|
|
|
- Reynard Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3
4
5
6 Table S1. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracelluarly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene expression in comparison to Mock cells Adjusted P- value Protein-protein interaction data type from Stringdb.com Upregulated pathways from Innatedb.com FOSB FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B E-06 experimentally AP-1 transcription factor network, Osteoclast differentiation TNF tumor necrosis factor E-06 coexpression, transcription in lymphocytes, Cytokinecytokine receptor interaction, Osteoclast differentiation, GPCR signaling, IL23- mediated signaling events, MAPK signaling pathway, Signal transduction through il1r, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, TWEAK, amb2 Integrin signaling, Downstream signaling in naïve CD8+ T cells, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, Hematopoietic cell lineage, Hepatitis C, Keratinocyte differentiation, Leishmaniasis, HIV-1 Nef: Negative effector of Fas and TNF-alpha, T cell receptor signaling pathway, TNFR1 signaling pathway, TNF receptor signaling pathway CXCL2 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand E-05 coexpression, curated databases, protein homology, GPCR ligand binding, Class A/1 (Rhodopsinlike receptors), NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, Signaling by GPCR, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events IL8 interleukin E-05 coexpression, curated databases, protein homology, AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, Calcineurinregulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, GPCR signaling, GPCR ligand binding, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Signaling by GPCR, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP), Peptide ligand-binding receptors, Hepatitis C, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events ATF3 activating transcription factor E-05 experimentally coexpression, protein homology, EGR2 early growth response E-05 experimentally coexpression, AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, Direct p53 effectors transcription in lymphocytes
7 PPP1R15A protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 15A E-07 coexpression, EGR4 early growth response E-04 experimentally transcription in lymphocytes, Downstream signaling in naïve CD8+ T cells TNFAIP3 tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein E-06 experimentally coexpression, CD40/CD40L signaling, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Tnfr2 signaling pathway, RIG-I/MDA5 mediated induction of IFN-alpha/beta pathways, TNF receptor signaling pathway TRAF1 TNF receptor-associated factor E-05 experimentally curated databases, coexpression, CD40/CD40L signaling, TWEAK, Tnfr2 signaling pathway, RANKL, Keratinocyte differentiation, HIV-1 Nef: Negative effector of Fas and TNF-alpha, TNF receptor signaling pathway CCL20 chemokine (C-C motif) ligand E-05 coexpression, curated GPCR ligand binding, Class A/1 (Rhodopsinlike receptors), NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, Signaling by GPCR, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling, G LIF leukemia inhibitory factor E-04 curated databases, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, GPCR signaling, Direct p53 effectors, Jak-STAT signaling pathway HBEGF heparin-binding EGFlike growth factor E-06 curated databases, GPCR signaling, Signaling by GPCR, ErbB receptor signaling network IRF1 interferon regulatory factor E-05 experimentally coexpression, curated Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, IL6-mediated signaling events, Interferon alpha/beta signaling, Hepatitis C, RIG-I/MDA5 mediated induction of IFNalpha/beta pathways EGR1 early growth response E-03 experimentally coexpression, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, transcription in lymphocytes, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, Downstream signaling in naïve CD8+ T cells, Interferon alpha/beta signaling, Oncostatin_M
8 IL6 BIRC3 interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) baculoviral IAP repeat containing E-04 coexpression, curated E-05 experimentally coexpression, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, Cytokinecytokine receptor interaction, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, GPCR signaling, IL23-mediated signaling events, Signal transduction through il1r, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Activated TLR4 signalling, Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade, Toll-Like Receptors Cascades, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, MyD88 dependent cascade initiated on endosome, Toll Like Receptor 7/8 (TLR7/8) Cascade, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, Signaling by GPCR, amb2 Integrin signaling, Signaling by Interleukins, Toll Like Receptor 9 (TLR9) Cascade, MyD88:Mal cascade initiated on plasma membrane, Toll Like Receptor 2 (TLR2) Cascade, Toll Like Receptor TLR1:TLR2 Cascade, Toll Like Receptor TLR6:TLR2 Cascade, IL6- mediated signaling events, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, MyD88 cascade initiated on plasma membrane, TRAF6 mediated induction of NFkB and MAP kinases upon TLR7/8 or 9 activation, Toll Like Receptor 10 (TLR10) Cascade, Toll Like Receptor 5 (TLR5) Cascade, Hematopoietic cell lineage, MyD88- independent cascade, TRIF-mediated TLR3/TLR4 signaling, Toll Like Receptor 3 (TLR3) Cascade, Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP) CD40/CD40L signaling, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Activated TLR4 signalling, Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade, Toll-Like Receptors Cascades, MyD88-independent cascade, TRIFmediated TLR3/TLR4 signaling, Toll Like Receptor 3 (TLR3) Cascade, Keratinocyte differentiation, HIV-1 Nef: Negative effector of Fas and TNF-alpha, TNF receptor signaling pathway NR4A1 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member E-04 experimentally coexpression, MAPK signaling pathway, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network CD83 CD83 molecule E-05 coexpression, MAFF v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog F (avian) E-06 experimentally coexpression, Oxidative stress induced gene expression via nrf2 PTGS2 prostaglandinendoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) E-04 coexpression, transcription in lymphocytes, Calcium signaling in the CD4+ TCR pathway, Leishmaniasis
9 NR4A3 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member E-04 experimentally EGR3 early growth response E-06 experimentally coexpression, transcription in lymphocytes GADD45B growth arrest and DNAdamage-inducible, beta E-05 experimentally protein homology, MAPK signaling pathway, IL12-mediated signaling events SOCS3 suppressor of cytokine signaling E-06 coexpression, curated ATF-2 transcription factor network, Osteoclast differentiation, IL23-mediated signaling events, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, Signaling by Interleukins, IL6- mediated signaling events, Interferon alpha/beta signaling, Hepatitis C, Oncostatin_M DUSP5 CSF2 dual specificity phosphatase 5 colony stimulating factor 2 (granulocytemacrophage) E-05 experimentally coexpression, ATF-2 transcription factor network, MAPK signaling pathway, Direct p53 effectors E-04 coexpression, AP-1 transcription factor network, transcription in lymphocytes, Cytokinecytokine receptor interaction, GPCR signaling, Calcium signaling in the CD4+ TCR pathway, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, Signaling by GPCR, Signaling by Interleukins, Hematopoietic cell lineage, GPCR downstream signaling, T cell receptor signaling pathway NFKBIE nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, epsilon E-05 experimentally coexpression, T cell receptor signaling pathway, TNFR1 signaling pathway, B cell receptor signaling pathway FOSL1 FOS-like antigen E-06 experimentally coexpression, protein homology, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, transcription in lymphocytes, Osteoclast differentiation, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, Calcium signaling in the CD4+ TCR pathway, Downstream signaling in naïve CD8+ T cells, PMAIP1 phorbol-12-myristate-13- acetate-induced protein E-06 experimentally curated Direct p53 effectors EDN1 endothelin E-05 AP-1 transcription factor network, GPCR signaling, GPCR ligand binding, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), Signaling by GPCR, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling
10 BCL2A1 BCL2-related protein A E-05 experimentally curated BCR signaling pathway CXCL3 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand E-05 coexpression, curated databases, protein homology, GPCR ligand binding, Class A/1 (Rhodopsinlike receptors), Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, Signaling by GPCR, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events BBC3 BCL2 binding component E-04 experimentally curated Direct p53 effectors SERPINB2 serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member E-04 curated databases, PLAUR plasminogen activator, urokinase receptor E-06 coexpression, curated Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, amb2 Integrin signaling ZFP36 zinc finger protein 36, C3H type, homolog (mouse) E-05 experimentally coexpression, PRDM1 PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain E-05 experimentally Direct p53 effectors PIM1 pim-1 oncogene E-04 experimentally curated Jak-STAT signaling pathway PTX3 pentraxin 3, long E-04 coexpression, IL1RL1 interleukin 1 receptorlike E-04 IL24 interleukin E-04 IL23-mediated signaling events
11 Table S2. Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of JRS4 Gene symbol intracellularly infected TEpi cells in comparison to mock TEpi cells. Full name Log2FC gene expression in comparison to Mock cells Adjusted P- value Protein-protein interaction data type from Stringdb.com Upregulated pathways from Innatedb.com ATF3 activating transcription factor E-03 experimentally coexpression, protein homology, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, Direct p53 effectors PTGS2 prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) E-03 curated databases, transcription in lymphocytes, Calcium signaling in the CD4+ TCR pathway, Leishmaniasis IL8 interleukin E-03 co-expression, protein homology, curated IL36G interleukin 36, gamma E-05 co-expression, AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, transcription in lymphocytes, GPCR signaling, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsinlike receptors), NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, Peptide ligandbinding receptors, Amoebiasis, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events, Nfkb activation by nontypeable hemophilus influenzae, Malaria CXCL2 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand E-03 co-expression, protein homology, curated Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events IL6 interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) E-02 co-expresssion, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, GPCR signaling, IL23-mediated signaling events, Signaling by GPCR, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, Amoebiasis, Jak- STAT signaling pathway, Hematopoietic cell lineage, Signal transduction through il1r, Graft-versus-host disease, Malaria, Il- 10 anti-inflammatory signaling pathway
12 CLDN4 claudin E-04 curated databases, protein homology, coexpression, TNF tumor necrosis factor E-03 co-expression, transcription in lymphocytes, GPCR signaling, IL23-mediated signaling events, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Amoebiasis, Hematopoietic cell lineage, Signal transduction through il1r, Graftversus-host disease, Osteoclast differentiation, Nfkb activation by nontypeable hemophilus influenzae, Malaria, Il-10 anti-inflammatory signaling pathway, Leishmaniasis SERPINB2 serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member E-03 curated databases, Amoebiasis MMP3 matrix metallopeptidase 3 (stromelysin 1, progelatinase) E-02 Signaling by GPCR CXCL3 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand E-03 co-expression, protein homology, curated Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events IL1RL1 interleukin 1 receptor-like E-02 experimentally TNFAIP3 tumor necrosis factor, alphainduced protein E-03 experimentally coexpression, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway DUSP1 dual specificity phosphatase E-03 experimentally coexpression, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, Direct p53 effectors, Nfkb activation by nontypeable hemophilus influenzae DLX2 distal-less homeobox E-02 IL24 interleukin E-03 co-expression, IL23-mediated signaling events, Jak- STAT signaling pathway OCLN occludin E-03 experimentally PIM1 pim-1 oncogene E-03 experimentally curated Jak-STAT signaling pathway
13 EGR2 early growth response E-02 experimentally transcription in lymphocytes FOSB FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B E-02 experimentally curated AP-1 transcription factor network, Osteoclast differentiation PPP1R15A protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 15A E-04 co-expresssion, curated DUSP5 dual specificity phosphatase E-03 experimentally coexpression, ATF-2 transcription factor network, Direct p53 effectors SOCS3 suppressor of cytokine signaling E-03 co-expresssion, curated ATF-2 transcription factor network, IL23- mediated signaling events, Jak-STAT signaling pathway, Osteoclast differentiation PRDM1 PR domain containing 1, with ZNF domain E-03 Direct p53 effectors HBEGF heparin-binding EGF-like growth factor E-03 curated databases, GPCR signaling, Signaling by GPCR, ErbB receptor signaling network, ErbB signaling pathway PDE4B phosphodiesterase 4B, camp-1.81specific 7.73E-03 experimentally Signaling by GPCR, GPCR downstream signaling PLAUR plasminogen activator, urokinase receptor E-04 co-expresssion, curated Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2 CD274 CD274 molecule E-04 co-expression, ZFP36 zinc finger protein 36, C3H type, homolog (mouse) E-03 co-expresssion, curated HCAR2 hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor E-03 curated databases, GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events PMAIP1 phorbol-12-myristate-13- acetate-induced protein E-03 Direct p53 effectors CLDN1 Rho family GTPase E-02 RND1 Rho family GTPase E-02 experimentally LMO7 LIM domain E-03 curated databases,
14 FOXA1 forkhead box A E-03 Direct p53 effectors RGS2 regulator of G-protein signaling 2, 24kDa E-02 curated databases, GPCR signaling, Signaling by GPCR, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events CCL20 chemokine (C-C motif) ligand E-02 co-expresssion, curated Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events CXCL1 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1 (melanoma growth stimulating activity, alpha) E-02 co-expression, protein homology, curated IL23-mediated signaling events, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, Amoebiasis, GPCR downstream signaling, G alpha (i) signalling events FOSL1 FOS-like antigen E-03 experimentally coexpression, protein homology, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, transcription in lymphocytes, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, Calcium signaling in the CD4+ TCR pathway, Osteoclast differentiation MMP10 matrix metallopeptidase 10 (stromelysin 2) E-02 experimentally coexpression, protein homology, curated EGR3 early growth response E-03 experimentally coexpression, transcription in lymphocytes VGLL3 vestigial like 3 (Drosophila) E-03 co-expression, IL13RA2 interleukin 13 receptor, alpha E-03 curated databases, coexpression, Jak-STAT signaling pathway GADD45B growth arrest and DNAdamage-inducible, beta E-02 co-expression, ADAMTS1 ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, E-02
15 JUN jun proto-oncogene E-03 experimentally coexpression, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, ATF-2 transcription factor network, Calcineurinregulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2, Calcium signaling in the CD4+ TCR pathway, Signal transduction through il1r, Direct p53 effectors, Osteoclast differentiation, Leishmaniasis, ErbB signaling pathway IL1B interleukin 1, beta E-02 experimentally coexpression, curated GPCR signaling, IL23-mediated signaling events, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Amoebiasis, Hematopoietic cell lineage, Signal transduction through il1r, Graft-versus-host disease, Osteoclast differentiation, Nfkb activation by nontypeable hemophilus influenzae, Malaria, Leishmaniasis GRHL1 grainyhead-like 1 (Drosophila) E-02 experimentally protein homology, MMP1 matrix metallopeptidase 1 (interstitial collagenase) E-03 protein homology, curated databases, AP-1 transcription factor network, Validated transcriptional targets of AP1 family members Fra1 and Fra2 MAFF v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog F (avian) E-02 experimentally coexpression, BMP2 bone morphogenetic protein E-03 curated databases, GPCR signaling NRG1 neuregulin E-03 co-expresssion, curated GPCR signaling, ErbB receptor signaling network, ErbB signaling pathway EDN1 endothelin E-02 co-expresssion, curated AP-1 transcription factor network, GPCR signaling, GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), Peptide ligand-binding receptors, GPCR downstream signaling PELI1 pellino E3 ubiquitin protein ligase E-03 curated databases, ADRB2 adrenoceptor beta 2, surface E-03 experimentally curated GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), GPCR downstream signaling RND3 Rho family GTPase E-03 experimentally coexpression, HAS2 hyaluronan synthase E-02
16 ADAMTS6 ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif, E-03 GRHL3 grainyhead-like 3 (Drosophila) E-03 experimentally protein homology,
17 Table S3: Metadata for transcriptome interaction network and pathway analysis of 5448 intracellularly infected Tepi cells in comparison to JRS4 infected cells. Gene symbol Full name Log2FC gene Adjusted P- expression in value comparison to JRS4- infected cells Protein-protein interaction data type from Stringdb.com Upregulated pathways from Innatedb.com FOSB FBJ murine osteosarcoma viral oncogene homolog B E-04 experimentally Osteoclast differentiation, AP-1 transcription factor network EGR4 early growth response E-03 experimentally IRF1 interferon regulatory factor E-04 experimentally coexpression, curated Calcineurin-regulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes, Downstream signaling in naïve CD8+ T cells Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, IL6- mediated signaling events, Innate Immune System TRAF1 TNF receptor-associated factor E-04 experimentally coexpression, curated CD40/CD40L signaling, Tnfr2 signaling pathway, HIV-1 Nef: Negative effector of Fas and TNFalpha, RANKL, TNF receptor signaling pathway, TWEAK BIRC3 baculoviral IAP repeat containing E-04 experimentally coexpression, curated CD40/CD40L signaling, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, HIV-1 Nef: Negative effector of Fas and TNF-alpha, Toll- Like Receptors Cascades, Activated TLR4 signalling, Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade, TNF receptor signaling pathway, Innate Immune System
18 TNF tumor necrosis factor E-04 coexpression, Calcineurin-regulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes, Osteoclast differentiation, Cytokinecytokine receptor interaction, MAPK signaling pathway, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, JAK STAT pathway and regulation, HIV-1 Nef: Negative effector of Fas and TNF-alpha, Downstream signaling in naïve CD8+ T cells, T cell receptor signaling pathway, Hematopoietic cell lineage, Nfat and hypertrophy of the heart, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, IL23- mediated signaling events, TNF receptor signaling pathway, TWEAK, Adipocytokine signaling pathway, GPCR signaling PTX3 pentraxin 3, long E-03 NFKBIE nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, epsilon E-04 experimentally coexpression, T cell receptor signaling pathway, Adipocytokine signaling pathway CD83 CD83 molecule E-03 coexpression, EGR2 early growth response E-04 experimentally coexpression, Calcineurin-regulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes, IL4-mediated signaling events GDF15 growth differentiation factor E-03 Direct p53 effectors CCL20 chemokine (C-C motif) ligand E-03 curated databases, coexpression, Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), GPCR ligand binding, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, Signaling by GPCR, GPCR downstream signaling LIF MAFF leukemia inhibitory factor v-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog F (avian) E-03 curated Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, JAK STAT pathway and regulation, Direct p53 effectors, Nfat and hypertrophy of the heart, GPCR signaling E-04 experimentally
19 NR4A3 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member E-03 experimentally BCL2A1 BCL2-related protein A E-04 experimentally curated PPP1R15A protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 15A E-04 TNFAIP2 NR4A1 HBEGF CX3CL1 tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 2 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 1 heparin-binding EGFlike growth factor chemokine (C-X3-C motif) ligand E E-03 experimentally coexpression, MAPK signaling pathway, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, TCR, Innate Immune System E-04 curated Signaling by GPCR, Nfat and hypertrophy of the heart, GPCR signaling, Innate Immune System E-04 Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), GPCR ligand binding, Peptide ligand-binding receptors, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, Direct p53 effectors, Signaling by GPCR GEM GTP binding protein overexpressed in skeletal muscle E-03 experimentally EGR1 early growth response E-02 experimentally curated databases, protein homology, Calcineurin-regulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes, AP-1 transcription factor network, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Downstream signaling in naïve CD8+ T cells, Oncostatin_M, TCR, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system PTGER4 prostaglandin E receptor 4 (subtype EP4) E-04 Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), GPCR ligand binding, Signaling by GPCR, GPCR downstream signaling ICAM1 intercellular adhesion molecule E-03 curated databases, coexpression, Glucocorticoid receptor regulatory network, Toll- Like Receptors Cascades, Activated TLR4 signalling, Toll Like Receptor 4 (TLR4) Cascade, Cytokine Signaling in Immune system, Toll-like receptor signaling pathway, Innate Immune System
20 BDKRB1 bradykinin receptor B E-03 curated databases Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), GPCR ligand binding, Peptide ligandbinding receptors, Signaling by GPCR, GPCR downstream signaling GADD45B growth arrest and DNAdamage-inducible, beta E-03 MAPK signaling pathway, IL12-mediated signaling events CXCL2 chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand E-03 coexpression, curated databases Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Class A/1 (Rhodopsin-like receptors), GPCR ligand binding, Peptide ligandbinding receptors, Chemokine receptors bind chemokines, Signaling by GPCR, GPCR downstream signaling EGR3 early growth response E-04 experimentally Calcineurin-regulated NFAT-dependent transcription in lymphocytes TNFAIP3 NFKBIZ tumor necrosis factor, alpha-induced protein 3 nuclear factor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells inhibitor, zeta E-03 experimentally coexpression, E-03 experimentally CD40/CD40L signaling, NOD-like receptor signaling pathway, Tnfr2 signaling pathway, TNF receptor signaling pathway, Innate Immune System CORO6 coronin E-03 experimentally coexpression, LRIG3 leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains E-03 experimentally ACTL10 actin-like E-03 experimentally coexpression, HIST1H2BF histone cluster 1, H2bf E-02 experimentally coexpression,
TNFSF13B tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily, member 13b NF-kB pathway cluster, Enrichment Score: 3.57
 Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
Appendix 2. Highly represented clusters of genes in the differential expression of data. Immune Cluster, Enrichment Score: 5.17 GO:0048584 positive regulation of response to stimulus GO:0050778 positive
* Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes.
 Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplemental Material Complete gene expression data using Affymetrix 3PRIME IVT ID Chip (54,614 genes) and human immature dendritic cells stimulated with rbmasnrs, IL-8 and control (media) has been deposited
Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No.
 Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Tables Supplementary Table S1. Primers used for quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction Marker Sequence (5 3 ) Accession No. Angiopoietin 1, ANGPT1 A CCCTCCGGTGAATATTGGCTGG NM_001146.3
Supplementary Figure 1: Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points
 A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
A. B. 8 4 Supplementary Figure : Func8onal Network Analysis of Kinases Significantly Modulated by MERS CoV Infec8on and Conserved Across All Time Points Examined. A) Venn diagram analysis of kinases significantly
REACTOME: Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) REACTOME:72764 Eukaryotic Translation Termination. REACTOME:72737 Cap dependent Translation Initiation
 A REACTOME:975957 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:975956 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:927802
A REACTOME:975957 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) enhanced by the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:975956 Nonsense Mediated Decay (NMD) independent of the Exon Junction Complex (EJC) REACTOME:927802
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array.
 Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Supplementary Table 1. Genes analysed for expression by angiogenesis gene-array. Gene symbol Gene name TaqMan Assay ID UniGene ID 18S rrna 18S ribosomal RNA Hs99999901_s1 Actb actin, beta Mm00607939_s1
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p <0.01 for 0.01 mm NS-398, 0.1mM ibuprofen and COX-2 RNAi.
 Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Table S1 Differentially expressed genes showing > 2 fold changes and p
Nature Immunology: doi: /ni.3745
 Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental settings. (a) Experimental setup and bioinformatic data analysis of transcriptomic changes induced in neonatal and adult monocytes by stimulation with 10 ng/ml LPS for
Supplementary Figure 1 Experimental settings. (a) Experimental setup and bioinformatic data analysis of transcriptomic changes induced in neonatal and adult monocytes by stimulation with 10 ng/ml LPS for
Supplementary Figure 1.
 Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Supplementary Figure 1. Increased expression of cell cycle pathway genes in insulin + Glut2 low cells of STZ-induced diabetic islets. A) random blood glucose measuers of STZ and vehicle treated MIP-GFP
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID
 Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
Additional file 2 List of pathway from PID Pathway ID Pathway name # components # enriched GO terms a4b1_paxdep_pathway Paxillin-dependent events mediated by a4b1 20 179 a4b1_paxindep_pathway Paxillin-independent
T Cell Activation. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009
 T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
A. Incorrect! It s not correct. Synergism of cytokines refers to two or more cytokines acting together.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 11: Cytokine and Cytokine Receptors Question No. 1 of 10 1. A single cytokine can act on several different cell types, which is known as. Question #1 (A) Synergism (B) Pleiotropism
Immunology - Problem Drill 11: Cytokine and Cytokine Receptors Question No. 1 of 10 1. A single cytokine can act on several different cell types, which is known as. Question #1 (A) Synergism (B) Pleiotropism
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. b-galactosidase staining of
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. b-galactosidase staining of senescent cells in 500 mg=dl glucose (10 magnification). SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S3. Toluidine blue staining of chondrogenic-differentiated adipose-tissue-derived
silent epidemic,. (WHO),
 Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
Tel: 02-740-8686; E-mail: hhbkim@snu.ac.kr silent epidemic,. (WHO),. 5 3, 1. 50 70. 50%, 25%, 20% (12~35%). 2.8% 0.7% 4. ( ). bone remodeling (osteoblast), (osteoclast),.. 3~4.. 70% (osteocyte) (bone lining
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers. A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs
 Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
Cytokines, adhesion molecules and apoptosis markers A comprehensive product line for human and veterinary ELISAs IBL International s cytokine product line... is extremely comprehensive. The assays are
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Chapter 11 CYTOKINES
 Chapter 11 CYTOKINES group of low molecular weight regulatory proteins secreted by leukocytes as well as a variety of other cells in the body (8~30kD) regulate the intensity and duration of the immune
Chapter 11 CYTOKINES group of low molecular weight regulatory proteins secreted by leukocytes as well as a variety of other cells in the body (8~30kD) regulate the intensity and duration of the immune
Regulating the Regulators for Cancer Immunotherapy: LAG-3 Finally Catches Up. Drew Pardoll Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center Johns Hopkins
 Regulating the Regulators for Cancer Immunotherapy: LAG-3 Finally Catches Up Drew Pardoll Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center Johns Hopkins The hostile immune microenvironment within a tumor Stat3 Stat3 NK Lytic
Regulating the Regulators for Cancer Immunotherapy: LAG-3 Finally Catches Up Drew Pardoll Sidney Kimmel Cancer Center Johns Hopkins The hostile immune microenvironment within a tumor Stat3 Stat3 NK Lytic
Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion
 Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Probe Set ID RefSeq Transcript ID Gene Title Gene Symbol 205980_s_at NM_001017526 /// NM_181334 /// NM_181335 Rho GTPase activating protein 8 /// PRR5- ARHGAP8 fusion ARHGAP8 /// LOC553158 FC ALK shrna
Toll-like Receptor Signaling
 Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Toll-like Receptor Signaling 1 Professor of Medicine University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, USA Why do we need innate immunity? Pathogens multiply very fast We literally swim in viruses
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
CPM (x 10-3 ) Tregs +Teffs. Tregs alone ICOS CLTA-4
 A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
A 2,5 B 4 Number of cells (x 1-6 ) 2, 1,5 1, 5 CPM (x 1-3 ) 3 2 1 5 1 15 2 25 3 Days of culture 1/1 1/2 1/4 1/8 1/16 1/32 Treg/Teff ratio C alone alone alone alone CD25 FoxP3 GITR CD44 ICOS CLTA-4 CD127
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7)
 Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Signaling Through Immune System Receptors (Ch. 7) 1. General principles of signal transduction and propagation. 2. Antigen receptor signaling and lymphocyte activation. 3. Other receptors and signaling
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors
 Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
Lecture 7: Signaling Through Lymphocyte Receptors Questions to Consider After recognition of its cognate MHC:peptide, how does the T cell receptor activate immune response genes? What are the structural
Immune suppression in Atlantic salmon: smoltification, sea water transfer and breeding
 Immune suppression in Atlantic salmon: smoltification, sea water transfer and breeding Aleksei Krasnov, Nofima FHFs fiskehelsesamling 1.-2. september 2015 Smoltifiction and breeding suppress immunity in
Immune suppression in Atlantic salmon: smoltification, sea water transfer and breeding Aleksei Krasnov, Nofima FHFs fiskehelsesamling 1.-2. september 2015 Smoltifiction and breeding suppress immunity in
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
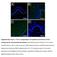 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Assessment of cell survival (MTT) Assessment of early apoptosis and cell death
 Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Overexpression of a functional calcium-sensing receptor dramatically increases osteolytic potential of MDA-MB-231 cells in a mouse model of bone metastasis through epiregulinmediated osteoprotegerin downregulation
Table S7B- Biocarta functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes unique to COX-2 expressers
 Table S7B- Biocarta functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes unique to COX-2 expressers ListHits ListTotal PopulationHits PopulationTotal Terms 3 72 10 1429 Glycolysis Pathway 3 72 11 1429 Regulation
Table S7B- Biocarta functional annotation of celecoxib-modulated genes unique to COX-2 expressers ListHits ListTotal PopulationHits PopulationTotal Terms 3 72 10 1429 Glycolysis Pathway 3 72 11 1429 Regulation
NTD Vaccine Design Toolkit and Training Workshop Providence, RI January 05, 2011 Cytokines Leslie P. Cousens, PhD EpiVax, Inc.
 NTD Vaccine Design Toolkit and Training Workshop Providence, RI January 05, 2011 Cytokines Leslie P. Cousens, PhD EpiVax, Inc. Cytokines Properties of Cytokines Cytokines are proteins with specific roles
NTD Vaccine Design Toolkit and Training Workshop Providence, RI January 05, 2011 Cytokines Leslie P. Cousens, PhD EpiVax, Inc. Cytokines Properties of Cytokines Cytokines are proteins with specific roles
T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation. FOCiS. Lecture outline
 1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
1 T Lymphocyte Activation and Costimulation Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family Inhibitory receptors of T cells Targeting costimulators for
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Inflammation and extracellular proteinases
 Inflammation and extracellular proteinases Plaque rupture 75% of MI (heart attack) Foamy macrophages Thin cap No collagen Thin fibrous cap (
Inflammation and extracellular proteinases Plaque rupture 75% of MI (heart attack) Foamy macrophages Thin cap No collagen Thin fibrous cap (
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction
 Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Receptor mediated Signal Transduction G-protein-linked receptors adenylyl cyclase camp PKA Organization of receptor protein-tyrosine kinases From G.M. Cooper, The Cell. A molecular approach, 2004, third
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics
 Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Biology, Pathology and Therapeutics Dr Sarah Sasson SydPATH Registrar 23 rd June 2014 TLRs: Introduction Discovered in 1990s Recognise conserved structures in pathogens Rely
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20177 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Kester, Maria Sophia van (Marloes) Title: Molecular aspects of cutaneous T-cell
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/20177 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Kester, Maria Sophia van (Marloes) Title: Molecular aspects of cutaneous T-cell
Pathway Map Reference Guide
 Pathway Map Reference Guide Focus Attention-grabber Your Pathway The most popular cell signaling pathways Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents AKT Signaling 4 camp Signaling 5 Cellular Apoptosis
Pathway Map Reference Guide Focus Attention-grabber Your Pathway The most popular cell signaling pathways Sample & Assay Technologies Table of contents AKT Signaling 4 camp Signaling 5 Cellular Apoptosis
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler
 Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Supplementary data Table S3. GO terms, pathways and networks enriched among the significantly correlating genes using Tox-Profiler DR CALUX Boys Girls Database Systemic lupus erythematosus 4.4 0.0021 6.7
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation
 1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 T Cell Activation, Costimulation and Regulation Abul K. Abbas, MD University of California San Francisco 2 Lecture outline T cell antigen recognition and activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV. Some molecular mechanisms of cancer
 VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
VIII Curso Internacional del PIRRECV Some molecular mechanisms of cancer Laboratorio de Comunicaciones Celulares, Centro FONDAP Estudios Moleculares de la Celula (CEMC), ICBM, Facultad de Medicina, Universidad
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection
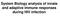 System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
System Biology analysis of innate and adaptive immune responses during HIV infection Model of T cell memory persistence and exhaustion Naive Ag+APC Effector TEM (Pfp, Gr.B, FasL, TNF) Ag stim. IL-2, IL-7,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
T-cell activation T cells migrate to secondary lymphoid tissues where they interact with antigen, antigen-presenting cells, and other lymphocytes:
 Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Interactions between innate immunity & adaptive immunity What happens to T cells after they leave the thymus? Naïve T cells exit the thymus and enter the bloodstream. If they remain in the bloodstream,
Supporting Information. Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes Triggered by Oxide Nanoparticles
 Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes Triggered Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 6 1 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.6. Supporting Information Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression
Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression Changes Triggered Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2011, Vol. 32, No. 6 1 DOI 10.5012/bkcs.2011.32.6. Supporting Information Evaluation of Toxicity and Gene Expression
Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of
 1 Supplementary material for: 2 3 4 5 6 Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of influenza A (H1N2) infection Louise Brogaard, Peter M. H. Heegaard, Lars
1 Supplementary material for: 2 3 4 5 6 Late regulation of immune genes and micrornas in circulating leukocytes in a pig model of influenza A (H1N2) infection Louise Brogaard, Peter M. H. Heegaard, Lars
ulcer healing role 118 Bicarbonate, prostaglandins in duodenal cytoprotection 235, 236
 Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Subject Index Actin cellular forms 48, 49 epidermal growth factor, cytoskeletal change induction in mucosal repair 22, 23 wound repair 64, 65 polyamine effects on cytoskeleton 49 51 S-Adenosylmethionine
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Gorgun et al. 10.1073/pnas.0901166106 SI Text Animals, Disease Detection and Infusion of CLL Cells. Mice were examined for lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly and at specific ages or
Supporting Information Gorgun et al. 10.1073/pnas.0901166106 SI Text Animals, Disease Detection and Infusion of CLL Cells. Mice were examined for lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly and at specific ages or
Immune response to infection
 Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Immune response to infection Dr. Sandra Nitsche (Sandra.Nitsche@rub.de ) 20.06.2018 1 Course of acute infection Typical acute infection that is cleared by an adaptive immune reaction 1. invasion of pathogen
Thanks to: Signal Transduction. BCB 570 "Signal Transduction" 4/8/08. Drena Dobbs, ISU 1. An Aging Biologist s. One Biologist s Perspective
 BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
BCB 570 "" Thanks to: One Biologist s Perspective Drena Dobbs BCB & GDCB Iowa State University Howard Booth Biology Eastern Michigan University for Slides modified from his lecture Cell-Cell Communication
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Chapter 13: Cytokines
 Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases
 54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD.
 Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
Allergy and Immunology Review Corner: Chapter 13 of Immunology IV: Clinical Applications in Health and Disease, by Joseph A. Bellanti, MD. Chapter 13: Mechanisms of Immunity to Viral Disease Prepared by
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS
 TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
TOLL-LIKE RECEPTORS AND CYTOKINES IN SEPSIS A/PROF WILLIAM SEWELL ST VINCENT S CLINICAL SCHOOL, UNSW SYDPATH, ST VINCENT S HOSPITAL SYDNEY GARVAN INSTITUTE INNATE VERSUS ADAPTIVE IMMUNE RESPONSES INNATE
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Applied Biosystems models 7500 (Fast block), 7900HT (Fast block), StepOnePlus, ViiA 7 (Fast block)
 RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
RT² Profiler PCR Array (96-Well Format and 384-Well [4 x 96] Format) Human HIV Infection and Host Response Cat. no. 330231 PAHS-051YA For pathway expression analysis Format Format A Format C Format D Format
RAS Genes. The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes.
 ۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
۱ RAS Genes The ras superfamily of genes encodes small GTP binding proteins that are responsible for the regulation of many cellular processes. Oncogenic ras genes in human cells include H ras, N ras,
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with. unipartite and bipartite structure. Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2
 Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
Supplementary information for: Community detection for networks with unipartite and bipartite structure Chang Chang 1, 2, Chao Tang 2 1 School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beiing 100871, China
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Interferon-gamma pathway is activated in a chronically HBV infected chimpanzee that controls HBV following ARC-520 RNAi treatment
 Interferon-gamma pathway is activated in a chronically HBV infected chimpanzee that controls HBV following ARC-520 RNAi treatment Zhao Xu, Deborah Chavez, Jason E. Goetzmann, Robert E. Lanford and Christine
Interferon-gamma pathway is activated in a chronically HBV infected chimpanzee that controls HBV following ARC-520 RNAi treatment Zhao Xu, Deborah Chavez, Jason E. Goetzmann, Robert E. Lanford and Christine
T cell Receptor. Chapter 9. Comparison of TCR αβ T cells
 Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Chapter 9 The αβ TCR is similar in size and structure to an antibody Fab fragment T cell Receptor Kuby Figure 9-3 The αβ T cell receptor - Two chains - α and β - Two domains per chain - constant (C) domain
Molecular basis of age-associated cytokine dysregulation in LPS-stimulated macrophages
 Uncorrected Version. Published on April 6, 2006 as DOI:10.1189/jlb.0106024 Molecular basis of age-associated cytokine dysregulation in LPS-stimulated macrophages R. Lakshman Chelvarajan,*, Yushu Liu, Diana
Uncorrected Version. Published on April 6, 2006 as DOI:10.1189/jlb.0106024 Molecular basis of age-associated cytokine dysregulation in LPS-stimulated macrophages R. Lakshman Chelvarajan,*, Yushu Liu, Diana
Innate Immunity. Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016
 Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
Innate Immunity Hathairat Thananchai, DPhil Department of Microbiology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University 2 August 2016 Objectives: Explain how innate immune system recognizes foreign substances
T cell maturation. T-cell Maturation. What allows T cell maturation?
 T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
T-cell Maturation What allows T cell maturation? Direct contact with thymic epithelial cells Influence of thymic hormones Growth factors (cytokines, CSF) T cell maturation T cell progenitor DN DP SP 2ry
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity
 Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Chapter 3 The Induced Responses of Innate Immunity Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system Pattern recognition by cells of the innate immune system 4 main pattern recognition receptors
Cytokines. Luděk Šefc. Cytokines Protein regulators of cellular communication. Cytokines x hormones
 Cytokines Luděk Šefc Cytokines Protein regulators of cellular communication Cytokines x hormones Hormones Cytokines Production sites few many Cell targets few many Presence in blood yes rarely Biological
Cytokines Luděk Šefc Cytokines Protein regulators of cellular communication Cytokines x hormones Hormones Cytokines Production sites few many Cell targets few many Presence in blood yes rarely Biological
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology
 Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
Darwinian selection and Newtonian physics wrapped up in systems biology Concept published in 1957* by Macfarland Burnet (1960 Nobel Laureate for the theory of induced immune tolerance, leading to solid
T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells
 T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of Rheumatology, CUMC September 17, 2008 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared
T cells III: Cytotoxic T lymphocytes and natural killer cells Margrit Wiesendanger Division of Rheumatology, CUMC September 17, 2008 Killer cells: CD8 + T cells (adaptive) vs. natural killer (innate) Shared
This is a free sample of content from Immune Tolerance. Click here for more information or to buy the book.
 A ACPAs. See Antibodies to citrullinated peptide antigens Activation-induced cell death (AICD), 25 AICD. See Activation-induced cell death AIRE, 3, 18 19, 24, 88, 103 104 AKT, 35 Alefacept, 136 ALPS. See
A ACPAs. See Antibodies to citrullinated peptide antigens Activation-induced cell death (AICD), 25 AICD. See Activation-induced cell death AIRE, 3, 18 19, 24, 88, 103 104 AKT, 35 Alefacept, 136 ALPS. See
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
Cancer. The fundamental defect is. unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells. Causes of Cancer. Altered growth and proliferation
 Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Cancer The fundamental defect is unregulated cell division. Properties of Cancerous Cells Altered growth and proliferation Loss of growth factor dependence Loss of contact inhibition Immortalization Alterated
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Expression of complement factors is induced in DBA/2 mice following administration of C. albicans
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Expression of complement factors is induced in DBA/2 mice following administration of C. albicans water-soluble mannoprotein-beta-glucan complex (CAWS) Noriko Nagi-Miura 1,, Daisuke
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Expression of complement factors is induced in DBA/2 mice following administration of C. albicans water-soluble mannoprotein-beta-glucan complex (CAWS) Noriko Nagi-Miura 1,, Daisuke
Time course of immune response
 Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
Time course of immune response Route of entry Route of entry (cont.) Steps in infection Barriers to infection Mf receptors Facilitate engulfment Glucan, mannose Scavenger CD11b/CD18 Allows immediate response
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
The Influence of Birch Bark Triterpenes on. Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts from Diabetic and
 1 1 2 3 The Influence of Birch Bark Triterpenes on Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts from Diabetic and Nondiabetic Donors 4 5 Tina Wardecki,#, Philipp Werner,#, Maria Thomas, Markus F. Templin, Gudula Schmidt,
1 1 2 3 The Influence of Birch Bark Triterpenes on Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts from Diabetic and Nondiabetic Donors 4 5 Tina Wardecki,#, Philipp Werner,#, Maria Thomas, Markus F. Templin, Gudula Schmidt,
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems
 The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
The elements of G protein-coupled receptor systems Prostaglandines Sphingosine 1-phosphate a receptor that contains 7 membrane-spanning domains a coupled trimeric G protein which functions as a switch
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells
 Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Immunology Basics Relevant to Cancer Immunotherapy: T Cell Activation, Costimulation, and Effector T Cells Andrew H. Lichtman, M.D. Ph.D. Department of Pathology Brigham and Women s Hospital and Harvard
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture 6 Notes: Control Systems in Gene Expression Pulling it all together: coordinated control of transcriptional regulatory molecules Simple Control:
PCxN: The pathway co-activity map: a resource for the unification of functional biology
 PCxN: The pathway co-activity map: a resource for the unification of functional biology Sheffield Institute for Translational Neurosciences Center for Integrative Genome Translation GENOME INFORMATICS
PCxN: The pathway co-activity map: a resource for the unification of functional biology Sheffield Institute for Translational Neurosciences Center for Integrative Genome Translation GENOME INFORMATICS
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma plasma B cell.
 Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Generation of post-germinal centre myeloma. DNA DAMAGE CXCR4 Homing to Lytic lesion activation CD38 CD138 CD56 Phenotypic markers Naive Secondary lymphoid organ Multiple myeloma is a malignancy of s caused
Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection.
 Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection. Genes found to be significantly upregulated (FDR2) in Y strain
Supplementary Table SI: Y strain T. cruzi infection results in the upregulation of 381 genes at the site of infection. Genes found to be significantly upregulated (FDR2) in Y strain
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
remember that T-cell signal determine what antibody to be produce class switching somatical hypermutation all takes place after interaction with
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The last lecture we discussed the antigen processing and presentation and antigen recognition then the activation by T lymphocyte and today we will continue with B cell recognition
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم The last lecture we discussed the antigen processing and presentation and antigen recognition then the activation by T lymphocyte and today we will continue with B cell recognition
Cholera host response gene networks: preliminary studies
 www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(10) Hypothesis Cholera host response gene networks: preliminary studies Paul Shapshak 1 *, Charurut Somboonwit 1, 2, Shu Cao 1, John T. Sinnott 1, 2 1Division of Infectious
www.bioinformation.net Volume 13(10) Hypothesis Cholera host response gene networks: preliminary studies Paul Shapshak 1 *, Charurut Somboonwit 1, 2, Shu Cao 1, John T. Sinnott 1, 2 1Division of Infectious
PATHOGEN INNOCUOUS ANTIGEN. No Danger- very low expression of costimulatory ligands Signal One Only
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv illai AICD Naive Activated Effector Memory Activated Effector Naive AICD Activated
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv illai AICD Naive Activated Effector Memory Activated Effector Naive AICD Activated
The g c Family of Cytokines Prof. Warren J. Leonard M.D.
 The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
The Family of Cytokines Chief, Laboratory of Molecular Immunology Director, Immunology Center National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute National Institutes of Health Department of Health and Human Services
Table 1: NFkB Target Gene Sets 1.Genes included in the subset of 15k genes selected according to a MAD-based variation filter
 Supplementary Information NFkB target gene sets The NFkB target gene sets are listed below (Table1). In addition to the previously performed mapping of Affymetrix probesets and corresponding Lymphochip
Supplementary Information NFkB target gene sets The NFkB target gene sets are listed below (Table1). In addition to the previously performed mapping of Affymetrix probesets and corresponding Lymphochip
KEY CONCEPT QUESTIONS IN SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
Signal Transduction - Part 2 Key Concepts - Receptor tyrosine kinases control cell metabolism and proliferation Growth factor signaling through Ras Mutated cell signaling genes in cancer cells are called
