Supporting Information
|
|
|
- Caroline Nash
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Supporting Information Keller et al /pnas MB1 Ori puc18 Ori AscI (8713) pdad downstream flank pdad PpdaD SphI (6970) Msed1993 ApaI (10721) Apr ApaLI (9115) NcoI (8) PmeI (8796) PvuI (8789) AsiSI (8789) FseI (8772) palm bp pdad upstream flank XmaI (1097) SmaI (1099) Pslp Msed0147 NotI (8731) PacI (2104) Msed1375 Msed0148 Msed0709 NdeI (4934) Fig. S1. Plasmid map of palm506-1 used to transform the Pyrococcus furiosus arginine decarboxylase deletion strain ΔpdaD to generate strain PF506. XhoI (4548) Apr psc101 origin ApaI (5039) pgl bp NheI (1) BmtI (5) GR3 upstream flank (PF0574) repa EcoRV (302) XmaI (516) SmaI (518) 65 bp of 3' end of pyrf marker cassette gdh promoter region (157 bp) HindIII (679) pyrf (PF1114) Terminator AscI (1395) NotI (1411) GR3 downstream flank (PF0575) NdeI (1905) SphI (1392) PmeI (1405) PvuII (1687) Fig. S2. Plasmid map of pgl007 vector targeting the region between the loci PF0574 and PF0575 in the P. furiosus genome. 1of6
2 psc101 origin repa GR3 downstream flank NotI (7263) Terminator NsiI (7089) Msed1993 AatII (6489) ApaI (10891) Apr ZraI (6487) Msed0709 pgl bp GR3 upstream flank XmaI (516) 65 bp of pyrf cassette 3' end SmaI (518) gdh promoter region (157 bp) pyrf (PF1114) Msed1375 Terminator SphI (1392) AscI (1395) Pslp Msed0147 PacI (2388) Msed0148 ClaI (3496) Fig. S3. Plasmid map of pgl010 used to transform P. furiosus strain COM1 to generate strain MW56. 1.E Cell density (ml -1 ) 1.E Temperature ( C) 20 1.E Time (hr) Fig. S4. Growth of P. furiosus strain PF506 at 98 C and subsequent temperature shift to 75 C. P. furiosus was grown in four 800-mL cultures at 98 C until the cell density reached cells/ml The temperature (shown as black line) was then shifted to 75 C, and individual bottles were removed and harvested after 0 h (blue diamond), 16 h (red square), 32 h (green triangle), and 48 h (purple circle). The enzyme activities in each cell type are summarized in Fig. 2B Specific activity (%) Time (min) Fig. S5. Stability of E2 and E3 using an E2 + E3 coupled assay at 75 C after incubation at 90 C for the indicated amount of time in cell-free extracts of P. furiosus strain PF506 (blue circles) and of the endogenous P. furiosus glutamate dehydrogenase (red squares). The specific activity of E2+E3 in PF506 (grown at 72 C) is about twofold higher than that measured in M. sedula. Activity is expressed as percentage maximum activity. 2of6
3 5.E C Cell density (ml -1 ) 5.E+07 5.E Time (hr) Fig. S6. Growth of P. furiosus COM1, MW56, and PF506 during the temperature shift from 98 C to 70 C. Cell densities of COM1 (blue diamonds), MW0056 (red squares), and PF506 (green triangles) are indicated. The 400-mL cultures were grown at 95 C for 9 h and then allowed to cool at room temperature to 70 C before being placed in a 70 C incubator. Specific activity (nmol/mg/min) Msed Pf 506 MW56 ΔPdaD COM1 Strain Fig. S7. Enzyme activities of E1 (blue) and coupled E2 + E3 (red) in cell-free extracts of the indicated P. furiosus strains after incubation at 70 C for 16 h compared with that measured for the cell extract of autotrophically grown Metallosphaera sedula cells (labeled Msed). A B Fig. S8. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry identification of 3-hydroxypropionic acid produced from acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-coa), CO 2, and H 2 (or NH) by cell-free extracts of P. furiosus strains ΔpdaD (A) and PF506 (B). The MS peak corresponding to the 3-HP derivative (m/z 224, green circle) was present above background only in the recombinant PF506 strain. 3of6
4 Maltose Glucose Inside Outside Glucose-6-phosphate AMP Fructose-6-phosphate AMP Fructose-1,6-phosphate 2x Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate 3-phosphoglycerate Fd ox Fd red 2H + H 2 Membrane-bound Hydrogenase (MBH) 2-phosphoglycerate Pyruvate phosphoenolpyruvate Pyruvate POR ATP Fd ox Fd red Acetyl-CoA + CO 2 ATP Acetate 2H + H 2 Membrane-bound Hydrogenase (MBH) Fig. S9. Maltose and pyruvate metabolism by P. furiosus and the key roles of pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase (POR) in acetyl-coa production and of the membrane-bound hydrogenase in H 2 production. 4of6
5 A HP 1.60 AU B Minutes 3-HP AU Minutes Fig. S10. In vivo production of 3-hydroxypropionic acid (3-HP) from maltose by whole cells of P. furiosus strain MW56 (A) and PF506 (B) after 10 min (blue) and 60 min (red) compared with a 1-mM 3-HP standard (black). A black arrow indicates the position of the 3-HP peaks. A total of 135 μm and 199 μm 3-HP was produced by cell suspensions of MW56 ( cells/ml) and PF506 ( cells/ml), respectively, after 60 min at 75 C. Table S1. Strains used and constructed in this study Strain Parent Genotype/description Source COM1 DSM 3638 ΔpyrF (1) ΔpdaD COM1 ΔpyrF ΔpdaD::P gdh pyrf (2) PF506 ΔpdaD ΔpyrF ΔpdaD::pdaD P slp E1αβγ-E2-E3 This work MW56 COM1 ΔpyrF P gdh pyrf P slp E1αβγ-E2-E3 This work E1αβγ, acetyl/propionyl-coa carboxylase; E2, malonyl/succinyl-coa reductase; E3, malonate semialdehyde reductase; gdh, glutamate dehydrogenase; pdad, arginine decarboxylase; P slp, P. furiosus S-layer gene promoter; pyrf, orotidine-5 -phosphate decarboxylase. 1. Lipscomb GL, et al. (2011) Natural competence in the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus facilitates genetic manipulation: Construction of markerless deletions of genes encoding the two cytoplasmic hydrogenases. Appl Environ Microbiol 77(7): Hopkins RC, et al. (2011) Homologous expression of a subcomplex of Pyrococcus furiosus hydrogenase that interacts with pyruvate ferredoxin oxidoreductase. PLoS ONE 6(10):e of6
6 Table S2. Gas chromatography mass spectrometry identification and quantitation of 3-hydroxypropionic acid produced from malonyl- CoA and NH or H 2 by cell-free extracts of P. furiosus strain PF506 Vial Added electron donor Substrate Theoretical 3-HP, mm 3-HP/inositol peak area Estimated 3- hydroxypropionic acid, mm 1 2 mm NH 2 mm malonyl-coa mm NH, H 2 2 mm malonyl-coa mm N, H 2 2 mm malonyl-coa mm N, H 2 None (control) mm N, H 2 None (control) The assays were carried out in a total volume of 1 ml containing 0.25 mg cell-free extract under H 2 in a shaking water bath. The amount of 3-hydroxypropionic acid produced was determined after 2 h at 72 C. Table S3. 3-Hydroxypropionic acid production by whole cells using maltose or pyruvate as the source of acetyl-coa P. furiosus strain Pyruvate Maltose MW nmol 100 nmol PF nmol 145 nmol The amount of 3-hydroxypropionic acid indicated was present in 1 ml of the P. furiosus cell suspension. Table S4. Primers used in the construction of the synthetic subpathway 1 operon Primer target Direction 5 to 3 sequence P. furiosus S-layer promoter Forward GAATCCCCGCGGCCCGGGCTGGCAGAATAGAA GCAACCAAAACTCTACTAAAGGGTGGCATTTTTCTCCACCTCCCAATAATCTG Msed_ Forward ATGCCACCCTTTAGTAGAGTTTTGG GTTGCAGTCATCTTCAAACCTCCTTACTTTATCACCACTAGGATATCTCC Msed1375 Forward GTGATAAAGTAAGGAGGTTTGAAGATGACTGCAACTTTTGAAAAACCGGAT CGTTCTCCTCATATGCTCCACCTCCCTTAGAGGGGTATATTTCCATGCTTC Msed_0709 Forward GGCAATGTCATATGAGGAGAACGCTAAAGGCCGCAATTC CCTTTTCAGTCATTGCATATCACCTCATCTCTTGTCTATGTAGCCCTTC Msed_1993 Forward TAGACAAGAGATGAGGTGATATGCAATGACTGAAAAGGTATCTGTAGTTGGAG CCAATGCATGCTTATTTTTCCCAAACTAGTTTGTATACCTTC 6of6
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations. Lecture 9
 Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism. General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith
 CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism Learning Objectives: q Role in
CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism General, Organic, & Biological Chemistry Janice Gorzynski Smith CHAPTER 24: Carbohydrate, Lipid, & Protein Metabolism Learning Objectives: q Role in
Notes CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
glpx Rv1100 Probe 4.4 kb 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda 25 kda 20 kda
 PvuI 2.0 k PvuI PvuI Rv1101c Rv1100 glpx fum 4.4 k PvuI PvuI ΔglpX Rv1101c Rv1100 HygR fum ΔglpX 5 k 4 k 3 k c 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda GLPX Δ Δ/C GLPX 2 k 1.5 k 25 kda 20 kda PRCB 1 k 0.5 k Supplementary
PvuI 2.0 k PvuI PvuI Rv1101c Rv1100 glpx fum 4.4 k PvuI PvuI ΔglpX Rv1101c Rv1100 HygR fum ΔglpX 5 k 4 k 3 k c 75 kda 50 kda 37 kda GLPX Δ Δ/C GLPX 2 k 1.5 k 25 kda 20 kda PRCB 1 k 0.5 k Supplementary
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
Supporting Information Bar-Even et al. 10.1073/pnas.0907176107 Fig. S1. A scheme of the reductive pentose phosphate cycle, as inspired from (81). Dashed line corresponds to RUBISCO's oxygenase reaction
Yield of energy from glucose
 Paper : Module : 05 Yield of Energy from Glucose Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Prof. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dept. of Biosciences, Saurashtra University, Rajkot - 360005
Paper : Module : 05 Yield of Energy from Glucose Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Prof. Ramesh Kothari, Professor Dept. of Biosciences, Saurashtra University, Rajkot - 360005
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION. C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete loss of electrons Reduction: partial or complete gain of electrons
Notes CELLULAR RESPIRATION SUMMARY EQUATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2. 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION
 AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
AP BIOLOGY CELLULAR ENERGETICS ACTIVITY #2 Notes NAME DATE HOUR SUMMARY EQUATION CELLULAR RESPIRATION C 6 H 12 O 6 + O 2 6CO 2 + 6H 2 O + energy (ATP) STEPWISE REDOX REACTION Oxidation: partial or complete
Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative
 1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
1 2 3 4 Bacterial cellulose synthesis mechanism of facultative anaerobe Kaihua Ji 1 +, Wei Wang 2, 3 +, Bing Zeng 1, Sibin Chen 1, Qianqian Zhao 4, Yueqing Chen 1, Guoqiang Li 1* and Ting Ma 1* 5 6 7 Figure
NAME KEY ID # EXAM 3a BIOC 460. Wednesday April 10, Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided!
 EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
EXAM 3a BIOC 460 Wednesday April 10, 2002 Please include your name and ID# on each page. Limit your answers to the space provided! 1 1. (5 pts.) Define the term energy charge: Energy charge refers to the
Answer three from questions 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9.
 BCH 4053 May 1, 2003 FINAL EXAM NAME There are 9 pages and 9 questions on the exam. nly five are to be answered, each worth 20 points. Answer two from questions 1, 2, 3, and 4 Answer three from questions
BCH 4053 May 1, 2003 FINAL EXAM NAME There are 9 pages and 9 questions on the exam. nly five are to be answered, each worth 20 points. Answer two from questions 1, 2, 3, and 4 Answer three from questions
BCH 4053 THIRD EXAM November 5, 1999
 BCH 4053 THIRD EXAM November 5, 1999 I remind you that you are bound by the Academic Honor Code. This means (1) you will not give or receive information during this exam, nor will you consult with unauthorized
BCH 4053 THIRD EXAM November 5, 1999 I remind you that you are bound by the Academic Honor Code. This means (1) you will not give or receive information during this exam, nor will you consult with unauthorized
CHAPTER 16. Glycolysis
 CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis Net reaction of Glycolysis Converts: 1 Glucose Hexose stage 2 pyruvate - Two molecules of ATP are produced - Two molecules of NAD + are reduced to NADH Triose stage Glucose + 2 ADP
CHAPTER 16 Glycolysis Net reaction of Glycolysis Converts: 1 Glucose Hexose stage 2 pyruvate - Two molecules of ATP are produced - Two molecules of NAD + are reduced to NADH Triose stage Glucose + 2 ADP
Discussion of Prism modules and predicted interactions (Fig. 4)
 SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Discussion of Prism modules and predicted interactions (Fig. 4) a. Interactions of the TCA-cycle, respiratory chain, and ATP synthetase with the amino acid biosynthesis modules. Given
SUPPLEMENTARY NOTES Discussion of Prism modules and predicted interactions (Fig. 4) a. Interactions of the TCA-cycle, respiratory chain, and ATP synthetase with the amino acid biosynthesis modules. Given
Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: Da. m/z. hrmif ( Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ Da. m/z.
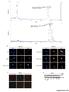 Intensity % Intensity % A Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: 12428.31 Da m/z hrmif (12428.31 Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ 12715.21 Da m/z B HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3 Merge HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3
Intensity % Intensity % A Human recombinat MIF protein (hrmif), MW: 12428.31 Da m/z hrmif (12428.31 Da) + 4-IPP (282 Da) MWtot ~ 12715.21 Da m/z B HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3 Merge HTC/C3 DAPI phistone-h3
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region
 Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Supplemental Figure S1. Tertiles of FKBP5 promoter methylation and internal regulatory region methylation in relation to PSS and fetal coupling. A, PSS values for participants whose placentas showed low,
Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple quadrupole mass spectrometer
 Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple ASMS 2012 ThP11-251 Zanariah Hashim 1 ; Yudai Dempo1; Tairo Ogura 2 ; Ichiro Hirano 2 ; Junko Iida
Quantitative analysis of hydrophilic metabolite using ion-paring chromatography with a high-speed triple ASMS 2012 ThP11-251 Zanariah Hashim 1 ; Yudai Dempo1; Tairo Ogura 2 ; Ichiro Hirano 2 ; Junko Iida
Julia Vorholt Lecture 7:
 752-4001-00L Mikrobiologie Julia Vorholt Lecture 7: Chemoorganotrophy Nov 5, 2012 Brock Biology of Microorganisms, Twelfth Edition Madigan / Martinko / Dunlap / Clark Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Inc.,
752-4001-00L Mikrobiologie Julia Vorholt Lecture 7: Chemoorganotrophy Nov 5, 2012 Brock Biology of Microorganisms, Twelfth Edition Madigan / Martinko / Dunlap / Clark Copyright 2009 Pearson Education Inc.,
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
CHAPTER 6 METABOLIC PATHWAY RECONSTRUCTION
 66 CHAPTER 6 METABOLIC PATHWAY RECONSTRUCTION 6.1 GENERAL A metabolic pathway is a series of biochemical reactions that occur within a cell and these chemical reactions are catalyzed by certain enzymes.
66 CHAPTER 6 METABOLIC PATHWAY RECONSTRUCTION 6.1 GENERAL A metabolic pathway is a series of biochemical reactions that occur within a cell and these chemical reactions are catalyzed by certain enzymes.
Late assembly of the Vibrio cholerae cell division machinery postpones
 2 Late assembly of the Vibrio cholerae cell division machinery postpones septation to the last % of the cell cycle 3 4 Elisa Galli, Evelyne Paly and François-Xavier Barre,# 5 6 7 Institute for Integrative
2 Late assembly of the Vibrio cholerae cell division machinery postpones septation to the last % of the cell cycle 3 4 Elisa Galli, Evelyne Paly and François-Xavier Barre,# 5 6 7 Institute for Integrative
2 2,3,4,6 tetramethyl glucose 4 2,3, 6 trimethyl glucose. What can you deduce about the structure of the hexasaccharide?
 1. A Draw the structure of glucose using either a ring or straight chain representation. Explain how (i) mannose and (ii) galactose differ from glucose. Which are (a) epimers; (b) enantiomers; (c) diastereomers?
1. A Draw the structure of glucose using either a ring or straight chain representation. Explain how (i) mannose and (ii) galactose differ from glucose. Which are (a) epimers; (b) enantiomers; (c) diastereomers?
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Carbohydrate Lipid and Protein! Metabolism! In the catabolism of carbohydrates, glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, which is then metabolized into acetyl CoA. Prepared
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Carbohydrate Lipid and Protein! Metabolism! In the catabolism of carbohydrates, glycolysis converts glucose into pyruvate, which is then metabolized into acetyl CoA. Prepared
3.2 Aerobic Respiration
 3.2 Aerobic Respiration Aerobic Cellular Respiration Catabolic pathways Breaks down energy-rich compounds to make ATP Requires oxygen Occurs in different parts of the cell C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) + 6O 2 (g) 6CO
3.2 Aerobic Respiration Aerobic Cellular Respiration Catabolic pathways Breaks down energy-rich compounds to make ATP Requires oxygen Occurs in different parts of the cell C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) + 6O 2 (g) 6CO
LIPID METABOLISM
 LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
LIPID METABOLISM LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS LIPOGENESIS FATTY ACID SYNTHESIS DE NOVO FFA in the blood come from :- (a) Dietary fat (b) Dietary carbohydrate/protein in excess of need FA TAG Site of synthesis:-
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis
 Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6
 Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6 The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages
Electron transport chain chapter 6 (page 73) BCH 340 lecture 6 The Metabolic Pathway of Cellular Respiration All of the reactions involved in cellular respiration can be grouped into three main stages
Integration of Metabolism
 Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
Integration of Metabolism Metabolism is a continuous process. Thousands of reactions occur simultaneously in order to maintain homeostasis. It ensures a supply of fuel, to tissues at all times, in fed
BCMB 3100 Fall 2013 Exam III
 BCMB 3100 Fall 2013 Exam III 1. (10 pts.) (a.) Briefly describe the purpose of the glycerol dehydrogenase phosphate shuttle. (b.) How many ATPs can be made when electrons enter the electron transport chain
BCMB 3100 Fall 2013 Exam III 1. (10 pts.) (a.) Briefly describe the purpose of the glycerol dehydrogenase phosphate shuttle. (b.) How many ATPs can be made when electrons enter the electron transport chain
Profiling of Endogenous Metabolites Using Time-of-Flight LC/MS with Ion Pair Reverse Phase Chromatography
 Profiling of Endogenous Metabolites Using Time-of-Flight LC/MS with Ion Pair Reverse Phase Chromatography Application Note Metabolomics Author Yuqin Dai Agilent Technologies, Inc. 31 Stevens Creek Blvd,
Profiling of Endogenous Metabolites Using Time-of-Flight LC/MS with Ion Pair Reverse Phase Chromatography Application Note Metabolomics Author Yuqin Dai Agilent Technologies, Inc. 31 Stevens Creek Blvd,
incorporation into fructose-6-phosphate and glucose-6-phosphate (F6P/G6P); 2-
 Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) Relative abundance (%) 100% 80% 60% 40% F6P / G6P M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 M+4 M+5 M+6 100% 80% 60% 40% 2PG / 3PG M+0 M+1 M+2 M+3 20% 20% 0%
GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels
 GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels - Catabolic process degradative pathway - Energy stored in sugars (carbohydrates) released to perform biological work - Transforms GLUCOSE to PYRUVATE
GLYCOLYSIS Generation of ATP from Metabolic Fuels - Catabolic process degradative pathway - Energy stored in sugars (carbohydrates) released to perform biological work - Transforms GLUCOSE to PYRUVATE
Chem 109 C. Fall Armen Zakarian Office: Chemistry Bldn 2217
 Chem 109 C Fall 2014 Armen Zakarian ffice: Chemistry Bldn 2217 o Catabolism of carbohydrates: 10 reactions of glycolysis Chapter 25 C C 2 C 2 D-glucose α-d-glucopyranose aworth projection α-d-glucopyranose
Chem 109 C Fall 2014 Armen Zakarian ffice: Chemistry Bldn 2217 o Catabolism of carbohydrates: 10 reactions of glycolysis Chapter 25 C C 2 C 2 D-glucose α-d-glucopyranose aworth projection α-d-glucopyranose
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 30 Amino Acid Degradation and the Urea Cycle 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company In the cytosol of a cell amino groups from amino acids
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 30 Amino Acid Degradation and the Urea Cycle 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company In the cytosol of a cell amino groups from amino acids
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes
 BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Background Information Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes A. BIOCHEMISTRY The basic pattern of glucose oxidation is outlined in Figure 3-1. Glucose is split
BIL 256 Cell and Molecular Biology Lab Spring, 2007 Background Information Tissue-Specific Isoenzymes A. BIOCHEMISTRY The basic pattern of glucose oxidation is outlined in Figure 3-1. Glucose is split
2: Describe glycolysis in general terms, including the molecules that exist at its start and end and some intermediates
 1 Life 20 - Glycolysis Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Know the location of glycolysis in a eukaryotic cell 2: Describe glycolysis in general terms, including the molecules that exist at
1 Life 20 - Glycolysis Raven & Johnson Chapter 9 (parts) Objectives 1: Know the location of glycolysis in a eukaryotic cell 2: Describe glycolysis in general terms, including the molecules that exist at
BIOLOGY. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 9.2 Light energy
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 9.2 Light energy
BCH 4054 Chapter 19 Lecture Notes
 BCH 4054 Chapter 19 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 19 Glycolysis 2 aka = also known as verview of Glycolysis aka The Embden-Meyerhoff Pathway First pathway discovered Common to almost all living cells ccurs in
BCH 4054 Chapter 19 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 19 Glycolysis 2 aka = also known as verview of Glycolysis aka The Embden-Meyerhoff Pathway First pathway discovered Common to almost all living cells ccurs in
Photosynthesis in chloroplasts. Cellular respiration in mitochondria ATP. ATP powers most cellular work
 Light energy ECOSYSTEM CO + H O Photosynthesis in chloroplasts Cellular respiration in mitochondria Organic molecules + O powers most cellular work Heat energy 1 becomes oxidized (loses electron) becomes
Light energy ECOSYSTEM CO + H O Photosynthesis in chloroplasts Cellular respiration in mitochondria Organic molecules + O powers most cellular work Heat energy 1 becomes oxidized (loses electron) becomes
Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
0.40. Biochemistry of Carbohydrates
 0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
0.40 Biochemistry of Carbohydrates Biochemistry of Carbohydrates ATP ADP Glycolysis The Breakdown of Glucose Primary Energy Source of Cells Central Metabolic Pathway All Reactions Occur in Cytoplasm Two
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 2 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17084 Metabolic anticipation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Hyungjin Eoh, Zhe Wang, Emilie Layre,
In the format provided by the authors and unedited. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION VOLUME: 2 ARTICLE NUMBER: 17084 Metabolic anticipation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Hyungjin Eoh, Zhe Wang, Emilie Layre,
RESPIRATION Worksheet
 A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
ANSC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism
 I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
I. Overall concepts A. Definitions ANC/NUTR 618 Lipids & Lipid Metabolism 1. De novo synthesis = synthesis from non-fatty acid precursors a. Carbohydrate precursors (glucose, lactate, and pyruvate) b.
Introduction. Ziling Ye 1 Xiaowei Li 1 Yongbo Cheng 1 Zhijie Liu 1 Gaoyi Tan 1 Fayin Zhu 1 Shuai Fu 3 Zixin Deng 1,2,5 Tiangang Liu 1,2,4
 DOI 10.1007/s10295-016-1793-z METABOLIC ENGINEERING AND SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY Evaluation of 3 hydroxypropionate biosynthesis in vitro by partial introduction of the 3 hydroxypropionate/4 hydroxybutyrate cycle
DOI 10.1007/s10295-016-1793-z METABOLIC ENGINEERING AND SYNTHETIC BIOLOGY Evaluation of 3 hydroxypropionate biosynthesis in vitro by partial introduction of the 3 hydroxypropionate/4 hydroxybutyrate cycle
Chapter 14. Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior
 Chapter 14 Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior Why do you Eat and Breath? To generate ATP Foods, Oxygen, and Mitochodria Cells Obtain Energy by the Oxidation of Organic Molecules Food making ATP making
Chapter 14 Energy conversion: Energy & Behavior Why do you Eat and Breath? To generate ATP Foods, Oxygen, and Mitochodria Cells Obtain Energy by the Oxidation of Organic Molecules Food making ATP making
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Overview: Life Is Work. Living cells. Require transfusions of energy from outside sources to perform their many tasks
 Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Overview: Life Is Work Living cells Require transfusions of energy from outside sources to perform their many tasks Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece The
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration Overview: Life Is Work Living cells Require transfusions of energy from outside sources to perform their many tasks Biology, 7 th Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece The
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy You should be able to: 1. Explain how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges. Name and describe the three stages of cellular respiration;
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy You should be able to: 1. Explain how redox reactions are involved in energy exchanges. Name and describe the three stages of cellular respiration;
Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis. Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes
 Topics Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 2 Metabolism Catabolism Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Breakdown of complex organic molecules in order to extract energy and dform simpler
Topics Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 2 Metabolism Catabolism Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Breakdown of complex organic molecules in order to extract energy and dform simpler
Mock Exam All of the following are oxidizing agents EXCEPT a. NADP+ b. NADH c. FAD d. e. cytochromes
 Mock Exam 2 1. The Calvin cycle differs from the citric acid cycle in that it a. produces ATP b. directly requires light to run c. depends on the products of an electron transport chain d. occurs in a
Mock Exam 2 1. The Calvin cycle differs from the citric acid cycle in that it a. produces ATP b. directly requires light to run c. depends on the products of an electron transport chain d. occurs in a
Midterm 2 Results. Standard Deviation:
 Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
Supplemental Data Functional characterization of core components of the Bacillus subtilis c- di-
 Supplemental Data Functional characterization of core components of the Bacillus subtilis c- di- GMP signaling pathway Xiaohui Gao 1,3, Sampriti Mukherjee 2, Paige M. Matthews 1, Loubna A. Hammad 1, Daniel
Supplemental Data Functional characterization of core components of the Bacillus subtilis c- di- GMP signaling pathway Xiaohui Gao 1,3, Sampriti Mukherjee 2, Paige M. Matthews 1, Loubna A. Hammad 1, Daniel
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions
 CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
CHE 242 Exam 3 Practice Questions Glucose metabolism 1. Below is depicted glucose catabolism. Indicate on the pathways the following: A) which reaction(s) of glycolysis are irreversible B) where energy
OVERVIEW OF THE GLYCOLYTIC PATHWAY Glycolysis is considered one of the core metabolic pathways in nature for three primary reasons:
 Glycolysis 1 Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - Overview of the Glycolytic Pathway Glycolysis generates a small amount of ATP Preview of the ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions of glycolysis - Stage 1: ATP
Glycolysis 1 Supplemental Reading Key Concepts - Overview of the Glycolytic Pathway Glycolysis generates a small amount of ATP Preview of the ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions of glycolysis - Stage 1: ATP
Points 1. Following is the overall reaction catalyzed by the Calvin-Benson cycle:
 BCH 4054 February 22, 2002 HOUR TEST 2 NAME_ Points 1. Following is the overall reaction catalyzed by the Calvin-Benson cycle: CO 2 + 3ATP + 2NADPH 1/3 glyceraldehyde-3-p + 3ADP + 2NADP + Give the structures
BCH 4054 February 22, 2002 HOUR TEST 2 NAME_ Points 1. Following is the overall reaction catalyzed by the Calvin-Benson cycle: CO 2 + 3ATP + 2NADPH 1/3 glyceraldehyde-3-p + 3ADP + 2NADP + Give the structures
Dalkeith High School Higher Human Biology Homework 3
 Dalkeith High School Higher Human Biology Homework 3 1. During which of the following chemical conversions is A T P produced? A B C Amino acids protein Glucose pyruvic acid Haemoglobin oxyhaemoglobin energy
Dalkeith High School Higher Human Biology Homework 3 1. During which of the following chemical conversions is A T P produced? A B C Amino acids protein Glucose pyruvic acid Haemoglobin oxyhaemoglobin energy
Background knowledge
 Background knowledge This is the required background knowledge: State three uses of energy in living things Give an example of an energy conversion in a living organism State that fats and oils contain
Background knowledge This is the required background knowledge: State three uses of energy in living things Give an example of an energy conversion in a living organism State that fats and oils contain
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Chapter 9
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Chapter 9 Assemble polymers, pump substances across membranes, move and reproduce The giant panda Obtains energy for its cells by eating plants which get
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Chapter 9 Assemble polymers, pump substances across membranes, move and reproduce The giant panda Obtains energy for its cells by eating plants which get
Respiration. Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism . Anabolism
 If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
If you ate a clown, would it taste funny? Oh, wait, that s cannibalism. Anabolism is about putting things together. Anabolism: The Use of Energy in Biosynthesis Anabolism energy from catabolism is used
Cellular Respiration. Overview of Cellular Respiration. Lecture 8 Fall Overview of Cellular Respiration. Overview of Cellular Respiration
 Overview of Cellular Respiration 1 Cellular Respiration Lecture 8 Fall 2008 All organisms need ATP to do cellular work Cellular Respiration: The conversion of chemical energy of carbon compounds into another
Overview of Cellular Respiration 1 Cellular Respiration Lecture 8 Fall 2008 All organisms need ATP to do cellular work Cellular Respiration: The conversion of chemical energy of carbon compounds into another
(de novo synthesis of glucose)
 Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Gluconeogenesis (de novo synthesis of glucose) Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the biosynthesis of new glucose. The main purpose of gluconeogenesis is to maintain the constant blood Glc concentration.
Respiration. Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: Autotrophs
 Respiration rganisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: Autotrophs Able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis Heterotrophs Live on organic compounds produced by
Respiration rganisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: Autotrophs Able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis Heterotrophs Live on organic compounds produced by
Student Number: To form the polar phase when adsorption chromatography was used.
 Name: Student Number: April 14, 2001, 1:30 AM - 4:30 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Lab Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. A. Scoot 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided.. 2. The last page
Name: Student Number: April 14, 2001, 1:30 AM - 4:30 PM Page 1 (of 4) Biochemistry II Lab Section Final Examination Examiner: Dr. A. Scoot 1. Answer ALL questions in the space provided.. 2. The last page
Metabolism III. Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis
 Metabolism III Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis Anabolism From a carbon source and inorganic molecules, microbes synthesize new organelles
Metabolism III Aim: understand gluconeogenesis, pentose phosphate pathway, photosynthesis and amino acid synthesis Anabolism From a carbon source and inorganic molecules, microbes synthesize new organelles
CIII Advances in Engineering Metabolism & Microbial Conversion
 CIII Advances in Engineering Metabolism & Microbial Conversion George Bennett, Ka-Yiu San, Rice University Manipulation and Balance of Reducing Equivalents to Enhance Productivity of Chemicals in E. coli
CIII Advances in Engineering Metabolism & Microbial Conversion George Bennett, Ka-Yiu San, Rice University Manipulation and Balance of Reducing Equivalents to Enhance Productivity of Chemicals in E. coli
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and organic molecules, which are used in cellular respiration
Insights into the Autotrophic CO 2 Fixation Pathway of the Archaeon Ignicoccus hospitalis: Comprehensive Analysis of the Central Carbon Metabolism
 JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, June 2007, p. 4108 4119 Vol. 189, No. 11 0021-9193/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jb.00047-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Insights into the
JOURNAL OF BACTERIOLOGY, June 2007, p. 4108 4119 Vol. 189, No. 11 0021-9193/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/jb.00047-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Insights into the
Bio Metabolism. Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry. Chloroplasts and mitochondria. What is food?
 Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry 1 Chloroplasts and mitochondria Heat Carbohydrate O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O Heat Chloroplast Mitochondria 2 What is food? Proteins - polymers of amino acids Carbohydrates
Metabolism Life is a bag of biochemistry 1 Chloroplasts and mitochondria Heat Carbohydrate O 2 CO 2 + H 2 O Heat Chloroplast Mitochondria 2 What is food? Proteins - polymers of amino acids Carbohydrates
Probe. Hind III Q,!?R'!! /0!!!!D1"?R'! vector. Homologous recombination
 Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Supple-Zhang Page 1 Wild-type locus Targeting construct Targeted allele Exon Exon3 Exon Probe P1 P P3 FRT FRT loxp loxp neo vector amh I Homologous recombination neo P1 P P3 FLPe recombination Q,!?R'!!
Bioenergy and Resource Management Centre Cranfield University, UK
 Bio-based Production of Platform Chemical 3-Hydroxypropanoic Acid Dr Vinod Kumar Lecturer in Bioenergy/Biomass Systems 25 th October 2017 Bioenergy and Resource Management Centre Cranfield University,
Bio-based Production of Platform Chemical 3-Hydroxypropanoic Acid Dr Vinod Kumar Lecturer in Bioenergy/Biomass Systems 25 th October 2017 Bioenergy and Resource Management Centre Cranfield University,
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways In General
 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
Glycolysis Part 2. BCH 340 lecture 4
 Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
Glycolysis Part 2 BCH 340 lecture 4 Regulation of Glycolysis There are three steps in glycolysis that have enzymes which regulate the flux of glycolysis These enzymes catalyzes irreversible reactions of
FREE ENERGY Reactions involving free energy: 1. Exergonic 2. Endergonic
 BIOENERGETICS FREE ENERGY It is the portion of the total energy change in a system that is available for doing work at constant temperature and pressure; it is represented as ΔG. Reactions involving free
BIOENERGETICS FREE ENERGY It is the portion of the total energy change in a system that is available for doing work at constant temperature and pressure; it is represented as ΔG. Reactions involving free
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
number Done by Corrected by Doctor
 number 12 Done by Baraa Ayed Corrected by Mamoon Mohammad Alqtamin Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Lactate production 1 P a g e Advantages of producing lactate Lactate is produced anaerobically to meet the following
number 12 Done by Baraa Ayed Corrected by Mamoon Mohammad Alqtamin Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Lactate production 1 P a g e Advantages of producing lactate Lactate is produced anaerobically to meet the following
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Nayef Karadsheh
 number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
number 13 Done by Asma Karameh Corrected by Saad hayek Doctor Nayef Karadsheh Gluconeogenesis This lecture covers gluconeogenesis with aspects of: 1) Introduction to glucose distribution through tissues.
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
 Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 1 High energy bonds ATP adenosine triphosphate N NH 2 N -O O P O O P O- O- O O P O- O CH 2 H O H N N adenine phosphoanhydride bonds (~) H OH ribose H OH Phosphoanhydride bonds
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 1 High energy bonds ATP adenosine triphosphate N NH 2 N -O O P O O P O- O- O O P O- O CH 2 H O H N N adenine phosphoanhydride bonds (~) H OH ribose H OH Phosphoanhydride bonds
Aerobic Respiration. The four stages in the breakdown of glucose
 Aerobic Respiration The four stages in the breakdown of glucose 1 I. Aerobic Respiration Why can t we break down Glucose in one step? (Flaming Gummy Bear) Enzymes gently lower the potential energy until
Aerobic Respiration The four stages in the breakdown of glucose 1 I. Aerobic Respiration Why can t we break down Glucose in one step? (Flaming Gummy Bear) Enzymes gently lower the potential energy until
Physiological Adaptation. Microbial Physiology Module 4
 Physiological Adaptation Microbial Physiology Module 4 Topics Coordination of Metabolic Reactions Regulation of Enzyme Activity Regulation of Gene Expression Global Control, Signal Transduction and Twocomponent
Physiological Adaptation Microbial Physiology Module 4 Topics Coordination of Metabolic Reactions Regulation of Enzyme Activity Regulation of Gene Expression Global Control, Signal Transduction and Twocomponent
GGAAATCCCTTAAAAGTCG TCTCA GAGCTGCGCTCGCCC GTGCCTGAAAACCGAAGA GG ACCAACGTGTCAGTGCTTT TTG GCATCCACACCGCATGG
 Table S1. Sequences of primers described in this report. Gene (loci number, predicted/ reported function) Forward primer (5 3 ) Reverse primer (5 3 ) 16S rrna gene GGAAATTTAAAAGTG TTA GATTATAGGATTAA TTA
Table S1. Sequences of primers described in this report. Gene (loci number, predicted/ reported function) Forward primer (5 3 ) Reverse primer (5 3 ) 16S rrna gene GGAAATTTAAAAGTG TTA GATTATAGGATTAA TTA
Spring 2012 BIBC 102 midterm Hampton et al. Metabolic Biochemistry Midterm Tuesday May 8, 2012; 3:30-5:50
 Metabolic Biochemistry Midterm Tuesday May 8, 2012; 3:30-5:50 Good afternoon and goooood evening. This midterm has two purposes. One is to solidify your knowledge of the frequently-used ideas and information
Metabolic Biochemistry Midterm Tuesday May 8, 2012; 3:30-5:50 Good afternoon and goooood evening. This midterm has two purposes. One is to solidify your knowledge of the frequently-used ideas and information
This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.)
 This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC 2010. (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.) Topic 10: CELLULAR RESPIRATION (lectures 14-16) OBJECTIVES: 1. Know the basic reactions that
This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC 2010. (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.) Topic 10: CELLULAR RESPIRATION (lectures 14-16) OBJECTIVES: 1. Know the basic reactions that
Summary of Coenzymes. Summary of Coenzymes, con t. Summary of Coenzymes, con t. Lecture 31 BCH 4053 Summer 2000
 Lecture 31 BCH 4053 Summer 2000 1 2 Summary of Coenzymes Coenzyme Thiamine Pyrophosphate NAD + and NADP + FAD and FMN Pyridoxal Phosphate Thiamine (B 1 ) Niacin Riboflavin (B 2 ) Pyridoxine (B 6 ) Class
Lecture 31 BCH 4053 Summer 2000 1 2 Summary of Coenzymes Coenzyme Thiamine Pyrophosphate NAD + and NADP + FAD and FMN Pyridoxal Phosphate Thiamine (B 1 ) Niacin Riboflavin (B 2 ) Pyridoxine (B 6 ) Class
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis
 Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis 2007-2008 What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Glycolysis Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol?
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis 2007-2008 What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Glycolysis Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol?
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry Structure and Function In Biochemistry
 University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
University of Guelph Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry 19-356 Structure and Function In Biochemistry Final Exam, April 21, 1997. Time allowed, 120 min. Answer questions 1-30 on the computer scoring
Objective: You will be able to construct an explanation for how each phase of respiration captures and stores free energy.
 Objective: You will be able to construct an explanation for how each phase of respiration captures and stores free energy. Do Now: Compare and contrast the three black equations below ADP + P + Energy
Objective: You will be able to construct an explanation for how each phase of respiration captures and stores free energy. Do Now: Compare and contrast the three black equations below ADP + P + Energy
Anaerobic Protist Metabolism
 Anaerobic Protist Metabolism Giardia, Entamoeba and Trichomonads Review glycolysis and oxidative decarboxylation Parasite Biochemistry (in general) Parasitic life style = ADAPTATIONS Specific niche = diversity
Anaerobic Protist Metabolism Giardia, Entamoeba and Trichomonads Review glycolysis and oxidative decarboxylation Parasite Biochemistry (in general) Parasitic life style = ADAPTATIONS Specific niche = diversity
ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS. Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions
 Handout Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions I. Kinetics A. Reaction rates 1. First order (reaction rate is
Handout Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions ANSC 689 PHYSIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY OF LIVESTOCK SPECIDS Enzyme Kinetics and Control Reactions I. Kinetics A. Reaction rates 1. First order (reaction rate is
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: (Glycolysis) AP Biology
 Cellular Respiration Stage 1: (Glycolysis) What s the point? The point is to make! Glycolysis: Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol? Why does that
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: (Glycolysis) What s the point? The point is to make! Glycolysis: Breaking down glucose glyco lysis (splitting sugar) glucose pyruvate 6C 2x 3C In the cytosol? Why does that
Glycolysis. BCH 340 lecture 3 Chapter 8 in Lippincott 5 th edition
 Glycolysis B 40 lecture hapter 8 in Lippincott 5 th edition All carbohydrates to be catabolized must enter the glycolytic pathway Glycolysis is degradation of glucose to generate energy (ATP) and to provide
Glycolysis B 40 lecture hapter 8 in Lippincott 5 th edition All carbohydrates to be catabolized must enter the glycolytic pathway Glycolysis is degradation of glucose to generate energy (ATP) and to provide
Campbell Biology 9. Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation. Chul-Su Yang, Ph.D., Lecture on General Biology 1
 Lecture on General Biology 1 Campbell Biology 9 th edition Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Chul-Su Yang, Ph.D., chulsuyang@hanyang.ac.kr Infection Biology Lab., Dept. of Molecular & Life
Lecture on General Biology 1 Campbell Biology 9 th edition Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Chul-Su Yang, Ph.D., chulsuyang@hanyang.ac.kr Infection Biology Lab., Dept. of Molecular & Life
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis (Ch. 6)
 Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis (Ch. 6) What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Harvesting stored energy Energy is stored in organic molecules carbohydrates, fats, proteins Heterotrophs
Cellular Respiration Stage 1: Glycolysis (Ch. 6) What s the point? The point is to make! 2007-2008 Harvesting stored energy Energy is stored in organic molecules carbohydrates, fats, proteins Heterotrophs
Carbohydrate Metabolism I
 Carbohydrate Metabolism I Outline Glycolysis Stages of glycolysis Regulation of Glycolysis Carbohydrate Metabolism Overview Enzyme Classification Dehydrogenase - oxidizes substrate using cofactors as
Carbohydrate Metabolism I Outline Glycolysis Stages of glycolysis Regulation of Glycolysis Carbohydrate Metabolism Overview Enzyme Classification Dehydrogenase - oxidizes substrate using cofactors as
Chem Lecture 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part I: Glycolysis
 Chem 352 - Lecture 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part I: Glycolysis Introduction Carbohydrate metabolism involves a collection of pathways. Glycolysis Hexoses 3-Carbon molecules Gluconeogenesis 3-Carbon molecules
Chem 352 - Lecture 8 Carbohydrate Metabolism Part I: Glycolysis Introduction Carbohydrate metabolism involves a collection of pathways. Glycolysis Hexoses 3-Carbon molecules Gluconeogenesis 3-Carbon molecules
Chapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway
 Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Donald Voet Judith G. Voet harlotte W. Pratt hapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Page No. 47-490 Introduction Glucose: is major source of metabolic
Principles of Biochemistry Fourth Edition Donald Voet Judith G. Voet harlotte W. Pratt hapter 15 Glycolysis and The Pentose Phosphate Pathway Page No. 47-490 Introduction Glucose: is major source of metabolic
Chapter 8. Metabolism. Topics in lectures 15 and 16. Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Ch. 9 Cellular Respira,on BIOL 222
 Ch. 9 Cellular Respira,on BIOL Energy Arrives as sunlight Photosynthesis Energy ECOSYSTEM Light energy Plants capture sunlight organic molecules and generates O Carbs used in cellular respira@on CO + H
Ch. 9 Cellular Respira,on BIOL Energy Arrives as sunlight Photosynthesis Energy ECOSYSTEM Light energy Plants capture sunlight organic molecules and generates O Carbs used in cellular respira@on CO + H
Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION
 TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 5, part A Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case Microbial
TORTORA FUNKE CASE Microbiology AN INTRODUCTION EIGHTH EDITION B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 5, part A Microbial Metabolism PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation prepared by Christine L. Case Microbial
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
