Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min
|
|
|
- Alexia Burke
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Abdominal Imaging 9 topics in 90 min Antonio C. Westphalen, MD PhD Departments of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging, and Urology Liver Biliary tree Gallbladder Pancreas Kidneys Small bowel Colon Abscess? Tubes and lines Outline Focus on most common problems faced by the hospitalist Brief description of the problem advantages and disadvantages main imaging findings Additional imaging further characterization follow-up 2 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 1
2 Liver Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease Obese patient Elevated liver enzymes RUQ pain Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis? / cirrhosis? 3 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min NALFD vs cirrhosis Ultrasound Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging Steatosis may be diffuse or focal; and it is a heterogeneous process. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis cannot be diagnosed with imaging. Cirrhosis: morphologic changes and evidence of portal hypertension. 4 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 2
3 Ultrasound Usually the first option when NAFLD is suspected Inexpensive, safe, readily available on the bed side, and highly accurate Full assessment of the parenchyma may be limited in severe cases. Hepatomegaly echogenicity / smooth vs nodular (split image of spleen use same setup) Poor visualization of deep parts of the liver 5 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Computed tomography Usually best in advanced disease with suspected cirrhosis Non-contrast CT for steatosis, contrast-enhanced for cirrhosis (GFR>45) Radiation exposure Low density compared with spleen on non-contrast CT (difference > 10 HU) Cirrhosis: nodular contour, widened gallbladder fossa, large caudate Portal hypertension: large PV (> 12-15mm), collaterals, splenomegaly, ascites Classical HCC are hypervascular lesions that washout on the delayed phase. 6 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 3
4 Magnetic resonance imaging Option to CT when suspect cirrhosis Best to characterize atypical/focal steatosis or indeterminate liver nodules In general, more sensitive than US and CT to detect fat Longer scan, breath holds, susceptible to artifacts (e.g. motion of ascites) In- and out-of-phase imaging If suspect cirrhosis, better to use gadolinium (contraindicated if GRF<30) 7 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Biliary tree Biliary obstruction Patient with cholestasis Elevated bilirubin, direct > indirect Elevated alkaline phosphatase Borderline elevated AST and ALT Intra- or extrahepatic obstruction? Cause? 8 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 4
5 Intra- or extrahepatic obstruction? Cause? Ultrasound Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging Extrahepatic obstruction is suggested by the presence of dilated ducts Normal ducts do not exclude acute/new or intermittent obstruction. Double duct sign (biliary and pancreatic ducts): pancreas, ampulla, scarring 9 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Ultrasound Always the first option for the assessment of bile ducts and gallbladder Inexpensive, safe, readily available on the bed side, and highly accurate May not detect the specific cause and level of obstruction. Bowel gas may obscure visualization of the CBD. Limited in markedly obese individuals. Try to always use the liver as a window to visualize the entire biliary tree Change decubitus/position to move air away from the area of interest Sometimes water PO helps 10 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 5
6 Computed tomography Better than US to determine the specific cause and level of obstruction. Visualizes the liver parenchyma more consistently than US. Very limited for CBD stones most are radiolucent. Radiation (40-50 years old). More expensive than US. Good option when a tumor is suspected IV contrast helps to determine the cause (late arterial & portal venous phases) Planning of percutaneous drainage 11 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Magnetic resonance imaging + MR cholangiopancreatography MRI for parenchyma / MRCP for ducts MRCP noninvasive and sensitive to detect stones, strictures, or dilatations. Requires good breath holds, fluid in the duodenum or ascites usually cause artifacts and limit visualization of ducts with MRCP. Good option when a CBD stone is suspected, but not visualized with US Option when tumor is suspected & iodinated contrast contraindicated (allergy) Best option when tumor is suspected & IV contrast contraindicated (low GFR) 12 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 6
7 Additional imaging Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) Diagnostic and therapeutic modality Imaging and sampling / removal of stones, stents, drains, & sphincterotomy Limited visualization of bile ducts proximal to the obstruction. Complications (10% risk overall, most commonly pancreatitis) Standard of reference (high accuracy and excellent spatial resolution) Best for obstruction at or distal to the confluence of right and left ducts Consider EUS (+/- FNA) if distal CBD tumor is suspected but not seen by other methods 13 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Remember! Biliary ductal dilatation of no clinical significance Mild central intrahepatic and CBD dilatation in older patients and after cholecystectomy 14 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 7
8 Gallbladder Acute cholecystitis Biliary colic / acute RUQ pain / Murphy sign Nausea / vomiting +/- fever Leukocytosis / mild cholestasis Confirm diagnosis and determine cause Complications? 15 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Acute cholecystitis? Cause? Complications? Ultrasound Computed tomography Distension of the gallbladder, gallbladder wall thickening, pericholecystic fluid, and gallstones suggest the diagnosis. Biliary sludge and gallbladder wall thickening without distension and pericholecystic fluid are commonly seen with chronic illnesses. Ascitic fluid versus pericholecystic fluid 16 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 8
9 Ultrasound Always the first option for the assessment of bile ducts and gallbladder Inexpensive, safe, readily available on the bed side, and highly accurate Ultrasonographic Murphy sign Thick GB walls or pericholecystic fluid? Turn Doppler on and look for vessels! Are GS mobile? Change decubitus. An impacted stone increases the probability of acute cholecystitis. 17 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Computed tomography Best option for assessment of complications May identify extrabiliary causes of acute cholecystitis Use of IV contrast is recommended Perforation: decompressed GB, pericholecystic fluid, hyperemia liver tissue Pancreatitis Abscess 18 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 9
10 Additional imaging HIDA cholescintigraphy, or HIDA scan Equivocal US results or acalculus cholecystitis Opacification of the gallbladder excludes the diagnosis Failure to fill the gallbladder suggests acute cholecystitis FP results: TPN or prolonged NPO, severe liver disease, sphincterotomy Cannot assess most complications Cannot assess alternative diagnoses 19 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Pancreas Pancreatitis Acutely ill, hypotensive / tachycardic Upper / epigastric pain radiating to back Nausea / vomiting Elevated amylase & lipase / leukocytosis Diagnosis? Stage? Complications? Cause? (uncommonly) 20 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 10
11 Diagnosis? Stage? Complications? Cause? Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging Usually not indicated if no signs of severe pancreatitis or rapid improvement. The ideal time to assess complications is 72 hours after onset of symptoms. To exclude cancer in patients > 40 yo with first episode of pancreatitis without identifiable cause 21 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Computed tomography Primary imaging tool to assess patients with pancreatitis Part of the revised Atlanta classification as a diagnostic criteria Also useful to guide percutaneous drainages or other interventions IV contrast is required pancreatic protocol (noncon, arterial, portal venous) Interstitial edematous pancreatitis versus necrotizing pancreatitits Pancreatic and peripancreatic collections 22 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 11
12 Interstitial edematous versus necrotizing pancreatitits Interstitial edematous pancreatitis Localized or diffuse enlargement Normal homogeneous or slightly heterogeneous enhancement (edema) Normal or mild inflammation of the peripancreatic tissues Marked heterogeneous enhancement within the first 5-7 days of onset could be IEP or ill-defined necrosis. CT performed after 5 7 days permits definitive characterization. 23 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Interstitial edematous versus necrotizing pancreatitits Necrotizing pancreatitis Parenchymal necrosis alone: < 5% Peripancreatic necrosis alone: 20% Parenchymal and peripancreatic necrosis: 75-80% Lack of enhancement on contrast-enhanced CT a week after onset Less than 30% and greater than 30% Heterogeneous areas with lack of enhancement that contain nonliquefied components 24 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 12
13 Pancreatic and peripancreatic fluid collections Pancreatic collections Acute necrotic collection 4 weeks walled-off necrosis Acute peripancreatic fluid collection 4 weeks pseudocyst Sterile or infected Acute: conform to the anatomic boundaries and have no discernable wall Chronic: round or oval surrounded by a well-defined enhancing wall Infection: diagnosed by the presence of gas (in the absence of GI tract fistula) 25 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Magnetic resonance imaging Suspected choledocholithiasis not yet visualized Characterize collections - nonliquefied material may mimic fluid of CT CT is contraindicated (eg, allergy to iodinated contrast or pregnancy) Cost and availability Accuracy MRI = CT CT is used to guide procedures 26 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 13
14 Additional imaging Ultrasound Gallstones and/or choledocholithiasis Guide drainage of collections Vascular assessment (venous thrombosis / pseudoaneurysms) 27 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Chronic pancreatitits Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging Parenchymal atrophy, PD dilatation and calcifications (CT only) Acute on chronic? Peripancreatic fluid/necrosis > parenchymal findings! Pancreatic cancer? Stenosis of the duct? 28 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 14
15 Adrenals Adrenal nodules Incidental findings Associate with endocrine symptoms Subclinical with hormonal imbalances Known primary cancer Diagnosis? Nest step? 29 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Diagnosis? Next step? Computed tomography Magnetic resonance imaging The goal of imaging is to characterize and adenoma versus a nonadenoma Dx of adenomas: intracytoplasmatic lipid and/or enhancement characteristics 1/3 of adenomas are lipid-poor 30 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 15
16 Computed tomography Primary imaging tool to diagnose adenomas Adrenal protocol: unenhanced CT plus/minus PV & delayed phases ( 12 min) Imaging guided biopsy Low density (< HU) on unenhanced CT: very high specificity and PPV Contrast washout characteristics (40% to 60% on delayed phase) 31 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Magnetic resonance imaging Generally used to characterize indeterminate lesions on CT Detection of microscopic lipid Breath holding, not useful if unenhanced CT density > 30 HU Relative signal loss from in-phase to out-of-phase images Virtually diagnostic of adenoma 32 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 16
17 Additional imaging PET-CT Reserved for patients with known primary cancer to exclude metastasis Indicated to investigate of masses > 4 cm, in lieu of biopsy Meta-analysis (patients with known primary cancer): Sensitivity = 97% / Specificity = 91% LR = 11.1 / LR = Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Beware! Computed tomography Metastases of renal cell carcinoma may have washout equivalent to adenomas Magnetic resonance imaging Metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma may have microscopic fat 34 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 17
18 Kidneys Urolithiasis Flank pain / renal colic Hematuria History of urolithiasis Diagnosis Obstruction? Probability stone passage? Complications? 35 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Urolithiasis Ultrasound Computed tomography KUB Consider history of urolithiasis and characteristics of symptoms Consider patient s age (radiation exposure) Consider pre-test probability of alternative diagnosis 36 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 18
19 Ultrasound Possibly the first option if known urolithiasis and classical symptoms Inexpensive, safe, readily available on the bed side Limited assessment of midureter due to gas in the GI tract Hydronephrosis Scan pelvis with bladder slightly full to better visualize distal ureter and UVJ Change patient decubitus to move gas / slow and continue pressure 37 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Computed tomography First option if nonclassical symptoms and need to exclude other causes of pain Visualizes virtually all stones, sensitivity 90% Radiation exposure young patients with repeated episodes of renal colic Noncontrast CT suffices in the vast majority of cases / IV if no urolithiasis Scan prone to more completely assess UVJ stones 6 mm threshold (axial plane) for spontaneous passage 38 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 19
20 Ultrasound or computed tomography? Westphalen AC. Acad. Emerg. Med Jul;18(7): Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Ultrasound or computed tomography? Westphalen AC. Acad. Emerg. Med Jul;18(7): Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 20
21 Ultrasound or computed tomography? Smith-Bindman R. N Engl J Med 2014; 371: Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min KUB Option to assess passage of stones after treatment (PNL of staghorn calculus) Easy to obtain in the bed side, little radiation Limited for the initial assessment of suspected urolithiasis overlap of bowel content and bones 42 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 21
22 Additional imaging Intravenous pyelography Rarely used nowadays 43 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Complications Calyceal rupture and pyonephrosis Calyceal rupture is a minor complication, usually treated with stenting Contrast-enhanced CT (delayed/excretory phase) Pyonephrosis is a medical emergency and requires immediate drainage Limited renal ultrasound Interventional radiology 44 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 22
23 Small bowel SBO versus ileus Abdominal distension / pain Nausea / vomiting History of abdominal surgery Diagnosis? If SBO, cause? Management? 45 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min SBO vs ileus Computed tomography KUB Initial assessment = computed tomography KUB may be an option for follow-up 46 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 23
24 Computed tomography Better first option for initial assessment of suspected SBO Fast, more sensitive than KUB, identifies a cause in ~ 80% of cases IV contrast (nonadhesive causes), PO contrast (transition point) SBO = proximal dilated loops of SB (> 3 cm), decompressed distally (RLQ) Ileus = diffuse distention, often borderline, normal stool/air in colon SBO in developed countries = adhesions (> 2/3 of cases) SBO in developing countries = incarcerated hernias (up to 80% of cases) 47 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min KUB May be used for follow-up of patients with SBO 50-60% sensitive for SBO, does not identifies cause of SBO Abdominal series (at least one standing or left lateral decubitus) SBO = air fluid levels at various heights, central predominance, with paucity of gas distally and in colon SBO = gasless abdomen if dilated and fluid filled SB, or after vomiting Ileus = borderline dilatation with air found throughout SB and in colon 48 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 24
25 Additional imaging KUB with PO Gastrografin (Diatrizoate Meglumine) Not for diagnostic use Predict the need of surgery and (?) shortens the course of partial SBO Usually done 48 hours after unsuccessful conservative therapy Contrast reaches the colon in 4-6 hours = conservative treatment Contrast does not reach the colon in 12 hours = surgery 49 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Closed loop obstruction Computed tomography 25% risk of strangulation and infarction Marked segmental distension of bowel, often C or U shape "beak sign": tapering bowel loops at the point of obstruction whirl": tightly twisted mesentery Contrast enhanced CT, due to high risk of ischemia and infarction 50 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 25
26 Bowel ischemia Computed tomography Imaging appearance similar independent of cause Unenhanced, late arterial phase, and portal venous phase of enhancement Contrast enhanced CT due to high risk of ischemia and infarction Wall thickening and free fluid Hyperemia or decreased enhancement of wall Pneumatosis intestinalis, pneumoperitoneum, pneumatosis portalis 51 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Colon Pseudomembranous colitis Diarrhea, fever, abdominal pain Abdominal distension Leukocytosis Broad-spectrum antibiotic use Diagnosis? C. difficile colitis? Or another cause? Complications? 52 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 26
27 Diagnosis? Complications? Computed tomography KUB Colonic distension (Diffuse) marked wall thickening, thumbprinting Toxic megacolon (perforation) 53 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Computed tomography More sensitive option for the diagnosis of colitis and its complications Etiology is suggested, but not necessarily definitively established Sensitivity and specificity approximately 85% and 48% (colonic abnormalities) IV contrast, no PO contrast (Diffuse) marked wall thickening, thumbprinting Paucity of pericolonic inflammation may help differentiate from other colitides 54 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 27
28 KUB Easy and quick exam, but normal early in the disease Useful for follow-up (q 12-24h); may identify development of toxic megacolon Bowel dilatation, mural thickening and thumbprinting on more advanced cases Underestimate the severity of disease Limited for detection of small pneumoperitoneum Abdominal series preferable to KUB 55 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Additional imaging Barium enema Limited role in the diagnosis Contraindicated in patients with severe (perforation) 56 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 28
29 Toxic megacolon KUB or CT Nonobstructive colonic dilatation plus systemic toxicity Marked distension > 6 cm transverse segment Loss of hautral markings, pseudopolyps, and air-fluid levels Risk of perforation high if cecum > 12 cm Ischemia Pneumoperitoneum 57 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Remember! Imaging findings often not specific for a particular etiology Must consider the clinical setting Interpretation of scans is improved with adequate history Song KS. Yonsei Med J (2): Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 29
30 Abscess Post operative/trauma/infection/inflammation 1 to 3 weeks to develop Fever, abdominal pain, anorexia Nausea, ileus, weight loss Leukocytosis Diagnosis Treatment planning 59 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Diagnosis? Treatment planning? Computed tomography Ultrasound Walled-off collection Amenability to percutaneous drainage Exclude associated complications, e.g. venous thrombosis 60 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 30
31 Computed tomography Primary imaging modality (diagnosis and drainage) IV (diagnosis) and oral contrast (drainage) are helpful Collection with enhancing walls and mass effect (Complex) fluid attenuation Presence of gas is the most specific finding Adjacent inflammatory findings (fat stranding/fluid) 61 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Ultrasound Easy, fast, and cheap to perform in the bedside Better for superficial, rather than deep abscesses Operator dependent Collection with thick walls and flow on color Doppler Complex fluid (floating echos) Gas is the most specific finding (echogenic and mobile foci with dirty shadow) Turn on color Doppler to find vessels prior to any percutaneous interventions 62 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min 31
32 Additional imaging 111 In-leukocyte scintigraphy? Equivocal US and CT results Elaborate procedure, requires strict patient collaboration ½ of abscesses are identified by 4 h after injection, more than 90% by 24 h FP results: interpretation must refer to CT findings FN results: chronic abscess (> 3 weeks); lymphocytic mediated infection, e.g. TB or other granulomatous processes; abscess in or adjacent to liver or spleen 63 Abdominal Imaging - 9 Topics in 90 min Thank You! antonio.westphalen@ucsf.edu 32
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University
 Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure Comments The speaker Alice Fung, MD Has relevant financial relationships to disclose. Received honorarium from (Guerbet). This individual
Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure Comments The speaker Alice Fung, MD Has relevant financial relationships to disclose. Received honorarium from (Guerbet). This individual
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno. Objectives. Why?
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS Assistant Clinical Professor Director of Emergency Ultrasound UCSF Fresno Objectives Discuss the goals of point-of-care biliary ultrasound Review the
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Imaging of common diseases of hepatobiliary and GI system
 Imaging of common diseases of hepatobiliary and GI system Natthaporn Tanpowpong, M.D. Diagnostic radiology Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University Normal plain radiograph A = Common bile duct
Imaging of common diseases of hepatobiliary and GI system Natthaporn Tanpowpong, M.D. Diagnostic radiology Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University Normal plain radiograph A = Common bile duct
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree
 A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
A patient with an unusual congenital anomaly of the pancreaticobiliary tree Thomas Hocker, HMS IV BIDMC Core Radiology Case Presentation September 17, 2007 Review of Normal Pancreaticobiliary Tract Anatomy
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Management of Gallbladder Disease
 Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Management of Gallbladder Disease Steven B. Johnson, MD, FACS, FCCM Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery Program Director, Phoenix Integrated Surgical Residency University of Arizona College of
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning
 Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Guidelines, Policies and Statements D5 Statement on Abdominal Scanning Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to ensure that this Guideline/Policy/Statement
Case Scenario 1. Discharge Summary
 Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Case Scenario 1 Discharge Summary A 69-year-old woman was on vacation and noted that she was becoming jaundiced. Two months prior to leaving on that trip, she had had a workup that included an abdominal
Elastography in the. technically difficult patient. EPIQ ultrasound system. Ultrasound
 Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Ultrasound Elastography in the technically difficult patient EPIQ ultrasound system Chairman Department of Diagnostic Radiology Allegheny General Hospital Pittsburgh, PA, USA You can offer more information
Hepatic Imaging: What Every Practitioner Should Know
 Hepatic Imaging: What Every Practitioner Should Know Shuchi K. Rodgers, MD Section Chief, Abdominal Imaging Director of Ultrasound Department of Radiology Einstein Medical Center rodgerss@einstein.edu
Hepatic Imaging: What Every Practitioner Should Know Shuchi K. Rodgers, MD Section Chief, Abdominal Imaging Director of Ultrasound Department of Radiology Einstein Medical Center rodgerss@einstein.edu
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Appendix 5. EFSUMB Newsletter. Gastroenterological Ultrasound
 EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
EFSUMB Newsletter 87 Examinations should encompass the full range of pathological conditions listed below A log book listing the types of examinations undertaken should be kept Training should usually
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients).
 Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Plain abdomen The standard films are supine & erect AP views (alternative to erect, lateral decubitus film is used in ill patients). The stomach can be readily identified by its location, gastric rugae
Biliary tree dilation - and now what?
 Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Biliary tree dilation - and now what? Poster No.: C-1767 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, S. Magalhães, M. Certo; Porto/PT Keywords: Pathology, Diagnostic
Plain Radiographs in Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain. Plain Radiographs in Non-Traumatic Abdominal Pain
 Jake Block, MD Associate Professor Associate Vice-Chairman for Clinical Operations Director, Musculoskeletal and Emergency Radiology Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Vanderbilt University
Jake Block, MD Associate Professor Associate Vice-Chairman for Clinical Operations Director, Musculoskeletal and Emergency Radiology Department of Radiology and Radiological Sciences Vanderbilt University
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell. Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer
 Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Biliary Tree Ultrasound - In a nutshell Pamela Parker Lead Sonographer Aims Review what we know about the biliary system Common pathologies Pitfalls Reporting tips The Nutshell Background Biliary examinations
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations. Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital
 Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Newcastle HPB MDM updated radiology imaging protocol recommendations Author Dr John Scott. Consultant Radiologist Freeman Hospital This document is intended as a guide to aid radiologists and clinicians
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento
 Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
Biliary Ultrasonography Kathleen O Brien MD MPH RDMS Kaiser Permanente South Sacramento https://www.google.com/search?sa=g&hl=en&q=public+disclosure&tbm=isch&tbs=simg:caqsigeahwelekju2aqaaawlelcmpwgaygpgcamskpib_1qnza7ai
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines. Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination
 Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination Approved by Council Feb 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to
Policies, Standards, and Guidelines Guidelines for Abdominal Ultrasound Examination Approved by Council Feb 2018 Disclaimer and Copyright The ASUM Standards of Practice Board have made every effort to
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases. Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants
 Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis and Cholestatic liver diseases Ahsan M Bhatti MD, FACP Bhatti Gastroenterology Consultants I have nothing to disclose Educational Objectives What is PSC? Understand the cholestatic
Disclosures. Extra-hepatic Biliary Disease and the Pancreas. Objectives. Pancreatitis 10/3/2018. No relevant financial disclosures to report
 Extra-hepatic Biliary Disease and the Pancreas Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures to report Jeffrey Coughenour MD FACS Clinical Associate Professor of Surgery and Emergency Medicine Division
Extra-hepatic Biliary Disease and the Pancreas Disclosures No relevant financial disclosures to report Jeffrey Coughenour MD FACS Clinical Associate Professor of Surgery and Emergency Medicine Division
Case Discussion Splenic Abscess
 Case Discussion Splenic Abscess Personal Data Gender: male Birth Date: 1928/Mar/06th Allergy: Mefenamic Smoking: 0.5 PPD for 55 years Alcohol: negative (?) 4 Months Ago Abdominal pain: epigastric area
Case Discussion Splenic Abscess Personal Data Gender: male Birth Date: 1928/Mar/06th Allergy: Mefenamic Smoking: 0.5 PPD for 55 years Alcohol: negative (?) 4 Months Ago Abdominal pain: epigastric area
IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 복부질환초음파 이재영
 IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 2013-4-3 복부질환초음파 이재영 나는오늘누구를위하여 종을울리나? 전통적의료 의사 공학설계자 의사 최첨단진단장비들 USG, CT, MRI 환자 환자 현대의료 사용자중심의사고 US in the Abdomen Detection DDx Look Behavior Response by external stimuli Guiding Tool
IT 의료융합 1 차임상세미나 2013-4-3 복부질환초음파 이재영 나는오늘누구를위하여 종을울리나? 전통적의료 의사 공학설계자 의사 최첨단진단장비들 USG, CT, MRI 환자 환자 현대의료 사용자중심의사고 US in the Abdomen Detection DDx Look Behavior Response by external stimuli Guiding Tool
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYSTS. Madhuri Rao MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital Center
 PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYSTS Madhuri Rao MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital Center 34 yo M Case Presentation PMH: Chronic pancreatitis (ETOH related) PSH: Nil Meds: Nil NKDA www.downstatesurgery.org Symptoms o Chronic
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYSTS Madhuri Rao MD PGY-5 Kings County Hospital Center 34 yo M Case Presentation PMH: Chronic pancreatitis (ETOH related) PSH: Nil Meds: Nil NKDA www.downstatesurgery.org Symptoms o Chronic
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Abdominal Ultrasound. Diane Hallinen, MD. Bloodroot
 Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Abdominal Ultrasound Diane Hallinen, MD Bloodroot Abdominal Ultrasound Vasculature Hepatobiliary Spleen Kidney Bladder Bowel Where to put the probe? Vasculature We are going to talk about Celiac Trunk
Jaundice. Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD
 Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
Jaundice Agnieszka Dobrowolska- Zachwieja, MD, PhD Jaundice definition Jaundice, as in the French jaune, refers to the yellow discoloration of the skin. It arises from the abnormal accumulation of bilirubin
IMAGING OF LIVER, BILIARY TREE, PANCREAS
 IMAGING OF LIVER, BILIARY TREE, PANCREAS Department of Radiology West China Hospital, Sichuan University Yao Jin Learning Points The methodology for imaging the LBP (liver, biliary tree, and pancreas )
IMAGING OF LIVER, BILIARY TREE, PANCREAS Department of Radiology West China Hospital, Sichuan University Yao Jin Learning Points The methodology for imaging the LBP (liver, biliary tree, and pancreas )
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease
 Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Approach to the Patient with Liver Disease Diagnosis of liver disease Careful history taking Physical examination Laboratory tests Radiologic examination and imaging studies Liver biopsy Liver diseases
Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center.
 Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in 2011 Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center Introduction Biliary emergencies are: Common Come in many flavors Deceiving: frequent
Imaging of Biliary Tract Emergencies in 2011 Jorge A. Soto, MD Professor of Radiology Boston University Medical Center Introduction Biliary emergencies are: Common Come in many flavors Deceiving: frequent
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds
 Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Dr Claire Smith, Consultant Radiologist St James University Hospital Leeds Imaging in jaundice and 2ww pathway Image protocol Staging Limitations Pancreatic cancer 1.2.4 Refer people using a suspected
Pancreas Case Scenario #1
 Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
Pancreas Case Scenario #1 An 85 year old white female presented to her primary care physician with increasing abdominal pain. On 8/19 she had a CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis. This showed a 4.6 cm mass
ENTEROCOLITIDES CAN YOU TELL THEM APART ON MDCT? Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Medical Center University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois
 ENTEROCOLITIDES CAN YOU TELL THEM APART ON MDCT? Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Medical Center University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 13:40-14:00
ENTEROCOLITIDES CAN YOU TELL THEM APART ON MDCT? Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Medical Center University of Chicago Evanston, Illinois SCBT/MR 2010 San Diego, California March 8, 2010 13:40-14:00
Management of Gallbladder Disease. Cory Buschmann, MD PGY-5 11/28/2017
 Management of Gallbladder Disease Cory Buschmann, MD PGY-5 11/28/2017 Financial disclosures None Content Scope of gallbladder diseases Evaluation H&P Labs Imaging Cholecystectomy vs cholecystostomy Ancillary
Management of Gallbladder Disease Cory Buschmann, MD PGY-5 11/28/2017 Financial disclosures None Content Scope of gallbladder diseases Evaluation H&P Labs Imaging Cholecystectomy vs cholecystostomy Ancillary
Appropriate Imaging Tests Lead to Meaningful Results. Dr. Richard Wasley May 2011
 Appropriate Imaging Tests Lead to Meaningful Results Dr. Richard Wasley May 2011 Summarize the advantages and limitations of specific imaging tests and why clinical information is so important to radiologists
Appropriate Imaging Tests Lead to Meaningful Results Dr. Richard Wasley May 2011 Summarize the advantages and limitations of specific imaging tests and why clinical information is so important to radiologists
Objectives. Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology. RUQ: Normal Anatomy. Emergency Ultrasound: Gallbladder Location
 Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Hepatobiliary Ultrasound: Anatomy, Technique, Pathology Laleh Gharahbaghian, MD FAAEM Associate Director, EM Ultrasound Co-Director, EM Ultrasound Fellowship Stanford University Medical Center Seric Cusick,
Bedside RUQ Ultrasound. Replace Formal ULS? Why Bedside ULS RUQ? RUQ Ultrasound. Bedside ULS is Limited, Goal-Directed
 Bedside RUQ Ultrasound RUQ Ultrasound Why do it How to do it Elizabeth Kwan UCSF Emergency Ultrasound Fellow Why Bedside ULS RUQ? Dx or Rule Out Acute Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis, Choledocolithiasis Earlier
Bedside RUQ Ultrasound RUQ Ultrasound Why do it How to do it Elizabeth Kwan UCSF Emergency Ultrasound Fellow Why Bedside ULS RUQ? Dx or Rule Out Acute Cholecystitis Cholelithiasis, Choledocolithiasis Earlier
A Review of Liver Function Tests. James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver
 A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
A Review of Liver Function Tests James Gray Gastroenterology Vancouver Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied, stored, or transmitted
Original Policy Date 12:2013
 MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
MP 6.01.30 Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography Medical Policy Section Radiology Is12:2013sue 3:2005 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date 12:2013 Return to Medical Policy Index Disclaimer
Case 1. Intro to Gallbladder & Pancreas Pathology. Case 1 DIAGNOSIS??? Acute Cholecystitis. Acute Cholecystitis. Helen Remotti M.D.
 Cholecystitis acute chronic Gallbladder tumors Adenomyoma (benign) Adenocarcinoma Pancreatitis acute chronic Pancreatic tumors Intro to Gallbladder & Pancreas Pathology Helen Remotti M.D. Case 1 70 year
Cholecystitis acute chronic Gallbladder tumors Adenomyoma (benign) Adenocarcinoma Pancreatitis acute chronic Pancreatic tumors Intro to Gallbladder & Pancreas Pathology Helen Remotti M.D. Case 1 70 year
Multi modality Imaging in Acute Pancreatitis. Marsha Lynch, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Core Clerkship in Radiology March 2009
 Multi modality Imaging in Acute Pancreatitis Marsha Lynch, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Core Clerkship in Radiology March 2009 Our Patient R: Introduction 52M with 10d history of nausea, vomiting
Multi modality Imaging in Acute Pancreatitis Marsha Lynch, HMS III Gillian Lieberman, MD BIDMC Core Clerkship in Radiology March 2009 Our Patient R: Introduction 52M with 10d history of nausea, vomiting
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases
 Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
Medical application of transabdominal ultrasound in gastrointestinal diseases Hsiu-Po Wang Department of Emergency Medicine National Taiwan University Hospital Real-time ultrasound has become a standard
4/9/2018 OBJECTIVES PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS
 PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
PANCREAOTO BILIARY ULTRASOUND: BEYOND CHOLECYSTITIS Jean Yves Sewah Kaiser Permanente West Los Angeles 1 OBJECTIVES Discuss the role of ultrasound in the evaluation of the gallbladder, biliary tree and
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic
 Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
Acute renal colic Radiological investigation in patients with renal colic Mikael Hellström Professor Department of Radiology Sahlgrenska University Hospital Göteborg University 0.9-1.8/1.000 inhabitants
Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen
 Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Prof. András Palkó MD, PhD Role of imaging in the evaluation of the acute abdomen Faculty of General Medicine University of Szeged Hungary 1 Definition Sudden onset of severe symptoms requiring emergency
Normal Sonographic Anatomy
 hapter 2:The Liver DUNSTAN ABRAHAM Normal Sonographic Anatomy Homogeneous, echogenic texture (Figure 2-1) Measures approximately 15 cm in length and 10 12.5 cm anterior to posterior; measurement taken
hapter 2:The Liver DUNSTAN ABRAHAM Normal Sonographic Anatomy Homogeneous, echogenic texture (Figure 2-1) Measures approximately 15 cm in length and 10 12.5 cm anterior to posterior; measurement taken
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies. V.Stoynova
 Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Imaging abdominal vascular emergencies V.Stoynova Abdominal vessels V. Stoynova 2 Acute liver bleeding trauma anticoagulant therapy liver disease : HCC, adenoma, meta, FNH, Hemangioma Diagnosis :CT angiography
Personal Profile. Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history. Hepatitis B carrier
 Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Personal Profile Name: 劉 XX Gender: Female Age: 53-y/o Past history Hepatitis B carrier Chief complaint Fever on and off for 2 days Present illness 94.10.14 Sudden onset of epigastric pain 94.10.15 Fever
Correspondence should be addressed to Justin Cochrane;
 Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 794282, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/794282 Case Report Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis Causing a Highway to the Colon with Subsequent
Case Reports in Gastrointestinal Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 794282, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/794282 Case Report Acute on Chronic Pancreatitis Causing a Highway to the Colon with Subsequent
What Is Pancreatitis?
 What Is Pancreatitis? Pancreatitis is inflammation (swelling) of the pancreas that is most often caused by gallstones or alcohol abuse. There are other causes that your gastroenterologist will look for,
What Is Pancreatitis? Pancreatitis is inflammation (swelling) of the pancreas that is most often caused by gallstones or alcohol abuse. There are other causes that your gastroenterologist will look for,
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE. T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar
 ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
Background. RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation. Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial
 RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial Background Incidence of pediatric gallbladder disease continues to rise U.S. Pediatric
RUQ Ultrasound Normal, Recommend Clinical Correlation Sohail R. Shah, MD, MSHA, FACS, FAAP Texas Children s Hosptial Background Incidence of pediatric gallbladder disease continues to rise U.S. Pediatric
General Data. 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性
 General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
What Are Gallstones? GALLSTONES. Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in. the gallbladder of some people.
 What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
What Are Gallstones? Gallstones are pieces of hard, solid matter that form over time in the gallbladder of some people. The gallbladder sits under the liver and stores bile (a key digestive juice ). Gallstones
Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis. Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně
 Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně New Classification: Acute Pancreatitis 2007 revision of Atlanta classification and definitions
Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně New Classification: Acute Pancreatitis 2007 revision of Atlanta classification and definitions
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain
 Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
Figure 2: Post-cholecystectomy biliary-like pain 1 patient with recurrent episodes of pain (not daily), in the epigastrium/right upper quadrant, lasting >30 mins, building to a steady level, interrupting
General'Surgery'Service'
 General'Surgery'Service' Patient Care Goals and Objectives 1)! Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric 2)! Interpret the results of clinical evaluations (history, physical examination) performed on patients being
General'Surgery'Service' Patient Care Goals and Objectives 1)! Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric 2)! Interpret the results of clinical evaluations (history, physical examination) performed on patients being
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US
 Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Pediatric Hepatobiliary, Pancreatic & Splenic US Susan J. Back, MD Department of Radiology, The Children s Hospital of Philadelphia No Disclosures Objectives Normal Abnormal: cases and US advances Objectives
Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis
 1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
1 Cholelithiasis & cholecystitis Dr. Muhammad Shamim FCPS (Pak), FACS (USA), FICS (USA) Assistant Professor, Dept. of Surgery College of Medicine, Prince Sattam bin Abdulaziz University Email: surgeon.shamim@gmail.com
Surgical Management of IBD. Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003
 Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Surgical Management of IBD Val Jefford Grand Rounds October 14, 2003 Introduction Important Features Clinical Presentation Evaluation Medical Treatment Surgical Treatment Cases Overview Introduction Two
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Radiological Investigations of Abdominal Trauma
 76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
76 77 Investigations of Abdominal Trauma Introduction: Trauma to abdominal organs is a common cause of patient morbidity and mortality among trauma patients. Causes of abdominal trauma include blunt injuries,
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
Acute Abdomen. Nirav Patel MD, FACS Banner University Medical Center - Phoenix
 Acute Abdomen Nirav Patel MD, FACS Banner University Medical Center - Phoenix ? Diffuse periumbilical with localization to RLQ + Nausea, anorexia, fevers - Diarrhea, emesis Exacerbated by movement, bumps
Acute Abdomen Nirav Patel MD, FACS Banner University Medical Center - Phoenix ? Diffuse periumbilical with localization to RLQ + Nausea, anorexia, fevers - Diarrhea, emesis Exacerbated by movement, bumps
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research 11/16/2017. Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument 11/16/2017
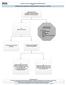 Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Evidence Process for Abdominal Pain Guideline Research Guideline Review using ADAPTE method and AGREE II instrument Approximately 139 Potentially relevant guidelines identified in various resources* 59
Afternoon Session Cases
 Afternoon Session Cases Case 1 19 year old woman Presented with abdominal pain to community hospital Mild incr WBC a14, 000, Hg normal, lipase 100 (normal to 75) US 5.2 x 3.7 x 4 cm mass in porta hepatis
Afternoon Session Cases Case 1 19 year old woman Presented with abdominal pain to community hospital Mild incr WBC a14, 000, Hg normal, lipase 100 (normal to 75) US 5.2 x 3.7 x 4 cm mass in porta hepatis
A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM
 A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM *Sumanta Kumar Ghosh and Biswajit Mukherjee ESIC Medical College, Joka, Kolkata, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Occurrence
A CASE REPORT OF SPONTANEOUS BILOMA - AN ENIGMATIC SURGICAL PROBLEM *Sumanta Kumar Ghosh and Biswajit Mukherjee ESIC Medical College, Joka, Kolkata, India *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Occurrence
General Surgery Service
 General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
General Surgery Service Patient Care Goals and Objectives Stomach/Duodenum and Bariatric assessed for a) Obesity surgery b) Treatment of i) Adenocarcinoma of the stomach ii) GIST iii) Carcinoid 2) Optimize
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Liver, Pancreas and Biliary System. Wirana Angthong, M.D.
 Liver, Pancreas and Biliary System Wirana Angthong, M.D. Objectives Outline Anatomy Imaging Techniques Common Diseases Outline Anatomy Imaging Techniques Common Diseases Liver anatomy Morphological anatomy:
Liver, Pancreas and Biliary System Wirana Angthong, M.D. Objectives Outline Anatomy Imaging Techniques Common Diseases Outline Anatomy Imaging Techniques Common Diseases Liver anatomy Morphological anatomy:
Treatment of chronic calcific pancreatitis endoscopy versus surgery
 Treatment of chronic calcific pancreatitis endoscopy versus surgery 35 - year old ladypresented to LPC Mumbai with intermittent abdominal pain. Pain was intermittent, colicky, more in epigastrium and periumbilical
Treatment of chronic calcific pancreatitis endoscopy versus surgery 35 - year old ladypresented to LPC Mumbai with intermittent abdominal pain. Pain was intermittent, colicky, more in epigastrium and periumbilical
U Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Lecture Objectives. MDCT in Acute Pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis: Etiologies
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Lecture Objectives MDCT in Acute Pancreatitis Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology niversity Hospital Zurich, Switzerland To describe the role of
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Lecture Objectives MDCT in Acute Pancreatitis Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology niversity Hospital Zurich, Switzerland To describe the role of
Diseases of liver. Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi 4/2/2019. Mob:
 Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Diseases of liver Dr. Mohamed. A. Mahdi Mob: 0123002800 4/2/2019 Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a complication of many liver disease. Permanent scarring of the liver. A late-stage liver disease. The inflammation
Hepatobiliary Disease
 Hepatobiliary Disease 大林慈濟綜合醫院 魏昌國 一般外科 Cholelithiasis 膽道結石 Incidence (USA) 10% in adult 85% cholesterol stones 15% pigment stone Risk factors Cholesterol stones Age Female(2x, 25% versus 12% at age 60),
Hepatobiliary Disease 大林慈濟綜合醫院 魏昌國 一般外科 Cholelithiasis 膽道結石 Incidence (USA) 10% in adult 85% cholesterol stones 15% pigment stone Risk factors Cholesterol stones Age Female(2x, 25% versus 12% at age 60),
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery
 12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
12 Blueprints Q&A Step 2 Surgery 34. A 40-year-old female has been referred to you for a recent ER and hospital admission, from which she was given a diagnosis of acute diverticulitis. Treatment at that
Comprehensive Study of Acute Pancreatitis (Diagnosis, Disease Course, and Clinical Management): A Retrospective and Prospective Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/449 Comprehensive Study of Acute Pancreatitis (Diagnosis, Disease Course, and Clinical Management): A Retrospective
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/449 Comprehensive Study of Acute Pancreatitis (Diagnosis, Disease Course, and Clinical Management): A Retrospective
Imaging Guided Biopsy. Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer
 Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Imaging Guided Biopsy Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc Lecturer,Reporting Sonographer Objective By the End of this lessons you should : Define what biopsy Justify Aim to perform biopsy
Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia
 Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
Publication for the Philips MRI Community ISSUE 49 2013 / 2 Liver imaging takes a step forward with Ingenia Lyon South Hospital strives to move from several studies first CT, then MR or PET to using just
LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL
 SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are epithelial invaginations in the gallbladder wall that from as a result of increased gallbladder pressures.
 Anatomy The complexity of the biliary tree can be broken down into much simpler segments. The intrahepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts which exit the liver and join to become
Anatomy The complexity of the biliary tree can be broken down into much simpler segments. The intrahepatic ducts converge to form the right and left hepatic ducts which exit the liver and join to become
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 8/27/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 35 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Anatomy Jessica Ferguson Ashley Dobos May 31, 2006 LIVER
 Anatomy Jessica Ferguson Ashley Dobos May 31, 2006 LIVER 1) Other Names: Reidel s Lobe normal anatomic variant; projection of the right lobe that can extend as far as the iliac crest (Tempkin, p.54, Anatomy).
Anatomy Jessica Ferguson Ashley Dobos May 31, 2006 LIVER 1) Other Names: Reidel s Lobe normal anatomic variant; projection of the right lobe that can extend as far as the iliac crest (Tempkin, p.54, Anatomy).
Request Card Task ANSWERS
 Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Request Card Task ANSWERS Medical Student Workbook Author: Dr Sam Leach, SpR Case 1 What differential diagnoses are most likely? Which investigation is most appropriate? Case 1 The most likely diagnosis
Case 1- B.N. 66 yr old F with PMHx of breast cancer s/ p mastectomy, HTN, DM presented with dysphagia to solids and liquids.
 Case 1- B.N 66 yr old F with PMHx of breast cancer s/ p mastectomy, HTN, DM presented with dysphagia to solids and liquids. Reports retching to clear esophagus. Case 1- B.N EGD: Stricture in the distal
Case 1- B.N 66 yr old F with PMHx of breast cancer s/ p mastectomy, HTN, DM presented with dysphagia to solids and liquids. Reports retching to clear esophagus. Case 1- B.N EGD: Stricture in the distal
Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology
 Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology 95% of bile acids reabsorbed; colic and chenodeoxycolic primary bile acids cholecystokinin (CCK) major stimulus of gallbladder
Vesalius SCALpel : Biliary (see also: biliary/pancreatic folios) Physiology 95% of bile acids reabsorbed; colic and chenodeoxycolic primary bile acids cholecystokinin (CCK) major stimulus of gallbladder
Evidence based imaging of the pancreas
 Evidence based imaging of the pancreas D.Vanbeckevoort, D.Bielen, K.Op de beeck, R.Vanslembrouck Department of Radiology Chairman Prof. Dr. R.Oyen Non-invasive imaging tests available for the diagnosis
Evidence based imaging of the pancreas D.Vanbeckevoort, D.Bielen, K.Op de beeck, R.Vanslembrouck Department of Radiology Chairman Prof. Dr. R.Oyen Non-invasive imaging tests available for the diagnosis
Severe necrotizing pancreatitis. ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc
 Severe necrotizing pancreatitis ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Acute pancreatitis Patients with acute pancreatitis van Dijk SM. Gut 2017;66:2024-2032 Diagnosis Revised Atlanta classification Abdominal
Severe necrotizing pancreatitis ICU Fellowship Training Radboudumc Acute pancreatitis Patients with acute pancreatitis van Dijk SM. Gut 2017;66:2024-2032 Diagnosis Revised Atlanta classification Abdominal
Provider Led Entity. CDI Quality Institute PLE Nontraumatic Abdominal Pain AUC
 Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Nontraumatic Abdominal Pain AUC Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with nontraumatic abdominal pain and the following clinical presentations
Provider Led Entity CDI Quality Institute PLE Nontraumatic Abdominal Pain AUC Appropriateness of advanced imaging procedures* in patients with nontraumatic abdominal pain and the following clinical presentations
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation
 Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
Pictorial review of Benign Biliary tract abnormality on MRCP/MRI Liver with Endoscopic (including splyglass) and Endoscopic Ultrasound correlation Poster No.: C-2617 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE. PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN
 PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN Pancreatic Fluid Collection (PFC) A result of pancreatic duct (PD) and side branch disruption,
PANCREATIC PSEUDOCYST DRAINAGE: ENDOSCOPIC APPROACHES & THE NURSING ROLE PRESENTED BY: Susan DePasquale, CGRN, MSN Pancreatic Fluid Collection (PFC) A result of pancreatic duct (PD) and side branch disruption,
