAC CAACTGGATAAGTCTTTTTGTAC AAAAGACTTATCCAGTTGGTTCACTTGGGTCAGGAGTGAA CCAACTGGATAAGTC GATCCACCGACTTATCCAGTTGGTTCACTGATGCTACCCTG ACCCAGTAGCATCAGTGAACCAACTGGATAAGTCTTTTTG TAC AAAAGACTTATCCAGTTGGTTCACTGATGCTACTGGGTCA GGGTAGCATCAGTGAACCAACTGGATAAGTC GATCCACCGACTTATCCAGTTGGTTCACTCCTGCTACCCTG ACCCAGTAGCCCAAGTGAACCAACTGGATAAGTCTTTTTG TAC AAAAGACTTATCCAGTTGGTTCACTTGGGCTACTGGGTCA GGGTAGCAGGAGTGAACCAACTGGATAAGTC GATCCACCGCTGCAAACATCCGACTGAACCCTGACCCAGT TCAGTCGGATGTTTGCAGCTTTTTGTAC AAAAGCTGCAAACATCCGACTGAACTGGGTCAGGGTTCAG TCGGATGTTTGCAGC GATCCACCGCTGCAAACATCCGACTGAAAGCTCCTGACCC AAGCTTTCAGTCGGATGTTTGCAGCTTTTTGTAC AAAAGCTGCAAACATCCGACTGAAAGCTTGGGTCAGGAGC TTTCAGTCGGATGTTTGCAGC GATCCACCGCTGCAAACATGCGACTGAAAGCTCCTGACCC AAGCTTTCAGTCGGATGTTTGCAGCTTTTTGTAC AAAAGCTGCAAACATCCGACTGAAAGCTTGGGTCAGGAGC TTTCAGTCGCATGTTTGCAGC
14 hsaldoa UTRpsiF hsaldoa UTRpsiR hsaldoa UTRmutF hsaldoa UTRmutR mmaldoa UTRpsiF mmaldoa UTRpsiR CTCGAGGCGGAGGTGTTCCCAGGCTGCCCCCAACACTCCA GGCCCTGCCCCCTCCCACTCTTGAAGA ACTAGTCTTCAAGAGTGGGAGGGGGCAGGGCCTGGAGTGT TGGGGGCAGCCTGGGAACACCTCCGCC CTCGAGGCGGAGGTGTTCCCAGGCTGCCCCCAAACCTGGA GGCCCTGCCCCCTCCCACTCTTGAAGA ACTAGTCTTCAAGAGTGGGAGGGGGCAGGGCCTCCAGGTT TGGGGGCAGCCTGGGAACACCTCCGCC CTCGAGCCAGAGCTGAACTAAGGCTGCTCCATCAACACTC CAGGCCCCTGCCTACCCACTTGCTATA ACTAGTATAGCAAGTGGGTAGGCAGGGGCCTGGAGTGTTG ATGGAGCAGCCTTAGTTCAGCTCTGGC 5 to 3 direction for each; S = sense, A = antisense. Mismatches in the mir-122 binding site of human ALDOA are underlined,
15 SUPPLEMENTARY REFERENCES 1. Selitsky, S.R., et al. Small trna-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than micrornas in chronic hepatitis B and C. Scientific reports 5, 7675 (2015). 2. Chang, J., et al. mir-122, a mammalian liver-specific microrna, is processed from hcr mrna and may downregulate the high affinity cationic amino acid transporter CAT-1. RNA biology 1, (2004). 3. Hommes, F.A. & Draisma, M.I. The development of L- and M-type aldolases in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 222, (1970). 4. Numazaki, M., Tsutsumi, K., Tsutsumi, R. & Ishikawa, K. Expression of aldolase isozyme mrnas in fetal rat liver. European journal of biochemistry / FEBS 142, (1984). 5. Xie, J., et al. Long-term, efficient inhibition of microrna function in mice using raav vectors. Nature methods 9, (2012).
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3731
 Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Supplementary Figure 1 Circadian profiles of Adarb1 transcript and ADARB1 protein in mouse tissues. (a) Overlap of rhythmic transcripts identified in the previous transcriptome analyses. The mouse liver
Nature Structural & Molecular Biology: doi: /nsmb Supplementary Figure 1. Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus.
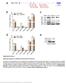 Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Figure 1 Differential expression of mirnas from the pri-mir-17-92a locus. (a) The mir-17-92a expression unit in the third intron of the host mir-17hg transcript. (b,c) Impact of knockdown
Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent Protein.
 prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
prfp-vector RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 prfp-mir-124 mir-93/124 RFP Exon1 Intron RFP Exon2 Untransfected prfp-vector prfp-mir-93 prfp-mir-124 Supplementary Fig. 1. Delivery of mirnas via Red Fluorescent
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO
 Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary Figure S1. Effect of Glucose on Energy Balance in WT and KHK A/C KO Mice. WT mice and KHK-A/C KO mice were provided drinking water containing 10% glucose or tap water with normal chow ad
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
Supplementary Figure 1 Asymmetrical function of 5p and 3p arms of mir-181 and mir-30 families and mir-142 and mir-154. (a) Control experiments using mirna sensor vector and empty pri-mirna overexpression
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/406/ra126/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The microrna mir-485 targets host and influenza virus transcripts to regulate antiviral immunity and restrict viral
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/406/ra126/dc1 Supplementary Materials for The microrna mir-485 targets host and influenza virus transcripts to regulate antiviral immunity and restrict viral
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons
 Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplemental Material mir-7a regulation of Pax6 in neural stem cells controls the spatial origin of forebrain dopaminergic neurons Antoine de Chevigny, Nathalie Coré, Philipp Follert, Marion Gaudin, Pascal
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original
 Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
Supplementary Fig. 1 eif6 +/- mice show a reduction in white adipose tissue, blood lipids and normal glycogen synthesis. The cohort of the original phenotypic screening was n=40. For specific tests, the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 -. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
-. -. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION DOI: 1.1/ncb86 a WAT-1 WAT- BAT-1 BAT- sk-muscle-1 sk-muscle- mir-133b mir-133a mir-6 mir-378 mir-1 mir-85 mir-378 mir-6a mir-18 mir-133a mir- mir- mir-341 mir-196a mir-17
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients.
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figures Figure S1. Reduction in glomerular mir-146a levels correlate with progression to higher albuminuria in diabetic patients. Figure S2. Expression level of podocyte
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
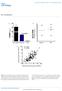 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2210 b. ICAM1 ng ml -1 P = 0.0001 Small RNA (15-30nts) ng ml -1 Cell Lysate Exosome HDL Plasma HDL Normal Human HDL mirnas R = 0.45 P < 0.0001 Normal Human Exosome mirnas Figure S1. Characterization
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus
 Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Fig. 1. GPRC5A post-transcriptionally down-regulates EGFR expression. (a) Plot of the changes in steady state mrna levels versus changes in corresponding proteins between wild type and Gprc5a-/-
Supplementary Information. MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory
 Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Supplementary Information MicroRNA-33b knock-in mice for an intron of sterol regulatory element-binding factor 1 (Srebf1) exhibit reduced HDL-C in vivo Takahiro Horie, Tomohiro Nishino, Osamu Baba, Yasuhide
Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD! Assistant Member! Department of Thoracic Surgery! Roswell Park Cancer Institute!
 Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Thoracic Surgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute MicroRNA biology, techniques and applications History Biogenesis Nomenclature Tissue specificity Mechanisms
Santosh Patnaik, MD, PhD Assistant Member Department of Thoracic Surgery Roswell Park Cancer Institute MicroRNA biology, techniques and applications History Biogenesis Nomenclature Tissue specificity Mechanisms
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1 IL-27 IL
 Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Tim-3 Supplementary Figure 1 Tc0 49.5 0.6 Tc1 63.5 0.84 Un 49.8 0.16 35.5 0.16 10 4 61.2 5.53 10 3 64.5 5.66 10 2 10 1 10 0 31 2.22 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 IL-10 28.2 1.69 IL-27 Supplementary Figure 1.
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation
 Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1 ITGB1 and ITGA11 increase with evidence for heterodimers following HSC activation. (a) Time course of rat HSC activation indicated by the detection of -SMA and COL1 (log scale).
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 a Location of GUUUCA motif relative to RNA position 4e+05 3e+05 Reads 2e+05 1e+05 0e+00 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 Distance upstream b 1: Egg 2: L3 3: Adult 4: HES 4e+05 3e+05 2e+05 start
Supplementary Figure 1 a Location of GUUUCA motif relative to RNA position 4e+05 3e+05 Reads 2e+05 1e+05 0e+00 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 Distance upstream b 1: Egg 2: L3 3: Adult 4: HES 4e+05 3e+05 2e+05 start
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers
 Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Heatmap of GO terms for differentially expressed genes. The terms were hierarchically clustered using the GO term enrichment beta. Darker red, higher positive
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
Supplementary Materials and Methods Whole Mount X-Gal Staining Whole tissues were collected, rinsed with PBS and fixed with 4% PFA. Tissues were then rinsed in rinse buffer (100 mm Sodium Phosphate ph
he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003)
 MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
MicroRNAs: Genomics, Biogenesis, Mechanism, and Function (D. Bartel Cell 2004) he micrornas of Caenorhabditis elegans (Lim et al. Genes & Development 2003) Vertebrate MicroRNA Genes (Lim et al. Science
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin
 Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Supplementary Figure 1: Additional metabolic parameters of obesity mouse models and controls. (a) Body weight, (b) blood glucose and (c) insulin resistance index of homeostatic model assessment (HOMA IR)
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges
 Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Circular RNAs (circrnas) act a stable mirna sponges cernas compete for mirnas Ancestal mrna (+3 UTR) Pseudogene RNA (+3 UTR homolgy region) The model holds true for all RNAs that share a mirna binding
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained
 Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Supplementary Figure 1. Confocal immunofluorescence showing mitochondrial translocation of Drp1. Cardiomyocytes treated with H 2 O 2 were prestained with MitoTracker (red), then were immunostained with
Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions. 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19
 Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19 1 MicroRNA biogenesis 1. Pri mirna: primary mirna 2. Drosha: RNaseIII 3. DCR 1: Dicer 1 RNaseIII
Cellular MicroRNA and P Bodies Modulate Host-HIV-1 Interactions 指導教授 : 張麗冠博士 演講者 : 黃柄翰 Date: 2009/10/19 1 MicroRNA biogenesis 1. Pri mirna: primary mirna 2. Drosha: RNaseIII 3. DCR 1: Dicer 1 RNaseIII
The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism
 Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
Supplementary Information The antiparasitic drug ivermectin is a novel FXR ligand that regulates metabolism Address correspondence to Yong Li (yongli@xmu.edu.cn, Tel: 86-592-218151) GW464 CDCA Supplementary
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence of cross-kingdom regulation by microrna
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:107-126. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cell Research (2012) 22:107-126. 2012 IBCB, SIBS, CAS All rights reserved 1001-0602/12 $ 32.00 www.nature.com/cr npg Exogenous plant MIR168a specifically targets mammalian LDLRAP1: evidence
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Cross species analysis of genomics data. Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets
 02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
02-716 Cross species analysis of genomics data Computational Prediction of mirnas and their targets Outline Introduction Brief history mirna Biogenesis Why Computational Methods? Computational Methods
Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination
 Yoon et al, page Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination Je-Hyun Yoon,, Kotb Abdelmohsen, Jiyoung Kim, Xiaoling Yang, Jennifer L. Martindale, Kumiko Tominaga-Yamanaka,
Yoon et al, page Scaffold function of long noncoding RNA HOTAIR in protein ubiquitination Je-Hyun Yoon,, Kotb Abdelmohsen, Jiyoung Kim, Xiaoling Yang, Jennifer L. Martindale, Kumiko Tominaga-Yamanaka,
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Ct=28.4 WAT 92.6% Hepatic CE (mg/g) P=3.6x10-08 Plasma Cholesterol (mg/dl)
 a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/7/310/ra11/dc1 Supplementary Materials for STAT3 Induction of mir-146b Forms a Feedback Loop to Inhibit the NF-κB to IL-6 Signaling Axis and STAT3-Driven Cancer
ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 1 ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Small trna-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than micrornas in chronic hepatitis B and C Sara R. Selitsky 1-3, Jeanette Baran-Gale 1,2, Masao Honda 4, Daisuke
1 ONLINE SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION Small trna-derived RNAs are increased and more abundant than micrornas in chronic hepatitis B and C Sara R. Selitsky 1-3, Jeanette Baran-Gale 1,2, Masao Honda 4, Daisuke
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein
 Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
Supplementary Figure 1. AdipoR1 silencing and overexpression controls. (a) Representative blots (upper and lower panels) showing the AdipoR1 protein content relative to GAPDH in two independent experiments.
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær 2013
 MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
MicroRNA in Cancer Karen Dybkær RNA Ribonucleic acid Types -Coding: messenger RNA (mrna) coding for proteins -Non-coding regulating protein formation Ribosomal RNA (rrna) Transfer RNA (trna) Small nuclear
genomics for systems biology / ISB2020 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq)
 RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) Module Outline MO 13-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 1 WE 15-Mar-2017 RNA sequencing: Introduction 2 MO 20-Mar-2017 Paper: PMID 25954002: Human genomics. The human transcriptome
Review and Public RAC Discussion of Protocol #
 Review and Public RAC Discussion of Protocol #0508 725 A phase I pilot study of safety and feasibility of stem cell therapy for AIDS lymphoma using stem cells treated with a lentivirus vector encoding
Review and Public RAC Discussion of Protocol #0508 725 A phase I pilot study of safety and feasibility of stem cell therapy for AIDS lymphoma using stem cells treated with a lentivirus vector encoding
Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2)
 Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplemental Methods Cells and reagents. Synaptopodin knockdown (1) and dynamin knockdown (2) podocytes were cultured as described previously. Staurosporine, angiotensin II and actinomycin D were all obtained
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Supplementary Figure 1 A B mir-141, human cell lines mir-2c, human cell lines mir-141, hepatocytes mir-2c, hepatocytes Relative RNA.1.8.6.4.2 Relative RNA.3.2.1 Relative RNA 1.5 1..5 Relative RNA 2. 1.5
Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples.
 Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
Supplementary files Table S1. Relative abundance of AGO1/4 proteins in different organs. Table S2. Summary of smrna datasets from various samples. Table S3. Specificity of AGO1- and AGO4-preferred 24-nt
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing. Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM
 MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
MicroRNAs, RNA Modifications, RNA Editing Bora E. Baysal MD, PhD Oncology for Scientists Lecture Tue, Oct 17, 2017, 3:30 PM - 5:00 PM Expanding world of RNAs mrna, messenger RNA (~20,000) trna, transfer
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2211 a! mir-143! b! mir-103/107! let-7a! mir-144! mir-122a! mir-126-3p! mir-194! mir-27a! mir-30c! Figure S1 Northern blot analysis of mir-143 expression dependent on feeding conditions.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis
 Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Review Article MicroRNA and Male Infertility: A Potential for Diagnosis * Abstract MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small non-coding single stranded RNA molecules that are physiologically produced in eukaryotic
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Supplementary information High fat diet-induced changes of mouse hepatic transcription and enhancer activity can be reversed by subsequent weight loss Majken Siersbæk, Lyuba Varticovski, Shutong Yang,
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Assessment of sample purity and quality.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Figure 1 Assessment of sample purity and quality. (a) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of formaldehyde-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections from a human testis biopsy collected concurrently with
Supplementary Table 2. Plasma lipid profiles in wild type and mutant female mice submitted to a HFD for 12 weeks wt ERα -/- AF-1 0 AF-2 0
 Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplementary Table 1. List of specific primers used for gene expression analysis. Genes Primer forward Primer reverse Hprt GCAGTACAGCCCCAAAATGG AACAAAGTCTGGCCTGTATCCA Srebp-1c GGAAGCTGTCGGGGTAGCGTC CATGTCTTCAAATGTGCAATCCAT
Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells.
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE AND TABLE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1. Expression of Cirbp mrna in mouse tissues and NIH3T3 cells. A) Cirbp mrna expression levels in various mouse tissues collected around the clock
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
Supplementary Figure 1 Characteristics of SEs in T reg and T conv cells. (a) Patterns of indicated transcription factor-binding at SEs and surrounding regions in T reg and T conv cells. Average normalized
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supp. Fig. 1. Autoimmunity. Tolerance APC APC. T cell. T cell. doi: /nature06253 ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 TCR CD28
 Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
Supp. Fig. 1 a APC b APC ICOS ICOS TCR CD28 mir P TCR CD28 P T cell Tolerance Roquin WT SG Icos mrna T cell Autoimmunity Roquin M199R SG Icos mrna www.nature.com/nature 1 Supp. Fig. 2 CD4 + CD44 low CD4
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Supplementary Figure 1 Id2 and Id3 define polyclonal T H 1 and T FH cell subsets. Id2 YFP/+ (a) or Id3 GFP/+ (b) mice were analyzed 7 days after LCMV infection. T H 1 (SLAM + CXCR5 or CXCR5 PD-1 ), T FH
Supplementary Material
 Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Supplementary Material Summary: The supplementary information includes 1 table (Table S1) and 4 figures (Figure S1 to S4). Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1 RTL-bearing nude mouse model. (A) Tumor
Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Figure 1 Lentiviral Delivery of Combinatorial mirna Expression Constructs Provides Efficient Target Gene Repression. a, Design for lentiviral combinatorial mirna expression and sensor constructs.
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/2/1/ra81/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Delivery of MicroRNA-126 by Apoptotic Bodies Induces CXCL12- Dependent Vascular Protection Alma Zernecke,* Kiril Bidzhekov,
Development of an RNA Interference Therapeutic Targeting Angiopoietin-Like Protein 3 for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia
 Development of an RNA Interference Therapeutic Targeting Angiopoietin-Like Protein 3 for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia November 12 th, 2018 So C. Wong Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Inc. Disclosures All authors
Development of an RNA Interference Therapeutic Targeting Angiopoietin-Like Protein 3 for Treatment of Hyperlipidemia November 12 th, 2018 So C. Wong Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals Inc. Disclosures All authors
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease
 Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Utility of Circulating micrornas in Cardiovascular Disease Pil-Ki Min, MD, PhD Cardiology Division, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine Introduction Biology of micrornas Circulating
Transcriptome-wide analysis of microrna expression in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae
 Biryukova et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:557 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Transcriptome-wide analysis of microrna expression in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae Inna Biryukova 1*, Tao Ye 2 and Elena
Biryukova et al. BMC Genomics 2014, 15:557 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Transcriptome-wide analysis of microrna expression in the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae Inna Biryukova 1*, Tao Ye 2 and Elena
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 Supplementary Figure 1. SC35M polymerase activity in the presence of Bat or SC35M NP encoded from the phw2000 rescue plasmid. HEK293T
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Over the past decade, it has become progressively more
 Reviews Methodological Reviews discuss methods that are of broad interest to the community of cardiovascular investigators and that enable a better understanding of cardiovascular biology, particularly
Reviews Methodological Reviews discuss methods that are of broad interest to the community of cardiovascular investigators and that enable a better understanding of cardiovascular biology, particularly
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with
 Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Supplementary Figure 1. Repression of hepcidin expression in the liver of mice treated with DMN Immunohistochemistry for hepcidin and H&E staining (left). qrt-pcr assays for hepcidin in the liver (right).
Milk micro-rna information and lactation
 Christophe Lefèvre, BioDeakin,. Deakin University, Geelong VIC Australia Milk micro-rna information and lactation New Signals in milk? - Markers of milk and lactation status? - Signal infant development?
Christophe Lefèvre, BioDeakin,. Deakin University, Geelong VIC Australia Milk micro-rna information and lactation New Signals in milk? - Markers of milk and lactation status? - Signal infant development?
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis. Midbrain Forebrain/ Forebrain/ Hindbrain Spinal cord Hindbrain Hindbrain
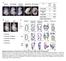 A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
A Normal Exencephaly Craniora- Spina bifida Microcephaly chischisis NTD Number of embryos % among NTD Embryos Exencephaly 52 74.3% Craniorachischisis 6 8.6% Spina bifida 5 7.1% Microcephaly 7 1% B Normal
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
Supplementary Figure 1 Huwe1 has high expression in HSCs and is necessary for quiescence. (a) Heat map visualizing expression of genes with a known function in ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis (KEGG: Ubiquitin
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Information Astrocytes regulate adult hippocampal neurogenesis through ephrin-b signaling Randolph S. Ashton, Anthony Conway, Chinmay Pangarkar, Jamie Bergen, Kwang-Il Lim, Priya Shah, Mina
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Confirmation of Dnmt1 conditional knockout out mice. a, Representative images of sorted stem (Lin - CD49f high CD24 + ), luminal (Lin - CD49f low CD24 + )
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.
 Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
Supplemental Figure S1. PLAG1 kidneys contain fewer glomeruli (A) Quantitative PCR for Igf2 and PLAG1 in whole kidneys taken from mice at E15.5, E18.5, P4, and P8. Values shown are means from four technical
7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans.
 Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Supplementary Figure 1 7SK ChIRP-seq is specifically RNA dependent and conserved between mice and humans. Regions targeted by the Even and Odd ChIRP probes mapped to a secondary structure model 56 of the
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004
 Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Molecular Biology (BIOL 4320) Exam #2 May 3, 2004 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses after the question number. Good
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni Supplementary Figure 1. Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
Supplementary Figure 1 Gene expression profile of CD4 + T cells and CTL responses in Bcl6-deficient mice. (a) Gene expression profile in the resting CD4 + T cells were analyzed by an Affymetrix microarray
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression
 omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
omiras: MicroRNA regulation of gene expression Sören Müller, Goethe University of Frankfurt am Main Molecular Bioinformatics Group, Institute of Computer Science Plant Molecular Biology Group, Institute
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1 Supplementary Figure 1, Adult hippocampal QNPs and TAPs uniformly express REST a-b) Confocal images of adult hippocampal mouse sections showing GFAP (green), Sox2 (red), and REST
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice
 Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice Fasted Refed GFP OGT GFP OGT Liver G6P (mmol/g) 0.03±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.60±0.04 0.42±0.10 A TGs (mg/g of liver) 20.08±5.17 16.29±0.8
Supplementary Table 1. Metabolic parameters in GFP and OGT-treated mice Fasted Refed GFP OGT GFP OGT Liver G6P (mmol/g) 0.03±0.01 0.04±0.02 0.60±0.04 0.42±0.10 A TGs (mg/g of liver) 20.08±5.17 16.29±0.8
Supplementary Figure 1
 Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
Combination index (CI) Supplementary Figure 1 2. 1.5 1. Ishikawa AN3CA Nou-1 Hec-18.5...2.4.6.8 1. Fraction affected (Fa) Supplementary Figure 1. The synergistic effect of PARP inhibitor and PI3K inhibitor
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT ACTB AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT LCOR
 Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Table S1. Primer sequences used for qrt-pcr. ACTB LCOR KLF6 CTBP1 CDKN1A CDH1 ATF3 PLAU MMP9 TFPI2 CACCATTGGCAATGAGCGGTTC AGGTCTTTGCGGATGTCCACGT AAGTCCATGTGCTGGCAGCACT ATCACCACTCCGAAGTCCGTCT CGGCTGCAGGAAAGTTTACA
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Figure 1 YAP negatively regulates IFN- signaling. (a) Immunoblot analysis of Yap knockdown efficiency with sh-yap (#1 to #4 independent constructs) in Raw264.7 cells. (b) IFN- -Luc and PRDs
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH
 EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
EPIGENETIC RE-EXPRESSION OF HIF-2α SUPPRESSES SOFT TISSUE SARCOMA GROWTH Supplementary Figure 1. Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of KP and KPH2 autochthonous UPS tumors. a) Genotyping of KPH2
High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases
 https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
https://helda.helsinki.fi High AU content: a signature of upregulated mirna in cardiac diseases Gupta, Richa 2010-09-20 Gupta, R, Soni, N, Patnaik, P, Sood, I, Singh, R, Rawal, K & Rani, V 2010, ' High
Supplementary methods:
 Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary methods: Primers sequences used in real-time PCR analyses: β-actin F: GACCTCTATGCCAACACAGT β-actin [11] R: AGTACTTGCGCTCAGGAGGA MMP13 F: TTCTGGTCTTCTGGCACACGCTTT MMP13 R: CCAAGCTCATGGGCAGCAACAATA
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 Characterization of stable expression of GlucB and sshbira in the CT26 cell line (a) Live cell imaging of stable CT26 cells expressing green fluorescent protein
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated
 Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
Supplementary Figure 1 (Related with Figure 4). Molecular consequences of Eed deletion. (a) ChIP analysis identifies 3925 genes that are associated with the H3K27me3 mark in chondrocytes (see Table S1,
MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy
 Lidia Park Genomics and Medicine November 23, 2008 MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy When Victor Ambros, Rosalind Lee, and Rhonda Feinbaum published the first finding of a microrna,
Lidia Park Genomics and Medicine November 23, 2008 MicroRNAs: Regulatory Function and Potential for Gene Therapy When Victor Ambros, Rosalind Lee, and Rhonda Feinbaum published the first finding of a microrna,
A phase I pilot study of safety and feasibility of stem cell therapy for AIDS lymphoma using stem cells treated with a lentivirus vector encoding
 A phase I pilot study of safety and feasibility of stem cell therapy for AIDS lymphoma using stem cells treated with a lentivirus vector encoding multiple anti-hiv RNAs John A. Zaia, M.D. John J. Rossi,
A phase I pilot study of safety and feasibility of stem cell therapy for AIDS lymphoma using stem cells treated with a lentivirus vector encoding multiple anti-hiv RNAs John A. Zaia, M.D. John J. Rossi,
