CHAPTER 13: THE CONDITIONS OF ROTARY MOTION
|
|
|
- Tyler Hill
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 13: THE CONDITIONS OF ROTARY MOTION KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University Revised by Hamilton & Weimar McGraw-Hill/Irwin Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
2 Rotary Force Eccentric Force When the direction of force is not in line with object s center of gravity, a combination of rotary and translatory motion is likely to occur. An object with a fixed axis rotates when force is applied off center. Eccentric force: a force whose direction is not in line with the center of gravity of a freely moving object or the center of rotation of an object with a fixed axis of rotation. 13-2
3 Examples of Eccentric Force Fig
4 Torque The turning effect of an eccentric force. Equals the product of the force magnitude and the length of the moment arm. Moment arm is the perpendicular distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation. Torque may be modified by changing either force or moment arm. Fig
5 Length of Moment Arm Perpendicular distance from the line of force to the axis of rotation. The moment arm is no longer the length of the forearm. Fig
6 Length of Moment Arm In the body, weight of a segment cannot be altered instantaneously. Therefore, torque of a segment due to gravitational force can be changed only by changing the length of the moment arm. d W d W Fig
7 Muscle Force Vectors Only the rotary component is actually a factor in torque production. The stabilizing component acts along the mechanical axis of the bone, through the axis of rotation. Thus, it is not eccentric, or off-center. 13-7
8 Summation of Torques The sum of two or more torques may result in no motion, linear motion, or rotary motion. Parallel eccentric forces applied in the same direction on opposite sides of the center of rotation; Ex. a balanced seesaw. If equal parallel forces are adequate to overcome the resistance, linear motion will occur; Ex. paddlers in a canoe. 13-8
9 Force Couple The effect of equal parallel forces acting in opposite direction. Fig 13.6 &
10 The Lever A rigid bar that can rotate about a fixed point (Fulcrum) when a force is applied to overcome a resistance. They are used to: Balance 2 or more forces. Favor force production. Favor speed and range of motion. Change the direction of the applied force
11 External Levers Using a small force to overcome a large resistance. Ex. a crowbar Using a large ROM to overcome a small resistance. Ex. Hitting a golf ball Used to balance a force and a load. Ex. a seesaw 13-11
12 External Lever:
13 Anatomical Levers Nearly every bone is a lever. The joint is the fulcrum. Contracting muscles are the force. Do not necessarily resemble bars. Ex. skull, scapula, vertebrae The resistance point may be difficult to identify. May be difficult to determine resistance. Weight and antagonistic muscles
14 Lever Arms Portion of lever between fulcrum & force point. Effort Arm (EA): Perpendicular distance between fulcrum & line of force of effort. Resistance Arm (RA): Perpendicular distance between fulcrum & line of resistance force. Fig
15 Classification of Levers Three points on the lever have been identified 1. Fulcrum 2. Effort force point of application 3. Resistance force point of application There are three possible arrangements of these points. This arrangement is the basis for the classification of levers
16 First-Class Lever E A R E = Effort A = Axis or fulcrum R = Resistance Fig
17 First-Class Lever Can be used to achieve all four functions of a simple machine. Depends on relative lengths of effort arm and resistance arm: 1. Balance 2 or more forces: If effort force and resistance force are equal, effort arm and resistance arm are equal. 2. Favor force production: If effort force and resistance force are equal, effort arm is longer than the resistance arm. 3. Favor speed and range of motion: If effort force and resistance force are equal, resistance arm is longer than the effort arm. 4. Change direction of applied force: If you push down on one side of a seesaw, the other side goes up
18 Second-Class Lever A R E E = Effort A = Axis or fulcrum R = Resistance Fig
19 Second-Class Levers Primary function is to magnify the effect of force production. The effort arm is always longer than the resistance arm
20 Third-Class Lever A E R E = Effort A = Axis or fulcrum R = Resistance Fig
21 Third-Class Levers Primary function is to magnify speed and range of motion. Resistance arm is longer than effort arm so even though the entire lever will move through the same angular distance, the effort moves a small linear distance, while the resistance moves through a larger linear distance
CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE
 CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
CHAPTER 15: KINESIOLOGY OF FITNESS AND EXERCISE KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF KINESIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF KINESIOLOGY KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION TO THE STUDY OF KINESIOLOGY KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
State of equilibrium is when the sum (or net effect) of forces acting on a body equals zero
 Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy,physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio - refers to living
Kinesiology is the science of, or study of, human motion. It brings together the fields of anatomy,physiology, biomechanics, physics and geometry relating them to human movement. Bio - refers to living
Musculoskeletal System. Terms. Origin (Proximal Attachment) Insertion (Distal Attachment)
 Musculoskeletal System Terms Origin (Proximal Attachment) Insertion (Distal Attachment) Agonist- prime mover Antagonist- provides a braking force Synergist- assists indirectly in the movement Musculoskeletal
Musculoskeletal System Terms Origin (Proximal Attachment) Insertion (Distal Attachment) Agonist- prime mover Antagonist- provides a braking force Synergist- assists indirectly in the movement Musculoskeletal
Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts
 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved 3-1 Biomechanics Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis
Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved 3-1 Biomechanics Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis
Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts
 Biomechanics Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis of biological systems and especially humans Necessary
Biomechanics Chapter 3 Basic Biomechanical Factors & Concepts Biomechanics - study of the mechanics as it relates to the functional and anatomical analysis of biological systems and especially humans Necessary
Lever system. Rigid bar. Fulcrum. Force (effort) Resistance (load)
 Lever system lever is any elongated, rigid (bar) object that move or rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum when force is applied to overcome resistance. Force (effort) Resistance (load) R Rigid
Lever system lever is any elongated, rigid (bar) object that move or rotates around a fixed point called the fulcrum when force is applied to overcome resistance. Force (effort) Resistance (load) R Rigid
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics. ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering. Principles of Biomechanics
 University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Principles of Biomechanics Introduction What is Biomechanics? The study of internal and external
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Principles of Biomechanics Introduction What is Biomechanics? The study of internal and external
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis
 Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
Introduction to Biomechanical Analysis LEARNING OBJECTIVES: At the end of this laboratory exercise the student will be able to: Identify forces used during activities Identify moments used during activities
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS
 CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
CHAPTER 2: MUSCULOSKELETAL SYSTEM: FRAMEWORK AND MOVEMENTS KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt
BIOMECHANICS. Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body.
 1 BIOMECHANICS Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body. I. Uses of Biomechanical Analyses Improvement of sports skill
1 BIOMECHANICS Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body. I. Uses of Biomechanical Analyses Improvement of sports skill
Basics of kinetics. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Basics of kinetics Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Mass The amount of matter in an object Weight A force, which depends on the mass and acceleration Free-body analysis A technique of looking
Basics of kinetics Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Mass The amount of matter in an object Weight A force, which depends on the mass and acceleration Free-body analysis A technique of looking
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018
 Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Biomechanics of Resistance Training. Tutor: Phil Watkins
 Biomechanics of Resistance Training Tutor: Phil Watkins Types of Resistance Training Isometric Free Weights- isotonic/isoinertial Variable Resistance Isokinetic Hydraulic and pneumatic Isointerial/ballsistic
Biomechanics of Resistance Training Tutor: Phil Watkins Types of Resistance Training Isometric Free Weights- isotonic/isoinertial Variable Resistance Isokinetic Hydraulic and pneumatic Isointerial/ballsistic
ANYTHING THAT IT IS CARRYING)
 1) A rigid structure (BONE) Levers in our body are formed from Bones, Joints and Muscles. A lever consists of 2) A force acting upon it (MUSCLE) to produce a turning movement (ANGULAR MOTION) 3) A fulcrum
1) A rigid structure (BONE) Levers in our body are formed from Bones, Joints and Muscles. A lever consists of 2) A force acting upon it (MUSCLE) to produce a turning movement (ANGULAR MOTION) 3) A fulcrum
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK. Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology MUSCLES, MOVEMENTS & BIOMECHANICS MSAK101-I Session 7 Learning Objectives: 1. List the three types
CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens
 CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
CHAPTER 9: THE SPINAL COLUMN AND THORAX KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State University
The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle
 AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
AML2506 Biomechanics and Flow Simulation Day 03B The Biomechanics of Human Skeletal Muscle Session Speaker Dr. M. D. Deshpande 1 Session Objectives At the end of this session the delegate would have understood
Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy
 Senior MESA Day Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy Bones, Joints, Muscles Review Arm Motion Kinematics: types of motion, location of motion, direction of motion, magnitude of motion, and degrees of freedom
Senior MESA Day Overview of the Human Arm Anatomy Bones, Joints, Muscles Review Arm Motion Kinematics: types of motion, location of motion, direction of motion, magnitude of motion, and degrees of freedom
Static Equilibrium. 4. What torques do you think act about the atlanto-occipital joint?
 HPP Activity A25.v1 Static Equilibrium Exploration GE 1. Sit upright with head held straight. Now bend your head forward and hold it steady. 1. What do you feel in your neck as you keep your head steady
HPP Activity A25.v1 Static Equilibrium Exploration GE 1. Sit upright with head held straight. Now bend your head forward and hold it steady. 1. What do you feel in your neck as you keep your head steady
CHAPTER 6: THE UPPER EXTREMITY: THE ELBOW, FOREARM, WRIST, AND HAND
 CHAPTER 6: THE UPPER EXTREMITY: THE ELBOW, FOREARM, WRIST, AND HAND KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D.,
CHAPTER 6: THE UPPER EXTREMITY: THE ELBOW, FOREARM, WRIST, AND HAND KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D.,
*Agonists are the main muscles responsible for the action. *Antagonists oppose the agonists and can help neutralize actions. Since many muscles have
 1 *Agonists are the main muscles responsible for the action. *Antagonists oppose the agonists and can help neutralize actions. Since many muscles have more than 1 action sometimes a muscle has to neutralize
1 *Agonists are the main muscles responsible for the action. *Antagonists oppose the agonists and can help neutralize actions. Since many muscles have more than 1 action sometimes a muscle has to neutralize
When considering the movement of limbs compared to a classic demonstration of levers the
 Sensors: Loggers: Force Any EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: SnapShot with Asks for Value function Teacher s notes 401 Forces in levers Read Body movement is created by applying forces across joints
Sensors: Loggers: Force Any EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: SnapShot with Asks for Value function Teacher s notes 401 Forces in levers Read Body movement is created by applying forces across joints
Brawn behind performance. John Milton BIO-39
 Brawn behind performance John Milton BIO-39 Brain or brawn? Newton was a sports fan I remember that I had often seen a tennis ball struck with an oblique racket describe such a curved line. For a circular
Brawn behind performance John Milton BIO-39 Brain or brawn? Newton was a sports fan I remember that I had often seen a tennis ball struck with an oblique racket describe such a curved line. For a circular
Lab: Muscle Action. As you perform the exercise name the muscle you are working and the action of that muscle.
 Lab: Muscle Action Name Anatomy and Physiology, Mrs. Grant Directions: Perform the following exercises in the weight room. Follow the directions carefully and do not use any weight. We are interested only
Lab: Muscle Action Name Anatomy and Physiology, Mrs. Grant Directions: Perform the following exercises in the weight room. Follow the directions carefully and do not use any weight. We are interested only
2.1 Lever systems, examples of their use and the mechanical advantages they provide
 2.1 Lever systems, examples of their use and the mechanical advantages they provide Learning objectives To understand the 3 different lever class systems To be able to describe the components of each lever
2.1 Lever systems, examples of their use and the mechanical advantages they provide Learning objectives To understand the 3 different lever class systems To be able to describe the components of each lever
MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL
 MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE - CONTAINS THE BLOOD VESSELS AND THE NERVES TO A MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE - LONGITUDINAL SECTION MUSCLE ATTACHMENTS: TENDONS
MUSCLE MECHANICS AND CONTROL STRUCTURE OF A SKELETAL MUSCLE NEUROVASCULAR BUNDLE - CONTAINS THE BLOOD VESSELS AND THE NERVES TO A MUSCLE SKELETAL MUSCLE - LONGITUDINAL SECTION MUSCLE ATTACHMENTS: TENDONS
Russ Ebbets, DC NY Chiropractic College Editor, Track Coach Biomechanics is...
 Biomechanics Russ Ebbets, DC NY Chiropractic College Editor, Track Coach spinedoctor229@hotmail.com Biomechanics is... The science of mechanical forces on living organisms The forces can be inside or outside
Biomechanics Russ Ebbets, DC NY Chiropractic College Editor, Track Coach spinedoctor229@hotmail.com Biomechanics is... The science of mechanical forces on living organisms The forces can be inside or outside
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects
 Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
Maximal isokinetic and isometric muscle strength of major muscle groups related to age, body weight, height, and sex in 178 healthy subjects Test protocol Muscle test procedures. Prior to each test participants
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction it simply shortens. Lippert
 When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction it simply shortens. Lippert Muscles are attached to bones and to describe the relative points of attachment, we use the terms origin and insertion. Lippert,
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction it simply shortens. Lippert Muscles are attached to bones and to describe the relative points of attachment, we use the terms origin and insertion. Lippert,
Performance Enhancement. Strength Training
 Performance Enhancement Strength Training Muscle Fiber type & Performance Slow twitch More efficient using oxygen to generate fuel for continuous extended muscle contractions Contract slowly, but continue
Performance Enhancement Strength Training Muscle Fiber type & Performance Slow twitch More efficient using oxygen to generate fuel for continuous extended muscle contractions Contract slowly, but continue
Chapter 2. Biomechanics IN THIS CHAPTER. Forces. Energy, Work, & Power. Torque. Stability. Momentum. Common Errors in Movement & Exercise
 Chapter 2 IN THIS CHAPTER Forces Energy, Work, & Power Torque Stability Momentum Common Errors in Movement & Exercise NCSF CPT Introduction is an encompassing term that joins human anatomy and physiology
Chapter 2 IN THIS CHAPTER Forces Energy, Work, & Power Torque Stability Momentum Common Errors in Movement & Exercise NCSF CPT Introduction is an encompassing term that joins human anatomy and physiology
Movement Analysis UNDERSTANDING MOVEMENT AND FORCE
 Movement Analysis UNDERSTANDING MOVEMENT AND FORCE Learning objectives for this topic After completing this chapter you should have knowledge and understanding of 1. First, second and third class levers
Movement Analysis UNDERSTANDING MOVEMENT AND FORCE Learning objectives for this topic After completing this chapter you should have knowledge and understanding of 1. First, second and third class levers
Introduction to Biomechanics
 Module Five: Introduction to Biomechanics INTRODUCTION In Level One you learnt to divide a skill into meaningful phases, identify the key elements within each phase, and develop an observation plan to
Module Five: Introduction to Biomechanics INTRODUCTION In Level One you learnt to divide a skill into meaningful phases, identify the key elements within each phase, and develop an observation plan to
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert
 When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
BME 207 Introduction to Biomechanics Spring 2015
 January 30, 2015 UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND Department of Electrical, Computer and iomedical Engineering ME 207 Introduction to iomechanics Spring 2015 Homework 2 Problems 3.1 through 3.10 in the textbook.
January 30, 2015 UNIVERSITY OF RHODE ISLAND Department of Electrical, Computer and iomedical Engineering ME 207 Introduction to iomechanics Spring 2015 Homework 2 Problems 3.1 through 3.10 in the textbook.
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics. Exam style questions - pages QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS. Answers
 CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
CHAPTER 2: Muscular skeletal system - Biomechanics Exam style questions - pages 32-35 1) A Level. Warm up is considered to be an essential element of a training programme. Explain how the muscular and
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert
 When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
When a muscle contracts, it knows no direction; it simply shortens. Lippert Muscle is the sole producer of active force in the body which makes it responsible for all active motions. Muscles also control
a. Magnitude, direction, point of application, line of action a. Weight is a force and mass is the quantity of matter in the body
 1. The four characteristics of a force include a. Magnitude, direction, point of application, line of action 2. Mass differs from weight because a. Weight is a force and mass is the quantity of matter
1. The four characteristics of a force include a. Magnitude, direction, point of application, line of action 2. Mass differs from weight because a. Weight is a force and mass is the quantity of matter
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System
 Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
Biomechanics of Skeletal Muscle and the Musculoskeletal System Hamill & Knutzen (Ch 3) Nordin & Frankel (Ch 5), or Hall (Ch. 6) Muscle Properties Ø Irritability Ø Muscle has the capability of receiving
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment
 Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
Chapter 20: Muscular Fitness and Assessment American College of Sports Medicine. (2010). ACSM's resource manual for guidelines for exercise testing and prescription (6th ed.). New York: Lippincott, Williams
05/06/14 Name Physics 130 Final Exam
 The following information pertains to questions 1 and 2: In running up the stairs if Fred converts 800 J of food energy into gravitational potential energy. Assume 20% of the food energy is converted into
The following information pertains to questions 1 and 2: In running up the stairs if Fred converts 800 J of food energy into gravitational potential energy. Assume 20% of the food energy is converted into
Figure 11-1: The lever-fulcrum principle is illustrated by flexion of the forearm.
 Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Chapter 11: The Muscular System Read pages 325 to 399 NAME Topic Outline And Objectives: A. How skeletal muscles produce movement, and naming muscles 1. Describe the relationship between bones and skeletal
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology. ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition
 Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Chapter 3: Applied Kinesiology ACE Personal Trainer Manual Third Edition Introduction Kinesiology is the study of the body s infinite number of movements, positions, and postures and is grounded in the
Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable
 Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 27, 2017 Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable N/A Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Technical Disclosure Commons Defensive Publications Series October 27, 2017 Improving Headphone Fit Using Design Of Cable N/A Follow this and additional works at: http://www.tdcommons.org/dpubs_series
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Chapter 11 The Muscular System. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 11 The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. the attachment of a tendon to the stationary
Chapter 11 The Muscular System Muscle Attachment Sites Skeletal muscles cause movements by exerting force on tendons, which pulls on bones or other structures. the attachment of a tendon to the stationary
Unsaved Test, Version: 1 1
 Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
Name: Choose the letter of the best answer. 1. Functions of the skeletal system include A. forcing blood to circulate through the body B. sending electrical signals to the brain C. providing support and
Suggested Answers to Chapter Review Questions
 Suggested Answers to Chapter Review Questions This document provides initial answers to review questions from chapters 1 through 8. The purpose of review questions is to practice and rehearse key biomechanical
Suggested Answers to Chapter Review Questions This document provides initial answers to review questions from chapters 1 through 8. The purpose of review questions is to practice and rehearse key biomechanical
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory
 CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
CSEP-Certified Certified Personal Trainer (CSEP-CPT) CPT) Musculoskeletal Fitness Theory 1 Basic Anatomy Key Concepts: 3.23-3.25 3.25 2 Force & Levers 1 st class» seesaw» muscles that extend neck R F AF
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
BIOMECHANIC OF MUSCULASKELETAL SYSTEM
 BIOMECHANIC OF MUSCULASKELETAL SYSTEM NEU Faculty of Medicine Dep of Biophysics Dr. Aslı AYKAÇ BIOMECHANICS Bio = Living Mechanics = Forces & Effects The application of mechanics to the living organism
BIOMECHANIC OF MUSCULASKELETAL SYSTEM NEU Faculty of Medicine Dep of Biophysics Dr. Aslı AYKAÇ BIOMECHANICS Bio = Living Mechanics = Forces & Effects The application of mechanics to the living organism
Illustrative exercises for the lectures
 Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
Biomechanics Illustrative exercises for the lectures Ingrid Svensson 2015 1 1. To practise the use of free-body diagram, consider the problem of analyzing the stress in man s back muscles when performing
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world
 Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
Pearson Education Limited Edinburgh Gate Harlow Essex CM20 2JE England and Associated Companies throughout the world Visit us on the World Wide Web at: www.pearsoned.co.uk Pearson Education Limited 2014
120 N 120 N. 1 m 3 m. 1 m 3 m 120 N. 1 m 3 m 40 N. 6 m. f ) 1m. 2m 60 N 50 N
 a) 1) What type of lever is represented. What is the force that must be applied to just lift the loads. What is the mechanical advantage of these levers. b) c) 2) How far is the resistance force from.
a) 1) What type of lever is represented. What is the force that must be applied to just lift the loads. What is the mechanical advantage of these levers. b) c) 2) How far is the resistance force from.
9/26/2012. Basic Terminology. Basic Terminology continued. Kinesiology Terminology. Kinesiology = The study of movement
 Kinesiology Terminology Basic Terminology Kinesiology = The study of movement This definition is so broad. What other fields of study come together to create kinesiology? Yes!! And it relates them all
Kinesiology Terminology Basic Terminology Kinesiology = The study of movement This definition is so broad. What other fields of study come together to create kinesiology? Yes!! And it relates them all
LION. Application Note PRECISION. Linear Position Measurement with Eddy-Current Sensors. LA March, Applicable Equipment: Applications:
 LION PRECISION Application Note LA02-0061 March, 2013 Linear Position Measurement with Eddy-Current Sensors Position, Displacement Applicable Equipment: Eddy-Current position measurement systems. Applications:
LION PRECISION Application Note LA02-0061 March, 2013 Linear Position Measurement with Eddy-Current Sensors Position, Displacement Applicable Equipment: Eddy-Current position measurement systems. Applications:
Students will: Explain how the muscles and bones of the human body function together as levers. Justify categorization of lever types.
 PHYSICAL THERAPY Essential Question: How Is the Body Like a M achine? Learning Targets: Students will: Explain how the muscles and bones of the human body function together as levers. Justify categorization
PHYSICAL THERAPY Essential Question: How Is the Body Like a M achine? Learning Targets: Students will: Explain how the muscles and bones of the human body function together as levers. Justify categorization
Raymond Wiegand, D.C. Spine Rehabilitation Institute of Missouri
 2D Pattern matching of frontal plane radiograph to 3D model identifies structural and functional deficiencies of the spinal pelvic system in consideration of mechanical spine pain (AKA Spine distortion
2D Pattern matching of frontal plane radiograph to 3D model identifies structural and functional deficiencies of the spinal pelvic system in consideration of mechanical spine pain (AKA Spine distortion
Organismic Biology Bio 207. Lecture 6. Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics. Prof.
 Organismic Biology Bio 207 Lecture 6 Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics Prof. Simchon Today s Agenda Skeletal muscle Neuro Muscular Junction
Organismic Biology Bio 207 Lecture 6 Muscle and movement; sliding filaments; E-C coupling; length-tension relationships; biomechanics Prof. Simchon Today s Agenda Skeletal muscle Neuro Muscular Junction
Arm Model. Wrap a rubber band around the three bamboo skewers so that they are in this position. This is the elbow joint.
 Arm Model Category: Biology: Human Body; Physics: Force & Motion Type: Make & Take Rough Parts List: 3 Pipe cleaners 2 Craft sticks 2 ½ Pieces of straw 3 Bamboo skewers 2 Rubber bands Tools List: Scissors
Arm Model Category: Biology: Human Body; Physics: Force & Motion Type: Make & Take Rough Parts List: 3 Pipe cleaners 2 Craft sticks 2 ½ Pieces of straw 3 Bamboo skewers 2 Rubber bands Tools List: Scissors
Chapter 8 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises
 Chapter 8 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's
Chapter 8 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's
Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints
 The Elbow & Radioulnar Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints Usually grouped
The Elbow & Radioulnar Chapter 6 The Elbow and Radioulnar Manual of Structural Kinesiology R.T. Floyd, EdD, ATC, CSCS Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints Usually grouped
Overview of the Components of the MSS
 Overview of the Components of the MSS Lecture Objectives Discuss the components and functions of the MSS. Describe the relation between bones and skeletal muscles in producing body movements. Identify
Overview of the Components of the MSS Lecture Objectives Discuss the components and functions of the MSS. Describe the relation between bones and skeletal muscles in producing body movements. Identify
Biomechanics and Its Application to Seating
 Biomechanics and Its Application K E L LY W A U G H, P T, M A P T, AT P S E N I O R I N S T R U C TO R / C L I N I C C O O R D I N ATO R A S S I S T I V E T E C H N O LO G Y PA R T N E R S S C H O O L
Biomechanics and Its Application K E L LY W A U G H, P T, M A P T, AT P S E N I O R I N S T R U C TO R / C L I N I C C O O R D I N ATO R A S S I S T I V E T E C H N O LO G Y PA R T N E R S S C H O O L
Skeletal Muscles and Functions
 Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
Skeletal Muscles and Functions Huei-Ming Chai, PT, Ph.D. School of Physical Therapy National Taiwan University Classification of Muscles striated muscles skeletal muscles: voluntary contraction cardiac
The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide
 DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
DEFINITION The study of the internal workings of the human body and how it moves. A user s guide OUR FOCUS Bones: structure, protection, levers Joints: allow for movement Muscles: cause movement Anatomical
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Upper Limb Biomechanics SCHOOL OF HUMAN MOVEMENT STUDIES
 Upper Limb Biomechanics Phases of throwing motion 1. Wind up Starts: initiate first movement Ends: lead leg is lifted & throwing hand removed from glove COG raised 2. Early Cocking Start: lead leg is lifted
Upper Limb Biomechanics Phases of throwing motion 1. Wind up Starts: initiate first movement Ends: lead leg is lifted & throwing hand removed from glove COG raised 2. Early Cocking Start: lead leg is lifted
Evaluation of Interactive Systems. Anthropometry & Anatomy
 Evaluation of Interactive Systems Anthropometry & Anatomy Caroline Appert - 2018/2019 References and Inspirations [1] Halla Olafsdottir s slides and discussions [2] http://researchguides.library.tufts.edu/
Evaluation of Interactive Systems Anthropometry & Anatomy Caroline Appert - 2018/2019 References and Inspirations [1] Halla Olafsdottir s slides and discussions [2] http://researchguides.library.tufts.edu/
3.1.2 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS
 3.1.2 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 3.1.1.1 Levers Mechanical Advantage starter 1. Stick in your Assessment Grids from last lesson. NOT FOLDED 2. Fill out the score underneath the start of the lesson Start = % End
3.1.2 MOVEMENT ANALYSIS 3.1.1.1 Levers Mechanical Advantage starter 1. Stick in your Assessment Grids from last lesson. NOT FOLDED 2. Fill out the score underneath the start of the lesson Start = % End
Anatomy, Biomechanics, Work Physiology, and Anthropometry. After completing and understanding of the current chapter students should be able to:
 Chapter 2 Anatomy, Biomechanics, Work Physiology, and Anthropometry Learning outcomes: After completing and understanding of the current chapter students should be able to: Describe the anatomical structure
Chapter 2 Anatomy, Biomechanics, Work Physiology, and Anthropometry Learning outcomes: After completing and understanding of the current chapter students should be able to: Describe the anatomical structure
Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416)
 Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Function and Activation It is not a straightforward matter to predict the activation pattern of a set of muscles when these muscles act on multiple
Multi-joint Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Function and Activation It is not a straightforward matter to predict the activation pattern of a set of muscles when these muscles act on multiple
Fundamentals of Biomechanics
 Duane Knudson Fundamentals of Biomechanics Second Edition Springer Preface Acknowledgments PARTI INTRODUCTION CHAPTERI INTRODUCTION TO BIOMECHANICS OF HUMAN MOVEMENT NINE FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOMECHANICS 29
Duane Knudson Fundamentals of Biomechanics Second Edition Springer Preface Acknowledgments PARTI INTRODUCTION CHAPTERI INTRODUCTION TO BIOMECHANICS OF HUMAN MOVEMENT NINE FUNDAMENTALS OF BIOMECHANICS 29
(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/ A1. Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003
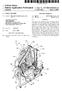 US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
US 20030166439A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2003/0166439 A1 Giannelli (43) Pub. Date: Sep. 4, 2003 (54) ROWING MACHINE Publication Classification (76) Inventor:
Muscle Tissue. Isometric Contraction. Isotonic Contractions 11/22/2016. Muscles. Anatomy Two Joints And Movements
 Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
Muscles Anatomy Two Joints And Movements Structure of a Muscle Organ Copyright 2008 by Saunders Muscle Tissue Highly elastic and vascularized, produces movement through elongation and contraction Types
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
Installation of force transducers
 Installation of force transducers Force transducers have reached a high technical standard in recent years. Transducers achieve part of their high accuracy due to improved possibilities for calibration.
Installation of force transducers Force transducers have reached a high technical standard in recent years. Transducers achieve part of their high accuracy due to improved possibilities for calibration.
DAY 2 III. WORKOUT RULES
 DAY 2 III. WORKOUT RULES A. Order of Exercise 1. Largest amount of muscle mass to smallest amount of muscle mass, eg., squats -- calf raises 2. Complex exercise to assisting, eg., squats -- leg ext. 3.
DAY 2 III. WORKOUT RULES A. Order of Exercise 1. Largest amount of muscle mass to smallest amount of muscle mass, eg., squats -- calf raises 2. Complex exercise to assisting, eg., squats -- leg ext. 3.
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Module Synopsis. Module 1. Biomechanical Concepts
 Module Synopsis The 12 modules composing the Foundation Course are comprised of a total of 109 sections, designed to be taken in series. Each section either has specific learning checks, or suggested tasks
Module Synopsis The 12 modules composing the Foundation Course are comprised of a total of 109 sections, designed to be taken in series. Each section either has specific learning checks, or suggested tasks
The High Jump. Terry VanLaningham Sacramento State. USTFCCCA National Convention
 The High Jump Terry VanLaningham Sacramento State USTFCCCA National Convention - 2014 Thank You! Boo for his friendship, mentorship and asking me to speak. Cliff Rovelto for his friendship, mentorship
The High Jump Terry VanLaningham Sacramento State USTFCCCA National Convention - 2014 Thank You! Boo for his friendship, mentorship and asking me to speak. Cliff Rovelto for his friendship, mentorship
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1
 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises 2007 McGraw-Hill Higher Education. All rights reserved. 8-1 Muscular Analysis of Upper Extremity Exercises Upper extremity - often one of body's weakest areas
DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS
 DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS Numerical and Curve Analysis Ref: Compendium of Isokinetics George Davies Report Parameters Peak Torque Highest muscular force output at any moment during a repetition.
DATA INTERPRETATION AND ANALYSIS Numerical and Curve Analysis Ref: Compendium of Isokinetics George Davies Report Parameters Peak Torque Highest muscular force output at any moment during a repetition.
- why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave?
 Cardiac Electrograph: - why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave? After depolarization the ventricle contracts but since the heart is a volume conductor (3D not 2D), when
Cardiac Electrograph: - why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave? After depolarization the ventricle contracts but since the heart is a volume conductor (3D not 2D), when
DUAL POSITION BACK EX/FLEX ATTACHMENT
 DUAL POSITION BACK EX/FLEX ATTACHMENT OPERATION MANUAL 830-450 FN: 08-261 Rev A 11/15 BIODEX Biodex Medical Systems, Inc. 20 Ramsey Road, Shirley, New York, 11967-4704 Tel: 800-224-6339 (Int l 631-924-9000),
DUAL POSITION BACK EX/FLEX ATTACHMENT OPERATION MANUAL 830-450 FN: 08-261 Rev A 11/15 BIODEX Biodex Medical Systems, Inc. 20 Ramsey Road, Shirley, New York, 11967-4704 Tel: 800-224-6339 (Int l 631-924-9000),
San José State University Department of Kinesiology KIN 158, Biomechanics, Section 01, Spring 2013
 San José State University Department of Kinesiology KIN 158, Biomechanics, Section 01, Spring 2013 Instructors: Class Days, Times, and Rooms: Prerequisites: Dr. James Kao Office: SSC 513 Phone: 408-924-3026
San José State University Department of Kinesiology KIN 158, Biomechanics, Section 01, Spring 2013 Instructors: Class Days, Times, and Rooms: Prerequisites: Dr. James Kao Office: SSC 513 Phone: 408-924-3026
JOINTS (ARTICULATIONS)
 CJ Shuster A & P I Note Series Articulations 1 JOINTS (ARTICULATIONS) - JOINTS or ARTICULATIONS - sites where 2 or more bones meet. Hold skeleton together & give it motility (by using muscles). All locomotion
CJ Shuster A & P I Note Series Articulations 1 JOINTS (ARTICULATIONS) - JOINTS or ARTICULATIONS - sites where 2 or more bones meet. Hold skeleton together & give it motility (by using muscles). All locomotion
In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions
 16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
16 Support System: Bones, Joints and Muscles l a b o r at o ry In Activity 12, What s Happening Inside? you learned about the functions of the skeletal and muscular systems in supporting and moving your
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416)
 Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
Muscle-Tendon Mechanics Dr. Ted Milner (KIN 416) Muscle Fiber Geometry Muscle fibers are linked together by collagenous connective tissue. Endomysium surrounds individual fibers, perimysium collects bundles
Manual Muscle Testing. Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department
 Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
Manual Muscle Testing Yasser Moh. Aneis, PhD, MSc., PT. Lecturer of Physical Therapy Basic Sciences Department Manual Muscle Testing Evaluation of the function and strength of individual muscles and muscles
9/26/2012. Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & Arthrokinematics (how the joints move) Planes & Axes. Planes & Axes continued
 Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
Osteokinematics (how the bones move) & (how the joints move) Planes & Axes Planes of Action = Three fixed lines of reference along which the body is divided. Each plane is at right angles (or perpendicular)
Etrouth Srikar 1, Habib Ali 2 1, 2 Dept. Biomedical Engineering, J.B Institute of Engineering and Technology, India
 Design of an Extremely Affordable and Zero Maintenance Mechanical Secondary Finger (S-finger) Prosthesis for Index Finger Amputees Etrouth Srikar 1, Habib Ali 2 1, 2 Dept. Biomedical Engineering, J.B Institute
Design of an Extremely Affordable and Zero Maintenance Mechanical Secondary Finger (S-finger) Prosthesis for Index Finger Amputees Etrouth Srikar 1, Habib Ali 2 1, 2 Dept. Biomedical Engineering, J.B Institute
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular
 Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
Re-establishing establishing Neuromuscular Control Why is NMC Critical? What is NMC? Physiology of Mechanoreceptors Elements of NMC Lower-Extremity Techniques Upper-Extremity Techniques Readings Chapter
Articulations Chapter 9
 Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device
 Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Validity of Data Extraction Techniques on the Kinetic Communicator (KinCom) Isokinetic Device By: Laurie L. Tis, PhD, AT,C * and David H. Perrin, PhD, AT,C Tis, L.L., & Perrin, D.H. (1993). Validity of
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
 CHAPTER 6 Muscles at Work After completing this chapter you should be able to: differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
CHAPTER 6 Muscles at Work After completing this chapter you should be able to: differentiate between the various types of muscle contractions; describe the factors that influence strength development;
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
Terms of Movements by Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi Three systems of the body work in coordination to perform various movements of the body. These are: A System of Bones (Osteology), A System of Muscles
