Original Article Adipose tissue hypoxia caused by cyanotic congenital heart disease and its impact on adipokine dysregulation
|
|
|
- Rosa Simpson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9): /ISSN: /IJCEP Original Article Adipose tissue hypoxia caused by cyanotic congenital heart disease and its impact on adipokine dysregulation Xianguo Wang 1, Xinzhong Chen 1, Dongsheng Xia 1, Yan Cao 2, Nianguo Dong 1 1 Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China; 2 Tongji College of Pharmacy, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei, China Received October 9, 2015; Accepted February 13, 2016; Epub September 1, 2016; Published September 15, 2016 Abstract: Objective: To investigate the effects of hypoxia induced by CCHD on the expression and secretion of adipokines. Methods: Subcutaneous adipose tissue and serum were obtained from elective cardiac surgery patients. In CCHD group, n = 17; and in ACHD (Acyanosis congenital heart disease) group, n = 15. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), inflammation-related adipokines, adiponectin (APN) and Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) markers were measured in mrna levels. Hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and ER stress markers were also measured in protein levels. Results: Immunohistochemical staining showed that protein expression level of VEGF was markedly increased relative to acyanotic groups. Adipose tissue was hypoxic in cyanotic groups. Adipose tissue hypoxia (ATH) led to a substantial increase in inflammation-related adipokines, and a remarkable reduction in adiponectin mrna levels. Endoplasmic reticulum stress markers were activated by hypoxia. ER stress has been linked to inflammation. These changes were partially reversed by the intervention of normoxia. We exposed normal adipose tissue to CoCl 2, a hypoxia mimic, and achieved results similar to the CCHD group. Conclusions: Adipose tissue in CCHD is hypoxic. The change of adiponectin and inflammation-related adipokines are partially caused by ER stress. Keywords: Adipose tissue, hypoxia, adipokines, cyanosis congenital heart disease, endoplasmic reticulum stress Introduction White adipose tissue has traditionally been considered a vehicle for the storage of triacylglycerols. Adipose tissue is now recognized as an important endocrine organ, secreting a variety of the adipokines that are involved in energy metabolism, inflammatory response, and cardiovascular functions, such as including TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, MCP-1 (monocyte chemoattractant protein-1), MIF (monocyte migration inhibitory factor), leptin, resistin, visfatin, and adiponectin [1, 2]. TNF-α, leptin, resistin, and visfatin are associated with insulin resistance and have pro-inflammatory and atherogenic effects [3]. In contrast, adiponectin has anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory, and anti-atherogenic effects [4]. Lower concentrations of adiponectin are found in patients with diabetes and coronary atherosclerosis [5, 6]. Hypoxia induces a series of adaptive responses, and transcription factor HIF-1α is a key signal in the cellular response to hypoxia. HIF-1α is composed of two subunits, HIF-1α, which is highly induced by hypoxia to yield the functional transcription factor, and HIF-1β, which is constitutively expressed [7]. The HIF-1α gene has been identified in the adipocytes and the cells of the stromal vascular fraction. HIF-1α is predominantly expressed in the stromal vascular fraction of obese subjects [8]. During the development of obesity, adipocytes become hypertrophic and increases in size up to μm in diameter. Because the diffusion limit of oxygen is at most 100 μm, hypertrophic adipocytes may have a less than adequate oxygen supply [9]. Many studies have focused on adipose tissue hypoxia in human obesity. These studies have shown hypoxia to be associated with increased expression of inflammatory genes and decreased expression of adiponectin. They have contributed to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance, which links obesity to many complications, such as type 2
2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Longterm hypoxia caused by the effects of cyanotic congenital heart disease (CCHD) on adipose tissue had only rarely been reported, so we investigated whether adipose tissue in CCHD patients involved changes in adipokine expression. Results showed that hypoxia resulted in increases in TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, MIF, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), GRP78 (Glucose-regulated protein 78), CHOP, and ATF-6 (Activating transcription factor 6) mrna levels. Protein expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress marker GRP78 and hypoxia marker HIF-1α were also increased, but adiponectin expression decreased at the mrna levels. These effects were reversed upon return to normoxia. This demonstrates that adipose tissue hypoxia in CCHD may have induced stress upon the endoplasmic reticulum stress and then caused decreases in adiponectin levels and extensive changes in the adipokines. Materials and methods Patients Between January 1 and October 30, 2011, 32 children with congenital heart disease, aged 1 month through 4 years, were included in the study. The patients were divided into two groups. The cyanotic group consisted of 17 patients with cyanotic congenital heart disease (10 boys, 7 girls). These patients all had arterial oxygen saturations of below 85%. The acyanotic group was composed of 15 patients with ACHD (9 boys, 6 girls). These patients all had arterial oxygen saturations over 93%. There was no difference in age, sex and medication between two groups. None of them had other diseases at the time of the study. Cardiac diagnoses were made on the basis of clinical and laboratory examinations, including echocardiography and magnetic resonance imaging. Cardiac diagnoses of cyanotic patients were tetralogy of Fallot (n = 9), transposition of great arteries (n = 4), double outlet right ventricle (n = 2) and pulmonary atresia (n = 2). Cardiac diagnoses of acyanotic patients were ventricular septal defect (n = 12), atrial septal defect (n = 2) and patent ductus arteriosus (n = 1). A total of 32 children who met the inclusion criteria constituted the study population. The study was approved by the ethics committee of Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China. Informed consent was obtained from the parents of all subjects before the study began. Blood samples and tissue collection Blood samples were drawn from the jugular vein prior to surgery and centrifuged at 300 g at 4 C for 15 minutes. Serum was stored frozen at -80 C. Subcutaneous adipose tissue samples weighing approximately mg were obtained at the manubrium sternum level. They were divided into two portions. One portion was frozen in liquid nitrogen immediately and then kept in a -80 C freezer until preparation of whole cell lysate or extraction of RNA. The other was kept in formaldehyde or HEPESsalts, used for VEGF immunohistochemistry staining (Zhongshan Goldenbridge, China) or tissue culture. Adipose tissue explant culture All procedures for AT explant culture were carried out using sterile technique. AT was placed into sterile filtered HEPES-salts buffer immediately transported under aseptic conditions to the laboratory. AT was washed free of lipid and blood clots and then processed further by cutting into mm³ pieces, washed. AT explants were cultured (50 mg AT/ml) under an atmosphere of 5% CO 2 in air at 37 C in defined medium (DM) (1:1 DME low/ham s F-10 containing 5 mm glucose supplemented with 25 mm HEPES, 15 mm NaHCO 3, 2 mm glutamine and 100 U/ml penicillin, 0.1 mg/ml streptomycin, plus 1 nm insulin, 30 nm dexamethasone, 3.3 μm D-biotin, 1.7 μm D-pantothenic acid) for culture. Nine adipose tissues from cyanotic patients were cultured for 24 h under normoxia (21% O 2 ). The adipose tissue of acyanotic patients was treated with CoCl 2 for up to 24 h. For CoCl 2 treatment, wells incubated without CoCl 2 were used as controls; 100 μm CoCl 2 was employed in a time course study. Cell viability was assessed by measuring the media glucose, ph, fat cell size, and histology, there were no significantly change over the culture period. All incubations at each time point were performed in replicates of up to three times. Measurement of adiponectin and adipokines by ELISA The serum and tissue culture media concentration of Adiponectin, IL-6, TNF-α were measured with the use of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) assay (Neobioscience, China). The intra- and inter-assay variance 9149 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
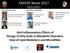
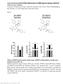
3 Figure 1. A. Immunocytochemical staining for VEGF in acyanotic group. B. Immunocytochemical staining of VEGF in the cyanotic group. Original magnification, 200. coefficients were lower than 9%. The assays were conducted in 96-well microplates according to the manufacturer s instructions. Samples were analyzed in triplicate following the instructions in the kit. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR Figure 2. Effects of hypoxia on (A) the mrna levels of HIF-1α and adipokines and on (B) P-PERK, HIF-1α, P- IRE1 and GRP78 protein secretion in human adipose tissue. Results are mean ± SE (n = 3). In A, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with the acyanotic group. In B, P-PERK, HIF-1α, P-IRE1 and GRP78 protein expression of the cyanotic group relative to the acyanotic group. Total RNA was extracted from homogenized fat pads using the TRIzol reagent (Takara, China) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Real-time quantitative RT-PCR (qrt-pcr) was conducted using the ABI 7900HT fast real-time PCR system (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). The following primers were ordered from Invitrogen: HIF-1α forward GACTCAAAGCGA- CAGATAACACG; HIF-1α reverse ATTCCAGCAG- ACTCAAATACAAGA; VEGF forward TTGTTGTGC- TGTAGGAAGCTCA; VEGF reverse CAGCTACTGC- CATCCAATCG; APN forward AGGCCGTGATGGC- AGAGAT; APN reverse TCCAATCCCACACTGAA- TGCT; TNF-α α forward GGTTCGAGAAGATGA- TCTGACTG; TNF-α reverse CTGCTGCACTTTGG- AGTGATC; IL-6 forward TTGGGTCAGGGGTGG- TTATT; IL-6 reverse GTGAAAGCAGCAAAGAG- GCA; MCP-1 forward CAAGTCTTCGGAGTTT- GGGTTT; MCP-1 reverse CTCATAGCAGCCACC- TTCATTC; MIF forward CCGTTTATTTCTCCC- CACCAG; MIF reverse TCCACCTTCGCCTAAGA- GCC; CHOP forward CCACTCTTGACCCTGCTT- CTC; CHOP reverse TGGTTCTCCCTTGGTCTTCC; ATF-6 forward AGTCAGTCCATTTTCAGTCTTGTTC; ATF-6 reverse AAGTTATTCAGTCTCGTCTCCTCG. Human β-actin was used as an endogenous reference. This housekeeping gene demonstrated no significant changes in expression when exposed to CoCl 2 and 1% O 2. Typically, amplifi Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
4 of triplicates was used for relative mrna level. To exclude bias due to averaging, data were transformed through the Power equation 2 -ΔΔCt. PCR efficiency was close to 100% in all runs, and all samples were analyzed in at least triplicate. Western blot analysis Whole adipose tissue protein was made using homogenization in a lysis buffer (1% Triton X-100, 50 mm KCl, 25 mm HEPES, ph 7.8, 10 μg/ml leupeptin, 20 μg/ml aprotinin, 125 mm dithiothreitol, 1 mm phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 1 mm sodium orthovanadate). Triglycerides were removed from the lysate before protein assay. Extraction of nuclear protein and Western blot analysis were conducted as described elsewhere [10]. Western blot analysis was carried out using P-PERK, HIF-1α, P-IRE1 and GRP78 antibodies (Epitomics, U.S.). Statistical analysis All of the experiments in this study were conducted at least three times, and results remained consistent. Data from representative experiments are presented. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 18.0 software (Statistical Program for the Social Sciences). The correlation values are means SE of multiple data points or samples to represent the final result. Student s t-test and two-way ANOVA were used for statistical analysis of the data. P values <0.05 were considered significant. Results Serum adipokines in acyanotic and cyanotic groups Figure 3. Adipose tissue from the cyanotic group was cultured under normoxic conditions for up to 24 h. A. Relative mrna levels of VEGF, IL-6, TNF-α, MCP- 1, MIF, and ERS markers mrna levels. B. HIF-1α and GRP78 protein secretion in human adipose tissue. Results are mean ± SE (n = 3). In A, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, compared with 0 h. In B, HIF-1α nd GRP78 protein expression of the cyanotic group relative to 0 h. cation began with 2 min at 50 C, 2 min at 95 C, and then 40 cycles of the following: 15 s at 95 C, 15 s at 58 C, and 45 s at 72 C. Data were obtained as cycle threshold (Ct) values and used to determine ΔCt values (ΔCt = Ct of gene of interest-ct of β-actin). The mean value Serum adiponectin levels were significantly higher in acyanotic than in cyanotic groups (P<0.01) (Figure 1). Serum TNF-α values were higher in the acyanotic groups than in the cyanotic groups (P<0.01). There was no significant difference in serum levels of IL-6 between the acyanotic and cyanotic groups. Immunohistochemistry Immunohistochemical staining of adipose tissue in cyanotic and acyanotic groups was shown in Figure 1. VEGF was used as a marker of hypoxia in adipose tissue. It showed that VEGF expression was significantly higher in the cyanotic group Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
5 Expression of adipokines in the adipose tissues of the cyanotic and acyanotic groups In the cyanotic group, the SPO 2 levels of patients were lower than 85% before the operation. The expression of a series of inflammation-related adipokine genes was then examined in the hypoxic adipose tissue. There was a significant reduction in mrna levels of adiponectin, and MCP-1. Adiponectin levels decreased three to fourfold. In contrast, hypoxia resulted in a marked increase in mrna levels for TNF-α and IL-6. The increase was about twofold for VEGF and two to fourfold for MIF, GRP78, CHOP, and ATF-6. HIF-1α mrna levels increased two to threefold. In the cyanotic group, P-PERK, HIF-1α, P-IRE1 and GRP78 protein levels were higher than in the acyanotic group (Figure 2). Adipose tissue in cyanotic group cultured under normoxic conditions When the adipose tissue in the cyanotic group was restored to normoxic conditions (21% O 2 ) led to a reversal in VEGF, L-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, and MIF mrna levels. Levels of GRP78, CHOP, and ATF-6 the mrna were lower than at 12 h after exposure to normoxic conditions. These changes in adiponectin levels were reversed after 2 h of reexposure to 21% O 2. HIF-1α protein level was lower after 2 h of reexposure to normoxic conditions. However, GRP78 protein level was lower after 12 h of reexposure (Figure 3). Adipose tissue in acyanotic group response to CoCl 2 treatment Figure 4. Effects of CoCl 2 on (A) the mrna levels of VEGF and adipokines and on (B) HIF-1α and GRP78 protein secretion in human adipose tissue. Adipose tissue from the acyanotic group was incubated in medium containing 100 μm CoCl 2 for 24 h. In A, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 compared with the acyanotic group. In B, HIF-1α and GRP78 prote in expression of the acyanotic group relative to 0 h. Hypoxic effects of adipose tissue can be mimicked by the divalent transition metal ion cobalt. Adipose tissue (in the acyanotic group) was treated with CoCl 2 at concentrations of 100 μm for 24 h. The expression of inflammation-related adipokines and ERS markers were then examined in the CoCl 2 -treated adipose tissue. There was a significant reduction in adiponectin mrna levels. Adiponectin mrna levels decreased three to eightfold. There was a marked increase in mrna levels for VEGF, IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, and MIF. The increase was four to eightfold for VEGF, and six to twentyfold for IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, and MIF. ERS markers GRP78, CHOP, and ATF-6 increased one to twofold (Figure 4) Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
6 Table 1. Adiponectin, TNF-α, and Il-6 levels of patients with CCHD and ACHD Acyanotic patients (n = 15) Cyanotic patients (n = 17) Adiponectin (ng/ml) 17.02± ±5.8** TNF-α (pg/ml) ± ±4.5** Il-6 (pg/ml) 16.22± ±1.27 **P<0.01. Adipose tissue in acyanotic group response to low O 2 tension When adipose tissue (in the acyanotic group) was cultured in 1% O 2 up to 24 h, the expression of inflammation-related adipokines and ERS markers were then examined. The results were similar to the above CoCl 2 treatment. So we didn t show the results. Discussion In obesity, adipocyte diameter increases to up to μm as a result of hypertrophy [11]. Because the diffusion limit of oxygen is around 100 μm [12], this hypertrophy leads to the local hypoxic areas in adipose tissue [12, 13]. Adipose tissue hypoxia induces an increase in the synthesis of adipokines, such as IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, and MIF which are linked to inflammation, and a reduction of adiponectin production and circulating levels. Recent studies have suggested that adipose tissue hypoxia (ATH) is a root of chronic inflammation in obesity [14]. Hypoxia in CCHD manifests as the reduction of oxygen content in the blood. In this study, we investigated the effects of hypoxia on adipose tissue in CCHD patients. Our results show that cyanotic patients were shorter and weighed less than acyanotic volunteers. This is consistent with the observations of David et al. [15]. They found no difference in adipocyte size, though total number of adipocytes in the cyanotic children decreased and body fat was reduced due to adipocyte hypocellularity. Serum TNF-α levels was higher in cyanotic groups than in the acyanotic group and adiponectin was lower in cyanotic groups (P<0.01) (Table 1). There was no significant difference in IL-6 levels. However, Yilmaz et al. have shown that TNF-α levels are significantly higher in both acyanotic patients and cyanotic patients than in healthy people, but there was no significant difference between acyanotic patients and cyanotic patients with respect to TNF-α levels [16]. This discrepancy might be due to different choices made by the patients and needs to be further clarified. The transcription factor HIF-1α is a key signal in the cellular response to hypoxia, the α-subunit of which is highly induced by hypoxia. HIF-1α protein is stabilized by hypoxia and degraded by an ubiquitin-dependent proteasome under normoxic conditions. HIF-1α gene expression was found to be increased throughout the adipose tissues of obese subjects, predominantly in the stromal vascular fraction. However, its expression decreased after weight loss [17]. Poulain-Godefroy et al. suggested that it is important to designate an amount of HIF-1α protein, rather than an amount of mrna, as a key marker in studies examining whether adipose tissue hypoxia occurs in human obesity. In cyanotic groups, VEGF expression (Figure 1) and hypoxia marker HIF-1α protein (Figure 2) were markedly higher than in acyanotic groups. According to these studies, we speculated that adipose tissue was hypoxic in cyanotic groups. Our study also showed that adipose tissue showed increased expression of a number of adipokines linked to inflammation, including TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, MIF, and decreased levels of adiponectin mrna expression (Figure 2). Levels of mrna coding for endoplasmic reticulum stress markers GRP78, CHOP, and ATF-6 were increased. These effects were partially reversed upon return to normoxia (Figure 4). CoCl 2, a known inducer of HIF-1α, has been widely employed as a hypoxia mimic, which is thought to act mainly by inhibiting the oxygenand Fe 2 +-dependent enzyme, HIF-1α Αprolyl-4- hydroxylase, leading to HIF-1α stabilization and the activation of cellular hypoxia-dependent pathways under normal oxygen levels. CoCl 2 has been used to examine the effects of chemically induced hypoxia on adipose tissues in ACHD. Our results show significantly increases in endoplasmic reticulum stress markers, accumulation of HIF-1α, increased expression of inflammation-related adipokine expression in mrna levels and decreased adiponectin (Figure 3). Other studies have also show that CoCl 2 induces HIF-1α expression in various cell 9153 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
7 types, including cancer cells and brown adipocytes [18]. Various stimuli can trigger ER stress. These stimuli include glucose and nutrient deprivation, hypoxia, and increased synthesis of secretory proteins [19]. To cope with ER stress, cells trigger a set of pathways known as unfolded protein response (UPR). This response is mediated by RNA-dependent protein-kinase-like ER eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2-kinase (PERK), inositol-requiring protein-1 (IRE1), and activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6) [20]. UPR causes increased transcription of genes involved in ER protein folding and slow protein synthesis at the translation level, alleviating the ER load [21]. ER stress and the UPR are linked to inflammation via several distinct mechanisms. IRE-1a can activate JNK and NFκB pathways. The NFκB pathway may also be activated through PERK signaling. JNK upregulates the expression of inflammatory genes through activation of the AP-1 transcription factor complexes [22]. IKK-NFκB pathway can induce the expression of multiple inflammatory genes, such as TNF-α and IL-6 [23]. CHOP is downstream of PERK. GRP78 was used to indicate the degree of ERS. ATF-6 in mrna level and IRE- 1a in protein level were measured in this study. Results show that the expression of ATF-6 and IRE-1a increased in hypoxic adipose tissue. Induction of UPR in endothelial cells has been reported to cause increased expression of inflammatory genes, including TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, and IL-8 [24]. It has been reported that exposure of 3T3-L1 adipocytes to hypoxia dysregulated the expression of adipocytokines such as adiponectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 and increased expression of the mrnas of ERS marker genes, CHOP and GRP78. This effect was mediated by ERS and posttranscriptional regulation [25]. Unlike adiponectin, hypoxia stimulated the expression of the genes encoding TNF-α, IL-6, MCP-1, MIF, and VEGF. VEGF is activated by hypoxia. An increase in VEGF mrna levels was observed in adipose tissues in CCHD. This was consistent with studies on rat white adipose tissue [26]. Hypoxia and treatment with CoCl 2 could cause transitory increases in MCP-1 mrna, which is an important factor in macrophage recruitment. MIF, a pro-inflammatory agent, was also stimulated by hypoxia. The expression of classic inflammatory factors TNF-α and IL-6 was upregulated by hypoxia. The adipose tissues were used in the present study, because, firstly, in white adipose tissues, the preparation and incubation of different cell fractions may alter their relative rates of adipokine production, and adipocytes engaged in crosstalk with non-adipocyte fractions. Second, we believe that adipose tissues obtained from patients reflected the real situation in disease conditions. Third, some studies were performed on 3T3l-1 adipocytes and mice exposed to hypoxia [25]. It was difficult to make quantitative comparisons regarding the extent to which various cell types contributed quantitatively to the overall production of inflammatory factors, though in vitro studies demonstrated that mature adipocytes were less important than the non-adipocyte fraction in the production and release of most cytokines and chemokines [27]. We obtained subcutaneous adipose tissue samples at the manubrium sterni level. Whether adipose tissues from different sites undergo the same change merits further investigation. In summary, we demonstrated that adipose tissues in CCHD are hypoxic and that this hypoxia dysregulates the production of adipocytokines in those tissues during CCHD. This effect is partially mediated by ER stress. These changes were partially reversed by normoxia intervention. If patients with CCHD undergo surgery in time and normal oxygen partial pressure is restored in the blood, some of the inflammation-related adipokine dysfunction may be reversed; the patient quality of life may be improved. Collectively, our results suggest that adipose tissue hypoxia is responsible for decreases in adiponectin levels and inflammation-related changes in adipokine levels. Acknowledgements This work was supported by the National Natural Science Fund of China (Grants , ), and the Doctoral Fund of the Ministry of Education of China (Grants ), and the Applied Basic Research Programs of Wuhan (No ). Disclosure of conflict of interest None Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
8 Address correspondence to: Dr. Xinzhong Chen, Department of Cardiovascular Surgery, Union Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan , Hubei, China. Tel: ; Fax: ; References [1] Hauner H. Secretory factors from human adipose tissue and their functional role. Proc Nutr Soc 2005; 64: [2] Rajala MW and Scherer PE. Minireview: The adipocyte--at the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology 2003; 144: [3] Trayhurn P, Wood IS. Adipokines: Inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr 2004; 92: [4] Guzik TJ, Mangalat D and Korbut R. Adipocytokines-novel link between inflammation and vascular function? J Physiol Pharmacol 2006; 57: [5] Maahs DM, Ogden LG, Kinney GL, Wadwa P, Snell-Bergeon JK, Dabelea D, Hokanson JE, Ehrlich J, Eckel RH and Rewers M. Low plasma adiponectin levels predict progression of coronary artery calcification. Circulation 2005; 111: [6] Pereira RI, Snell-Bergeon JK, Erickson C, Schauer IE, Bergman BC, Rewers M and Maahs DM. Adiponectin dysregulation and insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2012; 97: E [7] Cummins EP and Taylor CT. Hypoxia-responsive transcription factors. Pflugers Arch 2005; 450: [8] Cancello R, Henegar C, Viguerie N, Taleb S, Poitou C, Rouault C, Coupaye M, Pelloux V, Hugol D, Bouillot JL, Bouloumie A, Barbatelli G, Cinti S, Svensson PA, Barsh GS, Zucker JD, Basdevant A, Langin D and Clement K. Reduction of macrophage infiltration and chemoattractant gene expression changes in white adipose tissue of morbidly obese subjects after surgery-induced weight loss. Diabetes 2005; 54: [9] Haller H, Leonhardt W, Hanefeld M and Julius U. Relationship between adipocyte hypertrophy and metabolic disturbances. Endokrinologie 1979; 74: [10] Ye J, Gao Z, Yin J and He Q. Hypoxia is a potential risk factor for chronic inflammation and adiponectin reduction in adipose tissue of ob/ ob and dietary obese mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007; 293: E [11] Salans LB, Cushman SW and Weismann RE. Studies of human adipose tissue. Adipose cell size and number in nonobese and obese patients. J Clin Invest 1973; 52: [12] Helmlinger G, Yuan F, Dellian M and Jain RK. Interstitial ph and po2 gradients in solid tumors in vivo: High-resolution measurements reveal a lack of correlation. Nat Med 1997; 3: [13] Pasarica M, Rood J, Ravussin E, Schwarz JM, Smith SR and Redman LM. Reduced oxygenation in human obese adipose tissue is associated with impaired insulin suppression of lipolysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010; 95: [14] Ye J. Adipose tissue vascularization: Its role in chronic inflammation. Curr Diab Rep 2011; 11: [15] Baum D and Stern MP. Adipose hypocellularity in cyanotic congenital heart disease. Circulation 1977; 55: [16] Yilmaz E, Ustundag B, Sen Y, Akarsu S, Kurt AN and Dogan Y. The levels of ghrelin, TNF-αlpha, and il-6 in children with cyanotic and acyanotic congenital heart disease. Mediators Inflamm 2007; 2007: [17] Trayhurn P, Wang B and Wood IS. HIF-1α protein rather than mrna as a marker of hypoxia in adipose tissue in obesity: Focus on inflammation is associated with a decrease of lipogenic factors in omental fat in women. by Poulain-Godefroy et al. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2008; 295: R1097. [18] Nardinocchi L, Puca R, Sacchi A, D Orazi G. Inhibition of HIF-1lpha activity by homeodomain-interacting protein kinase-2 correlates with sensitization of chemoresistant cells to undergo apoptosis. Mol Cancer 2009; 8: 1. [19] Kaufman RJ. Stress signaling from the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum: Coordination of gene transcriptional and translational controls. Genes Dev 1999; 13: [20] Mori K. Tripartite management of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell 2000; 101: [21] Ma Y and Hendershot LM. The unfolding tale of the unfolded protein response. Cell 2001; 107: [22] Karin M and Gallagher E. From junk to pay dirt: Jun kinases, their biochemistry, physiology and clinical importance. IUBMB Life 2005; 57: [23] Deng J, Lu PD, Zhang Y, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Sonenberg N, Harding HP and Ron D. Translational repression mediates activation of nuclear factor kappa b by phosphorylated translation initiation factor 2. Mol Cell Biol 2004; 24: [24] Gargalovic PS, Gharavi NM, Clark MJ, Pagnon J, Yang WP, He A, Truong A, Baruch-Oren T, Berliner JA, Kirchgessner TG and Lusis AJ. The 9155 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
9 unfolded protein response is an important regulator of inflammatory genes in endothelial cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: [25] Hosogai N, Fukuhara A, Oshima K, Miyata Y, Tanaka S, Segawa K, Furukawa S, Tochino Y, Komuro R, Matsuda M and Shimomura I. Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 2007; 56: [26] Mick GJ, Wang X and McCormick K. White adipocyte vascular endothelial growth factor: Regulation by insulin. Endocrinology 2002; 143: [27] Fain JN. Release of interleukins and other inflammatory cytokines by human adipose tissue is enhanced in obesity and primarily due to the nonfat cells. Vitam Horm 2006; 74: Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2016;9(9):
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes
 Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
Changes and clinical significance of serum vaspin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes L. Yang*, S.J. Chen*, G.Y. Yuan, D. Wang and J.J. Chen Department of Endocrinology, Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the
 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Plasma exposure levels of MKC-3946 in mice. Plasma exposure levels from individual mice 4 hours post IP administration at the indicated dose mg/kg. Data represent
Effect of High-fat or High-glucose Diet on Obesity and Visceral Adipose Tissue in Mice
 ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
ACTA ACADEMIAE MEDICINAE SINICAE 410011 0731-85295846 lixia2014@vip. 163. com 4 C57BL /6 20-1 mrna 20 P < 0. 05 O 20 P > 0. 05 M2 P < 0. 05-1 mrna P < 0. 05 P > 0. 05 R589. 2 DOI 10. 3881 /j. issn. 1000-503X.
Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease
 Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease Xin-Liang Ma, MD, PhD Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, PA USA CVD As The #1 Causes of Death In USA Male Female Heart Disease and
Adipose Tissue Dysfunction and Diabetic Cardiovascular Disease Xin-Liang Ma, MD, PhD Thomas Jefferson University Philadelphia, PA USA CVD As The #1 Causes of Death In USA Male Female Heart Disease and
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ
 ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
ΦΛΕΓΜΟΝΗ ΚΑΙ ΔΙΑΒΗΤΗΣ ΘΩΜΑΣ ΠΑΠΑΔΟΠΟΥΛΟΣ, MD, PHD ΕΠΕΜΒΑΤΙΚΟΣ ΚΑΡΔΙΟΛΟΓΟΣ ΙΑΤΡΙΚΟ ΔΙΑΒΑΛΚΑΝΙΚΟ ΚΕΝΤΡΟ Inflammation as a cause of disease has entered the popular imagination. Diet ( macronutrients )
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer. Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea
 Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Crosstalk between Adiponectin and IGF-IR in breast cancer Prof. Young Jin Suh Department of Surgery The Catholic University of Korea Obesity Chronic, multifactorial disorder Hypertrophy and hyperplasia
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Annals of RSCB Vol. XVI, Issue 1
 ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM INVOLVEMENT IN APOPTOSIS OF NORMAL AND TREATED GINGIVAL FIBROBLASTS Ancuţa Goriuc, Raluca Jipu, Roxana Irina Iancu, M. Costuleanu GR. T. POPA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY,
ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM INVOLVEMENT IN APOPTOSIS OF NORMAL AND TREATED GINGIVAL FIBROBLASTS Ancuţa Goriuc, Raluca Jipu, Roxana Irina Iancu, M. Costuleanu GR. T. POPA UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
Supplementary Figure 1. DNA methylation of the adiponectin promoter R1, Pparg2, and Tnfa promoter in adipocytes is not affected by obesity. (a) Relative amounts of adiponectin, Ppar 2, C/ebp, and Tnf mrna
( ) Downloaded from ijem.sbmu.ac.ir at 20: on Friday March 22nd 2019 VEFG. HIIT. MICT. :.
 ( ) VEFG 2 1 1 ( ) (2 (1 : ( e-mail: Mostafa.rahimi20@gmail.com (MICT) (HIIT) :. (VEGF) ( ± ) :. (HIIT) (MICT) MICT. HIIT.. :. Real-time RT-PCR (P / ) VEGF.(P / ) :. : 96/5/15 : 96/4/20 96//6 : 1 2014
( ) VEFG 2 1 1 ( ) (2 (1 : ( e-mail: Mostafa.rahimi20@gmail.com (MICT) (HIIT) :. (VEGF) ( ± ) :. (HIIT) (MICT) MICT. HIIT.. :. Real-time RT-PCR (P / ) VEGF.(P / ) :. : 96/5/15 : 96/4/20 96//6 : 1 2014
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY
 AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
AT1 RECEPTOR BLOCKADE ATTENUATES INSULIN RESISTANCE AND MYOCARDIAL REMODELING IN RATS WITH DIET-INDUCED OBESITY SA Oliveira Jr, MP Okoshi, PF Martinez, DM Guizoni, BP Torres, M Dal Pai-Silva, K Okoshi,
Effect of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress inducer thapsigargin on the expression of extracellular-superoxide dismutase in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes
 Original Article JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn12-46 10.3164/jcbn.12-46 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition Japan Effect of
Original Article JCBN Journal 0912-0009 1880-5086 the Kyoto, jcbn12-46 10.3164/jcbn.12-46 Original Society Japan of Article Clinical for Free Biochemistry Radical Research and Nutrition Japan Effect of
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis
 Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Cell Metabolism, Volume 11 Supplemental Information Defective Hepatic Autophagy in Obesity Promotes ER Stress and Causes Insulin Resistance Ling Yang, Ping Li, Suneng Fu, Ediz S. Calay, and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist. Research Summary:
 Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Yiying Zhang, PhD Research Scientist Research Summary: Address: Naomi Berrie Diabetes Center at Columbia University Medical Center Russ Berrie Medical Science Pavilion 1150 St. Nicholas Avenue New York,
Human Leptin ELISA Kit
 Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
Product Manual Human Leptin ELISA Kit Catalog Numbers MET-5057 MET-5057-5 96 assays 5 x 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Leptin is a polypeptide hormone
CELLULAR HYPOXIA: A KEY MODULATOR OF ADIPOCYTE FUNCTION IN OBESITY?
 Adipobiology ISSN 1313-3705 Bul garian Society for Cell Biology CELLULAR HYPOXIA: A KEY MODULATOR OF ADIPOCYTE FUNCTION IN OBESITY? Paul Trayhurn, Fátima Pérez de Heredia, Bohan Wang, Cristiane de Oliveira,
Adipobiology ISSN 1313-3705 Bul garian Society for Cell Biology CELLULAR HYPOXIA: A KEY MODULATOR OF ADIPOCYTE FUNCTION IN OBESITY? Paul Trayhurn, Fátima Pérez de Heredia, Bohan Wang, Cristiane de Oliveira,
The FunCluster Package
 The FunCluster Package October 23, 2007 Version 1.07 Date 2007-10-23 Title Functional Profiling of Microarray Expression Data Author Corneliu Henegar Maintainer Corneliu Henegar
The FunCluster Package October 23, 2007 Version 1.07 Date 2007-10-23 Title Functional Profiling of Microarray Expression Data Author Corneliu Henegar Maintainer Corneliu Henegar
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11):
 902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
Peter Walter, UCSF IRE1 Signaling Affects Cell Fate during the Unfolded Protein Response
 Peter Walter, UCSF IRE1 Signaling Affects Cell Fate during the Unfolded Protein Response Jenn Hou Burke Group Literature Seminar November 19 th 2016 Protein Synthesis Pathway 4. Final Destination: proteins
Peter Walter, UCSF IRE1 Signaling Affects Cell Fate during the Unfolded Protein Response Jenn Hou Burke Group Literature Seminar November 19 th 2016 Protein Synthesis Pathway 4. Final Destination: proteins
* Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; Tel.: ; Fax:
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184-6223; doi:10.3390/ijms15046184 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications:
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 6184-6223; doi:10.3390/ijms15046184 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Obesity and Its Metabolic Complications:
Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15.
 Supplementary Table 1. Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15. Male Female Cytokine Control C-26 Control C-26 IL-1β 2.0 ± 0.8 9.6 ± 1.5* 1.8 ± 0.2 6.8 ± 1.4*
Supplementary Table 1. Serum cytokine levels in control and tumor-bearing male and female mice at day 15. Male Female Cytokine Control C-26 Control C-26 IL-1β 2.0 ± 0.8 9.6 ± 1.5* 1.8 ± 0.2 6.8 ± 1.4*
High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22
 Supplementary Information High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22 Max Gulhane 1, Lydia Murray 1, Rohan Lourie 1, Hui Tong 1, Yong H. Sheng 1, Ran
Supplementary Information High Fat Diets Induce Colonic Epithelial Cell Stress and Inflammation that is Reversed by IL-22 Max Gulhane 1, Lydia Murray 1, Rohan Lourie 1, Hui Tong 1, Yong H. Sheng 1, Ran
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3461 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 (associated to Figure 1). Cpeb4 gene-targeted mice develop liver steatosis. a, Immunoblot displaying CPEB4
Supplemental Material:
 Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity. Gijs Goossens, PhD
 Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity -The role of adipose tissue oxygenation - Gijs Goossens, PhD NUTRIM School of Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism Maastricht University Medical Centre
Adipose tissue dysfunction in obesity -The role of adipose tissue oxygenation - Gijs Goossens, PhD NUTRIM School of Nutrition and Translational Research in Metabolism Maastricht University Medical Centre
Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological. findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL EN-12-2276 Figure 1. Effects of FGF21 on adipose tissue. (A) Representative histological findings of epididymal adipose tissue (B) mrna expression of adipocytokines in adipose tissue.
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
HSN301 Diet and Disease Entire Note Summary
 Topic 1: Metabolic Syndrome Learning Objectives: 1. Define obesity 2. Factors causing obesity 3. Obesity as a risk factor for metabolic syndrome 4. The pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome 5. Treatment of
Topic 1: Metabolic Syndrome Learning Objectives: 1. Define obesity 2. Factors causing obesity 3. Obesity as a risk factor for metabolic syndrome 4. The pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome 5. Treatment of
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice
 Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
Caffeine Modulates Hyperoxia - Induced Angiogenesis in Newborn Mice Vikramaditya Dumpa, MD Lori C Nielsen, MS Huamei Wang, MD Vasanth HS Kumar, MD Supported by AAP Marshall Klaus Perinatal Research Grant
New therapeutic targets for T2DM
 New therapeutic targets for T2DM Targeting inflammation: NF- B, salsalate Gwanpyo Koh Department of Internal Medicine Jeju National University School of Medicine Introduction Obesity is occurring at epidemic
New therapeutic targets for T2DM Targeting inflammation: NF- B, salsalate Gwanpyo Koh Department of Internal Medicine Jeju National University School of Medicine Introduction Obesity is occurring at epidemic
FAPESP Week /21/2017
 Texas Tech University Dr Naima Moustaid-Moussa Texas Tech University FAPESP Week 2017 09/21/2017 University of Sao Paulo Dr Sonia Jancar ICB-USP Theresa Ramalho MS PhD candidate, Immunology ICB-USP Dr
Texas Tech University Dr Naima Moustaid-Moussa Texas Tech University FAPESP Week 2017 09/21/2017 University of Sao Paulo Dr Sonia Jancar ICB-USP Theresa Ramalho MS PhD candidate, Immunology ICB-USP Dr
Resistin expression in adipose tissues and its effect on glucose metabolism in rats with brain injury
 Resistin expression in adipose tissues and its effect on glucose metabolism in rats with brain injury R. Zhang 1, Z.Y. Wang 1, L.L. Zhu 1, F. Wu 1, D.Q. Chen 1, L.F. Sun 1 and Z.Q. Lu 2 1 Department of
Resistin expression in adipose tissues and its effect on glucose metabolism in rats with brain injury R. Zhang 1, Z.Y. Wang 1, L.L. Zhu 1, F. Wu 1, D.Q. Chen 1, L.F. Sun 1 and Z.Q. Lu 2 1 Department of
The Metabolic Syndrome Update The Metabolic Syndrome: Overview. Global Cardiometabolic Risk
 Update 2013 Marc Cornier, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes Anschutz Health and Wellness Center University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver Health
Update 2013 Marc Cornier, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Division of Endocrinology, Metabolism & Diabetes Anschutz Health and Wellness Center University of Colorado School of Medicine Denver Health
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Association of serum adipose triglyceride lipase levels with obesity and diabetes
 Association of serum adipose triglyceride lipase levels with obesity and diabetes L. Yang 1 *, S.J. Chen 1 *, G.Y. Yuan 1, L.B. Zhou 2, D. Wang 1, X.Z. Wang 1 and J.J. Chen 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
Association of serum adipose triglyceride lipase levels with obesity and diabetes L. Yang 1 *, S.J. Chen 1 *, G.Y. Yuan 1, L.B. Zhou 2, D. Wang 1, X.Z. Wang 1 and J.J. Chen 1 1 Department of Endocrinology,
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO. Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu ABSTRACT
 Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Naohito AOKI, Erina ARAKAWA and Miyuki ITO Department of Life Science, Graduate School of Bioresources, Mie University Tsu 514-857 ABSTRACT C57BL/6J mice (male, 4wk old) were fed low fat diet (LF), high
Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes: Making the Connections
 Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes: Making the Connections Alka M. Kanaya, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine & Epi/Biostats University of California, San Francisco February 26, 21 Roadmap 1.
Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Diabetes: Making the Connections Alka M. Kanaya, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine & Epi/Biostats University of California, San Francisco February 26, 21 Roadmap 1.
Supplemental Information. Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects. against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin. Resistance in Male Mice
 Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
Cell Reports, Volume 16 Supplemental Information Increased 4E-BP1 Expression Protects against Diet-Induced Obesity and Insulin Resistance in Male Mice Shih-Yin Tsai, Ariana A. Rodriguez, Somasish G. Dastidar,
LIPOCALIN 2 DEFICIENCY INFLUENCES TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β EFFECT ON INFLAMMATION AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX REMODELING IN INGUINAL ADIPOCYTES
 LIPOCALIN 2 DEFICIENCY INFLUENCES TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β EFFECT ON INFLAMMATION AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX REMODELING IN INGUINAL ADIPOCYTES A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
LIPOCALIN 2 DEFICIENCY INFLUENCES TRANSFORMING GROWTH FACTOR-β EFFECT ON INFLAMMATION AND EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX REMODELING IN INGUINAL ADIPOCYTES A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE FACULTY OF THE UNIVERSITY OF MINNESOTA
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Supplementary Materials 1 Supplementary Table 1. List of primers used for quantitative PCR analysis. Gene name Gene symbol Accession IDs Sequence range Product Primer sequences size (bp) β-actin Actb gi
Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications Epigenetics: Mechanisms and Implications for Diabetic Complications
 This Review is part of a thematic series on Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes and Obesity, which includes the following articles: The Impact of Macrophage Insulin Resistance on Advanced Atherosclerotic
This Review is part of a thematic series on Cardiovascular Complications of Diabetes and Obesity, which includes the following articles: The Impact of Macrophage Insulin Resistance on Advanced Atherosclerotic
The true cost of inpatient obesity impact on inflammatory stress and morbidity.
 The true cost of inpatient obesity impact on inflammatory stress and morbidity. Professor Bob Grimble, Institute of Human Nutrition, Institute of Developmental Sciences Building, University of Southampton
The true cost of inpatient obesity impact on inflammatory stress and morbidity. Professor Bob Grimble, Institute of Human Nutrition, Institute of Developmental Sciences Building, University of Southampton
Supplemental Data. Short Article. ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1. Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival. under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
 Cell Metabolism, Volume 7 Supplemental Data Short Article ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1 Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Suguru Yamaguchi, Hisamitsu Ishihara,
Cell Metabolism, Volume 7 Supplemental Data Short Article ATF4-Mediated Induction of 4E-BP1 Contributes to Pancreatic β Cell Survival under Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Suguru Yamaguchi, Hisamitsu Ishihara,
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Rat Primary Pre-adipocytes Culture Kit
 Primary Cell Co., Ltd Rat Primary Pre-adipocytes Culture Kit Primary Cells from rat mesenteric, epididymal, and subcutaneous adipose tissues. Catalog # PMC-VAC01-COS, PMC-EAC01-COS, PMC-SAC01-COS Notice
Primary Cell Co., Ltd Rat Primary Pre-adipocytes Culture Kit Primary Cells from rat mesenteric, epididymal, and subcutaneous adipose tissues. Catalog # PMC-VAC01-COS, PMC-EAC01-COS, PMC-SAC01-COS Notice
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome. and Type-2 Diabetes
 A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
A Central Role of MG53 in Metabolic Syndrome and Type-2 Diabetes Yan Zhang, Chunmei Cao, Rui-Ping Xiao Institute of Molecular Medicine (IMM) Peking University, Beijing, China Accelerated Aging in China
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
For Asian individuals the BMI numbers are 27.5 and 25 respectively These values are from the NICE guidelines of 2014
 Ken Cathcart DO FACE We need to define several things to start the talk Obesity is defined medically as a BMI of greater than 30 or a BMI >27 with co-morbidities such as hypertension, type 2 DM, dyslipidemia,
Ken Cathcart DO FACE We need to define several things to start the talk Obesity is defined medically as a BMI of greater than 30 or a BMI >27 with co-morbidities such as hypertension, type 2 DM, dyslipidemia,
ATHEROSCLEROTIC cardiovascular complications are the leading cause of. Diabetes Mellitus Has an Additional Effect on Coronary Artery Disease
 Diabetes Mellitus Has an Additional Effect on Coronary Artery Disease To Decrease Plasma Adiponectin Levels Kuei-Chuan CHAN, 1 MD, Hsi-Hsien CHOU, 1 PhD, Der-Jinn WU, 1 PhD, Yi-Liang WU, 1 MD, and Chien-Ning
Diabetes Mellitus Has an Additional Effect on Coronary Artery Disease To Decrease Plasma Adiponectin Levels Kuei-Chuan CHAN, 1 MD, Hsi-Hsien CHOU, 1 PhD, Der-Jinn WU, 1 PhD, Yi-Liang WU, 1 MD, and Chien-Ning
Antibodies for Unfolded Protein Response
 Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Novus-lu-2945 Antibodies for Unfolded rotein Response Unfolded roteins ER lumen GR78 IRE-1 GR78 ERK Cytosol GR78 TRAF2 ASK1 JNK Activator Intron RIDD elf2α Degraded mrna XB1 mrna Translation XB1-S (p50)
Changes in Cardiotrophin-1 and Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 with Weight Loss. Robert Lawrence Bowers
 Changes in Cardiotrophin-1 and Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 with Weight Loss by Robert Lawrence Bowers A dissertation submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of the
Changes in Cardiotrophin-1 and Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 with Weight Loss by Robert Lawrence Bowers A dissertation submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of the
alveolar macrophages (AMs) after 24 hours of in vitro culture in complete medium
 Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
Online Supplement for: NF-κB ACTIVATION IN ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGES REQUIRES IκB KINASE-β, BUT NOT NF-κB INDUCING KINASE Supershift and Competition Assays for NF-κB Competition and supershift assays were performed
renoprotection therapy goals 208, 209
 Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Subject Index Aldosterone, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 induction 163, 164, 168 Aminopeptidases angiotensin II processing 64 66, 214 diabetic expression 214, 215 Angiotensin I intrarenal compartmentalization
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
INTRODUCTION. Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells
 Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis
 Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Anti-inflammatory properties of SM04690, a small molecule inhibitor of the Wnt pathway as a potential treatment for knee osteoarthritis V. Deshmukh 1, T. Seo 1, C. Swearingen 1, Y. Yazici 1 1 Samumed,
Supplementary Figure 1 a
 Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Supplementary Figure a Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.).6... Trip-br transcripts Trans Trans Trans b..5. Trip-br Ctrl LPS Normalized expression/tbp (A.U.) c Trip-br transcripts. adipocytes.... Trans Trans
Males- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks) Females- Western Diet WT KO Age (wks)
 Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
Relative Arv1 mrna Adrenal 33.48 +/- 6.2 Skeletal Muscle 22.4 +/- 4.93 Liver 6.41 +/- 1.48 Heart 5.1 +/- 2.3 Brain 4.98 +/- 2.11 Ovary 4.68 +/- 2.21 Kidney 3.98 +/-.39 Lung 2.15 +/-.6 Inguinal Subcutaneous
HYPOXIA AND ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION IN OBESITY
 HYPOXIA AND ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION IN OBESITY Paul Trayhurn Physiol Rev 93: 1 21, 2013 doi:10.1152/physrev.00017.2012 Obesity Biology Research Unit, Institute of Ageing and Chronic Diseases,
HYPOXIA AND ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTION AND DYSFUNCTION IN OBESITY Paul Trayhurn Physiol Rev 93: 1 21, 2013 doi:10.1152/physrev.00017.2012 Obesity Biology Research Unit, Institute of Ageing and Chronic Diseases,
For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin
 Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Materials and Methods Pair Feeding Experiment For pair feeding, mice were fed 2.7g of HFD containing tofogliflozin (0.005%), which is average daily food intake of mice fed control HFD ad libitum at week
Study of the correlation between growth hormone deficiency and serum leptin, adiponectin, and visfatin levels in adults
 Study of the correlation between growth hormone deficiency and serum leptin, adiponectin, and visfatin levels in adults Z.-P. Li 1, M. Zhang 2, J. Gao 3, G.-Y. Zhou 3, S.-Q. Li 1 and Z.-M. An 3 1 Golden
Study of the correlation between growth hormone deficiency and serum leptin, adiponectin, and visfatin levels in adults Z.-P. Li 1, M. Zhang 2, J. Gao 3, G.-Y. Zhou 3, S.-Q. Li 1 and Z.-M. An 3 1 Golden
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Electroacupuncture prevents white adipose tissue inflammation through modulation of hypoxia-inducible factors-1α-dependent pathway in obese mice
 Wen and Lee BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2015) 15:452 DOI 10.1186/s12906-015-0977-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Electroacupuncture prevents white adipose tissue inflammation through modulation
Wen and Lee BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine (2015) 15:452 DOI 10.1186/s12906-015-0977-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Electroacupuncture prevents white adipose tissue inflammation through modulation
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes
 Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Endocannabinoid-activated Nlrp3 inflammasome in infiltrating macrophages mediates β- cell loss in type 2 diabetes T Jourdan, G Godlewski, R Cinar, A Bertola, G Szanda, J Liu, J Tam, T Han, B Mukhopadhyay,
Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
Supplementary Figure 1 Metabolic ER stress and inflammation in white adipose tissue (WAT) of mice with dietary obesity. Male C57BL/6J mice were fed a normal chow (NC, 10% fat) or a high-fat diet (HFD,
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice
 Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
Effects of growth hormone secretagogue receptor agonist and antagonist in nonobese type 2 diabetic MKR mice Rasha Mosa (MBCHC, M.D, PhD candidate) School of Biomedical Sciences University of Queensland
MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF INSULIN RESISTANCE IN OBESITY
 January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 5-9) MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF INSULIN RESISTANCE IN OBESITY By André Marette, PhD Department of Anatomy and Physiology and Lipid Research Unit, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire
January 2008 (Vol. 1, Issue 1, pages 5-9) MOLECULAR MECHANISMS OF INSULIN RESISTANCE IN OBESITY By André Marette, PhD Department of Anatomy and Physiology and Lipid Research Unit, Centre Hospitalier Universitaire
In The Name Of God. In The Name Of. EMRI Modeling Group
 In The Name Of God In The Name Of God EMRI Modeling Group Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: Epithelial lining and covering Connective support Muscle movement
In The Name Of God In The Name Of God EMRI Modeling Group Cells work together in functionally related groups called tissues Types of tissues: Epithelial lining and covering Connective support Muscle movement
METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE
 METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE 2. LF UK Prof. Rudolf Poledne, PhD. TYPES OF ADIPOSE TISSUE brown adipose tissue subcutaneous adipose tissue visceral adipose tissue ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTIONS: thermal isolation
METABOLISM of ADIPOSE TISSUE 2. LF UK Prof. Rudolf Poledne, PhD. TYPES OF ADIPOSE TISSUE brown adipose tissue subcutaneous adipose tissue visceral adipose tissue ADIPOSE TISSUE FUNCTIONS: thermal isolation
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein
 Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Protection against doxorubicin-induced myocardial dysfunction in mice by cardiac-specific expression of carboxyl terminus of hsp70-interacting protein Lei Wang 1, Tian-Peng Zhang 1, Yuan Zhang 2, Hai-Lian
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle.
 Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Supplementary Figure 1. DJ-1 modulates ROS concentration in mouse skeletal muscle. (a) mrna levels of Dj1 measured by quantitative RT-PCR in soleus, gastrocnemius (Gastroc.) and extensor digitorum longus
Research Article Serum Ratio of Leptin to Adiponectin in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
 ISRN Biomarkers, Article ID 952636, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/952636 Research Article Serum Ratio of Leptin to Adiponectin in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
ISRN Biomarkers, Article ID 952636, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/952636 Research Article Serum Ratio of Leptin to Adiponectin in Patients with Chronic Periodontitis and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
2011, Editrice Kurtis
 J. Endocrinol. Invest. : -, 2011 DOI: 10.2/902 The role of visfatin in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus D.E. Gok 1, M. Yazici 1, G. Uckaya 1, S.E. Bolu 1, Y. Basaran 2, T. Ozgurtas, S.
J. Endocrinol. Invest. : -, 2011 DOI: 10.2/902 The role of visfatin in the pathogenesis of gestational diabetes mellitus D.E. Gok 1, M. Yazici 1, G. Uckaya 1, S.E. Bolu 1, Y. Basaran 2, T. Ozgurtas, S.
Upregulation of salivary α2 macroglobulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
 Upregulation of salivary α2 macroglobulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus J.K. Feng*, Y.F. Lu*, J. Li, Y.H. Qi, M.L. Yi and D.Y. Ma Center of Laboratory Medicine, The Affiliated Yuhuangding Hospital
Upregulation of salivary α2 macroglobulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus J.K. Feng*, Y.F. Lu*, J. Li, Y.H. Qi, M.L. Yi and D.Y. Ma Center of Laboratory Medicine, The Affiliated Yuhuangding Hospital
Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis
 193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
193 Mini Review Possible roles of adiponectin in inflammatory process of rheumatoid arthritis Miho Suzuki and Masahiko Mihara Product Research Department, Fuji-Gotemba Research Laboratories, Chugai Pharmaceutical
Clinical Study The Levels of Ghrelin, TNF-α, and IL-6 in Children with Cyanotic and Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease
 Mediators of Inflammation Volume 07, Article ID 323, 5 pages doi:.1155/07/323 Clinical Study The Levels of Ghrelin, TNF-α, and IL-6 in Children with Cyanotic and Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease Erdal
Mediators of Inflammation Volume 07, Article ID 323, 5 pages doi:.1155/07/323 Clinical Study The Levels of Ghrelin, TNF-α, and IL-6 in Children with Cyanotic and Acyanotic Congenital Heart Disease Erdal
Cell Quality Control. Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology
 Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Cell Quality Control Peter Takizawa Department of Cell Biology Cellular quality control reduces production of defective proteins. Cells have many quality control systems to ensure that cell does not build
Adipocyte Stress: The Endoplasmic Reticulum and Metabolic Disease. Margaret F. Gregor and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
 Adipocyte Stress: The Endoplasmic Reticulum and Metabolic Disease Margaret F. Gregor and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil Department of Genetics and Complex Diseases, Harvard School of Public Health Boston, MA,
Adipocyte Stress: The Endoplasmic Reticulum and Metabolic Disease Margaret F. Gregor and Gökhan S. Hotamisligil Department of Genetics and Complex Diseases, Harvard School of Public Health Boston, MA,
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Reduced Insulin Signaling and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Act Synergistically to Deteriorate Pancreatic β Cell Function
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. E114-E121, 2008 Reduced Insulin Signaling and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Act Synergistically to Deteriorate Pancreatic β Cell Function TOMOKAZU MATSUDA, YOSHIAKI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 54, No. 2, pp. E114-E121, 2008 Reduced Insulin Signaling and Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Act Synergistically to Deteriorate Pancreatic β Cell Function TOMOKAZU MATSUDA, YOSHIAKI
Materials and Methods
 Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
Short term hyperthermia prevents activation of proinflammatory genes in type B synoviocytes by blocking the activation of the transcription factor NF-κB Marica Markovic Institute of Medical Biochemistry,
B-cell. Astrocyte SCI SCI. T-cell
 RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: how are they interlinked?
 Rehman and Akash Journal of Biomedical Science (2016) 23:87 DOI 10.1186/s12929-016-0303-y RESEARCH Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: how are they interlinked?
Rehman and Akash Journal of Biomedical Science (2016) 23:87 DOI 10.1186/s12929-016-0303-y RESEARCH Mechanisms of inflammatory responses and development of insulin resistance: how are they interlinked?
Page 39 of 44. 8h LTA & AT h PepG & AT h LTA
 Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
Page 39 of 44 Fig. S1 A: B: C: D: 8h LTA 8h LTA & AT7519 E: F: 8h PepG G: 8h PepG & AT7519 Fig. S1. AT7519 overrides the survival effects of lipoteichoic acid (LTA) and peptidoglycan (PepG). (A) Human
MANUAL RBP4 (human) Competitive ELISA Kit Cat. No. AG-45A-0010YEK-KI01 For research use only. Not for diagnostic use.
 MANUAL RBP4 (human) Competitive ELISA Kit For research use only. Not for diagnostic use. Version 3 (04-May-2015) Cat. No. AG-45A-0010YEK-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents 1. Intended Use 3 2. Introduction
MANUAL RBP4 (human) Competitive ELISA Kit For research use only. Not for diagnostic use. Version 3 (04-May-2015) Cat. No. AG-45A-0010YEK-KI01 www.adipogen.com Table of Contents 1. Intended Use 3 2. Introduction
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
 Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians
 Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
Metabolic Syndrome in Asians Alka Kanaya, MD Asst. Professor of Medicine, UCSF Asian CV Symposium, November 17, 2007 The Metabolic Syndrome Also known as: Syndrome X Insulin Resistance Syndrome The Deadly
Fructose in Insulin Resistance- Focused on Diabetes 순천향대학교부천병원 내분비내과 정찬희
 Fructose in Insulin Resistance- Focused on Diabetes 순천향대학교부천병원 내분비내과 정찬희 Introduction Unique characteristics of Fructose Metabolism Mechanism for Fructose-Induced Insulin Resistance Epidemiological Studies
Fructose in Insulin Resistance- Focused on Diabetes 순천향대학교부천병원 내분비내과 정찬희 Introduction Unique characteristics of Fructose Metabolism Mechanism for Fructose-Induced Insulin Resistance Epidemiological Studies
ZL ZDF ZDF + E2 *** Visceral (g) ZDF
 Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
Body Weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ** * ZL ZDF 6 8 1 12 14 16 Age (weeks) B * Sub-cutaneous (g) 16 12 8 4 ZL ZDF Visceral (g) 25 2 15 1 5 ZL ZDF Total fat pad weight (g) 4 3 2 1 ZDF ZL Supplemental Figure 1: Effect
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU. PhD THESIS Summary
 ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
