US Evaluation of Axillary Lymph Nodes
|
|
|
- Susan Ada Goodman
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US Evaluation of Axillary Lymph Nodes Jose M. Net, MD Tarun M. Mirpuri, MD Michael J. Plaza, MD Cristina A. Escobar, MD Elizabeth E. Whittington, MD Fernando Collado-Mesa, MD Monica M. Yepes, MD All authors have disclosed no relevant relationships. Address correspondence to J.M.N., Breast Imaging Section, Department of Radiology, University of Miami Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Care Center, 1475 NW 12 th Ave, Miami, FL (
2 Introduction Axillary adenopathy is frequently encountered during breast cancer screening and in the diagnostic work-up of symptomatic patients. A broad spectrum of disease processes may result in axillary adenopathy. Knowledge of normal nodal morphologic characteristics and distribution and of the various possible causes of lymph node enlargement, combined with patient-specific clinical information, aids in accurate diagnosis. After viewing this presentation, readers should be able to: Describe the imaging appearance of the normal nodal anatomy Identify abnormal nodes List differential causes of unilateral versus bilateral adenopathy Discuss possible reasons for increased nodal density and nodal calcification Describe possible causes of a palpable axillary mass or masses, including processes that mimic axillary adenopathy
3 Key Concepts Ultrasonography (US) is the preferred modality for assessing axillary lymph nodes Thickness and uniformity of the nodal cortex are the most important criteria for distinguishing normal lymph nodes from abnormal ones Cortical thickness should be less than or equal to 3 mm; the cortical margin should be smooth, and the fatty hilum should be intact If an abnormal axillary node is found, the ipsilateral breast and contralateral axilla should be closely examined and the patient s medical history reviewed If adenopathy is unilateral: breast cancer, metastasis, and infectious cellulitis should be included in the differential diagnosis Ipsilateral breast cancer is the most common cause of unilateral axillary adenopathy If adenopathy is bilateral: consider the possibility of a systemic process Lymphoma, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), autoimmune or connective tissue disorder Various mimics of axillary adenopathy may prompt imaging work-up and should be included in the differential diagnosis of any palpable axillary abnormality Sebaceous cyst, accessory breast tissue, lipoma, and seroma are possible mimics In a patient with a known malignancy, normal nodal morphologic features do not necessarily permit the exclusion of malignancy from the differential diagnosis; a sentinel node biopsy may be needed for that purpose
4 Axillary Anatomy Axillary lymph nodes are described according to their location relative to the pectoralis minor muscle: Level I nodes are lateral to the muscle Level II nodes are deep to the muscle Level III nodes are medial to the muscle Nodes at level I are better depicted at US than are those at level II or III. (Courtesy of Albert Fung, MScBMC, Department of Surgical Oncology, University of Toronto Princess Margaret Hospital, Toronto, Ontario, Canada.) Level III Level I Level II Axial T1-weighted fat-saturated magnetic resonance (MR) image obtained after the injection of a gadolinium-based contrast material (left) and three-dimensional illustration (above) show the zonal anatomy of axillary lymph nodes.
5 Normal or Pathologic? Criteria for Assessing Axillary Lymph Nodes Observation Normal Abnormal Shape Reniform Rounded Cortical thickness 3 mm, smooth cortex with uniform thickness >3 mm, eccentric thickening of cortex Fatty hilum Present Displaced or absent Cortical echotexture Homogeneous Hypoechoic; may be heterogeneous with calcifications Color Doppler findings Blood supplied via a single vessel entering at the hilum Blood supplied by multiple peripheral vessels Margins Smooth Angulated, irregular Appearance relative to that of adjacent lymph nodes Similar Different
6 Differentiation at US: Normal Lymph Node vs Lymphadenopathy Normal shape: reniform Abnormal shape: rounded Normal cortical thickness: 3 mm Abnormal cortical thickness: >3 mm (continues)
7 Differentiation at US: Normal Lymph Node vs Lymphadenopathy Normal flow at Doppler imaging: blood supplied by a vessel entering the hilum Abnormal flow at Doppler imaging: blood supplied only by peripheral vessels Normal appearance of fatty hilum Fatty hilum displaced or absent
8 Unilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Differential Diagnosis Benign causes Regional infection (eg, cat-scratch disease, toxoplasmosis, tuberculosis, ipsilateral upper-extremity cellulitis, mastitis) Dermatopathic lymphadenopathy Silicone-induced granulomatous lymphadenitis Malignant causes Metastasis from primary breast cancer Metastasis from nonbreast primary malignancy (eg, melanoma; cancer of the thyroid, lung, gastrointestinal tract, pancreas, or ovary) Lymphoma occasionally occurs unilaterally
9 Unilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Metastasis from Primary Breast Cancer Right mediolateral oblique (MLO) and magnified views from screening mammography in a 47-year-old woman show a rounded, dense axillary node with irregular margins, but no obvious breast mass. Transverse US image shows a round, hypoechoic axillary node with replaced fatty hilum. US-guided core biopsy of the lymph node yielded metastatic mammary carcinoma.
10 Unilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Metastasis from Primary Breast Cancer MLO view obtained at screening mammography in a 50-year-old asymptomatic woman shows a right breast mass and ipsilateral axillary adenopathy. Gray-scale US image obtained in the same patient for further characterization of the abnormal nodes shows nodal rounding with eccentric cortical thickening and hilar encroachment.
11 Unilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Metastasis from Occult Primary Breast Cancer Left MLO mammogram in a 79-year-old woman with a palpable left axillary mass and history of a right mastectomy shows isolated axillary adenopathy (arrow) with no definite breast mass. US image shows a hypoechoic lymph node with replacement of the fatty hilum. No evidence of a primary breast malignancy was seen at US. MR image of the left breast and axilla shows an indistinct breast mass with surrounding clumped nonmass enhancement and a rounded axillary lymph node. Biopsy yielded invasive ductal carcinoma with metastasis to the ipsilateral axilla.
12 Axillary Metastases from Primary Breast Cancer: Summary
13 Metastases from Nonbreast Primary Malignancies: Melanoma Axillary mass in a 48-yearold woman with a history of melanoma. US image shows an enlarged, hypoechoic lymph node with loss of the normal fatty hilum, an appearance that is suggestive of malignancy. Metastasis from melanoma was subsequently found at biopsy.
14 Infectious Lymphadenitis: Cat-Scratch Disease Left mammogram and left axillary US images, obtained in a 46-year-old woman with acute symptoms like those of influenza, show markedly enlarged axillary lymph nodes, with cortical thickening and displacement of the fatty hilum. (Case continues.)
15 Infectious Lymphadenitis: Cat-Scratch Disease Photomicrographs (left: original magnification, 20; right: original magnification, 10; both, hematoxylin-eosin stain) of histologic slices obtained at surgical biopsy of a lymph node show necrotizing granulomatous lymphadenitis. These findings are characteristic of cat-scratch disease.
16 Dermatopathic Lymphadenopathy Mammogram obtained in a 57-yearold woman with palpable left axillary nodes and a history of multiple furuncles on her upper extremities shows an enlarged node (arrow) but no suspicious breast mass or calcifications. (Case continues on next slide.) Axillary US image shows a lymph node with a thickened cortex (red arrow) relative to that of a normal adjacent node (black arrow).
17 Dermatopathic Lymphadenopathy Photomicrograph (original magnification, 20; hematoxylin-eosin stain) of a lymph node biopsy specimen shows features consistent with a diagnosis of dermatopathic lymphadenopathy, including nodular expansion of the interfollicular region with histiocytes containing melanin (black arrows), eosinophils, and plasma cells. Prominent postcapillary venules (white arrow) and follicular hyperplasia also are seen.
18 Granulomatous Lymphadenitis Noninfectious subtypes: Sarcoidosis lymphadenitis Sarcoidlike lymphadenitis (eg, in Hodgkin and non-hodgkin lymphomas) Berylliosis Infectious and suppurative subtypes: Tularemic lymphadenitis Cat-scratch disease Yersiniosis Venereal lymphogranuloma Fungal lymphadenitis Infectious and nonsuppurative subtypes: Tuberculous lymphadenitis Atypical mycobacterial infection BCG lymphadenitis Toxoplasmic lymphadenitis (Piringer-Kuchinka lymphadenopathy) Syphilitic lymphadenitis Brucellosis lymphadenitis Fungal lymphadenitis
19 Granulomatous Lymphadenitis MLO view obtained at screening mammography shows a markedly enlarged left axillary lymph node in a 52-year-old asymptomatic woman with a history of negative findings at left breast biopsy. US image (left) shows an enlarged, heterogeneous lymph node in the left axilla. Photomicrograph (below; original magnification, 10; hematoxylineosin stain) of a specimen from US-guided core biopsy shows findings indicative of granulomatous lymphadenitis. The cause was not determined.
20 Histiocytic Reaction Left MLO and magnified views from screening mammography in a 52- year-old asymptomatic woman show an enlarged calcified axillary lymph node (arrows, left) and an ovoid circumscribed mass in the upper breast quadrants (far left). The mass had a cystic appearance at US. (The dermal calcifications are unrelated.) US image at right shows enlarged axillary lymph nodes with a thickened cortex. Pathologic analysis of a biopsy specimen showed the presence of reactive histiocytosis.
21 Bilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Differential Diagnosis Benign causes HIV Autoimmune and connective tissue diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma, dermatomyositis, systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and psoriasis Lymphoid hyperplasia due to infectious-inflammatory conditions such as infectious mononucleosis and cat-scratch disease Granulomatous lymphadenitis (sarcoidosis, tuberculosis) Malignant causes Lymphoma Leukemia HIV-associated malignancies (eg, Kaposi sarcoma) Metastases from lung cancer, melanoma, and (uncommonly) breast cancer
22 Bilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Lymphoma Bilateral enlarged lymph nodes are seen with no evidence of breast cancer at screening mammography (left) in a 67-year-old asymptomatic woman. US images (right) show nodal enlargement and cortical thickening. (Case continues.)
23 Bilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Lymphoma Photomicrographs (left: original magnification, 4; right: original magnification, 50; both, hematoxylin-eosin stain) of specimens from US-guided core biopsy of a left axillary lymph node show non-hodgkin lymphoma of the mantle cell type.
24 Bilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Leukemia Bilateral rounded and markedly enlarged axillary lymph nodes were seen on screening mammograms (left) obtained in a 68-year-old woman with recently diagnosed chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Axial CT image shows rounded axillary nodes (arrows, right).
25 Bilateral Axillary Adenopathy Due to HIV Infection MLO mammograms obtained in an asymptomatic 41-year-old woman with known HIV infection show bilateral enlarged axillary nodes. US images show enlarged axillary lymph nodes with loss of normal fatty hilum. USguided core biopsy yielded evidence of reactive lymphoid hyperplasia.
26 Bilateral Axillary Adenopathy: Toxoplasmic Lymphadenitis US images obtained in a 40-year-old man with a history of lymphoma and with newly palpable bilateral axillary lymph nodes show bilateral cortical thickening. Toxoplasmic lymphadenitis was diagnosed at USguided core biopsy and confirmed with serologic testing.
27 Dense and/or Calcified Axillary Adenopathy: BCG Adenitis Left MLO mammogram (far left) shows bulky, enlarged left axillary lymph nodes. Magnified view (near left) shows coarse calcifications within a node.
28 Dense and/or Calcified Axillary Adenopathy: Treated Lymphoma Comparison of left and right MLO views (above) obtained at screening mammography in a 53-year-old woman with a history of radiation therapy for lymphoma shows coarse rim- or eggshell-like calcifications in lymph nodes in the left axilla, findings most clearly seen on the magnified view (arrow, above right). Axillary US image shows a rounded, partly obscured hypoechoic mass (arrow, right) with a posterior shadow.
29 Dense and/or Calcified Axillary Adenopathy: Sarcoidosis MLO and magnified mammographic views show enlarged axillary lymph nodes with calcifications (arrows, left and center). Axial CT image (right) shows enlarged mediastinal and axillary lymph nodes.
30 Dense and/or Calcified Axillary Adenopathy: Gold Deposits Magnified views from screening mammography in a 68-year-old woman with a history of long-standing rheumatoid arthritis show high-density threadlike opacities indicative of gold deposition (left) and calcium deposits within axillary lymph nodes (arrow, right).
31 Dense and/or Calcified Axillary Adenopathy: Silicone Deposits Mammograms (left, center) obtained in a 64-year-old woman with severe bilateral breast pain and severely deformed breasts due to previous silicone implants and silicone injections show an enlarged axillary lymph node (arrow, center) with dense cortical deposits resembling calcium particles. Axillary US image (right) shows an enlarged lymph node with a snowstorm-like internal echotexture. (Case continues.)
32 Dense and/or Calcified Axillary Adenopathy: Silicone Deposits Photomicrographs (left: original magnification, 10; right, original magnification, 20; both, hematoxylin-eosin stain) of axillary lymph node biopsy specimens show granulomas and multinucleated giant cells, findings indicative of a foreign body inflammatory reaction. Multiple droplets of birefringent material embedded within the lymph node tissue were found to represent silicone deposits.
33 Other Palpable Axillary Masses: Inflamed Sebaceous Cyst Axillary US images obtained for evaluation of a rapidly growing palpable mass in the left axilla of a 47-year-old woman show an ovoid hypoechoic mass with mildly heterogeneous echotexture (arrow, left) and an adjacent rounded lymph node with a thickened cortex (arrow, right). (Case continues.)
34 Other Palpable Axillary Masses: Inflamed Sebaceous Cyst Photomicrograph (original magnification, 50; Papanicolaou stain) of a US-guided biopsy specimen of the hypoechoic mass with heterogeneous echotexture shows benign squamous epithelial cells and inflammatory cells, findings indicative of an inflamed sebaceous cyst.
35 Other Palpable Axillary Masses: Lipoma Mammogram obtained for evaluation of a palpable abnormality in the right axilla of a 43-year-old woman shows the inferior margin of a lipoma pseudocapsule (arrow, left) at the site of the Beekley triangle. Axillary US image (above) shows a solid mass with echogenicity similar to that of the fatty breast parenchyma. (Case continues.)
36 Other Palpable Axillary Masses: Lipoma Photomicrograph (original magnification, 20; hematoxylin-eosin stain) of a tissue specimen obtained at biopsy of the axillary mass shows adipose tissue with hemorrhage.
37 Other Palpable Axillary Masses: Seroma US image (above) shows a large fluid collection with a heterogeneous echotexture in the right axillary tail in a 72- year-old woman with a history of right mastectomy, breast reconstruction with a transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous (TRAM) flap, and axillary dissection for breast cancer. Axial short inversion time inversion-recovery (STIR) MR images show hyperintense signal in the collection (top right) with no associated enhancement on the subtraction image obtained after injection of a gadoliniumbased contrast material (bottom right).
38 Management of Axillary Lymphadenopathy Detected on Screening Mammograms Unilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with no suspicious breast findings BIRADS 0:Bilateral axillary US should be performed to confirm findings are unilateral/asymmetric If no known infectious or inflammatory source present (i.e. mastitis, breast abscess, cat scratch fever), then BIRADS 4, FNA/Biopsy; If proven metastatic disease from breast primary, consider MRI to identify occult breast primary. If a benign cause can be elucidated, BIRADS 3, recommend 6 month follow-up to monitor involution according to etiology.
39 Management of Axillary Lymphadenopathy Detected on Screening Mammograms Bilateral axillary lymphadenopathy with no suspicious breast findings Correlate with patient history and clinical exam. If underlying infectious/ inflammatory condition (i.e. sarcoid, SLE, HIV), then BIRADS 2, Benign If known lymphoma then BIRADS assessment should be based on breast findings If no benign cause can be elucidated, BIRADS 4, consider biopsy to establish etiology. If lymphoma is considered, retrieve core samples in saline for cytometric flow work-up
40 Summary Findings of axillary lymphadenopathy at mammography or physical examination should be further evaluated with US Lymph node morphologic features are the most important factor for distinguishing between normal and abnormal nodes Normal lymph nodes have a smooth and uniform cortex with a thickness of up to 3 mm and with preservation of the fatty hilum Cortical thickness of more than 3 mm, eccentric cortical thickening, and displacement or replacement of the fatty hilum are indicative of an abnormal process If nodal abnormality is identified, the contralateral axillary nodes also should be assessed If adenopathy is unilateral, a thorough search should be performed for ipsilateral primary breast cancer at mammography and US, with MR imaging performed if necessary If adenopathy is bilateral, the imaging findings should be compared with the clinical history Various benign and malignant processes may lead to axillary lymphadenopathy If abnormal nodes are seen, the patient s medical history should be reviewed for pertinent information; clinical correlation is essential Processes that may mimic axillary adenopathy should be included in the differential diagnosis of any palpable axillary abnormality and should prompt a thorough imaging evaluation Sebaceous cyst, accessory breast tissue, and lipoma are commonly encountered Biopsy is often needed before the presence of a metastasis from underlying primary breast cancer or a primary nonbreast malignancy can be ruled out A normal appearance of the axillary lymph nodes is an insufficient basis for exclusion of malignancy from the differential diagnosis
41 Suggested Readings American College of Radiology. ACR BI-RADS atlas. 5 th ed. Reston, VA: ACR, American College of Radiology. Mammography Quality Standards Act (MQSA): frequently asked questions. /MammoFAQ.pdf. Asano S. Granulomatous lymphadenitis. J Clin Exp Hematop 2012;52(1):1 16. Bedi DG, Krishnamurthy R, Krishnamurthy S, et al. Cortical morphologic features of axillary lymph nodes as a predictor of metastasis in breast cancer: in vitro sonographic study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2008; 191(3): Buchanan CL, Morris EA, Dorn PL, et al. Utility of breast magnetic resonance imaging in patients with occult primary breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 2005;12: Cao MM, Hoyt AC, Bassett LW. Mammographic signs of systemic disease. RadioGraphics 2011; 31: Carithers HA. Cat-scratch disease: an overview based on a study of 1,200 patients. Am J Dis Child 1985;139: Halsted WS. The results of radical operations for the cure of carcinoma of the breast. Part I. Ann Surg 1907;46(1):1 19. Kim EY, Ko EY, Han BK, et al. Sonography of axillary masses: what should be considered other than the lymph nodes? J Ultrasound Med 2009;28: Koehler JE, Duncan LM. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case : A 56-year-old man with fever and axillary lymphadenopathy. N Engl J Med 2005; 353: Krementz ET, Cerise EJ, Cjaraveilla JM, Morgan LK. Metastases of undetermined source. CA 1977; 27: (continues)
42 Suggested Readings Monaco SE, Khalbuss WE, Pantanowitz L. Benign non-infectious causes of lymphadenopathy: a review of cytomorphology and differential diagnosis. Diagn Cytopathol 2012;40(10): doi: /dc Epub 2012 Feb 20. Moriarty RA, Margileth AM. Cat-scratch disease. Infect Dis Clin North Am 1987;1: Noguchi M, Katev N, Miyazaki I. Diagnosis of axillary lymph node metastases in patients with breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat 1996;40: Patel T, Given-Wilson RM, Thomas V. The clinical importance of axillary lymphadenopathy detected on screening mammography: revisited. Clin Radiol 2005;60(1): Solomon SB, Gatewood OM, Brem RF. HIV infection: analysis of mammographic findings. Breast J 1999;5: Westbrook KC, Ballaser HS. Breast carcinoma in axillary lymph nodes as an indicator of breast cancer. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1962; 114:5 8.
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Medical Education. CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M
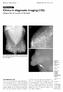 1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
1062 Medical Education CME Article Clinics in diagnostic imaging (125) Padungchaichote W, Kongmebhol P, Muttarak M la Ib Ic Fig. I (a) Bilateral mediolateral oblique mammograms; (b) spot right craniocaudal
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Index. C Calcifications fat necrosis 1, 61 fat necrosis 4, 69 nipple/peri-areolar involvement 1, 165
 A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities. Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine
 Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Standard Breast Imaging Modalities Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Standard breast imaging modalities Mammography Ultrasound MRI Imaging
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes
 Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
Yonsei Med J 49(2):249-254, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.2.249 The Safety and Efficiency of the Ultrasound-guided Large Needle Core Biopsy of Axilla Lymph Nodes Ki Hong Kim, 1 Eun Ju Son, 1 Eun-Kyung Kim,
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis: A Case Detected by Breast Cancer Screening Examination
 Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Hindawi Publishing Corporation Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 9016517, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/9016517 Case Report CT Findings of Axillary Tuberculosis Lymphadenitis:
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Imaging superficial lymph nodes: Is there a clue for malignancy?
 Imaging superficial lymph nodes: Is there a clue for malignancy? Poster No.: C-2477 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Zaghouani Ben Alaya, N. Benzina, Z. Kmira, W. Kermani, 1 1 1
Imaging superficial lymph nodes: Is there a clue for malignancy? Poster No.: C-2477 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Zaghouani Ben Alaya, N. Benzina, Z. Kmira, W. Kermani, 1 1 1
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Cervical Lymph Nodes
 Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
Cervical Lymph Nodes Diana Gaitini, MD Unit of Ultrasound, Department of Medical Imaging Rambam Medical Center and Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Institute of Technology Haifa, Israel Learning Targets
BI-RADS and Breast MRI. Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018
 BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
S. Murgo, MD. Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels
 S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
S. Murgo, MD Chr St-Joseph, Mons Erasme Hospital, Brussels? Introduction Mammography reports are sometimes ambiguous and indecisive. ACR has developped the BIRADS. BIRADS consists of a lexicon in order
Primary Breast Liposarcoma
 Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Primary Breast Liposarcoma Bhagyam Nagarajan 1*, GayatriAutkar 1, Keyuri Patel 1, Meghal Sanghvi 1 1. Department of Radiology, Wockhardt Hospital, Mumbai, India * Correspondence: Dr Bhagyam Nagarajan,
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report
 Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Metachronic solitary breast metastasis from renal cell carcinoma: case report Abstract We describe the case of a patient with solitary and metachronic breast metastasis, 3 years after nephrectomy for renal
Advances in Breast Surgery. Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015
 Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Advances in Breast Surgery Catherine Campo, D.O. Breast Surgeon Meridian Health System April 17, 2015 Objectives Understand the surgical treatment of breast cancer Be able to determine when a lumpectomy
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks
 Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
Breast Imaging Update: Old Dog New Tricks Claire McKay, DO M&S Imaging Assoc. San Antonio, TX cmckayhart@juno.com Goals Describe modalities available, old and new Provide understanding of pros and cons
Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign
 Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. A. Choudhery, P. Gupta, S. Foshee, F. Garcia-Morales, G.
Gynecomastia and Its Mimics: Not All Male Breast Lesions are Benign Poster No.: C-0139 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. A. Choudhery, P. Gupta, S. Foshee, F. Garcia-Morales, G.
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
Kimura s Disease in the Lower Extremity: A Case Report Mimicking the Malignant Soft Tissue Mass
 Kimura s Disease in the Lower Extremity: A Case Report Mimicking the Malignant Soft Tissue Mass Jee Young Lee, M.D. 1, Kyung Jin Suh, M.D. 2, Hong-Geun Jung, M.D. 3 We present a case of a 37-year-old woman
Kimura s Disease in the Lower Extremity: A Case Report Mimicking the Malignant Soft Tissue Mass Jee Young Lee, M.D. 1, Kyung Jin Suh, M.D. 2, Hong-Geun Jung, M.D. 3 We present a case of a 37-year-old woman
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN
 Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology
 Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Journal of Medical Imaging and Radiation Oncology 60 (2016) 506 513 MEDICAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Malignant hyperechoic breast lesions at ultrasound: A pictorial essay Stephen Tiang, 1 Cecily Metcalf,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Sarcoidosis Appearing as a Primary Manifestation of Sarcoidosis: A Case Report 1
 Breast Sarcoidosis Appearing as a Primary Manifestation of Sarcoidosis: A Case Report 1 Hye-Jeong Lee, M.D., Eun-Kyung Kim, M.D., Min Jung Kim, M.D., Ki Keun Oh, M.D., Se Hoon Kim, M.D. 2 Breast sarcoidosis
Breast Sarcoidosis Appearing as a Primary Manifestation of Sarcoidosis: A Case Report 1 Hye-Jeong Lee, M.D., Eun-Kyung Kim, M.D., Min Jung Kim, M.D., Ki Keun Oh, M.D., Se Hoon Kim, M.D. 2 Breast sarcoidosis
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications. BI-RADS 5 th Edition
 UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
UW Radiology Review Course Breast Calcifications Grace Kalish, MD Vantage Radiology BI-RADS 5 th Edition Benign Skin Vascular Large rod like Coarse popcorn Suspicious Amorphous Coarse heterogenous Fine
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management
 Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management Poster No.: C-1418 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Song, B. K. Seo, K. R. Cho, O. H. Woo, Y.-S. Kim ; 1 1
Granulomatous mastitis: Radio-pathologic correlation and management Poster No.: C-1418 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Song, B. K. Seo, K. R. Cho, O. H. Woo, Y.-S. Kim ; 1 1
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
AMSER Case of the Month: September 2018 60-year-old woman with a left breast mass noted on screening mammography. Catherine McNulty, MS4 Tulane University School of Medicine Dr. Robin Sobolewski Breast
Preoperative Evaluation
 Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Preoperative Evaluation Lateral compartment lymph nodes are easier to detect and are amenable to FNA Central compartment lymph nodes are much more difficult to detect and FNA (Tg washout testing is compromised)
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
 Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
Ultrasound for Pre-operative Evaluation of Well Differentiated Thyroid Cancer Its Not Just About the Nodes AACE Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2017 Robert A. Levine, MD,
BI-RADS Update. Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital
 BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
BI-RADS Update Martha B. Mainiero, MD, FACR, FSBI Brown University Rhode Island Hospital No Disclosures BI-RADS History 1980s Quality Issues ACR Accreditation BI-RADS 1994 2003 4 th Edition MRI, US January
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging. Medical University of South Carolina Charleston
 Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
Abid Irshad, MD Director Breast Imaging Medical University of South Carolina Charleston Cases Financial disclosure: I or my family have no financial interest related to the material discussed in this presentation
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS. Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions
 SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings
 Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Inflammatory Breast Carcinoma: Mammographic, Ultrasonographic, MRI and Pathologic Findings Poster No.: C-2248 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, J. Lopes Dias, H. A. M.
Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions
 Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions Poster No.: C-1870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Aouini, I. Megdiche, D. Ben Hammadi, N. BEN MAMI, I. Attia, R. Neila, A. Zidi;
Breast imaging of benign fat containing lesions Poster No.: C-1870 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Aouini, I. Megdiche, D. Ben Hammadi, N. BEN MAMI, I. Attia, R. Neila, A. Zidi;
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses. Case #1
 University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
University of Washington Radiology Review Course: Strange and Specific Diagnoses Katherine E. Dee, MD Seattle Breast Center Via Radiology 2014 Case #1 37 year old presents with bilateral palpable lumps.
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY
 Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Alena Levit MD Avice O Connell MD University of Rochester, Rochester, NY Purpose Review imaging spectrum of both common benign and malignant breast lesions Describe and demonstrate CT features with mammogram,
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012. Lymph Nodes. John McGrath
 Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Radiology- Pathology Conference 4/29/2012 Lymph Nodes John McGrath 1 Presentation material is for education purposes only. All rights reserved. 2012 URMC Radiology Page 1 of 24 Case 1: 51 year-old male
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging
 Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Identification of tumor recurrence after breast cancer surgery with multimodality imaging Poster No.: C-0727 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Y. Cheung, J. H. Moon ; Gyeonggi-do/KR,
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient. Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester
 Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
Imaging the Symptomatic Patient Avice M.O Connell MD,FACR,FSBI Professor of Imaging Sciences Director, Women s Imaging University of Rochester The four most common symptoms Mass Pain Discharge Infection
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 SAM - Breast MRI 1
 National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Interpectoral Venous Angioma Presenting as a Breast Mass
 Case Report Interpectoral Venous ngioma Presenting as a reast Mass Dae Jung Kim, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Ki Keun Oh, MD, Joon Jeong, MD C hest wall
Case Report Interpectoral Venous ngioma Presenting as a reast Mass Dae Jung Kim, MD, Eun Ju Son, MD, Soon Won Hong, MD, Eun-Kyung Kim, MD, Jin Young Kwak, MD, Ki Keun Oh, MD, Joon Jeong, MD C hest wall
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Kidney Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT
 Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Kidney Case 1 Surgical Pathology Report February 9, 2007 Clinical History: This 45 year old woman was found to have a left renal mass. CT urography with reconstruction revealed a 2 cm medial mass which
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ductal carcinoma in situ, underestimation, ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy
 Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
Ductal carcinoma in situ diagnosed after an ultrasoundguided 14-gauge core needle biopsy of breast masses: Can underestimation be predicted preoperatively? Poster No.: C-0442 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific
Breast Imaging Lexicon
 9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
9//201 200 BI RADS th Edition 201 BI RADS th Edition Breast Imaging Lexicon Mammographic Pathology and Assessment Categories Deborah Thames, R.T.(R)(M)(QM) The Advanced Health Education Center Nonmember:
Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET
 Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions 1. 21 year old female presenting with left breast palpable mass, what is the most appropriate
Management of Palpable Abnormalities in the Breast Katerina Dodelzon, MD July 31, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions 1. 21 year old female presenting with left breast palpable mass, what is the most appropriate
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer
 Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Pre-operative Ultrasound of Lymph Nodes in Thyroid Cancer AACE - Advances in Medical and Surgical Management of Thyroid Cancer - 2018 Robert A. Levine, MD, FACE, ECNU Thyroid Center of New Hampshire Geisel
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings.
 Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
Invasive lobular carcinoma of the breast; spectrum of imaging findings. Poster No.: C-0847 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. Mandich, T. Diaz de Bustamante, L. Koren, M. Arroyo,
ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES. At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to:
 1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
1 ANNEX 1 OBJECTIVES At the completion of the training period, the fellow should be able to: 1. Breast Surgery Evaluate and manage common benign and malignant breast conditions. Assess the indications
Fat Necrosis: A Grand Imposter
 Fat Necrosis: A Grand Imposter Poster No.: C-0751 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. C. Flores Salinas, Y. A. Ramirez Galvan, A. Garza Báez, C. M. Ferrara Chapa; Monterrey/MX Keywords:
Fat Necrosis: A Grand Imposter Poster No.: C-0751 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. C. Flores Salinas, Y. A. Ramirez Galvan, A. Garza Báez, C. M. Ferrara Chapa; Monterrey/MX Keywords:
Breast Cancer Update 2018 The Latest in Diagnosis and Treatment SARATH K, PALAKODETI, DO, FAACS GENERAL, BREAST, AND COSMETIC SURGEON TOLEDO CLINIC
 Breast Cancer Update 2018 The Latest in Diagnosis and Treatment SARATH K, PALAKODETI, DO, FAACS GENERAL, BREAST, AND COSMETIC SURGEON TOLEDO CLINIC Objectives Identify breast lesions and masses, and know
Breast Cancer Update 2018 The Latest in Diagnosis and Treatment SARATH K, PALAKODETI, DO, FAACS GENERAL, BREAST, AND COSMETIC SURGEON TOLEDO CLINIC Objectives Identify breast lesions and masses, and know
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines. Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
 Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting Approved by Council June 2018 Approved: June 2018 Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting Approved by Council June 2018 Approved: June 2018 Guidelines on Breast Ultrasound Examination and Reporting
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity.
 Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Case Scenario 1: This case has been slightly modified from the case presented during the live session to add clarity. Background: 46 year old married premenopausal female with dense breasts has noticed
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Breast Cancer Imaging
 Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Breast Cancer Imaging I. Policy University Health Alliance (UHA) will cover breast imaging when such services meet the medical criteria guidelines (subject to limitations and exclusions) indicated below.
Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection
 Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
Original article Bilateral breast cancer: the role of mammography and ultrasonography in early detection Onthira Lekamnuaypon, M.D., 1 Pailin Kongmebhol, M.D., 1 Malai Muttarak, M.D. 1 Neelaya Sukhamwang,
UNC Breast Imaging Division July 2018
 UNC Breast Imaging Division July 2018 This module is to educate residents on ACR BI-RADS Atlas 2 nd edition Ultrasound Sonomammographic anatomy Sonographic features most associated with malignancy Clinical
UNC Breast Imaging Division July 2018 This module is to educate residents on ACR BI-RADS Atlas 2 nd edition Ultrasound Sonomammographic anatomy Sonographic features most associated with malignancy Clinical
Axillary lymph nodes, the usual suspects
 Axillary lymph nodes, the usual suspects Poster No.: C-0202 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. I. Fernández Martín, B. Cajal Campo, E. Dominguez Franjo, 1 2 1 1 2 1 J. C. Díez Hernández,
Axillary lymph nodes, the usual suspects Poster No.: C-0202 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. I. Fernández Martín, B. Cajal Campo, E. Dominguez Franjo, 1 2 1 1 2 1 J. C. Díez Hernández,
Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography
 Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography Poster No.: C-1957 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H. J. Lim, K. R. Cho, K. W. Hwang, B. K. Seo, O.
Pathologic outcomes of coarse heterogeneous calcifications detected on mammography Poster No.: C-1957 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper Authors: H. J. Lim, K. R. Cho, K. W. Hwang, B. K. Seo, O.
Original Report. Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical, Mammographic, and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography
 Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Singapore Med J 2002 Vol 43(5) : 229-233 O r i g i n a l A r t i c l e Evaluation of the Contralateral Breast in Patients with Ipsilateral Breast Carcinoma: The Role of Mammography M Muttarak, S Pojchamarnwiputh,
Breast Imaging Donald L. Renfrew, MD
 This free educational material is provided by 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Breast cancer is the most frequent non-skin cancer diagnosis in women, with an
This free educational material is provided by 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Breast cancer is the most frequent non-skin cancer diagnosis in women, with an
Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET
 Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions/Answers/Rationales/References 1. Below
Tips and Tricks to performing Magnetic Resonance Imaging Guided Breast Interventional Procedures Habib Rahbar, MD, FSBI October 23, 2018, 7:00pm ET SAM Questions/Answers/Rationales/References 1. Below
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contents. vii. Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii
 Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Contents Preface... Acknowledgments... v xiii SECTION I 1. Introduction... 3 Knowledge-Based Diagnosis... 4 Systematic Examination of the Lymph Node... 7 Cell Type Identification... 9 Cell Size and Cellularity...
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach. Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina
 Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Breast Imaging: Multidisciplinary Approach Madelene Lewis, MD Assistant Professor Associate Program Director Medical University of South Carolina No Disclosures Objectives Discuss a multidisciplinary breast
Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification. Alex Tessnow, MD, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Associate Professor of Medicine Dallas, Texas
 Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification Alex Tessnow, MD, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Associate Professor of Medicine Dallas, Texas Which of the following is true? A. All echogenic foci
Thyroid Nodules: US Risk Stratification Alex Tessnow, MD, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Associate Professor of Medicine Dallas, Texas Which of the following is true? A. All echogenic foci
RSNA, /radiol Appendix E1. Methods
 RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018
 AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 42 year old with right breast mass Rina Kiyota Petek Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, OMS-III Kossivi Dantey, MD Bibianna Klepchick, MD Matthew Hartman,
AMSER Case of the Month: November 2018 42 year old with right breast mass Rina Kiyota Petek Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine, OMS-III Kossivi Dantey, MD Bibianna Klepchick, MD Matthew Hartman,
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1
 The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
The Value of Ultrasonographic Detection for Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer 1 Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Asiry Hwang, M.D., Hye-Young Choi, M.D., Seung Yon Baek, M.D. Purpose: We evaluated the
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay
 CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
CDIS: what's beyond microcalcifications? - Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1096 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. N. Lucas, C. A. S. Ruano, I. Oliveira, J. M. G. Lourenco, Z. 1 1 1
Indications for Breast MRI: Case-Based Review
 AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Indications for Breast MRI: Case-Based Review Amy Argus 1, Mary C. Mahoney Objective The educational objectives of this continuing medical education
AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Indications for Breast MRI: Case-Based Review Amy Argus 1, Mary C. Mahoney Objective The educational objectives of this continuing medical education
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up
 Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Breast Cancer Diagnosis, Treatment and Follow-up What is breast cancer? Each of the body s organs, including the breast, is made up of many types of cells. Normally, healthy cells grow and divide to produce
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm
 Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
Evaluation of the Axilla Post Z-0011 Trial New Paradigm Belinda Curpen, MD, FRCPC; Tetyana Dushenkovska; Mia Skarpathiotakis MD, FRCPC; Carrie Betel, MD, FRCPC; Kalesha Hack, MD, FRCPC; Lara Richmond,
