Determination of Hematocrit Interference in Blood Samples Derived from Patients with Different Blood Glucose Concentrations
|
|
|
- Augusta Oliver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 7, Issue 1, January 2013 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE Determination of Hematocrit Interference in Blood Samples Andreas, M.D., Ph.D., 1 Christina Schipper, Ph.D., 1 Sanja Ramljak, Ph.D., 1 Frank Flacke, Ph.D., 2 Jochen Sieber, M.D., 2 Thomas Forst, M.D., 1 and Petra B. Musholt, M.D. 1 Abstract Background: We performed a blood glucose meter hematocrit (HCT) interference test with lower sample manipulation requirements by using blood samples from patients with different blood glucose (BG) levels. Methods: Blood from five patients with different BG levels (2.8, 5.6, 8.3, 13.9, 19.4 mmol/liter) was manipulated to contain five different HCT concentrations (35/40/45/50/55%). Each sample was measured three times in parallel with 14 BG testing devices (reference method: YSI 2300 STAT Plus Glucose Analyzer). The largest mean deviations in both directions from the reference method (normalized to 100% at 45% HCT) were added as a measure for hematocrit interference factor (HIF). A HIF >10% was considered to represent clinically relevant HCT interference. Results: Few devices showed no clinically relevant HCT interference at high/low BG levels: BGStar (7.2%, 7.3%), ibgstar (9.0%, 8.6%), Contour (10.0%, 4.6%), OneTouch Verio 2 (10.0%, 5.2%), and GlucoMen LX (7.2%, 5.1%). Other devices showed interference at one or both glucose ranges: ACCU-CHEK Aviva (12.6%, 10.7%), Aviva Nano (7.2%, 10.5%), Breeze2 (3.6%, 30.2%), GlucoCard G+ (12.6%, 7.0%), OneTouch Ultra 2 (12.6%, 25.6%), FreeStyle Freedom Lite (9.0%, 11.0%), Precision Xceed (16.2%, 15.3%), and MediTouch (19.8%, 28.0%). The deviations in all devices were less pronounced in the HCT range of 35 50%. Conclusions: The results of this trial with less sample manipulation (HCT only) confirmed previous examinations with HCT and glucose manipulation. The same devices showed HCT stability as previously observed. Artificial sample manipulation may be less crucial than expected when evaluating HCT interference. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2013;7(1): Author Affiliations: 1 IKFE Institute for Clinical Research and Development, Mainz, Germany; and 2 Sanofi Diabetes, Global Medical Department, Frankfurt, Germany Abbreviations: (BG) blood glucose, (HCT) hematocrit, (HIF) hematocrit interference factor, (ISO) International Organization for Standarization, (MARD) mean absolute relative deviation, (SD) standard deviation Keywords: blood glucose, hematocrit, interference, self-monitoring Corresponding Author: Andreas, M.D., Ph.D., IKFE Institute for Clinical Research and Development, Parcusstr. 8, D Mainz, Germany; address andreasp@ikfe.de 170
2 Introduction Blood glucose (BG) meter accuracy can be affected by the underlying measurement technology, environmental factors, patient proficiency factors, and interfering substances. 1 Hematocrit (HCT) has long been known to interfere with many glucose measurement technologies. 2,3 Therefore, glucose meters are calibrated to provide accurate readings within a normal physiological range of values, typically 30 50%. Lower than normal HCT values (<30 to <35%) result in overestimation of laboratory glucose levels when glucose strip methods are used, whereas HCT values higher than normal (>45%) result in underestimates of laboratory values. 4 8 Various hypotheses have been proposed to explain the impact of abnormal HCT levels on glucose testing: altered viscosity of the blood, prevention of plasma from reaching the reaction surface of the test strip, change in diffusion kinetics, and/or increased packed red cell volume and displacement of plasma volume leading to insufficient plasma volume in the measurement chamber for accurate testing. 9 In recent laboratory investigations, we have been able to demonstrate that some of the modern glucose measurement technologies are stable against HCT interference, while others are not Technical solutions to correct for possible HCT interference include the parallel measurement of HCT with a subsequent correction algorithm as employed by point-of-care devices and handheld patient meters employing the same technology. 10,11 Another solution is the application of a physical and mathematical algorithm derived from a dynamic electrochemistry approach as employed by BGStar and ibgstar (Sanofi, Frankfurt, Germany). Dynamic electrochemistry involves making multiple measurements at different conditions (e.g., by varying frequencies and voltage) and readjusting the input stimulation signal in response to how the electron transfer kinetics at the electrode and the related chemistry is progressing. This dynamic adjustment results in a much richer output signal that forms the basis for a fingerprint that the meter s algorithms can analyze to develop correction factors to minimize distortion caused by interfering factors. 12,13 All our investigations, however, were performed in artificial laboratory settings with manipulated venous samples to achieve different BG and HCT ranges. While sample specimen and environmental factors were controlled in our experiments for all devices, other factors, such as the complexity of chemical reactions, the involvement of different co-enzymes, and additional unknown strip components may have further influenced the results. The more manipulations performed, the higher the likelihood that artificially introduced factors will affect the results (e.g., oxygen pressure in the sample) and influence readings. In this present investigation, we tried to reduce laboratory sample manipulation requirements by drawing blood samples from patients with different BG concentrations as induced by a clinical accuracy study protocol. We used this opportunity to perform another HCT interference study requiring only manipulation of the HCT value in the drawn blood sample. Materials and Methods This HCT interference protocol was performed as a substudy of an International Organization for Standardization (ISO) conform clinical system accuracy study protocol in accordance with local ethical and regulatory requirements. In the clinical trial, glucose and insulin interventions were used to achieve the different BG ranges as requested by ISO for clinical accuracy testing. 14 The results of this accuracy study are published elsewhere. 15 The responsible ethical review board approved the clinical accuracy study and the HCT interference sub-study and the participants gave written informed consent prior to any study procedure. Patients were required to be between 18 and 65 years of age, had to be healthy or have type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Criteria for exclusion included any serious concomitant disease, uptake of drugs known to interfere with capillary BG readings, drug or alcohol abuse, and any condition precluding successful compliance with study requirements as assessed by the investigator. The primary objective of the HCT interference evaluation was to demonstrate that the BGStar and ibgstar devices meet the HCT interference requirements as set forth in the Dutch TNO 2001Quality Guideline. 16 This guideline allows 171
3 a maximum deviation of ±10% for hyperglycemic values (>120 mg/dl, 6.5 mmol/liter) and ±18 mg/dl (1.0 mmol/liter) for hypoglycemic and normoglycemic ( 120 mg/dl, 6.5mmol/liter) values obtained from venous whole blood samples compared to a venous plasma reference method at HCT levels from 35 to 55% when tested at 5% increments. The secondary objectives were to demonstrate the absence of HCT interference in terms of mean deviation at a broader HCT range (25 65%) and at five different venous BG concentrations (50 60 mg/dl, mg/dl, mg/dl, mg/dl, mg/dl) in comparison with 11 competitive BG meter devices. The devices included in this investigation were: BGStar and ibgstar (Sanofi, Frankfurt, Germany), ACCU-CHEK Aviva and Aviva Nano (Roche Diagnostics, Indianapolis, IN), Contour and Breeze2 (Bayer Healthcare, Tarrytown, NY), OneTouch Ultra 2 and OneTouch Verio 2 (Lifescan, Milpitas, CA), FreeStyle Freedom Lite and Precision Xceed (Abbott Medisense, Alameda, CA), GlucoMen LX and GlucoCard G+ (Menarini, Florence, Italy) and MediTouch (Medisana, Dusseldorf, Germany). Venous heparinized whole blood samples were obtained from five patients with the following BG concentrations: 50 mg/dl (2.8 mmol/liter), 100 mg/dl (5.6 mmol/liter), 149 mg/dl (8.3 mmol/liter), 250 mg/dl (13.9 mmol/liter), and 349 mg/dl (19.8 mmol/liter). In order to achieve the planned HCT ranges of 25%, 30%, 35%, 40%, 45%, 50%, 55%, 60%, and 65%, part of the samples was gently centrifuged (3 min, 300xg) and the respective HCT value was established by careful addition of plasma or the cell fraction derived from the same sample. After gentle suspension of the blood sample, HCT and oxygen pressure were determined using the ABL80 FLEX CO-OX point-of-care device (Drott, Wiener Neudorf, Austria). If the oxygen pressure of an individual sample was outside of the physiological range (80 100%), the sample was discarded and preparation was repeated. Otherwise, parallel measurements were immediately performed with all tested devices within min and the reference method (YSI 2300 STAT Plus Glucose Analyzer, Life Sciences/Kreienbaum, Langenfeld, Germany, glucose oxidase method) test was performed before and after the device testing. Device measurements were performed in triplicate with two devices and two different strip lots per meter type obtained through regular local distribution channels. Total laboratory hands-on time per sample was less than 45 min. Statistical Analysis Data from each meter was tabulated. Mean values and standard deviations (SDs) for each meter type/sample combination were calculated. The mean glucose value with the HCT of 45% was set to be 100% in order to determine the bias (% deviation) at the different HCT and glucose levels. Results were analyzed to assess compliance with the TNO 2001 Quality Guideline [deviation <±10 % for values >120 mg/dl, (6.5 mmol/liter) and <±18 mg/dl (1.0 mmol/liter) for values 120 mg/dl]. The means of these deviations were used for calculating the mean absolute relative deviation (MARD) for each meter at the five glucose concentrations. A MARD <15% for the individual glucose level and a MARD over the entire glucose ranges <10% was defined as indicative for no clinically relevant influence of HCT on the BG readings. The data was calculated for each meter and individual glucose concentration. In addition, the mean deviation over the entire glucose range was determined for each meter type. Comparisons between mean values were calculated by means of the two-sided Student s t-test. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant. Results The blood samples were drawn from five subjects [four male, one female, age (mean ± SD): 61 ± 5 yrs., one with type 1 diabetes, four with type 2 diabetes]. Following careful manipulation of the HCT concentrations with confirmation of the HCT and oxygen pressure acceptance criteria, all measurements were carried out by an appropriate number of laboratory staff members in parallel for each meter within 20 min. The mean deviations observed for the combined samples at high and at low glucose concentrations and at HCT ranges 35 55% as defined by the TNO Quality Guideline are provided in Table 1. It can be seen that all BG meters fulfilled the TNO HCT interference requirements (<±1 mmol/liter for values <6.5 mmol/liter and <10% for values 6.5 mmol/liter, respectively). However, when testing the extended HCT range from 25 to 65%, larger deviations were 172
4 Table 1. Mean deviations of BG meter readings vs the reference method (YSI Stat Plus Glucose Analyzer) in the HCT range from 35% to 55% for values <6.5 mmol/liter (117 mg/dl) or 6.5 mmol/liter Device Low BG concentration <6.5 mmol/liter (117 mg/dl) High BG concentration 6.5 mmol/liter (117 mg/dl) Mean of total deviation (mmol/liter) Mean of total deviation (%) AccuChek Aviva AccuChek Aviva Nano BGStar ibgstar Breeze Contour GlucoMen LX GlucoCard G Freestyle Freedom Lite Precision Xceed OneTouch Ultra OneTouch Verio MediTouch observed in several devices as shown in Table 2. BGStar and ibgstar, together with three other devices (Contour, OneTouch Verio 2, and GlucoMen LX) showed stability against HCT interference over the entire HCT range. Two devices (FreeStyle Freedom Lite and GlucoCard G+) presented with slightly moderate deviations, while AccuChek Aviva and AccuChek Aviva Nano had larger deviations in the higher HCT range. The remaining devices (Breeze, OneTouch Ultra 2, Precision Xceed, and MediTouch) showed pronounced HCT interference over the entire HCT range. Table 2. Mean deviation (in mmol/liter) from the mean value measured at 45% HCT calculated from all five BG concentrations. To demonstrate HCT interference, values at 45% have been normalized to be 0.0 mmol/liter Device HCT(%) AccuChek Aviva AccuChek Aviva Nano BGStar ibgstar Breeze Contour FreeStyle Freedom Lite Precision Xceed GlucoMen LX GlucoCard G OneTouch Ultra OneTouch Verio MediTouch
5 The mean absolute deviations in mg/dl for the combined BG samples <6.5 mmol/liter (117 mg/dl) are provided in Figure 1 and the MARD for values 6.5 mmol/liter (117 mg/dl) are given in Figure 2. It can be seen that some devices performed very well at low glucose levels with mean deviations below 8 mg/dl over the entire HCT range (GlucoMen LX, BGStar, ibgstar, FreeStyle Freedom Lite, OneTouch Verio 2), while almost all devices stayed below 5% for MARD at the high glucose ranges (except MediTouch with 5.8%). Figure 1. Mean absolute deviation (in mg/dl) of the different BG meters from the reference method (YSI Stat 2300 Glucose Analyzer) in the samples with BG concentrations <6.5 mmol/liter (117 mg/dl) and with a HCT of 45%. A better benchmark comparison to determine HCT interference is the calculation of the hematocrit interference factor (HIF). It is calculated by adding the highest observed mean deviation over the entire glucose range above the 45% result to the highest absolute deviation below the 45% result, as described previously. 10,12 The result and ranking of the devices based on this parameter is provided in Figure 3. An HIF <15% for the individual glucose level and a mean HIF over the entire glucose ranges <0% was defined as indicative for no clinically relevant influence of HCT on the BG readings. The rationale for this arbitrarily defined threshold is provided by the fact that regulatory acceptance for a meter is given when the values are within a 15% range from the reference value (for values > 5.4 mmol/liter or 100 mg/dl) at normal HCT (new draft ISO guideline 17 ). The HCT-induced error is a potential additive to the criteria. We consider an HIF of <10% to be a maximal clinically acceptable value, as it would lead to a theoretical total error of 25%. It can be seen that several meters fulfilled the HCT stability criteria, while others did not (namely OneTouch Ultra 2, Breeze, Precision Xceed, and MediTouch). 174
6 Figure 2. Mean absolute relative deviation (in %) of the different BG meters from the reference method (YSI Stat 2300 Glucose Analyzer) in the samples with BG concentrations >6.5 mmol/liter (117 mg/dl) and with a HCT of 45%. Discussion Interfering substances are known to influence the quality of BG meters for patient self-measurement. One known interfering substance is blood viscosity as determined by the HCT value, which can be eliminated by direct HCT measurement and appropriate correction of the obtained signal 11,21 or by application of a mathematical correction for HCT interference by means of assessment of the different kinetics involved in the different confounding signals under different measurement conditions as employed by dynamic electrochemistry. 13,22 Prevalence of HCT variation is usually underestimated by physicians and diabetes nurse educators and is subject to seasonal variation. 18 Deviation from normal HCT levels can be induced by lifestyle interventions (e.g., smoking, prolonged exercise), by environmental conditions (e.g., high elevations, seasonal variation), demographic conditions (e.g., age), and disease and drug related conditions (e.g., hematological disorders, hypermenorrhea, pregnancy, or renal disease). 19,20 Hematocrit values, which are sampled at yearly peaks and through time points, with intervals of up to 6 months, may have 15% relative change (95% level), which indicates the potential within-subject variability in a normal healthy adult (e.g., a change from 0.42 to 0.48). 18 The practical relevance of HCT interference has been investigated only in high-risk populations (e.g., intensive care unit or neonatal patients), but information from community-based studies is lacking. 21 Recently, a first thorough investigation of the HCT distribution in an urban community has been published demonstrating a range 30 50% in 175
7 a healthy reference population, (20 60% in community patients, 10 70% in hospital patients, and 15 40% in intensive care patients). 22 In older patients also suffering from various additional chronic diseases, these variations can be much more pronounced and may have an impact on the patient s prognosis. 23 Therefore, HCT interference on BG meter results may represent a potential risk factor for diabetes patients whose well-being may be endangered by wrong insulin doses resulting from inaccurate BG readings. Using artificially produced samples in a laboratory setting, we have been able to demonstrate that devices employing dynamic electrochemistry are unaffected by HCT variation. 10,12 Laboratory tests with devices employing dynamic electrochemistry, however, require an extremely careful handling of the sample. The composition of whole blood samples deteriorates with aggressive centrifugation or vigorous shaking of samples as requested by many laboratory protocols applied during sample preparation for proficiency testing of BG meters. Artificially increasing oxygen pressure in the blood has an impact on the BGStar and ibgstar readings and needs to be completely avoided. When testing for HCT interference, however, a sample needs to be manipulated twice. First, a certain BG range needs to be established through addition of glucose or glucose consumption by the blood cells in the sample. Second, the desired HCT ranges have to be introduced through addition of cell free plasma or a cell suspension derived from the same blood sample. Figure 3. The HIF (addition of the highest observed mean deviation over the entire glucose range above the 45% result to the highest absolute deviation below the 45% result) of the tested devices as calculated from the entire HCT range. Devices with an HIF <10% are considered to be stable against HCT interference. 176
8 In our present study, we aimed to reduce sample variability. Glucose manipulation was avoided by drawing blood with different glucose levels as induced by intravenous glucose or intravenous insulin treatment in a clinical experiment. All experiments were performed with a sufficient number of investigators to ensure that each meter/strip combination was done without delay (within 20 min after oxygen testing) and in parallel for all device/strip lot combinations. The five BG samples were very carefully manipulated with respect to the HCT ranges and a physiological oxygen pressure was confirmed prior to the measurements. With this approach, we have been able to confirm the stability of BGStar and ibgstar against HCT interference. Our results for the other meters are generally in line with our results from previous investigations. We also confirmed HCT stability for Contour, OneTouch Verio 2, and GlucoCard G+. In addition, GlucoMen LX and AccuChek Aviva Nano showed much better performance than observed in the previous laboratory setting. These findings can be explained by technology improvements, which have been introduced by manufacturers in the time period between the previous and the current investigations. Sensitivity to HCT was again confirmed for the other devices. Given the overall comparability of the results of the pure laboratory approach with the present clinical-laboratory approach of sample preparation, it can be expected that HCT interference evaluations with samples derived entirely from artificial laboratory manipulations when performed by an experienced scientist may be a suitable way to test BG meter technologies. In conclusion, in this study with a hybrid clinical and laboratory approach for preparation of the test samples, the results from previous laboratory trials confirm that dynamic electrochemistry is an effective way to stabilize BG readings against HCT interference. Funding: This study was supported by a grant from Sanofi, Paris, France. Acknowledgements: The authors would like to thank the collaborators and patients of IKFE Clinic and IKFE Research Laboratory, who participated with great motivation in the performance of the measurements. Disclosures: Andreas, Thomas Forst, and Petra B. Musholt have received research grants, travel support, and speaker fees from SANOFI. Frank Flacke and Jochen Sieber are employees of SANOFI. References: 1. Ginsberg BH. Factors affecting blood glucose monitoring: Sources of error in measurement. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2009;3(4): Consensus statement on self-monitoring of blood glucose. Diabetes Care. 1987;10(1): American Diabetes Association. Clinical practice recommendations Diabetes Care. 1996;19 Suppl 1:S Pavlicek V, Garzoni D, Urech P, Brändle M. Inaccurate self-monitoring of blood glucose readings in patients on chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis with icodextrin. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2006;114(3): Puntmann I, Wosniok W, Haeckel R. Comparison of several point-of-care testing (POCT) glucometers with an established laboratory procedure for the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes using the discordance rate: a new statistical approach. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2003;41(6): Tang Z, Lee JH, Louie RF, Kost GJ. Effects of different hematocrit levels on glucose measurements with handheld meters for point-of-care testing. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000;124(8): Phillipou G, Seaborn CJ, Hooper J, Phillips PJ. Capillary blood glucose measurements in hospital in-patients using portable glucose meters. Aust N Z J Med. 1993;23(6): Smith EA, Kilpatrick ES. Intra-operative blood glucose measurements: the effect of haematocrit on glucose test strips. Anesthesia. 1994;49(2): Louie RF, Tang Z, Sutton DV, Lee JH, Kost GJ. Point-of-care glucose testing: effects of critical care variables, influence of reference instruments, and a modular glucose meter design. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2000;124(2):
9 10. Ramljak S, Lock JP, Schipper C, Musholt PB, Forst T, Lyon M, A. Hematocrit interference of blood glucose meters for patient selfmeasurement. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2013;7(1): A, Harzer O, Musholt PB, Scherer S, Löbig M, Forst T. Study on the performance of different blood glucose measurement systems when influenced by interfering substances. Diabetes Stoffw. Herz 2009;18: Musholt PB, Schipper C, Thomé N, Ramljak S, Schmidt M, Forst T, A. Dynamic electrochemistry corrects for hematocrit interference on blood glucose determinations with patient self-measurement devices. J. Diabetes Sci Technol. 2011;5(5): Iyengar S, Wiley M, Nadeau D. Performance of the WaveSense -Enabled glucose monitoring system across multiple lots. Diabetes, Stoffw Herz, 2007;16(1): DIN EN ISO 15197: In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems Requirements for Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus [ISO 15197:2003(E)]. 15. A, Mitri M, Musholt PB, Sachsenheimer D, Borchert M, Yap A, Forst T. Clinical assessment of the accuracy of blood glucose measurement devices. Curr Med. Res. Opin. 2012;28(4): Epub 2012 Mar TNO Quality Guideline PG/TG/ , Portable in-vitro blood monitor systems for (self)- monitoring - Blood Glucose Monitors - Particular requirements and test methods. Netherlands Organization for Applied Scientific Research, DIN EN ISO Draft: In Vitro Diagnostic Test Systems Requirements for Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Testing in Managing Diabetes Mellitus (ISO/DIS 15197:2010). 18. Thirup P. Haematocrit: within-subject and seasonal variation. Sports Med. 2003;33(3): Takubo T, Tatsumi N. Reference values for hematologic laboratory tests and hematologic disorders in the aged]. Rinsho Byori. 2000;48(3): Macdougall IC, Ritz E. The Normal Hematocrit Trial in dialysis patients with cardiac disease: are we any the less confused about target hemoglobin? Nephrol Dial Transplant. 1998;13(12): Christensen RD, Henry E, Jopling J, Wiedmeier SE. The CBC: reference ranges for neonates. Semin Perinatol. 2009;33(1): Lyon ME, Lyon AW. Patient acuity exacerbates the discrepancy between whole blood and plasma methods through error in molality to molarity conversion: Mind the gap!. Clin Biochem. 2011;44(5 6): Epub 2011 Jan Volkova N, Arab L. Evidence-based systematic literature review of hemoglobin/hematocrit and all-cause mortality in dialysis patients. Am J Kidney Dis. 2006;47(1):
GlucoMen LX PLUS blood glucose and blood ketone meter. Accuracy Evaluation to New ISO 15197:2013, with Technical and Specification Data
 GlucoMen LX PLUS: Accuracy Evaluations to ISO 15197:2013 with Technical and Specification Data GlucoMen LX PLUS blood glucose and blood ketone meter Accuracy Evaluation to New ISO 15197:2013, with Technical
GlucoMen LX PLUS: Accuracy Evaluations to ISO 15197:2013 with Technical and Specification Data GlucoMen LX PLUS blood glucose and blood ketone meter Accuracy Evaluation to New ISO 15197:2013, with Technical
BLOOD GLUCOSE METERS ACCURACY REQUIREMENTS
 BLOOD GLUCOSE METERS ACCURACY REQUIREMENTS International Standard ISO 15197:2013 (Second Edition 15/05/2013) In vitro diagnostic test systems Requirements for blood-glucose monitoring systems for self-testing
BLOOD GLUCOSE METERS ACCURACY REQUIREMENTS International Standard ISO 15197:2013 (Second Edition 15/05/2013) In vitro diagnostic test systems Requirements for blood-glucose monitoring systems for self-testing
MQ Comparison of glucometers using whole blood
 MQ 2017-1 Comparison of glucometers using whole blood Note: The instrument comparison is structured as a survey. This is a sample test, not a complete evaluation. Introduction Glucose self-testing devices
MQ 2017-1 Comparison of glucometers using whole blood Note: The instrument comparison is structured as a survey. This is a sample test, not a complete evaluation. Introduction Glucose self-testing devices
MQ Comparison of glucometers using heparin whole blood
 MQ 2014-1 Comparison of glucometers using heparin whole blood Note: The instrument comparison is structured as a survey. This is a sample test, not a complete evaluation. Introduction Glucose self-testing
MQ 2014-1 Comparison of glucometers using heparin whole blood Note: The instrument comparison is structured as a survey. This is a sample test, not a complete evaluation. Introduction Glucose self-testing
MQ Comparison of glucometers using whole blood
 MQ 2018-2 Comparison of glucometers using whole blood Note: The instrument comparison is structured as a survey. This is a sample test, not a complete evaluation. Introduction Glucose self-testing devices
MQ 2018-2 Comparison of glucometers using whole blood Note: The instrument comparison is structured as a survey. This is a sample test, not a complete evaluation. Introduction Glucose self-testing devices
FreeStyle Lite A Blood Glucose Meter That Requires No Coding
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2008 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Shridhara, Ph.D. Abstract Background: Abbott Diabetes Care introduced the FreeStyle Lite blood
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 4, July 2008 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Shridhara, Ph.D. Abstract Background: Abbott Diabetes Care introduced the FreeStyle Lite blood
White Paper, Evaluation of WaveSense JAZZ Blood Glucose Monitoring System Analytical Performance to EN ISO 15197:2015 Standard
 White Paper, Evaluation of WaveSense JAZZ Blood Glucose Monitoring System Analytical Performance to EN ISO 15197:2015 Standard 7500-10032 Rev F Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Changes introduced
White Paper, Evaluation of WaveSense JAZZ Blood Glucose Monitoring System Analytical Performance to EN ISO 15197:2015 Standard 7500-10032 Rev F Table of Contents Executive Summary 3 Changes introduced
Relationship between glucose meter error and glycemic control efficacy
 Relationship between glucose meter error and glycemic control efficacy Brad S. Karon, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic
Relationship between glucose meter error and glycemic control efficacy Brad S. Karon, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Department of Laboratory Medicine and Pathology Mayo Clinic
Bern Harrison, B.A., Cheryl Leazenby, B.S., and Solveig Halldorsdottir, Ph.D.
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 4, July 2011 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORTS Accuracy of the CONTOUR Blood Glucose Monitoring System Bern, B.A., Cheryl Leazenby,
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 5, Issue 4, July 2011 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORTS Accuracy of the CONTOUR Blood Glucose Monitoring System Bern, B.A., Cheryl Leazenby,
System accuracy evaluation of FORA Test N Go Blood Glucose Monitoring System versus YSI 2300 STAT Plus glucose analyzer following ISO 15197:2013
 System Accuracy Evaluation of Project number: Fora092614-01 System accuracy evaluation of Blood Glucose Monitoring System versus YSI 2300 STAT Plus glucose analyzer following ISO 15197:2013 Date: 13 th
System Accuracy Evaluation of Project number: Fora092614-01 System accuracy evaluation of Blood Glucose Monitoring System versus YSI 2300 STAT Plus glucose analyzer following ISO 15197:2013 Date: 13 th
Accuracy Evaluation of Five Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems: The North American Comparator Trial
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 7, Issue 5, September 2013 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE Accuracy Evaluation of Five Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems: The North American
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 7, Issue 5, September 2013 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE Accuracy Evaluation of Five Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems: The North American
Validity and Reliability of a Glucometer Against Industry Reference Standards
 514315DSTXXX10.1177/1932296813514315Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologySalacinski et al research-article2014 Original Article Validity and Reliability of a Glucometer Against Industry Reference
514315DSTXXX10.1177/1932296813514315Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologySalacinski et al research-article2014 Original Article Validity and Reliability of a Glucometer Against Industry Reference
System accuracy evaluation of FORA Test N Go Blood Glucose Monitoring System versus YSI 2300 STAT Plus glucose analyzer following ISO 15197:2013
 System accuracy evaluation of FORA Test N Go Blood Glucose Monitoring System versus YSI 2300 STAT Plus glucose analyzer following ISO 15197:2013 Abstract Objective: The goal of the study was to assess
System accuracy evaluation of FORA Test N Go Blood Glucose Monitoring System versus YSI 2300 STAT Plus glucose analyzer following ISO 15197:2013 Abstract Objective: The goal of the study was to assess
Equivalent Accuracy Evaluation of FORA Premium V10 Blood Glucose Monitoring System as Compared to Fora V30 Blood Glucose Monitoring System
 Equivalent Accuracy Evaluation of FORA Premium V10 Blood Glucose Monitoring System as Compared to Fora V30 Blood Glucose Monitoring System Abstract Objective: Both Fora Premium V10 and V30 blood glucose
Equivalent Accuracy Evaluation of FORA Premium V10 Blood Glucose Monitoring System as Compared to Fora V30 Blood Glucose Monitoring System Abstract Objective: Both Fora Premium V10 and V30 blood glucose
Ultra Blue. Test Strips UNISTRIP. Charlotte, NC V2-10/25/2018 TECHNOLOGIES,LLC
 VS UNISTRIP TECHNOLOGIES,LLC Charlotte, NC 28269 1-866-889-6229 V2-10/25/2018 UniStrip Generic Blood Glucose VS OneTouch Ultra Blue 1. Purpose This study is intended to evaluate the difference in values
VS UNISTRIP TECHNOLOGIES,LLC Charlotte, NC 28269 1-866-889-6229 V2-10/25/2018 UniStrip Generic Blood Glucose VS OneTouch Ultra Blue 1. Purpose This study is intended to evaluate the difference in values
Accuracy and Usability Evaluation of Six Commercially Available Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems
 Original Article Accuracy and Usability Evaluation of Six Commercially Available Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/34055.11671 Internal Medicine Section Anastasios Tentolouris 1,
Original Article Accuracy and Usability Evaluation of Six Commercially Available Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2018/34055.11671 Internal Medicine Section Anastasios Tentolouris 1,
510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY ASSAY ONLY TEMPLATE
 510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY ASSAY ONLY TEMPLATE A. 510(k) Number: k103542 B. Purpose for Submission: Alternative blood glucose test strips for use with LifeScan OneTouch
510(k) SUBSTANTIAL EQUIVALENCE DETERMINATION DECISION SUMMARY ASSAY ONLY TEMPLATE A. 510(k) Number: k103542 B. Purpose for Submission: Alternative blood glucose test strips for use with LifeScan OneTouch
" EXTERNAL QUALITY EVALUATION PROGRAM FOR POCT GLUCOSE TESTING years of experience
 Commissie voor Klinische Biologie Commission de Biologie Clinique " EXTERNAL QUALITY EVALUATION PROGRAM FOR POCT GLUCOSE TESTING 8 3 years of experience CM Van Campenhout JC Libeer WIV/ISP/IPH Clinical
Commissie voor Klinische Biologie Commission de Biologie Clinique " EXTERNAL QUALITY EVALUATION PROGRAM FOR POCT GLUCOSE TESTING 8 3 years of experience CM Van Campenhout JC Libeer WIV/ISP/IPH Clinical
Blood Glucose Test Strip Guidelines
 Berkshire West Integrated Care System Representing Berkshire West Clinical Commisioning Group Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire West Primary Care
Berkshire West Integrated Care System Representing Berkshire West Clinical Commisioning Group Royal Berkshire NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust Berkshire West Primary Care
Country-Specific Glucose Monitor List
 Country-Specific Glucose Monitor List Country Name: United States Important Information This is a non-comprehensive list, current as of December 2017. Absence of a specific glucose monitor or test strips
Country-Specific Glucose Monitor List Country Name: United States Important Information This is a non-comprehensive list, current as of December 2017. Absence of a specific glucose monitor or test strips
DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS)
 Type 2 Diabetes DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS) Clinical Guideline Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) should be considered but not be routinely offered for adults with type 2 diabetes
Type 2 Diabetes DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS) Clinical Guideline Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) should be considered but not be routinely offered for adults with type 2 diabetes
DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS)
 Type 2 Diabetes DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS) Clinical Guideline Self-monitoring of blood glucose should be offered to all newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients as an integral part
Type 2 Diabetes DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS) Clinical Guideline Self-monitoring of blood glucose should be offered to all newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients as an integral part
It s Just a Waived Glucose, Isn t It?
 It s Just a Waived Glucose, Isn t It? What Is the Next Step? Becky Damiani, MT (ASCP), Senior Inspection Specialist Laboratory Accreditation Program Objectives Understand the CLIA requirements surrounding
It s Just a Waived Glucose, Isn t It? What Is the Next Step? Becky Damiani, MT (ASCP), Senior Inspection Specialist Laboratory Accreditation Program Objectives Understand the CLIA requirements surrounding
Effects of Simulated Altitude on Blood Glucose Meter Performance: Implications for In-Flight Blood Glucose Monitoring
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 6, Issue 4, July 2012 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Simulated Altitude on Blood Glucose Meter Performance: Tolu, M.B.B.S., M.R.C.P.,
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 6, Issue 4, July 2012 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effects of Simulated Altitude on Blood Glucose Meter Performance: Tolu, M.B.B.S., M.R.C.P.,
Accuracy and Precision Performance of the Accu-Chek Mobile System. Introduction. Method
 Accuracy and Precision Performance of the Accu-Chek Mobile System I. ACCURACY The accuracy of the system was assessed according to ISO 15197. Introduction The purpose of this study was to determine the
Accuracy and Precision Performance of the Accu-Chek Mobile System I. ACCURACY The accuracy of the system was assessed according to ISO 15197. Introduction The purpose of this study was to determine the
Interference and Point-of-Care Testing Devices
 Interference and Point-of-Care Testing Devices Nam K. Tran, PhD, HCLD, (ABB), FACB Associate Clinical Professor Director of Clinical Chemistry, Special Chemistry/Toxicology and POCT 1 Learning Objectives
Interference and Point-of-Care Testing Devices Nam K. Tran, PhD, HCLD, (ABB), FACB Associate Clinical Professor Director of Clinical Chemistry, Special Chemistry/Toxicology and POCT 1 Learning Objectives
CHEMICAL REAGENTS 478 CHEMICAL REAGENTS. This document is dated 1 st March 2018
 This document is dated 1 st March 2018 Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR
This document is dated 1 st March 2018 Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR
DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS)
 DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS) Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Guideline Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) should be considered but not routinely offered for adults with type 2 diabetes
DIABETES BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING AT HOME (ADULTS) Type 2 Diabetes Clinical Guideline Self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) should be considered but not routinely offered for adults with type 2 diabetes
CHEMICAL REAGENTS 478 CHEMICAL REAGENTS. This document is dated 1 st October 2017
 This document is dated 1 st October 2017 Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR
This document is dated 1 st October 2017 Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR
Evaluation of Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX Blood Glucose Monitoring System
 Evaluation of Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX Blood Glucose Monitoring System Summary Objectives: To demonstrate that the TRUE METRIX Blood Glucose Monitoring System, from Trividia Health,
Evaluation of Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX Blood Glucose Monitoring System Summary Objectives: To demonstrate that the TRUE METRIX Blood Glucose Monitoring System, from Trividia Health,
HYDROXYBUTERATE) Gluco Rx Evolve KetoneTest Strips
 Scottish Drug Tariff Part 9 This document is dated 1 st November 2018 Page REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE FOR KETONES (BETA- HYDROXYBUTERATE) 478 DETECTION
Scottish Drug Tariff Part 9 This document is dated 1 st November 2018 Page REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR BLOOD GLUCOSE FOR KETONES (BETA- HYDROXYBUTERATE) 478 DETECTION
Guidance for the choice of blood glucose testing meters, strips and lancets
 Guidance for the choice of blood glucose testing meters, strips and lancets This guidance is intended to assist healthcare professionals in their selection of appropriate blood glucose meters and testing
Guidance for the choice of blood glucose testing meters, strips and lancets This guidance is intended to assist healthcare professionals in their selection of appropriate blood glucose meters and testing
Clinical Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX AIR Blood Glucose Monitoring System
 Clinical Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX AIR Blood Glucose Monitoring System Summary Objectives: To demonstrate that the TRUE METRIX AIR Blood Glucose Monitoring System, from Trividia
Clinical Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX AIR Blood Glucose Monitoring System Summary Objectives: To demonstrate that the TRUE METRIX AIR Blood Glucose Monitoring System, from Trividia
Using Blood Glucose Meters in the Hospital: Defining Critically Ill and Addressing Accreditation Issues
 Using Blood Glucose Meters in the Hospital: Defining Critically Ill and Addressing Accreditation Issues Stephen E. Kahn, PhD, DABCC, FACB Professor and Vice Chair, Clinical Services, Pathology Loyola University
Using Blood Glucose Meters in the Hospital: Defining Critically Ill and Addressing Accreditation Issues Stephen E. Kahn, PhD, DABCC, FACB Professor and Vice Chair, Clinical Services, Pathology Loyola University
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa
 MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa CARE OF PATIENT POLICY & PROCEDURE Policy Number: 4:10 Subject: Policy: Glucose Monitoring (Accuchek) Nursing department staff and laboratory staff
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa CARE OF PATIENT POLICY & PROCEDURE Policy Number: 4:10 Subject: Policy: Glucose Monitoring (Accuchek) Nursing department staff and laboratory staff
GUIDELINE FOR SELF MONITORING OF BLOOD GLUCOSE IN ADULTS WITH DIABETES
 It is recognised that self- monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) may have an important role to play for some patients with. It can allow individuals to see what impact particular behaviours, such as dietary
It is recognised that self- monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) may have an important role to play for some patients with. It can allow individuals to see what impact particular behaviours, such as dietary
FreeStyle Mini Blood Glucose Results Are Accurate and Suitable for Use in Glycemic Clamp Protocols
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society CLINICAL APPLICATIONS FreeStyle Mini Blood Glucose Results Are Accurate and Suitable for Use in
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society CLINICAL APPLICATIONS FreeStyle Mini Blood Glucose Results Are Accurate and Suitable for Use in
Report. Evaluation of system accuracy of the blood glucose monitoring system VivaChek Ino according to DIN EN ISO 15197: 2013
 Institute of Diabetes Gerhardt Katsch Karlsburg (IDK) Report Evaluation of system accuracy of the blood glucose monitoring system VivaChek Ino according to DIN EN ISO 15197: 2013 Sponsor: The study was
Institute of Diabetes Gerhardt Katsch Karlsburg (IDK) Report Evaluation of system accuracy of the blood glucose monitoring system VivaChek Ino according to DIN EN ISO 15197: 2013 Sponsor: The study was
CHEMICAL REAGENTS 478 PART 9 CHEMICAL REAGENTS. This document is dated 1 st March 2016.
 PART 9 This document is dated 1 st March 2016. Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS
PART 9 This document is dated 1 st March 2016. Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS
Evaluation of Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose System
 Evaluation of Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose System Summary Objectives: To demonstrate that the TRUE METRIX Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose System*, from Trividia
Evaluation of Accuracy and User Performance of the TRUE METRIX Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose System Summary Objectives: To demonstrate that the TRUE METRIX Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose System*, from Trividia
CHEMICAL REAGENTS 478 PART 9 CHEMICAL REAGENTS. This document is dated 1 st July 2015.
 PART 9 This document is dated 1 st July 2015. Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS
PART 9 This document is dated 1 st July 2015. Page 478 REAGENT SOLUTIONS 478 URINE TESTING REAGENTS 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR GLYCOSURIA 478 DETECTION STRIPS FOR KETONURIA (ACETONURIA) 478 DETECTION STRIPS
NICO /14 Nipro Diagnostics, Inc.
 Clinical Performance of the TRUEresult twist Blood Glucose Monitoring System () Using ISO 15197:13 Criteria for Accuracy Utilizing GDH-FAD Enzyme NICO-8 1/1 Nipro Diagnostics, Inc. NICO_8_mmol.indd CLINICAL
Clinical Performance of the TRUEresult twist Blood Glucose Monitoring System () Using ISO 15197:13 Criteria for Accuracy Utilizing GDH-FAD Enzyme NICO-8 1/1 Nipro Diagnostics, Inc. NICO_8_mmol.indd CLINICAL
System Accuracy Evaluation of 43 Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose according to DIN EN ISO 15197
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 6, Issue 5, September 2012 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE System Accuracy Evaluation of 43 Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems Guido, M.D.,
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 6, Issue 5, September 2012 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLE System Accuracy Evaluation of 43 Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems Guido, M.D.,
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa
 MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa CARE OF PATIENT POLICY & PROCEDURE Policy Number: 4:10 Subject: Policy: Glucose Monitoring (Accuchek) Nursing department staff and laboratory staff
MARSHALLTOWN MEDICAL & SURGICAL CENTER Marshalltown, Iowa CARE OF PATIENT POLICY & PROCEDURE Policy Number: 4:10 Subject: Policy: Glucose Monitoring (Accuchek) Nursing department staff and laboratory staff
Handheld and portable glucose devices are used for
 Effects of ph on Glucose Measurements With Handheld Glucose Meters and a Portable Glucose Analyzer for Point-of-Care Testing Zuping Tang, MD; Xiaogu Du, MD; Richard F. Louie, BS; Gerald J. Kost, MD, PhD
Effects of ph on Glucose Measurements With Handheld Glucose Meters and a Portable Glucose Analyzer for Point-of-Care Testing Zuping Tang, MD; Xiaogu Du, MD; Richard F. Louie, BS; Gerald J. Kost, MD, PhD
For more comprehensive information, please refer to the t:connect Application User Guide available online at: Getting Started Guide.
 Congratulations on the purchase of your new insulin pump from Tandem Diabetes Care. Your decision to use insulin pump therapy is a sign of your commitment to actively manage your diabetes. This guide provides
Congratulations on the purchase of your new insulin pump from Tandem Diabetes Care. Your decision to use insulin pump therapy is a sign of your commitment to actively manage your diabetes. This guide provides
Clinical Chemistry / INTENSIVE INSULIN THERAPY AND GLUCOSE VALUES
 Clinical Chemistry / INTENSIVE INSULIN THERAPY AND GLUCOSE VALUES Accuracy of Roche Accu-Chek Inform Whole Blood Capillary, Arterial, and Venous Glucose Values in Patients Receiving Intensive Intravenous
Clinical Chemistry / INTENSIVE INSULIN THERAPY AND GLUCOSE VALUES Accuracy of Roche Accu-Chek Inform Whole Blood Capillary, Arterial, and Venous Glucose Values in Patients Receiving Intensive Intravenous
GD50. Simple. Accurate. Reliable. Test Simply. Live Better. All FORA Diamond Series Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems use FORA Diamond Test Strips.
 GD50 Higher Measuring Accuracy Simple. Accurate. Reliable. Test Simply. Live Better. All FORA Diamond Series Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems use FORA Diamond Test Strips. GD50 Simple. Accurate. Reliable.
GD50 Higher Measuring Accuracy Simple. Accurate. Reliable. Test Simply. Live Better. All FORA Diamond Series Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems use FORA Diamond Test Strips. GD50 Simple. Accurate. Reliable.
Aina Blood Monitoring System
 Aina Blood Monitoring System Analytical Performance Summary The Aina Blood Monitoring System is a high quality and versatile multi-parameter diagnostic platform that is CE-marked and approved for sale
Aina Blood Monitoring System Analytical Performance Summary The Aina Blood Monitoring System is a high quality and versatile multi-parameter diagnostic platform that is CE-marked and approved for sale
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring. Kevin Walls April 12, :30 PM-7:30 PM.
 Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Kevin Walls April 12, 2018 6:30 PM-7:30 PM. Technology is evolving Technology is evolving at such a rapid rate it s hard to keep up. Imagine living a healthier life without
Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring Kevin Walls April 12, 2018 6:30 PM-7:30 PM. Technology is evolving Technology is evolving at such a rapid rate it s hard to keep up. Imagine living a healthier life without
Comparison of Lancing Devices for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Regarding Lancing Pain
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 3, Issue 5, September 2009 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Lancing Devices for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Regarding Lancing
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 3, Issue 5, September 2009 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of Lancing Devices for Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Regarding Lancing
Type 2 Diabetes Recommended SMBG
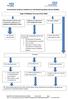 Herefordshire Diabetes Guideline for Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose (SMBG) Type 2 Diabetes Recommended SMBG Diet controlled/ metformin only/ combination of metformin and pioglitazone/dpp4/sglt2 or GLP1
Herefordshire Diabetes Guideline for Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose (SMBG) Type 2 Diabetes Recommended SMBG Diet controlled/ metformin only/ combination of metformin and pioglitazone/dpp4/sglt2 or GLP1
Glucometers Gastrostomy Tubes Nasogastric Tubes Insulin pumps Continuous Glucose monitoring system Closed Loop Smart phones/tablets
 Devices Glucometers Gastrostomy Tubes Nasogastric Tubes Insulin pumps Continuous Glucose monitoring system Closed Loop Smart phones/tablets Accuracy Glucometers The ISO (International Organization for
Devices Glucometers Gastrostomy Tubes Nasogastric Tubes Insulin pumps Continuous Glucose monitoring system Closed Loop Smart phones/tablets Accuracy Glucometers The ISO (International Organization for
COBAS, ACCU-CHECK INFORM, MODULAR and LIFE NEEDS ANSWERS are trademarks of Roche Roche
 Accu-Chek Inform II test strip Results of the evaluation study on newborns, conducted by the Flevo Hospital (FVZH) Almere and the Maxima Medical Center (MMC) Veldhoven in the Netherlands COBAS, ACCU-CHECK
Accu-Chek Inform II test strip Results of the evaluation study on newborns, conducted by the Flevo Hospital (FVZH) Almere and the Maxima Medical Center (MMC) Veldhoven in the Netherlands COBAS, ACCU-CHECK
In humans, self-monitoring of blood glucose is crucial
 J Vet Intern Med 2014;28:1405 1413 ISO-Based Assessment of Accuracy and Precision of Glucose Meters in Dogs Y. Brito-Casillas, P. Figueirinhas, J.C. Wiebe, L. Lopez-Rıos, D. Perez-Barreto, C. Melian, and
J Vet Intern Med 2014;28:1405 1413 ISO-Based Assessment of Accuracy and Precision of Glucose Meters in Dogs Y. Brito-Casillas, P. Figueirinhas, J.C. Wiebe, L. Lopez-Rıos, D. Perez-Barreto, C. Melian, and
Comparison of Three Whole Blood Creatinine Methods for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate Before Radiographic Contrast Administration
 Clinical Chemistry / Whole Blood Creatinine for egfr Comparison of Three Whole Blood Creatinine Methods for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate Before Radiographic Contrast Administration Nichole
Clinical Chemistry / Whole Blood Creatinine for egfr Comparison of Three Whole Blood Creatinine Methods for Estimation of Glomerular Filtration Rate Before Radiographic Contrast Administration Nichole
Assessment of a Critical Limit Protocol for Point-of-Care Glucose Testing
 CLINICAL CHEMISTRY Original Article Assessment of a Critical Limit Protocol for Point-of-Care Glucose Testing GIFFORD LUM, MD A critical limit protocol requiring that all point of care glucose meter readings
CLINICAL CHEMISTRY Original Article Assessment of a Critical Limit Protocol for Point-of-Care Glucose Testing GIFFORD LUM, MD A critical limit protocol requiring that all point of care glucose meter readings
Blood glucose test strips (BGTS) evaluation protocol and results. Update April Version 4.1. Note:
 Blood glucose test strips (BGTS) evaluation protocol and results Update April 2016 Version 4.1 Note: December 2017: Prescribing data indicates overall compliance with the GMMMG recommended BGTS of 86%.
Blood glucose test strips (BGTS) evaluation protocol and results Update April 2016 Version 4.1 Note: December 2017: Prescribing data indicates overall compliance with the GMMMG recommended BGTS of 86%.
Home Glucose Monitoring
 Home Glucose Monitoring Blood Glucose Monitors Name (Manufacturer/Distributor) Size (inches) Weight (ounces) Active (Roche) 4.6 X 1.07 X 0.9 2.01 without Advantage (Roche) 3.3 X 2.8 X 0.8 1.8 without Test
Home Glucose Monitoring Blood Glucose Monitors Name (Manufacturer/Distributor) Size (inches) Weight (ounces) Active (Roche) 4.6 X 1.07 X 0.9 2.01 without Advantage (Roche) 3.3 X 2.8 X 0.8 1.8 without Test
Quality Specifications for POCT
 Quality Specifications for POCT the patient journey perspective Christopher P Price Department of Clinical Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK Quality Specifications fit-for-purpose QUALITY
Quality Specifications for POCT the patient journey perspective Christopher P Price Department of Clinical Biochemistry, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK Quality Specifications fit-for-purpose QUALITY
Walsall CCG Supported Blood Glucose Meters April 2018
 Meter Name Picture Type Strips Lancets Information Company PRIMARY CARE INITIATION TEE2+ Uncomplicated Type 2 diabetes patient on TEE2 test CareSens Lancets Easy to use. Large clear display Bluetooth functionality
Meter Name Picture Type Strips Lancets Information Company PRIMARY CARE INITIATION TEE2+ Uncomplicated Type 2 diabetes patient on TEE2 test CareSens Lancets Easy to use. Large clear display Bluetooth functionality
Technical Evaluation of Five Glucose Meters With Data Management Capabilities
 Clinical Chemistry / LABORATORY EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE METERS Technical Evaluation of Five Glucose Meters With Data Management Capabilities Jeffrey]. Chance, PhD, Dai J. Li,MD, PhD, Kerrie A. Jones, MS,
Clinical Chemistry / LABORATORY EVALUATION OF GLUCOSE METERS Technical Evaluation of Five Glucose Meters With Data Management Capabilities Jeffrey]. Chance, PhD, Dai J. Li,MD, PhD, Kerrie A. Jones, MS,
Performance of three portable blood glucose monitoring devices used in a veterinary application
 Performance of three portable blood glucose monitoring devices used in a veterinary application Prepared by Michael I. Lindinger, PhD, Vice-President of Research, The Nutraceutical Alliance, Campbellville,
Performance of three portable blood glucose monitoring devices used in a veterinary application Prepared by Michael I. Lindinger, PhD, Vice-President of Research, The Nutraceutical Alliance, Campbellville,
FDA Perspective - Public Health Notification: Potentially Fatal Errors with GDH-PQQ Glucose Monitoring Technology Courtney C. Harper, Ph.D.
 FDA Perspective - Public Health Notification: Potentially Fatal Errors with GDH-PQQ Glucose Monitoring Technology Courtney C. Harper, Ph.D., Director, Division of Chemistry and Toxicology Devices Office
FDA Perspective - Public Health Notification: Potentially Fatal Errors with GDH-PQQ Glucose Monitoring Technology Courtney C. Harper, Ph.D., Director, Division of Chemistry and Toxicology Devices Office
EVALUATION OF THE PERFORMANCE OF THE TRUETRACK BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM USING THE ISO 15197:2003 ACCURACY AND USER EVALUATION REQUIREMENTS
 EVALUATION OF THE PERFORMANCE OF THE TRUETRACK BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM USING THE ISO 15197:23 ACCURACY AND USER EVALUATION REQUIREMENTS Douglas E. Bell, PhD Teri A. Sasse, RN, MS BACKGROUND: The
EVALUATION OF THE PERFORMANCE OF THE TRUETRACK BLOOD GLUCOSE MONITORING SYSTEM USING THE ISO 15197:23 ACCURACY AND USER EVALUATION REQUIREMENTS Douglas E. Bell, PhD Teri A. Sasse, RN, MS BACKGROUND: The
Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous Glucose Sensors
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 2, Issue 5, September 2008 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Agreement between Glucose Trends Derived from Three Simultaneously Worn Continuous
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Insulin pump use: ~ 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM < 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM 2007 FDA estimates ~375,000 insulin pumps for
Evaluation Report: Eurolyser CRP test (ST0100 and ST0102) on. CUBE analyser (CA0100)
 Evaluation Report: Eurolyser CRP test (ST0100 and ST0102) on CUBE analyser (CA0100) Location Location: Eurolyser Diagnostica GmbH Operators: Simone Wieser; Franz Helminger; Michael Gruber Date: July-November
Evaluation Report: Eurolyser CRP test (ST0100 and ST0102) on CUBE analyser (CA0100) Location Location: Eurolyser Diagnostica GmbH Operators: Simone Wieser; Franz Helminger; Michael Gruber Date: July-November
WHITE PAPER LOOKING PAST THE WINDOW DRESSING: UNDERSTANDING BLOOD GLUCOSE TESTING STRIPS IN A FORMULARY ENVIRONMENT
 WHITE PAPER LOOKING PAST THE WINDOW DRESSING: UNDERSTANDING BLOOD GLUCOSE TESTING STRIPS IN A FORMULARY ENVIRONMENT PURPOSE This paper explores the science behind glucose test strips and proposes the format
WHITE PAPER LOOKING PAST THE WINDOW DRESSING: UNDERSTANDING BLOOD GLUCOSE TESTING STRIPS IN A FORMULARY ENVIRONMENT PURPOSE This paper explores the science behind glucose test strips and proposes the format
Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new (MDRD) prediction equation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 1909 1913 Original Article Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new () prediction equation
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 1909 1913 Original Article Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new () prediction equation
Clinical Performance of the TRUE2go Blood Glucose Monitoring System Exceeds Minimum Criteria for Accuracy Using ISO 15197:2013
 linical Performance of the TRUE2go lood Glucose Monitoring System Exceeds Minimum riteria for Accuracy Using ISO 197:213 LINIAL STUY SUMMARY EVALUATION OJETIVES This clinical evaluation: 1. Evaluates the
linical Performance of the TRUE2go lood Glucose Monitoring System Exceeds Minimum riteria for Accuracy Using ISO 197:213 LINIAL STUY SUMMARY EVALUATION OJETIVES This clinical evaluation: 1. Evaluates the
Smart & Simple Mobile Solutions.
 Higher Measuring Accuracy Smart & Simple Mobile Solutions. Test Simply. Live Better. FORA Diamond lets you connect all your Bluetooth devices. *Also available with a Micro USB. ifora Diabetes Manager All
Higher Measuring Accuracy Smart & Simple Mobile Solutions. Test Simply. Live Better. FORA Diamond lets you connect all your Bluetooth devices. *Also available with a Micro USB. ifora Diabetes Manager All
ISO 15197:2013 / EN ISO 15197:2015 Clinical Validation Study List for Blood Glucose Monitoring System
 List No. STUDY TITLE DATE / PLACE SCIENTIST BRIEF RESULTS TYPE OF STUDY 01 Intermeiate measurement precision Jan 2018 The FORA 6 Connect fulfille the requirements of evaluation of FORA 6 Connect Multi-functional
List No. STUDY TITLE DATE / PLACE SCIENTIST BRIEF RESULTS TYPE OF STUDY 01 Intermeiate measurement precision Jan 2018 The FORA 6 Connect fulfille the requirements of evaluation of FORA 6 Connect Multi-functional
Accessible Blood Glucose Monitor Interface
 Accessible Blood Glucose Monitor Interface Team 2 Matthew Bularzik, David Price, Michael Rivera Sponsored by the Rehabilitation Engineering Research Center Purpose People with diabetes must check their
Accessible Blood Glucose Monitor Interface Team 2 Matthew Bularzik, David Price, Michael Rivera Sponsored by the Rehabilitation Engineering Research Center Purpose People with diabetes must check their
Advances in Diabetes Technology Part II: Analysis of Diabetes Self Management Devices and Support Tools
 Advances in Diabetes Technology Part II: Analysis of Diabetes Self Management Devices and Support Tools Jennifer Trujillo, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS, CDE, BC ADM Associate Professor University of Colorado School
Advances in Diabetes Technology Part II: Analysis of Diabetes Self Management Devices and Support Tools Jennifer Trujillo, PharmD, FCCP, BCPS, CDE, BC ADM Associate Professor University of Colorado School
PROCEDURE. TITLE: Bedside Glucose Monitoring PC Laboratory. Issuing Department: Clinical Director Signature: Departments Involved:
 PROCEDURE TITLE: Bedside Glucose Monitoring Issuing Department: Clinical Director Signature: Departments Involved: Laboratory Nursing Effective Date: 10/97 Review Dates: 09/01, 07/02, 05/13 Revision Dates:
PROCEDURE TITLE: Bedside Glucose Monitoring Issuing Department: Clinical Director Signature: Departments Involved: Laboratory Nursing Effective Date: 10/97 Review Dates: 09/01, 07/02, 05/13 Revision Dates:
Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision. Items Required
 Update Approver/checker Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision Purpose and Scope Items Required 1. The Abbott FreeStyle Optium meter is a battery-powered device designed for the measurement of
Update Approver/checker Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision Purpose and Scope Items Required 1. The Abbott FreeStyle Optium meter is a battery-powered device designed for the measurement of
SENSOR ELECTRODE/PRECISION (Also Medisense Companion)
 DIABETIC PSEUDO-DIN LIST - Revised Mar 2017 For Provinces not listed, please submit using the diabetic pseudo DIN listed in your provincial formulary or the AB/ON pseudo DIN (except for insulin). Pricing
DIABETIC PSEUDO-DIN LIST - Revised Mar 2017 For Provinces not listed, please submit using the diabetic pseudo DIN listed in your provincial formulary or the AB/ON pseudo DIN (except for insulin). Pricing
Comparison of the Dose Accuracy of Prefilled Insulin Pens
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2009 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of the Dose Accuracy of Prefilled Insulin Pens Alexander, M.Sc., Johannes
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 3, Issue 1, January 2009 Diabetes Technology Society ORIGINAL ARTICLES Comparison of the Dose Accuracy of Prefilled Insulin Pens Alexander, M.Sc., Johannes
When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD. JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida
 When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida Financial Disclosures Dr. Beck does not have any personal conflicts of interest His employer, the JAEB Center
When Will CGM Replace SMBG? Roy W. Beck, MD, PhD JAEB Center for Health Research Tampa, Florida Financial Disclosures Dr. Beck does not have any personal conflicts of interest His employer, the JAEB Center
There has been increasing interest in glucose measurement
 J Vet Intern Med 28;22:1189 1195 Comparison of the Accu-Chek Aviva Point-of-Care Glucometer with Blood Gas and Laboratory Methods of Analysis of Glucose Measurement in Equine Emergency Patients A.R. Hollis,
J Vet Intern Med 28;22:1189 1195 Comparison of the Accu-Chek Aviva Point-of-Care Glucometer with Blood Gas and Laboratory Methods of Analysis of Glucose Measurement in Equine Emergency Patients A.R. Hollis,
Self-monitoring of blood glucose: Advice for providers and patients
 REVIEW SHANNON KNAPP, BSN, RN, CDE Manager of Diabetes Education, Department of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Cleveland Clinic POOJA MANROA, MD Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism,
REVIEW SHANNON KNAPP, BSN, RN, CDE Manager of Diabetes Education, Department of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Cleveland Clinic POOJA MANROA, MD Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism,
Mission Hb accurately detects both
 Mission Digital Hb-Testing System: Save Cost by testing 2- Parameters with Single Strip real time ie: i.e: Hemoglobin & Hematocrit-[PCV]. Presented By : Remedy Healthcare Private Limited, New Delhi, [INDIA].
Mission Digital Hb-Testing System: Save Cost by testing 2- Parameters with Single Strip real time ie: i.e: Hemoglobin & Hematocrit-[PCV]. Presented By : Remedy Healthcare Private Limited, New Delhi, [INDIA].
Performance-powered. The OneTouch. Ping insulin pump and meter-remote.
 Performance-powered. The OneTouch Ping insulin pump and meter-remote. I We don t just deliver insulin. We deliver outstanding clinical performance. P36337_OTP_DetAid_OmniPodUpdate_r12.indd 1 OneTouch Ping.
Performance-powered. The OneTouch Ping insulin pump and meter-remote. I We don t just deliver insulin. We deliver outstanding clinical performance. P36337_OTP_DetAid_OmniPodUpdate_r12.indd 1 OneTouch Ping.
The Effect of Alcohol Prep Pads and Blood Drop Number On Capillary Blood Glucose Values
 University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2017 The Effect of Alcohol Prep Pads and Blood Drop Number On Capillary
University of New Hampshire University of New Hampshire Scholars' Repository Honors Theses and Capstones Student Scholarship Spring 2017 The Effect of Alcohol Prep Pads and Blood Drop Number On Capillary
Title: Abbott Optium Xceed Glucose Meter Effective date: 16/05/2011. Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision. SOP updated.
 COPY Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision SOP updated Purpose and Scope Items Required 1. The Abbott Optium Xceed meter is a battery-powered device designed for the measurement of blood glucose
COPY Summary of Significant Changes at this Revision SOP updated Purpose and Scope Items Required 1. The Abbott Optium Xceed meter is a battery-powered device designed for the measurement of blood glucose
Prescription Refill List Insulin and Related Supplies
 Insulin and Related Supplies Name Date Local Pharamcy Name/Address : 30 day/ 5 refills 90 day/ 3 refills Mail Away Pharamacy Name/Address: 30 day/ 5 refills 90day / 3 refills *Check only those items that
Insulin and Related Supplies Name Date Local Pharamcy Name/Address : 30 day/ 5 refills 90 day/ 3 refills Mail Away Pharamacy Name/Address: 30 day/ 5 refills 90day / 3 refills *Check only those items that
On-chip Hematocrit Correction for Whole Blood Glucose Amperometric Sensing Strip Using a Post-Measurement Potential Step
 Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 12 (2017) 4990 4999, doi: 10.20964/2017.06.87 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org On-chip Hematocrit Correction for Whole Blood Glucose Amperometric
Int. J. Electrochem. Sci., 12 (2017) 4990 4999, doi: 10.20964/2017.06.87 International Journal of ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE www.electrochemsci.org On-chip Hematocrit Correction for Whole Blood Glucose Amperometric
Integrated Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose System: Handling Step Analysis
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 6, Issue 4, July 2012 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORT Integrated Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose System: Handling Step Analysis Guido, M.D.,
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 6, Issue 4, July 2012 Diabetes Technology Society TECHNOLOGY REPORT Integrated Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose System: Handling Step Analysis Guido, M.D.,
Biosensor and its electrochemical transducer
 YINAN TANG Background Biosensor and its electrochemical transducer Simple, inexpensive, accurate and sensitive platform Inherent miniaturization for both the detector and control instrumentation Application
YINAN TANG Background Biosensor and its electrochemical transducer Simple, inexpensive, accurate and sensitive platform Inherent miniaturization for both the detector and control instrumentation Application
Computing the Surveillance Error Grid Analysis: Procedure and Examples
 5959DSTXXX.77/99685959Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyKovatchev et al research-article Original Article Computing the Surveillance Error Grid Analysis: Procedure and Examples Journal of Diabetes
5959DSTXXX.77/99685959Journal of Diabetes Science and TechnologyKovatchev et al research-article Original Article Computing the Surveillance Error Grid Analysis: Procedure and Examples Journal of Diabetes
Analysis of Hemoglobin A1c from Dried Blood Spot Samples with the Tina-quant II Immunoturbidimetric Method
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 4, Issue 2, March 2010 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Analysis of Hemoglobin A1c from Dried Blood Spot Samples with the Tina-quant II Immunoturbidimetric
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 4, Issue 2, March 2010 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Analysis of Hemoglobin A1c from Dried Blood Spot Samples with the Tina-quant II Immunoturbidimetric
Blood glucose monitoring and compatibility equipment checker
 Introduction This resource has been created to assist pharmacists, and other appropriately trained members of the pharmacy team, to ensure compatibility of insulin products/devices and blood glucose monitoring
Introduction This resource has been created to assist pharmacists, and other appropriately trained members of the pharmacy team, to ensure compatibility of insulin products/devices and blood glucose monitoring
Millennium Technology for Critical Care
 C E U P D A T E P O I N T O F C A R E I I I Richard F. Louie Zuping Tang, MD David G. Shelby, MT Gerald J. Kost, MD, PhD Point-of-Care Testing: Millennium Technology for Critical Care ABSTRACT Point-of-care
C E U P D A T E P O I N T O F C A R E I I I Richard F. Louie Zuping Tang, MD David G. Shelby, MT Gerald J. Kost, MD, PhD Point-of-Care Testing: Millennium Technology for Critical Care ABSTRACT Point-of-care
Quality Control of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose: Why and How?
 Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 2, March 2007 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Quality Control of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose: Why and How? Bogdan, M.D., Ph.D. and
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology Volume 1, Issue 2, March 2007 Diabetes Technology Society SYMPOSIUM Quality Control of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose: Why and How? Bogdan, M.D., Ph.D. and
Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies
 1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
1979 Advances in Diabetes Care Technologies 2015 Introduction Roughly 20% - 30% of patients with T1DM and fewer than 1% of insulin-treated patients with T2DM use an insulin pump In 2007, the US FDA estimated
