Studies on the Cytotoxic Effect of Oil Refinery Sludge on Root Meristem
|
|
|
- Shauna Lawrence
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A dvances in Environmental Biology, 3(1): 10-14, 2009 ISSN , American-Eurasian Network for Scientific Information 10 This is a refereed journal and all articles are professionally screened and reviewed ORIGINAL ARTICLE Studies on the Cytotoxic Effect of Oil Refinery Sludge on Root Meristem Bhaben Tanti, Alak K. Buragohain, Snehashish Dutta, Lisha Gurung, Madhu Shastry, 1 Sailendra Prasad Borah 1 Cytogenetics and Plant Breeding Laboratory, Department of Botany, Gauhati University, Guwahati , Assam, India 2 Department of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology, Tezpur University, Tezpur , Assam, India Bhaben Tanti, Alak K. Buragohain, Snehashish Dutta, Lisha Gurung, Madhu Shast ry, Sa ilendra Pra s a d Borah: Studies on the Cytotoxic Effect of Oil Refinery Sludge on Root Meristem: Am.- Eurasian J. Sustain. Agric., 3(1): 10-14, 2009 ABSTRACT Cytotoxicity of the oil refinery sludge was studied using Allium cepa L. a s a test plant. Onion roots were treated with different concentrations of pollutant for d iffe re n t durations along with controls. The high mitotic index and lower percentage of abnormality was very much evident in roots treated with diluted pollutants. The mitotic index showed decreasing tendency with parallel increase in pollutant concentrations. Binucleate, sticky anaphase erosion, C-metaphase, polyploidy, unequal distribution of chromosomes, spiral nature of chromosome and distortion of poles are some of the common abnormalities observed in all treatments. Both duration and concentration of the treatment influenced the cell division. The types and percentage of abnormalities confirmed impact of sludge generated by oil refinery on crop and other biota in the agro-ecosystem. Key words: Oil refinery, pollutants, Allium cepa, Chromosomal abnormalities, Cytotoxicity. Introduction Rapid urbanization combined with industrialization has led to the generation and disposal of enormous amount of waste product to our environment [4]. Petroleum based industries including oil refineries are one of the major industrial sectors that generate tremendous amount of pollutants [10]. Crude oil is an oily mixture of different types of aliphatic, aromatic, polycyclic hydrocarbons (PAH) along with N, S, and O containing asulpha n t s [5]. PAH is not only toxic but also highly c a rcinogenic [7]. A huge amount of refinery effluents is released to the environment, which pollutes both terrestrial as well as aquatic ecosystems. Sludge management in petroleum refineries is an area, which need immediate attention. Generation of variety of sludge in refinery can be minimized by taking appropriate steps, if not can damage the soil properties that might prove to be harmful for the farmers in their agricultural field nearby [6]. The higher concentration of these pollutants is likely to affect metabolic and cellular activit ies because of the presence of highly toxic and carcinogenic components in them [1]. Contamination of refinery sludge creates a distinct type of ecological habitat that invariably change t he physico-chemical properties of soil leading to affect on germination of seeds, growth and development of plant lives. This oily sludge may completely eliminate the vegetation of a place hampering soil aeration, destroying rizosphere system including microbial populations. This brings a serious of disastrous changes in floral composition leading to habitat lost [8]. In this present in v estigation, therefore, an attempt was made to find out the possible toxic effects of effluents of petroleum-based industries on plant cells. Corresponding Author Bhaben Tanti, Cytogenetics and Plant Breeding Laboratory, Department of Botany, Gauhati University, Guwahati , Assam, India bt53@rediffmail.com
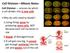
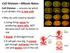
2 Materials and methods The refinery sludge was collected from the Noonmati Oil Refinery, which is located at about 10 km away from Guwahati city, Assam (India). Standard methods [2] were employed for the collection of sludge samples. The physico-chemical parameters of the samples were stud ie d using standard methods [3]. Higher plants provide valuable genetic assay s ystem for screening and monitoring environmental pollutants. Allium cepa L. has been considered as an excelle n t material for the assay of chromosome aberrations followin g chemical treatment. Their root meristem represents a normal proliferating plant pollution that is sensitive to changes in environmental conditions [16]. Healthy onion bulbs were selected to study the cytotoxicity. Bases of the bulbs were scraped to expose the fresh root primo rd ia l. These bulbs were than placed on the test tubes filled with distilled water in such a way that the bases of the bulbs were in contact with water surface. The bulbs, after they produced roots of about 1-2 cm length were taken out and placed on test tubes containing different concentrations of oily sludge [10%, 50%, 75% and 100% (raw sludge)] fo r 24, 48 and 72 hrs. A control set with dechlorinated tap water was maintained in all the cases. After treatment the root tips were excised and fixed in freshly prepared Carnoy s fixative (1:3 acetic acid and ethanol) fo r 24 hrs. Thereafter, the roo t tips were stored in 70% 0 alcohol at 4 C until they were used. The root tips were stained in 2% Aceto-orcein to s tudy the frequency of cell division and chromosomal abnormalities in different treatments. The frequency and types of chromosomal aberration were determined by examin ing about 1000 dividing cells fro m 10 root tips per treatment. The slides were observed under a compound light microscope (Leica ATC-2000). Toxicity to mitotic apparatus and karyotoxicity were also calculated. Results and discussions The physico-chemical characteristic of the oily sludge is presented in Table1. The sludge was acidic. The cytotoxic effects of oily sludge on somatic onion cells were estimated on the basis of changes in mitotic index and other induced abnormalities. The mitotic index and percentage of abnormalities observed a re given in Table 2, 3, and 4. The mitotic index declined as the concentration of sludge increased. The percentage of abnormalities, however, showed opposite trend. The p e rcentage of cell division and abnormalities induced varied in direct proportion to the sludge concentration and duration of exposure. Minimum cytotoxic ity was observed in 11 roots treated with 10% sludge while maximum effect was obtained in roots treated with raw sludge. Both concentration a nd duration of exposure affected mitotic index. The root tips treated with sludge for 24 hrs induced lowest percentage of abnormalities while highest percentage of abnormalities occurred in roots treated for 72 hrs. Borah and Talukdar[9] have reported that higher concentration and longer duration of treatment of the castor seed extract depressed the mitotic index greatly. The sludge concentration in the range of % induced higher percentage of abnormalities and low mitotic index. The root tips treated with lower concentration of sludge however showed higher mitotic index and lower percentage of abnormalities. Somashekar and Gurudev[19] recorded suppressive effect of industrial effluents o n mitotic characters. Anucleation in considerable number of c ells was an interesting finding of the present work. These cells might have developed due to cytokinesis without karyokinesis or due to the complete disintegration of the nuclear material. Considerable number of cells showed unequal distribution of chromosomes (Fig. 1G) that might be attributed to abnormality in spindle formation caus ing unequal dis tribution of chromosomes. Treatments of cells with 75% and 100% sludge produced cells showing nuclear disintegration. This aberration might have developed due to breaking of the nucleus. The nucleus gradually disappeared from the cytopla s m (Fig. 1D). Polyploid cells were encountered in all the treatments (Fig. 1A). Polyploidy might have occurred due to complete inhibition of spindle formation resu lting in the failure of separation of chromatids and confinement of chromosomes within one nucleus [18]. The increase in chromosome number might als o be due to the fragmentation of individual chromosome was also observed. These chromosomal fragments were disc o n t in u it ie s of chromatids. Fragmentations of chromosomes induce chromosomal mutation because of deletions and duplications, which may even lead to the death of cells [17]. Cytotoxic effects o f several types of chemicals on the spindle apparatus were also reported by other workers in different plants [12, 18, 20]. In majority of the treated onion cells the telophase stage was observed without any sign of cytokinesis. The chromosomal halves after getting distributed to respective poles remained within the dividing cells instead of forming two daughter cells (Fig. 1B). This ultimately resulted in the formation of binucleate cells. Inhibition of cytokinesis and formation of binucleate cells we re also reported in Vicia faba [15]. Abnormalities such as C-anaphase (Fig. 1H) and C-metaphase (Fig. 1I) were also observed. These abnormalities were reported to be induced by
3 12 Table 1: Physico-chemical parameters of raw sludge Parameters Raw sludge ph 5.98 Conductivity (microsiemens/cm) Oil and grease content (ppm) Organic matter % Water holding capacity % - Ash content % Metals (ppm) Pb Mn Ni Zn Na 3.80 K 0.90 Table 2: Effec of oily sludge on Allium cepa - 24 hrs treatment percentage of abnormalities and mitotic index. 10% % % % Control Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil 54.7 Table 3: Effec of oily sludge on Allium cepa - 48 hrs treatment percentage of abnormalities and mitotic index. 10% % % % Control Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil 51.7 Table 4: Effec of oily sludge on Allium cepa - 72 hrs treatment percentage of abnormalities and mitotic index. 10% % % % Control Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil Nil 51.3 Fig. 1: (A) Cell showing polyploidy (B) binucleate cell (C) spiral nature of chromos ome (D) Nuclear disintegration (E) Distortion of pole (F) sticky anaph as e (G) unequal distribution of chromosome (H) C-anaphase (I) C-metaphase
4 treatments with chemicals like colchicines and organophosphorous pesticides [12, 14]. C-metaphase appeared due to inactivation of the spindle apparatus leading to the delay in the division of the centromere. The action of the che micals like colchicines includes disturbance in protein and nucleic acid synthesis and antagonism between these substances [12]. This might also be as a consequence of inhibition of cell cycle in which chromosomal DNA is replicated but not distributed in its normal way [11]. T h e distortion of poles also observed (Fig. 1E). Appearance of stickiness of chromosomes at anaphase was encountered in all the cells treated with different concentrations of sludge. The frequency of sticky anaphase was more in cells treated with higher concentrations of sludge than those with lower concentrations (Fig. 1F). The stickiness of chromosome at anaphase caused inability of normal movement of the chromosomes at anaphase. The stickiness of chromosomes was also reported in cells treated with organophosphorus pesticides [12] and industrial effluents [19]. Kaufma[13] reported that depolymerization of DNA and partia l d issolution of nucleoproteins might le a d to formation of sticky chromosomes. Another interesting finding was the appearance of spiral nature of chromosome when cells were treated with 100% sludge for 72 hrs (Fig. 1C). The chromosome became spiral thread like structure due to uncoiling. It is important for understanding of the condensation of chromos omes particularly at metaphase. The percentage abnormalities and the types of abnormalities encountered in the pres e nt study were interesting. On the basis of the results it may be concluded that the polluted oily sludge were capable of inducing variety of somatic cell abnormalities. Number of structural aberrations observed in the present study also indicated that the sludge acted as potential mutagenic agents. Therefore, it is necessary that in addition to routine physico-chemical and biological analyses, the industrial effluents should also be evaluated for the cytological damages caused by them to plant cells. The present study revealed that pollution caused by oil industries not only destroyed the balance in the ecosystem but also produced considerable genetic modifications in the flora growing in such habitats. References 1. A le xa nder, M., Biodegradatio n o f chemic a ls of environmental concern. Science, 211: APHA, AW W A and W PCF, 1976 Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Sewage th and Industrial Wastes. 14 edn, APHA Inc., New York APHA, AW W A and W PCE, Standard methods for estimation o f water and wastewater. th 16 edn, New York. 4. A tlas, R.M., Microbial degrad ation of petroleum hydrocarbons: An environmental perspective. Microbiology Review, 45: Bahl, B.S. and A. Bahl, A textbook of organic chemistry. S. Chand & Comp a n y Ltd., pp: Balows, A., Hydro c arbon oxidizing Bacteria. The Prokaryotes, 3: Bartha, R., Biotechnology of petroleum pollutant biodegradation. Microbiology Ecology, 12: Baruah, D. and S.K. Sarma, Effects of crude oil pollution on species composition, biomass and production of a herbaceous community in the Lakwa oil fields of A s sam (India). International Journal of Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 22: Borah, S.P. and J. Talukdar, Studies on the cytotoxic effect of extract of castor seed (Ricinus communis L.). Cytologia, 67: Bossert, I. and R. Bartha, The fate of petroleum in the soil ecosystems. In: Atlas R.M., (edn) Petroleum Mic ro b io logy. New York: Macmillan, pp: Brown, R. and A.F. Dy e r, Cell division in higher plants. In: Plant Physiology (edn. Steward F. C.), 6: Deka, D.C., Studies on cytotoxic effects of certain organophosphorus insectic ides on some plants. Ph.D. Thesis (Unpublis hed), Gauhati University, India. 13. Kaufma, B.P., Cytochemical studies of changes induced in cellular materials by ionizing radiations. Annual New York Academy of Science, 59: Kaur, P. and I.S. Grover, Cytological effects of some Organophosphorus pesticides. Cytologia, 50: Kaushik, G.C., Cytological effects of Lantana camara L. leaf extract on Vicia faba root t ip c e lls. Advances in Plant Sci., 9: Kihlman, B.A., Root tips of Vicia feba for the study of induction of chromosomal aberrations. Mutation Research, 31: Rieger, R., A. Michaelis and M.M. Green, A Glossary of Genetics and Cytogenetics. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York. 18. Sharma, A.K. and A. Sharma, Chromosome Technique Theory and Practice, rd 3 ed. Butterworth, London. 19. Somashekar, R.K. and M.R. Gurudev, Somatic cell abnormalities induced by dye manufacturing industry wastewater. Cytologia, 50:
5 Sudhakar, R., N. Gowda and G. Ve n u, Mitotic abnormalities induced by silk dyeing industry e ffluents in the cells of Allium cepa. Cytologia, 66:
Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion
 Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Volume 16(1), 6-72, 212 JOURNAL of Horticulture, Forestry and Biotechnology www.journal-hfb.usab-tm.ro Cytological effects induced by Agil herbicide to onion Bonciu Elena 1* 1 University of Craiova, Faculty
Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis
 Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
Cytologia 42: 323-329, 1977 Effects of Some Growth Substances on Mitosis Ganesh1 Prasad and K. Das2 Department of Genetics and Plant Breeding, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi-221005, India Received
STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE
 ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
ECOPRINT 1: 3-, 200 ISSN 2- Ecological Society (ECOS), Nepal www.ecosnepal.com STUDY OF MITOTIC ACTIVITY AND CHROMOSOMAL BEHAVIOUR IN ROOT MERISTEM OF Allium cepa L. TREATED WITH MAGNESIUM SULPHATE Prabhakar
_??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: , Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler
 _??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: 647-652, 1987 Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler Accepted July, 28, 1986 R. K. Somashekar Department
_??_ 1987 by Cytologia, Tokyo C ytologia 52: 647-652, 1987 Meiotic Abnormalities Induced by Dye Industry Waste Water in Chlorophytum amaniense Engler Accepted July, 28, 1986 R. K. Somashekar Department
Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa
 Cytologia 44: 921-926, 1979 Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa K. B. Shanthamurthy and V. Rangaswamy Received April 6, 1978 Department of Post-Graduate Studies
Cytologia 44: 921-926, 1979 Cytological Effects of Paper Mills Effluents on Somatic Cells of Allium cepa K. B. Shanthamurthy and V. Rangaswamy Received April 6, 1978 Department of Post-Graduate Studies
Stages of Mitosis. Introduction
 Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Name: Due: Stages of Mitosis Introduction Mitosis, also called karyokinesis, is division of the nucleus and its chromosomes. It is followed by division of the cytoplasm known as cytokinesis. Both mitosis
Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion
 Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
Kasetsart J. (Nat. Sci.) 44 : 1010-1015 (2010) Toxicity and Genotoxicity of Pendimethalin in Maize and Onion Nuttapol Promkaew 1, Puangpaka Soontornchainaksaeng 1 *, Sansern Jampatong 2 and Piangchan Rojanavipart
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE
 Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Biology 4A Laboratory MITOSIS Asexual Reproduction OBJECTIVE To study the cell cycle and understand how, when and why cells divide. To study and identify the major stages of cell division. To relate the
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
Cell Division Mitosis Notes
 Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Cell Division Mitosis Notes Cell Division process by which a cell divides into 2 new cells Why do cells need to divide? 1.Living things grow by producing more cells, NOT because each cell increases in
Exercise 6. Procedure
 Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Exercise 6 Procedure Growing of root tips Select a few medium-sized onion bulbs. Carefully remove the dry roots present. Grow root tips by placing the bulbs on glass tubes (of about 3 4 cm. diameter) filled
Cell Division. Learning Objectives: Introduction. Revised Fall 2018
 Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Revised Fall 2018 Cell Division Learning Objectives: 1. Define cell cycle and the ordered sequence of events in the cell cycle (Interphase and The divisional phase or M phase) 2. Explain the stages in
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa
 Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Genotoxicity of Caffeinated Soft Drinks on Meristematic Root Cells of Allium Cepa Maya George 1, Arya George 2 Assistant Professor, Department of Zoology, Alphonsa College Pala, Kottayam (Dist), Kerala,
Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L.
 South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
South Indian Journal Of Biological Sciences 2016; 2(1); 35 40 ONLINE ISSN: 2454 4787 Research Article Evaluation of cytotoxic effects of synthetic pesticide attack on root meristems of Allium cepa L. Soumya
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP
 Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
Cell Cycle Notes --PreAP I. DNA Deoxyribonucleic acid; located in nucleus A. Long and thread-like DNA in a non-dividing cell B. Thick, short, coiled doubled DNA in a dividing cell chromosome 1. chromosome
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION. Cytokinesis. centromere. DNA Replication S-Phase. One Chromosome Two Chromatids. One Chromosome No Chromatids 10.
 MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
MITOSIS INTRODUCTION Cell reproduction usually involves two processes: 1) mitosis is the orderly separation and division of chromosomes in the nucleus and 2) cytokinesis is the division of the cytoplasm.
Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1
 Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
Cytologia 40: 383-388, 1975 Cytological Studies on the Responses of Onion Root - Tip Cells to Water-Soluble Tobacco Smoke Extracts from Various Experimental Cigarettes1 D. K. Gulati, P. S. Sabharwal and
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Overview of the CELL CYCLE
 BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
BIO 211: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY I 1 Please wait 20 seconds before starting slide show. Mouse click or Arrow keys to navigate. Hit ESCAPE Key to exit. CHAPTER 03 and Lab Overview of the CELL CYCLE Dr. Lawrence
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Mitosis: Cell Division
 Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Do Now: What process do you think this cartoon is describing? Mitosis: Cell Division Key Points On Cell Division Species must reproduce in order to survive from generation to generation. All living things
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test
 Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
Onion (Allium cepa) genotoxicity test 1. Purpose The Allium cepa assay is an efficient test for chemical screening and in situ monitoring for genotoxicity of environmental contaminants. The test has been
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS
 The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
The Cell Cycle MITOSIS Outcomes 1. Explain the events of the cell cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase Cytokinesis 2. Use a simulation to demonstrate the behaviour of chromosomes
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Research Article. Effect of azo dye corafix on root tip chromosomes of Allium cepa L.
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(5):857-862 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Effect of azo dye corafix on root tip chromosomes
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2016, 8(5):857-862 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Effect of azo dye corafix on root tip chromosomes
Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle
 Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
Name Date Unit 4 Student Notes Cell Cycle B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase);
1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m43135 1 1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis * Daniel Williamson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 The cell cycle and
OpenStax-CNX module: m43135 1 1.3.1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis * Daniel Williamson This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 The cell cycle and
Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother
 Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Cell Division ision Reproduction is a fundamental property of life. Cells are the fundamental unit of life. Reproduction occurs at the cellular level with one mother cell giving rise to two daughter cells.
Introduction: Alprazolam is a triazolobenzodiazepine used in panic disorders and other anxiety
 DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2013.67.388-392 Med Arh. 2013 Dec; 67(6): 388-392 Received: June 18th 2013 Accepted: October 15th 2013 Published online: 28/12/2013 Published print: 12/2013 ORIGINAL PAPER Chromosomal
DOI: 10.5455/medarh.2013.67.388-392 Med Arh. 2013 Dec; 67(6): 388-392 Received: June 18th 2013 Accepted: October 15th 2013 Published online: 28/12/2013 Published print: 12/2013 ORIGINAL PAPER Chromosomal
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013
 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
You should wear eye protection throughout this practical.
 Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
Practical 8 - Broad bean root tip squash This practical focuses on setting up and manipulating apparatus and making and recording observations. Further skills can be developed using additional information
T R L J. Version 2, 2018 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
NAME: OPTION GROUP: CELL DIVISION MITOSIS WORKBOOK 1 STUDY CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Instructions Regular revision throughout the year is essential. It s vital you keep a track of what you understand
6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES
 INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL 6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL TWO CHROMATIDS INTERPHASE 6 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL DNA CONTENT DOUBLED INTERPHASE NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL
INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL 6 REPLICATED CHROMOSOMES INTERPHASE 2 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL TWO CHROMATIDS INTERPHASE 6 NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL DNA CONTENT DOUBLED INTERPHASE NUCLEUS CYTOSOL CYTOSOL
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
The Cell Cycle. Materials 2 pipe cleaners of one color and 2 of another color Drawing paper
 The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
The Cell Cycle Introduction When the cell has reached its growth potential it will begin to divide. Additionally, if a cell has become damaged or worn out it can be replaced by surrounding cells through
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
The Cell Cycle and Cell Division
 Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
Content Vocabulary Directions: On each line, write the term from the word bank that correctly replaces the underlined words in each sentence. NOTE: You may need to change a term to its plural form. cell
GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L
 J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468 Vol. 93 (1 & 2) 2014 : 135-139 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L VISHNU SHANKAR SINHA AND NANDJEE KUMAR*
J. Indian bot. Soc. ISSN - 0019-4468 Vol. 93 (1 & 2) 2014 : 135-139 GENOTOXIC EFFECTS OF OCIMUM BASILICUM L AND LEUCAS ZEYLANICA L IN ROOT TIP CELLS OF ALLIUM CEPA L VISHNU SHANKAR SINHA AND NANDJEE KUMAR*
Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Cell Growth A. Limits to Cell Growth 1. Two main reasons why cells divide: a. Demands on DNA as the cell get too large Cell Growth b. Moving nutrients and waste across
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Comparative effects of colchicine, 8-hydroxyquinoline and paradichlorobenzene on arm ratio of mitotic chromosomes of Allium cepa L.
 International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
International Journal of Medicinal Plants and Alternative Medicine Vol. 2(2), pp. 021-026, August 2014 Available online at http://academeresearchjournals.org/journal/ijmpam ISSN 2327-560X 2013 Academe
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes-
 Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Cycle/Mitosis -Notes- LIMITS TO CELL GROWTH The a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on DNA. Additionally, the cell has more trouble moving enough and wastes across the cell membrane.
Cell Division (Mitosis)
 Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
Cell Division (Mitosis) Chromosomes The essential part of a chromosome is a single very long strand of DNA. This DNA contains all the genetic information for creating and running the organism. Each chromosome
LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Cell Biology Lecturer: Assist. Prof. Dr. Altijana Hromić-Jahjefendić Assistant: Furkan Enes Oflaz LAB EXPERIMENT 4: Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells Objective After completing this exercise, you should
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Chapter 6. Cell Reproduction
 Chapter 6 Cell Reproduction Chromosomes The growth and development of your body are controlled by instructions contained in your DNA DNA decides what you will be.. DNA & Chromosomes Very long molecules
Chapter 6 Cell Reproduction Chromosomes The growth and development of your body are controlled by instructions contained in your DNA DNA decides what you will be.. DNA & Chromosomes Very long molecules
Name Date Class. Interphase. (1) The. grows. DNA is duplicated.
 Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Concept Mapping The Cell Cycle Complete the cycle map about the cell cycle. These terms may be used more than once: cell, cytoplasm, metaphase, nuclear membrane, nucleoli, poles. (1) The Interphase grows.
Cell Cycle. Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer
 Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Interphase, Mitosis, Cytokinesis, and Cancer Cell Division One cell divides into 2 new identical daughter cells. Chromosomes carry the genetic information (traits) of the cell How many Chromosomes
Cell Cycle Phase. Interphase (G 1, S, G 2 ) Mitotic Phase (M phase) Prophase. Metaphase. Anaphase. Telophase
 Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
Part I: The Cell Cycle Use your resources at hand and the Explore Student Guide to outline what occurs within the cell during each stage of the cell cycle. Record this information in Table 1 below. Cell
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Science 9- Mr. Klasz
 Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
Science 9- Mr. Klasz Asexual reproduction requires only one parent. The offspring produced are identical to the parent. Asexual reproduction occurs in our somatic cells. This means all of our cells except
10-2 Cell Division. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
10-2 Cell Division Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall Cell Growth and Division In multicellular organisms, cell division makes new cells To replace old or damaged ones So organisms can grow In single-celled
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA MUNGO (L.) HEPPER
 EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
EFFECTS OF DITHANE M-45 (A FUNGICIDE) ON ROOT MERISTEM OF VIGNA Susanta Kumar Maity* MUNGO (L.) HEPPER Abstract: The cytotoxic effects of Dithane M-45, a fungicide were investigated in the mitotic cell
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION
 NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
NOTES- CHAPTER 6 CHROMOSOMES AND CELL REPRODUCTION Section I Chromosomes Formation of New Cells by Cell Division New cells are formed when old cells divide. 1. Cell division is the same as cell reproduction.
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Mitosis and Cellular Division. EQ: How do the cells in our body divide?
 Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Mitosis and Cellular Division EQ: How do the cells in our body divide? Cell division is the process by which cellular material is divided between two new daughter cells. 1 Mother Cell 2 Daughter cells.
Name: Date: Block: 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet
 10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
10-2 Cell Division Worksheet W hat do you think would happen if a cell were simple to split into two, without any advance preparation? Would each daughter cell have everything it needed to survive? Because
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells
 Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Mitosis in Onion Root Tip Cells A quick overview of cell division The genetic information of plants, animals and other eukaryotic organisms resides in several (or many) individual DNA molecules, or chromosomes.
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation
 B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
B.5ABCD Cell Differentiation Picture Vocabulary gene A segment of DNA nucleotides that codes for a specific protein to be produced and leads to the expression of a hereditary trait or characteristic cell
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Connecting
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis KEY CONCEPT Cells divide during mitosis and cytokinesis. MAIN IDEAS Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis. Mitosis and cytokinesis produce two genetically identical daughter
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1
 Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
Science 9 Chapter 5 Section 1 The Cell Cycle and Mitosis (pp. 136-151) The Importance of Cell Division Cells, like all living things, eventually wear out and cannot sustain life anymore. They need to be
The Cell Cycle. Biology
 The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
The Cell Cycle Biology Standards you are responsible for mastering. SB1a: Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer This Activity Packet belongs to:
 Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
Packet #10 Continuity - Reproduction, part 1 Summer 2014 This Activity Packet belongs to: At the end of the unit you will turn in this packet for a score. Record the completion due dates in the chart below.
5.2. Mitosis and Cytokinesis. Chromosomes condense at the start of mitosis.
 5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
5.2 Mitosis and Cytokinesis VOCABULARY chromosome histone chromatin chromatid centromere prophase metaphase anaphase telophase Biochemistry As you will learn in the chapter From DNA to Proteins, a nucleotide
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
NOTES. Cell Cycle & Mitosis
 NOTES for Cell Cycle & Mitosis Biology 2016 Johnson I. The Cell Cycle II. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6uckwiifmg (2:15-4:25) III. http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm A. Limits to Cell Size 1. As
NOTES for Cell Cycle & Mitosis Biology 2016 Johnson I. The Cell Cycle II. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q6uckwiifmg (2:15-4:25) III. http://www.cellsalive.com/mitosis.htm A. Limits to Cell Size 1. As
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
Chapter 5: Cell Growth and Division 1 Background Info Formation of New Cells ~2 trillion cells formed/day in human body ~25 million cells/second Cell division = cell reproduction DNA must be copied before
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
CELL DIVISION! Genes, Mitosis and Cytokinesis 12/17/14. G. Podgorski, Biol Mitosis!
 Genes, Mitosis and Cytokinesis 12/17/14 CELL DIVISION! Mitosis! ü Mitotic division results in genetically identical eukaryotic cells or a clone ü Mitosis is the basis of asexual! reproduction G. Podgorski,
Genes, Mitosis and Cytokinesis 12/17/14 CELL DIVISION! Mitosis! ü Mitotic division results in genetically identical eukaryotic cells or a clone ü Mitosis is the basis of asexual! reproduction G. Podgorski,
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Cell Cycle Grade:«grade» Subject:Biology Date:«date» 1 As a cell becomes larger, its surface area increases faster than its volume. 2 As a cell becomes larger, its volume
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages )
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division Section 10 1 Cell Growth (pages 241 243) Key Concept What problems does growth cause for cells? Limits to Cell Growth (pages 241 243) 1 What are two reasons why cells
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Ch. 10 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
