The Relationship Between Bone Metastasis from Human Breast Cancer and Integrin v 3 Expression
|
|
|
- Rebecca Elliott
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Relationship Between Bone Metastasis from Human Breast Cancer and Integrin v 3 Expression SHIN TAKAYAMA 1, SEIICHIRO ISHII 2, TADASHI IKEDA 1, SHIGERU MASAMURA 1, MASAKAZU DOI 1 and MASAKI KITAJIMA 1 1 Department of Surgery, Keio University School of Medicine, 35 Shinanomachi, Shinjuku-ku, Tokyo, ; 2 Department of Surgery, Kawasaki City Hospital, 12-1, Shinkawa-dori, Kawasaki-shi, Kanagawa-ken, , Japan Abstract. Background: Osteoclast activation plays an essential role in the development of bone metastasis (BM). Integrin v 3 mediates the attachment of osteoclasts to bone matrix, and it is overexpressed in bone-residing breast cancer cells. We studied BM from breast cancer in relation to its Integrin v 3 expression. Materials and Methods: Integrin v 3 expression in 4 human breast cancer cell lines (MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-435, MKL-4 and T-47D) was determined by immunohistochemistry, flow cytometry and reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). Results: Integrin v 3 was expressed in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB- 435, but not in MKL-4 or T-47D, using both immunohistochemistry and flow cytometry. By RT-PCR, positive bands for both v and 3 subunits were identified in MDA-MB-231 and 435, while only the v subunit mrna was present in MKL-4 and T-47D. BM was common in vivo following inoculation with MDA-MB-231 or 435, but not with MKL-4. Conclusion: Integrin v 3 expression appears to play a key role in the development of BM from breast cancer. Bone is the most common metastatic site in breast cancer. Among primary breast cancer patients, 30% develop bone metastasis (BM) as the first event and 70% have BM at autopsy. However, the process of establishment of BM in bone and the bone marrow is not well understood. Integrins are alpha, beta heterodimeric transmembrane proteins. Integrins mediate adhesion to the extracellular matrix and cell-to-cell adhesive interactions (1). We know that Integrin v 3 mediates various biological events, including the adhesion of osteoclasts to the bone matrix and angiogenesis, among others. For osteoclastic activation in bone matrix to Correspondence to: Shin Takayama, Department of Surgery, Keio University School of Medicine, 35 Shinanomachi, Shinnjuku-ku, Tokyo, Japan, stakayam@sc.itc.keio.ac.jp Key Words: Bone metastasis, breast cancer, integrins, osteoclasts, osteoclast activation. occur, osteoclasts must adhere to bone matrix through Integrin v 3. Helen et al. (2) showed that Integrin v 3 is overexpressed by bone-residing breast cancer cells and suggested either that subclonal selection of Integrin v 3 - expression tumor cell populations or up-regulation of Integrin v 3 in the bone microenvironment must take place for BM to occur. Breast cancer cells adhere to the interstitial space of the bone matrix, but they lack the ability to resorb bone matrix by themselves. So breast cancer cells must be assisted by osteoclasts that can resorb bone matrix (3). If, by expressing Integrin v 3, cancer cells can adhere to bone matrix, they are likely to interact with osteoblasts and osteoclasts. In this study, we sought to determine whether Integrin v 3 is an adhesion molecule related to the establishment of BM from human breast cancer. Materials and Methods Animals. Eight-week-old nude rats were purchased and housed at the Laboratory Animal Center of Keio University, Japan, in a pathogen-free environment for the duration of the experiment. The Institutional Review Borad of the animal facility approved the study protocol. Cell lines. Four different breast cancer cell lines were studied: MDA-MB-231 (ATCC HTB 26), a human breast adenocarcinoma isolated from a pleural effusion; MKL-4, a cotransfectant of the MCF-7 cell line with fgf-4 and lacz, which micrometastasises to several organs (gift of Dr. Kurebayashi, Kawasaki Medical School, Japan); T-47D (ATCC HTB 133), a human breast ductal carcinoma isolated from a pleural effusion; and MDA-MB-435 (ATCC HTB 129), a human breast ductal carcinoma isolated from a pleural effusion. Cell culture. Cells were grown in Eagle s minimal essential medium (E-MEM) or Dulbecco s modified Eagle medium (D-MEM) in a gas mixture of 5% CO 2 and 95% air at 37ÆC. Passage and medium exchange were performed once a week. Immunohistochemistry. Cells on the slide were frozen and stained with anti-integrin v 3 monoclonal antibody LM609 (1:100) and anti-integrin 2 1 monoclonal antibody BHA2.1 (1:100). The cells /2005 $
2 Figure 1. Roentgenograms of rats with bone metastasis after injection of MDA-MB-231 cancer cells at A : 4 weeks and B: 6 weeks. were fixed in acetone for 30 sec, air-dried for 2 min, washed by Tris-buffered saline with calcium (TBS-Ca) for 2 min, blocked with 3% H 2 O 2 for 10 min, washed twice with TBS-Ca for 5 min, and then incubated with LM609 or BHA2.1. overnight at 4ÆC. The next day, the slides were washed three times with TBS for 5 min, placed in ENVISION+ (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark) that had polymerimmuno complex at room temperature for 30 min, again washed three times with TBS for 5 min, and stained by diaminobenzidine (DAB) for 30 sec. Flow cytometry. Cells were stained with 5 Ìg/mL mouse mab LM609 specific to Integrin v 3 or mouse mab BHA2.1 specific to Integrin 2 1 and incubated with anti-mouse-igg FITC conjugate F(ab )2 Fragment (Sigma, St Louis, MO, USA). Viable cells were analyzed on a FACScan flow cytometer (Becton Dickinson, Franklin Lakes, NJ, USA). Population gates were set using cells incubated with normal mouse IgG (4). Reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). RNA was isolated from human breast cancer cells. One microliter of cdna was used per 25 ÌL of PCR reaction mixuture. The reaction mixuture contained TaKaRa Z-Taq, 10 X Z-taq buffer, dntp mixuture, MgCl 2 and PCR enhance (TaKaRa, Shiga-ken, Japan). We used the sequence reported in Baljit et al. (5) for v and in Illera et al. (6) for 3. The 5 primer for v was 5 - GACTGTGTGGAAGACAATGTCTGTAAACCC, and the 3 primer was 5 -CCAGCTAAGAGTTGAGTTCCAGCC; the size was 305 bp. These primers were extended from human v cdna (GenBank accession no. M14648). For 3, the 5 primer was 5 - CTGGTGTTTACCACTGATGCCAAG, and the 3 primer was 5 - TGTTGAGGCAGGTGGCATTGAAGG and the size was 393 bp. These primers were extended from human 3 cdna (GenBank accession no. L28832). PCR amplification for v was performed using a three-step process: i) initial extension at 94ÆC, for 1 min; ii) annealing at 65ÆC, for 1 min; and iii) final extension at 72ÆC, for 2 80
3 Takayama et al: Bone Metastasis and Integrin Expression min, and for 3 : i) initial extension at 95ÆC, for 10 min; ii) annealing at 60ÆC, for 2 min; iii) annealing at 72ÆC, for 3 min; and iv) final extension at 72ÆC, for 10 min. The amplified products were separated on 1% agarose gels using a 1-kilobase DNA ladder for size comparision. Surgical procedure and evaluation of BM. The procedure was performed as described in detail elsewhere, with minor modifications (7). Briefly, after anesthetizing 8-week-old nude rats by intraperioneal injection of ketaral 0.7 ml, a small incision was made in the left cervical skin under a dissecting microscope. A polyethylene catheter (PE-10, Becton Dickinson) was inserted into the thoracic aorta from the left common carotid artery. Cells (10 6 or 5x10 6 suspended in 0.2 ml of Hank s balanced salt solution) were injected slowly into the thoracic aorta. Then the catheter was removed, and the left common carotid artery was ligated. Whole body radiographs were taken 4 and 6 weeks after injection to identify BM. X-ray confirmed the detection of the lesions (Figure 1). Results Immunohistochemical study identified the overexpression of Integrin v 3 in two human breast cancer cell lines, MDA- MB-231 and MDA-MB-435, but not in MKL-4 or T47D (Figure 2). On flow cytometry, Integrin v 3 was detected in 82% and 92% of MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 cells, respectively, and in 26% and 3% of MKL-4 and T-47D cells. v and 3 subunit mrna was isolated from each human breast cancer cell line by RT-PCR study. Positive bands for both the v and 3 subunits were noted in MDA-MB-231 and 435, while only the v subunit was detected in MKL-4 and T-47D (Figure 3). These three studies were consistent in showing that Integrin v 3 is expressed in MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB- 435, but not in MKL-4 or T-47D. Further, Integrin 2 1 was overexpressed in all human breast cancer cell lines on both immunohistochemical study and flow cytometry study (Table I). In vivo, the frequency of developing BM using MDA-MB- 231 cells was high [9/11 (81.8%)].We were able to develop BM [8/10 (80.0%)] in rats using MDA-MB-435 cells, as well. Attempts to develop BM using MKL-4 failed [1/9 (11.0%)] (Table II). Discussion This study investigated the relationship between bone metastasis from breast cancer and Integrin v 3. We previously reported that tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRACP) is a useful marker for metastatic bone disease and of the response to treatment in breast cancer, and that both urinary pyridinoline and urinary deoxypyridinoline correlated with the volume of bone metastasis in a rat model (8). Those results showed that tumor cells initially produce micrometastatic foci in the bone marrow, followed by osteoclastic bone resorption, activated by humoral factors that are released from tumor or stromal cells. Recently, Integrin v 3 has been shown to play an important role in the attachment of osteoclasts to bone matrix (9), and the stimulation of Integrin v 3 expression by human osteoclasts stimulates adhesion and migration in the bone matrix (10). Currently, Integrin v 3 antagonists are being developed as inhibitors of bone resorption (11). On the other hand, breast cancers commonly cause osteolytic metastasis according to the type of interaction between breast cancer cells and osteoblasts and osteoclasts (3). Breast cancer cells residing in bone overexpress Integrin v 3, suggesting either a subclonal selection of Integrin v 3 -expressing tumor cell populations or up-regulation of Integrin v 3 in the bone microenvironment. We assumed that, if breast cancer cells overexpressed Integrin v 3, they are more likely to adhere to bone matrix and interact with osteoblasts and osteoclasts. We studied the expression of Integrin v 3 in four human breast cancer cell lines in various ways. Integrin v 3 was expressed in two human breast cancer cell lines, MDA-MB- 231 and MDA-MB-435, but not in MKL-4 or T-47D. This result is consistent with a previous report (12). Thus, it is clear that different human breast cancer cell lines differ in their expression of Integrin v 3, though all human breast cancer cell lines expressed Integrin 2 1. Integrin 2 1 is a collagen receptor which is commonly expressed in human breast cancer and its loss has been reported to be associated with the invasive phenotype of breast cancer (13). However, in the present study, Integrin 2 1 was not related to BM. Our attempts to create a model of BM using MDA-MB- 231 and 435 cells with Integrin v 3 were successful. We considered the seed and soil theory consistent with our data (14), i.e., both cells are likely to adhere to bone matrix only when the bone marrow environment had the ligand for Integrin v 3, osteopontin. It is reasonable to question the homology between human and rat cdna for Integrin v 3. Dolon et al. (15) reported that rat cdna fragments shared 86 to 91% homology with their respective human sequences. So, at least theoretically, using human cdna in this rat model is justified. We successfully developed BM by inoculating rats with MDA-MB-231 [9/11 (81.8%)] and MDA-MB-435 cells [8/10 (80.0%)], both of which express Integrin v 3. On the other hand, we failed to consistently develop BM using MKL-4 cells which lack Integrin v 3 [1/9 (11.0%)]. This result shows that expression of Integrin v 3 by breast cancer cells is critical to the formation of BM. We have shown that the dis-integrin echistatin, arg-glyasp (RGD)-containing peptide, blocks migration of 81
4 Figure 2. Overexpression of Integrin v 3 demonstrated immunohistochemically in A: MDA-MB-231 and B: MKL-4. Figure 3. v and 3 subunit mrna in human breast cancer cell lines. Table I. Expression of Integrins v 3 and 2 1 in breast cancer cell lines. v MDA-MB MDA-MB MKL T-47D - + Table II. Frequency of bone metastasis (BM) after injection of breast cancer cell lines. Cell lines Frequency of BM (%) MDA-MB-231 9/11 (81.8) MDA-MB-435 8/10 (80.0) MKL-4 1/9 (11.0) 82
5 Takayama et al: Bone Metastasis and Integrin Expression basement membrane in vitro, and the formation of BM using MDA-MB-435 in vivo (16). That outcome encouraged us to define Integrin s relationship to BM thoroughly. The details of the mechanism by which Integrin v 3 is related to BM are unclear. We do not know whether activation of Integrin v 3 in human breast cancer cells stimulates adhesion or migration in response to osteopontin in vivo, as it does in the osteoclast. The breast cancer cells that express Integrin v 3 clearly acquire the ability to adhere to the bone matrix. Further study of Integrin v 3 s role in the development of BM from human breast cancer is required. Conclusion 1) Integrin v 3 is expressed in the MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cell lines, but not in MKL-4 or T47D. 2) MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 are more likely to cause bone metastasis in rats than MKL-4. References 1 Ota I and Matsuura S: Adhesion molecules and cancer metastasis. Rinsho Byori 45(6): , Helen L, Alphan F and Kitazawa S: Integrin alpha v beta 3 expression by bone-residing breast cancer metastases. Diagn Mol Pathol 5(2): , Rachel JT, Theresa AG and Juan JY: Breast cancer cells interact with osteoblasts to support osteoclast formation. Endocrinology 140(10): , Deryugina EI, Bourdon MA and Jungwirth K: Functional activation of integrin alpha V beta 3 in tumor cells expressing membrane-type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. Int J Cancer 86(1): 15-23, Singh B, Fu C and Bhattacharya J: Vascular expression of the alpha(v)beta(3)-integrin in lung and other organs. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 278(1): L217-L226, Illera MJ, Cullinan E and Gui Y: Blockade of the alpha(v) beta(3) integrin adversely affects implantation in the mouse. Biol Reprod 62(5): , Tamura H, Ishii S and Ikeda T: Therapeutic efficacy of pamidronate in combination with chemotherapy to bone metastasis of breast cancer in a rat model. Surg Oncol 5(3): , Wada N, Ishii S and Ikeda T: Serum tartrate resistant acid phosphatase as a potential marker of bone metastasis from breast cancer. Anticancer Res 19(5C): , Stephen C, Wah-Tung H and Gwilym J: The integrin specificity of human recombinant osteopontin. Biochemical Pharmacol 58: , Faccio R, Grano M and Colucci S: Activation of alpha v beta 3 integrin on human osteoclast-like cells stimulates adhesion and migration in response to osteopontin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 249(2): , Hartman GD and Duggan ME: Alpha(v) beta(3) Integrin antagonists as inhibitors of bone resorption. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 9(6): , Meyer T, Marshall JF and Hart IR: Expression of alpha v integrins and vitronectin receptor identity in breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 77(4): , Oda K, Itoh H and Utsunomiya H: Bio-histochemical aspects of integrins (alpha 2 beta 1, alpha 6 beta 1) in invasive mammary carcinomas: an immunohistochemical study. Pathol Int 44(6): , Paget S: The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. Lancet 1: , Shinar D. M, Schmidt A and Halperin D: Expression of alpha v beta 3 integrin subunits in rat osteoclasts in situ. Bone Min Res 8(4): , Doi M, Ishii S and Takayama S: The blockade of integrin v 3 for prevention of bone metastasis (BM) of human breast cancer. J Bone Min Metabol 19 Supplement: 36(Proc.), Received October 12, 2004 Accepted December 20,
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Can we prevent metastasis?
 Can we prevent metastasis? A research example to translate from the bench to the bedside Diane Palmieri, Ph.D. Women s Cancers Section Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology CCR, NCI Some Basic Truths Most
Can we prevent metastasis? A research example to translate from the bench to the bedside Diane Palmieri, Ph.D. Women s Cancers Section Laboratory of Molecular Pharmacology CCR, NCI Some Basic Truths Most
Online Data Supplement. Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2
 Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Online Data Supplement Anti-aging Gene Klotho Enhances Glucose-induced Insulin Secretion by Upregulating Plasma Membrane Retention of TRPV2 Yi Lin and Zhongjie Sun Department of physiology, college of
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness
 World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
World Health Organization Recommended laboratory tests to identify influenza A/H5 virus in specimens from patients with an influenza-like illness General information Highly pathogenic avian influenza (HPAI)
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century.
 Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
Seeds and soil theory by Stephen Paget at the end of the XIX century. In The Distribution Of Secondary Growths In Cancer Of The Breast Paget presents and analyzes 735 fatal cases of breast cancer, complete
PD-L1 Analyte Control DR
 Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
Quality in Control PD-L1 Analyte Control DR PD-L1_PI_v2 Product Codes: HCL019, HCL020 and HCL021 Contents PD-L1 Analyte Control DR 2 What is PD-L1? 3 The Role of PD-L1 in Cancer 3 PD-L1 Assessment 4 PD-L1
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products
 stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Stem Cell Qualified Extracellular Matrix Proteins Stem cell research requires the finest
stem cell products Basement Membrane Matrix Products Rat Mesenchymal Stem Cell Growth and Differentiation Products Stem Cell Qualified Extracellular Matrix Proteins Stem cell research requires the finest
The Role of CD164 in Metastatic Cancer Aaron M. Havens J. Wang, Y-X. Sun, G. Heresi, R.S. Taichman Mentor: Russell Taichman
 The Role of CD164 in Metastatic Cancer Aaron M. Havens J. Wang, Y-X. Sun, G. Heresi, R.S. Taichman Mentor: Russell Taichman The spread of tumors, a process called metastasis, is a dreaded complication
The Role of CD164 in Metastatic Cancer Aaron M. Havens J. Wang, Y-X. Sun, G. Heresi, R.S. Taichman Mentor: Russell Taichman The spread of tumors, a process called metastasis, is a dreaded complication
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts
 Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Fructose Upregulates FGF23 Expression In MC3T3 Pre-osteoblasts Edek A. Williams, B.S.E., Veronique Douard, Ph.D., Joseph M. Lomuti, B.S., Ronaldo Ferraris, Ph.D., J. C. Fritton, Ph.D.. Rutgers University,
Osteoclast Culture Kit
 K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 CC-109 Mouse Osteoclast Precursor Cells,
K-ASSAY KAMIYA BIOMEDICAL COMPANY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 CC-109 Mouse Osteoclast Precursor Cells,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) Immunohistochemical Study on Blood Antigens in Primary Breast Carcinom Tomita, Masao; Nakagoe, Toru; Kawah Tagawa, Yutaka Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia.
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
ANTICANCER RESEARCH 25: (2005)
 Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Against Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein Suppresses Osteolytic Bone Metastasis of Human Breast Cancer Cells Derived from MDA-MB-231 HIDEMI SAITO 1, TOSHIAKI TSUNENARI 1,
Humanized Monoclonal Antibody Against Parathyroid Hormone-related Protein Suppresses Osteolytic Bone Metastasis of Human Breast Cancer Cells Derived from MDA-MB-231 HIDEMI SAITO 1, TOSHIAKI TSUNENARI 1,
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER. Andrew Leask.
 CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
Cancer model Liver metastasis I
 Cancer model Liver metastasis I H. Suemizu, M. Monnai, Y. Ohnishi, M. Ito, N. Tamaoki, and M. Nakamura. 2007. Identification of a key molecular regulator of liver metastasis in human pancreatic carcinoma
Cancer model Liver metastasis I H. Suemizu, M. Monnai, Y. Ohnishi, M. Ito, N. Tamaoki, and M. Nakamura. 2007. Identification of a key molecular regulator of liver metastasis in human pancreatic carcinoma
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury
 Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Neutrophils contribute to fracture healing by synthesizing fibronectin+ extracellular matrix rapidly after injury Bastian OW, Koenderman L, Alblas J, Leenen LPH, Blokhuis TJ. Neutrophils contribute to
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
1. The metastatic cascade. 3. Pathologic features of metastasis. 4. Therapeutic ramifications. Which malignant cells will metastasize?
 1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
1. The metastatic cascade 3. Pathologic features of metastasis 4. Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of Paget s disease of the nipple (intraductal
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
 Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Expression and clinical significance of ADAM17 protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma H.B. Liu, Y. Zhu, Q.C. Yang, Y. Shen, X.J. Zhang and H. Chen Department of Pathology First People s Hospital
Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992, 37
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Study on the Expression of EGFR a Content in the Stomach Cancer Tissu Nakazaki Takayuki Citation Acta Medica Nagasakiensia. 1992 37 Issue Date 1992-12-25
Senior Thesis. Presented to. The Faculty of the School of Arts and Sciences Brandeis University
 Greenwald 1 Mouse intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) isoforms demonstrate different binding affinities to mouse macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1) and preliminary evidence for alternatively-spliced variants
Greenwald 1 Mouse intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) isoforms demonstrate different binding affinities to mouse macrophage-1 antigen (Mac-1) and preliminary evidence for alternatively-spliced variants
Research Article Stromal Expression of CD10 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation with ER, PR, HER2-neu, and Ki67
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research International Breast Cancer Volume 20, Article ID 47957, 4 pages doi:0.406/20/47957 Research Article Stromal Expression of CD0 in Invasive Breast Carcinoma and Its Correlation
A Novel Chromatographic Method for Ep-CAM mrna Detection in Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
 A Novel Chromatographic Method for Ep-CAM mrna Detection in Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer CHARISIOS KARANIKIOTIS 1, IOANNIS SKIADAS 2, MARIA KARINA 3, STAVROULA
A Novel Chromatographic Method for Ep-CAM mrna Detection in Peripheral Blood and Bone Marrow of Patients with Metastatic Colorectal Cancer CHARISIOS KARANIKIOTIS 1, IOANNIS SKIADAS 2, MARIA KARINA 3, STAVROULA
IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA
 & IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
& IMMUNOHISTOCHEMICAL EXPRESSION OF TISSUE INHIBITOR OF METALLOPROTEINASE-1 (TIMP-1) IN INVASIVE BREAST CARCINOMA Suada Kuskunović*, Svjetlana Radović, Mirsad Dorić, Ajna Hukić, Mirsad Babić, Ivana Tomić,
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer
 Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
Chapter 2 Staging of Breast Cancer Zeynep Ozsaran and Senem Demirci Alanyalı 2.1 Introduction Five decades ago, Denoix et al. proposed classification system (tumor node metastasis [TNM]) based on the dissemination
TITLE: Crosstalk Between Cancer Cells and Bones Via the Hedgehog Pathway Determines Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0400 TITLE: Crosstalk Between Cancer Cells and Bones Via the Hedgehog Pathway Determines Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Lalita Shevde-Samantrese
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0400 TITLE: Crosstalk Between Cancer Cells and Bones Via the Hedgehog Pathway Determines Bone Metastasis of Breast Cancer PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Dr. Lalita Shevde-Samantrese
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3.
 Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Table S1. Primers and PCR protocols for mutation screening of MN1, NF2, KREMEN1 and ZNRF3. MN1 (Accession No. NM_002430) MN1-1514F 5 -GGCTGTCATGCCCTATTGAT Exon 1 MN1-1882R 5 -CTGGTGGGGATGATGACTTC Exon
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) for washing the cells TE buffer (nuclease-free) ph 7.5 for use with the PrimePCR Reverse Transcription Control Assay
 Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Catalog # Description 172-5080 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 100 x 50 µl reactions 172-5081 SingleShot Cell Lysis Kit, 500 x 50 µl reactions For research purposes only. Introduction The SingleShot Cell Lysis
Expressional Changes In Growth And Inflammatory Mediators During Achilles Tendon Repair In Diabetic Rats.
 Expressional Changes In Growth And Inflammatory Mediators During Achilles Tendon Repair In Diabetic Rats. Paul W. Ackermann, MD, PhD 1, Aisha Ahmed, PhD 1, Nicos Schizas, MD 1, Jian Li, MD, PhD 1, Mahmood
Expressional Changes In Growth And Inflammatory Mediators During Achilles Tendon Repair In Diabetic Rats. Paul W. Ackermann, MD, PhD 1, Aisha Ahmed, PhD 1, Nicos Schizas, MD 1, Jian Li, MD, PhD 1, Mahmood
Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT
 Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons
 SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons 6/18/08 Akeila Bellahcène and Vincent Castronovo of the Metastasis Research laboratory of the University of Liège are among the first researchers to have discovered
SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons 6/18/08 Akeila Bellahcène and Vincent Castronovo of the Metastasis Research laboratory of the University of Liège are among the first researchers to have discovered
TITLE: A Tissue Engineering Approach to Study the Progression of Breast Tumor Metastasis in Bone
 AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0749 TITLE: A Tissue Engineering Approach to Study the Progression of Breast Tumor Metastasis in Bone PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mingxin Che, M.D., Ph.D. Daotai Nie, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-04-1-0749 TITLE: A Tissue Engineering Approach to Study the Progression of Breast Tumor Metastasis in Bone PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Mingxin Che, M.D., Ph.D. Daotai Nie, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the
 Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
Supplementary Figure 1. Generation of knockin mice expressing L-selectinN138G. (a) Schematics of the Sellg allele (top), the targeting vector, the targeted allele in ES cells, and the mutant allele in
IL-24 AND ITS ROLE IN WOUND HEALING
 IL-24 AND ITS ROLE IN WOUND HEALING Nancy J. Poindexter, Ryan Williams, Garth Powis, Sunil Chada, and Elizabeth A. Grimm & Introgen Therapeutics, Inc., Houston, TX IL-24/MDA 24/MDA-77 is a Tumor Suppressor
IL-24 AND ITS ROLE IN WOUND HEALING Nancy J. Poindexter, Ryan Williams, Garth Powis, Sunil Chada, and Elizabeth A. Grimm & Introgen Therapeutics, Inc., Houston, TX IL-24/MDA 24/MDA-77 is a Tumor Suppressor
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Cancer Biology Course. Invasion and Metastasis
 Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Cancer Biology Course Invasion and Metastasis 2016 Lu-Hai Wang NHRI Cancer metastasis Major problem: main reason for killing cancer patients, without it cancer can be cured or controlled. Challenging questions:
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice
 Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland
 Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Pathology International 2008; 58: 322 326 doi:10.1111/j.1440-1827.2008.02231.x Case Report Aggressive invasive micropapillary salivary duct carcinoma of the parotid gland Hidetaka Yamamoto, 1 Hideoki Uryu,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS
 Molecular Diagnostics Symposium 2014 Zurich, 27 February 2014 ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS Stijn Deborggraeve Parasite Diagnostics Unit, Institute of Tropical Medicine
Molecular Diagnostics Symposium 2014 Zurich, 27 February 2014 ISOTHERMAL AMPLIFICATION IN MOLECULAR DIAGNOSIS OF SLEEPING SICKNESS Stijn Deborggraeve Parasite Diagnostics Unit, Institute of Tropical Medicine
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma plasma B cell.
 Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63
 68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
68 Chin J Cancer Res 22(1):68-72, 2010 www.springerlink.com Original Article Effect of Survivin-siRNA on Drug Sensitivity of Osteosarcoma Cell Line MG-63 Jing-Wei Wang 1, Yi Liu 2, Hai-mei Tian 2, Wei
Osteoclast Culture Kit
 K-ASSAY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 091708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION
K-ASSAY Osteoclast Culture Kit For the culture of Osteoclasts from precursor cells. Cat. No.: CC-107 Rat Osteoclast Precursor Cells, V-1 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 091708 K-ASSAY PRODUCT INFORMATION
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1
 Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and
 Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Supplementary Figure 1. SA-β-Gal positive senescent cells in various cancer tissues. Representative frozen sections of breast, thyroid, colon and stomach cancer were stained with SA-β-Gal and nuclear fast
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown. Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC
 Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Cancers of unknown primary : Knowing the unknown Prof. Ahmed Hossain Professor of Medicine SSMC Definition Cancers of unknown primary site (CUPs) Represent a heterogeneous group of metastatic tumours,
Acute myocardial infarction (MI) on initial presentation was diagnosed if there was 20 minutes
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Diagnosis for acute myocardial infarction Acute myocardial infarction (MI) on initial presentation was diagnosed if there was 20 minutes or more of chest pain
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Diagnosis for acute myocardial infarction Acute myocardial infarction (MI) on initial presentation was diagnosed if there was 20 minutes or more of chest pain
Supplemental information
 Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Carcinoemryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6) promotes EGF receptor signaling of oral squamous cell carcinoma metastasis via the complex N-glycosylation y Chiang et al. Supplemental
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
1.The metastatic cascade. 2.Pathologic features of metastasis. 3.Therapeutic ramifications
 Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Metastasis 1.The metastatic cascade 2.Pathologic features of metastasis 3.Therapeutic ramifications Sir James Paget (1814-1899) British Surgeon/ Pathologist Paget s disease of bone Paget s disease of the
Supplementary Materials. for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis
 Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Supplementary Materials for Garmy-Susini, et al, Integrin 4 1 signaling is required for lymphangiogenesis and tumor metastasis 1 Supplementary Figure Legends Supplementary Figure 1: Integrin expression
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma
 Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Clinical significance of CD44 expression in children with hepatoblastoma H.-Y. Cai 1 *, B. Yu 1 *, Z.-C. Feng 2, X. Qi 1 and X.-J. Wei 1 1 Department of General Surgery, General Hospital of Beijing Military
Chapter 4. Estrogen receptor expression in human macrophages
 Chapter 4 Estrogen receptor expression in human macrophages 4.1. Introduction Macrophages respond to estrogen present in their microenvironment and hence should express functional estrogen receptors unless
Chapter 4 Estrogen receptor expression in human macrophages 4.1. Introduction Macrophages respond to estrogen present in their microenvironment and hence should express functional estrogen receptors unless
Cancer cells in vitro
 Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
Absence of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus in Patients with Pulmonary
 Online Data Supplement Absence of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Cornelia Henke-Gendo, Michael Mengel, Marius M. Hoeper, Khaled Alkharsah, Thomas
Online Data Supplement Absence of Kaposi s Sarcoma-Associated Herpesvirus in Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Cornelia Henke-Gendo, Michael Mengel, Marius M. Hoeper, Khaled Alkharsah, Thomas
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
TRACP & ALP double-stain Kit
 Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
Table of Content I. Description... 2 II. Introduction... 2 III. Principles... 2 IV. Kit components... 3 V. Storage... 3 VI. Preparation of reagents... 3 VII. Methods... 4-7 Cell fixation... 4 Activity
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model
 CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
CpG ODN 1826 enhances radiosensitivity of the human lung cancer cell line A549 in a rat model W. Yan, T.-Y. Sun, C.-M. Yang, M. Jia, J. Li, H.-L. Tang and Y.-F. Zhou The Cadre Ward of Air Force General
Cytochalasins from an Australian marine sediment-derived Phomopsis sp. (CMB-M0042F): Acid-mediated intra-molecular cycloadditions enhance
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION Cytochalasins from an Australian marine sediment-derived Phomopsis sp. (CMB-M42F): Acid-mediated intra-molecular cycloadditions enhance chemical diversity Zhuo Shang, Ritesh Raju,
SUPPORTING INFORMATION Cytochalasins from an Australian marine sediment-derived Phomopsis sp. (CMB-M42F): Acid-mediated intra-molecular cycloadditions enhance chemical diversity Zhuo Shang, Ritesh Raju,
Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2],
![Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2], Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2],](/thumbs/86/93801604.jpg) Supplementary information Methods Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2], and A/Hong Kong/213/03 [H5N1]) were grown in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells
Supplementary information Methods Cells and viruses. Human isolates (A/Kawasaki/173/01 [H1N1], A/Yokohama/2057/03 [H3N2], and A/Hong Kong/213/03 [H5N1]) were grown in Madin-Darby canine kidney (MDCK) cells
TITLE: Breast Tumor-Generated Type 1 Collagen Breakdown Fragments Act as Matrikines to Drive Osteolysis
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0639 TITLE: Breast Tumor-Generated Type 1 Collagen Breakdown Fragments Act as Matrikines to Drive Osteolysis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ching Hua William Wu PhD. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-08-1-0639 TITLE: Breast Tumor-Generated Type 1 Collagen Breakdown Fragments Act as Matrikines to Drive Osteolysis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Ching Hua William Wu PhD. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer
 Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer Aom Isbell http://www2.massgeneral.org/cancerresourceroom/types/gi/index.asp Spring/Summer 1, 2012 Alexandros Tzatsos, MD PhD Bardeesy Lab: Goals and Objectives
Generating Mouse Models of Pancreatic Cancer Aom Isbell http://www2.massgeneral.org/cancerresourceroom/types/gi/index.asp Spring/Summer 1, 2012 Alexandros Tzatsos, MD PhD Bardeesy Lab: Goals and Objectives
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis
 Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Nagoya Med. J., 107 Development of important genes during breast carcinogenesis AYA NAIKI-ITO Department of experimental pathology and tumor biology Nagoya City University Graduate School of Medical Sciences
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases. Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary
 Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
Ca, Mg metabolism, bone diseases Tamás Kőszegi Pécs University, Department of Laboratory Medicine Pécs, Hungary Calcium homeostasis Ca 1000g in adults 99% in bones (extracellular with Mg, P) Plasma/intracellular
The value of urine samples from men with nongonococcal
 124 Genitourin Med 1991;67:124-128 The value of urine samples from men with nongonococcal urethritis for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis P E Hay, B J Thomas, C Gilchrist, H M Palmer, C B Gilroy,
124 Genitourin Med 1991;67:124-128 The value of urine samples from men with nongonococcal urethritis for the detection of Chlamydia trachomatis P E Hay, B J Thomas, C Gilchrist, H M Palmer, C B Gilroy,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form
 S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11. Dr H Awad FRCPath
 Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Neoplasia 2018 lecture 11 Dr H Awad FRCPath Clinical aspects of neoplasia Tumors affect patients by: 1. their location 2. hormonal secretions 3. paraneoplastic syndromes 4. cachexia Tumor location Even
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
TRACP & ALP Assay Kit
 Cat. # MK301 For Research Use TRACP & ALP Assay Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Introduction...3 Components...4 Materials Required but not Provided...4 V. Storage...4
Cat. # MK301 For Research Use TRACP & ALP Assay Kit Product Manual Table of Contents I. Description...3 II. III. IV. Introduction...3 Components...4 Materials Required but not Provided...4 V. Storage...4
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or
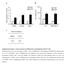 Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of ALDH-positive cell population in MCF-7 cells. (a) Expression level of stem cell markers in MCF-7 cells or ALDH-positive cell population by qpcr. Data represent
Kit Components Product # EP42720 (24 preps) MDx 2X PCR Master Mix 350 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Primer Mix 70 µl Cryptococcus neoformans Positive
 3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
3430 Schmon Parkway Thorold, ON, Canada L2V 4Y6 Phone: 866-667-4362 (905) 227-8848 Fax: (905) 227-1061 Email: techsupport@norgenbiotek.com Cryptococcus neoformans End-Point PCR Kit Product# EP42720 Product
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Elution of Tumoricidal Doses of Bortezomib from a Resorbable Cement Carrier
 Elution of Tumoricidal Doses of Bortezomib from a Resorbable Cement Carrier Matthew Allen, Vet MB, PhD, Brittani Jones, BS. The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA. Disclosures: M. Allen: 5; Johnson
Elution of Tumoricidal Doses of Bortezomib from a Resorbable Cement Carrier Matthew Allen, Vet MB, PhD, Brittani Jones, BS. The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH, USA. Disclosures: M. Allen: 5; Johnson
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
HER2 status assessment in breast cancer. Marc van de Vijver Academic Medical Centre (AMC), Amsterdam
 HER2 status assessment in breast cancer Marc van de Vijver Academic Medical Centre (AMC), Amsterdam 13e Bossche Mamma Congres 17 th June 2015 Modern cancer therapies are based on sophisticated molecular
HER2 status assessment in breast cancer Marc van de Vijver Academic Medical Centre (AMC), Amsterdam 13e Bossche Mamma Congres 17 th June 2015 Modern cancer therapies are based on sophisticated molecular
EFFECT OF INTEGRIN α5 ON CANCER CELL MOTILITY IN 2D AND 3D MATRICES
 EFFECT OF INTEGRIN α5 ON CANCER CELL MOTILITY IN 2D AND 3D MATRICES by Jung Min Byun A thesis submitted to Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
EFFECT OF INTEGRIN α5 ON CANCER CELL MOTILITY IN 2D AND 3D MATRICES by Jung Min Byun A thesis submitted to Johns Hopkins University in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Master of Science
Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1 Role of Raf-1 in TLR2-Dectin-1-mediated cytokine expression. Quantitative real-time PCR of indicated mrnas in DCs stimulated with TLR2-Dectin-1 agonist zymosan
Product Datasheet. IGF-I R Antibody (3G5C1) NB Unit Size: 0.1 ml
 Product Datasheet IGF-I R Antibody (3G5C1) NB110-87052 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 2 Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications,
Product Datasheet IGF-I R Antibody (3G5C1) NB110-87052 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 2 Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications,
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
TITLE: Autocrine and Paracrine Control of Breast Cancer Growth by Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin
 AD Award Number: DAMD17-02-1-0572 TITLE: Autocrine and Paracrine Control of Breast Cancer Growth by Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: William Rosner, M.D. Scott M. Kahn, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
AD Award Number: DAMD17-02-1-0572 TITLE: Autocrine and Paracrine Control of Breast Cancer Growth by Sex Hormone-Binding Globulin PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: William Rosner, M.D. Scott M. Kahn, Ph.D. CONTRACTING
Recombinant Integrins
 Recombinant Integrins Ligand INTEGRIN α subunit S S β subunit Recombinant Integrins Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins that play key roles in regulating cell-cell and cell-extracellular
Recombinant Integrins Ligand INTEGRIN α subunit S S β subunit Recombinant Integrins Integrins are heterodimeric integral membrane proteins that play key roles in regulating cell-cell and cell-extracellular
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Higher expression of deoxyuridine triphosphatase (dutpase) may predict the metastasis potential of colorectal cancer
 1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kurume University Hospital, Kurume, Japan; 2 Department of Surgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan; 3 Biostatistics Center, Kurume University,
1 Department of Diagnostic Pathology, Kurume University Hospital, Kurume, Japan; 2 Department of Surgery, Kurume University School of Medicine, Kurume, Japan; 3 Biostatistics Center, Kurume University,
Abnormal expression of PTEN and PIK3CA in pemetrexed-resistant human pancreatic cancer cell line Patu8988
 Abnormal expression of PTEN and PIK3CA in pemetrexed-resistant human pancreatic cancer cell line Patu8988 X. Shi, H.T. Gu, S.B. Lin, Y. Zhang, J. Yang and C.J. Qian Department of General Surgery, Affiliated
Abnormal expression of PTEN and PIK3CA in pemetrexed-resistant human pancreatic cancer cell line Patu8988 X. Shi, H.T. Gu, S.B. Lin, Y. Zhang, J. Yang and C.J. Qian Department of General Surgery, Affiliated
