Laith Sorour. Facial nerve (vii):
|
|
|
- Emmeline Griffin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Laith Sorour Cranial nerves 7 & 8 Hello, there are edited slides please go back to them to see pictures, they are not that much important in this lecture but still, and yes slides are included :p Let s goooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooo! Facial nerve (vii): It s a mixed cranial nerve which means it has a Motor modality and Sensory modality. First, The Motor modalities: 1-Motor fibers (SVE) and originate from the pons and innervate facial expression muscles (facial, scalp muscles) 2-Parasympathetic innervation (GVE) are via pterygopalatine and submandibular ganglia and they innervate various glands in the head like The salivary glands (secretion of saliva) (sublingual and submandibular + small salivary glands but NOT the parotid gland although it pierces it through its course) and the Lacrimal Gland (secretion of tears) ***so lesions to motor modalities of facial nerve will lead to facial palsy and defect in salivation and lacrimation. Secondly, Sensory modalities: **All sensory fibers go to the Geniculate ganglion in facial canal. *Ganglion=gray matter outside CNS. We have 3 types of sensory fibers: 1-SVA from the taste buds of the anterior 2/3 of the tongue and external 2-GVA from soft palate and beginning of oropharynx 3-GSA from external ear (many nerves sense the external ear because its embryological formation is from more than one arch) Now lets about Facial nerve nuclei: 1-The main motor nucleus (SVE): located deep in the reticular formation in the lower part of the pons, it connects with the cortex and then innervates the upper
2 muscles of facial expression bilaterally (from both sides) and the lower muscles contralateral (left hemisphere innervate right side and like this). *so any lesion in UMN will affect the lower muscles of the contralateral side but the upper muscles will not be affected. -Fibers go posteriorly looping around abducent nucleus and this gives us Colliculus facialis and will combine with the other nerves and give Facial nerve which ascends between pons and medulla until it inters Internal acoustic meatus 2- Parasympathetic nuclei (GVE) **Superior salivatory which connects with hypothalamus **Lacrimal which connects with hypothalamus and Sensory nuclei of Trigeminal (v) \but why?? Because trigeminal nerve innervates the sensation of the eyeball so as reflex lacrimal glands will secrete tears (Corneal irritation will secrete tears) *crying in the corner because life is hard* 3-Sensory nucleus 1st order neuron geniculate ganglion (as we said before all fibers go here) 2nd order neuron Nucleus of the tractus solitarius (SVA, GVA) They are responsible for Taste and sensation from palate, the nucleus located in the posterolateral region of the medulla and the Axons cross midline 3rd order neuron PVM of thalamus Axons internal capsule corona radiata cortex (postcentral gyrus) ** Facial nerve has two roots 1- motor root (SVE) & nervus intermedius which contains the sensory and parasympathetic fibers of the facial nerve (GVE,SVA,GVA,GSA) The facial nerve course it begins In the Pons ( cerebellopontine angle) Internal acoustic meatus then will reach the middle ear and will go in facial canal and move on medial wall and then posterior wall until it exits through stylomastoid foramen into infratemporal fossa. *so because of its complicated course it can be easily affected, like in otitis media.
3 Now lets talk about Facial nerve branches: 1-Nerve to stapidius muscle (SVE) from facial canal from posterior wall of the tympanic cavity to stapedius muscle where it originates in the middle ear \\ so the lesion may affect hearing. 2-Posterior auricular n. (SVE) It innervates Stylohyoid muscles & POSTERIOR belly of digastric muscle *Ant belly of digastric is innervated by mandibular branch of trigeminal n. 3-** important I think : IT gives 5 terminal branches ( SVE) in the Parotid gland *****The facial nerve pierces the parotid gland dividing it into superficial and deep and splits into five terminal branches innervating the muscles of facial expression (temporal, zygomatic, buccal, marginal mandibular, cervical)**** *so any injury to parotid gland or a parotid tumor may cause palsy *FACIAL nerve does NOT innervate parotid gland it just pierces it. 4-Greater petrosal nerve (GVE,GVA)(mainly parasympathetic lacrimal and small salivary glands) Exits from hiatus of facial canal which opens into cranial cavity near foramen lacerum goes to pterygoid canal where it fuses with deep petrosal nerve (sympathetic) and gives nerve of pterygoid canal pterygopalatine ganglion (parasympathetic ganglion) it distributes post-ganglionic neurons like zygomatic branch goes to cranium an lacrimal gland and other branches to nasal cavity and palate *we took these is Respiratory system with Dr. Abd Al-Amir. 5-Chorda tympani n. (GVE submandibular & sublingual glands) (SVA ant. 2/3 of the tongue\taste) (GVA) Chorda tympani leaves the facial nerve within facial canal in posterior wall of tympanic cavity canal in the petrotympanic fissure (*almost outside of auditory meatus ) foramen at the spine of sphenoid and combines with lingual nerve (V3) of trigeminal
4 Lesions of facial nerve : Bell s palsy: paralysis of facial expression mm. --> Unable to show teeth and close eye Loss of corneal reflex (efferent limb) Loss of taste from the anterior ⅔ of tongue (corda tympani) Unable to distinguish taste sensations (sweet, bitter, sour & salt) Decrease salivation (corda tympani) less lacrimation and worsening of hearing because it innervates stapedius muscle *Slide 14: it was explained previously but please go back to edited slides to understand it better since it is a picture with notes. Vestibulocochlear Nerve (VIII) It has two branches: 1-vestibular 2-cochlear Formerly called the acoustic or auditory nerve Brainstem (between pons & medulla) Internal acoustic meatus and will inter inner ear. Mainly a sensory nerve but cochlear has an efferent for ulduar hair cells 1-Cochlear branch Associated with hearing Receptors in the spiral organ in the cochlea The cell bodies in the spiral ganglion at base of spinal lamina Axons travel to nuclei in the medulla if damaged deafness or tinnitus (ringing) is produced Auditory Nuclei/Pathway: 1st order neuron spiral ganglion 2nd order neurons Cochlear nuclei: it is located with the vestibular nuclei In the lateral side?? fossa between pons and medulla Two nuclei Anterior & posterior Relations inferior cerebellar peduncles Axons cross and uncross midline
5 3rd order neurons Posterior nucleus of trapezoid body & superior olivary nucleus Axons lateral lemniscus 4th order neurons Inferior colliculus Medial geniculate body (5th) internal capsule auditory cortex (superior temporal gyrus) 2-Vestibular branch: Associated with equilibrium Receptors in the semicircular canals; saccule, and utricle The cell bodies in vestibular ganglion Axons travel to nuclei in the thalamus; some fibers also travel to the cerebellum Lesion results in disequilibrium, vertigo, nystagmus, ataxia The Vestibular Nuclei/Pathway Location 4th ventricle *Vestibular nuclei (2nd order neurons) have 4 nuclei that connects mainly with cerebellum and the lateral connects with spinal cord Lateral vistibulospinal tract Superior Medial Inferior Inputs from cerebellum Axons (so when you move your head eyes move too) in cerebral cortex (postcentral gyrus) Sorry for any mistakes and the last slides doctor didn t explain well because he explained them in the previous lecture. PEACE OUT
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII
 Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
Cranial Nerve VII & VIII Lecture Objectives Follow up the course of facial nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Follow up the central connections of the facial
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways
 General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
General Sensory Pathways of the Face Area, Taste Pathways and Hearing Pathways Lecture Objectives Describe pathways for general sensations (pain, temperature, touch and proprioception) from the face area.
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
The Seventh Cranial Nerve The Facial By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 The Seventh Cranial Nerve The Facial By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Functional Components: SVE: Fibers originate from nucleus of facial nerve, and supply facial muscles GVE: Fibers derived from superior
The Seventh Cranial Nerve The Facial By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Functional Components: SVE: Fibers originate from nucleus of facial nerve, and supply facial muscles GVE: Fibers derived from superior
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve)
 Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerve VIII (The Vestibulo-Cochlear Nerve) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
CN modalities Sensory: SSA (Vision) Mixed: GSE, proprioceptive. Mixed: GSE, proprioceptive
 CN 2 3 4 6 modalities Sensory: SSA (Vision) course Rods and cones of the retina bipolar neurons gangli on cells Optic nerve optic foramen Optic chiasm Optic tracts Sup colliculi LGN Optic radiation cortex
CN 2 3 4 6 modalities Sensory: SSA (Vision) course Rods and cones of the retina bipolar neurons gangli on cells Optic nerve optic foramen Optic chiasm Optic tracts Sup colliculi LGN Optic radiation cortex
lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben
 lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben ** Hello SERTONIN! note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures in the previous lecture we talk about ascending tract and its
lecture #2 Done by : Tyma'a Al-zaben ** Hello SERTONIN! note:: the slide included within the sheet but make sure back to slide for pictures in the previous lecture we talk about ascending tract and its
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Trigeminal Nerve (V)
 Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Trigeminal Nerve (V) Lecture Objectives Discuss briefly how the face is developed. Follow up the course of trigeminal nerve from its point of central connections, exit and down to its target areas. Describe
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Omar Sami. Aseel Abdeen. Muhammad Al-Salem. 1 P a g e
 Omar Sami Aseel Abdeen Muhammad Al-Salem 1 P a g e Using only section 2 record, I wrote this sheet; as the video is not ready yet. Despite pointing the structures, I ve tried to include all the scientific
Omar Sami Aseel Abdeen Muhammad Al-Salem 1 P a g e Using only section 2 record, I wrote this sheet; as the video is not ready yet. Despite pointing the structures, I ve tried to include all the scientific
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb. Lina Mansour. Reyad Jabiri. 0 P a g e
 2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
2 Mohammad Hisham Al-Mohtaseb Lina Mansour Reyad Jabiri 0 P a g e This is only correction for the last year sheet according to our record. If you already studied this sheet just read the yellow notes which
Auditory and Vestibular Systems
 Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
Auditory and Vestibular Systems Objective To learn the functional organization of the auditory and vestibular systems To understand how one can use changes in auditory function following injury to localize
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA
 PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
PTERYGOPALATINE FOSSA Outline Anatomical Structure and Boundaries Foramina and Communications with other spaces and cavities Contents Pterygopalatine Ganglion Especial emphasis on certain arteries and
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
human anatomy 2016 lecture fifteen Dr meethak ali ahmed neurosurgeon
 Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Cranial Nerves Organization of the Cranial Nerves The cranial nerves are named as follows: I. Olfactory II. Optic III. Oculomotor IV. Trochlear V. Trigeminal VI. Abducent VII. Facial VIII. Vestibulocochlear
Doctor Osama Asa ad Khader. Mohammad Alsalem
 6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
6 Doctor 2015 Osama Asa ad Khader Mohammad Alsalem A quick revision for the spinal cord blood supply: Arterial Blood supply of spinal cord The spinal cord got its arterial supply by two ways: Longitudinal
Trigeminal nerve. Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me
 Trigeminal nerve Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me Hala nsour 2/26/2018 P a g e 1 this lecture contain two topics
Trigeminal nerve Slide in bold and please go back to see the pictures, if I skipped any part of record that because it wasn t clear to me Hala nsour 2/26/2018 P a g e 1 this lecture contain two topics
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
CHAPTER 13 PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Functional division of nervous system = afferent info to the CNS ascending spinal cord = efferent info from CNS descending spinal cord somatic skin, muscles visceral
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy
 Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Introduction to Head and Neck Anatomy Nervous Tissue Controls and integrates all body activities within limits that maintain life Three basic functions 1. sensing changes with sensory receptors 2. interpreting
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp
 Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
Unit VIII Problem 3 Neuroanatomy: Brain Stem, Cranial Nerves and Scalp - Brain stem: It is connected to the cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. Rostral end of brain stem: diencephalon is the area which
DEVELOPMENT OF BRAIN
 Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Ahmed Fathalla OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should: List the components of brain stem. Describe the site of brain stem. Describe the relations between components of brain stem & their
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi
 Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Brainstem &diencephalon Done by : Areej Al-Hadidi Brainstem Functions Ascending and descending tracts Reflex centers Cardiovascular and respiratory centers Coughing, sneezing, swallowing Nuclei of the
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheets, Distributions Page 1
 Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Trigeminal Nerve Worksheet #1 Distribution by Nerve Dr. Darren Hoffmann Dental Gross Anatomy, Spring 2013 We have drawn out each of the branches of CN V in lecture and you have an idea now for their basic
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying
 Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerve Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor
Cranial nerve Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerve Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida. Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull
 Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
Biology 323 Human Anatomy for Biology Majors Week 10; Lecture 1; Tuesday Dr. Stuart S. Sumida Cranial Nerves and Soft Tissues of the Skull FOREBRAIN MIDBRAIN HINDBRAIN Forebrain: Cerebrum Perception,
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
CRANIAL NERVES. Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy
 CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
CRANIAL NERVES Dr. Amani A. Elfaki Associate Professor Department of Anatomy LEARNING OBJECTIVES Named the cranial nerves Identify the funcunal component of each cranial nerve Identify the effect of each
Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically
 CN I II III IV V 1 Supra-orbital ethmoidal nn. Ext. nasal V 2 Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically Nucleus of Origin Olfactory tracts of frontal lobe of cerebrum Optic tracts from optic chiasma and
CN I II III IV V 1 Supra-orbital ethmoidal nn. Ext. nasal V 2 Tracing the Cranial Nerves Osteologically Nucleus of Origin Olfactory tracts of frontal lobe of cerebrum Optic tracts from optic chiasma and
THE BRAINSTEM. Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania
 THE BRAINSTEM Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania Overview of Brainstem Functions The brainstem serves numerous crucial neurologic functions. The most clinically relevant functions include:
THE BRAINSTEM Raymond S. Price, MD University of Pennsylvania Overview of Brainstem Functions The brainstem serves numerous crucial neurologic functions. The most clinically relevant functions include:
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata
 Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
Lecture 4 The BRAINSTEM Medulla Oblongata Introduction to brainstem 1- Medulla oblongata 2- Pons 3- Midbrain - - - occupies the posterior cranial fossa of the skull. connects the narrow spinal cord
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs
 General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
General Sensory Pathways of the Trunk and Limbs Lecture Objectives Describe gracile and cuneate tracts and pathways for conscious proprioception, touch, pressure and vibration from the limbs and trunk.
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy
 By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
By Dr. Saeed Vohra & Dr. Sanaa Alshaarawy 1 By the end of the lecture, students will be able to : Distinguish the internal structure of the components of the brain stem in different levels and the specific
Omran Saeed. Luma Taweel. Mohammad Almohtaseb. 1 P a g e
 2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
2 Omran Saeed Luma Taweel Mohammad Almohtaseb 1 P a g e I didn t include all the photos in this sheet in order to keep it as small as possible so if you need more clarification please refer to slides In
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves)
 Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Cranial Nerves IX-X (Glossopharyngeal & Vagus Nerves) Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Lec#10 Part 2. Dawood Alatefi. Mariam Hassouneh. Dr.Mohammed Al-Salem
 Lec#10 Part 2 Dawood Alatefi Mariam Hassouneh Dr.Mohammed Al-Salem This part s record is found on the Batch s channel as LabA.3, starting from 0.00min until 26.20min. Hope this ll be an easy part on you;
Lec#10 Part 2 Dawood Alatefi Mariam Hassouneh Dr.Mohammed Al-Salem This part s record is found on the Batch s channel as LabA.3, starting from 0.00min until 26.20min. Hope this ll be an easy part on you;
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
CN I Olfactory. CN II Optic. CN III Oculomotor. Special Sensory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb. Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid
 CN I Olfactory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Olfactory Bulb Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid Anosmia Loss of sense of smell Uncinate Fits olfactory hallucinations To Olfactory Epithelium
CN I Olfactory Efferent fibers to Olfactory Bulb Olfactory Tract Olfactory Bulb Cribiform Plate of Ethmoid Anosmia Loss of sense of smell Uncinate Fits olfactory hallucinations To Olfactory Epithelium
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II. Nerves covered in other lectures. A reminder about embryology. Prof. Stuart Bunt
 Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
Brainstem and Cranial Nerves II Prof. Stuart Bunt Nerves covered in other lectures 1 Olfactory 2 Optic 3,4,6 Extraocular eye muscles 8 Vestibulo-cochlear 5 Motor and Sensory to the face and muscles of
CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS
 CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS Introduction Facial nerve paralysis, whilst not a disease of the ear itself, commonly arises within the ear due to its anatomical course, and often as a result of ear
CHAPTER 13. FACIAL NERVE PARALYSIS Introduction Facial nerve paralysis, whilst not a disease of the ear itself, commonly arises within the ear due to its anatomical course, and often as a result of ear
Imaging of facial paralysis
 Imaging of facial paralysis Poster No.: C-2151 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Martinez Molina, L. Aleman Romero, L. A. Sanchez Alonso, A. Puerta Sales, V. Garcia Medina; Murcia/ES
Imaging of facial paralysis Poster No.: C-2151 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Martinez Molina, L. Aleman Romero, L. A. Sanchez Alonso, A. Puerta Sales, V. Garcia Medina; Murcia/ES
Parotid Gland. Parotid Gland. Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible. Medial pterygoid.
 Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Parotid region Parotid Gland Largest of 3 paired salivary glands (submandibular; sublingual) Ramus of Mandible Medial pterygoid Cross section of mandible Masseter D S SCM Parotid Gland Mastoid Process
Brainstem. Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem
 Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
Brainstem Brainstem 脑 脊髓 Brainstem Telencephalon Diencephalon Cerebellum Brain stem Ventral view Lateral view 10 pairs of the cranial nerves are attached to the brain stem The brainstem Midbrain Pons Medulla
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES
 INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
INTRODUCTION: ANATOMY UNDERLYING CLINICAL TESTS OF CRANIAL NERVES CRANIAL NERVE I - OLFACTORY I - OLFACTORY NERVE - SMELL TEST: SMELL ODORS (note: not ammonia; pain in nasal cavity CN5 DAMAGE: LOSS OF
Group D: Central nervous system yellow
 Group D: Central nervous system yellow Central nervous system 1. General structure of nervous system (neuron, glia, synapsis, mediators, receptors) Main points: types of neurons and glial cells, synapses,
Group D: Central nervous system yellow Central nervous system 1. General structure of nervous system (neuron, glia, synapsis, mediators, receptors) Main points: types of neurons and glial cells, synapses,
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy. Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali
 Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy Dr. Mohamed Rahil Ali Trigeminal nerve Largest cranial nerve Mixed nerve Small motor root and large sensory root Motor root Nucleus of motor root present in the pons and medulla
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Anatomy #9. Rashed AL-Jomared. The Cranial Nerves IX. Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji
 Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
Anatomy #9 The Cranial Nerves IX Rashed AL-Jomared Amneh Hazaimeh & Alanood Bostanji السالم عليكم This lecture talks about the cranial nerves IX & X:: *Glossopharyngeal nerve : The nerve gets out of the
ParasymPathetic Nervous system. Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem
 ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
ParasymPathetic Nervous system Done by : Zaid Al-Ghnaneem In this lecture we are going to discuss Parasympathetic, in the last lecture we took sympathetic and one of the objectives of last lecture was
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
PHYSIOLOHY OF BRAIN STEM Learning Objectives The brain stem is the lower part of the brain. It is adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. 1 Mid Brain 2 Pons 3 Medulla Oblongata The
Sensory system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord
 15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
15 The Nervous System: Sensory and Motor Tracts of the Spinal Cord PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction Millions of sensory
Learning Outcomes. The Carotid 20/02/2013. Scalp, Face, Parotid. Layers of the Scalp. The Parotid Gland. The Scalp. The Carotid The Facial Artery
 Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Brain Stem. 1. Midbrain 2. Pons 3. Medulla Oblongata
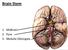 Brain Stem 1. Midbrain 2. Pons 3. Medulla Oblongata 1 Ext. features Medulla Oblongata *Direct continuation of Spinal Cord *Extend from foramen magnum to lower Pons *More than 2.5 cm in length. *Lower part
Brain Stem 1. Midbrain 2. Pons 3. Medulla Oblongata 1 Ext. features Medulla Oblongata *Direct continuation of Spinal Cord *Extend from foramen magnum to lower Pons *More than 2.5 cm in length. *Lower part
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Cranial Nerves VII to XII
 Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
Cranial Nerves VII to XII MSTN121 - Neurophysiology Session 13 Department of Myotherapy Cranial Nerve VIII: Vestibulocochlear Sensory nerve with two distinct branches. Vestibular branch transmits information
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery. Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla
 Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Faculty of Dental Medicine and Surgery Sem 4 Cranial Nerves Dr. Abbas Garib Alla Cranial Nerves I through XII FUNCTIPONAL CLSSIFICATION OF THE CN parasympathetic nerves 1973 PHARYNGEAL ARCHES nerves 1975
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
 Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
Spinal Cord Tracts DESCENDING SPINAL TRACTS: Are concerned with somatic motor function, modification of ms. tone, visceral innervation, segmental reflexes. Main tracts arise form cerebral cortex and others
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM
 PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE BRAIN STEM Dr Syed Shahid Habib Professor & Consultant Clinical Neurophysiology Dept. of Physiology College of Medicine & KKUH King Saud University OBJECTIVES At the end of this lecture
Skull-2. Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Skull-2 Norma Basalis Interna Norma Basalis Externa Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Norma basalis interna Base of the skull- superior view The interior of the base of the
Sensory systems. Taste/gustatory
 Sensory systems Taste/gustatory Sensory systems basic concepts Modality of Sensation Receptor Sensory Tract primary neuron secondary neuron tertiary neuron termination Receptors of sensory systems - primary
Sensory systems Taste/gustatory Sensory systems basic concepts Modality of Sensation Receptor Sensory Tract primary neuron secondary neuron tertiary neuron termination Receptors of sensory systems - primary
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Dr. Sami Zaqout, IUG Medical School
 The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
The skull The skull is composed of several separate bones united at immobile joints called sutures. Exceptions? Frontal bone Occipital bone Vault Cranium Sphenoid bone Zygomatic bones Base Ethmoid bone
Sheet lab 3. Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation:
 Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
Sheet lab 3 Page 8B Section1 of medulla at pyramidal {motor} decussation: This section is at lower third of medulla and is the most close part to spinal cord and it has some characteristic of spinal cord
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents
 Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Unit 18: Cranial Cavity and Contents Dissection Instructions: The calvaria is to be removed without damage to the dura mater which is attached to the inner surface of the calvaria. Cut through the outer
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts.
 Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Descending Tracts I: To describe the pyramidal and extrapyramidal tracts. II: To discuss the functions of the descending tracts. III: To define the upper and the lower motor neurons. 1. The corticonuclear
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals Gelatinous mass. Cilia. Hair cells. Vestibular nerve. Vestibular ganglion
 VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
VESTIBULAR SYSTEM (Balance/Equilibrium) The vestibular stimulus is provided by Earth s, and. Located in the of the inner ear, in two components: 1. Vestibular sacs - gravity & head direction 2. Semicircular
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The functional Anatomy of the Cranial nerves
 The State Medical and Pharmaceutical University Nicolae Testemitanu Republic of Moldova Department of Human Anatomy The functional Anatomy of the Lecturer Globa Lilian Like spinal nerves, cranial nerves
The State Medical and Pharmaceutical University Nicolae Testemitanu Republic of Moldova Department of Human Anatomy The functional Anatomy of the Lecturer Globa Lilian Like spinal nerves, cranial nerves
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5)
 Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Dr.Noor Hashem Mohammad Lecture (5) 2016-2017 If the mandible is discarded, the anterior part of this aspect of the skull is seen to be formed by the hard palate. The palatal processes of the maxillae
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D.
 Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Autonomic Nervous System, Visceral Sensation and Visceral Reflexes Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES After studying the material of this lecture, the student should know the: 1. basic divisions of the autonomic
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve
 19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
19 Anatomy of the Trigeminal Nerve.1 Introduction 0. The Central Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 1..1 Origin 1.. Trigeminal Nuclei.3 The Peripheral Part of the Trigeminal Nerve 4.3.1 Ophthalmic Nerve 4.3.
