Figure S1. Cos-7. Cos-7 GFP. pjnk C2C12 C2C12 GFP * 60. pjnk. WT lamin A. H222P lamin A
|
|
|
- Austin Nelson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
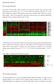
1 Figure S1 A Cos-7 C NT WT lamin A Cos-7 H222P lamin A 100 % JNK nucleus / positives GFP GFP pjnk ** NT D C2C12 NT WT lamin A GFP pjnk H222P lamin A C2C12 H222P lamin A 100 % JNK nucleus / positives GFP B WT lamin A 80 * NT WT lamin A H222P lamin A
2 Supplemental data Figure S1. Expression of H222P lamin A in transfected Cos-7 and C2C12 leads to enhanced nuclear translocation of phospho-jnk. (A-B) Effect of H222P lamin A on nuclear translocation of pjnk in transfected Cos-7 (A) and C2C12 (B) cells. Representative photomicrographs are shown for non-transfected cells (NT), transfected cells expressing a GFP fusion of wild type lamin A (WT lamin A) and transfected cells expressing a GFP fusion of lamin A with the H222P amino acid substitution (H222P lamin A). Arrowheads show enhanced nuclear localization of pjnk in cells expressing GFP-H222P lamin A. Bars: 10 m. (C-D) Percentages of Cos-7 (C) and C2C12 (D) cells with pjnk primarily in the nucleus. Non-transfected cells (NT), transfected cells expressing a GFP fusion of wild type lamin A (WT lamin A) and transfected cells expressing a GFP fusion of lamin A with the H222P aa substitution (H222P lamin A) were randomly counted and scored for nuclear pjnk (see arrowheads in A for example). Transfected cells were determined by presence of GFP signal. Values are means % standard deviations for n=200 cells per group (*p<0.05, **p<0.005).
3 Table S1. Genes with altered expression as defined by q<0.05 and >1 log 2 -fold change in hearts from Lmna H222P/+ mice. Probe set name Gene symbol Gene name fold q-value _at Myl7 myosin, light polypeptide 7, regulatory _at Sln sarcolipin _at Myl4 myosin, light polypeptide 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic _at Paip1 polyadenylate binding protein-interacting protein _at Myh7 myosin, heavy polypeptide 7, cardiac muscle, beta _at Prg4 proteoglycan _at Cacna1c calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, alpha 1C subunit _at Car3 carbonic anhydrase _at Serpina3n serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade A, member 3N _a_at Ugt1a6 UDP glycosyltransferase 1 family, polypeptide A _at Wdfy1 WD repeat and FYVE domain containing _at Pdlim3 PDZ and LIM domain _a_at Rex3 reduced expression _at Osbpl3 oxysterol binding protein-like _at Calr3 calreticulin _at A930025J12RIK RIKEN cdna A930025J12 gene _at C20RIK RIKEN cdna C20 gene _at Cap1 CAP, adenylate cyclase-associated protein 1 (yeast) _a_at Idb2 inhibitor of DNA binding _a_at Cnot7 CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit _at C19RIK RIKEN cdna C19 gene _s_at Gnai1 guanine nucleotide binding protein, alpha inhibiting _at H08RIK RIKEN cdna H08 gene _at Adn adipsin _at C3 complement component _at Rbp7 retinol binding protein 7, cellular _at Atp1a2 ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 2 polypeptide _x_at AV AV Mus musculus pancreas C57BL/6J adult Mus musculus _at AV AV RIKEN full-length enriched, adult male olfactory _s_at Ifi202b interferon activated gene 202B _at Gprk5 G protein-coupled receptor kinase _at Comp cartilage oligomeric matrix protein _a_at C130038G02RIK RIKEN cdna C130038G02 gene _at Acdc adipocyte, C1Q and collagen domain containing _s_at Pbx3 pre B-cell leukemia transcription factor _at Efemp1 epidermal growth factor-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein _at Cxcl12 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand _at Fgl2 fibrinogen-like protein _a_at Csrp2 cysteine and glycine-rich protein _at AK unknown _at BC unknown _at Mmrn2 multimerin _at Osmr oncostatin M receptor _at Cyp2e1 cytochrome P450, family 2, subfamily e, polypeptide _at C730034d20rik RIKEN cdna C730034D20 gene _s_at Catnal1 catenin alpha-like _x_at Slitl2 Slit-like 2 (Drosophila) _a_at Nfia nuclear factor I/A _a_at BC unknown _x_at D6MIT97 DNA segment, Chr 6, Massachusetts Institute of Technology _at BC cdna sequence BC _at Son Son cell proliferation protein _a_at N18RIK RIKEN cdna N18 gene _at AV AV Mus musculus 18-day embryo C57BL/6J Mus musculus _at Serpine2 serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade E, member _at C330016O16RIK RIKEN cdna C330016O16 gene _x_at Plagl1 pleiomorphic adenoma gene-like _at Dkk3 dickkopf homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) _s_at BC unknown _at BB BB RIKEN full-length enriched, B16 F10Y cells Mus _at Cp ceruloplasmin _at Slp sex-limited protein _x_at M09RIK RIKEN cdna M09 gene _a_at Nov nephroblastoma overexpressed gene _at Cfh complement component factor h
4 _at H2-T23 histocompatibility 2, T region locus _at Ahr aryl-hydrocarbon receptor _s_at Rhobtb3 Rho-related BTB domain containing _at Ednra endothelin receptor type A _a_at Sox4 SRY-box containing gene _at Deadc1 deaminase domain containing _a_at Fmo2 flavin containing monooxygenase _at Egr1 early growth response _at Gpx3 glutathione peroxidase _at Vcam1 vascular cell adhesion molecule _s_at Acp1 acid phosphatase 1, soluble _at Bambi BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor, homolog (Xenopus laevis) _at H18RIK RIKEN cdna H18 gene _at Ak unknown _a_at Glo1 glyoxalase _a_at Nedd4 neural precursor cell expressed, developmentally down-regulated gene _at G04RIK RIKEN cdna G04 gene _at H2-Q7 histocompatibility 2, Q region locus _at Fus fusion, derived from t(12;16) malignant liposarcoma (human) _at Dpep1 dipeptidase 1 (renal) _at Zfp297 zinc finger protein _x_at BC unknown _x_at Ddr1 discoidin domain receptor family, member _at Fhl1 four and a half LIM domains _x_at Wdr6 WD repeat domain _at Loc similar to 60S ribosomal protein L _a_at Abhd6 abhydrolase domain containing _at Av AV RIKEN full-length enriched, adult male colon Mus _x_at AV expressed sequence AV _a_at BC unknown _at Loc similar to sodium channel beta 4 subunit _a_at Alas2 aminolevulinic acid synthase 2, erythroid _a_at M12573 unknown _at M22RIK RIKEN cdna M22 gene _at Cxcl7 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand _at BB BB RIKEN full-length enriched, 0 day neonate eyeball _at Hrasls HRAS-like suppressor _s_at Pttg1 pituitary tumor-transforming _at Cyfip2 cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein
5 Table S2. Genes with altered expression as defined by q<0.05 and >1 log 2 -fold change in hearts from Lmna H222P/H222P mice. Probe set name Gene symbol Gene name fold q-value _at Myl7 myosin, light polypeptide 7, regulatory E _at Sln sarcolipin _at Myl4 myosin, light polypeptide 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic _at Myh7 myosin, heavy polypeptide 7, cardiac muscle, beta _at AK unknown _at Car3 carbonic anhydrase _s_at Ifi202b interferon activated gene 202B _a_at Rex3 reduced expression _at Paip1 polyadenylate binding protein-interacting protein _at Prg4 proteoglycan _at Anf atrial natriuretic factor _at Arvcf armadillo repeat gene deleted in velo-cardio-facial syndrome _at Serpina3n serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade A, member 3N _s_at Gnai1 guanine nucleotide binding protein, alpha inhibiting _at BC unknown _at Wdfy1 WD repeat and FYVE domain containing _a_at Sox4 SRY-box containing gene _at Dkk3 dickkopf homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) _at Atp1a2 ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 2 polypeptide _a_at Col1a2 procollagen, type I, alpha _at Osbpl3 oxysterol binding protein-like _at BC cdna sequence BC _a_at Cnot7 CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit _a_at Csrp2 cysteine and glycine-rich protein _a_at C130038G02RIK RIKEN cdna C130038G02 gene _at BC cdna sequence BC _at Cxcl12 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand _x_at H2-Aa histocompatibility 2, class II antigen A, alpha _at Pdlim3 PDZ and LIM domain _at D830013H23RIK RIKEN cdna D830013H23 gene _at Fgl2 fibrinogen-like protein _a_at Wif1 Wnt inhibitory factor _at C730034D20RIK RIKEN cdna C730034D20 gene _at Igf1 insulin-like growth factor _a_at Idb2 inhibitor of DNA binding _at Egr1 early growth response _at Comp cartilage oligomeric matrix protein _at Serpine2 serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade E, member _x_at Plagl1 pleiomorphic adenoma gene-like _at Gpx3 glutathione peroxidase _at Dcn decorin _at Dbp D site albumin promoter binding protein _at Bambi BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor, homolog (Xenopus laevis) _a_at Ii Ia-associated invariant chain _at C20RIK RIKEN cdna C20 gene _a_at BC unknown _at BC unknown _at Vcam1 vascular cell adhesion molecule _x_at Vegfc vascular endothelial growth factor C _at C330016O16RIK RIKEN cdna C330016O16 gene _at Deadc1 deaminase domain containing _at Rtn4 reticulon _at Son Son cell proliferation protein _s_at Acta2 actin, alpha 2, smooth muscle, aorta _x_at K24RIK RIKEN cdna K24 gene _at Mglap matrix gamma-carboxyglutamate (gla) protein _at Mmp14 matrix metalloproteinase 14 (membrane-inserted) _s_at Pbx3 pre B-cell leukemia transcription factor _at O13RIK RIKEN cdna O13 gene _at Fzd2 frizzled homolog 2 (Drosophila) _s_at O10RIK RIKEN cdna O10 gene _at Rbp7 retinol binding protein 7, cellular _a_at Ifi203 interferon activated gene _at Etv1 ets variant gene _at E17RIK RIKEN cdna E17 gene
6 _a_at Nov nephroblastoma overexpressed gene _at Cap1 CAP, adenylate cyclase-associated protein 1 (yeast) _at C330023F11RIK RIKEN cdna C330023F11 gene _at AW expressed sequence AW _at Mmrn2 multimerin _at Masp1 mannan-binding lectin serine protease _at E030026I10RIK RIKEN cdna E030026I10 gene _at Ahr aryl-hydrocarbon receptor _at Peg3 paternally expressed _at Pdgfra platelet derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide _at Ifi30 interferon gamma inducible protein _s_at H2-Ab1 histocompatibility 2, class II antigen A, beta _at AK unknown _at Gprk5 G protein-coupled receptor kinase _at Fhl1 four and a half LIM domains _at H2-Eb1 histocompatibility 2, class II antigen E beta _at BG mac09f12.x1 Soares mouse 3NbMS Mus musculus cdna clone _a_at Btg1 B-cell translocation gene 1, anti-proliferative _at H2-T23 histocompatibility 2, T region locus _at BC unknown _x_at Ddr1 discoidin domain receptor family, member _s_at Slc38a1 solute carrier family 38, member _at Esrrbl1 estrogen-related receptor beta like _at Cp ceruloplasmin _at Rbp1 retinol binding protein 1, cellular _x_at Mrvldc1 MARVEL (membrane-associating) domain containing _x_at Ap1s2 adaptor-related protein complex 1, sigma 2 subunit _at Gucy1a3 guanylate cyclase 1, soluble, alpha _at Frg1 FSHD region gene _at C05RIK RIKEN cdna C05 gene _at Loc similar to sodium channel beta 4 subunit _at BB BB RIKEN full-length enriched, 0 day neonate thymus _at AI UI-M-BG0-aht-a-04-0-UI.s1 NIH_BMAP_MSC Mus musculus cdna _at G12RIK RIKEN cdna G12 gene _a_at BC unknown _s_at Spna1 spectrin alpha _at Pex19 peroxisome biogenesis factor _at BC unknown _at H15RIK RIKEN cdna H15 gene _at Kcna5 potassium voltage-gated channel, shaker-related subfamily, member _a_at H23RIK RIKEN cdna H23 gene _x_at AV expressed sequence AV _x_at Tubgcp5 tubulin, gamma complex associated protein _at M12573 unknown _at Hrasls HRAS-like suppressor _at BB BB RIKEN full-length enriched, 0 day neonate eyeball _a_at Pttg1 pituitary tumor-transforming _at Cyfip2 cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein _at G02RIK RIKEN cdna G02 gene
7 Table S3. Genes commonly affected as defined by q<0.05 and >1 log 2 -fold change in hearts from Lmna H222P/H222P and Lmna H222P/+ mice. Lmna H222P/H222P Lmna H222P/+ Probe set name Gene symbol Gene name fold q-value fold q-value _at Myl7 myosin, light polypeptide 7, regulatory E _at Sln sarcolipin _at Myl4 myosin, light polypeptide 4, alkali; atrial, embryonic _at Myh7 myosin, heavy polypeptide 7, cardiac muscle, beta _at Car3 carbonic anhydrase _s_at Ifi202b interferon activated gene 202B _a_at Rex3 reduced expression _at Paip1 polyadenylate binding protein-interacting protein _at Prg4 proteoglycan _s_at Gnai1 guanine nucleotide binding protein, alpha inhibiting _at BC unknown _at Wdfy1 WD repeat and FYVE domain containing _a_at Sox4 SRY-box containing gene _at Dkk3 dickkopf homolog 3 (Xenopus laevis) _at Atp1a2 ATPase, Na+/K+ transporting, alpha 2 polypeptide _at Osbpl3 oxysterol binding protein-like _a_at Cnot7 CCR4-NOT transcription complex, subunit _a_at Csrp2 cysteine and glycine-rich protein _a_at C130038G02RIK RIKEN cdna C130038G02 gene _at BC cdna sequence BC _at Cxcl12 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand _at Pdlim3 PDZ and LIM domain _at Fgl2 fibrinogen-like protein _at C730034D20RIK RIKEN cdna C730034D20 gene _a_at Idb2 inhibitor of DNA binding _at Egr1 early growth response _at Comp cartilage oligomeric matrix protein _at Serpine2 serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor, clade E, member _x_at Plagl1 pleiomorphic adenoma gene-like _at Gpx3 glutathione peroxidase _at Bambi BMP and activin membrane-bound inhibitor, homolog (Xenopus laevis) _at C20RIK RIKEN cdna C20 gene _a_at BC unknown _at BC unknown _at Vcam1 vascular cell adhesion molecule _at C330016O16RIK RIKEN cdna C330016O16 gene _at Deadc1 deaminase domain containing _at Son Son cell proliferation protein _s_at Pbx3 pre B-cell leukemia transcription factor _at Rbp7 retinol binding protein 7, cellular _a_at Nov nephroblastoma overexpressed gene _at Cap1 CAP, adenylate cyclase-associated protein 1 (yeast) _at Mmrn2 multimerin _at Ahr aryl-hydrocarbon receptor _at Gprk5 G protein-coupled receptor kinase _at Fhl1 four and a half LIM domains _at H2-T23 histocompatibility 2, T region locus _x_at Ddr1 discoidin domain receptor family, member _at Cp ceruloplasmin _at Loc similar to sodium channel beta 4 subunit _a_at BC unknown _x_at AV expressed sequence AV _at M12573 unknown _at Hrasls HRAS-like suppressor _at BB BB RIKEN full-length enriched, 0 day neonate eyeball _a_at Pttg1 pituitary tumor-transforming _at Cyfip2 cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein
8 Table S4. Genes from MAPK pathways affected as defined by q<0.05 in hearts from Lmna H222P/H222P mice. Gene symbol Gene name q-value Tgfb2 transforming growth factor, beta E-07 Fgf9 fibroblast growth factor E-06 Mapk8 mitogen activated protein kinase E-05 Evi1 ecotropic viral integration site E-05 Pdgfra platelet derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide 4.59E-05 Ddit3 DNA-damage inducible transcript E-05 Pdgfa platelet derived growth factor, alpha 1.61E-04 Ikbkg inhibitor of kappab kinase gamma 5.91E-04 Rap1b RAS related protein 1b 6.48E-04 Tgfbr2 transforming growth factor, beta receptor II 6.56E-04 Rasa1 RAS p21 protein activator E-04 Map3k7 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase E-04 Fgf12 fibroblast growth factor E-04 Flnb filamin, beta Tgfbr1 transforming growth factor, beta receptor I Rasa2 RAS p21 protein activator Ppp3ca protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, alpha isoform Stk4 serine/threonine kinase Tgfb3 transforming growth factor, beta Il1b interleukin 1 beta Stmn1 stathmin Dusp9 dual specificity phosphatase Mapk7 mitogen activated protein kinase Tnfrsf1a tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1a Prkx protein kinase, X-linked Nfkb2 nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells 2, p49/p Pla2g12b phospholipase A2, group XIIB Mapk14 mitogen activated protein kinase Arrb2 arrestin, beta Map3k7ip2 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 interacting protein Fgf14 fibroblast growth factor Map2k4 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase Map3k4 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Rapgef4 Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) B230120H23Rik RIKEN cdna B230120H23 gene Fgfr1 fibroblast growth factor receptor Nfatc2 nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent Mapk1 mitogen activated protein kinase Casp3 caspase Atf2 activating transcription factor Pdgfrb platelet derived growth factor receptor, beta polypeptide Rasgrp1 RAS guanyl releasing protein Pla2g2f phospholipase A2, group IIF Map3k5 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Map4k4 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase Ntf3 neurotrophin Prkacb protein kinase, camp dependent, catalytic, beta Fgf13 fibroblast growth factor Nras neuroblastoma ras oncogene Crk v-crk sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog (avian) Cdc42 cell division cycle 42 homolog (S. cerevisiae) Mapk9 mitogen activated protein kinase Mef2c myocyte enhancer factor 2C Ikbkb inhibitor of kappab kinase beta Pak1 p21 (CDKN1A)-activated kinase Stk3 serine/threonine kinase 3 (Ste20, yeast homolog) Pla2g4a phospholipase A2, group IVA (cytosolic, calcium-dependent) Mapk8ip3 mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein Ntrk2 neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type Map2k1 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase Elk4 ELK4, member of ETS oncogene family Il1r2 interleukin 1 receptor, type II Ppm1a protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform
9 Elk1 ELK1, member of ETS oncogene family Map3k12 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Grb2 growth factor receptor bound protein Dusp4 dual specificity phosphatase Atf4 activating transcription factor Ptprr protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R Map3k14 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase Ppp3cb protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, beta isoform Map4k3 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase Map4k1 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase Mapkapk5 MAP kinase-activated protein kinase Tmem37 transmembrane protein Tnik TRAF2 and NCK interacting kinase Prkca protein kinase C, alpha Sos1 Son of sevenless homolog 1 (Drosophila) Hspa5 heat shock 70kD protein 5 (glucose-regulated protein) Ntrk1 neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type Rps6ka4 ribosomal protein S6 kinase, polypeptide Srf serum response factor Pdgfb platelet derived growth factor, B polypeptide
10 Table S5. Genes from MAPK pathways affected as defined by q<0.05 in hearts from Lmna H222P/+ mice. Gene symbol Gene name q-value Fgf12 fibroblast growth factor E-06 Evi1 ecotropic viral integration site E-04 Raf1 v-raf-leukemia viral oncogene E-04 Tgfbr2 transforming growth factor, beta receptor II 2.29E-04 B230120H23Rik RIKEN cdna B230120H23 gene 2.45E-04 Ppm1a protein phosphatase 1A, magnesium dependent, alpha isoform 2.59E-04 Stmn1 stathmin E-04 Mapk8 mitogen activated protein kinase E-04 Fgf10 fibroblast growth factor E-04 Rasgrp1 RAS guanyl releasing protein E-04 Map3k7ip2 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 interacting protein E-04 Pdgfra platelet derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide 4.98E-04 Rap1b RAS related protein 1b 6.48E-04 Dusp9 dual specificity phosphatase E-04 Srf serum response factor 7.34E-04 Flnb filamin, beta 8.02E-04 Map3k5 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Pak1 p21 (CDKN1A)-activated kinase Tgfb2 transforming growth factor, beta Rasa2 RAS p21 protein activator Rasgrf1 RAS protein-specific guanine nucleotide-releasing factor Fgfr1 fibroblast growth factor receptor Mapk1 mitogen activated protein kinase Tnfrsf1a tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily, member 1a Rasa1 RAS p21 protein activator Pdgfa platelet derived growth factor, alpha Stk4 serine/threonine kinase Map4k3 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase Traf6 Tnf receptor-associated factor Map2k1 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase Ntrk2 neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type Arrb2 arrestin, beta Map3k12 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Ppp3ca protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, alpha isoform Ikbkb inhibitor of kappab kinase beta Fgf9 fibroblast growth factor Tgfbr1 transforming growth factor, beta receptor I Nf1 neurofibromatosis Il1r2 interleukin 1 receptor, type II Tmem37 transmembrane protein Fgfr4 fibroblast growth factor receptor Elk4 ELK4, member of ETS oncogene family Pla2g4a phospholipase A2, group IVA (cytosolic, calcium-dependent) Prkaca protein kinase, camp dependent, catalytic, alpha Dusp7 dual specificity phosphatase Map2k7 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase Atf4 activating transcription factor Stk3 serine/threonine kinase 3 (Ste20, yeast homolog) Casp4 caspase 4, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase Map3k7 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Ptpn5 protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type Map3k14 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase Il1b interleukin 1 beta Egf epidermal growth factor Ikbkg inhibitor of kappab kinase gamma Map2k6 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase Map2k1ip1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase 1 interacting protein Acvr1b activin A receptor, type 1B Map4k4 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase Rap1a RAS-related protein-1a Mapk9 mitogen activated protein kinase Map3k7ip1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 7 interacting protein
11 Map3k4 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Kras v-ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog Casp14 caspase Dusp4 dual specificity phosphatase Casp1 caspase Nfatc2 nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent Rapgef4 Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) Nr4a1 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member Map3k3 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase Hspa1l heat shock protein 1-like Ntf3 neurotrophin Fgf14 fibroblast growth factor Fasl Fas ligand (TNF superfamily, member 6) Mef2c myocyte enhancer factor 2C Ppp3cb protein phosphatase 3, catalytic subunit, beta isoform Fgf22 fibroblast growth factor Casp6 caspase Mknk1 MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase Sitpec signaling intermediate in Toll pathway-evolutionarily conserved Mapk13 mitogen activated protein kinase Fgfr2 fibroblast growth factor receptor Chuk conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase Casp9 caspase Mknk2 MAP kinase-interacting serine/threonine kinase Fgf1 fibroblast growth factor Atf2 activating transcription factor Ikbke inhibitor of kappab kinase epsilon Akt3 thymoma viral proto-oncogene Pla2g12b phospholipase A2, group XIIB Prkcb1 protein kinase C, beta Nlk nemo like kinase Nfkb1 nuclear factor of kappa light chain gene enhancer in B-cells 1, p Ntf5 neurotrophin Ppm1b protein phosphatase 1B, magnesium dependent, beta isoform Pak2 p21 (CDKN1A)-activated kinase Ppp3r2 protein phosphatase 3, regulatory subunit B, alpha isoform (calcineurin B, type II) Ntrk1 neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor, type Mapk8ip3 mitogen-activated protein kinase 8 interacting protein Daxx Fas death domain-associated protein Prkcc protein kinase C, gamma Mapkapk2 MAP kinase-activated protein kinase Crk v-crk sarcoma virus CT10 oncogene homolog (avian) Nras neuroblastoma ras oncogene Pla2g6 phospholipase A2, group VI Nfatc4 nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic, calcineurin-dependent Fgf5 fibroblast growth factor Map4k2 mitogen activated protein kinase kinase kinase kinase Hspb1 heat shock protein Ptprr protein tyrosine phosphatase, receptor type, R
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p <0.01 for 0.01 mm NS-398, 0.1mM ibuprofen and COX-2 RNAi.
 Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection.
 Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection. Genes found to be significantly upregulated (FDR2) in Y strain
Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection. Genes found to be significantly upregulated (FDR2) in Y strain
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Cell Signaling part 2
 15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
15 Cell Signaling part 2 Functions of Cell Surface Receptors Other cell surface receptors are directly linked to intracellular enzymes. The largest family of these is the receptor protein tyrosine kinases,
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling
 Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Biol403 MAP kinase signalling The mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway is a signalling cascade activated by a diverse range of effectors. The cascade regulates many cellular activities including
Enzyme-coupled Receptors. Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors
 Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Enzyme-coupled Receptors Cell-surface receptors 1. Ion-channel-coupled receptors 2. G-protein-coupled receptors 3. Enzyme-coupled receptors Cell-surface receptors allow a flow of ions across the plasma
Cellular Signaling Pathways. Signaling Overview
 Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
Cellular Signaling Pathways Signaling Overview Signaling steps Synthesis and release of signaling molecules (ligands) by the signaling cell. Transport of the signal to the target cell Detection of the
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. b-galactosidase staining of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
Signal Transduction Cascades
 Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Signal Transduction Cascades Contents of this page: Kinases & phosphatases Protein Kinase A (camp-dependent protein kinase) G-protein signal cascade Structure of G-proteins Small GTP-binding proteins,
Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4
 Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4 Johan Lennartsson Molecular Cell Biology (1BG320), 2014 Johan.Lennartsson@licr.uu.se 1 Receptor tyrosine kinase-induced signal transduction Erk MAP kinase pathway
Principles of cell signaling Lecture 4 Johan Lennartsson Molecular Cell Biology (1BG320), 2014 Johan.Lennartsson@licr.uu.se 1 Receptor tyrosine kinase-induced signal transduction Erk MAP kinase pathway
G-Protein Signaling. Introduction to intracellular signaling. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
G-Protein Signaling Introduction to intracellular signaling Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Cell signaling Cells communicate via extracellular signaling molecules (Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
U118MG. Supplementary Figure 1 U373MG U118MG 3.5 A CCF-SSTG
 A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
A172 CCF-SSTG1 15 - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10101112131617192022-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22 T98G U373MG - - - 1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7 8 10 10 11 12 13 16 17 19 20 22-1 1 1 2 2 3 4 6 7
Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion
 Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Assessment of cell survival (MTT) Assessment of early apoptosis and cell death
 Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Revision. camp pathway
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Revision camp pathway camp pathway Revision camp pathway Adenylate cyclase Adenylate Cyclase enzyme Adenylate cyclase catalyses the formation of camp from ATP. Stimulation or inhibition
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Revision camp pathway camp pathway Revision camp pathway Adenylate cyclase Adenylate Cyclase enzyme Adenylate cyclase catalyses the formation of camp from ATP. Stimulation or inhibition
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Determination Differentiation. determinated precursor specialized cell
 Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Biology of Cancer -Developmental Biology: Determination and Differentiation -Cell Cycle Regulation -Tumor genes: Proto-Oncogenes, Tumor supressor genes -Tumor-Progression -Example for Tumor-Progression:
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7)
 Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Supplementary Information
 Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Scientific Reports Supplementary Information Upregulated expression of FGF13/FHF2 mediates resistance to platinum drugs in cervical cancer cells Tomoko Okada, Kazuhiro Murata, Ryoma Hirose, Chie Matsuda,
Signaling. Dr. Sujata Persad Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research
 Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
Signaling Dr. Sujata Persad 3-020 Katz Group Centre for Pharmacy & Health research E-mail:sujata.persad@ualberta.ca 1 Growth Factor Receptors and Other Signaling Pathways What we will cover today: How
In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell
 Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
Supplementary Methods BrdU incorporation in vivo In vivo bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) incorporation was performed to analyze cell proliferation in the heart. Mice were subjected to LI-TAC, and 5 days later
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval
 Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
Lecture #27 Lecturer A. N. Koval Hormones Transduce Signals to Affect Homeostatic Mechanisms Koval A. (C), 2011 2 Lipophilic hormones Classifying hormones into hydrophilic and lipophilic molecules indicates
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS
 SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS No. Protein 1 serum albumin precursor gi 30794280 2 annexin A2 gi 27807289 3 Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding
SUPPLEMENTAL TABLE I. Identified Proteins in Bovine Testicular Hyaluronidase Type I-S via LC-MS/MS No. Protein 1 serum albumin precursor gi 30794280 2 annexin A2 gi 27807289 3 Phosphatidylethanolamine-binding
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors
 Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
MAPK Pathway
 MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
MAPK Pathway Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) are proteins that are serine/ threonine specific kinases which are activated by a wide range of stimuli including proinflammatory cytokines, growth
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available
 Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
Diagnostic test Suggested website label Description Hospitals available Abbott Molecular Inc, PATHVYSION HER-2 DNA Probe Kit (FISH) PathVysion kit A diagnostic tool used to determine whether a particular
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Cell signaling. How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings?
 Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
Cell signaling How do cells receive and respond to signals from their surroundings? Prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes are largely independent and autonomous. In multicellular organisms there is a
1. Activated receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) phosphorylates themselves
 Enzyme-coupled receptors Transmembrane proteins Ligand-binding domain on the outer surface Cytoplasmic domain acts as an enzyme itself or forms a complex with enzyme 1. Activated receptor tyrosine kinases
Enzyme-coupled receptors Transmembrane proteins Ligand-binding domain on the outer surface Cytoplasmic domain acts as an enzyme itself or forms a complex with enzyme 1. Activated receptor tyrosine kinases
Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh
 22 Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh Faisal Mohammad Receptors can be membrane proteins (for water-soluble hormones/ligands) or intracellular (found in the cytosol or nucleus and bind to DNA, for lipid-soluble
22 Sarah Jaar Marah Al-Darawsheh Faisal Mohammad Receptors can be membrane proteins (for water-soluble hormones/ligands) or intracellular (found in the cytosol or nucleus and bind to DNA, for lipid-soluble
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 19: Cell Signaling Pathways and Gene Expression Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which statement about cell signaling is correct? Question #1 (A) Cell signaling involves receiving
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies
 Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies Dr. Maricel G. Kann Assistant Professor Dept of Biological Sciences UMBC 2 The term protein domain
Protein Domain-Centric Approach to Study Cancer Somatic Mutations from High-throughput Sequencing Studies Dr. Maricel G. Kann Assistant Professor Dept of Biological Sciences UMBC 2 The term protein domain
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus. VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department
 Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Genome of Hepatitis B Virus VIRAL ONCOGENE Dr. Yahwardiah Siregar, PhD Dr. Sry Suryani Widjaja, Mkes Biochemistry Department Proto Oncogen and Oncogen Oncogen Proteins that possess the ability to cause
Computational Systems Biology: Biology X
 Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#10:(November-22-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 1 Micro-Environment Story How does the rest of our body influences the cancer cell?
Bud Mishra Room 1002, 715 Broadway, Courant Institute, NYU, New York, USA L#10:(November-22-2010) Cancer and Signals 1 1 Micro-Environment Story How does the rest of our body influences the cancer cell?
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Table S1. Differentially expressed transcripts between hepatic inkt cells. sorted form WT and plck-hcd1d tg mice. Differentially expressed
 Supplementary Information Table S1. Differentially expressed transcripts between hepatic inkt cells sorted form and plck-hcd1d tg mice. Differentially expressed transcripts identified by gene expression
Supplementary Information Table S1. Differentially expressed transcripts between hepatic inkt cells sorted form and plck-hcd1d tg mice. Differentially expressed transcripts identified by gene expression
CO 2 tolerance of Atlantic salmon post-smolts in recirculating aquaculture systems
 CO 2 tolerance of Atlantic salmon post-smolts in recirculating aquaculture systems Vasco Mota*, Tom Nilsen, Elizabeth Ytteborg, Grete Baeverfjord, Aleksei Krasnov, Jelena Kolarevic, Lars Ebbesson, Steven
CO 2 tolerance of Atlantic salmon post-smolts in recirculating aquaculture systems Vasco Mota*, Tom Nilsen, Elizabeth Ytteborg, Grete Baeverfjord, Aleksei Krasnov, Jelena Kolarevic, Lars Ebbesson, Steven
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit
 The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
The Tissue Engineer s Toolkit Stimuli Detection and Response Ken Webb, Ph. D. Assistant Professor Dept. of Bioengineering Clemson University Environmental Stimulus-Cellular Response Environmental Stimuli
MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008
 MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008 Name: ID: Instructions: Answer all 4 questions. The number of marks for each question indicates how many points you need to provide. Write your answers in point form,
MCB*4010 Midterm Exam / Winter 2008 Name: ID: Instructions: Answer all 4 questions. The number of marks for each question indicates how many points you need to provide. Write your answers in point form,
Supplementary Material. Part I: Sample Information. Part II: Pathway Information
 Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
Supplementary Material Part I: Sample Information Three NPC cell lines, CNE1, CNE2, and HK1 were treated with CYC202. Gene expression of 380 selected genes were collected at 0, 2, 4, 6, 12 and 24 hours
Signal Transduction Pathways. Part 2
 Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
Signal Transduction Pathways Part 2 GPCRs G-protein coupled receptors > 700 GPCRs in humans Mediate responses to senses taste, smell, sight ~ 1000 GPCRs mediate sense of smell in mouse Half of all known
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
Validated Mouse Quantitative RT-PCR Genes Gene Gene Bank Accession Number Name
 5HT1a NM_008308.4 Serotonin Receptor 1a 5HT1b NM_010482.1 Serotonin Receptor 1b 5HT2a NM_172812.2 Serotonin Receptor 2a ACO-2 NM_080633.2 Aconitase 2 Adora2A NM_009630.02 Adenosine A2a Receptor Aif1 (IbaI)
5HT1a NM_008308.4 Serotonin Receptor 1a 5HT1b NM_010482.1 Serotonin Receptor 1b 5HT2a NM_172812.2 Serotonin Receptor 2a ACO-2 NM_080633.2 Aconitase 2 Adora2A NM_009630.02 Adenosine A2a Receptor Aif1 (IbaI)
Lecture: CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways
 Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Lecture: 10 17 2016 CHAPTER 13 Signal Transduction Pathways Chapter 13 Outline Signal transduction cascades have many components in common: 1. Release of a primary message as a response to a physiological
Supplementary Figure 1 A. Relative mrna level for cells. Number of Wells. treated with different sirnas
 Supplementary Figure 1 A Relative mrna level for cells treated with different sirnas 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Control FRS2 PTEN PTPR FGFR1 CDH5 ACTN1 RAC2 Gene targeted and probed C Number
Supplementary Figure 1 A Relative mrna level for cells treated with different sirnas 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 Control FRS2 PTEN PTPR FGFR1 CDH5 ACTN1 RAC2 Gene targeted and probed C Number
Regulation of cell function by intracellular signaling
 Regulation of cell function by intracellular signaling Objectives: Regulation principle Allosteric and covalent mechanisms, Popular second messengers, Protein kinases, Kinase cascade and interaction. regulation
Regulation of cell function by intracellular signaling Objectives: Regulation principle Allosteric and covalent mechanisms, Popular second messengers, Protein kinases, Kinase cascade and interaction. regulation
Chapter 9. Cellular Signaling
 Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
Chapter 9 Cellular Signaling Cellular Messaging Page 215 Cells can signal to each other and interpret the signals they receive from other cells and the environment Signals are most often chemicals The
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors
 Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
Signal Transduction: G-Protein Coupled Receptors Federle, M. (2017). Lectures 4-5: Signal Transduction parts 1&2: nuclear receptors and GPCRs. Lecture presented at PHAR 423 Lecture in UIC College of Pharmacy,
Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the. ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP
 Protein kinase Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the following equation: 2 ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP ATP represents adenosine trisphosphate, ADP
Protein kinase Protein kinases are enzymes that add a phosphate group to proteins according to the following equation: 2 ATP + protein OH > Protein OPO 3 + ADP ATP represents adenosine trisphosphate, ADP
Chapter 20. Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors. Three general types of extracellular signaling. endocrine signaling. paracrine signaling
 Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Chapter 20 Cell - Cell Signaling: Hormones and Receptors Three general types of extracellular signaling endocrine signaling paracrine signaling autocrine signaling Endocrine Signaling - signaling molecules
Table S1: Data-generating Model:
 Table S1: Data-generating Model: Below are the parameters used for the data-generating model (section 1.5). The model was generated using CNORode. The data generating model is included below (figure S1).
Table S1: Data-generating Model: Below are the parameters used for the data-generating model (section 1.5). The model was generated using CNORode. The data generating model is included below (figure S1).
Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases
 54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes.
 What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
What would you observe if you fused a G1 cell with a S cell? A. Mitotic and pulverized chromosomes. B. Mitotic and compact G1 chromosomes. C. Mostly non-compact G1 chromosomes. D. Compact G1 and G2 chromosomes.
Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric
 Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric septic shock Hector R. Wong, Natalie Z. Cvijanovich, Nick Anas, Geoffrey L. Allen, Neal J. Thomas, Michael T. Bigham, Scott
Developing a clinically feasible personalized medicine approach to pediatric septic shock Hector R. Wong, Natalie Z. Cvijanovich, Nick Anas, Geoffrey L. Allen, Neal J. Thomas, Michael T. Bigham, Scott
Chapter 15: Signal transduction
 Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Chapter 15: Signal transduction Know the terminology: Enzyme-linked receptor, G-protein linked receptor, nuclear hormone receptor, G-protein, adaptor protein, scaffolding protein, SH2 domain, MAPK, Ras,
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
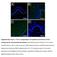 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Signal Transduction I
 Signal Transduction I Prof. Tianhua Zhou Department of Cell Biology Zhejiang University School of Medicine Office hours by appointment tzhou@zju.edu.cn Signal transduction: Key contents for signal transduction:
Signal Transduction I Prof. Tianhua Zhou Department of Cell Biology Zhejiang University School of Medicine Office hours by appointment tzhou@zju.edu.cn Signal transduction: Key contents for signal transduction:
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system
 Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Cell Biology Lecture 9 Notes Basic Principles of cell signaling and GPCR system Basic Elements of cell signaling: Signal or signaling molecule (ligand, first messenger) o Small molecules (epinephrine,
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary figure 1: Pathway enrichment for each comparison. The first column shows enrichment with differentially expressed genes between the diet groups at t = 0, the second
Supplementary figures Supplementary figure 1: Pathway enrichment for each comparison. The first column shows enrichment with differentially expressed genes between the diet groups at t = 0, the second
Supplemental Table 1 Age and gender-specific cut-points used for MHO.
 Supplemental Table 1 Age and gender-specific cut-points used for MHO. Age SBP (mmhg) DBP (mmhg) HDL-C (mmol/l) TG (mmol/l) FG (mmol/l) Boys 6-11 90th * 90th * 1.03 1.24 5.6 12 121 76 1.13 1.44 5.6 13 123
Supplemental Table 1 Age and gender-specific cut-points used for MHO. Age SBP (mmhg) DBP (mmhg) HDL-C (mmol/l) TG (mmol/l) FG (mmol/l) Boys 6-11 90th * 90th * 1.03 1.24 5.6 12 121 76 1.13 1.44 5.6 13 123
silent epidemic,. (WHO),
 Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
What causes cancer? Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Chemical factors (carcinogens) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite)
 Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Oncogenes What causes cancer? Chemical factors (carcinogens) Physical factors (radiation, ionization) Biological factors (virus, bacteria, parasite) DNA Mutation or damage Oncogenes Tumor suppressor genes
Revision. General functions of hormones. Hormone receptors. Hormone derived from steroids Small polypeptide Hormone
 االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Revision General functions of hormones. Hormone receptors Classification according to chemical nature Classification according to mechanism of action Compare and contrast between
االله الرحمن الرحيم بسم Revision General functions of hormones. Hormone receptors Classification according to chemical nature Classification according to mechanism of action Compare and contrast between
BL 424 Chapter 15: Cell Signaling; Signal Transduction
 BL 424 Chapter 15: Cell Signaling; Signal Transduction All cells receive and respond to signals from their environments. The behavior of each individual cell in multicellular plants and animals must be
BL 424 Chapter 15: Cell Signaling; Signal Transduction All cells receive and respond to signals from their environments. The behavior of each individual cell in multicellular plants and animals must be
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems
 The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
Signal Transduction: Information Metabolism. Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire
 Signal Transduction: Information Metabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire Introduction Information Metabolism How cells receive, process and respond
Signal Transduction: Information Metabolism Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire Introduction Information Metabolism How cells receive, process and respond
Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi. Bayan Abusheikha. Faisal
 24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
24 Ayman Mesleh & Leen Alnemrawi Bayan Abusheikha Faisal We were talking last time about receptors for lipid soluble hormones.the general mechanism of receptors for lipid soluble hormones: 1. Receptors
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2. Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system
 Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2 Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system The classical secondary messenger model of intracellular signalling A cell surface receptor binds
Vets 111/Biov 111 Cell Signalling-2 Secondary messengers the cyclic AMP intracellular signalling system The classical secondary messenger model of intracellular signalling A cell surface receptor binds
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature12864 Supplementary Table 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Peak Gene code Screen Function or Read analysis AMP reads camp annotation reads minor Tb927.2.1810 AMP ISWI Confirmed
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma plasma B cell.
 Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Early cell death (FGF) B No RunX transcription factor produced Yes No differentiation
 Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
Solution Key - Practice Questions Question 1 a) A recent publication has shown that the fat stem cells (FSC) can act as bone stem cells to repair cavities in the skull, when transplanted into immuno-compromised
q 2017 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. DOI: /690105
 q 2017 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. DOI: 10.1086/690105 Appendix from R. M. Cox et al., Hormonally Mediated Increases in Sex-Biased Gene Expression Accompany the Breakdown of Between-
q 2017 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. DOI: 10.1086/690105 Appendix from R. M. Cox et al., Hormonally Mediated Increases in Sex-Biased Gene Expression Accompany the Breakdown of Between-
MCB 4211 Basic Immunology 2nd Exam; 10/26/17 Peoplesoft #:
 For this first section, circle the letter that precedes the best answer for each of the following multiple-choice questions. LOOK AT ALL ALTERNATIVES BEFORE CHOOSING YOUR ANSWER. 1. The TcR (T cell receptor)
For this first section, circle the letter that precedes the best answer for each of the following multiple-choice questions. LOOK AT ALL ALTERNATIVES BEFORE CHOOSING YOUR ANSWER. 1. The TcR (T cell receptor)
Fetal-maternal alignment of regulatory T cells correlates with Interleukin 10 mediated Bcl-
 Fetal-maternal alignment of regulatory T cells correlates with Interleukin 10 mediated Bcl- 2 upregulation in pregnancy B. Santner-Nanan, K. Straubinger, P. Hsu, G. Parnell, B. Tang, B. Xu, A. Makris,
Fetal-maternal alignment of regulatory T cells correlates with Interleukin 10 mediated Bcl- 2 upregulation in pregnancy B. Santner-Nanan, K. Straubinger, P. Hsu, G. Parnell, B. Tang, B. Xu, A. Makris,
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer
 Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
Deregulation of signal transduction and cell cycle in Cancer Tuangporn Suthiphongchai, Ph.D. Department of Biochemistry Faculty of Science, Mahidol University Email: tuangporn.sut@mahidol.ac.th Room Pr324
 Table S1. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracelluarly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene expression in
Table S1. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracelluarly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene expression in
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company. 12 Signal Transduction
 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
2013 W. H. Freeman and Company 12 Signal Transduction CHAPTER 12 Signal Transduction Key topics: General features of signal transduction Structure and function of G protein coupled receptors Structure
Supplemental Table unique genes
 Supplemental Table 1 Inflammation KEGG ID Title Gene Count KEGG:mmu04662 B cell receptor signaling pathway 20 KEGG:mmu04060 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction 44 KEGG:mmu04010 MAPK signaling pathway
Supplemental Table 1 Inflammation KEGG ID Title Gene Count KEGG:mmu04662 B cell receptor signaling pathway 20 KEGG:mmu04060 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction 44 KEGG:mmu04010 MAPK signaling pathway
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1
 GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM FIGURE 17.1 1. The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete chemical signals, called hormones, into the blood. In addition, other organs and cells
Tyrosine kinases. Cell surface receptors ligand binding. Producer cell RNA. Target cell
 Tyrosine kinases http://msbl.helsinki.fi/tkseminar roducer cell Signaling molecules Receptor binding Signal transduction Target cell Activation of Gene expression RNA Biological responses proliferation,
Tyrosine kinases http://msbl.helsinki.fi/tkseminar roducer cell Signaling molecules Receptor binding Signal transduction Target cell Activation of Gene expression RNA Biological responses proliferation,
Cell Signaling (part 1)
 15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
15 Cell Signaling (part 1) Introduction Bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes respond to environmental signals and to signaling molecules secreted by other cells for mating and other communication. In multicellular
Supplementary Figure 1: Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points
 A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
BL 424 Test pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points.
 BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction- L4- L5
 Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction- L4- L5 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 PKC Phosphorylates many substrates, can activate kinase pathway, gene regulation PLC- signaling pathway
Receptors Functions and Signal Transduction- L4- L5 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD University of Jordan 1 PKC Phosphorylates many substrates, can activate kinase pathway, gene regulation PLC- signaling pathway
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11
 Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
Molecular biology :- Cancer genetics lecture 11 -We have talked about 2 group of genes that is involved in cellular transformation : proto-oncogenes and tumour suppressor genes, and it isn t enough to
