Supporting Information
|
|
|
- Melvyn McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with Laxman Yetukuri, 1 Sanni Söderlund, 2 Artturi Koivuniemi, 3 Tuulikki Seppänen-Laakso, 1 Perttu S. Niemelä, 1 Marja Hyvönen, 4 Marja-Riitta Taskinen, 2 Ilpo Vattulainen, 3,5,6 Matti Jauhiainen, 7,8 and Matej Orešič 1,8, * 1 VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, Espoo, Finland, 2 Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 3 Department of Physics, Tampere University of Technology, Tampere, Finland, 4 Department of Physics, University of Oulu, Finland, 5 Department of Physics, Aalto University School of Science and Engineering, Espoo, Finland, 6 MEMPHYS Center for Biomembrane Physics, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark, 7 National Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland, 8 Institute for Molecular Medicine Finland FIMM, Helsinki, Finland *Correspondence to: Matej Orešič, VTT Technical Research Centre of Finland, P.O. Box 1000, Espoo, FI VTT, Finland. Tel.: ; Fax: ; matej.oresic@vtt.fi. Supporting Information 1
2 Contents Table S1. Identified lipids selected based on P-values (P<0.0001) from student t-test between high and low HDL-C subjects Table S2. All potential lipid peaks ordered based on P-values (t-test between high and low HDL-C subjects) Table S3. HDL subspecies 2b, 2a, 3a, 3b, and 3c in low- and high-hdl subjects divided by gender 13 Fig. S1. Gender specific clustering observed in HDL lipidomics data Fig. S2. Fold ratio (high vs. low HDL-C) of triacylglycerols as dependent on distribution of double bonds (degree of saturation) and total acyl carbon chain length Fig. S3. Heat map of Pearson correlations for top VIP variables vs. clinical variables Fig. S4. Correlation analysis between specific lipid variables (lysopc(18:0) and SM(18:1/16:0)) vs. selected clinical parameters (HDL-C and HDL particle size) Fig. S5. Correlation analysis between specific lipid variables (TG (16:0/18:1/20:1) and ChoE(18:1)) vs. selected clinical parameters (HDL-C and HDL particle size) Fig. S6. Radii of gyrations of HDL particles Fig. S7. Root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) profiles for apoa-is in each simulation Fig. S8. Radial distribution functions for other than TG molecules in high-hdl simulation Fig. S9. Radial distribution functions for other than TG molecules in normal-hdl simulation Fig. S10. Radial distribution functions for other than TG molecules in low-hdl simulation
3 Table S1. Identified lipids selected based on P-values (P<0.0001) from student t-test between high and low HDL-C subjects. m/z, mass-to-charge ratio; RT, retention time; FDR, False discovery rate. m/z RT Lipid Name Mean fold change (High vs. low HDL-C) FDR q-value PC(16:0/20:3) 0.50 < PC(O-16:0/20:4) 0.62 < PC(34:0) 0.55 < PC(O-36:2) PC(O-36:5) TG(16:0/18:1/16:0) SM(d18:1/23:0) TG(16:0/18:1/20:1) PC(18:2/20:4) PC(18:0/22:5) TG(17:0/18:1/16:0) PC(18:2/18:2) SM(d18:1/23:1) PC(40:7) SM(d18:1/16:0)
4 Table S2. All potential lipid peaks ordered based on P-values (t-test between high and low HDL-C subjects). The reported lipids in Table 1 are the ones confirmed by MS/MS using ESI+ (and in some cases also ESI-). m/z, mass-to-charge ratio; RT, retention time in seconds; Lo, low HDL-C group; Hi, high HDL-C group; SEM, standard error of mean; MS/MS, not determined due to insufficient information at MS/MS, *two-sided t-test. Peak no M/Z RT LipidName Mode of identification Mean (Lo) Mean (Hi) SEM(Lo) SEM(Hi) P* PC(16:0/20:3) MS/MS < PC(O-16:0/20:4) MS/MS < PC(34:0) MS/MS < PC(O-36:2) MS/MS < PC(O-36:5) MS/MS < TG(16:0/18:1/16:0) MS/MS < SM(d18:1/23:0) MS/MS < TG(16:0/18:1/20:1) MS/MS < PC(18:2/20:4) MS/MS < PC(18:0/22:5) MS/MS < TG(17:0/18:1/16:0) MS/MS < PC(18:2/18:2) MS/MS < SM(d18:1/23:1) MS/MS < PC(40:7) MS/MS < SM(d18:1/16:0) MS/MS < PC(36:4)(sodiated) MS/MS < LysoPC(18:1) MS/MS < PC(33:4) MS/MS < PC(37:4)+PE(40:4) MS/MS < TG(18:1/16:0/18:1) MS/MS < PC(O-34:3) MS/MS < LysoPC(18:0) MS/MS < TG(17:0/18:1/18:2) MS/MS < PC(36:4)(sodiated) MS/MS < TG(18:2/16:0/18:1) MS/MS < TG(18:1/18:3/22:6) MS/MS < PC(38:6) MS/MS < TG(18:1/18:1/15:0) MS/MS < LysoPC(18:1)(sodiated) MS/MS < PC(18:2/18:2) MS/MS < PC(33:4) MS/MS <
5 SM(d18:1/24:1) MS/MS < SM(d18:1/22:0) MS/MS < PC(O-36:3) MS/MS < TG(18:1/16:0/16:1) MS/MS < PC(38:3) MS/MS PE(P-16:0/20:4) MS/MS TG(18:1/14:0/16:0) MS/MS SM(d18:1/21:0) MS/MS PC(O-34:2) MS/MS TG(18:0/18:1/18:1) MS/MS TG(16:0/18:0/16:0) MS/MS SM(d18:1/15:0) MS/MS PC(36:5) MS/MS TG(18:1/18:1/18:1) MS/MS SM(d18:1/23:0)(sodiated) MS/MS PC(sodiated) MS/MS PC(O-40:7) MS/MS SM(d18:1/14:0) MS/MS PC(16:0/20:5) MS/MS LysoPC(22:6) MS/MS PC(40:6) MS/MS SM(d18:1/16:0)(sodiated) MS/MS PC(40:4) MS/MS TG(18:2/18:1/18:1) MS/MS TG(16:0/18:2/18:2) MS/MS PC(36:5)(sodiated) MS/MS ChoE(18:1) MS/MS PC(O-32:1) MS/MS TG(18:2/16:1/17:0) MS/MS PC(34:3) MS/MS PC(O-40:3) MS/MS SM(d18:1/24:2) MS/MS PC(O-36:5) MS/MS PC(16:0/18:2) MS/MS PC(18:0/18:1) MS/MS TG(16:0/16:0/16:0) MS/MS PE(P-18:1/20:4) MS/MS LysoPC(18:0) MS/MS TG(18:1/18:2/18:2) MS/MS LysoPC(16:0) MS/MS ChoE(20:4) MS/MS TG(18:1/18:1/18:2) MS/MS
6 PC(36:2) MS/MS LysoPC(18:2) MS/MS PC(O-38:5) MS/MS PC(38:7) MS/MS PC(16:0/18:2) MS/MS PC(18:0/20:5) MS/MS PE(P-16:0/20:4) MS/MS PC(18:0/20:3) MS/MS PC(O-16:0/20:4) MS/MS TG(16:1/16:1/18:1) MS/MS PC(39:6) MS/MS TG(18:1/14:0/16:1) MS/MS PC(16:0/16:0) MS/MS PC(O-40:5) MS/MS PC(36:4) MS/MS TG(18:1/16:0/12:0) MS/MS PC(16:0/16:0) MS/MS TG(16:0/14:0/14:0) MS/MS PC(34:3) MS/MS PE(P-16:0/18:2) MS/MS PC(36:5) MS/MS PE(P-18:0/18:2)+PE(P :1/18:1) MS/MS TG(18:1/15:0/14:0) MS/MS PC(O-16:0/22:6) MS/MS TG(18:1/18:2/18:3) MS/MS PC(18:0/20:4) MS/MS TG(16:0/18:3/18:2) MS/MS SM(d18:1/18:0) MS/MS TG(18:1/18:2/18:3) MS/MS PC(16:1/16:0) MS/MS PC(40:4) MS/MS PC(18:0/18:2) MS/MS PC(34:3) MS/MS PC(36:2) MS/MS PC(38:4) MS/MS PE(O-38:6) MS/MS PC(40:6) MS/MS TG(18:1/18:1/18:2) MS/MS PC(16:0/22:6)(sodiated) MS/MS PC(O-38:7) MS/MS PE(O-38:7) MS/MS PC(34:1) MS/MS
7 TG(16:0/16:1/18:3) MS/MS ChoE(18:2) MS/MS PC(35:1) MS/MS TG(14:0/17:1/16:1) MS/MS PC(35:2) MS/MS PC(14:0/18:2) MS/MS SM(d18:1/18:1) MS/MS TG(16:0/18:2/14:1) MS/MS PC(O-16:0/22:6) MS/MS PC(33:0) MS/MS PC(16:0/18:2) MS/MS PC(30:0) MS/MS PC(37:1) MS/MS PC(40:7) MS/MS PC(30:1) MS/MS PC(40:8) MS/MS PC(18:2/20:4) MS/MS PC(36:6) MS/MS PE(O-36:3) MS/MS TG(18:3/18:2/18:2) MS/MS PC(O-40:4) MS/MS PC(40:6) MS/MS LysoPC(16:1) MS/MS PC(18:0/20:5) MS/MS DG(40:7) MS LysoPC(16:0)(sodiated) MS LysoPC(18:0)(sodiated) MS LysoPC(18:2) MS LysoPC(18:2)(sodiated) MS LysoPC(20:3) MS MAG(16:1) MS No match MS PC(26:1) MS PC(28:1) MS PC(32:1) MS PC(32:1)(sodiated) MS PC(32:2)(sodiated) MS PC(34:2e)(sodiated) MS PC(34:4) MS PC(34:5) MS < PC(34:5) MS PC(36:3) MS <
8 PC(36:5)(sodiated) MS PC(36:6) MS PC(36:7) MS PC(38:1) MS PC(38:6)(sodiated) MS PC(38:6)(sodiated) MS PC(38:9) MS PC(40:10) MS PC(40:5) MS PC(40:5)(sodiated) MS < PC(40:6)(sodiated) MS PC(40:7)(sodiated) MS PC(40:8) MS PC(40:9) MS PC(40:9) MS PC(42:5) MS PC(42:5) MS PC(42:6) MS PC(42:6) MS PC(42:6) MS PC(42:7) MS PC(42:8) MS PC(42:8) MS PC(O-32:1) MS PC(O-32:6) MS < PC(O-32:6) MS < PC(O-32:6) MS < PC(O-32:6) MS < PC(O-32:6) MS < PC(O-32:6) MS PC(O-36:2) MS PC(O-36:3) MS PC(O-36:5) MS PC(O-36:7) MS PC(O-38:5) MS PC(O-38:6) MS PC(O-38:6) MS PC(O-38:6) MS PC(O-38:7) MS < PC(O-38:8) MS PC(O-40:2) MS PC(O-40:5) MS
9 PC(O-40:6) MS PC(O-40:6) MS PC(O-40:7) MS PC(O-40:7) MS PC(O-40:7) MS PC(O-40:8) MS < PC(O-40:9) MS PE(32:0) MS PE(34:0) MS PE(34:3) MS PE(36:1) MS PE(36:2) MS < PE(38:0) MS PE(38:3) MS PE(38:3) MS PE(38:5) MS PE(40:2) MS PE(40:3) MS PE(40:3) MS PE(40:5) MS PE(42:1) MS PE(42:4) MS PE(42:9) MS PE(O-30:2) MS < PE(O-30:2) MS < PE(O-32:1) MS PE(O-34:2) MS PE(O-36:6) MS PE(O-38:3) MS PE(O-38:4) MS PE(O-40:6) MS < PE(O-40:6) MS PS(34:0) MS PS(38:2) MS PS(40:1) MS PS(40:2) MS PS(40:3) MS PS(40:4) MS PS(40:5) MS SM(d18:0/16:0) MS SM(d18:1/18:1)(sodiated) MS SM(d18:1/20:1) MS
10 SM(d18:1/22:5) MS SM(d18:1/22:5) MS SM(d18:1/23:5) MS SM(d18:1/24:2)(sodiated) MS SM(d18:1/24:4) MS SM(d18:1/24:6) MS SM(d18:1/25:1) MS TG(33:0) MS TG(36:0) MS TG(37:0) MS TG(46:2) MS TG(52:6) MS TG(54:3) MS TG(55:8) MS TG(55:8) MS TG(56:6) MS TG(56:6) MS TG(56:7) MS TG(56:8) MS PE(O-30:1) MS < PE(O-36:6) MS < SM(d18:1/22:0)(sodiated) MS < SM(d18:1/24:1)(sodiated) MS < PC(30:2) MS < PE(O-34:2) MS < PC(30:2) MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS No match MS/MS
11 No match MS/MS No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match MS/MS < No match <
12 No match No match No match No match MS/MS MS/MS <0.001 MS/MS <0.001 MS/MS <0.001 MS/MS <
13 Table S3. HDL subspecies 2b, 2a, 3a, 3b, and 3c in low- and high-hdl subjects divided by gender. LH,low HDL-C group; HH, high HDL-C group; IQR, interquartile range; *Mann-Whitney U test. HDL 2b (%) LH men Median (IQR) 12.9 ( ) LH women Median (IQR) 18.2 ( ) P-value* HH men Median (IQR) 46.8 ( ) HH women Median (IQR) 50.8 ( ) P-value* HDL 2a (%) 24.1 ( ) 28.5 ( ) ( ) 22.5 ( ) HDL 3a (%) 35.6 ( ) 33.3 ( ) ( ) 17.8 ( ) HDL 3b (%) 21.8 ( ) 14.5 ( ) ( ) 6.0 ( ) HDL 3c (%) 5.0 ( ) 3.3 ( ) ( ) 1.7 ( )
14 Scores on LV 2 (18.53%) L.Yetukuri et al., Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with Fig. S1. Gender specific clustering observed in HDL lipidomics data. Multivariate analysis of lipidomics data shows that subjects are clustered based on the HDL-cholesterol status, not on the gender. Supervised PLS-DA model was constructed using random subsets corss validation method based on four classes (two genders and HDL-C status). No gender specific clusters are observed as shown PLS-DA scores plot below. 40 LoHDLF 30 PLS-DA Scores plot LoHDLM LoHDLM HiHDLM HiHDLM HiHDLF HiHDLF HiHDLF HiHDLF HiHDLF LoHDLF HiHDLM HiHDLF HiHDLMHiHDLM HiHDLF HiHDLM LoHDLMLoHDLF HiHDLM LoHDLF HiHDLF LoHDLM LoHDLF LoHDLF LoHDLM LoHDLM LoHDLM Scores on LV 1 (32.37%) 14
15 Fold change Fold change L.Yetukuri et al., Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with Fig. S2. Fold ratio (high vs. low HDL-C) of triacylglycerols as dependent on distribution of double bonds (degree of saturation) and total acyl carbon chain length. Spearman rank correlations were applied to correlate fold ratio TG chain length or degree of saturation, respectively r = -0.17, p = Triglyceride carbon chain length r = 0.28, p = Total number of TG fatty acyl chain double bonds 15
16 PC(O-36:4) PC(34:0) PC(O-36:5) TG(16:0/18:1/18:1) TG(16:0/18:1/20:1) TG(16:0/18:1/16:0) TG(16:0/18:2/18:1) TG(16:0/18:1/16:1) P(O-.32:1) PC(16:0/16:0) PC(O-40:3) SM(d18:1/21:0) lysopc(22:6) PC(O-36:3) PC(O-34:3) PC(O-36:2) SM(d18.1:/16.0) SM(d18:1/23:1) PC(O-34:.2) SM(d18:1/15:0) PC(18:2/18:2) SM(d18:1/23:0) PC(18:2/:20:4) lysopc(18:1) lysopc(18:0) L.Yetukuri et al., Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with Fig. S3. Heat map of Pearson correlations for top VIP variables vs. clinical variables. Pearson correlation HDL_SIZE ApoA-I HDL-C Paraoxonase PLTP activity CETP activity PLTP mass Total Cholesterol TG Insulin BMI TNF_α CRP il_6 LDL-C 16
17 Conc n, mol/g Conc n, mol/g Conc n, mol/g L.Yetukuri et al., Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with Fig. S4. Correlation analysis between specific lipid variables (lysopc(18:0) and SM(18:1/16:0)) vs. selected clinical parameters (HDL-C and HDL particle size). A lysopc(18:0) SM(d18:1/16:0) x x 10 Low HDL-C Low HDL-C r=0.54, p= r=0.72, p= x 10-4 x 10-4 High HDL-C High HDL-C r=-0.06, p= r=0.71, p= B C HDL-C (mmol/l) lysopc(18:0) x 10-4 x r = 0.50, p = p = r = 0.580, p < p < D HDL-C (mmol/l) SM(d18:1/16:0) HDL size (nm) HDL size (nm) 17
18 Conc n, mol/g Conc n, mol/g Conc n, mol/g L.Yetukuri et al., Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with Fig. S5. Correlation analysis between specific lipid variables (TG (16:0/18:1/20:1) and ChoE(18:1)) vs. selected clinical parameters (HDL-C and HDL particle size). A TG(16:0/18:1/20:1) x10-4 x Low HDL-C Low HDL-C r=-0.06, p=0.75 r=0.33, p= x10-4 x High HDL-C HighHDL-C r=-0.43, p= r=0.02, p= ChoE(18:1) B HDL-C (mmol/l) HDL-C (mmol/l) C x r =-0.51, p = TG(16:0/18:1/20:1) HDL size (nm) 18
19 Fig. S6. Radii of gyrations of HDL particles. Results indicate that when moving from high HDL-C to low HDL-C the particle becomes smaller. This finding agree with size data acquired by electrophoresis. 19
20 Fig. S7. Root mean square fluctuation (RMSF) profiles for apoa-is in each simulation. The residual RMSF fluctuations differ markedly between the simulations. The reason for this could be that either the lipid composition or the conformation of apoa-i around the particles is different in each simulation. 20
21 Fig. S8. Radial distribution functions for other than TG molecules in high-hdl simulation. Note that one SM molecule was trapped under the ApoA-I in this particular simulation, which produced the noticeable region in SM plot near 1 nm. 21
22 Fig. S9. Radial distribution functions for other than TG molecules in normal-hdl simulation. 22
23 Fig. S10. Radial distribution functions for other than TG molecules in low-hdl simulation. 23
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Role of Lipids in Spheroidal High Density Lipoproteins Vuorela, Timo; Catte, Andrea; Niemela, Perttu S.; Hall, Anette; Hyvonen, Marja T.; Marrink, Siewert; Karttunen, Mikko; Vattulainen,
University of Groningen Role of Lipids in Spheroidal High Density Lipoproteins Vuorela, Timo; Catte, Andrea; Niemela, Perttu S.; Hall, Anette; Hyvonen, Marja T.; Marrink, Siewert; Karttunen, Mikko; Vattulainen,
Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein. particles in subjects with low and high HDL-cholesterol
 Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with low and high HDL-cholesterol Laxman Yetukuri, 1 Sanni Söderlund, 2 Artturi Koivuniemi, 3 Tuulikki Seppänen-Laakso,
Composition and lipid spatial distribution of High Density Lipoprotein particles in subjects with low and high HDL-cholesterol Laxman Yetukuri, 1 Sanni Söderlund, 2 Artturi Koivuniemi, 3 Tuulikki Seppänen-Laakso,
Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions analysed by ESI-MS/MS
 Supplement VLDL LDL HDL PC 3.3 1.77 1.3 LPC 4.82 2.5.35 SM 3.1 4.6 1.92 CER 2.17 6.3 4.15 PE 3.18 1.93 2.79 PE-pl 13.18 1.9 2.32 CE 2.9.65.4 FC.36 3.5 2.54 Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions
Supplement VLDL LDL HDL PC 3.3 1.77 1.3 LPC 4.82 2.5.35 SM 3.1 4.6 1.92 CER 2.17 6.3 4.15 PE 3.18 1.93 2.79 PE-pl 13.18 1.9 2.32 CE 2.9.65.4 FC.36 3.5 2.54 Suppl. Table 1: CV of pooled lipoprotein fractions
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. None
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST None Plasma Lipidomic Analysis of Stable and Unstable Coronary Artery Disease Peter J Meikle 1, Gerard Wong 1, Despina Tsorotes 1, Christopher K Barlow 1, Jacquelyn
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST None Plasma Lipidomic Analysis of Stable and Unstable Coronary Artery Disease Peter J Meikle 1, Gerard Wong 1, Despina Tsorotes 1, Christopher K Barlow 1, Jacquelyn
Metabolic Syndrome Modulates Association between Endothelial Lipase and. Lipid/Lipoprotein Plasma Levels in Acute Heart Failure Patients
 Metabolic Syndrome Modulates Association between Endothelial Lipase and Lipid/Lipoprotein Plasma Levels in Acute Heart Failure Patients Ines Potočnjak, Matias Trbušić, Sanda Dokoza Terešak, Bojana Radulović,
Metabolic Syndrome Modulates Association between Endothelial Lipase and Lipid/Lipoprotein Plasma Levels in Acute Heart Failure Patients Ines Potočnjak, Matias Trbušić, Sanda Dokoza Terešak, Bojana Radulović,
Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity
 Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity Professor Marja-Riitta Taskinen Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology Helsinki University Hospital, Finland Disclosures: Honorariums/
Metabolic defects underlying dyslipidemia in abdominal obesity Professor Marja-Riitta Taskinen Department of Medicine, Division of Cardiology Helsinki University Hospital, Finland Disclosures: Honorariums/
Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic
 Supplementary Information The title of the manuscript Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic stroke Xin-Wei He 1, Wei-Ling Li 1, Cai Li
Supplementary Information The title of the manuscript Serum levels of galectin-1, galectin-3, and galectin-9 are associated with large artery atherosclerotic stroke Xin-Wei He 1, Wei-Ling Li 1, Cai Li
PCs Acyl chain double bonds. PEs
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Male/Female ratio Male/Female ratio PCs 1.3 1.2 1.1 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0 1 2
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2014 Male/Female ratio Male/Female ratio PCs 1.3 1.2 1.1 1 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0 1 2
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics. Outlines
 The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
The use of mass spectrometry in lipidomics Jeevan Prasain jprasain@uab.edu 6-2612 utlines Brief introduction to lipidomics Analytical methodology: MS/MS structure elucidation of phospholipids Phospholipid
Bringing metabolic profiling into clinical practice. Linda Mustelin, MD, PhD, MPH Senior Medical Scientist Nightingale Health
 Bringing metabolic profiling into clinical practice Linda Mustelin, MD, PhD, MPH Senior Medical Scientist Nightingale Health Nightingale Health Ltd. Finnish biotech company specialized in comprehensive
Bringing metabolic profiling into clinical practice Linda Mustelin, MD, PhD, MPH Senior Medical Scientist Nightingale Health Nightingale Health Ltd. Finnish biotech company specialized in comprehensive
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones?
 1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
1Why lipids cannot be transported in blood alone? 2How we transport Fatty acids and steroid hormones? 3How are dietary lipids transported? 4How lipids synthesized in the liver are transported? 5 Lipoprotien
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Lipid extraction. Tissue was pulverized with a mortar and pestle or a ball-grinding method (Mikro Dismembrator, Sartorius). All subsequent steps were performed
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Methods Lipid extraction. Tissue was pulverized with a mortar and pestle or a ball-grinding method (Mikro Dismembrator, Sartorius). All subsequent steps were performed
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3561
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol
 Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
Chapter (5) Etiology of Low HDL- Cholesterol The aim of this chapter is to summarize the different etiological factors mainly the role of life-style and different disease conditions contributing to the
Metabolomics and systems biology approaches to study health and disease. Matej Oreši
 Metabolomics and systems biology approaches to study health and disease Matej Oreši 14.12.2011 1/19/2012 2 Biomarker concept in domain of human health [Wikipedia definition] A substance used as an indicator
Metabolomics and systems biology approaches to study health and disease Matej Oreši 14.12.2011 1/19/2012 2 Biomarker concept in domain of human health [Wikipedia definition] A substance used as an indicator
Mass-Spectrometric Analysis of Lipids (Lipidomics)
 Mass-Spectrometric Analysis of Lipids (Lipidomics) 1. Identification 2. Quantification 3. Metabolism Why to do lipidomics? Biology: Functions of different lipids? Medicine: Diagnostics and Therapy Industry:
Mass-Spectrometric Analysis of Lipids (Lipidomics) 1. Identification 2. Quantification 3. Metabolism Why to do lipidomics? Biology: Functions of different lipids? Medicine: Diagnostics and Therapy Industry:
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics
 Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
Mass Spectrometry based metabolomics Metabolomics- A realm of small molecules (
CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL
 CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL You will notice that the endogenous pathway is very similar to the exogenous pathway What is the average daily amount of triacylglycerol
CHAPTER FORTY FIVE ENDOGENOUS LIPID TRANSPORT PATHWAY: VLDL AND IDL You will notice that the endogenous pathway is very similar to the exogenous pathway What is the average daily amount of triacylglycerol
Replacement Of Partially Hydrogenated Soybean Oil By Palm Oil In Margarine Without Unfavorable Effects On Serum Lipoproteins
 Replacement Of Partially Hydrogenated Soybean Oil By Palm Oil In Margarine Without Unfavorable Effects On Serum Lipoproteins Muller H, Jordal O, et al. (998) Replacement of partially hydrogenated soybean
Replacement Of Partially Hydrogenated Soybean Oil By Palm Oil In Margarine Without Unfavorable Effects On Serum Lipoproteins Muller H, Jordal O, et al. (998) Replacement of partially hydrogenated soybean
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules. KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life.
 KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. Carbon-based
KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. Carbon forms covalent bonds with up to four other atoms, including other carbon atoms. Carbon-based
Comprehensive Lipid Profiling of Human Liver Tissue Extracts of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
 Comprehensive Lipid Profiling of Human Liver Tissue Extracts of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Multiplexed Precursor Ion Scanning and LipidView Software Brigitte Simons 1 and Bianca Arendt 2 1 AB SCIEX,
Comprehensive Lipid Profiling of Human Liver Tissue Extracts of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Multiplexed Precursor Ion Scanning and LipidView Software Brigitte Simons 1 and Bianca Arendt 2 1 AB SCIEX,
Coarse-grained model for phospholipid/cholesterol bilayer employing inverse Monte Carlo with thermodynamic constraints
 THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 126, 075101 2007 Coarse-grained model for phospholipid/cholesterol bilayer employing inverse Monte Carlo with thermodynamic constraints Teemu Murtola Laboratory of Physics,
THE JOURNAL OF CHEMICAL PHYSICS 126, 075101 2007 Coarse-grained model for phospholipid/cholesterol bilayer employing inverse Monte Carlo with thermodynamic constraints Teemu Murtola Laboratory of Physics,
Principles of Shotgun Lipidomics
 Principles of Shotgun Lipidomics Xianlin Han Diabetes and Obesity Research Center Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute Lake Nona Orlando, FL 32827 What is shotgun lipidomics? Original definition
Principles of Shotgun Lipidomics Xianlin Han Diabetes and Obesity Research Center Sanford-Burnham Medical Research Institute Lake Nona Orlando, FL 32827 What is shotgun lipidomics? Original definition
Supporting information
 Supporting information A novel lipidomics workflow for improved human plasma identification and quantification using RPLC-MSn methods and isotope dilution strategies Evelyn Rampler 1,2,3, Angela Criscuolo
Supporting information A novel lipidomics workflow for improved human plasma identification and quantification using RPLC-MSn methods and isotope dilution strategies Evelyn Rampler 1,2,3, Angela Criscuolo
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Materials and Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Materials and Methods HPLC-UV of phospholipid classes and HETE isomer determination. Fractionation of platelet lipid classes was undertaken on a Spherisorb S5W 150 x 4.6 mm column (Waters
Nutrition & Wellness for Life 2012 Chapter 6: Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Tools: Printer 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut along dashed lines Copyright Goodheart-Willcox Co., Inc. All rights reserved. Tissue in which the body
Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention
 Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention Piyushkumar A. Mundra,, Peter J. Meikle, LIPID Study Investigators JCI Insight. 2018;3(17):e121326..
Large-scale plasma lipidomic profiling identifies lipids that predict cardiovascular events in secondary prevention Piyushkumar A. Mundra,, Peter J. Meikle, LIPID Study Investigators JCI Insight. 2018;3(17):e121326..
Free Volume Properties of Sphingomyelin, DMPC, DPPC, and PLPC Bilayers
 PUBLISHED IN: JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL AND THEORETICAL NANOSCIENCE, VOL. 2, PP. 40-43 (2005). Free Volume Properties of Sphingomyelin, DMPC, DPPC, and PLPC Bilayers M. Kupiainen, E. Falck, S. Ollila, P.
PUBLISHED IN: JOURNAL OF COMPUTATIONAL AND THEORETICAL NANOSCIENCE, VOL. 2, PP. 40-43 (2005). Free Volume Properties of Sphingomyelin, DMPC, DPPC, and PLPC Bilayers M. Kupiainen, E. Falck, S. Ollila, P.
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
ANSC/NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Dietary fat and Cardiovascular Disease
 ANSC/NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Dietary fat and Cardiovascular Disease I. Investigations in humans relating dietary fat intake to serum cholesterol A. Ansel Keys: the Keys Formula Cholesterol
ANSC/NUTR) 618 LIPIDS & LIPID METABOLISM Dietary fat and Cardiovascular Disease I. Investigations in humans relating dietary fat intake to serum cholesterol A. Ansel Keys: the Keys Formula Cholesterol
Document Version Publisher s PDF, also known as Version of Record (includes final page, issue and volume numbers)
 Coarse-grained model for phospholipid/cholesterol bilayer employing inverse Monte Carlo with thermodynamic constraints Murtola, T.; Falck, E.; Karttunen, M.E.J.; Vattulainen, I. Published in: Journal of
Coarse-grained model for phospholipid/cholesterol bilayer employing inverse Monte Carlo with thermodynamic constraints Murtola, T.; Falck, E.; Karttunen, M.E.J.; Vattulainen, I. Published in: Journal of
Supplementary table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants by paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) gene polymorphisms
 Supplementary table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants by paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) gene polymorphisms QQ QR/RR n = 36 n = 80 Men (%) 20 (55) 54 (67) 0.216 Age (years) 57 ± 10 56 ±
Supplementary table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of participants by paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) gene polymorphisms QQ QR/RR n = 36 n = 80 Men (%) 20 (55) 54 (67) 0.216 Age (years) 57 ± 10 56 ±
7/11/17. Cell Function & Chemistry. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Development of a High Coverage Pseudotargeted Lipidomics Method Based on Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Qiuhui Xuan 1,2#, Chunxiu Hu 1#, Di Yu 1,2,
Supporting Information Development of a High Coverage Pseudotargeted Lipidomics Method Based on Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Qiuhui Xuan 1,2#, Chunxiu Hu 1#, Di Yu 1,2,
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness. Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source
 Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Nutrition, Food, and Fitness Chapter 6 Fats: A Concentrated Energy Source Tools: Printer (color optional) 4 sheets of 8.5 x 11 paper Scissors Directions: 1. Print 2. Fold paper in half vertically 3. Cut
Annotation of potential isobaric and isomeric lipid species measured with the AbsoluteIDQ p180 Kit (and p150 Kit)
 We provide the Phenotype to the Genotype! DocNr. 35017 V 2 2017-02 Annotation of potential isobaric and isomeric lipid species measured with the (and p150 Kit) Introduction Lipidomics, a branch of metabolomics
We provide the Phenotype to the Genotype! DocNr. 35017 V 2 2017-02 Annotation of potential isobaric and isomeric lipid species measured with the (and p150 Kit) Introduction Lipidomics, a branch of metabolomics
A: All atom molecular simulation systems
 Cholesterol level affects surface charge of lipid membranes in physiological environment Aniket Magarkar a, Vivek Dhawan b, Paraskevi Kallinteri a, Tapani Viitala c, Mohammed Elmowafy c, Tomasz Róg d,
Cholesterol level affects surface charge of lipid membranes in physiological environment Aniket Magarkar a, Vivek Dhawan b, Paraskevi Kallinteri a, Tapani Viitala c, Mohammed Elmowafy c, Tomasz Róg d,
Biophysical Journal Volume 96 May
 Biophysical Journal Volume 96 May 2009 4099 4108 4099 Atomistic Simulations of Phosphatidylcholines and Cholesteryl Esters in High-Density Lipoprotein-Sized Lipid Droplet and Trilayer: Clues to Cholesteryl
Biophysical Journal Volume 96 May 2009 4099 4108 4099 Atomistic Simulations of Phosphatidylcholines and Cholesteryl Esters in High-Density Lipoprotein-Sized Lipid Droplet and Trilayer: Clues to Cholesteryl
Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC. Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC
 Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Supplement Table I: primers for Real Time RT-PCR Gene Foward Reverse Hmgcoar AGCTTGCCCGAATTGTATGTG TCTGTTGTAACCATGTGACTTC Cyp7α GGGATTGCTGTGGTAGTGAGC GGTATGGAATCAACCCGTTGTC Cyp27a1 GTGGTCTTATTGGGTACTTGC
Table S1. Characteristics associated with frequency of nut consumption (full entire sample; Nn=4,416).
 Table S1. Characteristics associated with frequency of nut (full entire sample; Nn=4,416). Daily nut Nn= 212 Weekly nut Nn= 487 Monthly nut Nn= 1,276 Infrequent or never nut Nn= 2,441 Sex; n (%) men 52
Table S1. Characteristics associated with frequency of nut (full entire sample; Nn=4,416). Daily nut Nn= 212 Weekly nut Nn= 487 Monthly nut Nn= 1,276 Infrequent or never nut Nn= 2,441 Sex; n (%) men 52
The Metabolic Syndrome Update The Metabolic Syndrome Update. Global Cardiometabolic Risk
 The Metabolic Syndrome Update 2018 Marc Cornier, M.D. Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes Anschutz Health and Wellness Center University of Colorado School of Medicine
The Metabolic Syndrome Update 2018 Marc Cornier, M.D. Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes Anschutz Health and Wellness Center University of Colorado School of Medicine
Lipoproteins Metabolism
 Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Lipoproteins Metabolism LEARNING OBJECTIVES By the end of this Lecture, the student should be able to describe: What are Lipoproteins? Describe Lipoprotein Particles. Composition of Lipoproteins. The chemical
Elevated Serum Levels of Adropin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and its Association with
 Elevated Serum Levels of Adropin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and its Association with Insulin Resistance Mehrnoosh Shanaki, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Shahid Beheshti
Elevated Serum Levels of Adropin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and its Association with Insulin Resistance Mehrnoosh Shanaki, Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Shahid Beheshti
Atomistic MD simulation reveals the mechanism by which CETP penetrates into HDL enabling lipid transfer from HDL to CETP
 Atomistic MD simulation reveals the mechanism by which CETP penetrates into HDL enabling lipid transfer from HDL to CETP Geraldine Cilpa-Karhu, 1, * Matti Jauhiainen, and Marja-Liisa Riekkola * Laboratory
Atomistic MD simulation reveals the mechanism by which CETP penetrates into HDL enabling lipid transfer from HDL to CETP Geraldine Cilpa-Karhu, 1, * Matti Jauhiainen, and Marja-Liisa Riekkola * Laboratory
Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme
 P-CN1716E Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme ASMS 2017 MP-406 Tsuyoshi Nakanishi 1, Masaki Yamada 1, Ningombam Sanjib Meitei 2, 3 1 Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan,
P-CN1716E Phospholipid characterization by a TQ-MS data based identification scheme ASMS 2017 MP-406 Tsuyoshi Nakanishi 1, Masaki Yamada 1, Ningombam Sanjib Meitei 2, 3 1 Shimadzu Corporation, Kyoto, Japan,
Pattern of lipid biomarkers and risk of cardiovascular disease
 Pattern of lipid biomarkers and risk of cardiovascular disease Robert Clarke Clinical Trial Service Unit University of Oxford 9 January 2017 Biomarkers for dietary fats Blood lipids (LDL, HDL, triglycerides,
Pattern of lipid biomarkers and risk of cardiovascular disease Robert Clarke Clinical Trial Service Unit University of Oxford 9 January 2017 Biomarkers for dietary fats Blood lipids (LDL, HDL, triglycerides,
Lipids digestion and absorption, Biochemistry II
 Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Lipids digestion and absorption, blood plasma lipids, lipoproteins Biochemistry II Lecture 1 2008 (J.S.) Triacylglycerols (as well as free fatty acids and both free and esterified cholesterol) are very
Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients
 2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
2012 international Conference on Diabetes and metabolism (ICDM) Review of guidelines for management of dyslipidemia in diabetic patients Nan Hee Kim, MD, PhD Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University
Supplemental Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Food & Function. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2016 Supplemental Information Supplementary Materials and Methods Materials Assay kits of total
LC/MS/MS SOLUTIONS FOR LIPIDOMICS. Biomarker and Omics Solutions FOR DISCOVERY AND TARGETED LIPIDOMICS
 LC/MS/MS SOLUTIONS FOR LIPIDOMICS Biomarker and Omics Solutions FOR DISCOVERY AND TARGETED LIPIDOMICS Lipids play a key role in many biological processes, such as the formation of cell membranes and signaling
LC/MS/MS SOLUTIONS FOR LIPIDOMICS Biomarker and Omics Solutions FOR DISCOVERY AND TARGETED LIPIDOMICS Lipids play a key role in many biological processes, such as the formation of cell membranes and signaling
N-3 Fatty Acids Non-HDL-Cand LDL-C Thomas Dayspring MD, FACP
 Omega or N-3 Fatty Acids (FA) significantly reduce TG synthesis and significantly deplete the TG content of VLDL particles indicated by significantly reduced V. FA are the substrate for TG synthesis. N3-FA
Omega or N-3 Fatty Acids (FA) significantly reduce TG synthesis and significantly deplete the TG content of VLDL particles indicated by significantly reduced V. FA are the substrate for TG synthesis. N3-FA
Dissertation VTT PUBLICATIONS 741. Laxmana Rao Yetukuri. Bioinformatics approaches for the analysis of lipidomics data
 Dissertation VTT PUBLICATIONS 741 Laxmana Rao Yetukuri Bioinformatics approaches for the analysis of lipidomics data VTT PUBLICATIONS 741 Bioinformatics approaches for the analysis of lipidomics data
Dissertation VTT PUBLICATIONS 741 Laxmana Rao Yetukuri Bioinformatics approaches for the analysis of lipidomics data VTT PUBLICATIONS 741 Bioinformatics approaches for the analysis of lipidomics data
May 13, 2017 Data Back Ban of Artificial Trans Fats
 EDUCATOR GUIDE May 13, 2017 Data Back Ban of Artificial Trans Fats Cross-Curricular Discussion After students have had a chance to review the article Data back ban of artificial trans fats, lead a classroom
EDUCATOR GUIDE May 13, 2017 Data Back Ban of Artificial Trans Fats Cross-Curricular Discussion After students have had a chance to review the article Data back ban of artificial trans fats, lead a classroom
Supplemental Table S2: Subgroup analysis for IL-6 with BMI in 3 groups
 Supplemental Table S1: Unadjusted and Adjusted Hazard Ratios for Diabetes Associated with Baseline Factors Considered in Model 3 SMART Participants Only Unadjusted Adjusted* Baseline p-value p-value Covariate
Supplemental Table S1: Unadjusted and Adjusted Hazard Ratios for Diabetes Associated with Baseline Factors Considered in Model 3 SMART Participants Only Unadjusted Adjusted* Baseline p-value p-value Covariate
Obesity Prevention and Control: Provider Education with Patient Intervention
 Obesity Prevention and : Provider Education with Patient Summary Evidence Table and Population Cohen et al. (1991) 1987-1988 : RCT Location: Pittsburgh, PA Physician training session by a behavioral psychologist
Obesity Prevention and : Provider Education with Patient Summary Evidence Table and Population Cohen et al. (1991) 1987-1988 : RCT Location: Pittsburgh, PA Physician training session by a behavioral psychologist
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Investigating the effect of antiretroviral switch to tenofovir alafenamide on lipid profiles in people living with HIV within the UCD ID Cohort
 Investigating the effect of antiretroviral switch to tenofovir alafenamide on lipid profiles in people living with HIV within the UCD ID Cohort A. Lacey 1, W. Tinago 1, E. Alvarez Barco 1, A.J. Macken
Investigating the effect of antiretroviral switch to tenofovir alafenamide on lipid profiles in people living with HIV within the UCD ID Cohort A. Lacey 1, W. Tinago 1, E. Alvarez Barco 1, A.J. Macken
Impact of Chromatography on Lipid Profiling of Liver Tissue Extracts
 Impact of Chromatography on Lipid Profiling of Liver Tissue Extracts Application Note Clinical Research Authors Mark Sartain and Theodore Sana Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, California, USA Introduction
Impact of Chromatography on Lipid Profiling of Liver Tissue Extracts Application Note Clinical Research Authors Mark Sartain and Theodore Sana Agilent Technologies, Inc. Santa Clara, California, USA Introduction
Gender-Based and Age-Related Peculiarities of Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Heart Failure Secondary to Overweight and Obesity
 71 P.P.Bidzilya Gender-Based and Age-Related Peculiarities of Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Heart Failure Secondary to Overweight and Obesity Zaporizhzhya State Medical University, Zaporizhzhya, Ukraine
71 P.P.Bidzilya Gender-Based and Age-Related Peculiarities of Lipid Metabolism in Chronic Heart Failure Secondary to Overweight and Obesity Zaporizhzhya State Medical University, Zaporizhzhya, Ukraine
Andrejs Kalvelis 1, MD, PhD, Inga Stukena 2, MD, Guntis Bahs 3 MD, PhD & Aivars Lejnieks 4, MD, PhD ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Riga Stradins University
 CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do We Correctly Assess the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease? Characteristics of Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Depending on the Sex and Age of Patients
CARDIOVASCULAR RISK FACTORS ORIGINAL ARTICLE Do We Correctly Assess the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease? Characteristics of Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease Depending on the Sex and Age of Patients
APPENDIX AVAILABLE ON THE HEI WEB SITE
 APPENDIX AVAILABLE ON THE HEI WEB SITE Research Report 178 National Particle Component Toxicity (NPACT) Initiative Report on Cardiovascular Effects Sverre Vedal et al. Section 1: NPACT Epidemiologic Study
APPENDIX AVAILABLE ON THE HEI WEB SITE Research Report 178 National Particle Component Toxicity (NPACT) Initiative Report on Cardiovascular Effects Sverre Vedal et al. Section 1: NPACT Epidemiologic Study
MALDI Activity 4 MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Data Analysis
 MALDI Activity 4 MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Data Analysis Model 1: Introduction to Triacylglycerides (TAGs) In MALDI Activity 3 you learned how to open your raw mass spectrum data and use the MMass program
MALDI Activity 4 MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry: Data Analysis Model 1: Introduction to Triacylglycerides (TAGs) In MALDI Activity 3 you learned how to open your raw mass spectrum data and use the MMass program
HDL and Its Galaxy of Proteins: What Do they Do? Jay Heinecke, University of Washington
 HDL and Its Galaxy of Proteins: What Do they Do? Jay Heinecke, University of Washington Disclosures NIH AHA Insilicos Consultant Merck Research Support GSK Research Support Pfizer Research Support Corcept
HDL and Its Galaxy of Proteins: What Do they Do? Jay Heinecke, University of Washington Disclosures NIH AHA Insilicos Consultant Merck Research Support GSK Research Support Pfizer Research Support Corcept
Lipid annotation with MS2Analyzer. Yan Ma 10/24/2013
 Lipid annotation with MS2Analyzer Yan Ma 10/24/2013 Checklist before you start You need to have: 1.A computer with Java environment and Office(2003 or higher) 2.MS/MS spectra in MGF files 3.Latest version
Lipid annotation with MS2Analyzer Yan Ma 10/24/2013 Checklist before you start You need to have: 1.A computer with Java environment and Office(2003 or higher) 2.MS/MS spectra in MGF files 3.Latest version
Obtaining Answers to Biological Questions Sample Prep to Data Analysis. Jeremiah D. Tipton, Ph.D. SCIEX Advanced Workflow Specialist in OMICS
 Obtaining Answers to Biological Questions Sample Prep to Data Analysis Jeremiah D. Tipton, Ph.D. SCIEX Advanced Workflow Specialist in OMICS OMICS Research Why Quantitative OMICS? 2 2015 AB Sciex SCIEX
Obtaining Answers to Biological Questions Sample Prep to Data Analysis Jeremiah D. Tipton, Ph.D. SCIEX Advanced Workflow Specialist in OMICS OMICS Research Why Quantitative OMICS? 2 2015 AB Sciex SCIEX
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. A novel truncated form of Apolipoprotein A-I transported by dense LDL is increased in. diabetic patients
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL A novel truncated form of Apolipoprotein A-I transported by dense LDL is increased in diabetic patients Cubedo et al: ApoA-I truncated form in diabetes By Judit Cubedo a, Teresa Padró
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL A novel truncated form of Apolipoprotein A-I transported by dense LDL is increased in diabetic patients Cubedo et al: ApoA-I truncated form in diabetes By Judit Cubedo a, Teresa Padró
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL
 Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
Behind LDL: The Metabolism of ApoB, the Essential Apolipoprotein in LDL and VLDL Sung-Joon Lee, PhD Division of Food Science Institute of Biomedical Science and Safety Korea University Composition of Lipoproteins:
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Number of patients 14
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1 Number of patients 14 Age, years 54.9 ± 10.0 Female gender, n (%) 6 (42.9) Diabetes, n (%) 2 (14.3) History of hypertension, n (%) 5 (35.7) Ever smoker, n (%)
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplemental Table 1 Number of patients 14 Age, years 54.9 ± 10.0 Female gender, n (%) 6 (42.9) Diabetes, n (%) 2 (14.3) History of hypertension, n (%) 5 (35.7) Ever smoker, n (%)
Ct=28.4 WAT 92.6% Hepatic CE (mg/g) P=3.6x10-08 Plasma Cholesterol (mg/dl)
 a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
a Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna8 Ct=4.3 Ct=8.4 Ct=8.8 Ct=8.9 Ct=.8 Ct=.5 Relative TM6SF mrna Level P=.5 X -5 b.5 Liver WAT Small intestine Relative TM6SF mrna Level..5 9.6% Control AAV mtm6sf-shrna mtm6sf-shrna6
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Uncropped version of Fig. 2a. RM indicates that the translation was done in the absence of rough mcirosomes. (b) LepB construct containing the GGPG-L6RL6-
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. (a) Uncropped version of Fig. 2a. RM indicates that the translation was done in the absence of rough mcirosomes. (b) LepB construct containing the GGPG-L6RL6-
MASS SPECTROMETRY BASED METABOLOMICS. Pavel Aronov. ABRF2010 Metabolomics Research Group March 21, 2010
 MASS SPECTROMETRY BASED METABOLOMICS Pavel Aronov ABRF2010 Metabolomics Research Group March 21, 2010 Types of Experiments in Metabolomics targeted non targeted Number of analyzed metabolites is limited
MASS SPECTROMETRY BASED METABOLOMICS Pavel Aronov ABRF2010 Metabolomics Research Group March 21, 2010 Types of Experiments in Metabolomics targeted non targeted Number of analyzed metabolites is limited
Expanded View Figures
 Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
Solip Park & Ben Lehner Epistasis is cancer type specific Molecular Systems Biology Expanded View Figures A B G C D E F H Figure EV1. Epistatic interactions detected in a pan-cancer analysis and saturation
SITA 100 mg (n = 378)
 Supplementary Table 1. Summary of Sulfonylurea Background Therapy at Baseline and During the Treatment Period. Sulfonylurea at baseline, n (%) SITA 100 mg (n = 378) CANA 300 mg (n = 377) Total (N = 755)
Supplementary Table 1. Summary of Sulfonylurea Background Therapy at Baseline and During the Treatment Period. Sulfonylurea at baseline, n (%) SITA 100 mg (n = 378) CANA 300 mg (n = 377) Total (N = 755)
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Leibowitz M, Karpati T, Cohen-Stavi CJ, et al. Association between achieved low-density lipoprotein levels and major adverse cardiac events in patients with stable ischemic
Supplementary Online Content Leibowitz M, Karpati T, Cohen-Stavi CJ, et al. Association between achieved low-density lipoprotein levels and major adverse cardiac events in patients with stable ischemic
Save My Exams! The Home of Revision For more awesome GCSE and A level resources, visit us at Lipids.
 Lipids Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet International A Level Biology Edexcel Molecules, Transport and Health Lipids Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 63 minutes Score: /52 Percentage:
Lipids Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet International A Level Biology Edexcel Molecules, Transport and Health Lipids Mark Scheme Time Allowed: 63 minutes Score: /52 Percentage:
The effect of plant sterols and different low doses of omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil on lipoprotein subclasses
 The effect of plant sterols and different low doses of omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil on lipoprotein subclasses 18 June 2015 Doris Jacobs Unilever R&D Vlaardingen Background Elevated low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
The effect of plant sterols and different low doses of omega-3 fatty acids from fish oil on lipoprotein subclasses 18 June 2015 Doris Jacobs Unilever R&D Vlaardingen Background Elevated low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
Supporting Information
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Supporting Information Modulating Interactions between Ligand-Coated Nanoparticles and Phase-Separated
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Nanoscale. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 018 Supporting Information Modulating Interactions between Ligand-Coated Nanoparticles and Phase-Separated
Types of Statistics. Censored data. Files for today (June 27) Lecture and Homework INTRODUCTION TO BIOSTATISTICS. Today s Outline
 INTRODUCTION TO BIOSTATISTICS FOR GRADUATE AND MEDICAL STUDENTS Files for today (June 27) Lecture and Homework Descriptive Statistics and Graphically Visualizing Data Lecture #2 (1 file) PPT presentation
INTRODUCTION TO BIOSTATISTICS FOR GRADUATE AND MEDICAL STUDENTS Files for today (June 27) Lecture and Homework Descriptive Statistics and Graphically Visualizing Data Lecture #2 (1 file) PPT presentation
Comprehensive Two-Dimensional HPLC and Informative Data Processing for Pharmaceuticals and Lipids
 PO-CON1576E Comprehensive Two-Dimensional HPLC and Informative Data Processing for Pharmaceuticals and Lipids HPLC 2015 PSB-MULTI-06 Yoshiyuki WATABE, Tetsuo IIDA, Daisuke NAKAYAMA, Kanya TSUJII, Saki
PO-CON1576E Comprehensive Two-Dimensional HPLC and Informative Data Processing for Pharmaceuticals and Lipids HPLC 2015 PSB-MULTI-06 Yoshiyuki WATABE, Tetsuo IIDA, Daisuke NAKAYAMA, Kanya TSUJII, Saki
Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations.
 Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations Leanne Hodson Fatty acid composition as a biomarker of intake Complements dietary
Blood fatty acids understanding the relevance of different tissue fractions and interpreting circulating concentrations Leanne Hodson Fatty acid composition as a biomarker of intake Complements dietary
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
9/11/18. Cell Function & Chemistry. Molecular and Cellular Biology. 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell
 Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Molecular and Cellular Biology Cell Function & Chemistry 2. Bio-Chemical Foundations & Key Molecules of a Cell Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Interaction Molecular Bonds Define Cellular Functions Water H 2 O Interactions
Plasma fibrinogen level, BMI and lipid profile in type 2 diabetes mellitus with hypertension
 World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
World Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences ISSN (Print): 2321-3310; ISSN (Online): 2321-3086 Published by Atom and Cell Publishers All Rights Reserved Available online at: http://www.wjpsonline.org/ Original
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Apolipoprotein B (APOB or ApoB) are the primary apolipoproteins of chylomicrons and low-density lipoproteins (LDL - known commonly by the misnomer "bad cholesterol"
Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques)
 Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques) Dr Judy Sheard Senior Lecturer Co-Director, Computing Education Research Group Monash University judy.sheard@monash.edu
Quantitative Methods in Computing Education Research (A brief overview tips and techniques) Dr Judy Sheard Senior Lecturer Co-Director, Computing Education Research Group Monash University judy.sheard@monash.edu
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
INTRODUCTION. FI Tornio, Finland. 5 Abbreviations used: IDL, intermediate-density lipoprotein; NMR, nuclear
 Effects of sea buckthorn and bilberry on serum metabolites differ according to baseline metabolic profiles in overweight women: a randomized crossover trial 1 4 Petra S Larmo, Antti J Kangas, Pasi Soininen,
Effects of sea buckthorn and bilberry on serum metabolites differ according to baseline metabolic profiles in overweight women: a randomized crossover trial 1 4 Petra S Larmo, Antti J Kangas, Pasi Soininen,
A comparative study on the fasting and post prandial lipid levels as a cardiovascular risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Original Research Article A comparative study on the fasting and post prandial lipid levels as a cardiovascular risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus Deepa Kalikavil Puthenveedu 1, Sundaraj
Original Research Article A comparative study on the fasting and post prandial lipid levels as a cardiovascular risk factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus Deepa Kalikavil Puthenveedu 1, Sundaraj
Supplementary Figure 1 (previous page). EM analysis of full-length GCGR. (a) Exemplary tilt pair images of the GCGR mab23 complex acquired for Random
 S1 Supplementary Figure 1 (previous page). EM analysis of full-length GCGR. (a) Exemplary tilt pair images of the GCGR mab23 complex acquired for Random Conical Tilt (RCT) reconstruction (left: -50,right:
S1 Supplementary Figure 1 (previous page). EM analysis of full-length GCGR. (a) Exemplary tilt pair images of the GCGR mab23 complex acquired for Random Conical Tilt (RCT) reconstruction (left: -50,right:
Supplemental Information. LipiDex: An Integrated Software Package. for High-Confidence Lipid Identification
 Cell Systems, Volume 6 Supplemental Information LipiDex: An Integrated Software Package for High-Confidence Lipid Identification Paul D. Hutchins, Jason D. Russell, and Joshua J. Coon Figure S1. Omics
Cell Systems, Volume 6 Supplemental Information LipiDex: An Integrated Software Package for High-Confidence Lipid Identification Paul D. Hutchins, Jason D. Russell, and Joshua J. Coon Figure S1. Omics
Control 7 d cold 7 d CL
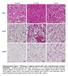 Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Control 7 d cold 7 d ibat iwat gwat Supplementary Figure 1. Histology of adipose tissues after cold or 3-adrenergic receptor stimulation. C57BL/6J wild-type mice were housed at 4 C or injected daily with
Supplementary material
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition involves triacylglycerol accumulation in DU145
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for Molecular BioSystems. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2015 Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition involves triacylglycerol accumulation in DU145
BCH 447. Triglyceride Determination in Serum
 BCH 447 Triglyceride Determination in Serum Introduction: Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed by lipase to glycerol and free fatty acids. Triglyceride determinations when performed
BCH 447 Triglyceride Determination in Serum Introduction: Triglycerides are esters of fatty acids and are hydrolyzed by lipase to glycerol and free fatty acids. Triglyceride determinations when performed
3.1.3 Lipids. Source: AQA Spec
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
LEPTIN AS A NOVEL PREDICTOR OF DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH THE METABOLIC SYNDROME
 LEPTIN AS A NOVEL PREDICTOR OF DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH THE METABOLIC SYNDROME Diana A. Chirinos, Ronald Goldberg, Elias Querales-Mago, Miriam Gutt, Judith R. McCalla, Marc Gellman and Neil Schneiderman
LEPTIN AS A NOVEL PREDICTOR OF DEPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH THE METABOLIC SYNDROME Diana A. Chirinos, Ronald Goldberg, Elias Querales-Mago, Miriam Gutt, Judith R. McCalla, Marc Gellman and Neil Schneiderman
Fats, Cholesterol, and Hormones
 Fats, Cholesterol, and Hormones 1 Types of Fats Lipids biological origin sparingly soluble in water Main classes of lipids Fatty Acids long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid on one end Triacylglycerols
Fats, Cholesterol, and Hormones 1 Types of Fats Lipids biological origin sparingly soluble in water Main classes of lipids Fatty Acids long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid on one end Triacylglycerols
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
