The effects of a selective inhibitor of c-fos/ activator protein-1 on endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury in mice
|
|
|
- Norma Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Miyazaki et al. BMC Nephrology 212, 13:153 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The effects of a selective inhibitor of c-fos/ activator protein-1 on endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury in mice Hiroyuki Miyazaki 1*, Jun Morishita 1, Masaaki Ueki 1, Kahoru Nishina 1, Shunichi Shiozawa 2 and Nobuhiro Maekawa 1 Abstract Background: Sepsis has been identified as the most common cause of acute kidney injury (AKI) in intensive care units. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induces the production of several proinflammatory cytokines including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, a major pathogenetic factor in septic AKI. c-fos/activator protein (AP)-1 controls the expression of these cytokines by binding directly to AP-1 motifs in the cytokine promoter regions. T-5224 is a new drug developed by computer-aided drug design that selectively inhibits c-fos/ap-1 binding to DNA. In this study, we tested whether T-5224 has a potential inhibitory effect against LPS-induced AKI, by suppressing the TNF-alpha inflammatory response and other downstream effectors. Methods: To test this hypothesis, male C57BL/6 mice at 7 weeks old were divided into three groups (control, LPS and T-5224 groups). Mice in the control group received saline intraperitoneally and polyvinylpyrrolidone solution orally. Mice in the LPS group were injected intraperitoneally with a 6 mg/kg dose of LPS and were given polyvinylpyrrolidone solution immediately after LPS injection. In the T-5224 group, mice were administered T-5224 orally at a dose of 3 mg/kg immediately after LPS injection. Serum concentrations of TNF-alpha, interleukin (IL)- 1beta, IL-6 and IL-1 were measured by ELISA. Moreover, the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 mrna in kidney was examined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Finally, we evaluated renal histological changes. Results: LPS injection induced high serum levels of TNF-alpha, IL-1beta and IL-6. However, the administration of T-5224 inhibited the LPS-induced increase in these cytokine levels. The serum levels of IL-1 in the LPS group and T-5224 group were markedly elevated compared with the control group. T-5224 also inhibited LPS-induced ICAM-1 mrna expression. Furthermore histological studies supported an anti-inflammatory role of T Conclusions: In endotoxin-induced AKI, T-5224 inhibited the production of TNF-alpha and other downstream effectors. In contrast, T-5224 did not inhibit IL-1, an anti-inflammatory cytokine. These data support that the use of T-5224 is a promising new treatment for septic kidney injury. Keywords: Sepsis, Acute kidney injury, TNF-α, Lipopolysaccharide, Activator protein-1 Background Recently, the incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) has increased considerably. AKI occurs in 19 51% of patients with sepsis or septic shock, while sepsis is a contributing factor in approximately half of patients with severe AKI [1]. Although medical practice has advanced in the last decade, the pathophysiology of sepsis-induced * Correspondence: hiromm78@gmail.com 1 Division of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Chuo-ku, Kobe, Hyogo 65-17, Japan Full list of author information is available at the end of the article AKI is incompletely understood, and the mortality rate remains high. Current treatments for sepsis-induced AKI including intensive insulin therapy and early goal-directed therapy have been reported to be beneficial; however, there are still no radical treatments to completely treat septic AKI [1]. Several inflammatory mediators have been assigned a key role in sepsis. In response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS), macrophages and other cells express and release multiple proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α [2]. Although these molecules are 212 Miyazaki et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Miyazaki et al. BMC Nephrology 212, 13:153 Page 2 of 7 crucial for host defense against invading bacteria, excessive production of these mediators can result in a lethal systemic inflammatory response syndrome, which leads to shock, vascular dysfunction, disseminated intravascular coagulation and multiple organ dysfunction/injury [3]. Specifically, the role of TNF-α has been shown to be critical in the inflammatory response in endotoxemiarelated AKI [3]. The responses to LPS are mostly dependent on the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways and activation of MAPK by dual phosphorylation can enhance the transcriptional activity of activator protein (AP)-1 [4]. The transcription factor, c-fos/ap-1, directly controls the expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-6, by binding directly to AP-1 motifs in the promoter region of these genes. Aikawa et al [5]. designed and synthesized a selective inhibitor of c-fos/ap-1, termed T-5224, using three-dimensional (3D) pharmacophore modeling based on a crystal structure of the AP-1 DNA complex, and found that selective inhibition of c-fos/ap-1 resolved disease in a mouse model of arthritis. Inhibition of matrixdegrading matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) is essential for effective disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. T inhibited the transactivation of matrix-degrading MMPs via a promoter AP-1 binding motif and protected the joints in a mouse model of rheumatoid arthritis. Moreover, T-5224 decreased levels of TNF-α and efficiently protected mice from arthritic joint destruction. In the present study, we investigated whether T-5224 has an inhibitory effect on LPS-induced AKI in mice by suppressing the inflammatory response, including TNFα and other downstream effectors. Furthermore, as LPS administration can trigger an influx of neutrophils into organs such as the kidney, a process directed by the local expression of adhesion molecules on endothelium, we tested the effect of T-5224 on intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 expression in the injured kidney. Methods Animals This study was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and performed according to the Kobe University Animal Experimental Regulation (Kobe, Japan). Male C57BL/6 mice (CLEA Japan, Inc., Tokyo, Japan) aged 7 weeks were used throughout the study. They were maintained on standard rodent chow and allowed free access to water. Reagents LPS (Escherichia coli 111:B4) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich Co. (St. Louis, MO,USA).T-5224, 3-{5-[4- (Cyclopentyloxy)-2-hydroxybenzoyl]-2-[(3-hydroxy-1,2- benzisoxazol-6-yl) methoxy]phenyl} propionic acid, was synthesized and kindly supplied by Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd (Toyama, Japan) [5]. T-5224 is insoluble in water; therefore this reagent was dissolved in a polyvinylpyrrolidone solution, and adjusted to a concentration of 3 mg/ml. Animal protocols, blood chemistry and measurement of serum cytokine levels First we examined the peak of serum TNF-α levels after intraperitoneal administration a 6 mg/kg dose of LPS (1.25 mg/ml) [6] using a commercially available enzymelinked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit (R&D systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA). For the preparation of serum, mice were anesthetized with an intraperitoneal injection of sodium pentobarbital (Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan) and blood samples were collected from mice via the femoral artery. One-milliliter aliquots of blood samples were centrifuged (6,7 g for 3 min) and then supernatants were stored as serum at 8 C until used for analysis. To evaluate the effect of T-5224 on LPS-induced AKI, mice were assigned to one of three groups (control group, LPS group and T-5224 group). Mice in LPS group were administered orally with polyvinylpyrrolidone solution in the same volume of T-5224 solution immediately after LPS injection, while in the T-5224 group mice were administered orally with T-5224 (3 mg/kg) in the same manner. In the control group, mice received polyvinylpyrrolidone solution orally soon after intraperitoneal saline injection. Blood samples were collected for each measurement at the optimal time. Serum samples from all groups were sent to a commercial laboratory service (Special Reference Laboratories, Tokyo, Japan) to measure serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels. Serum creatinine (Cr) concentrations were also examined by enzymatic method in their laboratory. Serum IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-1 were measured using ELISA. ELISA kits were purchased from R&D Systems, Inc. for IL-1β and IL-6 measurements and Life Technologies (Grand Island, NY, USA) for IL-1 and were used according to the manufacturer's protocols. Real-time PCR for ICAM-1 expression Quantitative real-time PCR was performed to examine ICAM-1 mrna expression in LPS-induced AKI. The kidney was removed at 6 h after LPS or saline injection [6]. Total RNA from kidney was isolated using Trizol reagent (Life Technologies), according to the manufacturer's protocol. First strand cdna was synthesized from 5 μg total RNA, using random hexamers with PrimeScript (Takara Bio Inc., Otsu, Japan). Real-time RT-PCR was performed on StepOnePlus (Life Technologies) using TaqMan Universal PCR Master Mix (Life Technologies) and TaqMan gene expression assays (Life Technologies) for ICAM-1 (assay ID: Mm51623_m1) and β-actin
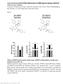
3 Miyazaki et al. BMC Nephrology 212, 13:153 Page 3 of 7 (assay ID: Mm67939_s1) were used for quantification of mrna expression of the respective genes, according to the manufacturer's protocol. ICAM-1 levels were normalized by those of β-actin. Data were shown as the quantity relative to the control group. Histology For histopathological observation, the mice were sacrificed and kidneys were removed at 48 h after LPS injection. Each tissue was fixed in 1% formalin, embedded in paraffin, sectioned, and then stained with hematoxylin and eosin for morphological examination. Statistical analysis All data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). The Kruskal Wallis test was used to test for overall group differences and the Steel-Dwass test was used to test for between-group differences. Values of P<.5 were considered to represent statistical significance. Results In this study, no mice in LPS group and T-5224 group died at 48 h after intraperitoneal administration of LPS with 6 mg/kg. T-5224 dose-dependently inhibits LPS-induced serum TNF-α Serum TNF-α levels in mice peaked at 2 h after LPS injection (Figure 1a). Therefore, we examined the serum TNF-α levels at this point in all further experiments. Next, we investigated the dose-dependent effects of T-5224 on TNF-α expression in endotoxin-induced AKI. All doses of T-5224 significantly inhibited serum TNF-α levels compared to controls (Figure 1b). We also confirmed that T-5224 inhibited TNF-α dose dependently, as a dose of 3 mg/kg was more effective in reducing TNF-α production than that of 3 or 1 mg/kg (Figure 1b). T-5224 reduced serum BUN and Cr and pro-inflammatory cytokines Blood samples were collected for the measurement of serum BUN, Cr, IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-1 at the various optimal times (Figure 2). We examined serum BUN and Cr levels to evaluate kidney function. At the time of LPS or saline injection, serum BUN and Cr levels were comparable in all groups (Figure 3). In the LPS group, however, serum BUN and Cr levels were significantly increased at 24 h after LPS injection and further increased at 48 h, signifying kidney damage, while in the control group serum BUN and Cr levels remained low. The administration of T-5224 reduced serum BUN and Cr levels at both 24 h and 48 h. For a better understanding of potential mechanisms whereby T-5224 exerted a protective effect on renal function, we also analyzed the levels of serum TNF-α and other downstream cytokines. Serum TNF-α levels in the LPS group were significantly higher than in the control group, while treatment with T-5224 significantly attenuated its expression dose-dependently (Figure 1b). LPS also induced a significant increase in serum IL-1β andil-6levelscomparedwiththecontrol group. In contrast, T-5224 treatment inhibited LPSinduced increases of these cytokines (Figure 4a, b). We also examined the expression of IL-1, an antiinflammatory cytokine, and found that stimulation with LPS resulted in an equally significant up-regulation of IL-1 in the LPS and T-5224 groups, compared with the control group. (a) (b) 2 2 Serum TNF-α (pg/ml) 1 1 Serum TNF-α (pg/ml) 1 1 # 2 4 control LPS Time (hours) LPS+T-5224 (mg/kg) Figure 1 T-5224 attenuates LPS-induced TNF-α. a, determination of the point for TNF-α measurement. b, dose-dependent effects of T-5224 on TNF-α at 2 h after intraperitoneal LPS injection. Serum TNF-α levels peaked after LPS injection at 2 h ( ± pg/ml). T-5224 attenuated LPS-induced TNF-α release dose-dependently (n = 7 8 per group). P <.1 vs. control group. #P <.5 vs. LPS group. P <.1 vs. LPS group.
4 Miyazaki et al. BMC Nephrology 212, 13:153 Page 4 of 7 LPS or saline injection h 2 h 4 h 6 h 24 h 48 h BUN Cr IL-1 IL-6 IL-1β Figure 2 Time course for blood collection. LPS or saline was injected to mice at h. Subsequently, blood was taken at different time points for the measurement of BUN, Cr, IL-1, IL-6 and IL-1β. T-5224 inhibits ICAM-1 mrna in endothelium To determine whether T-5224 was capable of inhibiting the infiltration of neutrophils into the injured kidney, we measured mrna expression of ICAM-1 by quantitative real-time RT-PCR (Figure 5). Following LPS challenge, ICAM-1 mrna levels in the kidney were significantly higher than in the control group. However, T-5224 significantly inhibited LPS-induced ICAM-1 mrna expression. T-5224 attenuated LPS-induced histopathological changes in kidney To evaluate histopathological characteristics of kidney in mice, the tissue sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin were made (Figure 6). After LPS injection, histopathological examination revealed kidney damage characterized by renal tubular degeneration and dilatation with variable flattening of the cytoplasm and loss of brush border. In contrast, treatment with T-5224 reduced the extent of kidney injury. Discussion In the present study, we demonstrated that a selective c-fos/ap-1 inhibitor, T-5224, suppressed LPS-induced TNF-α production dose-dependently. The inhibition of TNF-α is considered an effective treatment for septic AKI. The current study indicates that renal protection induced by T-5224 administration during endotoxemia occurs by controlling the expression of TNF-α and other downstream mediators. Sepsis has been identified as the most common cause of AKI in intensive care units. Moreover, the combination of sepsis and AKI is associated with a very high mortality rate [1]. There is, therefore, an urgent need to identify novel therapeutic interventions with the potential to attenuate septic AKI. Numerous cytokines released from leukocytes and renal tubular cells in the injured kidney function as essential components of the initiation and extension of inflammation in AKI [7]. Hence, the pharmacological inhibition of these inflammatory mediators is a (a) BUN (mg/dl) control LPS LPS+T Time (hours) (b) Cr (mg/dl) control LPS LPS+T-5224 * # Time (hours) Figure 3 Effect of T-5224 on serum BUN and Cr levels after LPS injection. LPS induced serum BUN and Cr levels. a, BUN in the T-5224 group was significantly lower than that in the LPS group at both 24 h and 48 h (24 h, 65.5 ± 13.8 mg/dl vs. 1 ± 15.5 mg/dl; 48 h, 79.8 ± 41.9 mg/dl vs ± 37.4 mg/dl). b, T-5224 also attenuated the increase of serum Cr induced in LPS group (24 h,.13 ±.4 mg/dl vs..21 ±.1 mg/dl; 48 h,.32 ±.23 mg/dl vs..93 ±.11 mg/dl) (n = 6 12 per group). *P <.5 vs. control group. P <.1 vs. control group. #P <.5 vs. LPS group. P <.1 vs. LPS group.
5 Miyazaki et al. BMC Nephrology 212, 13:153 Page 5 of 7 (a) (b) 15 serum IL-1β (pg/ml) serum IL-6 (ng/ml) 1 5 (c) Control LPS LPS+T-5224 Control LPS LPS+T serum IL-1 (pg/ml) control LPS LPS+T-5224 Figure 4 Effect of T-5224 on serum cytokines following LPS administration. a, the administration of T-5224 decreased serum IL-1β (132.7 ± 32.3 pg/ml vs ± 85.9 pg/ml). b, IL-6 levels were decreased after T-5224 treatment (44.4 ± 16.6 ng/ml vs ± 29.1 ng/ml) as compared with the LPS group. c, serum IL-1 levels in the T-5224 group were similar to the LPS group ( ± 42.3 pg/ml vs ± pg/ml) (n = 6 9 per group). P <.1 vs. control group. P <.1 vs. LPS group. Normalized Relative Quantity (ICAM-1/β-actin) Control LPS LPS+T-5224 Figure 5 Effect of T-5224 on ICAM-1 mrna expression in injured kidney. Bars represent the relative ratio of ICAM-1 mrna to the control group. T-5224 significantly inhibited LPS-induced ICAM-1 mrna expression in the kidney (4.2 ± 1.4 vs. 8.2 ± 1.4) (n = 4 6 per group). P <.1 vs. control group. P <.1 vs. LPS group. potential therapeutic target in the treatment of endotoxemia with bacterial infection. Recent studies indicated TNF-α is critical in mediating LPS-induced kidney injury [8]. Inhibition of TNF-α by genetic or antibody techniques inhibited renal injury following ischemia [9], cisplatin [1] or LPS [11] administration. Aikawa et al. designed and synthesized a selective c-fos/ap-1 inhibitor termed T-5224 using 3D pharmacophore modeling based on the crystal structure of the AP-1 DNA complex [5]. c-fos/ap-1 controls the expression of inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α by binding directly to AP-1 motifs in the promoter of the gene, and T-5224 treatment resolved arthritis in a mouse model. The transcription factor AP-1 is also activated by LPS, leading to enhanced TNF-α transcription [12]. T-5224 inhibited the expression of TNF-α and other cytokines in a mouse arthritis model [5], suggesting it may also inhibit LPS-induced TNF-α production. Indeed, we demonstrated that T-5224 attenuated serum TNF-α levels dose-dependently following LPS administration and reduced serum BUN and Cr levels, indicating T-5224 can protect against LPS-induced AKI. Apart from the inhibition of serum TNF-α during endotoxemia, T-5224 decreased other serum cytokines, namely
6 Miyazaki et al. BMC Nephrology 212, 13:153 Page 6 of 7 Figure 6 Renal injury after LPS injection. A, LPS caused tubular injury as manifested by tubular degeneration and dilatation. B, In contrast, there was less tubular damage in T-5224 group. The sections shown were harvested 48 h after LPS injection and stained with H&E. Magnification: 4. IL-1β and IL-6. IL-1β is important in multiple organ failure and death during endotoxemia. IL-1β, a proinflammatory cytokine, evokes similar pathophysiological responses to TNF-α. Inhibition of IL-1β signaling by treatment with recombinant IL-1β receptor antagonist, resulted in decreased mortality in an animal model of endotoxic shock [13]. On the other hand, elevated plasma concentrations of IL-6 predict AKI in patients with severe sepsis [14] and mortality in sepsis correlates with the degree of IL-6 up regulation [15]. T-5224 showed a remarkable inhibition of IL-1β and IL-6 production in mice challenged with LPS, suggesting that T-5224 can protect renal function against LPS, at least in part, via inhibiting both IL-1β and IL-6 production. IL-1, an anti-inflammatory cytokine, plays an important role in improving survival in animals challenged with LPS and inhibits several macrophage functions including TNF-α production in vivo and in vitro [16]. However, one study has reported that TNF-α signaling can promote IL-1 production [17]. Considering this, there was a possibility that T-5224 might inhibit IL-1 production. However, T-5224 did not suppress IL-1 production in our study. This observation is of interest since modulating the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory responses and restoring immune homeostasis of patients is important in the treatment of sepsis. The effect of T-5224 on ICAM-1 mrna expression in the kidney was also examined. ICAM-1 is a member of the immunoglobulin-like supergene family of adhesion molecules known to mediate adherence of polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs) to endothelial cells [18]. Both LPS and TNF-α increase the cell surface expression of ICAM-1 [19], which is one of several downstream effectors induced by TNF-α. The present study demonstrated that mrna expression of ICAM-1 was significantly increased in the kidney at 6 h after LPS injection and was markedly attenuated by treatment of T The role of ICAM-1 in PMN accumulation has been suggested in endotoxemic AKI and a deficiency of ICAM-1 may confer protection against LPS-induced AKI, by decreasing neutrophil adhesion and abrogating signaling events that occur in endothelium upon ligation of ICAM- 1. Thus, our results suggested that T-5224 might also protect mice against LPS-induced AKI by decreasing ICAM-1 expression. We also examined renal histological change at 48 h after LPS injection. As previous study reported, LPS induced severe renal tubular injury [2]. In this study, mice in LPS group also developed tubular injury. However, less tubular damage was observed in T-5224 group. Furthermore, pathological findings were well correlated with reduced expressions of TNF-α and other downstream effectors. These results indicated that T-5224 conferred protection against structural injury caused by LPS. Interestingly we observed few neutrophils in kidney, which suggests that ICAM-1 itself may cause renal injury through other as yet unknown neutrophil-independent mechanisms. In the present study, T-5224 did not completely suppress all inflammatory mediators. One potential explanation for this could be that genes encoding TNF-α are also transcriptionally activated through nuclear factor (NF)-κB activation [21]. NF-κB, a transcription factor, is critically involved in the regulation of monocytic production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β. T-5224 specifically inhibits the DNA binding activity of c-fos/c-jun, without affecting that of NF-κB/ p65 [5]. There are also several limitations in our study. First, we only examined BUN and Cr for kidney function, although these markers are insensitive and nonspecific for acute changes to kidney function. Therefore, these biomarkers may not detect an ongoing injury to the kidney. Second, T-5224 was administrated immediately after LPS injection. Considering the clinical situation, the delayed administration of T-5224 should also be investigated in the future. Third, intravenous administration is generally more effective than oral administration. However, we demonstrated that oral treatment with T-5224 was effective enough to improve kidney injury in
7 Miyazaki et al. BMC Nephrology 212, 13:153 Page 7 of 7 the acute phase of sepsis. The development of T-5224 for intravenous drug use is now underway. Conclusions We have shown that T-5224 attenuated LPS-induced AKI in mice. This protection was associated with reduced expressions of serum TNF-α and other downstream cytokines including IL-1β and IL-6. In addition, the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-1 was not affected by T Moreover, renal ICAM-1 mrna induced by LPS was suppressed by T Abbreviations AKI: Acute kidney injury; AP-1: Activator protein-1; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; Cr: Creatinine; ELISA: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay; ICAM- 1: Intercellular adhesion molecule-1; IL: Interleukin; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; MMPs: Matrix-degrading matrix metalloproteinases; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-κb; PMN: Polymorphonuclear neutrophil; 3D: Three-dimensional; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-α, H&E, hematoxylin and eosin. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests (SS holds a patent relating to the content of the manuscript, but has never received reimbursements, fees, funding, or salary from a company relating to the content of the manuscript). Authors' contributions HM, JM and UM designed and coordinated the study. HM was responsible for blood sample collection, and data acquisition. JM and UM were involved in the interpretation of the data and manuscript drafting. JM, UM, KN and NM reviewed the manuscript. SS conceived the study. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Acknowledgements We thank Toyama Chemical Co., Ltd. for providing T-5224 generously and Miss Hiromi Tanaka for technical support. Author details 1 Division of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Chuo-ku, Kobe, Hyogo 65-17, Japan. 2 Department of Medicine, Kyushu University Beppu Hospital, 4546 Tsurumihara, Beppu, Oita , Japan. 8. Schrier RW: Cancer therapy and renal injury. JClinInvest22, 11: Daemen MA, van de Ven MW, Heineman E, Buurman WA: Involvement of endogenous interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Transplantation 1999, 67: Ramesh G, Reeves WB: TNF-alpha mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest 22, 11: Cunningham PN, Dyanov HM, Park P, Wang J, Newell KA, Quigg RJ: Acute renal failure in endotoxemia is caused by TNF acting directly on TNF receptor-1 in kidney. J Immunol 22, 168: Hambleton J, Weinstein SL, Lem L, DeFranco AL: Activation of c-jun N- terminal kinase in bacterial lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1996, 93: Ohlsson K, Bjork P, Bergenfeldt M, Hageman R, Thompson RC: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature 199, 348: Chawla LS, Seneff MG, Nelson DR, Williams M, Levy H, Kimmel PL, Macias WL: Elevated plasma concentrations of IL-6 and elevated APACHE II score predict acute kidney injury in patients with severe sepsis. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 27, 2: Hotchkiss RS, Swanson PE, Freeman BD, Tinsley KW, Cobb JP, Matuschak GM, Buchman TG, Karl IE: Apoptotic cell death in patients with sepsis, shock, and multiple organ dysfunction. Crit Care Med 1999, 27: Moore KW, de Waal Malefyt R, Coffman RL, O Garra A: Interleukin-1 and the interleukin-1 receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 21, 19: Hirata N, Yanagawa Y, Ogura H, Satoh M, Noguchi M, Matsumoto M, Togashi H, Onoe K, Iwabuchi K: The role of tumor necrosis factor-α for interleukin-1 production by murine dendritic cells. Cell Immunol 211, 266: Brown KA, Brain SD, Pearson JD, Edgeworth JD, Lewis SM, Treacher DF: Neutrophils in development of multiple organ failure in sepsis. Lancet 26, 368: Myers CL, Wertheimer SJ, Schembri-King J, Parks T, Wallace RW: Induction of ICAM-1 by TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and LPS in human endothelial cells after downregulation of PKC. Am J Physiol 1992, 263:C Cunningham PN, Michael Holers V, Alexander JJ, Guthridge JM, Carroll MC, Quigg RJ: Complement is activated in kidney by endotoxin but does not cause the ensuing acute renal failure. Kidney Int 2, 58: Baldwin AS Jr: The NF-κB and I-κB proteins: new discoveries and insights. Annu Rev Immunol 1996, 14: doi:1.1186/ Cite this article as: Miyazaki et al.: The effects of a selective inhibitor of c-fos/activator protein-1 on endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury in mice. BMC Nephrology :153. Received: 26 July 212 Accepted: 18 November 212 Published: 23 November 212 References 1. Schrier RW, Wang W: Acute renal failure and sepsis. N Engl J Med 24, 351: Danese S, Dejana E, Fiocchi C: Immune regulation by microvascular endothelial cells: directing innate and adaptive immunity, coagulation, and inflammation. J Immunol 27, 178: Riedemann NC, Guo RF, Ward PA: The enigma of sepsis. J Clin Invest 23, 112: Whitmarsh AJ, Davis RJ: Transcription factor AP-1 regulation by mitogenactivated protein kinase signal transduction pathways. J Mol Med 1996, 74: Aikawa Y, Morimoto K, Yamamoto T, Chaki H, Hashiramoto A, Narita H, Hirono S, Shiozawa S: Treatment of arthritis with a selective inhibitor of c-fos/activator protein-1. Nat Biotechnol 28, 26: Wu X, Guo R, Wang Y, Cunningham PN: The role of ICAM-1 in endotoxininduced acute renal failure. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 27, 293:F Goes N, Urmson J, Ramassar V, Halloran PF: Ischemic acute tubular necrosis induces an extensive local cytokine response. Evidence for induction of interferon-gamma, transforming growth factor-beta 1, granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, interleukin-2, and interleukin-1. Transplantation 1995, 59: Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
Mari Ishida 1, Masaaki Ueki 2,3*, Jun Morishita 4, Masaki Ueno 5, Shunichi Shiozawa 6 and Nobuhiro Maekawa 2
 Ishida et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:49 DOI 10.1186/s40560-015-0115-2 RESEARCH Open Access T-5224, a selective inhibitor of c-fos/ activator protein-1, improves survival by inhibiting serum
Ishida et al. Journal of Intensive Care (2015) 3:49 DOI 10.1186/s40560-015-0115-2 RESEARCH Open Access T-5224, a selective inhibitor of c-fos/ activator protein-1, improves survival by inhibiting serum
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology
 Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Attribution: University of Michigan Medical School, Department of Microbiology and Immunology License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Increased levels of circulating 8-oxodeoxyguanosine as a biomarker of sepsis severity in mice
 Hirata et al. Journal of Intensive Care 2014, 2:41 RESEARCH Open Access Increased levels of circulating 8-oxodeoxyguanosine as a biomarker of sepsis severity in mice Jun-ichi Hirata 1*, Munehiko Ohya 1,
Hirata et al. Journal of Intensive Care 2014, 2:41 RESEARCH Open Access Increased levels of circulating 8-oxodeoxyguanosine as a biomarker of sepsis severity in mice Jun-ichi Hirata 1*, Munehiko Ohya 1,
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
PUBLICATIONS. cells. J. Physiol. (London) 517P:91P (Manchester, England, UK).
 277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
277 PUBLICATIONS Abstracts Haddad JJ, Land SC (1999). Differential activation of oxygen-responsive transcription factors over fetal-to-neonatal alveolar oxygen tensions in rat fetal distal lung epithelial
Towards Precision Medicine in Sepsis Patients: Are We Close?
 Towards Precision Medicine in Sepsis Patients: Are We Close? CRRT San Diego 2018 Peter Pickkers Department of Medicine Radboud university medical centre, Nijmegen No LPS circulating (n=55) P < 0.05 LPS
Towards Precision Medicine in Sepsis Patients: Are We Close? CRRT San Diego 2018 Peter Pickkers Department of Medicine Radboud university medical centre, Nijmegen No LPS circulating (n=55) P < 0.05 LPS
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the
 3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
3 RESULTS As outlined under External contributions (see appendix 7.1), the group of Prof. Gröne at the DKFZ in Heidelberg (Dept. of Cellular and Molecular pathology) contributed to this work by performing
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung
 IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IKKα Causes Chromatin Modification on Pro-Inflammatory Genes by Cigarette Smoke in Mouse Lung Se-Ran Yang, Samantha Valvo, Hongwei Yao, Aruna Kode, Saravanan Rajendrasozhan, Indika Edirisinghe, Samuel
IL-17 in health and disease. March 2014 PSO13-C051n
 IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
IL-17 in health and disease March 2014 PSO13-C051n Originally Researchers Suggested That IL-12 and IL-4 drove Th Cell Differentiation Naïve CD4 + T cell Question: Which of these cell types is responsible
Materials and Methods
 Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
Protective effect of epigallocatechin gallate, a major constituent of green tea, against renal ischemia reperfusion injury in rats
 DOI 10.1007/s11255-015-1030-0 NEPHROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Protective effect of epigallocatechin gallate, a major constituent of green tea, against renal ischemia reperfusion injury in rats Jun Lv 1 Min
DOI 10.1007/s11255-015-1030-0 NEPHROLOGY - ORIGINAL PAPER Protective effect of epigallocatechin gallate, a major constituent of green tea, against renal ischemia reperfusion injury in rats Jun Lv 1 Min
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel:
 Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
Cytokines (II) Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceu5cs Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 aalshamsan@ksu.edu.sa Learning Objectives By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1 Understand the physiological
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/4/199/ra75/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Signaling by the Matrix Proteoglycan Decorin Controls Inflammation and Cancer Through PDCD4 and MicroRNA-21 Rosetta
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
alveolar macrophages (AMs) after 24 hours of in vitro culture in complete medium
 Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Histone modifications in kidney disease
 Histone modifications in kidney disease Masaomi Nangaku Division of Nephrology and Endocrinology The University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine Japan Mimura, Tanaka, & Nangaku. Semin Nephrol 2013
Histone modifications in kidney disease Masaomi Nangaku Division of Nephrology and Endocrinology The University of Tokyo Graduate School of Medicine Japan Mimura, Tanaka, & Nangaku. Semin Nephrol 2013
The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis
 Kajbaf and Lalau BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2013, 14:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis Farshad
Kajbaf and Lalau BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2013, 14:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis Farshad
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt.
 MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
MAF Shalaby Prof. Rheumatology Al Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt. AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE RA SLE VASCULITIS RELAPSING POLYCHONDRITIS SS DM/PM SJOGREN S SYNDROME RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS Classically immune mediated
Autoimmune Diseases. Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic
 Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Autoimmune Diseases Betsy Kirchner CNP The Cleveland Clinic Disclosures (financial) No relevant disclosures Learning Objectives Explain the pathophysiology of autoimmune disease Discuss safe administration
Subject Index. Bcl-2, apoptosis regulation Bone marrow, polymorphonuclear neutrophil release 24, 26
 Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Subject Index A1, apoptosis regulation 217, 218 Adaptive immunity, polymorphonuclear neutrophil role 31 33 Angiogenesis cancer 178 endometrium remodeling 172 HIV Tat induction mechanism 176 inflammatory
Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules
 MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
MICR2209 Structure and Function of Antigen Recognition Molecules Dr Allison Imrie allison.imrie@uwa.edu.au 1 Synopsis: In this lecture we will examine the major receptors used by cells of the innate and
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Chapter 13: Cytokines
 Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Chapter 13: Cytokines Definition: secreted, low-molecular-weight proteins that regulate the nature, intensity and duration of the immune response by exerting a variety of effects on lymphocytes and/or
Part-I: Screening. 3.1 Assessment of non-toxic concentration of test compounds in RAW cells. Results
 Part-I: Screening Our strategy was to look for compounds which can inhibit HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1) release in activated macrophages and check effect of screened compound on endotoxemic mice.
Part-I: Screening Our strategy was to look for compounds which can inhibit HMGB1 (high mobility group box 1) release in activated macrophages and check effect of screened compound on endotoxemic mice.
Gene expression profiling in pediatric septic shock: biomarker and therapeutic target discovery
 Gene expression profiling in pediatric septic shock: biomarker and therapeutic target discovery Hector R. Wong, MD Division of Critical Care Medicine Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Cincinnati
Gene expression profiling in pediatric septic shock: biomarker and therapeutic target discovery Hector R. Wong, MD Division of Critical Care Medicine Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Cincinnati
Innate Immunity & Inflammation
 Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
Innate Immunity & Inflammation The innate immune system is an evolutionally conserved mechanism that provides an early and effective response against invading microbial pathogens. It relies on a limited
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
B-cell. Astrocyte SCI SCI. T-cell
 RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
Basis and Clinical Applications of Interferon
 Interferon Therapy Basis and Clinical Applications of Interferon JMAJ 47(1): 7 12, 2004 Jiro IMANISHI Professor, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine Abstract: Interferon (IFN) is an antiviral substance
Interferon Therapy Basis and Clinical Applications of Interferon JMAJ 47(1): 7 12, 2004 Jiro IMANISHI Professor, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine Abstract: Interferon (IFN) is an antiviral substance
Introduction. Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats
 Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Acute sodium overload produces renal tubulointerstitial inflammation in normal rats MI Roson, et al. Kidney International (2006) Introduction Present by Kanya Bunnan and Wiraporn paebua Tubular sodium
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection
 Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Intrinsic cellular defenses against virus infection Detection of virus infection Host cell response to virus infection Interferons: structure and synthesis Induction of antiviral activity Viral defenses
Two projects. Innate immunity, human gene6cs and resistance to infec6on. HAMLET; a new type of tumor- killing molecular complex
 Two projects Innate immunity, human gene6cs and resistance to infec6on HAMLET; a new type of tumor- killing molecular complex Innate immune signaling Toxins d Capsule Metabolic genes Metalbinding proteins
Two projects Innate immunity, human gene6cs and resistance to infec6on HAMLET; a new type of tumor- killing molecular complex Innate immune signaling Toxins d Capsule Metabolic genes Metalbinding proteins
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Innate Immunity. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter 3. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Know Differences and Provide Examples Chapter * Innate Immunity * kin and Epithelial Barriers * Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive
Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis
 Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis John C. Marshall, MD FRCSC St. Michael s Hospital Critical Care Canada Forum 2012 Toronto, Canada October 29, 2012 University of Toronto Thanks to Songhui Jia
Neutrophils in the Pathogenesis of Sepsis John C. Marshall, MD FRCSC St. Michael s Hospital Critical Care Canada Forum 2012 Toronto, Canada October 29, 2012 University of Toronto Thanks to Songhui Jia
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses. Skin Biology Lecture Series
 Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
Cutaneous Immunology: Innate Immune Responses Skin Biology Lecture Series The Immune Response: Innate and Adaptive Components Source: Wolff, Goldsmith, Katz, Gilchrest, Paller, Leffell. Fitzpatrick s Dermatology
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases
 Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION
 CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
CYTOKINE RECEPTORS AND SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION What is Cytokine? Secreted popypeptide (protein) involved in cell-to-cell signaling. Acts in paracrine or autocrine fashion through specific cellular receptors.
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection. All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention. Infusates/ drugs. hub/lines Dressing
 Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
Pathophysiology of Catheter-Related Infection All sources of infection are potential targets for prevention catheter hematogeneous Infusates/ drugs hub/lines Dressing skin Critically ill patient: 2-4 vascular
Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15)
 Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15) I. General types of immunity (Chapter 15 introduction) a. Innate i. inborn ii. pattern recognition b. Adaptive i. "learned" through exposure
Independent Study Guide The Innate Immune Response (Chapter 15) I. General types of immunity (Chapter 15 introduction) a. Innate i. inborn ii. pattern recognition b. Adaptive i. "learned" through exposure
Novel mechanism of hepatocyte growth factor against prevention of inflammation and oxidative
 136 Mini Review Novel mechanism of hepatocyte growth factor against prevention of inflammation and oxidative stress Kazutaka Shimizu 1), Yoshiaki Taniyama 1, 2, ), Fumihiro Sanada 1), Masaaki Iwabayashi
136 Mini Review Novel mechanism of hepatocyte growth factor against prevention of inflammation and oxidative stress Kazutaka Shimizu 1), Yoshiaki Taniyama 1, 2, ), Fumihiro Sanada 1), Masaaki Iwabayashi
Accepted Manuscript. Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development. Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo
 Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Accepted Manuscript Innate immune cells regulate oncoimmunity and cancer development Ai-Ping Bai, Yuan Guo PII: S0016-5085(18)34974-6 DOI: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.057 Reference: YGAST 62119 To appear
Innate Immunity. Chapter 3. Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity. Know Differences and Provide Examples. Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin
 Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Chapter Know Differences and Provide Examples Innate Immunity kin and Epithelial Barriers Antimicrobial peptide psoriasin -Activity against Gram (-) E. coli Connection Between Innate and Adaptive Immunity
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Expression of complement factors is induced in DBA/2 mice following administration of C. albicans
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Expression of complement factors is induced in DBA/2 mice following administration of C. albicans water-soluble mannoprotein-beta-glucan complex (CAWS) Noriko Nagi-Miura 1,, Daisuke
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Expression of complement factors is induced in DBA/2 mice following administration of C. albicans water-soluble mannoprotein-beta-glucan complex (CAWS) Noriko Nagi-Miura 1,, Daisuke
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis. Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University
 Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
ACR Meeting November, 2012
 ACR Meeting November, 212 Arhalofenate is a Novel Dual-Acting Agent with Uricosuric and Anti-Inflammatory Properties Yun-Jung Choi, Vanina Larroca, Annette Lucman, Vic Vicena, Noe Abarca, Tim Rantz, Brian
ACR Meeting November, 212 Arhalofenate is a Novel Dual-Acting Agent with Uricosuric and Anti-Inflammatory Properties Yun-Jung Choi, Vanina Larroca, Annette Lucman, Vic Vicena, Noe Abarca, Tim Rantz, Brian
Acute Kidney Injury: Basic Research Interactive Workshop
 Acute Kidney Injury: Basic Research Interactive Workshop Lisa Robinson, MD, FRCP(C) Division of Nephrology, The Hospital for Sick Children Renal Transplant Program, SickKids Transplant Centre Program in
Acute Kidney Injury: Basic Research Interactive Workshop Lisa Robinson, MD, FRCP(C) Division of Nephrology, The Hospital for Sick Children Renal Transplant Program, SickKids Transplant Centre Program in
Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis
 193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH
 T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
T Cell Effector Mechanisms I: B cell Help & DTH Ned Braunstein, MD The Major T Cell Subsets p56 lck + T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ p56 lck CD8+ T cells γ δ ε ζ ζ Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 CD8 Cα Cβ Vα Vβ CD3 MHC II peptide
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
Agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-c, rosiglitazone, reduces renal injury and dysfunction in a murine sepsis model
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 1057 1065 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh705 Advance Access publication 29 March 2005 Original Article Agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-c, rosiglitazone, reduces
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2005) 20: 1057 1065 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfh705 Advance Access publication 29 March 2005 Original Article Agonist of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-c, rosiglitazone, reduces
Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases
 54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
54 Review Article Interleukin-6; pathogenesis and treatment of autoimmune inflammatory diseases Toshio Tanaka 1, 2), Masashi Narazaki 3), Kazuya Masuda 4) and Tadamitsu Kishimoto 4, ) 1) Department of
Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic
 Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic differentiation of acute myeogenouse leukemia cells that is enhanced by 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin D 3. To the Editor: Sunitinib,
Sunitinib, an orally available receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, induces monocytic differentiation of acute myeogenouse leukemia cells that is enhanced by 1,25-dihydroxyviatmin D 3. To the Editor: Sunitinib,
EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES
 EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES JAMES M. ANDERSON, MD, PhD DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR DEPARTMENTS OF PATHOLOGY, MACROMOLECULAR SCIENCE, AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING CASE WESTERN
EARLY INFLAMMATORY RESPONSES TO VASCULAR DEVICES JAMES M. ANDERSON, MD, PhD DISTINGUISHED UNIVERSITY PROFESSOR DEPARTMENTS OF PATHOLOGY, MACROMOLECULAR SCIENCE, AND BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING CASE WESTERN
Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases. Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka
 131 Mini Review Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka The First Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental
131 Mini Review Role of JAKs in myeloid cells and autoimmune diseases Satoshi Kubo, Kunihiro Yamaoka and Yoshiya Tanaka The First Department of Internal Medicine, University of Occupational and Environmental
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia
 Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
Effect of Interleukin 10 on the Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells from Patients with Aplastic Anemia YOSHINOBU ASANO, SHOICHIRO SHIBATA, SHINJI KOBAYASHI, SEIICHI OKAMURA, YOSHIYUKI NIHO First Department
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adaptive immune response biologic response modifiers and, 735 737 S-Adenosylmethionine (SAMe) for hepatitis, 825 826 Albinterferon for hepatitis,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adaptive immune response biologic response modifiers and, 735 737 S-Adenosylmethionine (SAMe) for hepatitis, 825 826 Albinterferon for hepatitis,
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH
 FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
FOR OPTIMAL GUT HEALTH KEMIN.COM/GUTHEALTH ALETA A SOURCE OF 1,3-BETA GLUCANS Aleta is highly bioavailable, offering a concentration greater than 5% of 1,3-beta glucans. Aleta provides a consistent response
Intravenous Vitamin C. Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury
 Intravenous Vitamin C Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury Alpha A. (Berry) Fowler, III, MD Professor of Medicine VCU Pulmonary Disease and Critical Care Medicine I Have No Disclosures Bacterial Sepsis Approximately
Intravenous Vitamin C Severe Sepsis Acute Lung Injury Alpha A. (Berry) Fowler, III, MD Professor of Medicine VCU Pulmonary Disease and Critical Care Medicine I Have No Disclosures Bacterial Sepsis Approximately
Cardiovascular Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
 Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Animal Models to Understand Immunity
 Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Animal Models to Understand Immunity Hussein El Saghire hesaghir@sckcen.be Innate Adaptive immunity Immunity MAPK and NF-kB TLR pathways receptors Fast Slow Non-specific Specific NOD-like receptors T-cell
Neue Wirkungsmechanismen von Transfusionsplasma
 Neue Wirkungsmechanismen von Transfusionsplasma Lorenzo ALBERIO Médecin chef Hématologie générale et Hémostase Service et Laboratoire centrale d Hématologie CHUV, Lausanne Trauma patient Bleeding Thrombosis
Neue Wirkungsmechanismen von Transfusionsplasma Lorenzo ALBERIO Médecin chef Hématologie générale et Hémostase Service et Laboratoire centrale d Hématologie CHUV, Lausanne Trauma patient Bleeding Thrombosis
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon
 Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
Acute Kidney Injury for the General Surgeon UCSF Postgraduate Course in General Surgery Maui, HI March 20, 2011 Epidemiology & Definition Pathophysiology Clinical Studies Management Summary Hobart W. Harris,
NOTES. Received 24 January 2003/Returned for modification 21 February 2003/Accepted 6 June 2003
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2003, p. 5355 5359 Vol. 71, No. 9 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5355 5359.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Sept. 2003, p. 5355 5359 Vol. 71, No. 9 0019-9567/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/IAI.71.9.5355 5359.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. NOTES
Basis of Immunology and
 Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Basis of Immunology and Immunophysiopathology of Infectious Diseases Jointly organized by Institut Pasteur in Ho Chi Minh City and Institut Pasteur with kind support from ANRS & Université Pierre et Marie
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice
 Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
Sepsis and Multiple Organ Failure. J.G. van der Hoeven Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre
 Sepsis and Multiple Organ Failure J.G. van der Hoeven Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Sepsis - initiation Microorganism Tissue Damage Pathogen Associated Molecular Pattern (PAMP) Pattern Recognition
Sepsis and Multiple Organ Failure J.G. van der Hoeven Radboud University Nijmegen Medical Centre Sepsis - initiation Microorganism Tissue Damage Pathogen Associated Molecular Pattern (PAMP) Pattern Recognition
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Long-term protection studies. 45 minutes of ischemia was induced in wild type (S1pr2 +/+ ) and S1pr2 -/- by MCAO. A) 5 days later brains were harvested
MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit]
![MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit] MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit]](/thumbs/75/71629507.jpg) MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit] For research use only. Not for diagnostic use Version 1 (March-5-2013) Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents
MANUAL IL-1alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit [Interleukin-1 alpha (mouse) ELISA Kit] For research use only. Not for diagnostic use Version 1 (March-5-2013) Cat. No. AG-45B-0003-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
The role of microcirculatory and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsisinduced acute kidney injury (AKI): a. model of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction
 The role of microcirculatory and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsisinduced acute kidney injury (AKI): a model of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction Hernando Gomez, MD Mentors: Michael R. Pinsky, MD John
The role of microcirculatory and mitochondrial dysfunction in sepsisinduced acute kidney injury (AKI): a model of sepsis-induced organ dysfunction Hernando Gomez, MD Mentors: Michael R. Pinsky, MD John
1. TLR. TLR Toll-like receptors. Toll Toll-like receptor, TLR TLR TLR TLR. type I TLR TLR. Toll
 54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
54pp.145 152 2004 1. TLR T B TLR Toll-like receptors TLR TLR I IFN TLR T B B T Toll NF- B 1996 565-0871 3-1 TEL 06-6879-8303 FAX 06-6879-8305 E-mail uemattsu@biken.osaka-u.ac.jp Toll Toll-like receptor,
Crush Injury. Professeur D. MATHIEU. Medicine
 Crush Injury Professeur D. MATHIEU Department of Critical Care and Hyperbaric Medicine University Hospital of Lille - France Definitions Crush Injury An injury sustained when a body part is subjected to
Crush Injury Professeur D. MATHIEU Department of Critical Care and Hyperbaric Medicine University Hospital of Lille - France Definitions Crush Injury An injury sustained when a body part is subjected to
Supplementary Figure 1. Antibiotic partially rescues mice from sepsis. (ab) BALB/c mice under CLP were treated with antibiotic or PBS.
 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Antibiotic partially rescues mice from sepsis. (ab) BALB/c mice under CLP were treated with antibiotic or PBS. (a) Survival curves. WT Sham (n=5), WT CLP or WT CLP antibiotic
1 Supplementary Figure 1. Antibiotic partially rescues mice from sepsis. (ab) BALB/c mice under CLP were treated with antibiotic or PBS. (a) Survival curves. WT Sham (n=5), WT CLP or WT CLP antibiotic
Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium. fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production
 Supplementary Information Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production Aeyung Kim, Minju Im, Nam-Hui Yim
Supplementary Information Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production Aeyung Kim, Minju Im, Nam-Hui Yim
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System
 Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Newly Recognized Components of the Innate Immune System NOD Proteins: Intracellular Peptidoglycan Sensors NOD-1 NOD-2 Nod Protein LRR; Ligand Recognition CARD RICK I-κB p50 p65 NF-κB Polymorphisms in Nod-2
Interference of the general anesthetics propofol and isoflurane on lung morphology in mice septic
 Interference of the general anesthetics propofol and isoflurane on lung morphology in mice septic Davim A 1., Santos E 2 1 Departament of Anatomy. Centro Universitário do Rio Grande do Norte UNI-RN 2 Departament
Interference of the general anesthetics propofol and isoflurane on lung morphology in mice septic Davim A 1., Santos E 2 1 Departament of Anatomy. Centro Universitário do Rio Grande do Norte UNI-RN 2 Departament
Immunology for the Rheumatologist
 Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Immunology for the Rheumatologist Rheumatologists frequently deal with the immune system gone awry, rarely studying normal immunology. This program is an overview and discussion of the function of the
Interleukin-17 enhances the removal of respiratory syncytial virus in mice by promoting neutrophil migration and reducing interferon-gamma expression
 Interleukin-17 enhances the removal of respiratory syncytial virus in mice by promoting neutrophil migration and reducing interferon-gamma expression G. Zhang 1, K.F. Zhou 2 and Z.H. Lu 1 1 Department
Interleukin-17 enhances the removal of respiratory syncytial virus in mice by promoting neutrophil migration and reducing interferon-gamma expression G. Zhang 1, K.F. Zhou 2 and Z.H. Lu 1 1 Department
Supplementary Figure 1:
 Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Supplementary Figure 1: (A) Whole aortic cross-sections stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E), 7 days after porcine-pancreatic-elastase (PPE)-induced AAA compared to untreated, healthy control aortas
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients
 Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Analysis of regulatory T cell subsets in the peripheral blood of immunoglobulin A nephropathy (IgAN) patients S. Yang, B. Chen, J. Shi, F. Chen, J. Zhang and Z. Sun Department of Nephrology, Huaihe Hospital
Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15.
 Supplementary Table 1. Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15. Male Female Cytokine Control C-26 Control C-26 IL-1β 2.0 ± 0.8 9.6 ± 1.5* 1.8 ± 0.2 6.8 ± 1.4*
Supplementary Table 1. Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15. Male Female Cytokine Control C-26 Control C-26 IL-1β 2.0 ± 0.8 9.6 ± 1.5* 1.8 ± 0.2 6.8 ± 1.4*
Amelioration of Sepsis by TIE2 Activation- Induced Vascular Protection. Jenn Hou Burke Group Literature Seminar June 18 th 2016
 Amelioration of Sepsis by TIE2 Activation- Induced Vascular Protection Jenn Hou Burke Group Literature Seminar June 18 th 2016 Sepsis Globally, more than 19 million people are affected each year Causes
Amelioration of Sepsis by TIE2 Activation- Induced Vascular Protection Jenn Hou Burke Group Literature Seminar June 18 th 2016 Sepsis Globally, more than 19 million people are affected each year Causes
Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al
 Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al Suppl. Fig. 1 Tissue DN C Proteins kd TSC1-17 TSC 1 loxp bp -48-285 ctin PEMs Neutrophils
Supplementary Figures for TSC1 controls macrophage polarization to prevent inflammatory disorder by Linnan Zhu et al Suppl. Fig. 1 Tissue DN C Proteins kd TSC1-17 TSC 1 loxp bp -48-285 ctin PEMs Neutrophils
University of Groningen. Detoxification of LPS by alkaline phosphatase Tuin, Annemarie
 University of Groningen Detoxification of LPS by alkaline phosphatase Tuin, Annemarie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
University of Groningen Detoxification of LPS by alkaline phosphatase Tuin, Annemarie IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please
New biomarkers for ANCA-associated Vasculitis? Juliana Bordignon Draibe
 New biomarkers for ANCA-associated Vasculitis? Juliana Bordignon Draibe Summary Introduction Antibodies: ANCAs, Anti-LAMP-2, Anti-moesin B and T lymphocytes Markers of vascular activation: complement,
New biomarkers for ANCA-associated Vasculitis? Juliana Bordignon Draibe Summary Introduction Antibodies: ANCAs, Anti-LAMP-2, Anti-moesin B and T lymphocytes Markers of vascular activation: complement,
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, psoriasis
 IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
IMO-8400, a novel TLR7, TLR8 and TLR9 antagonist, inhibits disease development in mouse models of psoriasis Weiwen e Ja Jiang, Fu-Gang Zhu, Dong Yu, Ekambar R. Kandimalla, a a, Nicola La Monica, and Sudhir
Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer?
 Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer? Małgorzata Lipinska-Gediga Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Medical University Wroclaw,
Endothelium as a part of septic Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome (MODS)-is endocan an answer? Małgorzata Lipinska-Gediga Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Therapy Medical University Wroclaw,
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION. Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret
 ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
ROLE OF INFLAMMATION IN HYPERTENSION Dr Barasa FA Physician Cardiologist Eldoret Outline Inflammation in CVDs the evidence Basic Science in Cardiovascular inflammation: The Main players Inflammation as
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI
 SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
SCIRF Award #2016 I-03 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Neuron-specific Enolase and SCI 10-month Technical Progress Report Enolase is a multifunctional glycolytic enzyme involved in growth control, hypoxia,
