Inhibition of Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Snail Targeting Artificial MicroRNA Interference
|
|
|
- Rosamond West
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inhibition of Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells with a Snail Targeting MicroRNA RESEARCH COMMUNICATION Inhibition of Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Snail Targeting Artificial MicroRNA Interference Hui-Min Guo, Xiao-Qi Zhang, Chun-Hong Xu, Xiao-Ping Zou* Abstract The zinc-finger factor Snai1 plays an important role in the down-regulation of E-cadherin expression and in the induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) during cancer progression. In gastric cancer tissues, we noted that Snail is abnormally high expressed and is remarkably associated with the lymph node metastasis. Using a plasmid containing newly synthesized artificial microrna (amirna), we transfected gastric cancer cells to block Snail expression. Both Snail protein and mrna levels were significantly decreased in stably transfected cells, while protein and mrna expression of E-cadherin was up-regulated. In addition, migration and invasion potential were significantly decreased after knockdown of Snail. Keywords: Snail - E-cadherin - artificial microrna - epithelial-mesenchymal transition - gastric cancer Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev, 12, Introduction Gastric cancer is the second deadliest malignant neoplasm, with a 5-year survival rate of approximately 20% (Jemal et al., 2004). Invasion and metastasis of the cancer were the primary factors affecting the survival rate of patients (Hippo et al., 2001). Yet, the biochemical mechanisms that regulate invasion and metastasis remain poorly understood. Local invasion is the most important event prior to tumor metastasis. In the process of invasion, tumor cells undergo the mutation from epithelial to mesenchymal phenotype, which is termed as epithelialmesenchymal transition (EMT), thus increasing cell mobility and promoting tumor cell invasion (Larue et al., 2005; Moreno-Bueno et al., 2008; Olmeda et al., 2008). Since the discovery of EMT in tumors, much progress has been made towards understanding the mechanisms by which it occurs and towards the identification of factors involved in this process. E-cadherin plays an important role in cell to cell adhesion (Nurismah et al., 2008; Stepniak et al., 2009), and the decrease of E-cadherin expression is considered as the hallmark of EMT (Thiery et al., 2002). In the past decades, the molecular mechanisms of the down-regulation of E-cadherin expression during tumor progression have been well delineated (Christofori et al., 1999; Batlle et al., 2000), involving both genetic and epigenetic alternations, such as hypermethylation of E-cadherin promoter, chromosome remodeling, gene mutation and transcription repression. Among the alternations mentioned above, transcription repression has recently been proved to be the predominant mechanism in different human cancer cell lines. The zinc-finger factor Snai1, a key member of the Snail superfamily of transcriptional repressor, plays an important role in the down-regulation of E-cadherin expression and in the induction of EMT during embryogenesis and cancer progression (Batlle et al., 2000). Till now, numerous studies on the function of Snai1 in regulating E-cadherin expression have been published. Nevertheless, most of these studies have focused on its function in colon cancer (Pena et al., 2009), breast cancer (Van et al., 2011), and ovarian cancer (Blechschmidt et al., 2008). As for gastric cancer, little information regarding the role and mechanism of Snail in the process of metastasis of gastric cancer has been reported. RNA interference has become an efficient approach to study the gene function in past years. Small interfering RNAs (sirnas) and micrornas (mirnas) are two main types of small RNAs applied in RNA interference (Ossowski et al., 2008). The sirna is released from a double-stranded RNA by RNaseIII-like enzymes, whereas the mirna is released from a definite mirna precursor by Dicer, in forms of 21-nucleotide RNA. By contrast with sirna, mirna could specifically bind target gene in both transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation without off-target effects (Van et al., 2008). Artifical mirnas (amirna), which was first used in human cell lines (Zeng et al., 2002) and later in Arabidopsis (Chung et al., 2006), was developed on the basis of endogenous mirna. The efficiency of amirna in blocking the gene expression has been well supported by previous studies. In the current study, we observed the expression of the transcription factor Snail and E-cadherin in the gastric cancer tissues, as well as in the surrounding normal Department of Gastroenterology, the Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, China *For correspondence: zouxiaoping795@hotmail.com Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12,
2 Hui-Min Guo et al Table 1. Sequences of Designed Oligonucleotides Oligo the sequence of DNA Single-Stranded oligomerization (5 to 3 ) MR135-1-F TGCTGTGGATTAGAGTCCTGCAGCTCGTTTTGGCCACTGACTGACGAGCTGCAACTCTAATCCA MR135-1-R CCTGTGGATTAGAGTTGCAGCTCGTCAGTCAGTGGCCAAAACGAGCTGCAGGACTCTAATCCAC MR135-2-F TGCTGAGGACAGAGTCCCAGATGAGCGTTTTGGCCACTGACTGACGCTCATCTGACTCTGTCCT MR135-2-R CCTGAGGACAGAGTCAGATGAGCGTCAGTCAGTGGCCAAAACGCTCATCTGGGACTCTGTCCTC MR135-3-F TGCTGAGAAGGTCCGAGCACACGCCTGTTTTGGCCACTGACTGACAGGCGTGTTCGGACCTTCT MR135-3-R CCTGAGAAGGTCCGAACACGCCTGTCAGTCAGTGGCCAAAACAGGCGTGTGCTCGGACCTTCTC MR135-4-F TGCTGTGAGCAGCCGGACTCTTGGTGGTTTTGGCCACTGACTGACCACCAAGACCGGCTGCTCA MR135-4-R CCTGTGAGCAGCCGGTCTTGGTGGTCAGTCAGTGGCCAAAACCACCAAGAGTCCGGCTGCTCAC Negative-F tgctgaaatgtactgcgcgtggagacgttttggccactgactgacgtctccacgcagtacattt Negative-R cctgaaatgtactgcgtggagacgtcagtcagtggccaaaacgtctccacgcgcagtacatttc gastric mucosa. Using the newly developed amirna, we generated a stably transfected cell line SGC amirna to investigate the relationship between Snail and E-cadherin in vitro. In addition, whether knockdown of Snail could efficiently suppress the invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer cells was also investigated. Materials and Methods Patients and samples Under the approval of the local ethics committee, a total of 212 patients from our center, who had undergone surgery for newly diagnosed gastric cancer between 2008 and 2010, were retrospectively reviewed. The informed consent was obtained from each patient. Samples of the primary gastric cancer tissues and the surrounding normal gastric mucosa were obtained in the surgery and then paraffin-embedded. According to Lauren s classification, all the samples were histologically verified by two experienced pathologists. The inclusion criteria were as follows: being primary tumor; having not received any therapy prior to surgery; being of diffuse-type gastric cancer. 74 patients met the criteria and were included in the study. There were 45 males and 29 females. The age ranged from 30 to 68 years old, averaged 58.2±5.7. Paraffin-embedded samples were immunohistochemically analyzed to detect the expression of Snail and E-cadherin. The expression of Snail and E-cadherin were compared between the gastric cancer tissues and normal gastric mucosa. The data of lymph node metastasis (LNM) was recorded for each patient. Immunohistochemistry All paraffin-embedded tissue sections (4 μm) were baked at 60 C for 6 hours. Slides were deparaffinized in xylene, rehydrated in graded alcohol, and washed in water. Endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked by incubation with 0.3% H 2 O 2. Slides were placed in an autoclave cooker filled with 1 mmol/l EDTA (ph 8.0), and antigen retrieval was accomplished by steam heating for 10 minutes. After being treated with 10% normal goat serum for 25 minutes to block nonspecific protein binding, monoclonal antibody against E-cadherin (1:1000, Abcam, USA) and polyclonal antibody against Snai1 (1:1000, Abcam, USA) were applied to the slides at 4 C in a humid chamber overnight. After reaction with a mouse biotinylated secondary antibody, antigen-antibody reaction was visualized with diaminobenzidine serving 3434 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12, 2011 as the chromogen. All slides were counterstained with hematoxylin. Breast cancer were used as positive control for E-cadherin and Snail, respectively. Negative controls were carried out by omission of the primary antibody. Two observers blinded to the clinical or molecular information of our study scored each slide independently. Immunohistochemical evaluation Expression of Snail1 and E-cadherin was assessed by a semi-quantitative scoring system (Blechschmidt et al., 2008). The scoring of Snail expression was listed as below: a score of 0 indicates no immunoreactivity or immunoreactivity in less than 1% of tumor cells; a score of 1+ indicates immunoreactivity in 1% of tumor cells; a score of 2+ indicates immunoreactivity in 2-5% of tumor cells; a score of 3+ indicates immunoreactivity in more than 5% of tumor cells. Snail staining was graded as positive only when nuclear staining was detectable. All cases were divided into two groups, with negative group representing cases of score 0 and with positive group representing cases of score 1+, 2+, and 3+. The scoring of E-cadherin expression was listed as follows: a score of 0 indicates no immunoreactivity or immunoreactivity in less than 10% of tumor cells; a score of 1+ indicates low-intensity immunoreactivity in more than or equal to 10% of tumor cells; a score of 2+ indicates medium-intensity immunoreactivity in more than or equal to 10% of tumor cells; a score of 3+ indicates high-intensity immunoreactivity in more than or equal to 10% of tumor cells. All cases were divided into two groups, representing preserved E-cadherin expression (scoring 3+) or reduced E-cadherin expression (scoring 0, 1+, and 2+) respectively. Design of amirna and plasmid construction The pcdn6.2-gw/emgfp-mir-based mirna expressive plasmid (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA), driving the expression of amirna with polymerase Ⅱ and containing a spectinomycin resistant gene, was used in our study. The synthesized pre-mirna sequence structure was based on the murine mir-155. According to the sequences of conserved region in Snail genome, we designed four target sequences against the S region of the Snail genome using Invitrogen RNAi design algorithm at rnaidesigner.invitrogen.com/rnaiexpress/. The BLAST algorithm was used to ensure the specifically targeting ability of the designed sequences. The oligonucleotides, as shown in Table 1, were annealed and ligated into
3 Table 2. The Sequences of the Real-time PCR Primer Pair and the Fragment Size Name Sequence Size Snail1 5 -TATGCTGCCTTCCCAGGCTTG bp 3 -ATGTGCATCTTGAGGGCACCC-5 E-cadherin 5 -TCGACACCCGATTCAAAGTGG bp 3 -TTCCAGAAACGGAGGCCTGAT-5 GAPDH 5 -GGCGTTTTGCAATGCAGATGTAG bp 3 -CACAGGAGCCGTCACTTCTCTTG-5 pcdna6.2-gw/emgfp-mir vector. As a negative control, the pcdna6.2-gw/emgfp-mir-neg contained an insert that was predicted not to target any known human gene. Cells in the control group were mock-transfected with Lipofectamine 2000 alone. Cell culture and transfection Human gastric cancer cell line SGC-7901 was cultured in RPMI1640 medium (GIBCO/BRL) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (Hangzhou Sijiqing Biological Engineering Materials, China) and antibiotics (100 u/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin). Cells were amplified at 37 in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 and 95% air (Thermo Direct Heat CO2, USA). Transfections were performed using Lipofectamine 2000 reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Briefly, cells were trypsinized and plated in 6-well plates at a density of cells/ml (1 ml/well) for 24 h before transfection. 10 μl of Lipofectamine was diluted by Opti-MEMⅠ(Gibco, USA) for a final volume of 250 μl and incubated at room temperature for 5 min. 4.0 μg of amirna expression vector was also diluted by Opti-MEMⅠ to a final volume of 250 μl and incubated at room temperature for 5 min. Then the diluted lipofectamine was mixed with the diluted amirna expression vector and incubated for another 20 min. The normal SGC-7901 cells and the cells transfected with negative control plasmid were used as the negative controls. After being cultured at 37 for 6h, the medium was completely removed and the cells were replenished with fresh medium. With the silencing effect evaluated by western blot, stably transfected cell clones were obtained by a long-term culture in a selected medium containing 5 mg/l Blasticidin. Total RNA extraction and Real-time PCR Total RNA was extracted and purified from cells of SGC-7901, SGC-7901-Mock, and SGC-7901-miRNA with Trizol reagent (Invitrogen Corp, USA). cdna synthesis was performed according to the manufacturer s instructions (Invitrogen Corp). Amplification of 10% of these cdnas by Real-time PCR was performed in a threestep thermal cycling incubations (30 s at 95 ; 5 s at 95 ; 34s at 60 ) for 40 cycles, then in a final extension (15s at 95, 1min at 60, 15s at 95 ) according to the manufacturer s recommendations (TaKaRa Corp). The sequences of the Real-time PCR primer pair and the fragment size are shown in Table 2. Western-blot analysis The whole cell lysates from SGC-7901, SGC Mock and SGC-7901-MiRNA were prepared in Inhibition of Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells with a Snail Targeting MicroRNA RIPA lysis buffer. Lysates from SGC-7901 and SGC Mock cells served as control. Lysates were then subjected to sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on 10% or 7.5% acrylamide gels. The membranes were firstly incubated with primary antibodies at 4 C overnight, and then incubated with peroxidaseconjugated anti-mouse or anti-rabbit immunoglobulins in Tris-buffered saline Tween which contains 5% non-fat dry milk. At last, the membranes were processed with the enhanced chemiluminescence reagents according to the manufacturer s instructions. The expression of GAPDH was used as an internal control. Cell migration and invasion assays 75.0 Cell migration and invasion assays were performed and evaluated as expounded in a standard protocol (Romanelli et al., 2006). We used Boyden chambers with 0.8 mm porosity polyvinylpyrrolidone-free polycarbonate filters 50.0 that were coated with nothing for cell migration assay, and for invasion assay when coated with 50 lg/ml of Matrigel solution. The migration and invasion potencies 25.0 of the cell clones were quantified by counting crystal violet-stained cells that either migrated to the lower surface of polycarbonate filters or invaded Matrigel, with a Zeiss microscope (Olympus, USA) equipped with 0 brightfield optics. For each filter, the number of cells in five randomly chosen fields was counted, and the mean value was determined. Statistical analysis Statistical comparisons were performed with the software package SPSS All the data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Mean differences were compared using traditional analysis of variance, and student t test was used for two-group comparisons. A p value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results Immunohistochemical detection of Snail and E-cadherin in gastric cancer tissues and surrounding normal gastric mucosa Using immunohistochemistry analysis, we found that Snail was over-expressed in primary human gastric cancer. Among the gastric cancer tissues of 74 patients, 42(56.8%) samples showed positive Snail expression. The reduced E-cadherin expression was detected in 36(48.7%) samples. In the normal gastric mucosa, we failed to detect Snail expression, while all these samples showed E-cadherin expression. Among samples of the 48 patients with LNM, 33(68.7%) showed a positive Snail expression. Statistic analysis showed that the LNM incidence in Snail positive samples was remarkably higher than in Snai1 negative ones (78.5% vs. 46.8%, p=0.019).representative results of Snail and E-cadherin staining are shown in Figure 1. Detection of protein and mrna expression of both Snai1 and E-cadherin after transfection Once the recombinant plasmids were transfected into SGC-7901 cells, the expression of Emerald green Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12,
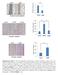
4 Hui-Min Guo et al A B C D Figure 1. Representative Photographs of Tissue of Human Gastric Cancer and Corresponding Normal Gastric Mucosa were Stained by Immunohistochemically for E-cadherin (A, B) and Snail (C, D) expression. A, C: normal gastric mucosa; B, D: gastric cancer tissue Figure 3. mrna Expression of Human Snail (A) and E-cadherin (B) in parental SGC-7901 and SGC-7901-Mock, SGC-7901-amiRNA stable clones; (C) Protein expression of snail and E-cadherin in the same cell clones as those in RT-PCR analysis. GAPDH served as the loading control Figure 4. Snail1 Stably Silenced Cells Showed Lower Migration and Invasion Ability. A-C: migration analysis E-G: invasion analysis. A, E: SGC-7901 B, F: SGC-7901-Mock C, F: SGC-7901-amiRNA Figure 2. Effect of AmiRNA-Snail with Transient Transfection on Snail Protein Levels. Both MR and MR had significant inhibitory effect on Snail protein (p<0.01) fluoresecent protein (EmGFP) could be observed directly under fluorescence microscope. After cultured for 48h, we found that the transfection efficiency of these vectors into SGC-7901 cells were over 75%, and the expression of Snai1 proteins could be detected by western blot. There was no significant difference between parental cells and cells transfected with mock vector. Compared with parental cells, both MR and MR resulted in a significantly reduced level of Snai1 protein in SGC amiRNA (p<0.01) (Figure 2). MR amirna was more efficient than MR amirna, with 91.5% inhibitory rate in Snai1 protein. Therefore, MR amirna transfected cells and mock vector transfected cells were selected by Blasticidin, 3436 Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12, 2011 and stably transfected cells (SGC-7901-amiRNA and SGC-7901-Mock) were obtained. The effectiveness of Snail interference in the stable clones was determined by RT-PCR. As shown in Fig.3A, low mrna expression (< 10% of the corresponding control) of Snail was observed in SGC-7901-amiRNA clones, while SGC-7901-Mock cells showed normal Snail mrna expression similar to the parental SGC-7901 cells. Analysis of E-cadherin mrna expression levels (Figure 3B) indicated up-regulation of E-cadherin transcription in cells with silenced Snail expression. Up-regulation of E-cadherin protein expression in the SGC-7901-amiRNA clones was further confirmed by Western blot (Figure 3C). The effect of Snail knockdown on the migration and invasion potencies of gastric cancer cells The results of Transwell experiment showed that the number of cells in down-pore of uncoated micromembrane was 20±4.2 in the transfected group, significantly less in comparison with 105±7.6 in parent cells group and 110±9.2 in mocked cells group (P <0.05). For micro-membrane coated with Matrigel solution, we detected a remarkable reduction of the number of cell in all groups. The cell number in the transfected group was significantly less than in mocked cells group and in parent cells group (5.0±1.2 vs. 15.2±2.1 & 16.3±1.7, p<0.05).
5 Inhibition of Invasion and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells with a Snail Targeting MicroRNA Discussion co-efficiency of these repressors is still warranted, so as to clearly clarify the regulation of E-cadherin and occurrence Cancer cell metastasis is mediated by increased of EMT. mobility and invasiveness via EMT (Jechlinger et al., Through immunohistochemical assay of the gastric 2003). Snail, a zinc-finger transcription factor, was cancer tissues, we substantiated that Snail plays a critical reported to trigger EMT by directly repressing E-cadherin role in EMT and the subsequent cancer metastasis. expression (Nakayama et al., 1998). The current study We hypothesized that Snail inhibition may serve as a has shown that Snail is abnormally high expressed in the promising target for therapeutic strategies to prevent gastric cancer tissues, and is remarkably associated with cancer metastasis. Thus, a knowledge of the molecular the LNM. Through in vitro study, we found that there mechanisms that control its expression or function is of exists an inverse correlation between Snail and E-cadherin great importance in understanding the process of cancer mrna and protein production in gastric cancer cell lines. invasion. To validate this hypothesis, and to further Inhibition of the Snail expression could result in the high investigate the role and mechanism of Snail in the process expression of E-cadherin, which had a significant influence of metastasis of gastric cancer, we studied the gene on the metastatic property of the cancer cells. function of Snail using RNA interference induced by The process of EMT is always accompanied by the amirna. amirna have been proved to be a promising loss of cell-cell adhesion mediated by E-cadherin, which tool applied in the cancer research (Liang et al., 2007; plays a critical role in the maintenance of cell polarity Wang et al., 2008), mainly attributed to its high efficiency and epithelial integrity (Perl et al., 1998). E-cadherin and specificity in the knockdown of target gene. Recently, transcription in vitro and in vivo could be repressed a new RNA polymerase II expression vector based upon by the zinc-finger transcription factor Snail, which murine mir-155 sequence came into use (Chung et al., was reported to bind to the sequence in the E-cadherin 2006). In the current study, we constructed mir155-based promoter (Thiery et al., 2002). Snail-expressing cells Snail-targeting pre-mirna pol II vectors. Using this became invasive, supporting its role in tumor progression newly synthesized mirna, we obtained stably transfected (Barbera et al., 2004). To date, over expression of Snail has gastric cancer cell lines. The results of RT-PCR and been extensively investigated in different human cancer western blot showed that both Snail protein and mrna tissues and cell lines (Blechschmidt et al., 2008; Pena levels were significantly decreased in pcdna.snail-mir et al., 2009; Van et al., 2011). Elmoneim and Zaghloul group. Meanwhile, the protein and mrna expression of (2011) used Immunohistochemistry to examine Snail E-cadherin was up-regulated. Besides, according to the protein expression in 132 invasive breast carcinomas. results of the migration and invasion potency assay of In their study, Snail was detected in approximately 40% the cancer cells, we found that knockdown of Snail was of the carcinoma tissue, while it was negative in normal significantly associated with the cancer cell metastasis. glandular structures around the tumor. In present study, Namely, effective and specific blockade of Snail could we have a similar finding with previous studies, that result in a remarkable change of the expression of Snail is significantly high expressed in cancer tissues E-cadherin, which in turn reversed the process of EMT than in normal tissue. The protein expression of Snail and decreased the invasion potency of the cancer cell. was detected in 56.8 % of the whole gastric cancer Some recent studies have made use of several sirna tissues. By contrast, absent Snail expression was found duplex oligonucleotides against Snail to assess the effect in the normal surrounding gastric mucosa. In addition, of transient silencing of the factor (Espineda et al., 2004; a correlation between Snail expression and lymph node Kajita et al., 2004). Olmeda et al. (2007) blocked Snail status was detected in our study. We found that Snail with shrna and reported the resultant down-regulation remarkably increased in node-positive cancer tissue, when of E-cadherin and reduction of the tumor growth. It is compared with its expression in node-negative cancer. the first time, to our knowledge, that stable silencing of This result is in agreement with previous results (Blanco Snail expression in gastric cancer cells was achieved et al., 2002; Elmoneim et al., 2011), which showed that by amirna. Our study evidenced that amirna could Snail expression correlates with the presence of lymph efficiently reverse the expression ratio of Snail to node metastases. Moreover, our results also revealed an E-cadherin and prevent cancer metastasis, and this may inverse correlation between protein expression of Snail shed light on the clinical treatment of cancer. and E-cadherin. This finding is in line with the report of Some limitations still exist in our study. First, there Rosivatz et al. (2002), who firstly provided the evidence was only one gastric cancer cell line used in the current that an increase in Snail mrna expression is associated study, which might lead to the insufficiency in illustrating with down-regulation of E-cadherin in gastric cancer. the role of Snail in human cancer progression and Interestingly, in some samples with absence or lowintensity of Snail expression, E-cadherin expression was for the substantiation of the efficiency of the currently metastasis. Second, an in vivo study is quite essential found to be at a low level. Earlier studies (Rosivatz et al., used amirna in inhibiting the migration and invasion 2002; Castro et al., 2007) have revealed that some other potencies of gastric cancer. Third, the 5-year survival E-cadherin repressors, including Twist, Slug, and SIPI, rate of the patients could not be collected in the current could result in a decreased expression of E-cadherin. In study, as a result of relatively short follow-up period. gastric cancer cell, it s very likely that these repressors In the future study, this clearly needs to be taken into regulated the expression of E-cadherin together with consideration, so as to provide a better evaluation of the Snail, as indicated by our results. Further study into the clinical significance of Snail. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12,
6 Hui-Min Guo et al Acknowledgements We sincerely thank Dr. Leilei Xu from the Department of Spinal Surgery of Drum Tower Hospital who made the primary contribution to the proofreading of the manuscript. References Barbera MJ, Puig I, Dominguez D, et al (2004). Regulation of Snail transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Oncogene, 23, Batlle E, Sancho E, Franci C, et al (2000). The transcription factor snail is a repressor of E-cadherin gene expression in epithelial tumour cells. Nat Cell Biol, 2, Blanco MJ, Moreno-Bueno G, Sarrio D, et al (2002). Correlation of Snail expression with histological grade and lymph node status in breast carcinomas. Oncogene, 21, Blechschmidt K, Sassen S, Schmalfeldt B, et al (2008). The E-cadherin repressor Snail is associated with lower overall survival of ovarian cancer patients. Br J Cancer, 98, Castro AC, Rosivatz E, Schott C, et al (2007). Slug is overexpressed in gastric carcinomas and may act synergistically with SIP1 and Snail in the down-regulation of E-cadherin. J Pathol, 211, Chung KH, Hart CC, Al-Bassam S, et al (2006). Polycistronic RNA polymerase II expression vectors for RNA interference based on BIC/miR-155. Nucleic Acids Res, 34, e53. Christofori G, Semb H (1999). The role of the cell-adhesion molecule E-cadherin as a tumour-suppressor gene. Trends Biochem Sci, 24, Elmoneim HM, Zaghloul NM (2011). Expression of e-cadherin, n-cadherin and snail and their correlation with clinicopathological variants: an immunohistochemical study of 132 invasive ductal breast carcinomas in Egypt. Clinics (Sao Paulo), 66, Espineda CE, Chang JH, Twiss J, et al (2004). Repression of Na,K-ATPase beta1-subunit by the transcription factor snail in carcinoma. Mol Biol Cell, 15, Hippo Y, Yashiro M, Ishii M et al (2001). Differential gene expression profiles of scirrhous gastric cancer cells with high metastatic potential to peritoneum or lymph nodes. Cancer Res, 61, Jechlinger M, Grunert S, Tamir IH, et al (2003). Expression profiling of epithelial plasticity in tumor progression. Oncogene, 22, Jemal A, Clegg LX, Ward E, et al (2004). Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, , with a special feature regarding survival. Cancer, 101, Kajita M, McClinic KN, Wade PA (2004). Aberrant expression of the transcription factors snail and slug alters the response to genotoxic stress. Mol Cell Biol, 24, Larue L, Bellacosa A (2005). Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in development and cancer: role of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase/akt pathways. Oncogene, 24, Liang Z, Wu H, Reddy S, et al (2007). Blockade of invasion and metastasis of breast cancer cells via targeting CXCR4 with an artificial microrna. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 363, Moreno-Bueno G, Portillo F, Cano A (2008). Transcriptional regulation of cell polarity in EMT and cancer. Oncogene, 27, Nakayama H, Scott IC, Cross JC (1998). The transition to endoreduplication in trophoblast giant cells is regulated by the msna zinc finger transcription factor. Dev Biol, 199, Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, Vol 12, 2011 Olmeda D, Jorda M, Peinado H, et al (2007). Snail silencing effectively suppresses tumour growth and invasiveness. Oncogene, 26, Olmeda D, Montes A, Moreno-Bueno G, et al (2008). Snai1 and Snai2 collaborate on tumor growth and metastasis properties of mouse skin carcinoma cell lines. Oncogene, 27, Ossowski S, Schwab R, Weigel D (2008). Gene silencing in plants using artificial micrornas and other small RNAs. Plant J, 53, Pena C, Garcia JM, Larriba MJ, et al (2009). SNAI1 expression in colon cancer related with CDH1 and VDR downregulation in normal adjacent tissue. Oncogene, 28, Perl AK, Wilgenbus P, Dahl U, et al (1998). A causal role for E-cadherin in the transition from adenoma to carcinoma. Nature, 392, Romanelli RG, Petrai I, Robino G, et al (2006). Thrombopoietin stimulates migration and activates multiple signaling pathways in hepatoblastoma cells. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol, 290, G Rosivatz E, Becker I, Specht K, et al (2002). Differential expression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulators snail, SIP1, and twist in gastric cancer. Am J Pathol, 161, Stepniak E, Radice GL, Vasioukhin V (2009). Adhesive and signaling functions of cadherins and catenins in vertebrate development. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, 1, a2949. Thiery JP (2002). Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer, 2, Van Nes JG, de Kruijf EM, Putter H, et al (2011). Co-expression of SNAIL and TWIST determines prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat, DOI /s y. Van Dongen S, Abreu-Goodger C, Enright AJ (2008). Detecting microrna binding and sirna off-target effects from expression data. Nat Methods, 5, Wang Z, He YL, Cai SR, et al (2008). Expression and prognostic impact of PRL-3 in lymph node metastasis of gastric cancer: its molecular mechanism was investigated using artificial microrna interference. Int J Cancer, 123, Zeng Y, Wagner EJ, Cullen BR (2002). Both natural and designed micro RNAs can inhibit the expression of cognate mrnas when expressed in human cells. Mol Cell, 9,
Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 6: 1489-1493, 2013 Roles of transcriptional factor Snail and adhesion factor E-cadherin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma JINQUAN CAI Department of Urology, Fuzhou
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
(A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and a
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of Shh signaling components in a panel of gastric cancer. (A) RT-PCR for components of the Shh/Gli pathway in normal fetus cell (MRC-5) and
Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing SOX4
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 4584-4590 Long noncoding RNA CASC2 inhibits metastasis and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of lung adenocarcinoma via suppressing
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
supplementary information
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
DOI: 10.1038/ncb1875 Figure S1 (a) The 79 surgical specimens from NSCLC patients were analysed by immunohistochemistry with an anti-p53 antibody and control serum (data not shown). The normal bronchi served
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7
 The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
The Open Breast Cancer Journal, 2011, 3, 1-5 1 Open Access Influence of RNA Interference Targeting Rab5a on Proliferation and Invasion of Breast Cancer Cell Line MCF-7 Nier Cha 1,2, Xinyue Gu 1, Fengyun
Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer
 RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH FUND FOR THE CONTROL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES Epstein-Barr virus driven promoter hypermethylated genes in gastric cancer J Yu *, KF To, QY Liang K e y M e s s a g e s 1. Somatostatin receptor 1
RESEARCH ARTICLE. Wen-Shuang Wang 1,2, Xing-Sheng Yang 2, Min Xia 1, Hai-Yang Jiang 1, Jian-Qing Hou 1 * Abstract. Introduction
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.9.4435 RESEARCH ARTICLE Silencing of Twist Expression by RNA Interference Suppresses Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition, Invasion, and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.9.4435 RESEARCH ARTICLE Silencing of Twist Expression by RNA Interference Suppresses Epithelial-mesenchymal Transition, Invasion, and Metastasis of Ovarian Cancer
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC-
 Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Supplemental material and methods Reagents. Hydralazine was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich. Cell Culture. The human thyroid follicular carcinoma cell lines FTC-238, FTC-236 and FTC- 133, human thyroid medullary
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplemental Figure 1
 1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
1 Supplemental Figure 1 Effects of DATE shortening on HGF promoter activity. The HGF promoter region (-1037 to +56) containing wild-type (30As) or truncated DATE (26As, 27As, 28A, 29As) from breast cancer
Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis by regulating EZH2 and repressing E-cadherin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
JBUON 2018; 23(1): 157-162 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long noncoding RNA linc-ubc1 promotes tumor invasion and metastasis
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Expression profile of tumor suppressor gene RASSF1 in lacrimal gland carcinoma
 Expression profile of tumor suppressor gene RASSF1 in lacrimal gland carcinoma C.H. Zeng, B. Guo, J. Chen, W.M. He and Q.L. Luo Ophthalmology Department of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Sichuan,
Expression profile of tumor suppressor gene RASSF1 in lacrimal gland carcinoma C.H. Zeng, B. Guo, J. Chen, W.M. He and Q.L. Luo Ophthalmology Department of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Sichuan,
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer?
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Ling Xu, Wei-Qi Dai, Xuan-Fu Xu, Fan Wang, Lei He, Chuan-Yong Guo*
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.7.3203 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Multiple-target Anti-microRNA Antisense Oligodeoxyribonucleotides on Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells Ling
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2012.13.7.3203 RESEARCH ARTICLE Effects of Multiple-target Anti-microRNA Antisense Oligodeoxyribonucleotides on Proliferation and Migration of Gastric Cancer Cells Ling
(A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC,
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Cell line characterization (A) Cells grown in monolayer were fixed and stained for surfactant protein-c (SPC, green) and co-stained with DAPI to visualize the nuclei.
Phenomena first observed in petunia
 Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Vectors for RNAi Phenomena first observed in petunia Attempted to overexpress chalone synthase (anthrocyanin pigment gene) in petunia. (trying to darken flower color) Caused the loss of pigment. Bill Douherty
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Data. Supplementary Methods:
 Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods: Cell viability assay. Cells were seeded overnight at a density of 2,000 cells per well in 96-well plates in RPMI with 10% FBS and then treated with the relevant
Supplementary Data Supplementary Methods: Cell viability assay. Cells were seeded overnight at a density of 2,000 cells per well in 96-well plates in RPMI with 10% FBS and then treated with the relevant
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date:
 microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
microrna Presented for: Presented by: Date: 2 micrornas Non protein coding, endogenous RNAs of 21-22nt length Evolutionarily conserved Regulate gene expression by binding complementary regions at 3 regions
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, MD
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0126 TITLE: Chemical strategy to translate genetic/epigenetic mechanisms to breast cancer therapeutics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiang-Dong Fu, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-11-1-0126 TITLE: Chemical strategy to translate genetic/epigenetic mechanisms to breast cancer therapeutics PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Xiang-Dong Fu, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the. mutated sequence.
 Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Supplementary Figure 1. The mir-182 binding site of SMAD7 3 UTR and the mutated sequence. 1 Supplementary Figure 2. Expression of mir-182 and SMAD7 in various cell lines. (A) Basal levels of mir-182 expression
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer. Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL
 MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
MicroRNA expression profiling and functional analysis in prostate cancer Marco Folini s.c. Ricerca Traslazionale DOSL What are micrornas? For almost three decades, the alteration of protein-coding genes
mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 7: 1757-1761, 2014 mir 375 inhibits the proliferation of gastric cancer cells by repressing ERBB2 expression ZHI YONG SHEN *, ZI ZHEN ZHANG *, HUA LIU, EN HAO ZHAO
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
The clinical significance of HPIP and the associated prognosis in cervical cancer
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 41), pp: 70262-70270 The clinical significance of HPIP and the associated prognosis in cervical cancer Fanling Meng 1,*, Haixia Liu 1,*, Shuang Liu 1 and Rong Ma 1 1 Department of
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 41), pp: 70262-70270 The clinical significance of HPIP and the associated prognosis in cervical cancer Fanling Meng 1,*, Haixia Liu 1,*, Shuang Liu 1 and Rong Ma 1 1 Department of
The pseudogene TUSC2P promotes TUSC2 function by binding multiple micrornas
 Received 9 Aug 3 Accepted Nov 3 Published 7 Jan DOI:.38/ncomms39 The pseudogene promotes TUSC function by binding multiple micrornas OPEN Zina Jeyapalan Rutnam,, *, William W. Du,, *, Weining Yang, Xiangling
Received 9 Aug 3 Accepted Nov 3 Published 7 Jan DOI:.38/ncomms39 The pseudogene promotes TUSC function by binding multiple micrornas OPEN Zina Jeyapalan Rutnam,, *, William W. Du,, *, Weining Yang, Xiangling
Original Article SLUG promotes invasion and metastasis of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells through repression of E-cadherin
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(8):8373-8379 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026764 Original Article SLUG promotes invasion and metastasis of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells through repression of E-cadherin
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(8):8373-8379 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0026764 Original Article SLUG promotes invasion and metastasis of anaplastic thyroid cancer cells through repression of E-cadherin
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, School of Pharmacy, Northeastern University, Boston, MA 02115, USA 2
 Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Pancreatic Cancer Cell Exosome-Mediated Macrophage Reprogramming and the Role of MicroRNAs 155 and 125b2 Transfection using Nanoparticle Delivery Systems Mei-Ju Su 1, Hibah Aldawsari 2, and Mansoor Amiji
Supplementary Information and Figure legends
 Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Supplementary Information and Figure legends Table S1. Primers for quantitative RT-PCR Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) Target Sequence (5 -> 3 ) DAB2IP F:TGGACGATGTGCTCTATGCC R:GGATGGTGATGGTTTGGTAG Snail F:CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC
Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients
 1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
1568 Correlation between estrogen receptor β expression and the curative effect of endocrine therapy in breast cancer patients LIYING GUO 1, YU ZHANG 2, WEI ZHANG 3 and DILIMINA YILAMU 1 1 Department of
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
Research Communication The Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM25 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting Metastasis Associated 1 Protein
 Research Communication The Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM25 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting Metastasis Associated 1 Protein Hong-liang Zang Sheng-nan Ren Hong Cao Xiao-feng Tian * Department
Research Communication The Ubiquitin Ligase TRIM25 Inhibits Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Targeting Metastasis Associated 1 Protein Hong-liang Zang Sheng-nan Ren Hong Cao Xiao-feng Tian * Department
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
TGF-β1 promotes cells invasion and migration by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transformation in oral squamous cell carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2137-2144 TGF-β1 promotes cells invasion and migration by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transformation in oral squamous cell carcinoma
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 2137-2144 TGF-β1 promotes cells invasion and migration by inducing epithelial mesenchymal transformation in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Research Communication
 IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
IUBMB Life, 64(7): 628 635, July 2012 Research Communication MicroRNA-181b Targets camp Responsive Element Binding Protein 1 in Gastric Adenocarcinomas Lin Chen*, Qian Yang*, Wei-Qing Kong*, Tao Liu, Min
MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences MicroRNA-132 inhibits migration, invasion and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating TGFβ1/Smad2 in human non-small cell lung cancer J.-X.
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma
 Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma RYOJI KAIZAKI 1, MASAKAZU YASHIRO 1,2, OSAMU SHINTO 1, KOICHI YASUDA 1, TARO MATSUZAKI 1, TETSUJI SAWADA 1 and KOSEI HIRAKAWA 1 1 Department of Surgical
Expression of ERas Oncogene in Gastric Carcinoma RYOJI KAIZAKI 1, MASAKAZU YASHIRO 1,2, OSAMU SHINTO 1, KOICHI YASUDA 1, TARO MATSUZAKI 1, TETSUJI SAWADA 1 and KOSEI HIRAKAWA 1 1 Department of Surgical
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel
 KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
KDR gene silencing inhibits proliferation of A549cells and enhancestheir sensitivity to docetaxel R. Wei and J.-P. Zang Department of Respiratory Medicine, People s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou, China
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
High Expression of Forkhead Box Protein C2 is Related to Poor Prognosis in Human Gliomas
 DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.24.10621 RESEARCH ARTICLE High Expression of Forkhead Box Protein C2 is Related to Poor Prognosis in Human Gliomas Yao-Wu Wang 1, Chun-Li Yin 2, Hong-Yi Zhang
DOI:http://dx.doi.org/10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.24.10621 RESEARCH ARTICLE High Expression of Forkhead Box Protein C2 is Related to Poor Prognosis in Human Gliomas Yao-Wu Wang 1, Chun-Li Yin 2, Hong-Yi Zhang
Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive
 Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Online Data Supplement: Epithelial interleukin-25 is a key mediator in Th2-high, corticosteroid-responsive asthma Dan Cheng, Zheng Xue, Lingling Yi, Huimin Shi, Kan Zhang, Xiaorong Huo, Luke R. Bonser,
Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients
 Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Title Plasma Bmil mrna as a potential prognostic biomarker for distant metastasis in colorectal cancer patients Author(s) Pun, JC; Chan, JY; Chun, BK; Ng, KW; Tsui, SY; Wan, TMH; Lo, OSH; Poon, TCJ; Ng,
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma
 Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Patterns of E.cadherin and Estrogen receptor Expression in Histological Sections of Sudanese Patients with Breast Carcinoma Hadia. Mohammed. Abdalla. Abdalrhman *, Elsadig.A.Adam, Ayda.D.A.Allatif 3,'Namareg.E.Afadul
Expression and Significance of GRP78 and HER-2 in Colorectal Cancer
 Expression and Significance of GRP78 and HER-2 in Colorectal Cancer Qiu-xia Ji 1, Li-li Wang 2, Lin Li 3, Xiaoming Xing 2 1 Department of Pathology, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China 2 Department of Pathology,
Expression and Significance of GRP78 and HER-2 in Colorectal Cancer Qiu-xia Ji 1, Li-li Wang 2, Lin Li 3, Xiaoming Xing 2 1 Department of Pathology, Qingdao University, Qingdao, China 2 Department of Pathology,
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas
 DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
DOI:10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.12.3301 RESEARCH ARTICLE Astrocyte Elevated Gene 1 (AEG-1): A Promising Candidate for Molecular Targeted Therapy in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinomas Maryam Seyedmajidi 1, Shabnam
Cancer cells in vitro
 Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium. Rosita Winkler
 Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
Fundamental research on breast cancer in Belgium Rosita Winkler Medline search for «breast cancer» and Belgium limits: english, posted in the last 5 years. Result: 484 papers - fundamental / clinical -
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer
 The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
The Biology and Genetics of Cells and Organisms The Biology of Cancer Mendel and Genetics How many distinct genes are present in the genomes of mammals? - 21,000 for human. - Genetic information is carried
Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs ) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis
 EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
EC Dental Science Special Issue - 2017 Role of Paired Box9 (PAX9) (rs2073245) and Muscle Segment Homeobox1 (MSX1) (581C>T) Gene Polymorphisms in Tooth Agenesis Research Article Dr. Sonam Sethi 1, Dr. Anmol
Original Article Clinical significance of SOX2 and snail expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9569-9574 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0027666 Original Article Clinical significance of SOX2 and snail expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Na Miao 1*,
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):9569-9574 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0027666 Original Article Clinical significance of SOX2 and snail expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma Na Miao 1*,
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population
 Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
Relationship between SPOP mutation and breast cancer in Chinese population M.A. Khan 1 *, L. Zhu 1 *, M. Tania 1, X.L. Xiao 2 and J.J. Fu 1 1 Key Laboratory of Epigenetics and Oncology, The Research Center
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:!
 LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
LIST OF ORGANS FOR HISTOPATHOLOGICAL ANALYSIS:!! Neural!!!!!!Respiratory:! Brain : Cerebrum,!!! Lungs and trachea! Olfactory, Cerebellum!!!!Other:! Spinal cord and peripheral nerves! Eyes, Inner ear, nasal
Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2016; 20: 5126-5131 Overexpression of long-noncoding RNA ZFAS1 decreases survival in human NSCLC patients F.-M. TIAN 1, F.-Q. MENG 2, X.-B. WANG
Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 7178-7182 Circular RNA_LARP4 is lower expressed and serves as a potential biomarker of ovarian cancer prognosis T. ZOU, P.-L. WANG, Y.
RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian cancer
 JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
JBUON 2019; 24(2): 715-719 ISSN: 1107-0625, online ISSN: 2241-6293 www.jbuon.com E-mail: editorial_office@jbuon.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE RCD24, B7-H4 and PCNA expression and clinical significance in ovarian
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro
 Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
Blocking the expression of the hepatitis B virus S gene in hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with an anti-gene locked nucleic acid in vitro Y.-B. Deng, H.-J. Qin, Y.-H. Luo, Z.-R. Liang and J.-J. Zou
Association of BTBD7 with Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Patients
 477 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2015; 6(5): 477-481. doi: 10.7150/jca.11715 Association of BTBD7 with Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
477 Ivyspring International Publisher Research Paper Journal of Cancer 2015; 6(5): 477-481. doi: 10.7150/jca.11715 Association of BTBD7 with Metastasis and Poor Prognosis in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or
 Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
Supplementary Figure 1. The CagA-dependent wound healing or transwell migration of gastric cancer cell. AGS cells transfected with vector control or 3xflag-CagA expression vector were wounded using a pipette
LncRNA RGMB-AS1 is activated by E2F1 and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1979-1986 LncRNA RGMB-AS1 is activated by E2F1 and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma Z. ZHANG 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 1979-1986 LncRNA RGMB-AS1 is activated by E2F1 and promotes cell proliferation and invasion in papillary thyroid carcinoma Z. ZHANG 1,
Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes
 Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
Ch. 19 Regulation of Gene Expression in Eukaryotes BIOL 222 Differential Gene Expression in Eukaryotes Signal Cells in a multicellular eukaryotic organism genetically identical differential gene expression
The splicing regulation and clinical significance of epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 in invasion and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer
 The splicing regulation and clinical significance of epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 in invasion and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer Jie Tang MD, Ph.D, Professer Vice director of Department
The splicing regulation and clinical significance of epithelial splicing regulatory protein 1 in invasion and metastasis of epithelial ovarian cancer Jie Tang MD, Ph.D, Professer Vice director of Department
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins.
 Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Alternative RNA processing: Two examples of complex eukaryotic transcription units and the effect of mutations on expression of the encoded proteins. The RNA transcribed from a complex transcription unit
Roles of the AIB1 protein in the proliferation and transformation of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Roles of the AIB1 protein in the proliferation and transformation of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma L. Li 1 *, P. Wei 2 *, M.-H. Zhang 1, W. Zhang 2, Y. Ma 1, X. Fang 1, C.-L. Hao 1 and Z.-H.
Roles of the AIB1 protein in the proliferation and transformation of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma L. Li 1 *, P. Wei 2 *, M.-H. Zhang 1, W. Zhang 2, Y. Ma 1, X. Fang 1, C.-L. Hao 1 and Z.-H.
Silencing Dicer expression enhances cellular proliferative and invasive capacities in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 31: 867-873, 2014 Silencing Dicer expression enhances cellular proliferative and invasive capacities in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma SHUGUANG ZENG 1*, JING YANG 1*, JIANJIANG ZHAO
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 31: 867-873, 2014 Silencing Dicer expression enhances cellular proliferative and invasive capacities in human tongue squamous cell carcinoma SHUGUANG ZENG 1*, JING YANG 1*, JIANJIANG ZHAO
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
