SYLLABUS. Neuromuscular Physiopathology II (PHPA-212) 3.5 units, 55 hours (5 hours lecture/week),
|
|
|
- Eugenia Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SYLLABUS NAME OF COURSE: LENGTH OF COURSE: Neuromuscular Physiopathology II (PHPA-212) 3.5 units, 55 hours (5 hours lecture/week), COURSE DESCRIPTION: This course examines a number of nervous system functions and the pathologies that affect them. The mechanisms by which the nervous system controls sensory and motor processes, vision and autonomic function will be explored along with pathologies that affect these functions. PREREQUISITES: PHYS-122, PHPA-131, ANAT-138 COURSE OFFERED BY: REQUIRED TEXTS: Basic Sciences Department NMPHPA 2 - course notes (Canvas) NMPHPA 2 - study guide (Canvas) Blumenfeld H. Neuroanatomy through Clinical Cases, 2 nd ed., 2010 RECOMMENDED TEXTS: Waxman S. Clinical Neuroanatomy. 27 th ed., 2013 Kierman, J Barr s The Human Nervous System. 10 th ed., 2014 Nolte J. The Human Brain. 6 th ed, 2009 Snell R., Westmoreland B. Clinical Neuroanatomy. 7 th ed., 2010 Cramer G., Darby S. Basic & Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord and ANS, 3 nd ed., 2014 REFERENCE TEXTS: Kandel ER. Principles of Neural Science. 5 th ed, 2013 MATERIALS: handouts may be provided METHOD OF INSTRUCTION: lecture, assignments, Q&A as applicable/as time allows EVALUATION: MT 1 (Wed. week 5): 25% MT 2 (Wed. week 9): 25% Final (comprehensive): 50% Assignments pass/fail Exam questions may be drawn from the following formats (in any combination or proportion): * multiple choice, T/F, * fill in the blank, short answer * short answer/written Approved OAA/Department February P a g e
2 Quarter grades will be assigned according to the following percentage ranges: A Superior Work % B Above Average Work 80-89% C Average Work 70-79% F Failure - The student must REPEAT the course below 70% I Incomplete - The Student has failed to take all required exams and/or has failed to turn in other required work. 0 Overcut - The Student has accumulated more than 10% absence in the course. EXTRA CREDIT: There will be no extra credit work permitted in this class. Grades and the Grading System Final Grades are available online through the CAMS student portal. If there are any questions on grading procedures, computation of grade point average, or the accuracy of the grade report, please contact the Registrar s Office or the Office of Academic Affairs. Grades will be reported and evaluation will be based on the Academic Policies, Procedures, & Services. Please refer to Evaluation Policy (Policy ID: OAA.0007) In order to maintain Satisfactory Academic Progress, a student must maintain a 2.0 or better in each and every course. Any grade less than a C must be remedied by repeating the class. Please refer to Satisfactory Academic Progress (Policy ID: OAA.0006) Attendance: Conduct and Responsibilities: Make-up Exams: Request for Special Testing: Please refer to Attendance Policy (Policy ID: OAA.0002) Please refer to the Personal Conduct, Responsibility and Academic Responsibility Policy (Policy ID: OAA.0003) Please refer to Make-up Assessment Policy (Policy ID: OAA.0001) Please refer to Request for Special Testing (Policy ID: OAA.0004) Accommodation for Students with Disabilities: If you have approved accommodations, please make an appointment to meet with your instructor as soon as possible. If you believe you require an accommodation, but do not have an approved accommodation letter, please see the Academic Counselor Lori Pino in the Office of Academic Affairs. Contact info: Lpino@lifewest.edu or ext Please refer to Service for Students with Disabilities Policy (Policy ID: OAA.0005) Electronic Course Management: Canvas is LCCW s Learning Management System (LMS). Canvas will be used throughout the
3 quarter during this course. Lectures, reminders, and messages will be posted. In addition, documents such as the course syllabus and helpful information about the class project will be posted. Students are expected to check Canvas at least once a week in order to keep updated. The website address for Canvas is Please refer to the Educational Technologies Policy (Policy ID: OAA.0009) PROCEDURES FOR REVIEWING EXAMS: The instructor had not authorized distribution of old exams. Any possession of old exams is prohibited. The instructor may either conduct review sessions in class or may meet with a student to review his or her exam during office hours for two weeks following the exam (unless there is a shorter time period until the last scheduled office hour during the last week of classes.) Students may not review mid-term exams during final exam week. The possession of any exam other than during a review session constitutes unprofessional conduct. COURSE GOAL: As the last basic science course in neurology, the goal of NMPHPA 2 is to help students solidify and expand their understanding of the structure and function of the nervous system, to further prepare the student for the NBCE part 1 examinations, and to serve as a bridge between the basic science courses of neuroanatomy, neurophysiology, neuropathology, and the clinical application subjects of neurologic examination and diagnosis. COURSE OBJECTIVES OVERVIEW (see detailed, week-by-week objectives after the Student Learning Outcomes and Program Learning Outcomes sections below) 1. Review the basic embryology of the nervous system. 2. Review and further discuss the anatomy and physiology (structure and function) of the nervous system: CNS: a. cerebral hemispheres b. diencephalon (thalamus & hypothalamus) c. brainstem & cranial nerves d. cerebellum e. basal ganglia f. spinal cord PNS: a. spinal nerves b. peripheral nerves 3. Describe the somatosensory system from receptors to the somatosensory cortex. Approved OAA/Department February P a g e
4 4. Describe the somatomotor system from somatomotor cortex to skeletal muscle. 5. Describe the basic anatomy and function of the autonomic nervous system. 6. Discuss relevant pathologies affecting each portion of the nervous system. 7. Discuss the neurologic mechanisms involved in modulation of nociception: a. suprasegmental b. segmental (spinal gating) 8. Discuss the dysafferentation model of subluxation and differentiate it from the garden hose model. 9. Discuss sclerogenic connective tissue referred pain and referral patterns from cervical and lumbar joints. STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (SLOs): 1. The student will be able to discuss the basic clinically relevant anatomy and physiology of the nervous system (brain, spinal cord, spinal nerves, & peripheral nerves). [PLO: 1, 8] 2. The student will be able to discuss relevant pathologies affecting each portion of the nervous system, including the nature of the pathology, and the major associated symptoms and signs. [PLO: 1, 8] 3. The student will be able to describe dermatome and peripheral nerve sensory distributions, and for any given area of pain/tingling/numbness the student will be able to identify the likely involved spinal nerve and peripheral nerve. [PLO: 1, 2, 4, 8] 4. The student will be able to analyze neurologic exam data to localize classic neurologic lesions - peripheral and central. [PLO: 1, 2, 4, 6, 8] 5. The student will be able to compare & contrast UMN & LMN lesion signs. [PLO: 1, 4] 6. The student will be able to explain the concept of sclerogenic referred connective tissue pain, and describe referred pain patterns associated with cervical and lumbar joints. [PLO: 1, 2, 4, 8, 10] 7. The student will able to explain the neural mechanisms involved in modulation of nociception (segmental and suprasegmental), and how the chiropractic adjustment potentially activates these mechanisms. [PLO: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 10
5 Program Learning Outcomes (PLO): Students graduating with a Doctor of Chiropractic degree will be proficient in the following: 1. ASSESSMENT AND DIAGNOSIS: An assessment and diagnosis requires developed clinical reasoning skills. Clinical reasoning consists of data gathering and interpretation, hypothesis generation and testing, and critical evaluation of diagnostic strategies. It is a dynamic process that occurs before, during, and after the collection of data through history, physical examination, imaging, laboratory tests and case-related clinical services. 2. MANAGEMENT PLAN: Management involves the development, implementation and documentation of a patient care plan for positively impacting a patient s health and wellbeing, including specific therapeutic goals and prognoses. It may include case follow-up, referral, and/or collaborative care. 3. HEALTH PROMOTION AND DISEASE PREVENTION: Health promotion and disease prevention requires an understanding and application of epidemiological principles regarding the nature and identification of health issues in diverse populations and recognizes the impact of biological, chemical, behavioral, structural, psychosocial and environmental factors on general health. 4. COMMUNICATION AND RECORD KEEPING: Effective communication includes oral, written and nonverbal skills with appropriate sensitivity, clarity and control for a wide range of healthcare related activities, to include patient care, professional communication, health education, and record keeping and reporting. 5. PROFESSIONAL ETHICS AND JURISPRUDENCE: Professionals comply with the law and exhibit ethical behavior. 6. INFORMATION AND TECHNOLOGY LITERACY: Information literacy is a set of abilities, including the use of technology, to locate, evaluate and integrate research and other types of evidence to manage patient care. 7. CHIROPRACTIC ADJUSTMENT/MANIPULATION: Doctors of chiropractic employ the adjustment/manipulation to address joint and neurophysiologic dysfunction. The adjustment/manipulation is a precise procedure requiring the discrimination and identification of dysfunction, interpretation and application of clinical knowledge; and, the use of cognitive and psychomotor skills. 8. INTERPROFESSIONAL EDUCATION: Students have the knowledge, skills and values necessary to function as part of an inter-professional team to provide patientcentered collaborative care. Inter-professional teamwork may be demonstrated in didactic, clinical or simulated learning environments. 9. BUSINESS: Assessing personal skills and attributes, developing leadership skills, leveraging talents and strengths that provide an achievable expectation for graduate success. Adopting a systems-based approach to business operations. Networking with practitioners in associated fields with chiropractic, alternative medicine and allopathic medicine. Experiencing and acquiring the hard business skills required to open and operate an on-going business concern. Participating in practical, real time events that promote business building and quantifiable marketing research outcomes 10. PHILOSOPHY: Demonstrates an ability to incorporate a philosophically based Chiropractic paradigm in approach to patient care. Demonstrates an understanding of both traditional and contemporary Chiropractic philosophic concepts and principles. Demonstrates an understanding of the concepts of philosophy, science, and art in chiropractic principles and their importance to chiropractic practice. Approved OAA/Department February P a g e
6 COURSE OBJECTIVES - DETAILED - review the syllabus: policies & procedures - provide an overview of the course Week 1-5: MT 1 content - differentiate the dysafferentation and garden hose theories of subluxation - discuss the basic principles of neurologic exam & diagnosis - define basic neurologic terms (radiculopathy, neuropathy, myelopathy, etc.) - provide an overview of nervous system structure and function - discuss the division of the nervous system into motor and sensory divisions, and into somatic and visceral divisions (GSE, GVE, GSA, GVA) - review spinal cord anatomy - gray matter - dorsal, ventral, and lateral horns (IML), lamina of Rexed - white matter (anterior, lateral, posterior columns) - tracts located in the different columns - compare and contrast somatomotor and visceromotor output/projections - compare & contrast the transmission of pain/temp and tactile sensation in the CNS (STT vs. DC/ML) - review the basic anatomy of upper & lower motor neurons (UMN & LMN); - describe the lateral vs. medial motor systems of the spinal cord, - describe the vestibulospinal tract s role in maintaining balance and UMN innervation of intrinsic spinal muscles - describe the role of the medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) in the coordination of head and eye movement - describe the basic anatomy of the autonomic nervous system (ANS), including the - intermediolateral cell column (IML), - pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic neurons, - sympathetic paravertebral chain - sympathetic innervation of the upper & lower extremities - sympathethetic innervation of the head & face, and Horner's syndrome
7 - provide a review of PNS structure/function: spinal & peripheral nerves - discuss spinal nerves and their anatomic relations to IVFs and discs in the cervical and lumbar spine - discuss causes of radiculopathy - discuss the localizing value of the distribution of pain, tingling, and numbness - review dermatomes and peripheral nerve sensory distributions - review the motor functions of spinal nerves ( myotomes ) & peripheral nerves - review the distribution and functions of peripheral nerves in the UE & LE - identify peripheral nerve entrapment sites (pronator teres, supinator, etc.) - discuss Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) - discuss the significance of saddle anesthesia as a red flag for cauda equina syndrome (CES), the potential parasympathetic S&S of CES, and the appropriate clinical management of CES - discuss the clinical picture of vertebral DJD - introduce the concept of CT referred (sclerogenic) pain; describe sclerogenic referred pain pattern from cervical & lumbar joints - introduce radiculopathy - introduce cervical spondylotic myelopathy: pathophysiology, radiologic measurement of the spinal canal, S&S - briefly discuss the cerebrum (further discussion in week 10, as time allows) - lobes and their basic function(s) - somatosensory cortex, and its homunculus distribution (also see SS system) - motor cortex, and its homunculus distribution (also see somatomotor system) - vascular supply - language centers - prefrontal cortex - subcortical nuclei ('corpus striatum') - briefly discuss the basal ganglia (also see somatomotor system) - main components - connection with motor cortex - relation between side of lesion and side of clinical S&S - briefly discuss cerebellum (also see somatomotor system) - functional divisions - main functions - connections to motor cortex - relation between side of lesion and side of clinical S&S - briefly discuss the thalamus (further discussion in week 10, as time allows) - briefly discuss the hypothalamus (further discussion in week 10, as time allows) Approved OAA/Department February P a g e
8 - Somatosensory system: discuss the somatosensory system from receptor to somatosensory cortex - discuss the primary afferent fibers, their receptors & functions, and their categorization based upon conduction velocity - discuss the deep tendon (DTR) / muscle stretch reflex (MSR) - differentiate the function of muscle spindle and GTO - describe how GTO mechanisms may explain the reduction of taut fibers after an adjustment - review the sensory distributions of spinal nerves (dermatomes) & peripheral nerves - review somatosensory transmission in the spinal cord - discuss spinal cord pathologies - review syringomyelia - review Brown-Sequard syndrome - discuss somatosensory transmission in the brainstem - review somatosensory transmission from the body through the brainstem - discuss somatosensory transmission from the face (trigemino-spinal tract and nucleus), and the classic somatosensory deficits associated with dorsolateral medullary (Wallenberg) syndrome - discuss cervicogenic facial pain (convergence of nociceptive input from the upper cervical region and the face) - review thalamic relay of somatosensory information - describe thalamic pain syndrome, and differentiate neuropathic and nociceptive pain - discuss the somatosensory cortex - review the somatosensory body map (homunculus), and it s vascular supply - discuss agnosis : astereognosis, agraphognosis / agraphesthesia and extinction - discuss modulation of nociception - discuss segmental modulation of nociception ( spinal gating ), and the relevance of chiropractic - discuss "suprasegmental" modulation of nociception - start discussion of somatomotor system (as time allows) - review the basic concept of UMNs & LMNs
9 Week 6-9: Midterm 2 content - Somatomotor system: discuss somatomotor system anatomy, physiology, and pathology from motor cortex to skeletal muscle - discuss UMN & LMN anatomy and function - review the motor cortex (homunculus, vascular supply, etc.) - review UMNs in brain and spinal cord - differentiate alpha & gamma motor neuron innervation of extrafusal & intrafusal muscle fibers - discuss the control of the sensitivity the muscle spindle receptor - compare & contrast the clinical S&S of UMN and LMN lesions - discuss examples of UMN lesion - CVA/stroke - spinal cord injury - multiple sclerosis - subacute combined systems disease (posterolateral sclerosis) - parasagittal meningioma - discuss examples of LMN lesion - Bell s palsy - poliomyelitis - Guillain-Barre syndrome (acute inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy) - discuss NMJ anatomy, physiology, and pathology - discuss Myasthenia Gravis - discuss botulism and Lambert-Eaton syndrome - discuss myopathy - define muscular dystrophy - describe the S&S of myopathy - list the lab tests used to confirm suspected myopathy - discuss the cerebellum - discuss cerebellar anatomy, physiology, and pathology - describe the transverse and longitudinal anatomy - describe the cortical and subcortical anatomy Approved OAA/Department February P a g e
10 - describe the microscopic anatomy (cells, fiber types) - discuss the functional regions - discuss the S&S of cerebellar lesion - describe tests of limb coordination and appropriate terminology - discuss the Romberg test - differentiate positive vs. negative Romberg signs - discuss the significance of a positive Romberg sign - describe how polyneuropathy and multiple sclerosis may cause a positive Romberg sign - discuss basal ganglia anatomy, physiology, and pathology - list the components of the basal ganglia - describe the connection of the basal ganglia & the motor cortex - discuss the major S&S of basal ganglia lesion - discuss Parkinson disease - describe the pathophysiology of PD - describe the common S&S of PD Week 9-10: additional content for final exam - discuss cranial nerve anatomy, physiology, and pathology - identify cranial nerves with sensory, motor, and reflex functions - identify cranial nerves with parasympathetic functions - discuss causes of loss of smell (anosmia) - describe the visual pathway, and discuss the visual deficits associated with pre-chiasmal, chiasmal, and retro-chiasmal lesions - discuss the pupillary/light and consensual pupillary/light reflex - discuss the innervation and control of extraocular movement - discuss dysconjugate gaze and diplopia - differentiate parasympathetic & sympathetic effects on pupillary size - differentiate ptosis caused by CN III lesion and Horner s syndrome based upon pupillary size; - describe the sensory, motor, and reflex functions of the trigeminal nerve - discuss Opthalmic Herpes - discuss trigeminal neuralgia - describe the jaw jerk reflex - describe the corneal/blink reflex - describe the sensory, motor, and reflex functions of the facial nerve - discuss Bell s palsy (LMN facial weakness), and differentiate it from UMN facial weakness; discuss the natural history of Bell s palsy - describe cranial nerve innervation of taste - describe cranial nerve innervation of salivation - discuss the sensory functions of CN VIII - describe the auditory pathway
11 - define conductive & sensorineural hearing loss - discuss acoustic neuroma & cerebellopontine angle tumors - describe vestibular input, and its connections and functions - discuss the significance of uvula deviation and palatal paresis - discuss the significance of tongue deviation upon protrusion - discuss the innervation of the SCM and upper trapezius AS time allows (based upon holidays and other class cancellations): - Cerebral hemisphere: further discussion of cerebral hemisphere anatomy, physiology, and pathology - describe the components of the cerebral hemispheres (cortex, subcortex, corpus striatum) - list the components of the basal ganglia; describe the connections of the basal ganglia and motor cortex, common S&S of BG lesions - list the lobes of the cerebral cortex and their basic functions - describe the primary & uni-modal association sensory cortical regions - describe the primary & uni-modal motor cortical regions (primary motor & motor association cortex) - describe the multi-modal association cortical regions (PTO & prefrontal) - discuss the functions of the prefrontal cortex, and implications of dysfunction - describe the body map (homunculus) of the somatosensory & somatomotor cortex - describe the vascular supply to the cerebral cortex (int. carotid vs VB; ACA vs MCA) - describe the language centers of the cerebral cortex; describe & differentiate Wernicke s & Broca s aphasia - define seizure, tonic-clonic & absence seizure - discuss dementia & Alzheimer s disease - Thalamus: further discussion of thalamic anatomy, physiology, and pathology - discuss the integrative functions of the thalamus (thalamus as gate-keeper rather than gateway ) - discuss Dr. Carrick s article Changes in brain function following manipulation of the cervical spine, and the concepts of blind spots & hemisphericity - describe the relay functions of the thalamus (somatosensory, special sensory, somatomotor, limbic, etc.) - discuss the diffuse-projecting nuclei of the thalamus, and their role regulating cortical neuronal activity (consciousness & arousal aspect of nociception) - discuss the reticular nucleus and it s role in regulating neuronal activity of other thalamic nuclei Approved OAA/Department February P a g e
12 - Hypothalamus: discuss hypothalamus anatomy, physiology, and pathology - describe role in maintenance of homeostasis - describe role in autonomic function - define Horner s syndrome, and discuss its etiology (Pancoast tumor, etc.), and S&S - describe role in endocrine function, and connections to the anterior and posterior pituitary - describe role in suprasegmental modulation of nociception
SYLLABUS. 2 units, 33 hours (3 hours lecture/week)
 SYLLABUS NAME OF COURSE: Neurologic Examination (DIAG-237) LENGTH OF COURSE: 2 units, 33 hours (3 hours lecture/week) COURSE DESCRIPTION: PREREQUISITES: CO-REQUISITES: These courses cover the examination
SYLLABUS NAME OF COURSE: Neurologic Examination (DIAG-237) LENGTH OF COURSE: 2 units, 33 hours (3 hours lecture/week) COURSE DESCRIPTION: PREREQUISITES: CO-REQUISITES: These courses cover the examination
SYLLABUS. Systemic & Histology Anatomy Lecture ANAT-110/610(lab) 3.5 units, 55 hrs (5 hrs lecture /week) lec; 1 unit, 20 hrs lab
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Systemic & Histology Anatomy Lecture ANAT-110/610(lab) 3.5 units, 55 hrs (5 hrs lecture /week) lec; 1 unit, 20 hrs lab An introduction
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Systemic & Histology Anatomy Lecture ANAT-110/610(lab) 3.5 units, 55 hrs (5 hrs lecture /week) lec; 1 unit, 20 hrs lab An introduction
SYLLABUS. DIAG-340, HC-310, ACS324, ACS345 AND (DIAG327 OR DIAG351) AND (DIAG327 OR DIAG352) Clinical Sciences Department
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Differential Diagnosis A-DIAG-408 Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Recommended Texts: Required Text: 2 units, 33 hours (3 hour lecture/week)
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Differential Diagnosis A-DIAG-408 Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Recommended Texts: Required Text: 2 units, 33 hours (3 hour lecture/week)
SYLLABUS. Name of Course: Physiotherapy 1 (Active Care/Rehabilitation) ACS 322
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Physiotherapy 1 (Active Care/Rehabilitation) ACS 322 Length of Course: 44 hours, 4 hours of lecture per week Course Description: Prerequisites: This course is an introduction to
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Physiotherapy 1 (Active Care/Rehabilitation) ACS 322 Length of Course: 44 hours, 4 hours of lecture per week Course Description: Prerequisites: This course is an introduction to
Clinical Sciences Department. Notes on reserve in the library
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Practical Radiology ACS 407 Length of Course: 2 units, 33 hours Course Description: This course is directed to the understanding of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the spine and
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Practical Radiology ACS 407 Length of Course: 2 units, 33 hours Course Description: This course is directed to the understanding of Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the spine and
SYLLABUS. Recommended Texts: Marieb, E. N., & Hoehn, K. Ninth Edition Human Anatomy and Physiology. (PAGES 173 through 275) AND
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: ANAT 111/611 (LEC/LAB) Skeletal Anatomy Length of Course: 22 hours, 1.5 units (2 hours lecture per week) Course Description: This course uses an integrative approach to the skeletal
SYLLABUS Name of Course: ANAT 111/611 (LEC/LAB) Skeletal Anatomy Length of Course: 22 hours, 1.5 units (2 hours lecture per week) Course Description: This course uses an integrative approach to the skeletal
SYLLABUS. 1.5 units, 30 hour (1 hour lecture/2 hour lab)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisite: Course Offered By: Required Text: Recommended Text: Reference Text: BASIC ACTIVATOR METHODS TECH-185 1.5 units, 30 hour (1 hour
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisite: Course Offered By: Required Text: Recommended Text: Reference Text: BASIC ACTIVATOR METHODS TECH-185 1.5 units, 30 hour (1 hour
SYLLABUS. 2.0 units, 33 hours (3 hours lecture per week)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Bone and Joint Pathodiagnosis, PATH-315 2.0 units, 33 hours (3 hours lecture per week) Course Description: This course focuses on the pathophysiology and clinical
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Bone and Joint Pathodiagnosis, PATH-315 2.0 units, 33 hours (3 hours lecture per week) Course Description: This course focuses on the pathophysiology and clinical
SYLLABUS. Extremity Biomechanics and Examination of the Upper Extremity (DIAG 351/851) 1 unit, 22 Hours (1 Hour Lecture, 1 Hour Lab/Wk)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Required Texts: Recommended Texts: Extremity Biomechanics and Examination of the Upper Extremity (DIAG 351/851)
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Required Texts: Recommended Texts: Extremity Biomechanics and Examination of the Upper Extremity (DIAG 351/851)
SYLLABUS. 1.5 Units, 31 Hours (1 hour lecture, 2 hours lab per week)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Method of Instruction: Required Text: Recommended Text: Reference Texts: Materials: Gonstead Analysis TECH
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Method of Instruction: Required Text: Recommended Text: Reference Texts: Materials: Gonstead Analysis TECH
SYLLABUS. Name of Course: Diversified Analysis - TECH 124/ units, 31 hours - 2 hrs lab & 1 hr lecture
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Diversified Analysis - TECH 124/624 Length of Course: 1.5 units, 31 hours - 2 hrs lab & 1 hr lecture Course Description: The course functions as an introduction to the use of various
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Diversified Analysis - TECH 124/624 Length of Course: 1.5 units, 31 hours - 2 hrs lab & 1 hr lecture Course Description: The course functions as an introduction to the use of various
SYLLABUS. 1.5 units, 31 hours (1 hr. lecture/2 hrs. lab-demo/week)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Department Objective: Integrated Drop Table TECH-325/825 1.5 units, 31 hours (1 hr. lecture/2 hrs. lab-demo/week)
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Department Objective: Integrated Drop Table TECH-325/825 1.5 units, 31 hours (1 hr. lecture/2 hrs. lab-demo/week)
SYLLABUS. 3.5 units, 55 hours (5 hours lecture/week) DIAG-226, DIAG-239, HC-310. Technique Department
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Diagnosis and Management of Spinal Disorders (TECH -333) Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Required Text: 3.5 units, 55 hours (5 hours lecture/week)
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Diagnosis and Management of Spinal Disorders (TECH -333) Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Required Text: 3.5 units, 55 hours (5 hours lecture/week)
SYLLABUS. 3.5 units; 55 hours (5 hrs lecture per week)
 SYLLABUS NAME OF COURSE: Biochemistry 1 - CHEM 121 LENGTH OF COURSE: 3.5 units; 55 hours (5 hrs lecture per week) COURSE DESCRIPTION: Biochemistry 1 studies the structure, function and performance relationships
SYLLABUS NAME OF COURSE: Biochemistry 1 - CHEM 121 LENGTH OF COURSE: 3.5 units; 55 hours (5 hrs lecture per week) COURSE DESCRIPTION: Biochemistry 1 studies the structure, function and performance relationships
Basic Sciences Department
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Biochemistry 2, CHEM 133 Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Required Texts: 3.5 units; 55 hours (5 hrs lecture per week) Biochemistry 2 studies
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Biochemistry 2, CHEM 133 Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Required Texts: 3.5 units; 55 hours (5 hrs lecture per week) Biochemistry 2 studies
SYLLABUS. Advanced Adjusting for Physically Compromised Patients TECH units, 30 hours (2 hour lecture/1 hour lab/week)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Required Text: Advanced Adjusting for Physically Compromised Patients TECH-188 1.5 units, 30 hours (2 hour
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Required Text: Advanced Adjusting for Physically Compromised Patients TECH-188 1.5 units, 30 hours (2 hour
SYLLABUS. Network Spinal Analysis Basic Care Technique Elective ACS-084
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Network Spinal Analysis Basic Care Technique Elective ACS-084 Length of Course: 1.5 units, 30 hours Course Description: This elective course explores the theory, analysis and protocol
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Network Spinal Analysis Basic Care Technique Elective ACS-084 Length of Course: 1.5 units, 30 hours Course Description: This elective course explores the theory, analysis and protocol
SYLLABUS. The student will learn the basic psychomotor skills necessary for the assessment of the human spine.
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Course Goal: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Palpation I (Bony Spinal Palpation) TECH-116 1 unit, 20 hours (2 hours lab-demo/week) In this
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Course Goal: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Palpation I (Bony Spinal Palpation) TECH-116 1 unit, 20 hours (2 hours lab-demo/week) In this
SYLLABUS. 2.5 units, 51 hours (1 hr lecture, 4 hours lab/week)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Diversified Technique I - TECH-130/630 2.5 units, 51 hours (1 hr lecture, 4 hours lab/week) Course Description: This is the first adjustive technique course offered
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Diversified Technique I - TECH-130/630 2.5 units, 51 hours (1 hr lecture, 4 hours lab/week) Course Description: This is the first adjustive technique course offered
SYLLABUS. Extremity Biomechanics and Examination of the Lower Extremity DIAG 352/ unit,32 Hours (2 Hours Lecture, 1 Hour Lab/Wk)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Extremity Biomechanics and Examination of the Lower Extremity DIAG 352/852 Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Required Texts: Recommended Texts:
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Extremity Biomechanics and Examination of the Lower Extremity DIAG 352/852 Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered by: Required Texts: Recommended Texts:
SYLLABUS. The Pathology of Infectious Diseases (PATH-217)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: The Pathology of Infectious Diseases (PATH-217) 3 units, 44 hrs. (4 hrs. lecture/week) The course is a study
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: The Pathology of Infectious Diseases (PATH-217) 3 units, 44 hrs. (4 hrs. lecture/week) The course is a study
Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences
 Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
Spinal Cord I Lecture Outline and Objectives CNS/Head and Neck Sequence TOPIC: FACULTY: THE SPINAL CORD AND SPINAL NERVES, Part I Department of Neurology/Division of Anatomical Sciences LECTURE: Monday,
SYLLABUS. Class notes Available in the bookstore Yochum TR. Essentials of Skeletal Radiology. 3 rd ed. 2005
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Required Text: Recommended Text: Reference Texts: Materials: Method of Instruction: RADIOLOGY 1 (ACS-313)
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisites: Course Offered By: Required Text: Recommended Text: Reference Texts: Materials: Method of Instruction: RADIOLOGY 1 (ACS-313)
Guide to Draw It to Know It Neuroanatomy (relative to Medical Neuro, UI-COM Urbana)
 Guide to Draw It to Know It Neuroanatomy (relative to Medical Neuro, UI-COM Urbana) Note: Sometimes DITKI goes into far more detail than is necessary for the course, and in other cases not enough. As helpful
Guide to Draw It to Know It Neuroanatomy (relative to Medical Neuro, UI-COM Urbana) Note: Sometimes DITKI goes into far more detail than is necessary for the course, and in other cases not enough. As helpful
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Spinal Cord Organization. January 12, 2011
 Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
Spinal Cord Organization January 12, 2011 Spinal Cord 31 segments terminates at L1-L2 special components - conus medullaris - cauda equina no input from the face Spinal Cord, Roots & Nerves Dorsal root
The Nervous System. Divisions of the Nervous System. Branches of the Autonomic Nervous System. Central versus Peripheral
 The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
The Nervous System Divisions of the Nervous System Central versus Peripheral Central Brain and spinal cord Peripheral Everything else Somatic versus Autonomic Somatic Nerves serving conscious sensations
Laith Sorour. Facial nerve (vii):
 Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII
 Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to Sensory Pathways and
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain
 Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
Nervous System: Part IV The Central Nervous System The Brain Can you survive when part of your brain is destroyed? 2 Essential Knowledge 3.D.2 2. Cells communicate with each other through direct contact
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Spring Semester OST 571 Neuromusculoskeletal Lecture-Lab Schedule Revised
 Revised 1-07-16 Week 1: Monday, January 11, 2016 9:00-9:50 a.m. 001 - Principles of Neurobiology/Orientation Lovell Online 10:00-10:50 a.m. 002 - Cells, synapses & neurotransmitter systems Nazaroff Online
Revised 1-07-16 Week 1: Monday, January 11, 2016 9:00-9:50 a.m. 001 - Principles of Neurobiology/Orientation Lovell Online 10:00-10:50 a.m. 002 - Cells, synapses & neurotransmitter systems Nazaroff Online
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies
 The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests
The Neurologic Examination: High-Yield Strategies S. Andrew Josephson, MD Examination Approach Two types of neurologic examinations 1. Screening Examination 2. Testing Hypotheses Select high-yield tests
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Spring Semester OST 571 Neuromusculoskeletal Lecture-Lab Schedule
 Week 1: Monday, January 5, 2015 9:00-9:50 a.m. 001 - Principles of Neurobiology Lovell Online 10:00-10:50 a.m. 002 - Cells, synapses & neurotransmitters Nazaroff Online 11:00-11:50 a.m. 003 - Development
Week 1: Monday, January 5, 2015 9:00-9:50 a.m. 001 - Principles of Neurobiology Lovell Online 10:00-10:50 a.m. 002 - Cells, synapses & neurotransmitters Nazaroff Online 11:00-11:50 a.m. 003 - Development
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTE M Structure and Functio n THIRD EDITIO N PER BRODAL A Brief Survey, x i Studying the Structures and Function of the Nervous System, xii i Animal Experiments Crucial for Progress,
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Arterial Blood Supply
 Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
Arterial Blood Supply Brain is supplied by pairs of internal carotid artery and vertebral artery. The four arteries lie within the subarachnoid space Their branches anastomose on the inferior surface of
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Homework Week 2. PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section)
 Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
Homework Week 2 Due in Lab PreLab 2 HW #2 Synapses (Page 1 in the HW Section) Reminders No class next Monday Quiz 1 is @ 5:30pm on Tuesday, 1/22/13 Study guide posted under Study Aids section of website
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
INTRODUCTION to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science
Nervous System. The Peripheral Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Reflexes Pathways
 Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Nervous System Agenda Review of CNS v. PNS PNS Basics Cranial Nerves Spinal Nerves Sensory Motor Review of CNS v. PNS Central nervous system (CNS) Brain Spinal cord Peripheral nervous system (PNS) All
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
OVERVIEW. Today. Sensory and Motor Neurons. Thursday. Parkinsons Disease. Administra7on. Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online
 OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
OVERVIEW Today Sensory and Motor Neurons Thursday Parkinsons Disease Administra7on Exam One Bonus Points Slides Online 7 major descending motor control pathways from Cerebral Cortex or Brainstem
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX
 CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
CEREBRUM & CEREBRAL CORTEX Seonghan Kim Dept. of Anatomy Inje University, College of Medicine THE BRAIN ANATOMICAL REGIONS A. Cerebrum B. Diencephalon Thalamus Hypothalamus C. Brain Stem Midbrain Pons
The Spinal Cord. The Nervous System. The Spinal Cord. The Spinal Cord 1/2/2016. Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum.
 The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
The Nervous System Spinal Cord Continuation of CNS inferior to foramen magnum Simpler than the brain Conducts impulses to and from brain Two way conduction pathway Reflex actions Passes through vertebral
Sympathetic Nervous System
 Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
Sympathetic Nervous System Lecture Objectives Review the subdivisions of the nervous system. Review the general arrangement and compare the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Describe the following
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D.
 SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
SOMATOSENSORY SYSTEMS: Pain and Temperature Kimberle Jacobs, Ph.D. Sensory systems are afferent, meaning that they are carrying information from the periphery TOWARD the central nervous system. The somatosensory
NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY
 NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
NTRODUCTON to NERVOUS SYSTEM ANATOMY M1 - Gross and Developmental Anatomy Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology and Dr. Michael H. Peters Professor of Chemical and Life Science Engineering
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center Course Syllabus Anatomy and Embryology for dental students (2)
 The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center Course Syllabus Anatomy and Embryology for dental students (2) Course title Anatomy and embryology for dental student (2) 2 Course number
The University of Jordan Accreditation & Quality Assurance Center Course Syllabus Anatomy and Embryology for dental students (2) Course title Anatomy and embryology for dental student (2) 2 Course number
Course Title: ANAT 6310, Fundamentals of Structure and Function in the Human Nervous System (4 credits)
 Course Title: ANAT 6310, Fundamentals of Structure and Function in the Human Nervous System (4 credits) Course Timeframe: March 17- May 2, 2014 Co-Course Directors: John Caldwell, Ph.D Professor, Cell
Course Title: ANAT 6310, Fundamentals of Structure and Function in the Human Nervous System (4 credits) Course Timeframe: March 17- May 2, 2014 Co-Course Directors: John Caldwell, Ph.D Professor, Cell
NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE. Academic Year Study Guide
 NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide CNS Objectives At the end of this course, students should recognize the followings: 1. Histological structure of the brain meninges and the supporting
NERVOUS SYSTEM MODULE Academic Year 2004-2005 Study Guide CNS Objectives At the end of this course, students should recognize the followings: 1. Histological structure of the brain meninges and the supporting
Course Calendar
 Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Clinical Neuroscience BMS 6706C Charles, Ph.D., Course Director charles.ouimet@med.fsu.edu (850) 644-2271 2004 2005 Course Calendar Click here to return to the syllabus Meeting Hours for entire semester:
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Chapter 14, Part 2! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial Nerves! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! White Matter of the Cerebrum! 1.
Cerebral hemisphere. Parietal Frontal Occipital Temporal
 Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Cerebral hemisphere Sulcus / Fissure Central Precental gyrus Postcentral gyrus Lateral (cerebral) Parieto-occipital Cerebral cortex Frontal lobe Parietal lobe Temporal lobe Insula Amygdala Hippocampus
Big Ideas. (e.g. puberty, immune function (autoimmune disorders)) 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
Nervous Systems Big Ideas 2.E.1: Timing and coordination of specific events are necessary for the normal development of an organism, and these events are regulated by a variety of mechanisms. (e.g. puberty,
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial Nerves! pp !
 Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Chapter 14, Part 2! The Cerebrum and Cranial pp. 482 505! SECTION 14-9! The cerebrum, the largest region of the brain, contains motor, sensory, and association areas! 2! 1! ! Chapter 14 Part 2 Brain/Cranial
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System
 C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
C h a p t e r 15 Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the Somatic Nervous System PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education,
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
Syllabus Directional Non-Force Technique 001 (TECH-193)
 Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisite: Tech 130 Course Offered By: Syllabus Directional Non-Force Technique 001 (TECH-193) 30 hours / 1.5 units This is an introduction to the
Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Prerequisite: Tech 130 Course Offered By: Syllabus Directional Non-Force Technique 001 (TECH-193) 30 hours / 1.5 units This is an introduction to the
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway
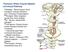 Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
Posterior White Column-Medial Lemniscal Pathway Modality: Discriminative Touch Sensation (include Vibration) and Conscious Proprioception Receptor: Most receptors except free nerve endings Ist Neuron:
SENSORY PLASTICITY. Sensory Plasticity
 801 Sensory Plasticity SENSORY PLASTICITY You may have the idea that the visual, auditory and somatosensory systems are static pathways (i.e., the neural wiring is in place and simply does its job). To
801 Sensory Plasticity SENSORY PLASTICITY You may have the idea that the visual, auditory and somatosensory systems are static pathways (i.e., the neural wiring is in place and simply does its job). To
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D.
 Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Spinal Cord H. Ruth Clemo, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should be familiar with: 1. Surface anatomy of the spinal cord. 2. Internal structure and organization
Human Anatomy. Autonomic Nervous System
 Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
Human Anatomy Autonomic Nervous System 1 Autonomic Nervous System ANS complex system of nerves controls involuntary actions. Works with the somatic nervous system (SNS) regulates body organs maintains
PSY 215 Lecture #5 (01/26/2011) (Anatomy of the Brain) Dr. Achtman PSY 215. Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96
 Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Corrections: none needed PSY 215 Lecture 5 Anatomy of the Brain Chapter 4, pages 86-96 Announcements: Reminder: The first midterm is in one week! Everyone is encouraged to start studying (recommend 30/night
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
SYLLABUS. Spinal Orthopedic Exam class notes (Canvas)
 SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Pre-requisites: Co-requisite: Course Offered By: Required Texts: Spinal Orthopedic Exam LAB (DIAG-739) 10 hours (1 hr lab/wk), 0.5 units This
SYLLABUS Name of Course: Length of Course: Course Description: Pre-requisites: Co-requisite: Course Offered By: Required Texts: Spinal Orthopedic Exam LAB (DIAG-739) 10 hours (1 hr lab/wk), 0.5 units This
Somatosensory System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
Somatosensory System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Dr. Riedl s review session this week: Tuesday (Oct 10) 4-5pm in MCB 3-146B 2 Sensory Systems Sensory
C14 / CNS / MC3. What two stuctures make up the central nervous system?
 C14 / CNS / MC3 What two stuctures make up the central nervous system? The CNS starts embryonic development as a neural tube. What adult structures develop from the neural tube? What structures are part
C14 / CNS / MC3 What two stuctures make up the central nervous system? The CNS starts embryonic development as a neural tube. What adult structures develop from the neural tube? What structures are part
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem
 Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Internal Organisation of the Brainstem Major tracts and nuclei of the brainstem (Notes) The brainstem is the major pathway for tracts and houses major nuclei, that contain sensory, motor and autonomics
Upon completion of this course, physical and occupational therapy students will be able to:
 B. Overview ANAT 323 Clinical Neuroanatomy course will focus on the structural and functional relationships of the central nervous system. The human neuroanatomy will be introduced via pathological cases
B. Overview ANAT 323 Clinical Neuroanatomy course will focus on the structural and functional relationships of the central nervous system. The human neuroanatomy will be introduced via pathological cases
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation.
 Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
Chapter 14: Integration of Nervous System Functions I. Sensation A. General Organization 1. General senses have receptors a. The somatic senses provide information about & 1. Somatic senses include: a.
THE BACK. Dr. Ali Mohsin. Spinal Cord
 Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
Spinal Cord THE BACK Dr. Ali Mohsin The spinal cord is the elongated caudal part of the CNS. It starts as the inferior continuation of the medulla oblongata at the level of foramen magnum, & ends as an
