Chapter 50: Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
|
|
|
- Crystal O’Brien’
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Name Period As in Chapter 49, there are several topics in this chapter that we will emphasize only lightly. If your teacher stresses human anatomy and physiology, you may be expected to go into more depth. In this Reading Guide, we will ask you to cover only material that might be on an AP Biology exam. Concept 50.1 Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system 1. In the Reading Guide for Chapter 49, you labeled a reflex pathway, including receptors. Here is a list of the different types of receptors. Explain each type, and give an example. mechanoreceptors chemoreceptors electromagnetic receptors thermoreceptors pain receptors 2. What is perception? Explain the difference between what you see and what you perceive when you see an optical illusion like this. Concept 50.2 The mechanoreceptors responsible for hearing and equilibrium detect moving fluid or settling particles 3. Explain how statocysts function. What are the statoliths? 4. Label the following ear structures. Note their functions as you study the ear. auditory canal tympanic membrane Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 1
2 AP Biology Reading Guide malleus, incus, stapes round window outer ear middle ear inner ear semicircular canals cochlea auditory nerve Eustachian tube organ of Corti hair cells Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 2
3 5. Read the section on Hearing very carefully. As you read the second paragraph, and study Figure 50.8, begin writing a list of events. Step 1 is done for you. Prompts are given for the next events. (1) Moving air waves causes tympanic membrane (eardrum) to vibrate. (2) Bones/stapes (3) Oval window (4) Fluid inside the cochlea (5) Hair cells/mechanoreceptors (6) Round window 6. The sense of equilibrium is centered in the inner ear. Explain how the three fluid-filled semicircular canals and otoliths allow you to detect motion in different planes. Concept 50.3 The senses of taste and smell rely on similar sets of sensory receptors 7. What type of receptor is found in the taste buds? List the five types of tastes here. Note 1: Have you ever been asked to do taste tests and draw a map of the tasting areas of the tongue? Any region of the tongue can detect any of the five types of taste! Note 2: Sensations of sweet, umami, and bitter, as well as scent detection, all require a G protein-coupled receptor and a signal transduction pathway with second messengers just a reminder that this is a common mechanism! 8. As with taste, the receptors for smell are. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 3
4 AP Biology Reading Guide Concept 50.4 Similar mechanisms underlie vision throughout the animal kingdom 9. Label this figure of the eye, and give the function of these structures: sclera choroid cornea retina lens aqueous humor vitreous humor fovea optic nerve 10. Complete the following chart. Photoreceptor Function rods Location cones 11. Devise a diagram to show the conversion of retinal + opsin to rhodopsin. Include light activation as well as return to inactive state. (This is not Figure ) Note: Again, this system uses G proteins and signal transduction. Concept 50.5 The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function 12. Skeletal muscle is attached to bone and striated. What does striated mean? Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 4
5 AP Biology Reading Guide 13. A single muscle cell is also called a muscle fiber. Like a nested doll, each fiber contains the listed structures. As you label the diagram of skeletal muscle, write a description of each term. muscle muscle fiber myofibrils sarcomere thick filaments thin filaments 14. The mechanism of muscle contraction is described by the sliding-filament model. In the space below, draw a sketch of a sarcomere in a relaxed muscle. Below it, draw a sketch of a sarcomere in a contracted muscle. On your figure, label actin and myosin. 15. Describe the myosin molecule. 16. As you see in Figure 50.27, muscle contraction occurs when actin and myosin interact. Myosin heads bind to actin, forming cross-bridges. What molecule binds to myosin to provide the energy of contraction? Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 5
6 AP Biology Reading Guide 17. In the relaxed muscle fiber, the myosin-binding sites are blocked by a regulatory proteins bound to the actin. Use Figure to identify the actin, tropomyosin, troponin complex, and Ca2+ binding sites. 18. In a muscle fiber, the specialized endoplasmic reticulum is known as the. 19. What causes the release of Ca2+? 20. As you recall from Chapter 48 on nerve impulse transmission, an action potential will cause release of neurotransmitter at the stimulated neuron s synaptic terminal. Let s put all this together by studying a single figure. The stimulated neuron is a motor neuron that will release the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Label this figure with all possible details. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 6
7 21. Here is a jumbled summary of steps involved in muscle contraction. Put them into correct order in the chart below, and then place the number for each step in the correct location on the preceding diagram Calcium ions bind to troponin molecules of thin filaments. Acetylcholine is released from synaptic vesicles. Acetylcholine binds to receptors on the muscle fibers. This allows Na + ions to rush, causing depolarization. The troponin/tropomyosin complex is moved so the myosin-binding site of actin is exposed. Depolarization continues across the sarcolemma and down the transverse tubule system. Ca ++ is released from cisterns of the SR (sarcoplasmic reticulum). Nerve impulse arrives at the neuromuscular junction. Myosin heads rotate, bind the actin, and pull the actin fibers toward the center of the sarcomere. In the presence of Ca ++, myosin acts as an enzyme. It catalyzes breakdown of ATP. Energy is transferred from ATP to the myosin head; myosin is activated. Steps of Muscle Contraction Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 7
8 22. What is meant by a motor unit? 23. The three types of muscles are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth. Select from these three choices to answer the following questions. a) has intercalated disks. b) lacks striations. c) is striated and voluntary. d) has both fast-twitch and slow-twitch fibers. e) is associated with the heart. Concept 50.6 Skeletal systems transform muscle contraction into locomotion 24. Your text describes three types of skeletons. Explain how a hydrostatic skeleton works. 25. List three phyla that have a hydrostatic skeleton. 26. What is an exoskeleton? From what is it made? 27. Which phylum is characterized by an exoskeleton? Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 8
9 28. All chordates have an endoskeleton. What minerals are common in bone and cartilage? Testing Your Knowledge: Self-Quiz Answers Now you should be ready to test your knowledge. Place your answers here: Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. 9
Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
Name: AP Biology Mr. Croft Chapter 38 Active Reading Guide Nervous and Sensory Systems Section 1 1. This concept begins with a look at the evolution of nervous systems. You will want to study this to tie
-Detect heat or cold and help maintain body temperature
 Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Sensory Receptors -Transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the central nervous system -Reception occurs when a receptor detectd a stimulus -Perception occurs in the brain as this information
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Senses and Sense Organs
 Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Senses and Sense Organs SENSORY SYSTEMS Human experience is effected by both internal and external stimuli. Humans are able to distinguish among many different types of stimuli by means of a highly developed
Chapter 50. You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium. Chemoreception taste and smell
 1 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms 2 Chapter 50 You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium Chemoreception taste and smell Photoreceptors vision It s interesting.
1 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms 2 Chapter 50 You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium Chemoreception taste and smell Photoreceptors vision It s interesting.
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Sensory and Motor Mechanisms
 Chapter 50 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 50 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from
Chapter 18. The Senses SENSORY RECEPTION. Introduction: Superhuman Senses. Introduction: Superhuman Senses
 Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
Chapter 29 The Senses
 Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Name 29 The Senses and Muscle Contraction Test Date
 Name 29 The Senses and Muscle Contraction Test Date Study Guide You must know: The location and function of several types of sensory receptors. How skeletal muscle contracts. Cellular events that lead
Name 29 The Senses and Muscle Contraction Test Date Study Guide You must know: The location and function of several types of sensory receptors. How skeletal muscle contracts. Cellular events that lead
Special Senses. Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others
 Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
5. What component of the sarcomere is not attached to the Z line?
 Model 2: Anatomy of a Sarcomere 1. Label the thick filament and the thin filament in Model 2. 2. How many sarcomeres are shown in Model 2? 3. Using Model 2, based on the locations of thick and thin filaments,
Model 2: Anatomy of a Sarcomere 1. Label the thick filament and the thin filament in Model 2. 2. How many sarcomeres are shown in Model 2? 3. Using Model 2, based on the locations of thick and thin filaments,
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
The Senses. Chapter 10 7/8/11. Introduction
 Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
TASTE: Taste buds are the sense organs that respond to gustatory stimuli. Chemoreceptors that respond to chemicals broken down from food in the saliva
 UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
UNIT 5: Nervous System- Senses Somatic Senses Somatic senses are associated with receptors in the skin, muscles, joints, and viscera (organs of the body) Include senses of touch, pressure, temperature,
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Senses- Ch. 12. Pain receptors- respond to tissue damage in all tissues except in the brain
 Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
Senses- Ch. 12 5 general types of sensory neurons or receptors are known. These specialized neurons detect stimuli from the eyes, ears, nose, mouth, and skin. The stimuli are changed into electrical signals
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Amplification Strengthening of stimulus signal. (1) Reception Receptor detects stimuli
 Chapter 50: Sensory / Motor Mechanisms Ability to distinguish stimuli depends on the brain: Sensations: Electrical impulses that reach the brain via sensory neurons Perceptions: Interpretation of electrical
Chapter 50: Sensory / Motor Mechanisms Ability to distinguish stimuli depends on the brain: Sensations: Electrical impulses that reach the brain via sensory neurons Perceptions: Interpretation of electrical
Animal Skeletons. Earthworm peristaltic movement. Hydrostatic Skeletons
 Animal Skeletons The Musculo-Skeletal System Functions: Support Protection Movement all movement results from: muscle working against a skeleton 3 Types of skeletons hydrostatic exoskeleton endoskeleton
Animal Skeletons The Musculo-Skeletal System Functions: Support Protection Movement all movement results from: muscle working against a skeleton 3 Types of skeletons hydrostatic exoskeleton endoskeleton
Chapter 18 Senses SENSORY RECEPTION 10/21/2011. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations. Sensory Receptors and Sensations
 SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
SENSORY RECEPTION Chapter 18 Senses s convert stimulus energy to action potentials s 1. Are specialized cells, or 2. Specialized endings that detect stimuli All stimuli are forms of energy s in eyes detect
Ability to distinguish stimuli depends on the brain:
 1 Chapter 50: Sensory / Motor Mechanisms Campbell et al. Figure 50.2 Ability to distinguish stimuli depends on the brain: Sensations: Electrical impulses that reach the brain via sensory neurons Perceptions:
1 Chapter 50: Sensory / Motor Mechanisms Campbell et al. Figure 50.2 Ability to distinguish stimuli depends on the brain: Sensations: Electrical impulses that reach the brain via sensory neurons Perceptions:
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing
 20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
Special Senses. Accessory Structures of the Eye. The Eye and Vision. Accessory Structures of the Eye. Accessory Structures of the Eye
 8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
CHAPTER 6 2/9/2016. Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common.
 Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Learning Objectives List the four traits that all muscle types have in common. CHAPTER 6 The Muscular System Demonstrate and explain the use of antagonistic muscle pairs. Describe the attachment of muscle
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function
 Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function
 Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System
 Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Excretory System Endocrine System Reproductive System Lymphatic/Immune Systems
Nervous System Integumentary System Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Excretory System Endocrine System Reproductive System Lymphatic/Immune Systems
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
The Muscular System PART A
 6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
1. Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the nervous system Fig. 49.2
 1. Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the nervous system Fig. 49.2 Sensory reception begins with the detection of stimulus energy by sensory receptors. Exteroreceptors
1. Sensory receptors transduce stimulus energy and transmit signals to the nervous system Fig. 49.2 Sensory reception begins with the detection of stimulus energy by sensory receptors. Exteroreceptors
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction. Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry
 Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Skeletal Muscle and the Molecular Basis of Contraction Lanny Shulman, O.D., Ph.D. University of Houston College of Optometry Like neurons, all muscle cells can be excited chemically, electrically, and
Protection, Support, and Movement-Skin, Skeleton, and Muscle Notes
 I. Movement in animals A. Basics: 1. different modes of transportation (running, flying, swimming) have evolved with adaptations for animals to overcome difficulties associated with each type of locomotion
I. Movement in animals A. Basics: 1. different modes of transportation (running, flying, swimming) have evolved with adaptations for animals to overcome difficulties associated with each type of locomotion
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP
 The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
o A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye
 Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
The Sensory Systems. Lesson 7.1: The Eye Lesson 7.2: The Ear Lesson 7.3: Smell and Taste
 7 The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1: The Eye Lesson 7.2: The Ear Lesson 7.3: Smell and Taste Chapter 7: The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1 The Eye The Eye anatomy of the eye external internal vision injuries,
7 The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1: The Eye Lesson 7.2: The Ear Lesson 7.3: Smell and Taste Chapter 7: The Sensory Systems Lesson 7.1 The Eye The Eye anatomy of the eye external internal vision injuries,
[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]
![[CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY] [CHAPTER 12: THE NERVOUS SYSTEM] [ANSWER KEY]](/thumbs/71/65616244.jpg) WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
WORDBANK: Cholinesterase Dopamine Axon Choroid layer Cochlea Incus Action Potential Cataract Cornea Astigmatism Dendrite Malleus Alzheimer s Disease Central Excitatory Response Fovea Centralis Acetylcholine
For this lab you will use parts of Exercise #18 in your Wise lab manual. Please be sure to read those sections before coming to lab
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Sensory Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 9 Sensory Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 9 Sensory Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii Honolulu
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test
 Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
Biology 3201 The Nervous System Test 1. The central nervous system consists of: a. Nerves and neurons c. spinal chord and nerves b. brain and neurons d. brain and spinal chord 2. This part of the brain
The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the:
 Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Muscle Physiology. Dr. Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology Dr. Ebneshahidi Skeletal Muscle Figure 9.2 (a) Functions of the muscular system 1. Locomotion body movements are due to skeletal muscle contraction. 2. Vasoconstriction and vasodilatation
Muscle Physiology. Introduction. Four Characteristics of Muscle tissue. Skeletal Muscle
 Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
The Musculoskeletal System. Chapter 46
 The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
The Musculoskeletal System Chapter 46 Types of Skeletal Systems Changes in movement occur because muscles pull against a support structure Zoologists recognize three types: 1. Hydrostatic skeletons a fluid
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
Unit 8 Quiz. Source:
 Unit 8 Quiz Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:schematic_diagram_of_the_human_eye.svg 1. Label this structure of the human eye with the appropriate terms. Note you do not need to label every
Unit 8 Quiz Source: http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:schematic_diagram_of_the_human_eye.svg 1. Label this structure of the human eye with the appropriate terms. Note you do not need to label every
Overview of Sensory Receptors
 Sensory Systems Chapter 45 Overview of Sensory Receptors Sensory receptors provide information from our internal and external environments that is crucial for survival and success -Exteroceptors sense
Sensory Systems Chapter 45 Overview of Sensory Receptors Sensory receptors provide information from our internal and external environments that is crucial for survival and success -Exteroceptors sense
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System
 Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
The olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity. Nasal conchae cause turbulance of incoming air
 Special Senses I. Olfaction II. Gustation A. Anatomy and general info The olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity Nasal conchae cause turbulance of incoming air Olfactory glands
Special Senses I. Olfaction II. Gustation A. Anatomy and general info The olfactory epithelium is located at the roof of the nasal cavity Nasal conchae cause turbulance of incoming air Olfactory glands
Essential questions. What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2
 Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
Chapter 38: Sense Organs
 Chapter 38: Sense Organs AP Curriculum Alignment Big Idea 1 technically requests that students be able to choose a eukaryotic structure, such as the brain, to provide evidence that organisms continue to
Chapter 38: Sense Organs AP Curriculum Alignment Big Idea 1 technically requests that students be able to choose a eukaryotic structure, such as the brain, to provide evidence that organisms continue to
Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye. Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin
 Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 The Senses 4 Hearing 3 Layers of Ear EXTERNAL
Surgical Anatomy Ear and Eye Presenters: Dr. Jim Hurrell and Dr. Dennis McCurnin A Warm Welcome from My Faculty TEAM and Me!!! 2 The Pledge of Allegiance 3 The Senses 4 Hearing 3 Layers of Ear EXTERNAL
THE VERTEBRATE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NAME: DATE: PARTNER: THE VERTEBRATE NERVOUS SYSTEM The vertebrate nervous system includes sensation, integration, and motor output. Sensation includes specialized senses (vision, taste, hearing, etc.)
NAME: DATE: PARTNER: THE VERTEBRATE NERVOUS SYSTEM The vertebrate nervous system includes sensation, integration, and motor output. Sensation includes specialized senses (vision, taste, hearing, etc.)
Sense Organs. Chapter 38
 Sense Organs Chapter 38 Chemical Senses Chemoreceptors are the receptors responsible for smell and taste. Because all members of the animal kingdom have developed a sense of taste and/or smell, chemoreceptors
Sense Organs Chapter 38 Chemical Senses Chemoreceptors are the receptors responsible for smell and taste. Because all members of the animal kingdom have developed a sense of taste and/or smell, chemoreceptors
SPECIAL SENSES. Anatomy & Physiology
 SPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & Physiology BELL WORK: DEFINE LACRIMAL ACHROMATIC OTOSCOPE TENNITIS VERTIGO STANDARD 25) Define key terms associated with vision disorders, ear disorders, nose disorders, and mouth
SPECIAL SENSES Anatomy & Physiology BELL WORK: DEFINE LACRIMAL ACHROMATIC OTOSCOPE TENNITIS VERTIGO STANDARD 25) Define key terms associated with vision disorders, ear disorders, nose disorders, and mouth
The Sliding Filament Theory
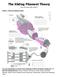 The Sliding Filament Theory Model 1: Muscle Histology Review How do muscle cells contract? Use your knowledge of muscle tissue histology to fill in the blanks numbered 1-11 with the following terms: Fasicle,
The Sliding Filament Theory Model 1: Muscle Histology Review How do muscle cells contract? Use your knowledge of muscle tissue histology to fill in the blanks numbered 1-11 with the following terms: Fasicle,
Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts
 Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Biology 067 - Muscular system A. Type of muscles: Smooth Cardiac Skeletal Location Around tubes Heart tissue attached to skeleton Function Moves stuff thru Heart beat pumps Moves body parts tubes blood
Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz. Remember, you need to know the structure and the function!
 Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz Remember, you need to know the structure and the function! What is this called? What is this? Schwann cell What is this called? Basal lamina
Nerve Muscle Relationship and Neural Muscular Junction Quiz Remember, you need to know the structure and the function! What is this called? What is this? Schwann cell What is this called? Basal lamina
Nerve Cell (aka neuron)
 Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
Nerve Cell (aka neuron) Neuromuscular Junction Nerve cell Muscle fiber (cell) The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential The Nerve Stimulus and Action Potential Skeletal muscles must be stimulated by a motor
Introduction. Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups. General senses Special senses
 Introduction Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups General senses Special senses Central Processing and Adaptation Adaptation the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation Tonic receptors
Introduction Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups General senses Special senses Central Processing and Adaptation Adaptation the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation Tonic receptors
Choroid Retina Fovea. Sclera. Suspensory ligament Cornea Iris. Optic nerve. Pupil. Aqueous humor Lens. Central artery and vein of the retina
 Figure 50.1 Figure 50.17aa Sclera Suspensory ligament Cornea Iris Pupil Choroid Retina Fovea Optic nerve Aqueous humor Lens Vitreous humor Optic disk Central artery and vein of the retina Figure 50.26
Figure 50.1 Figure 50.17aa Sclera Suspensory ligament Cornea Iris Pupil Choroid Retina Fovea Optic nerve Aqueous humor Lens Vitreous humor Optic disk Central artery and vein of the retina Figure 50.26
Bio11 schedule. Chapter 13 and 14. The Nervous System. The Nervous System. Organization of Nervous Systems. Nerves. Nervous and Sensory Systems
 Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Bio11 schedule Lecture Nervous system and senses Lab Current events reports (10 pts) Urinalysis Lecture exam 2 Thursday Feb 24 Same format as before Study guide will be posted Your total points so far
Class XI Chapter 20 Locomotion and Movement Biology
 Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Question 1: Draw the diagram of a sarcomere of skeletal muscle showing different regions. The diagrammatic representation of a sarcomere is as follows: Question 2: Define sliding filament theory of muscle
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD.
 Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Anatomy and Physiology 1 Chapter 10 self quiz Pro, Dima Darwish,MD. 1) Which of the following is a recognized function of skeletal muscle? A) produce movement B) maintain posture C) maintain body temperature
Chapter 49: Nervous Systems
 AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Name Period Chapter 49: Nervous Systems Concept 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells 1.
AP Biology Reading Guide Fred and Theresa Holtzclaw Chapter 49 Nervous Systems Name Period Chapter 49: Nervous Systems Concept 49.1 Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells 1.
Chapter 8 Notes. Muscles
 Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
Chapter 8 Notes Muscles 8.1 Intro Three muscle types Skeletal Smooth cardiac 8.2 Structure of Skeletal Muscle Composition Skeletal muscle tissue Nervous tissue Blood Connective tissue Connective tissue
PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM
 PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW Review of muscle so we can see how the neuromuscular system works This is not on today's note Skeletal Muscle Cell: Cellular System A) Excitation System Electrical
PSK4U THE NEUROMUSCULAR SYSTEM REVIEW Review of muscle so we can see how the neuromuscular system works This is not on today's note Skeletal Muscle Cell: Cellular System A) Excitation System Electrical
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION
 SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
1. Which of the following types of organisms lacks a nervous system? A) sea anemone B) squid C) spiders D) sponges
 Exam 1A 1. Which of the following types of organisms lacks a nervous system? A) sea anemone B) squid C) spiders D) sponges 2. Why are muscles always associated with some type of skeleton? A) The skeleton
Exam 1A 1. Which of the following types of organisms lacks a nervous system? A) sea anemone B) squid C) spiders D) sponges 2. Why are muscles always associated with some type of skeleton? A) The skeleton
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour:
 Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: Dem Bones Textbook p84-85, 88-99 61 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that you understand
Name: Teacher: Olsen Hour: Dem Bones Textbook p84-85, 88-99 61 In all exercises, quizzes and tests in this class, always answer in your own words. That is the only way that you can show that you understand
High graded potential at receptor ending causes rapid firing of its afferent neuron. Afferent neuron. Fig. 6-1, p. 142
 What are receptor neurons? Specialized neurons that respond to physical or chemical stimuli Respond by changing ion channels, altering graded potentials Afferent neuron High graded potential at receptor
What are receptor neurons? Specialized neurons that respond to physical or chemical stimuli Respond by changing ion channels, altering graded potentials Afferent neuron High graded potential at receptor
Where sensations get received
 What are receptor neurons? Specialized neurons that respond to physical or chemical stimuli Respond by changing ion channels, altering graded potentials Afferent neuron High graded potential at receptor
What are receptor neurons? Specialized neurons that respond to physical or chemical stimuli Respond by changing ion channels, altering graded potentials Afferent neuron High graded potential at receptor
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Page 1. Neurons Transmit Signal via Action Potentials: neuron At rest, neurons maintain an electrical difference across
 Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Chapter 33: The Nervous System and the Senses Neurons: Specialized excitable cells that allow for communication throughout the body via electrical impulses Neuron Anatomy / Function: 1) Dendrites: Receive
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13): Skeletal System (from chapter 5 in the textbook), Nervous System
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 3 Review Sheet The third midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, and 13): Skeletal System (from chapter 5 in the textbook), Nervous System
Sensory system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09b Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Muscle Cell Structure Muscle cells are specialized to contract. An individual muscle is actually a bundle of hundreds to thousands
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 09b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Muscle Cell Structure Muscle cells are specialized to contract. An individual muscle is actually a bundle of hundreds to thousands
o A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye
 Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses General senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain Special senses o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory
Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses General senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain Special senses o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision 70 percent of all sensory
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle Physiological Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle
 Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
Muscular Tissue. Functions of Muscular Tissue. Types of Muscular Tissue. Skeletal Muscular Tissue. Properties of Muscular Tissue
 Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
The Senses. senses are almost impossible to describe, and yet we use them every moment of the day.
 The Senses Objectives 31.4.1 Discuss the sense of touch and identify the various types of sensory receptors in the skin. THINK ABOUT IT We live in a world of sensations. Think about how many of your experiences
The Senses Objectives 31.4.1 Discuss the sense of touch and identify the various types of sensory receptors in the skin. THINK ABOUT IT We live in a world of sensations. Think about how many of your experiences
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY
 Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
Physiology Unit 2 SENSORY PHYSIOLOGY In Physiology Today Sensory System Sensory information Conscious sensations Unconscious sensations Sensory processing Transferring stimulus energy into a graded potential
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular System STUDY GUIDE
 NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
NPHS Anatomy & Physiology Questions to answer: 1) List three functions of the muscular system. 1) movement 2) thermogenesis (generates heat) 3) posture & body/joint support CLASS SET Unit 4: The Muscular
Chapter 9 Muscle. Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle. Striated muscle
 Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
Chapter 9 Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle Striated muscle Chapter 9 Muscle (cont.) The sliding filament mechanism, in which myosin filaments bind to and move actin
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
Rods vs Cones 3/10/2014. Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors. Turning Light Waves Into Electrical Messages (Transduction)
 Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors The typical neuron is designed to receive neurotransmitter messages from other neurons. Sensory receptors, on the other hand, are specialized to receive sensory
Example 1: Light Sensitive Visual Receptors The typical neuron is designed to receive neurotransmitter messages from other neurons. Sensory receptors, on the other hand, are specialized to receive sensory
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law).
 The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
Hearing. By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa
 Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Hearing By: Jimmy, Dana, and Karissa Anatomy - The ear is divided up into three parts - Sound enters in through the outer ear and passes into the middle where the vibrations are received and sent to the
Chapter 10: Muscles. Vocabulary: aponeurosis, fatigue
 Chapter 10: Muscles 37. Describe the structural components of skeletal muscle tissue from the molecular to the organ level. 38. Describe the structure, function, and importance of sarcomeres. 39. Identify
Chapter 10: Muscles 37. Describe the structural components of skeletal muscle tissue from the molecular to the organ level. 38. Describe the structure, function, and importance of sarcomeres. 39. Identify
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle
 Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Muscular System. This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions:
 Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
